Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo
|
|
|
- Dayna Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and (boxed area) at higher magnification (B). (B) Individual epg of the MFA of hs A2 are marked. epg4, epg7 and epg10 are GFP positive. In the MFA the Repo staining is not always clearly recognizable in maximum projections as several PG are hidden behind muscles. Along the NER, moody-gal4-expressing epg3 is indicated. moody-gal4 is additionally expressed in tracheal cells. Anterior is up.
2 Fig. S2. epg1 hypertrophy in third instar. Maximum projection showing mcherry-labelled epg1 in L3 in hs A5. During larval development, epg1 spreads almost along the entire NER resulting in a total length of more than 1 mm. The epg1 nucleus is marked by an arrowhead. mcherry signal alone is illustrated in the boxed area. The region presented in Movie 2 is indicated by the white bar on the left side. In addition to epg1, epg2 progenies forming the perineurial sheath along the NER in hs A2 are also mcherry labelled (bent arrow). Anterior is up.
3 Fig. S3. VNC surface glia cover the proximal part of the NER. (A) Maximum projection showing the posterior tip of the VNC exhibiting several mcherry-labelled glial cells. (A9) mcherry alone. Among these are two subperineurial glia of the VNC (nuclei marked by an arrow) that ensheath the proximal part of the peripheral nerve tract in hs A6 and A7 (arrowheads in A9). In addition, glial membranes can be observed covering a structure branching off the peripheral nerve (asterisk). Probably, this carries afferent sensory axons projecting into the VNC. The right-hand side of this animal was not analysed due to multiple labellings within the VNC and the PNS. Anterior is up.
4 Fig. S4. Phenotypes resulting from embryonic UV irradiation of epg2. (A) Summary of the number and position of remaining PG along the NER of irradiated hs in L3. Larva 10, 13 and 14 display no significant PG reduction along the NER. (B-D) Position of remaining PG along the NER of three dissected larvae stained for Repo (red) and Fas2 (blue). Anterior is up.
5 Fig. S5. 22C10-expressing neurons can be detected between ISN and TN. Confocal stacks of the identical hs as presented in Fig. 6E; however, antibody staining against 22C10 (magenta) was performed on this larva subsequently. 22C10-expressing neurons can be seen projecting between ISN and TN (arrowhead). Probably, these are covered by epg7 protrusions in the corresponding region (arrowhead in Fig. 6E). Anterior is up.
6 Fig. S6. epg4, epg7 and epg10 express Neurexin IV. (A-F-) Antibody staining against the cell-adhesion molecule Neurexin IV (NrxIV) was performed on Flybow-labelled epg4, epg7 and epg10 in L3 to confirm their subperineurial identity. NrxIV staining for epg4 and epg10 shows the same mcherry-labelled epg as that presented in Fig. 6B,H. (A,C,E) Maximum projections of triplelabelled subperineurial glia (mcherry, GFP, NrxIV). Enlarged views of selected focal planes (B,D,F) are followed by the expression of (ngfp) cd8-egfp (B9,D9,F9), mcherry (B0,D0,F0) and NrxIV (B-,D-,F-) alone. Anterior is up. Fig. S7. TN projections enter the VNC separately through the dorsal median cells. Confocal stacks of L3 carrying repo- Gal4>UAS-nuclear-GFP (ngfp) and UAS-CD8::GFP transgenes stained for Fas2 (magenta) and GFP (green). (A,A9) The overview (A) shows the VNC and a section of the PNS. Main peripheral nerve tracts are labelled in hs A2. Fas2-expressing TN projections can be followed due to their exposed position (arrowheads; A9 shows Fas2 staining alone). The TN does not fasciculate with the main peripheral nerve tract along the NER, but enters the VNC at the dorsal midline. (B,B9) At higher magnification the Y-shaped entry point of both TNs projecting into the VNC from each side can be seen (asterisks). Anterior is up.
7 Movie 1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Confocal z-stacks of the region designated in Fig. S1. Individual PG in the MFA and moody-gal4-expressing epg3 are labelled. Anterior is up. Movie 2. epg1 protrusions form the innermost wrapping sheath along the NER. Confocal z-stacks of the NER region designated in Fig. S2. Due to its morphology, the mcherry-labelled epg1 can clearly be identified as wrapping glia lying within the fascicle surrounded by cd8-egfp-positive subperineurial and perineurial glia. Anterior is up.
8 Movie 3. Three-dimensional reconstruction of epg7 and PNS morphology. A three-dimensional reconstruction of the mcherrylabelled epg7 (red) shown in Fig. 6E. It was generated using Imaris software based on confocal stacks (z-step size, 0.8 μm). The reconstruction demonstrates the actual course of the peripheral nerve tracts through the larval tissue. For example, the proximal part of the ISN projects in a more superficial layer (underneath the muscle field in that region) compared with the distal part of the ISN, which lies on top of the muscles. Anterior is up. Movie 4. Sponge-like morphology of a CBG in the VNC. Confocal z-stacks of an mcherry-labelled CBG (magenta) in the VNC of L3. This glial subtype surrounds neuronal somata in the cortex resulting in a sponge-like morphology. Anterior is up.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Attractive and repulsive functions of Slit are mediated by different receptors in the Drosophila trachea
 Development 129, 4941-4951 (2002) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2002 DEV7966 4941 Attractive and repulsive functions of Slit are mediated by different receptors in the Drosophila
Development 129, 4941-4951 (2002) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2002 DEV7966 4941 Attractive and repulsive functions of Slit are mediated by different receptors in the Drosophila
Peripheral Glia Direct Axon Guidance across the CNS/PNS Transition Zone
 Developmental Biology 238, 47 63 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0411, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Peripheral Glia Direct Axon Guidance across the CNS/PNS Transition Zone Katharine J.
Developmental Biology 238, 47 63 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0411, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Peripheral Glia Direct Axon Guidance across the CNS/PNS Transition Zone Katharine J.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1244624/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cytoneme-Mediated Contact-Dependent Transport of the Drosophila Decapentaplegic Signaling Protein Sougata Roy, Hai Huang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1244624/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Cytoneme-Mediated Contact-Dependent Transport of the Drosophila Decapentaplegic Signaling Protein Sougata Roy, Hai Huang,
Positional Cues in the Drosophila Nerve Cord: Semaphorins Pattern the Dorso-Ventral Axis
 Positional Cues in the Drosophila Nerve Cord: Semaphorins Pattern the Dorso-Ventral Axis Marta Zlatic 1,2,3 *, Feng Li 1, Maura Strigini 4, Wesley Grueber 2, Michael Bate 1 * 1 Department of Zoology, University
Positional Cues in the Drosophila Nerve Cord: Semaphorins Pattern the Dorso-Ventral Axis Marta Zlatic 1,2,3 *, Feng Li 1, Maura Strigini 4, Wesley Grueber 2, Michael Bate 1 * 1 Department of Zoology, University
Figure 1. Automated 4D detection and tracking of endosomes and polarity markers.
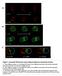 A t = 0 z t = 90 B t = 0 z t = 90 C t = 0-90 t = 0-180 t = 0-300 Figure 1. Automated 4D detection and tracking of endosomes and polarity markers. A: Three different z planes of a dividing SOP shown at
A t = 0 z t = 90 B t = 0 z t = 90 C t = 0-90 t = 0-180 t = 0-300 Figure 1. Automated 4D detection and tracking of endosomes and polarity markers. A: Three different z planes of a dividing SOP shown at
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Overexpression of YFP::GPR-1 in the germline. The pie-1 promoter and 3 utr were used to express yfp::gpr-1 in the germline. Expression levels from the yfp::gpr-1(cai 1.0)-expressing
Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila
 Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila Melissa M. Rolls and Chris Q. Doe, Inst. Neurosci and Inst. Mol. Biol., HHMI, Univ. Oregon, Eugene, Oregon 97403 Correspondence
Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila Melissa M. Rolls and Chris Q. Doe, Inst. Neurosci and Inst. Mol. Biol., HHMI, Univ. Oregon, Eugene, Oregon 97403 Correspondence
Developmental Dynamics of Peripheral Glia in Drosophila melanogaster
 GLIA 30:122 133 (2000) Developmental Dynamics of Peripheral Glia in Drosophila melanogaster KATHARINE J. SEPP, JOOST SCHULTE, AND VANESSA J. AULD* Department of Zoology, University of British Columbia,
GLIA 30:122 133 (2000) Developmental Dynamics of Peripheral Glia in Drosophila melanogaster KATHARINE J. SEPP, JOOST SCHULTE, AND VANESSA J. AULD* Department of Zoology, University of British Columbia,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS. Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
Distribution, classification, and development of Drosophila glial cells in the late embryonic and early larval ventral nerve cord
 Roux's Arch Dev Biol (1995) 204:284-307 Springer-Verlag 1995 Kei Ito - Joachim Urban Gerhard Martin Technau Distribution, classification, and development of Drosophila glial cells in the late embryonic
Roux's Arch Dev Biol (1995) 204:284-307 Springer-Verlag 1995 Kei Ito - Joachim Urban Gerhard Martin Technau Distribution, classification, and development of Drosophila glial cells in the late embryonic
Organization and Function of the Blood Brain Barrier in Drosophila
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 16, 2008 28(3):587 597 587 Development/Plasticity/Repair Organization and Function of the Blood Brain Barrier in Drosophila Tobias Stork, 1 Daniel Engelen, 1 Alice
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 16, 2008 28(3):587 597 587 Development/Plasticity/Repair Organization and Function of the Blood Brain Barrier in Drosophila Tobias Stork, 1 Daniel Engelen, 1 Alice
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
Cell Type-Specific Expression of Fasciclin II Isoforms Reveals Neuronal Glial Interactions during Peripheral Nerve Growth
 Developmental Biology 234, 24 41 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0247, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Cell Type-Specific Expression of Fasciclin II Isoforms Reveals Neuronal Glial Interactions
Developmental Biology 234, 24 41 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0247, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Cell Type-Specific Expression of Fasciclin II Isoforms Reveals Neuronal Glial Interactions
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and
 Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
The Nervous System. Nervous System Organization. Nerve Tissue. Two parts to the nervous system 11/27/2016
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
Neurochemistry 1. Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906
 Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2717
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Supplementary Fig. 1. Dendrite length is not secondary to body length. Dendrite growth proceeds independently of the rate of body growth and decreases in rate in adults. n 20 on dendrite measurement, n
Axon-Schwann cell interactions during peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish larvae
 Ceci et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Axon-Schwann cell interactions during peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish larvae Maria Laura Ceci 1, Camila Mardones-Krsulovic
Ceci et al. Neural Development 2014, 9:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Axon-Schwann cell interactions during peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish larvae Maria Laura Ceci 1, Camila Mardones-Krsulovic
Reciprocal Interactions between Neurons and Glia Are Required for Drosophila Peripheral Nervous System Development
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 10, 2003 23(23):8221 8230 8221 Development/Plasticity/Repair Reciprocal Interactions between Neurons and Glia Are Required for Drosophila Peripheral Nervous System
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 10, 2003 23(23):8221 8230 8221 Development/Plasticity/Repair Reciprocal Interactions between Neurons and Glia Are Required for Drosophila Peripheral Nervous System
Systematic Screening of Drosophila Deficiency Mutations for Embryonic Phenotypes and Orphan Receptor Ligands
 Systematic Screening of Drosophila Deficiency Mutations for Embryonic Phenotypes and Orphan Receptor Ligands Ashley P. Wright 1, A. Nicole Fox 1, Karl G. Johnson 2, Kai Zinn 1 * 1 Division of Biology,
Systematic Screening of Drosophila Deficiency Mutations for Embryonic Phenotypes and Orphan Receptor Ligands Ashley P. Wright 1, A. Nicole Fox 1, Karl G. Johnson 2, Kai Zinn 1 * 1 Division of Biology,
The secreted cell signal Folded Gastrulation regulates glial morphogenesis and axon guidance in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology 308 (2007) 158 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio The secreted cell signal Folded Gastrulation regulates glial morphogenesis and axon guidance in Drosophila Anuradha Ratnaparkhi 1,
Developmental Biology 308 (2007) 158 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio The secreted cell signal Folded Gastrulation regulates glial morphogenesis and axon guidance in Drosophila Anuradha Ratnaparkhi 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09714 Supplementary Figure 1 The mouse olfactory system and summary of our results. a, Schematic of the mouse olfactory system (sagittal view). See text for more details. The red and
doi:10.1038/nature09714 Supplementary Figure 1 The mouse olfactory system and summary of our results. a, Schematic of the mouse olfactory system (sagittal view). See text for more details. The red and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. JAK/STAT in early wing development (a-f) Wing primordia of second instar larvae of the indicated genotypes labeled to visualize expression of upd mrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. JAK/STAT in early wing development (a-f) Wing primordia of second instar larvae of the indicated genotypes labeled to visualize expression of upd mrna
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types of neurons from a neuroblast
 Development 126, 4065-4076 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8625 4065 Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types
Development 126, 4065-4076 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8625 4065 Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
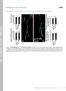 Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in
 Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Expression of a set of glial cell-specific markers in the Drosophila embryonic central nervous system
 BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2014; 47(6): 354-359 www.bmbreports.org Expression of a set of glial cell-specific markers in the Drosophila embryonic central nervous system Hui Jeong Ahn 1, Sang-Hak Jeon 2 & Sang
BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2014; 47(6): 354-359 www.bmbreports.org Expression of a set of glial cell-specific markers in the Drosophila embryonic central nervous system Hui Jeong Ahn 1, Sang-Hak Jeon 2 & Sang
Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Major Internal Features of a Neuron The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. A typical neuron has a soma
Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Major Internal Features of a Neuron The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. A typical neuron has a soma
Interactions between a Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatase and a Cell Surface Ligand Regulate Axon Guidance and Glial-Neuronal Communication
 Article Interactions between a Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatase and a Cell Surface Ligand Regulate Axon Guidance and Glial-Neuronal Communication Hyung-Kook (Peter) Lee, 1 Amy Cording, 1,2 Jost Vielmetter,
Article Interactions between a Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatase and a Cell Surface Ligand Regulate Axon Guidance and Glial-Neuronal Communication Hyung-Kook (Peter) Lee, 1 Amy Cording, 1,2 Jost Vielmetter,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Segment-specific prevention of pioneer neuron apoptosis by cellautonomous, postmitotic Hox gene activity
 First posted online on 10 November 2004 as 10.1242/dev.01521 Access Development the most recent epress version at online http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.01521 publication date November
First posted online on 10 November 2004 as 10.1242/dev.01521 Access Development the most recent epress version at online http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.01521 publication date November
Reading. Lecture VI. Making Connections 9/17/12. Bio 3411 Lecture VI. Making Connections. Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012
 Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Lecture VI. Making Connections Bio 3411 Monday September 17, 2012!! 1! Reading NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp!507?536! 4 th ed, pp 577-609 Bentley, D., & Caudy, M. (1983). Nature, 304(5921), 62-65. Dickson,
Supporting Information
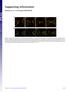 Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
MCN. Complex Genetic Interactions among Four Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases Regulate Axon Guidance in Drosophila
 MCN Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 17, 274 291 (2001) doi:10.1006/mcne.2000.0939, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Complex Genetic Interactions among Four Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases
MCN Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 17, 274 291 (2001) doi:10.1006/mcne.2000.0939, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Complex Genetic Interactions among Four Receptor Tyrosine Phosphatases
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
3. Names: Date: Student Exploration: Cell Types Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are you supposed to be learning in this activity? 2. Why do you think learning this
Figure S1: Phylogenetic analysis of the Platynereis Notch pathway core components, Pdu-
 Electronic supplementary material legends from The Notch pathway in the annelid Platynereis: Insights into chaetogenesis and neurogenesis processes ; Eve Gazave, Quentin I. B. Lemaître and Guillaume Balavoine;
Electronic supplementary material legends from The Notch pathway in the annelid Platynereis: Insights into chaetogenesis and neurogenesis processes ; Eve Gazave, Quentin I. B. Lemaître and Guillaume Balavoine;
Specification of Drosophila motoneuron identity by the combinatorial action of POU and LIM-HD factors
 Research article 5429 Specification of Drosophila motoneuron identity by the combinatorial action of POU and LIM-HD factors Sarah J. Certel and Stefan Thor*, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical
Research article 5429 Specification of Drosophila motoneuron identity by the combinatorial action of POU and LIM-HD factors Sarah J. Certel and Stefan Thor*, Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) innervate Divisions: a. Afferent
 Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures
 Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures 1. Identify the structures in the diagram. (3 marks) 2. List the 3 cell structures not found in animal cells but are found in plants cells. (1 mark) 3. Where is DNA found
Quiz 1: Cells and Cell Structures 1. Identify the structures in the diagram. (3 marks) 2. List the 3 cell structures not found in animal cells but are found in plants cells. (1 mark) 3. Where is DNA found
Electron microscopy of glial cells of the central nervous system in the crab Ucides cordatus
 Brazilian Glial cells Journal in crustaceans of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 327-331 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 327 Electron microscopy of glial cells of the central nervous system
Brazilian Glial cells Journal in crustaceans of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 327-331 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 327 Electron microscopy of glial cells of the central nervous system
Supplementary Figures
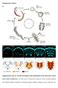 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1: Normal development and organization of the embryonic ventral nerve cord in Platynereis. (A) Life cycle of Platynereis dumerilii. (B-F) Axonal scaffolds and
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
The Nervous System Chapter 44 Nervous System Organization All animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli -Sensory receptors = Detect stimulus -Motor effectors = Respond to it -The nervous
Pioneering and pathfinding by an identified neuron in the embryonic leech
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 86, 155-167, (1985) 155 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Pioneering and pathfinding by an identified neuron in the embryonic leech JOHN Y. KUWADA
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 86, 155-167, (1985) 155 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Pioneering and pathfinding by an identified neuron in the embryonic leech JOHN Y. KUWADA
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
Supplementary Data Supplementary figures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Supplementary figures Figure S1 - Evaluation of functional motor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Biomaterials Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Data Supplementary figures Figure S1 - Evaluation of functional motor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites Marie Versaevel 1, Jean-Baptiste Braquenier 2, Maryam Riaz 1, Thomas Grevesse 1, Joséphine
Supplementary Information Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites Marie Versaevel 1, Jean-Baptiste Braquenier 2, Maryam Riaz 1, Thomas Grevesse 1, Joséphine
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
Nervous system development in lecithotrophic larval and juvenile stages of the annelid Capitella teleta
 Meyer et al. Frontiers in Zoology (2015)12:15 DOI 10.1186/s12983-015-0108-y RESEARCH Open Access Nervous system development in lecithotrophic larval and juvenile stages of the annelid Capitella teleta
Meyer et al. Frontiers in Zoology (2015)12:15 DOI 10.1186/s12983-015-0108-y RESEARCH Open Access Nervous system development in lecithotrophic larval and juvenile stages of the annelid Capitella teleta
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
BIOLOGY. 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Communication in Neurons
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
Astrocytes Play a Key Role in Drosophila Mushroom Body Axon Pruning
 Astrocytes Play a Key Role in Drosophila Mushroom Body Axon Pruning Yaniv Hakim, Shiri P. Yaniv, Oren Schuldiner* Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Weizmann Institute of Sciences, Rehovot, Israel Abstract
Astrocytes Play a Key Role in Drosophila Mushroom Body Axon Pruning Yaniv Hakim, Shiri P. Yaniv, Oren Schuldiner* Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Weizmann Institute of Sciences, Rehovot, Israel Abstract
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
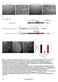 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
 KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
KAP Biology Dept Kenyon College Differential gene expression and development Mechanisms of cellular determination Induction Pattern formation Chapter 11. Development: Differentiation and Determination
Glia in the fly wing are clonally related to epithelial cells and use the nerve as a pathway for migration
 Development 120, 523-534 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 523 Glia in the fly wing are clonally related to epithelial cells and use the nerve as a pathway for migration
Development 120, 523-534 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 523 Glia in the fly wing are clonally related to epithelial cells and use the nerve as a pathway for migration
BIOLOGY 11/10/2016. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Concept 48.1: Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
PI3K signaling and Stat92E converge to modulate glial responsiveness to axonal injury
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 11-4-2014 PI3K signaling and Stat92E converge to modulate glial responsiveness
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 11-4-2014 PI3K signaling and Stat92E converge to modulate glial responsiveness
Current address: Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience. University of Florida, St. Augustine, FL 32080
 *Manuscript The eneuro atlas: a modifiable, searchable 3D atlas that individually identifies the majority of interneurons in the Drosophila embryonic CNS and provides tools for functional access Ellie
*Manuscript The eneuro atlas: a modifiable, searchable 3D atlas that individually identifies the majority of interneurons in the Drosophila embryonic CNS and provides tools for functional access Ellie
Nirupama Deshpande, Rainer Dittrich, Gerhard M. Technau and Joachim Urban* SUMMARY
 Development 128, 3253-3261 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV8801 3253 Successive specification of Drosophila neuroblasts NB 6-4 and NB 7-3 depends on interaction
Development 128, 3253-3261 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV8801 3253 Successive specification of Drosophila neuroblasts NB 6-4 and NB 7-3 depends on interaction
Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn.
 Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn. The Chemical Senses: Olfaction Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department
Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn. The Chemical Senses: Olfaction Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department
NN-A29932: Supplementary Data 1 Diversity and Wiring Variability of Olfactory Local Interneurons in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe
 NN-A29932: Supplementary Data 1 Diversity and Wiring Variability of Olfactory Local Interneurons in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Ya-Hui Chou, Maria L. Spletter, Emre Yaksi, Jonathan C. S. Leong, Rachel
NN-A29932: Supplementary Data 1 Diversity and Wiring Variability of Olfactory Local Interneurons in the Drosophila Antennal Lobe Ya-Hui Chou, Maria L. Spletter, Emre Yaksi, Jonathan C. S. Leong, Rachel
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with
 Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Flamingo, a seven-pass transmembrane cadherin, cooperates with Netrin/Frazzled in Drosophila midline guidance
 Flamingo, a seven-pass transmembrane cadherin, cooperates with Netrin/Frazzled in Drosophila midline guidance Cristina Organisti1, Irina Hein1, Ilona C. Grunwald Kadow1* and Takashi Suzuki2* 1 Max Planck
Flamingo, a seven-pass transmembrane cadherin, cooperates with Netrin/Frazzled in Drosophila midline guidance Cristina Organisti1, Irina Hein1, Ilona C. Grunwald Kadow1* and Takashi Suzuki2* 1 Max Planck
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons
Single-Cell Analysis of Drosophila Larval Neuromuscular Synapses
 Developmental Biology 229, 55 70 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9983, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Single-Cell Analysis of Drosophila Larval Neuromuscular Synapses Bao Hoang 1 and Akira
Developmental Biology 229, 55 70 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9983, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Single-Cell Analysis of Drosophila Larval Neuromuscular Synapses Bao Hoang 1 and Akira
Tiling of the Drosophila epidermis by multidendritic sensory neurons
 Development 129, 2867-2878 (2002) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2002 DEV9829 2867 Tiling of the Drosophila epidermis by multidendritic sensory neurons Wesley B. Grueber, Lily
Development 129, 2867-2878 (2002) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2002 DEV9829 2867 Tiling of the Drosophila epidermis by multidendritic sensory neurons Wesley B. Grueber, Lily
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1178343/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Starvation Protects Germline Stem Cells and Extends Reproductive Longevity in C. elegans This PDF file includes: Giana Angelo
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1178343/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Starvation Protects Germline Stem Cells and Extends Reproductive Longevity in C. elegans This PDF file includes: Giana Angelo
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its
 Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Supplementary Figure 1: Mechanism of Lbx2 action on the Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway. (a) The Wnt/ -catenin signalling pathway and its transcriptional activity in wild-type embryo. A gradient of canonical
Nervous System Part II
 Nervous System Part II 175 Types of Neurons 1. Motor Neurons 2. Sensory Neurons 3. Interneurons 176 Motor (Efferent) Neurons take information from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). Characterized
Nervous System Part II 175 Types of Neurons 1. Motor Neurons 2. Sensory Neurons 3. Interneurons 176 Motor (Efferent) Neurons take information from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). Characterized
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring
 Development 126, 3679-3692 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8610 3679 Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring Jennifer A.
Development 126, 3679-3692 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV8610 3679 Genes required for axon pathfinding and extension in the C. elegans nerve ring Jennifer A.
ATranscriptionFactorNetworkCoordinates Attraction, Repulsion, and Adhesion Combinatorially to Control Motor Axon Pathway Selection
 Article ATranscriptionFactorNetworkCoordinates Attraction, Repulsion, and Adhesion Combinatorially to Control Motor Axon Pathway Selection Aref Arzan Zarin, 1,2 Jamshid Asadzadeh, 1,2 Karsten Hokamp, 1
Article ATranscriptionFactorNetworkCoordinates Attraction, Repulsion, and Adhesion Combinatorially to Control Motor Axon Pathway Selection Aref Arzan Zarin, 1,2 Jamshid Asadzadeh, 1,2 Karsten Hokamp, 1
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila
 Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong a,1, Da-som Yang a, Young Gi Hong a, Sarah P. Mitchell b,c, Matthew P. rown b,c, and
Varicose and cheerio collaborate with pebble to mediate semaphorin-1a reverse signaling in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong a,1, Da-som Yang a, Young Gi Hong a, Sarah P. Mitchell b,c, Matthew P. rown b,c, and
Concerted control of gliogenesis by InR/TOR and FGF signalling in the Drosophila post-embryonic brain
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 2763 Development 139, 2763-2772 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.074179 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Concerted control of gliogenesis by InR/TOR and FGF signalling in the Drosophila
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2763 Development 139, 2763-2772 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.074179 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Concerted control of gliogenesis by InR/TOR and FGF signalling in the Drosophila
DETERMINING THE DIFFERENTIAL ROLES OF THE DOCK FAMILY OF GEFS IN DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT
 DETERMINING THE DIFFERENTIAL ROLES OF THE DOCK FAMILY OF GEFS IN DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT A DISSERTATION IN Cell Biology & Biophysics and Molecular Biology & Biochemistry Presented to the Faculty of the
DETERMINING THE DIFFERENTIAL ROLES OF THE DOCK FAMILY OF GEFS IN DROSOPHILA DEVELOPMENT A DISSERTATION IN Cell Biology & Biophysics and Molecular Biology & Biochemistry Presented to the Faculty of the
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works
 Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
Nervous System: Part II How A Neuron Works Essential Knowledge Statement 3.E.2 Continued Animals have nervous systems that detect external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and
Involvement of Slit Robo signaling in the development of the posterior commissure and concomitant swimming behavior in Xenopus laevis
 Tosa et al. Zoological Letters (2015) 1:28 DOI 10.1186/s40851-015-0029-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Involvement of Slit Robo signaling in the development of the posterior commissure and concomitant swimming
Tosa et al. Zoological Letters (2015) 1:28 DOI 10.1186/s40851-015-0029-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Involvement of Slit Robo signaling in the development of the posterior commissure and concomitant swimming
The Transmembrane Semaphorin Sema I Is Required in Drosophila for Embryonic Motor and CNS Axon Guidance
 Neuron, Vol. 20, 207 220, February, 1998, Copyright 1998 by Cell Press The Transmembrane Semaphorin Sema I Is Required in Drosophila for Embryonic Motor and CNS Axon Guidance Hung-Hsiang Yu, Houmam H.
Neuron, Vol. 20, 207 220, February, 1998, Copyright 1998 by Cell Press The Transmembrane Semaphorin Sema I Is Required in Drosophila for Embryonic Motor and CNS Axon Guidance Hung-Hsiang Yu, Houmam H.
Physiology 2 nd year. Neuroscience Optional Lecture
 Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Experiment 3: Nerve Conduction
 Experiment 3: Nerve Conduction Overview The interior of a cell is negatively charged with respect to the outside, and the magnitude of the potential difference is usually between 50 and 80 mv. Some cells,
Experiment 3: Nerve Conduction Overview The interior of a cell is negatively charged with respect to the outside, and the magnitude of the potential difference is usually between 50 and 80 mv. Some cells,
Control and Integration. Nervous System Organization: Bilateral Symmetric Animals. Nervous System Organization: Radial Symmetric Animals
 Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
The glycosyltransferase Fringe promotes Delta-Notch signaling between neurons and glia, and is required for subtype-specific glial gene expression
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 591 Development 134, 591-600 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02754 The glycosyltransferase Fringe promotes Delta-Notch signaling between neurons and glia, and is required for subtype-specific glial
RESEARCH ARTICLE 591 Development 134, 591-600 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02754 The glycosyltransferase Fringe promotes Delta-Notch signaling between neurons and glia, and is required for subtype-specific glial
Focal adhesion kinase controls morphogenesis of the Drosophila optic stalk
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 1539 Development 134, 1539-1548 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.001529 Focal adhesion kinase controls morphogenesis of the Drosophila optic stalk Satoshi Murakami 1,2, Daiki Umetsu 1,2, Yuko Maeyama
RESEARCH ARTICLE 1539 Development 134, 1539-1548 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.001529 Focal adhesion kinase controls morphogenesis of the Drosophila optic stalk Satoshi Murakami 1,2, Daiki Umetsu 1,2, Yuko Maeyama
The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila
 Article The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong, 1 Katarina Juhaszova, 1 and Alex L. Kolodkin 1, 1 Solomon H. Snyder
Article The Control of Semaphorin-1a-Mediated Reverse Signaling by Opposing Pebble and RhoGAPp190 Functions in Drosophila Sangyun Jeong, 1 Katarina Juhaszova, 1 and Alex L. Kolodkin 1, 1 Solomon H. Snyder
Student Exploration: Cell Types
 Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Name: Period: Student Exploration: Cell Types Vocabulary: ATP, bacteria, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), cell, cellular respiration, compound light microscope, eukaryote, multicellular, muscle cell, neuron, organelle,
Patterning Axon Targeting of Olfactory Receptor Neurons by Coupled Hedgehog Signaling at Two Distinct Steps
 Patterning Axon Targeting of Olfactory Receptor Neurons by Coupled Hedgehog Signaling at Two Distinct Steps Ya-Hui Chou, 1,2 Xiaoyan Zheng, 1,3 Philip A. Beachy, 1,3 and Liqun Luo 1,2, * 1 Howard Hughes
Patterning Axon Targeting of Olfactory Receptor Neurons by Coupled Hedgehog Signaling at Two Distinct Steps Ya-Hui Chou, 1,2 Xiaoyan Zheng, 1,3 Philip A. Beachy, 1,3 and Liqun Luo 1,2, * 1 Howard Hughes
