BLOOD. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 陈咏梅 YONG-MEI CHEN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
|
|
|
- Clarissa Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BLOOD PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 陈咏梅 YONG-MEI CHEN Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College
2 Content Composition & functions of plasma PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. Structure & functions of erythrocytes Classification, structure & functions of leukocytes Structure & functions of platelets Hemopoiesis
3 Blood smear Wright & Giemsa stain (azures)
4 Hemogram Blood female: /L Neutrophils Granular ~ Eosinophils Formed Leukocytes Basophils element /L Lymphocytes ~ 45% Agranular ~ Monocytes Platelets ( ) 10 9 /L Plasma ~ 55% male: /L Erythrocytes Hematocrit: 40-50% in men & 35-45% in women
5 I. Plasma: yellowish & translucent 1. Compositions:
6 Plasma proteins: albumin, α,β,γ-globulin clotting protein (prothrombin, fibrinogen, etc.) complement protein (C 1 -C 9 ) lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, HDL) 2. Functions: Transportation, regulation & defense 3. Serum:
7 II. Formed element: PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 1. Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cell, RBC) (1) Structure: 1) biconcave disc 2) d 7-8μm sectioned slide Histologic ruler
8 (1) Structure: PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. 1) biconcave disc 2) d 7-8μm 3) acidophilic 4) no nucleus 5) no organelles 6) rich in hemoglobin 7) deformable membrane
9 Hemoglobin (Hb): globin + iron-containing heme HbA & HbF
10 RBC membrane proteins: PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. a) Integral ~: Na + -K + pump, Ca 2+ pump, and glucose transport protein, band 3 protein, and glycophorins etc. Blood group ABO group Rh group hemolytic transfusion reaction
11 RBC membrane proteins: b) Peripheral ~: spectrin, actin, and ankyrin etc. serving as a membrane skeleton. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. RBC membrane is flexible & deformable
12 (2) Functions: O 2 transport and CO 2 transport Alveoli Cell in the tissue
13 (3) Normal value of erythrocytes PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. Erythrocytes Hemoglobin male: /L female: /L male: g/l female: g/l
14 (4) Change of RBC 1) Physical adaptation: 2) Pathological changes: D > 9μm: macrocytes; D < 6μm: microcytes Anisocytosis
15 Anemia: RBC < /L, Hb < 100g/L eg: Iron-deficiency ~, Sickle cell ~, Mediterranean ~ etc.
16 (5) Osmotic equilibrium between RBC and plasma PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. blood shadow or blood ghost
17 (6) Reticulocyte: 0.5~1.5% of RBC anucleate, contain some organelles, e.g.: rrna demonstrated by brilliant cresyl blue methods ( 煌焦油蓝 )
18 (7) Life span: about 120days PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry.
19 2. Leukocytes (White Blood Cell, WBC) Blood Inactive WBC PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. diapedetis Active WBC
20 (1) Introduction: Neutrophils 50-70% Granular ~ Eosinophils 0.5-3% Leukocytes /L Agranular ~ 1) Granular leukocytes Basophils < 1% Lymphocytes 20-30% Monocytes 3-8% a. Azurophilic granules: staining purple, lysosomes b. Specific granules:
21 (1) Introduction: Neutrophils 50-70% Granular ~ Eosinophils 0.5-3% Leukocytes /L Agranular ~ 2) Agranular leukocytes a. Azurophilic granules 3) Life span: variable Basophils < 1% Lymphocytes 20-30% Monocytes 3-8%
22 (2) Classification: 1) Neutrophils: 12-15μm a. Structure: Nucleus: band-form or multilobed, 2-5 lobes PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. Specific granules: neutrophilic ~: small, barely visible in LM, containing alkaline phosphatase, collagenase and lysozyme etc.
23 b. Functions: Chemotaxis: Phagocytosis and destruction of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Pus & pyocyte
24 2) Eosinophils: 12-15μm a. Structure: Nucleus: bilobed PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. Specific granules: Eosinophilic ~: staining orange-pink, large, elongated, crystalline core, refractile, and containing major basic protein, histaminase, myeloperoxidase, etc.
25 b. Functions: Chemotaxis: Phagocytosis of Ag-Ab-complexes and destruction of parasites.
26 3) Basophils: 12-15μm a. Structure: Nucleus: lobed, S-shaped, or irregular, often masked by the overlying specific granules
27 Specific granules: Basophilic ~: metachromasia, staining blue purple and containing heparin, histamin, PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A). Leukotriene b. Functions: mediating the allergic reactions.
28 4) Lymphocytes: a. Structure: Small lymphocytes: 6-8μm, nucleus: cytoplasm 9:1 Deeply-stained spherical nucleus, sometimes with an indentation, located eccentrically; cytoplasm is basophilic, sky-blue, contains fine azurophilic granules.
29 Medium-sized lymphocytes: 9-12μm Large lymphocytes: 13-18μm PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. b. Classification and functions: B-Lymphocytes: 20-30%, responsible for humoral immunity T-Lymphocytes: 70-80%, responsible for cell-mediated immunity Natural killer cells:
30 5) Monocytes: 12-20μm a. Structure: oval, kidney- or horseshoe-shaped nucleus, eccentric position; cytoplasm is basophilic, bluishgray, and contains fine azurophilic granules. PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. b. Functions: Precursor cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system
31 3. Platelets: (Thrombocytes) 2-4μm (1) Structure: often in clumps 1) anucleate, biconvex round or ovoid discs.
32 2) Hyalomere: peripheral clear zone dense tubular system PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. open canalicular system microtubules 3) Granulomere: central darker zone α, λ, δ granules
33 (2) Functions: promote blood clotting & controlling hemorrhage thrombocytopenic purpura PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. (3) Life span: ~ 10 days.
34 Hemopoiesis (Blood Cell Formation) I. Hemopoietic Organ: 1. Mesoblastic phase: york sac 2. Hepatic phase: 3. Splenic phase: 4. Myeloid phase: bone marrow
35 Red Bone Marrow Yellow Bone Marrow RBM YBM
36 Structure of Red Bone Marrow: (1) Stroma: reticular tissue (2) Hemopoietic cord: hemopoietic cells & macrophages (3) Sinusoids:
37 pluripotential hemopoietic stem cells PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. progenitor cells (committed stem cells) colony-forming cells (CFC) or colony-forming units (CFU). precursor cells (blasts) colony-stimulating factors (CSF), growth factors or hematopoietins, e.g.: Erythropoietin (EPO), G-CSF, GM-CSF etc
38 Monoblast Myeloblast
39
40 II. Erythropoiesis ~7d Major morphological changes: PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry. (1) Cell volume: (2) Cytoplasm: basophilic acidophilic (3) Nucleus: disappear nucleoli: disappear chromatin condensation
41 III. Granulopoiesis ~11d Granules PUMC Dept. of Anat. Hist. & Embry.
42 IV. Thrombopoiesis Megakaryoblast Promegakaryocyte Megakaryocyte Platelet
BLOOD. YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel: address:
 BLOOD YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@yahoo.com.cn Content Composition & functions of plasma Structure &
BLOOD YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@yahoo.com.cn Content Composition & functions of plasma Structure &
Erythrocyte. Erythrocytes (unstained) thin membrane. refractive index varies by hemoglobin content; ghost cells seen with low hemoglobin
 Erythrocyte SYNONYMS RBC, red cell VITAL STATISTICS size... diameter 7-8 μm shape... round to slightly oval biconcave disk, crenated in hypertonic specimens with irregular edges and surfaces, spherical
Erythrocyte SYNONYMS RBC, red cell VITAL STATISTICS size... diameter 7-8 μm shape... round to slightly oval biconcave disk, crenated in hypertonic specimens with irregular edges and surfaces, spherical
HEMATOLOGY/ HEMATOPOIESIS. Introduction
 HEMATOLOGY/ HEMATOPOIESIS Introduction HEMATOLOGY Introduction Study of blood & its components Window of rest of body BLOOD Raison d etre Delivery of nutrients Oxygen Food Vitamins Removal of wastes Carbon
HEMATOLOGY/ HEMATOPOIESIS Introduction HEMATOLOGY Introduction Study of blood & its components Window of rest of body BLOOD Raison d etre Delivery of nutrients Oxygen Food Vitamins Removal of wastes Carbon
A2.19. Supplementary Materials for Appendix 2
 A2.19 Supplementary Materials for Appendix 2 A2.20 Parameter Ref. Low Ref. High 12 Month 6 Month 3 Month Rabbit ID# B-51 B-71 B-51 B-52 B-53 B-54 B-55 B-56 B-57 B-58 B-59 B-60 B-61 B-62 B-63 B-64 B-65
A2.19 Supplementary Materials for Appendix 2 A2.20 Parameter Ref. Low Ref. High 12 Month 6 Month 3 Month Rabbit ID# B-51 B-71 B-51 B-52 B-53 B-54 B-55 B-56 B-57 B-58 B-59 B-60 B-61 B-62 B-63 B-64 B-65
Lecture 1: Anatomy of a Blood Test - Window on the Cell Theory
 Lecture 1: Anatomy of a Blood Test - Window on the Cell Theory Quantitative Models of Biological Function Mannella et al. APh/BE161: Physical Biology of the Theriot et al. Cell The Beauty of the Beating
Lecture 1: Anatomy of a Blood Test - Window on the Cell Theory Quantitative Models of Biological Function Mannella et al. APh/BE161: Physical Biology of the Theriot et al. Cell The Beauty of the Beating
Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation
 Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation Mitosis is a type of cell division by binary fission (splitting in two) which occurs in certain eukaryotic cells. Mitosis generates new body
Mitosis, development, regeneration and cell differentiation Mitosis is a type of cell division by binary fission (splitting in two) which occurs in certain eukaryotic cells. Mitosis generates new body
Using multiwavelength UV-visible spectroscopy for the characterization of red blood cells: An investigation of hypochromism
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Using multiwavelength UV-visible spectroscopy for the characterization of red blood cells: An investigation
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2004 Using multiwavelength UV-visible spectroscopy for the characterization of red blood cells: An investigation
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
THE MECHANISM OF DENUCLEATION IN CIRCULATING ERYTHROBLASTS
 Published Online: 1 October, 1967 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.35.1.237 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 12, 2018 THE MECHANISM OF DENUCLEATION IN CIRCULATING ERYTHROBLASTS CHARLES F.
Published Online: 1 October, 1967 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.35.1.237 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on October 12, 2018 THE MECHANISM OF DENUCLEATION IN CIRCULATING ERYTHROBLASTS CHARLES F.
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
STRUCTURE OF THE CELL The cell is the smallest standard unit of the organisms. - nucleus - vital functions (growth, metabolism, irritability, movement,reproduction) - independent existence in certain conditions
Lecture 17: Cell Mechanics
 Lecture 17: Cell Mechanics We will focus on how the cell functions as a mechanical unit, with all of the membrane and cytoskeletal components acting as an integrated whole to accomplish a mechanical function.
Lecture 17: Cell Mechanics We will focus on how the cell functions as a mechanical unit, with all of the membrane and cytoskeletal components acting as an integrated whole to accomplish a mechanical function.
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15
 Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Unit 10: Anatomy and Physiology Unit code: K/503/1682 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit aims to develop learner understanding of physical support and movement in animals, body transport systems,
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 17 Clinical Systems Today Week in PBS&D Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Spectrophotometry Autoanalyzers Chromatology - Gas Chromatgraphs (Mass) Spectroscopy
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT. Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University
 CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
CELL DIVISION Dr. Mahmood S. Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University Cell Division The key roles of cell division Unicellular
Tokuhiro JSHIHARA, Chotatsu TSUKAYAMA, Fumiya UCHINO
 (39) JOURNAL OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 39 Vol. 22, No. I, 39-44, 1973 Intramitochondrial Filamentous Structures in Human Reticulum Cells in the Bone Marrow Tokuhiro JSHIHARA, Chotatsu TSUKAYAMA, Fumiya UCHINO
(39) JOURNAL OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 39 Vol. 22, No. I, 39-44, 1973 Intramitochondrial Filamentous Structures in Human Reticulum Cells in the Bone Marrow Tokuhiro JSHIHARA, Chotatsu TSUKAYAMA, Fumiya UCHINO
(Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation)
 (Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation) Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry: blood,
(Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation) Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry: blood,
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
The Morphometrical Characterisation of Normal Blood Cells of Two airbreathing fishes, Clarias batrachus and Anabas testudineus
 International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN - The Morphometrical Characterisation of Normal Blood s of Two airbreathing fishes, Clarias batrachus and Anabas testudineus Abstract Acharya
International Research Journal of Biological Sciences ISSN - The Morphometrical Characterisation of Normal Blood s of Two airbreathing fishes, Clarias batrachus and Anabas testudineus Abstract Acharya
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
Thin Smear and RBC Count Page 1 of 5
 2016-09-26 Thin Smear and RBC Count Page 1 of 5 Name: Roll No.: Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: (a) Identify blood cell types in a smear and quantify their proportions. (b) Quantify RBC concentration
2016-09-26 Thin Smear and RBC Count Page 1 of 5 Name: Roll No.: Lab: Blood Smear and RBC Count Aim: (a) Identify blood cell types in a smear and quantify their proportions. (b) Quantify RBC concentration
The Cell Notes 1 of 11
 The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
The Cell The basic unit of structure and function in living things The smallest units in living things The smallest units in living things that show the characteristics of life Organisms can be made of
DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION MODELING FOR THE ANALYSIS OF HEMATOLOGICAL DISEASES BY ALTERNATIVE G-CSF TREATMENT
 DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION MODELING FOR THE ANALYSIS OF HEMATOLOGICAL DISEASES BY ALTERNATIVE G-CSF TREATMENT A THESIS REPORT Submitted by BALAMURALITHARAN S. Under the guidance of Dr. S.RAJASEKARAN in
DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION MODELING FOR THE ANALYSIS OF HEMATOLOGICAL DISEASES BY ALTERNATIVE G-CSF TREATMENT A THESIS REPORT Submitted by BALAMURALITHARAN S. Under the guidance of Dr. S.RAJASEKARAN in
Hematology Proficiency Test Program. Statistical Summary June 2014 (Event 14-2)
 Hematology Proficiency Test Program Statistical Summary June 2014 (Event 14-2) This statistical report summarizes participant data for the Hematology proficiency survey shipped 9 June 2014. Five test samples
Hematology Proficiency Test Program Statistical Summary June 2014 (Event 14-2) This statistical report summarizes participant data for the Hematology proficiency survey shipped 9 June 2014. Five test samples
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 9. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 9 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University RED BLOOD CELL MEMBRANE PROTEINS The Dynamic Nature of the Plasma Membrane SEM of human erythrocytes
Dept. of Biomed. Eng. BME302: Biomedical Instrumentation Kyung Hee Univ. Chapter 11 Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation
 Chapter 11 Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry:
Chapter 11 Clinical Laboratory Instrumentation Analysis of patient specimens: to aid in the diagnosis and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy Clinical phathology or clinical laboratory department Chemistry:
Cells and Their Organelles
 Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the basic unit of life. The following is a glossary of animal cell terms. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing
Mathematical Models for Erythropoiesis
 Mathematical Models for Erythropoiesis Joseph M. Mahaffy Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences San Diego State University January 2003 p.1/37 Collaborators Jacques Bélair - Université de
Mathematical Models for Erythropoiesis Joseph M. Mahaffy Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences San Diego State University January 2003 p.1/37 Collaborators Jacques Bélair - Université de
A Structured Population Model for Erythropoiesis
 A Structured Population Model for Erythropoiesis Doris H. Fuertinger 1, Franz Kappel 1, Peter Kotanko 2, Nathan W. Levine 2, Stephan Thijssen 2 1 Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computation, University
A Structured Population Model for Erythropoiesis Doris H. Fuertinger 1, Franz Kappel 1, Peter Kotanko 2, Nathan W. Levine 2, Stephan Thijssen 2 1 Institute for Mathematics and Scientific Computation, University
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Anatomy & Physiology Grade: 11-12
 Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: 8 weeks Topic(s): Introduction, Tissues, Integumentary System Describe the major components and functions of physiological systems, including skeletal, muscle,
Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi 5-part hematology analyzer
 Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi -part hematology analyzer A complete blood count (CBC) is frequently requested by physicians to obtain information about a patient s blood status, and tests are routinely
Clinical performance of Swelab Lumi -part hematology analyzer A complete blood count (CBC) is frequently requested by physicians to obtain information about a patient s blood status, and tests are routinely
THE CELL 3/15/15 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I THE CELLULAR BASIS OF LIFE
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Lecture: M 6-9:30 Randall Visitor Center Lab: W 6-9:30 Swatek Anatomy Center, Centennial Complex Required Text: Marieb 9 th edition Dr. Trevor Lohman DPT (949) 246-5357 tlohman@llu.edu
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Lecture: M 6-9:30 Randall Visitor Center Lab: W 6-9:30 Swatek Anatomy Center, Centennial Complex Required Text: Marieb 9 th edition Dr. Trevor Lohman DPT (949) 246-5357 tlohman@llu.edu
Name: Date: Hour:
 Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
Name: Date: Hour: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Comprehension Questions 1. At what level of organization does life begin? 2. What surrounds all cells? 3. What is meant by semipermeable? 4. What 2 things make up the cell
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Muscle Cells skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle
 Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
Chapter Life Is Cellular
 Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Chapter 7 7-1 Life Is Cellular The Discovery of the Cell Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe tiny little organisms in pond water. The Discovery of the Cell In 1665, Robert Hooke
Animal structure and function
 Animal structure and function The nervous system Parts of the nervous system 43C, 44B, 45D Brain structure and function Eyes Retina Neurons: How neurons communicate: Resting potential: The resting
Animal structure and function The nervous system Parts of the nervous system 43C, 44B, 45D Brain structure and function Eyes Retina Neurons: How neurons communicate: Resting potential: The resting
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms. Section 2: Inside Cells
 Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
Unit 2: The Structure and function of Organisms Section 2: 42 Essential Question: Are all cells the same? - Vocabulary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Organelle Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises. In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis.
 A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis. Before trying to do these steps, we should have read the
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis In-lab Guide Lab Exercises In this "Lab Exercise", we will be looking at cellular anatomy and mitosis. Before trying to do these steps, we should have read the
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Chapter 7. Cell Structure & Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function Scientists & Discoveries Early 1600 s (Holland): 1st microscope was constructed Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1600 s) used single lens as a microscope to study and very carefully
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
8. MATHEMATICAL MODELS OF HEMATOPOIETIC CELL REPLICATION AND CONTROL
 8. MATHEMATICAL MODELS OF HEMATOPOIETIC CELL REPLICATION AND CONTROL Michael C. Mackey 8.1 INTRODUCTION The biological sciences offer an abundance of examples in which the dynamics are dependent on the
8. MATHEMATICAL MODELS OF HEMATOPOIETIC CELL REPLICATION AND CONTROL Michael C. Mackey 8.1 INTRODUCTION The biological sciences offer an abundance of examples in which the dynamics are dependent on the
Chapter 3. Cells. Cells. Cells
 Chapter 3 Cells Cells Cytology The basic unit of life Humans have about 75 trillion cells Largest human cell is the egg While there are many varieties to cells there are many common characteristics. Cells
Chapter 3 Cells Cells Cytology The basic unit of life Humans have about 75 trillion cells Largest human cell is the egg While there are many varieties to cells there are many common characteristics. Cells
CHAPTER 3. Cell Structure and Genetic Control. Chapter 3 Outline
 CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
CHAPTER 3 Cell Structure and Genetic Control Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell Nucleus and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division
KEY POINTS TO EMPHASIZE WHEN TEACHING THE CELL
 CHAPTER 2: THE CELL: BASIC UNIT OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter presents the cell, the fundamental structure and functional unit of the human body (and all living things). In chapter
CHAPTER 2: THE CELL: BASIC UNIT OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter presents the cell, the fundamental structure and functional unit of the human body (and all living things). In chapter
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
1 Prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts have many features in common.
 1 Prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts have many features in common. (a) (i) The diagram below shows a mitochondrion. Two of the features labelled are typical of prokaryotes. Place a tick ( ) in
1 Prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts have many features in common. (a) (i) The diagram below shows a mitochondrion. Two of the features labelled are typical of prokaryotes. Place a tick ( ) in
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
chapter 7 Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Who was one of the first people to identify and see cork cells? a. Anton van
Overview of Cells. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory
 Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Overview of Cells Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Organelles The Endosymbiotic Theory Prokaryotic Cells Archaea Bacteria Come in many different shapes and sizes.5 µm 2 µm, up to 60 µm long Have large
Cell Types. Prokaryotes
 Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Cell Types Prokaryotes before nucleus no membrane-bound nucleus only organelle present is the ribosome all other reactions occur in the cytoplasm not very efficient Ex.: bacteria 1 Cell Types Eukaryotes
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
A SIX MONTH OLD GIRL WITH HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA Case study by Jim Perkins, M.D. ( 2009)
 A SIX MONTH OLD GIRL WITH HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA Case study by Jim Perkins, M.D. ( 2009) CLINICAL PRESENTATION A six month old girl presented with lethargy after four days of cough, rhinorrhea, and fever, and
A SIX MONTH OLD GIRL WITH HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA Case study by Jim Perkins, M.D. ( 2009) CLINICAL PRESENTATION A six month old girl presented with lethargy after four days of cough, rhinorrhea, and fever, and
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Human biology Cells: The Basic Units of Life Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Reference Text book of human biology by John Kenneth Inglis 3 rd Ed (1985) Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cell theory Cell theory consists
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure
 Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 1: Cell Structure Lesson 1.1.1 I will know I am successful if I can: 1. Label all parts of plant and animal cells and state their functions 2. State the differences between plant
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Slides Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Outline. Cell Structure and Function. Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles! Nucleus Outline! Endomembrane System! Cytoskeleton! Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella 1 2 Cell Theory
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles! Nucleus Outline! Endomembrane System! Cytoskeleton! Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella 1 2 Cell Theory
Flux Balance Analysis
 Lecture 10: Flux Balance Analysis Tue 7 March 2006 with the collaboration of Luna De Ferrari 1 Images and text from: E. Klipp, Systems Biology in Practice, Wiley-VCH, 2005 Ch 5 Edwards JS, Palsson BO,
Lecture 10: Flux Balance Analysis Tue 7 March 2006 with the collaboration of Luna De Ferrari 1 Images and text from: E. Klipp, Systems Biology in Practice, Wiley-VCH, 2005 Ch 5 Edwards JS, Palsson BO,
Bulk Transport. Active Transport. cell drinking. Highly specific! cell eating
 Bulk Transport cell eating cell drinking Active Transport Highly specific! Bulk transport is the active intracellular membrane transport of large numbers of solute particles or a large volume of solution
Bulk Transport cell eating cell drinking Active Transport Highly specific! Bulk transport is the active intracellular membrane transport of large numbers of solute particles or a large volume of solution
The Pituitary Gland. Pituitary Gland
 The Pituitary Gland Pituitary Gland The Hypophysis (Pituitary gland) Is the master gland, produces several hormones which influence the activity of other endocrine glands. Suspended from hypothalamus by
The Pituitary Gland Pituitary Gland The Hypophysis (Pituitary gland) Is the master gland, produces several hormones which influence the activity of other endocrine glands. Suspended from hypothalamus by
Cells: The Living Units
 Golgi Apparatus Cells: The Living Units Chapter 3, PPT 2 Membrane Yes, stacked and flattened Description Stacked and flattened membranous sacs Modify, concentrate, and package proteins & lipids made at
Golgi Apparatus Cells: The Living Units Chapter 3, PPT 2 Membrane Yes, stacked and flattened Description Stacked and flattened membranous sacs Modify, concentrate, and package proteins & lipids made at
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
Chapter 3: Cells. Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College
 Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 3 Cells vary in size possess distinctive shapes measured in micrometers 2 A Composite Cell hypothetical cell major parts nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane 3
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 3 Cells vary in size possess distinctive shapes measured in micrometers 2 A Composite Cell hypothetical cell major parts nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane 3
5a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Cells
 5a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Cells 5a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: AOIs of the erectors
5a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Cells 5a A&P: Introduction to the Human Body - Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: AOIs of the erectors
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Biochemical and haematological profile of donkeys in the Czech and Slovak Republics: influence of age and sex
 ACTA VET. BRNO 2017, 86: 151 157; https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201786020151 Biochemical and haematological profile of donkeys in the Czech and Slovak Republics: influence of age and sex Markéta Sedlinská
ACTA VET. BRNO 2017, 86: 151 157; https://doi.org/10.2754/avb201786020151 Biochemical and haematological profile of donkeys in the Czech and Slovak Republics: influence of age and sex Markéta Sedlinská
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Class: Date: Ch 7 Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to a. follow
Microscope History Robert Hooke
 1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
1 Microscope History Robert Hooke First described cells in 1665. He viewed thin slices of cork and compared the boxy partitions he observed to the cells (small rooms) in a monastery. (1635 1702) 2 Microscope
ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS WITHOUT AN OBVIOUS CAUSE Case Study by Jim Perkins, MD ( 2010)
 ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS WITHOUT AN OBVIOUS CAUSE Case Study by Jim Perkins, MD ( 2010) A 31 year old pregnant woman at 41 weeks, 2 days gestation was admitted to the hospital for induction of labor because
ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS WITHOUT AN OBVIOUS CAUSE Case Study by Jim Perkins, MD ( 2010) A 31 year old pregnant woman at 41 weeks, 2 days gestation was admitted to the hospital for induction of labor because
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Cell Structure and Cell Cycle
 E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
CELL LAB OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION: CELL UNIT. After completing this lab you should be able to:
 AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
AP BIOLOGY CELL UNIT ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR CELL LAB OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, 2. Prepare wet mount slides
5. The cells in the liver that detoxify poison substances contain lots of a. smooth ER b. rough ER c. Golgi apparatus d. lysosomes e.
 Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
Chapter 7 practice 1. What scientist originally came up with the term "cell"? a. von Leeuwenhoek d. Watson b. Hooke e. Virchow c. van der Waals 2. When you wish to look at the coat of a virus on the surface
dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology)
 dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology) jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 8 1 october 2015 cellular identity can be re-programmed III adult
dynamic processes in cells (a systems approach to biology) jeremy gunawardena department of systems biology harvard medical school lecture 8 1 october 2015 cellular identity can be re-programmed III adult
Course Outcome Summary
 Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Course Information: Description: Instruction Level: 11-12 Total Credits: Prerequisites: Textbooks: Course Content: (SCANAT) Advanced Anatomy & Physiology A basic understanding of the human body is essential
Cells. B. the development of advanced techniques to determine the chemical composition of substances
 ells Name: ate: 1. Which factor contributed most to the development of the cell theory? 1.. the discovery of many new species during the last century. the development of advanced techniques to determine
ells Name: ate: 1. Which factor contributed most to the development of the cell theory? 1.. the discovery of many new species during the last century. the development of advanced techniques to determine
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
c Copyright 2011 by Karen M. Bliss All Rights Reserved
 ABSTRACT BLISS, KAREN M. Modeling of Red Blood Cell Dynamics in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. (Under the direction of H.T. Banks and H.T. Tran.) Kidneys are the main site of production of the hormone
ABSTRACT BLISS, KAREN M. Modeling of Red Blood Cell Dynamics in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. (Under the direction of H.T. Banks and H.T. Tran.) Kidneys are the main site of production of the hormone
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body
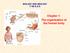 BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
BIOLOGY AND GEOLOGY 3º DE E.S.O. Chapter 1: The organisation of the human body 1. INTRODUCTION: LEVELS OF ORGANISATION What is a cell? Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of
Normal Cell Morphology in Canine and Feline Cytology
 Normal Cell Morphology in Canine and Feline Cytology Normal Cell Morphology in Canine and Feline Cytology An Identification Guide Written and translated by Lorenzo Ressel DVM, PhD, FHEA, DiplECVP, MRCVS
Normal Cell Morphology in Canine and Feline Cytology Normal Cell Morphology in Canine and Feline Cytology An Identification Guide Written and translated by Lorenzo Ressel DVM, PhD, FHEA, DiplECVP, MRCVS
e e = expected individuals with observed genotype Unit 1- Intro to AP and Taxonomy
 Unit 1- Intro to AP and Taxonomy 1. The Galapagos Islands were extremely important to Darwin and the Theory of Evolution. Darwin discovered many organisms and scientific ideas that were instrumental to
Unit 1- Intro to AP and Taxonomy 1. The Galapagos Islands were extremely important to Darwin and the Theory of Evolution. Darwin discovered many organisms and scientific ideas that were instrumental to
Basic Chemistry. Chemistry Review. Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology
 Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Prelab Exercise 1. Cell structure
 Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Life is Cellular Section 7.1
 Life is Cellular Section 7.1 Objectives Understand Cell theory Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Understand different types of microscopy, and how they work in more detail What is a Cell?
Life is Cellular Section 7.1 Objectives Understand Cell theory Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Understand different types of microscopy, and how they work in more detail What is a Cell?
Cells Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cells Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction The cell is the basic unit of biological organization Basic composition protoplasm cell membrane Organelles uman cells vary in size, shape and function From microscopic
Cells Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction The cell is the basic unit of biological organization Basic composition protoplasm cell membrane Organelles uman cells vary in size, shape and function From microscopic
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10
 Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 21, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers
Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University September 21, 2015 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany. Lecture 10 September 21, 2015 1 / 33 Outline 1 Questions and answers
OCR (A) Biology A-level
 OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.6: Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation Notes The role of mitosis and the cell cycle is to produce identical daughter cells for growth and asexual reproduction
OCR (A) Biology A-level Topic 2.6: Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation Notes The role of mitosis and the cell cycle is to produce identical daughter cells for growth and asexual reproduction
Nucleus. The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that store, protect and express most of the genetic information(dna) found in the cell.
 Nucleus The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that store, protect and express most of the genetic information(dna) found in the cell. Since regulation of gene expression takes place in the nucleus,
Nucleus The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that store, protect and express most of the genetic information(dna) found in the cell. Since regulation of gene expression takes place in the nucleus,
Cell structure and functions
 Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
Cell structure and functions Cells: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 4: Exchange and Transport Notes Single celled organisms do not have specialised transport systems. Substances can enter the cell by passive transport as diffusion distance
Edexcel (B) Biology A-level Topic 4: Exchange and Transport Notes Single celled organisms do not have specialised transport systems. Substances can enter the cell by passive transport as diffusion distance
