Influence of the Transom-Hollow Length on Wave Resistance
|
|
|
- Mervyn Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summary Influence of the Transom-Hollow Length on Wave Resistance Lawrence J. Doctors The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia Previous experimental data for the wave profiles behind a series of transom-stern ship models has been re-analyzed in this paper. Convenient regression formulas for the unwetting of the stern and the length of the transom hollow are provided. Predictions of wave resistance and, hence, total resistance can be improved by using this approach, together with the traditional thin-ship formulation for resistance. However, the accuracy of these predictions is improved further if one also considers that there must be a minimal effective hollow length based on the flow behind the well-known backward-facing step. 1 Introduction The prediction of the wave resistance of a high-speed marine vessel can be done effectively by the use of linearized-free-surface potential-flow theory, based on the thin-ship approach of Michell (1898). Thus, Doctors and Day (1997) applied the theory to a catamaran model tested in a towing tank, using a pair of centerplane source distributions one for each demihull. Furthermore, the resistance due to the assumed fully unwet transom was computed by considering the missing hydrostatic pressure. The total drag was then estimated through a simple summation of the wave resistance, hydrostatic resistance, and frictional resistance. One can also apply a frictional form factor f F to improve this estimate of the frictional or viscous resistance. The idealization of the flow is presented in Figure 1. 2 Experiments in Towing Tank A set of five geosim transom-stern models was constructed. These models are wallsided. They possess a parabolic entrance, a parallel midship and a parallel run back to the transom. Each of the models was tested at five drafts. This permitted the investigation to cover the range of beam-to-draft ratios: 1 B/T 4. This work has been described in detail by Doctors (2003) and Doctors and Beck (2005). The two parts of Figure 2 give the dimensionless wave profiles ζ/l for the case of B/T = 2 for two different transom Froude numbers F T = U/ gt. Complete flow separation typically occurs near these Froude numbers. Here, ζ is the wave elevation, L is the model length, T is the static draft at the stern of the vessel and U is the speed of the vessel. The curves for the five models collapse together well. Also shown in Figure 2 are the parabolas which have been fitted to the experimental free surface. The intersection point of these parabolas with the undisturbed free surface provides the length of the transom hollow. 3 Regression Curves Figure 3(a) shows the fraction of the transom that is dry η dry. This is based on the transom draft at rest (the case shown here) or, alternatively, on the dynamic transom draft. A regression curve of the form: η dry = C 1 F C 2 T (B/T ) C 3 R C 4 NT, (1)
2 5 Transom-Unwetting Model We finally turn to an explicit comparison of different models of the transom-stern flow. Figure 1: Definition of the Problem: Geometric Parameters has also been fitted. Both the beam-to-draft ratio B/T and the Reynolds number R NT = gt 3 /ν are included in the formulation. A similar regression formula for the hollow length has been fitted in Figure 3(b). The curves have been truncated using horizontal lines; it is assumed that one desires the effective length for the calculation of resistance. This length includes the dead-water region. 4 Resistance Prediction We now turn to the matter of the resistance of the vessel. Two examples, corresponding to two different values of the beam-to-draft ratio, are presented in Figure 4. The graphs show the wave resistance R W, the hydrostatic resistance R H, and the frictional resistance R F, plotted against the length Froude number F = U/ gl. The total predicted resistance R T, being a simple sum of these components, is also shown. The experimental total resistance is plotted for comparison purposes. The resistance has been made dimensionless by the weight of the model W. Good correlation between the theoretical resistance and the experimental resistance is demonstrated, even at low Froude numbers. This comparison appears in Figure 5 for two values of the beam-to-draft ratio. Five computational methods or physical approaches are shown. The first method (indicated by the key Full ) simply assumes that the transom is fully dry at all speeds; this is the approach of Doctors and Day (1997). The overestimation of resistance is very large at a low Froude number for these models. The second method (indicated by the key Fit,D ) is based on the present work. In this case, the drop in the water level on the transom and the length of the hollow behind the transom are based on an analysis of the abovementioned experiments in which the dynamic draft is used to nondimensionalize the data. It is seen that this technique greatly improves the predictions in the low-speed range. The third method (indicated by the key Fit,S ) is identical to the second method, except that in the analysis of the experiments the static draft is used to nondimensionalize the data. It is believed that this approach is somewhat more consistent, since the resistance calculations also ignore sinkage and trim. This surmise is borne out by the slightly improved agreement with the experimental results for the resistance. The fourth method (indicated by the key Fit,S,B ) is an improvement to the third method, in that a minimal hollow length is also assumed. This minimum is that from an analysis of the flow behind a traditional backward-facing step. Thus, it was assumed that the hollow length could never be less than times the transom draft. The fact that these predictions are even better suggests that there is a dead-water region extending beyond the visible hollow and that this plays a critical rôle in the creation of the wave resistance.
3 Figure 2: Parabolic Fit to Wave Profiles Figure 2: Parabolic Fit to Wave Profiles (a) F T = 2.4 (b) F T = 2.6 Figure 3: Analysis Based on Static Definition (a) Unwetting of Transom Figure 3: Analysis Based on Static Definition (b) Length of Hollow Finally, the fifth method (also indicated by the key Fit,S,B ) is the same as the fourth method, except that a frictional form factor given by f F = 1.35 has also been employed. This choice seems to be reasonable in view of the sharp bilges that the models possess; it also provides excellent resistance predictions over the entire Froude-number range. 6 Conclusions This research has demonstrated that this enhanced model for the water flow behind the transom leads to an accurate estimate of the transom hydrostatic drag. Additionally, a very good prediction of the wave resistance and the total resistance of such vessels is provided, even at very low speeds. It is recommended that effort be invested in testing larger models in order to further study the relevance of the Reynolds number. 7 Acknowledgments The tests were performed in the Towing Tank at the Australian Maritime College (AMC) by Mr Simon Robards, postgraduate student at UNSW, under the able supervision of Mr Gregor Macfarlane of the AMC.
4 Figure 4: Components of Resistance Figure 4: Components of Resistance (a) B/T = (b) B/T = Figure 5: Transom-Stern Flow Model Figure 5: Transom-Stern Flow Model (a) B/T = (b) B/T = The author acknowledges the assistance of the Australian Research Council (ARC) Discovery-Projects Grant Scheme (via Grant Number DP ). This work was also partially supported by Office of Naval Research (ONR) contract N The University of New South Wales (UNSW) provided infrastructure support. 8 References Doctors, L.J.: Hydrodynamics of the Flow behind a Transom Stern, Proc. Twenty-Ninth Israel Conference on Mechanical Engineering, Paper 20-1, Technion, Haifa, Israel, 11 pp (May 2003) Doctors, L.J. and Beck, R.F: The Separation of the Flow Past a Transom Stern, Proc. First International Conference on Marine Research and Transportation (ICMRT 05), Ischia, Italy, 14 pp (September 2005) Doctors, L.J. and Day, A.H.: Resistance Prediction for Transom-Stern Vessels, Proc. Fourth International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation (FAST 97), Sydney, Australia, Vol. 2, pp (July 1997) Michell, J.H.: The Wave Resistance of a Ship, Philosophical Magazine, London, Series 5, Vol. 45, pp (1898)
5 Doctors, L. Influence of the transom-hollow length on wave resistance Discusser - D.H. Peregrine: With regard to Reynolds number: the separation from the base of the transom is likely to be affected by the boundary layer from the bottom of the vessel thus Re based on wetted length may be most relevant. Also whether or not this boundary layer is turbulent. Reply: Yes, these comments are absolutely correct. The suction process that causes the water drop behind the transom stern is similar to the process that results ion the negative back pressure behind a blunt projectile, for example. The phenomenon seems to be depended on the development of the boundary layer ahead of the transom. It is intended to continue this research and to analyze the results based on the vessel-length Reynolds number, as suggested.
Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through. Regression Analysis
 Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through Xuan P. Pham Research Student Dept. of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Australian Maritime College PO Box 986, Launceston, TAS 7250, Australia.
Wave Resistance Prediction of Hard-Chine Catamarans through Xuan P. Pham Research Student Dept. of Naval Architecture & Ocean Engineering Australian Maritime College PO Box 986, Launceston, TAS 7250, Australia.
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew Dominic J. Taunton Dominic A.
 A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
A Study of Resistance of High-Speed Catamarans and Scale Effects on Form Factor Sarawuth Srinakaew, Dominic J. Taunton, Dominic A. Hudson Fluid Structure Interactions Group, University of Southampton ss17e111@soton.ac.uk
THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS. 5-8 May 1997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA
 THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS 5-8 May 997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA REGRESSION ANALYSIS OF SYSTEMATIC SERIES CALM WATER PERFORMANCE Predrag Bojovic
THIRD INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT FOR MARINE APPLICATIONS 5-8 May 997, Newport, Rhode Island, USA REGRESSION ANALYSIS OF SYSTEMATIC SERIES CALM WATER PERFORMANCE Predrag Bojovic
The Twenty-Sixth Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics. The Resistance Components of a Surface-Effect Ship Lawrence J. Doctors. Chris B.
 Proceedings of The Twenty-Sixth Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Rome, Italy September 17 22, 2006 The Resistance Components of a Surface-Effect Ship Lawrence J. Doctors School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
Proceedings of The Twenty-Sixth Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Rome, Italy September 17 22, 2006 The Resistance Components of a Surface-Effect Ship Lawrence J. Doctors School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber
 Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
Mooring Model for Barge Tows in Lock Chamber by Richard L. Stockstill BACKGROUND: Extensive research has been conducted in the area of modeling mooring systems in sea environments where the forcing function
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! The total calm water resistance is given by:
 Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
Welcome to the Ship Resistance Predictor! What does this Excel Sheet do? This Excel sheet helps you calculate the Total Calm Water Resistance for a Ship at a given forward speed It also calculates from
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Resistance Resistance Test
 -0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
-0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects
 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos
 Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
J. (2008) 52 (4) ISSN
 Doctors, Lawrence J. and Day, Alexander and Clelland, David (2008) Unsteady effects during resistance tests on a ship model in a towing tank. Journal of Ship Research, 52 (4). pp. 263-273. ISSN 0022-4502,
Doctors, Lawrence J. and Day, Alexander and Clelland, David (2008) Unsteady effects during resistance tests on a ship model in a towing tank. Journal of Ship Research, 52 (4). pp. 263-273. ISSN 0022-4502,
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid
 Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE
 N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
Wave Resistance Prediction of a Cataaran by Linearised Theory M.INSEL Faculty of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, TURKEY A.F.MOLLAND, J.F.WELLICOME Departent of
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics. Prof. Z. Zong Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, Espoo
 MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics Prof. Z. Zong zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teacher: Prof. Z. Zong, zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teaching
MEC-E2001 Ship Hydrodynamics Prof. Z. Zong zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teacher: Prof. Z. Zong, zhi.zong@aalto.fi Room 213a, K3, Puumiehenkuja 5A, 02510 Espoo Teaching
RESISTANCE OF AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERLES. HIGH SPEED DISPLACEMENT HULL FoRMs
 IV SYMPOSIUM ON HIGH SPEED MARINE VEHICLES 18-21 March 1997, Naples, Italy RESISTANCE OF AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERLES OF HIGH SPEED DISPLACEMENT HULL FoRMs Predrag Bojovic Australian Maritime Engineering CRC
IV SYMPOSIUM ON HIGH SPEED MARINE VEHICLES 18-21 March 1997, Naples, Italy RESISTANCE OF AMECRC SYSTEMATIC SERLES OF HIGH SPEED DISPLACEMENT HULL FoRMs Predrag Bojovic Australian Maritime Engineering CRC
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Stokes' law and Reynold number Dr. Zifei Liu The motion of a particle in a fluid environment, such as air or water m dv =F(t) - F dt d - 1 4 2 3 πr3
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Stokes' law and Reynold number Dr. Zifei Liu The motion of a particle in a fluid environment, such as air or water m dv =F(t) - F dt d - 1 4 2 3 πr3
1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. A. True B. False
 CHAPTER 07 1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. 2.A qualitative description of physical quantities can be given in terms of. YOUR ANSWER:
CHAPTER 07 1.The pressure drop per unit length that develops due to friction cannot generally be solved analytically. 2.A qualitative description of physical quantities can be given in terms of. YOUR ANSWER:
INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS. Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak
 INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS by Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree in Naval Architecture and Marine
INVESTIGATION OF TRIMARAN INTERFERENCE EFFECTS by Brendan Carr Robert Dvorak A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree in Naval Architecture and Marine
ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
5 SIMILITUDE. 5.1 Use of Nondimensional Groups
 5 SIMIITDE 5. se of Nondimensional Groups For a consistent description of physical processes, we require that all terms in an equation must have the same units. On the basis of physical laws, some quantities
5 SIMIITDE 5. se of Nondimensional Groups For a consistent description of physical processes, we require that all terms in an equation must have the same units. On the basis of physical laws, some quantities
Computation of the wavemaking resistance of a Harley surface effect ship
 Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH
 5th WSEAS International Conference on FLUID MECHANICS (FLUIDS'08) Acapulco, Mexico, January 5-7, 008 FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH EBERHARD WOLFF Departamento de Metal Mecanica Instituto
5th WSEAS International Conference on FLUID MECHANICS (FLUIDS'08) Acapulco, Mexico, January 5-7, 008 FRICTION IN SHIP RESISTANCE - A DIFFERENT APPROACH EBERHARD WOLFF Departamento de Metal Mecanica Instituto
Motions and Resistance of a Ship in Regular Following Waves
 Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
A Drag Estimate for Concept-Stage Ship Design Optimization
 The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Electronic Theses and Dissertations Fogler Library 9 A Drag Estimate for Concept-Stage Ship Design Optimization Douglas Read Follow this and additional works
The University of Maine DigitalCommons@UMaine Electronic Theses and Dissertations Fogler Library 9 A Drag Estimate for Concept-Stage Ship Design Optimization Douglas Read Follow this and additional works
Definitions. Temperature: Property of the atmosphere (τ). Function of altitude. Pressure: Property of the atmosphere (p). Function of altitude.
 Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Definitions Chapter 3 Standard atmosphere: A model of the atmosphere based on the aerostatic equation, the perfect gas law, an assumed temperature distribution, and standard sea level conditions. Temperature:
Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity)
 Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity) College of Shipbuilding and Engineering Harbin Engineering University ------------- Zhu Xin Supervisor: Prof. Duan Wen-yang 1
Research and application of 2-D water entry simulation (constant velocity) College of Shipbuilding and Engineering Harbin Engineering University ------------- Zhu Xin Supervisor: Prof. Duan Wen-yang 1
IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.6 Example von Kármán s Laminar Boundary Layer Problem
 CEE 3310 External Flows (Boundary Layers & Drag, Nov. 11, 2016 157 7.5 Review Non-Circular Pipes Laminar: f = 64/Re DH ± 40% Turbulent: f(re DH, ɛ/d H ) Moody chart for f ± 15% Bernoulli-Based Flow Metering
CEE 3310 External Flows (Boundary Layers & Drag, Nov. 11, 2016 157 7.5 Review Non-Circular Pipes Laminar: f = 64/Re DH ± 40% Turbulent: f(re DH, ɛ/d H ) Moody chart for f ± 15% Bernoulli-Based Flow Metering
FACTORS OF SAFETY FOR RICHARDSON EXTRAPOLATION
 FACTORS OF SAFETY FOR RICHARDSON ETRAPOLATION by Tao ing 1 and Fred Stern Sponsored by The Office of Naval Research Grant N00014-01-1-0073 IIHR Technical Report No. 476 IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering
FACTORS OF SAFETY FOR RICHARDSON ETRAPOLATION by Tao ing 1 and Fred Stern Sponsored by The Office of Naval Research Grant N00014-01-1-0073 IIHR Technical Report No. 476 IIHR Hydroscience & Engineering
The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory
 J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
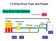 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Ship Resistance Prediction Methods II We have been discussing about resistance
Ship Resistance And Propulsion Prof. Dr. P. Krishnankutty Ocean Department Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 14 Ship Resistance Prediction Methods II We have been discussing about resistance
Local Velocity Field Measurements around the KCS Model (SRI M.S.No.631) in the SRI 400m Towing Tank
 Local Velocity Field Measurements around the KCS Model (SRI M.S.No.631) in the SRI 400m Towing Tank 1. Introduction The present report describes the local velocity field measurements around a model of
Local Velocity Field Measurements around the KCS Model (SRI M.S.No.631) in the SRI 400m Towing Tank 1. Introduction The present report describes the local velocity field measurements around a model of
Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO & THEIR TOMAS
 2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
2014 Ship Project A ASSIGNMENT ONE RAN XIAO 467643 & THEIR TOMAS 224051 Resistance estimation Methodology brief As our ship concept is in form of catamaran, it is not proper to simply introduce the method
Integration to Compute Volumes, Work. Goals: Volumes by Slicing Volumes by Cylindrical Shells Work
 Week #8: Integration to Compute Volumes, Work Goals: Volumes by Slicing Volumes by Cylindrical Shells Work 1 Volumes by Slicing - 1 Volumes by Slicing In the integration problems considered in this section
Week #8: Integration to Compute Volumes, Work Goals: Volumes by Slicing Volumes by Cylindrical Shells Work 1 Volumes by Slicing - 1 Volumes by Slicing In the integration problems considered in this section
Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts
 Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts Michael L. Banner School of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney 2052, Australia Tel :
Refined Source Terms in WAVEWATCH III with Wave Breaking and Sea Spray Forecasts Michael L. Banner School of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney 2052, Australia Tel :
Hydraulic Engineering
 PDHonline Course H146 (4 PDH) Hydraulic Engineering Instructor: Mohamed Elsanabary, Ph.D., Prov. Lic. Engineering. 2013 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax:
PDHonline Course H146 (4 PDH) Hydraulic Engineering Instructor: Mohamed Elsanabary, Ph.D., Prov. Lic. Engineering. 2013 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax:
15 March 2010 Re: Draft Native Vegetation of the Sydney Metropolitan Catchment Management Authority Area GIS layers and explanatory reports
 SYDNEY COASTAL COUNCILS GROUP Inc. C/- City of Sydney Council Level 14, 456 Kent Street GPO Box 1591, SYDNEY NSW 2001 Phone: (02) 9246 7791 Facsimile: (02) 9265 9660 Email: info@sydneycoastalcouncils.com.au
SYDNEY COASTAL COUNCILS GROUP Inc. C/- City of Sydney Council Level 14, 456 Kent Street GPO Box 1591, SYDNEY NSW 2001 Phone: (02) 9246 7791 Facsimile: (02) 9265 9660 Email: info@sydneycoastalcouncils.com.au
Lecture-4. Flow Past Immersed Bodies
 Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
Lecture-4 Flow Past Immersed Bodies Learning objectives After completing this lecture, you should be able to: Identify and discuss the features of external flow Explain the fundamental characteristics
LECTURE 1 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS:
 LECTURE 1 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO FLUID AND BASIC EQUATIONS 2.0 REYNOLDS NUMBER AND CRITICAL VELOCITY 3.0 APPROACH TOWARDS REYNOLDS NUMBER REFERENCES Page 1 of
LECTURE 1 THE CONTENTS OF THIS LECTURE ARE AS FOLLOWS: 1.0 INTRODUCTION TO FLUID AND BASIC EQUATIONS 2.0 REYNOLDS NUMBER AND CRITICAL VELOCITY 3.0 APPROACH TOWARDS REYNOLDS NUMBER REFERENCES Page 1 of
WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS
 ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
ARAB ACADEMY FOR SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND MARITIME TRANSPORT COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WATERJET PROPULSION SYSEM FOR HIGH SPEED CRAFTS Thesis Submitted to The Marine Engineering Department In
Chapter 8: Flow in Pipes
 Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate the major and minor losses associated with pipe flow in piping networks
Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate the major and minor losses associated with pipe flow in piping networks
GENERAL SOLUTIONS FOR THE INITIAL RUN-UP OF A BREAKING TSUNAMI FRONT
 International Symposium Disaster Reduction on Coasts Scientific-Sustainable-Holistic-Accessible 14 16 November 2005 Monash University, Melbourne, Australia GENERAL SOLUTIONS FOR THE INITIAL RUN-UP OF A
International Symposium Disaster Reduction on Coasts Scientific-Sustainable-Holistic-Accessible 14 16 November 2005 Monash University, Melbourne, Australia GENERAL SOLUTIONS FOR THE INITIAL RUN-UP OF A
Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model Testing
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Powering for Medium Speed Wave-Piercing Catamarans comparing Waterjet and Screw Propeller Performance using Model
ITTC Recommended Procedures
 I Recommended Analysis in Resistance ests 7.5- -- Page of 0. PURPOSE O GUIDELINE... able of ontents 3.5 Data Reduction... 6. MEASURANDS... 3. UNERAINY SOURES... 3. Model Geometry... 3 3. est Installation...
I Recommended Analysis in Resistance ests 7.5- -- Page of 0. PURPOSE O GUIDELINE... able of ontents 3.5 Data Reduction... 6. MEASURANDS... 3. UNERAINY SOURES... 3. Model Geometry... 3 3. est Installation...
Dimensions represent classes of units we use to describe a physical quantity. Most fluid problems involve four primary dimensions
 BEE 5330 Fluids FE Review, Feb 24, 2010 1 A fluid is a substance that can not support a shear stress. Liquids differ from gasses in that liquids that do not completely fill a container will form a free
BEE 5330 Fluids FE Review, Feb 24, 2010 1 A fluid is a substance that can not support a shear stress. Liquids differ from gasses in that liquids that do not completely fill a container will form a free
ITTC Circular Letter
 ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
ITTC Circular Letter May, 2016 Load variation tests The speed/power sea trials procedures, ITTC Recommended rocedures 7.5-04-01-01.1 and -01.2, and IO15016:2015 require that load variation tests are performed
Hydromechanics: Course Summary
 Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
Hydromechanics: Course Summary Hydromechanics VVR090 Material Included; French: Chapters to 9 and 4 + Sample problems Vennard & Street: Chapters 8 + 3, and (part of it) Roberson & Crowe: Chapter Collection
Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series
 Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, 4, last revision September 6 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula
Bare Hull Upright Resistance Prediction Based on the Delft Systematic Yacht Hull Series Copyright Ulrich Remmlinger, Germany, 4, last revision September 6 Abstract. A regression analysis yields a new formula
Fluid Mechanics III. 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity
 Fluid Mechanics III 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity Similarity The real world is non-dimensional. The proposition the Eiffel Tower is tall has no sense unless we state what is the object we compare
Fluid Mechanics III 1. Dimensional analysis and similarity Similarity The real world is non-dimensional. The proposition the Eiffel Tower is tall has no sense unless we state what is the object we compare
Master Thesis. Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations
 Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Modeling. Eric G. Paterson. Spring Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering The Pennsylvania State University.
 Eric G. Paterson Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering The Pennsylvania State University Spring 2005 Blackboard notes Blackboard notes Nondimensionalization of an equation is useful only when
Eric G. Paterson Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering The Pennsylvania State University Spring 2005 Blackboard notes Blackboard notes Nondimensionalization of an equation is useful only when
KCATM 2013 Algebra Team Test. E) No Solution. C x By. E) None of the Above are correct C) 9,19
 KCTM 03 lgebra Team Test School ) Solve the inequality: 6 3 4 5 5 3,,3 3, 3 E) No Solution Both and B are correct. ) Solve for : By C C B y C By B C y C By E) None of the bove are correct 3) Which of the
KCTM 03 lgebra Team Test School ) Solve the inequality: 6 3 4 5 5 3,,3 3, 3 E) No Solution Both and B are correct. ) Solve for : By C C B y C By B C y C By E) None of the bove are correct 3) Which of the
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder
 International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
International Shipbuilding Progress 60 (2013) 309 343 309 DOI 10.3233/ISP-130101 IOS Press Confined water effects on the viscous flow around a tanker with propeller and rudder L. Zou and L. Larsson Chalmers
Applied Fluid Mechanics
 Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
Applied Fluid Mechanics 1. The Nature of Fluid and the Study of Fluid Mechanics 2. Viscosity of Fluid 3. Pressure Measurement 4. Forces Due to Static Fluid 5. Buoyancy and Stability 6. Flow of Fluid and
DRAG REDUCTION BY BIOPOLYMER OF MONEPTERUS ALBUS SLIME ON SHIP MODEL WALL
 Jurnal Mekanikal June 2011, No. 32, 96-107 DRAG REDUCTION BY BIOPOLYMER OF MONEPTERUS ALBUS SLIME ON SHIP MODEL WALL Yanuar *, M A Talahatu, Sunaryo and Warjito Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty
Jurnal Mekanikal June 2011, No. 32, 96-107 DRAG REDUCTION BY BIOPOLYMER OF MONEPTERUS ALBUS SLIME ON SHIP MODEL WALL Yanuar *, M A Talahatu, Sunaryo and Warjito Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
 Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (08 30-35 doi 0.765/59-5879/08.0.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability CUI Jian, WU Zixin and CHEN Weimin Shanghai Ship and Shipping
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (08 30-35 doi 0.765/59-5879/08.0.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Research on Prediction of Ship Manoeuvrability CUI Jian, WU Zixin and CHEN Weimin Shanghai Ship and Shipping
Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel
 RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
RescOp - Development of rescue operations in the Gulf of Finland International Seminar: MARITIME SAFETY IN THE GULF OF FINLAND Interaction of Ships within Navigable Ice Channel Vadim K. Goncharov Department
On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
FLUID MECHANICS PROF. DR. METİN GÜNER COMPILER
 FLUID MECHANICS PROF. DR. METİN GÜNER COMPILER ANKARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF AGRICULTURE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY AND TECHNOLOGIES ENGINEERING 1 5. FLOW IN PIPES 5.1.3. Pressure and Shear Stress
FLUID MECHANICS PROF. DR. METİN GÜNER COMPILER ANKARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF AGRICULTURE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURAL MACHINERY AND TECHNOLOGIES ENGINEERING 1 5. FLOW IN PIPES 5.1.3. Pressure and Shear Stress
FLOW SEPARATION. Aerodynamics Bridge-Pier Design Combustion Chambers Human Blood Flow Building Design Etc.
 FLOW SEPARATION Aerodynamics Bridge-Pier Design Combustion Chambers Human Blood Flow Building Design Etc. (Form Drag, Pressure Distribution, Forces and Moments, Heat And Mass Transfer, Vortex Shedding)
FLOW SEPARATION Aerodynamics Bridge-Pier Design Combustion Chambers Human Blood Flow Building Design Etc. (Form Drag, Pressure Distribution, Forces and Moments, Heat And Mass Transfer, Vortex Shedding)
Phase-averaged analysis of an oscillating water column wave energy converter
 Phase-averaged analysis of an oscillating water column wave energy converter Alan Fleming, BEng (Hons) National Centre for Maritime Engineering and Hydrodynamics Australian Maritime College Submitted in
Phase-averaged analysis of an oscillating water column wave energy converter Alan Fleming, BEng (Hons) National Centre for Maritime Engineering and Hydrodynamics Australian Maritime College Submitted in
A Note on Methods. ARC Project DP The Demand for Higher Density Housing in Sydney and Melbourne Working Paper 3. City Futures Research Centre
 A Note on Methods ARC Project DP0773388 The Demand for Higher Density Housing in Sydney and Melbourne Working Paper 3 City Futures Research Centre February 2009 A NOTE ON METHODS Dr Raymond Bunker, Mr
A Note on Methods ARC Project DP0773388 The Demand for Higher Density Housing in Sydney and Melbourne Working Paper 3 City Futures Research Centre February 2009 A NOTE ON METHODS Dr Raymond Bunker, Mr
Computational fluid dynamics investigation on total resistance coefficient of a high-speed deep-v catamaran in shallow water
 International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering ISSN: 2229-8649 (Print); ISSN: 2180-1606 (Online); Volume 14, Issue 2 pp. 4369-4382 June 2017 Universiti Malaysia Pahang Publishing DOI: https://doi.org/10.15282/ijame.14.2.2017.18.0347
International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering ISSN: 2229-8649 (Print); ISSN: 2180-1606 (Online); Volume 14, Issue 2 pp. 4369-4382 June 2017 Universiti Malaysia Pahang Publishing DOI: https://doi.org/10.15282/ijame.14.2.2017.18.0347
The CPT in unsaturated soils
 The CPT in unsaturated soils Associate Professor Adrian Russell (UNSW) Mr David Reid (Golder Associates) Prof Nasser Khalili (UNSW) Dr Mohammad Pournaghiazar (UNSW) Dr Hongwei Yang (Uni of Hong Kong) Outline
The CPT in unsaturated soils Associate Professor Adrian Russell (UNSW) Mr David Reid (Golder Associates) Prof Nasser Khalili (UNSW) Dr Mohammad Pournaghiazar (UNSW) Dr Hongwei Yang (Uni of Hong Kong) Outline
Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in the Adriatic Sea
 Towards Green Marine Technology and Transport Guedes Soares, Dejhalla & Pavleti (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02887-6 Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in
Towards Green Marine Technology and Transport Guedes Soares, Dejhalla & Pavleti (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02887-6 Seakeeping characteristics of intact and damaged ship in
Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity
 Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 1, 1993 WIT Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 1743-3509 Hull loads and response, hydroelasticity effects on fast monohulls E. Jullumstr0 & J.V. Aarsnes Division of
Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on Pump Performance
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships
 Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships Treball Final de Grau Facultat de Nàutica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Treball realitzat per: Rafael Pacheco Blàzquez Dirigit per:
Analysis of the resistance due to waves in ships Treball Final de Grau Facultat de Nàutica de Barcelona Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Treball realitzat per: Rafael Pacheco Blàzquez Dirigit per:
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER
 UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
UNIT II CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER Convection is the mode of heat transfer between a surface and a fluid moving over it. The energy transfer in convection is predominately due to the bulk motion of the fluid
Viscous Flow in Ducts
 Dr. M. Siavashi Iran University of Science and Technology Spring 2014 Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate
Dr. M. Siavashi Iran University of Science and Technology Spring 2014 Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of laminar and turbulent flow in pipes and the analysis of fully developed flow 2. Calculate
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows
 Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
Fluid Mechanics Prof. T.I. Eldho Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 17 Laminar and Turbulent flows Welcome back to the video course on fluid mechanics. In
DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE
 DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE 1 Kiran Torangatti, 2 Dr.Basawaraj 1 Research Scholar, Department of Aerospace Propulsion and Technology, VTU-CPGS Bangalore -560018,Karnataka,
DRAG PREDICTION AND VALIDATION OF STANDARD M549, 155mm PROJECTILE 1 Kiran Torangatti, 2 Dr.Basawaraj 1 Research Scholar, Department of Aerospace Propulsion and Technology, VTU-CPGS Bangalore -560018,Karnataka,
Investigation of side wall and ship model interaction
 Yuan, Zhi-Ming and Incecik, Atilla (6) Investigation of side wall and ship model interaction. In: 6 International Conference on Maritime Technology, 6-7-6-6-7-8., This version is available at https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/5797/
Yuan, Zhi-Ming and Incecik, Atilla (6) Investigation of side wall and ship model interaction. In: 6 International Conference on Maritime Technology, 6-7-6-6-7-8., This version is available at https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/5797/
A Student Research Project To Compare the Theoretical Pressure Drops Across Heat Sinks to Actual Measured Pressure Drops
 A Student Research Project To Compare the Theoretical Pressure Drops Across Heat Sinks to Actual Measured Pressure Drops Robert Edwards School of Engineering Penn State Erie, The Behrend College Erie,
A Student Research Project To Compare the Theoretical Pressure Drops Across Heat Sinks to Actual Measured Pressure Drops Robert Edwards School of Engineering Penn State Erie, The Behrend College Erie,
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct. 22,
 CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct., 018 115 5.5 Review vorticity twice the local rotation rate: ω x = w y v z, ω y = u z w x, ω z = v x u y Dimensional Analysis Buckingham Pi Theorem: k =
CEE 3310 Dimensional Analysis & Similitude, Oct., 018 115 5.5 Review vorticity twice the local rotation rate: ω x = w y v z, ω y = u z w x, ω z = v x u y Dimensional Analysis Buckingham Pi Theorem: k =
ν δ - 1 -
 ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
ν δ - 1 - δ ν ν δ ν ν - 2 - ρ δ ρ θ θ θ δ τ ρ θ δ δ θ δ δ δ δ τ μ δ μ δ ν δ δ δ - 3 - τ ρ δ ρ δ ρ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ δ - 4 - ρ μ ρ μ ρ ρ μ μ ρ - 5 - ρ τ μ τ μ ρ δ δ δ - 6 - τ ρ μ τ ρ μ ρ δ θ θ δ θ - 7
DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS
 4th MASHCON, Hamburg - Uliczka et al. (eds) - 6 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393-38- (Online) DOI:.845/978-3-9393-38-_3 DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS A Gronarz,
4th MASHCON, Hamburg - Uliczka et al. (eds) - 6 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-9393-38- (Online) DOI:.845/978-3-9393-38-_3 DEVELOPMENT OF A SQUAT FORMULA BASED ON NUMERICAL CALCULATIONS A Gronarz,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management TECHNOLOGY (ICETEM14) (IJDMT) 30-31,December, 2014, Ernakulam,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management TECHNOLOGY (ICETEM14) (IJDMT) 30-31,December, 2014, Ernakulam,
On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies
 On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies Chang-Ho Lee AMIT Inc., Chestnut Hill MA, USA June 9, 006 Abstract. Conservation of momentum is applied to finite fluid volume surrounding a body
On the evaluation quadratic forces on stationary bodies Chang-Ho Lee AMIT Inc., Chestnut Hill MA, USA June 9, 006 Abstract. Conservation of momentum is applied to finite fluid volume surrounding a body
Chapter 7: Dimensional Analysis
 7-1 Dimension and Units 7-2 Dimensional Homogeneity 7-3 Dimensional Analysis and Similarity 7-4 Methods of Repeating Variables 7-5 Experimental Testing and Incomplete Similarity 7-1 Dimensions and Units
7-1 Dimension and Units 7-2 Dimensional Homogeneity 7-3 Dimensional Analysis and Similarity 7-4 Methods of Repeating Variables 7-5 Experimental Testing and Incomplete Similarity 7-1 Dimensions and Units
Object Impact on the Free Surface and Added Mass Effect Laboratory Fall 2005 Prof. A. Techet
 Object Impact on the Free Surface and Added Mass Effect.016 Laboratory Fall 005 Prof. A. Techet Introduction to Free Surface Impact Free surface impact of objects has applications to ocean engineering
Object Impact on the Free Surface and Added Mass Effect.016 Laboratory Fall 005 Prof. A. Techet Introduction to Free Surface Impact Free surface impact of objects has applications to ocean engineering
Experimental tests and Numerical analysis for an Air Cavity Yacht
 UNIVERSITY OF MESSINA Department of Engineering Doctorate in Engineering and Chemical of Materials and Constructions (XXX cycle) Experimental tests and Numerical analysis for an Air Cavity Yacht PhD Candidate:
UNIVERSITY OF MESSINA Department of Engineering Doctorate in Engineering and Chemical of Materials and Constructions (XXX cycle) Experimental tests and Numerical analysis for an Air Cavity Yacht PhD Candidate:
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati Presented by: BENZOHRA Abdelmalek
 Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Chapter (3) Water Flow in Pipes
 Chapter (3) Water Flow in Pipes Water Flow in Pipes Bernoulli Equation Recall fluid mechanics course, the Bernoulli equation is: P 1 ρg + v 1 g + z 1 = P ρg + v g + z h P + h T + h L Here, we want to study
Chapter (3) Water Flow in Pipes Water Flow in Pipes Bernoulli Equation Recall fluid mechanics course, the Bernoulli equation is: P 1 ρg + v 1 g + z 1 = P ρg + v g + z h P + h T + h L Here, we want to study
Chapter 8: Flow in Pipes
 8-1 Introduction 8-2 Laminar and Turbulent Flows 8-3 The Entrance Region 8-4 Laminar Flow in Pipes 8-5 Turbulent Flow in Pipes 8-6 Fully Developed Pipe Flow 8-7 Minor Losses 8-8 Piping Networks and Pump
8-1 Introduction 8-2 Laminar and Turbulent Flows 8-3 The Entrance Region 8-4 Laminar Flow in Pipes 8-5 Turbulent Flow in Pipes 8-6 Fully Developed Pipe Flow 8-7 Minor Losses 8-8 Piping Networks and Pump
Calculation of the Flow around the KVLCC2M Tanker
 Calculation of the Flow around the KVLCC2M Tanker L. Eça 1, M. Hoekstra 2 and S.L. Toxopeus 2 1 Instituto Superior Técnico, Portugal 2 Maritime Research Institute, Netherlands SUMMARY The flow around the
Calculation of the Flow around the KVLCC2M Tanker L. Eça 1, M. Hoekstra 2 and S.L. Toxopeus 2 1 Instituto Superior Técnico, Portugal 2 Maritime Research Institute, Netherlands SUMMARY The flow around the
Investigation of ship maneuvering with hydrodynamic effects between ship and bank
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology (8) 3~36 www.springerlink.com/content/738-494 Investigation of ship maneuvering with hydrodynamic effects between
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology (8) 3~36 www.springerlink.com/content/738-494 Investigation of ship maneuvering with hydrodynamic effects between
Basic Fluid Mechanics
 Basic Fluid Mechanics Chapter 6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 4/16/2018 C6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 1 6.1 Introduction For the present chapter we will limit our study to incompressible
Basic Fluid Mechanics Chapter 6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 4/16/2018 C6A: Internal Incompressible Viscous Flow 1 6.1 Introduction For the present chapter we will limit our study to incompressible
Strathprints Institutional Repository
 Strathprints Institutional Repository Tezdogan, Tahsin and Incecik, Atilla and Turan, Osman (2016) A numerical investigation of the squat and resistance of ships advancing through a canal using CFD. Journal
Strathprints Institutional Repository Tezdogan, Tahsin and Incecik, Atilla and Turan, Osman (2016) A numerical investigation of the squat and resistance of ships advancing through a canal using CFD. Journal
