Methods of evaluating estimators and best unbiased estimators Hamid R. Rabiee
|
|
|
- Sara Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stochastic Processes Methods of evaluating estimators and best unbiased estimators Hamid R. Rabiee 1
2 Outline Methods of Mean Squared Error Bias and Unbiasedness Best Unbiased Estimators CR-Bound for variance Sufficiency and UMVUE 2
3 Which estimator? Task of choosing between estimators! This chapter Introduces some basic criteria for evaluating estimators. 3
4 Mean Squared Error Mean squared error Of estimator W Of parameter θ E θ w θ 2 Mean squared error 4
5 Mean Squared Error Why MSE? Any increasing function on W θ could be good. But MSE: Analytically tractable E θ W θ 2 = Var θ W + (E θ W θ) 2 = Var θ W + (Bias θ W) 2 Two components of MSE variability of estimator (precision) and bias (accuracy). Bias: difference between the expected value of Wand θ. 5
6 MSE for an unbiased estimator Unbiased Estimator Bias 0 E θ W = θ, θ For an unbiased estimator: E θ W θ 2 = Var θ W 6
7 Normal distribution estimators Example: Let X 1, X 2,, X n be iid N μ, σ 2. X : unbiased estimator for μ S 2 = n i=1 n 1 X i X 2 and σ 2 = Are both estimator for σ 2 n i=1 X i X 2 σ 2 has lower MSE but S 2 is unbiased. n 7
8 Best Unbiased Estimator Comparison of estimators based on MSE is not practically possible, Since the class of all estimators is too large. To limit the class of estimators, we only consider unbiased estimators. We have to find an unbiased estimator with minimum MSE. It equivalent to find an unbiased estimator with minimum variance. Why? 8
9 Best Unbiased Estimator For any unbiased estimator the MSE is equal to the variance. Definition (UMVUE): An estimator W* is a best unbiased estimator of τ(θ) if it satisfies E θ W = τ(θ) for all θ and for any other estimator of W with E θ W = τ θ we have Var W Var W for all θ. It s also called MVUE 9
10 Best Unbiased Estimator Example: x 1, x 2,, x n are samples from iid poison(λ). Let X and S 2 be the sample mean and variance. We have to calculatevar X and Var(S 2 ). Is it sufficient?? 10
11 Best Unbiased Estimator Example: x 1, x 2,, x n are samples from iid poison(λ). Let X and S 2 be the sample mean and variance. We have to calculatevar X and Var(S 2 ). How can we sure that there are not better (with less variance) estimator?? We should find a lower band, B θ on the variance of any unbiased estimator. W is an UMVUE if Var θ W = B(θ) 11
12 Cramer-Rao Theorem Theorem (Cramer-Rao): Let X 1,, X n be a sample with pdf f(x θ) and let W(X) = W(X 1,, X n ) be any estimator where E θ (W(X)) is a differentiable function of θ. Suppose the joint pdf f x 1, x 2,, x n θ satisfies: d dθ h x f x θ dx 1 dx n = h x θ f x θ dx 1 dx n (1) for any function h(x) with E(h(X)) <. Then Var W X d dθ E θw X E θ (( θ log f(x θ))2 ) 2 12
13 Cramer-Rao bound for unbiased estimators If W is an unbiased estimator of θ then 1 Var W X E θ ( log f(x θ))2 θ Why? 13
14 Fisher information The Fisher information is a way of measuring the amount of information that an observable random variable X carries about an unknown parameter θ upon which the probability of X depends. The value I(θ) = E θ ( θ log f(x θ))2 is the fisher information and can also be derived by I(θ) = E θ 2 Note that: 0 I θ log f(x θ)) θ2 < 14
15 Fisher information and CR bound The variance of any unbiased estimator θ of θ is bounded by the inverse of Fisher information: Var θ 1 I(θ) 15
16 CR bound Example: Distribution N(μ, σ 2 ), μ is known, but σ 2 is unknown. Show T = n i=1 X i μ 2 What is variance of T? Find UMVUE for σ 2. n is unbiased for σ 2. 16
17 CR bound, iid case Let X 1,, X n be a sample with pdf f(x θ) and let W(X) = W(X 1,, X n ) be any estimator where E(W) is a differentiable function of θ. If the joint pdf satisfies the necessary condition for CR bound then: Why? Var W X d dθ E θw X ne θ (( θ log f(x θ))2 ) 2 17
18 CR bound, iid case Let X 1,, X n be a sample with pdf f(x θ) and let W(X) = W(X 1,, X n ) be any estimator where E(W) is a differentiable function of θ. If the joint pdf satisfies the necessary condition for CR bound then: E θ Var W X ne θ d dθ E θw X 2 ( log f(x θ))2 θ ( θ log f(x θ))2 = E θ ( θ log f(x i θ)) 2, independency E θ ( θ log f(x θ))2 = ne θ ( log f(x θ))2 θ 18
19 Best Unbiased Estimator (Cont.) Example: Let X 1,, X n be iid Poisson(λ). Prove that X is a UMVUE of λ. Solution: X is an unbiased estimator X has variance equal to the Cramer- Rao lower bound 19
20 When Cramer-Rao does not apply Example: Let X 1,, X n be iid with pdf f x θ = 1 θ The Cramer-Rao bound:, 0<x< θ. VarW θ2 n To find unbiased estimator there is a guess: Y = max X 1,, X n E θ Y = n n+1 θ n+1 n Y is unbiased. 20
21 When Cramer-Rao does not apply Var θ n+1 n Y = 1 n(n+2) θ2 This is uniformly smaller than θ2 n Cramer-Rao is not applicable θ 0 Because: d h x f x θ dx = d dθ dθ + θ h(x) h x = h(θ) θ 0 Unless h θ θ θ (1 θ )dx = 0 for all θ. θ 0 θ 0 θ h(x) 1 θ dx f x θ dx If the range of pdf, depends on the parameter, the theorem will not be applicable. 21
22 Sufficiency and Unbiasedness Theorem (Rao-Blackwell): Let W be any unbiased estimator of τ(θ) and let T be a sufficient statistic for all θ. Define ϕ T = E W T. Then E θ ϕ T = τ(θ) and Var(ϕ T ) Var(W) for all θ, that is ϕ T is a uniformly better unbiased estimator of τ θ. 22
23 Uniqeness of UMVUE Theorem: If W is the best unbiased estimator of τ(θ), then W is unique. Proof sketch: Suppose W is another UMVUE, and consider W = 1 2 W + W E W = τ θ Find the Variance of W. 23
24 How to find UMVUE Theorem: Let T be a complete sufficient statistic for a parameter θ, and let φ(t) be any estimator based on T. Then T is unique UMVUE of its expected value. What if there is no candidate estimator based on T? If T is a CSS for a parameter θ and h x 1, x 2,, x n is any unbiased estimator of τ(θ). Then φ T = E h x 1, x 2,, x n T is the UMVUE of τ(θ). 24
25 Binomial best unbiased estimation Example: Let X 1,, X n be iid binomial k, θ. Estimate the probability of exactly one success. τ θ = P θ X = 1 = kθ 1 θ k 1 Simple-minded estimator h X 1 = 1 if X 1 = 1 0 otherwise n φ X i i=1 n = E h X 1 X i i=1 = k k(n 1) X i 1 kn X i 25
26 Consistency Definition: A sequence of estimators W n = W n X 1,, X n is a consistent sequence of estimators of the parameter θ if for every ε > 0 and every θ Θ lim P θ( W n W < ε) = 1 n Theorem: If W n is a sequence of estimators of a parameter θ satisfying lim Var W n = 0 and lim Bias W n = 0. n n Then W n is a consistent sequence of estimators of θ. 26
Last Lecture. Biostatistics Statistical Inference Lecture 14 Obtaining Best Unbiased Estimator. Related Theorems. Rao-Blackwell Theorem
 Last Lecture Biostatistics 62 - Statistical Inference Lecture 14 Obtaining Best Unbiased Estimator Hyun Min Kang February 28th, 213 For single-parameter exponential family, is Cramer-Rao bound always attainable?
Last Lecture Biostatistics 62 - Statistical Inference Lecture 14 Obtaining Best Unbiased Estimator Hyun Min Kang February 28th, 213 For single-parameter exponential family, is Cramer-Rao bound always attainable?
557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II BIAS AND VARIANCE
 557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II BIAS AND VARIANCE An estimator, T (X), of θ can be evaluated via its statistical properties. Typically, two aspects are considered: Expectation Variance either in terms
557: MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS II BIAS AND VARIANCE An estimator, T (X), of θ can be evaluated via its statistical properties. Typically, two aspects are considered: Expectation Variance either in terms
Unbiased Estimation. Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others.
 Unbiased Estimation Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others. To compare ˆθ and θ, two estimators of θ: Say ˆθ is better than θ if it
Unbiased Estimation Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others. To compare ˆθ and θ, two estimators of θ: Say ˆθ is better than θ if it
Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3)
 Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3) Example: Suppose we observe X 1,..., X n iid N(θ, σ 2 0 ), with σ2 0 known, and wish to estimate θ. Two possible estimators are: ˆθ = X sample mean
Evaluating the Performance of Estimators (Section 7.3) Example: Suppose we observe X 1,..., X n iid N(θ, σ 2 0 ), with σ2 0 known, and wish to estimate θ. Two possible estimators are: ˆθ = X sample mean
1. (Regular) Exponential Family
 1. (Regular) Exponential Family The density function of a regular exponential family is: [ ] Example. Poisson(θ) [ ] Example. Normal. (both unknown). ) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 2. Theorem (Exponential family &
1. (Regular) Exponential Family The density function of a regular exponential family is: [ ] Example. Poisson(θ) [ ] Example. Normal. (both unknown). ) [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] 2. Theorem (Exponential family &
Mathematical Statistics
 Mathematical Statistics Chapter Three. Point Estimation 3.4 Uniformly Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator(UMVUE) Criteria for Best Estimators MSE Criterion Let F = {p(x; θ) : θ Θ} be a parametric distribution
Mathematical Statistics Chapter Three. Point Estimation 3.4 Uniformly Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimator(UMVUE) Criteria for Best Estimators MSE Criterion Let F = {p(x; θ) : θ Θ} be a parametric distribution
Unbiased Estimation. Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others.
 Unbiased Estimation Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others. To compare ˆθ and θ, two estimators of θ: Say ˆθ is better than θ if it
Unbiased Estimation Binomial problem shows general phenomenon. An estimator can be good for some values of θ and bad for others. To compare ˆθ and θ, two estimators of θ: Say ˆθ is better than θ if it
Lecture 4: UMVUE and unbiased estimators of 0
 Lecture 4: UMVUE and unbiased estimators of Problems of approach 1. Approach 1 has the following two main shortcomings. Even if Theorem 7.3.9 or its extension is applicable, there is no guarantee that
Lecture 4: UMVUE and unbiased estimators of Problems of approach 1. Approach 1 has the following two main shortcomings. Even if Theorem 7.3.9 or its extension is applicable, there is no guarantee that
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003
 Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your answer
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part I October 18, 2003 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your answer
Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic
 Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic Unbiased estimation Unbiased or asymptotically unbiased estimation plays an important role in
Chapter 3: Unbiased Estimation Lecture 22: UMVUE and the method of using a sufficient and complete statistic Unbiased estimation Unbiased or asymptotically unbiased estimation plays an important role in
Chapter 3. Point Estimation. 3.1 Introduction
 Chapter 3 Point Estimation Let (Ω, A, P θ ), P θ P = {P θ θ Θ}be probability space, X 1, X 2,..., X n : (Ω, A) (IR k, B k ) random variables (X, B X ) sample space γ : Θ IR k measurable function, i.e.
Chapter 3 Point Estimation Let (Ω, A, P θ ), P θ P = {P θ θ Θ}be probability space, X 1, X 2,..., X n : (Ω, A) (IR k, B k ) random variables (X, B X ) sample space γ : Θ IR k measurable function, i.e.
ST5215: Advanced Statistical Theory
 Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Lecture 17: UMVUE and the first method of derivation Estimable parameters Let ϑ be a parameter in the family P. If there exists
Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Wednesday, October 19, 2011 Lecture 17: UMVUE and the first method of derivation Estimable parameters Let ϑ be a parameter in the family P. If there exists
All other items including (and especially) CELL PHONES must be left at the front of the room.
 TEST #2 / STA 5327 (Inference) / Spring 2017 (April 24, 2017) Name: Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. You will be supplied with scratch paper, and a copy of the Table of Common Distributions
TEST #2 / STA 5327 (Inference) / Spring 2017 (April 24, 2017) Name: Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. You will be supplied with scratch paper, and a copy of the Table of Common Distributions
Statistics and Econometrics I
 Statistics and Econometrics I Point Estimation Shiu-Sheng Chen Department of Economics National Taiwan University September 13, 2016 Shiu-Sheng Chen (NTU Econ) Statistics and Econometrics I September 13,
Statistics and Econometrics I Point Estimation Shiu-Sheng Chen Department of Economics National Taiwan University September 13, 2016 Shiu-Sheng Chen (NTU Econ) Statistics and Econometrics I September 13,
Chapters 9. Properties of Point Estimators
 Chapters 9. Properties of Point Estimators Recap Target parameter, or population parameter θ. Population distribution f(x; θ). { probability function, discrete case f(x; θ) = density, continuous case The
Chapters 9. Properties of Point Estimators Recap Target parameter, or population parameter θ. Population distribution f(x; θ). { probability function, discrete case f(x; θ) = density, continuous case The
Elements of statistics (MATH0487-1)
 Elements of statistics (MATH0487-1) Prof. Dr. Dr. K. Van Steen University of Liège, Belgium November 12, 2012 Introduction to Statistics Basic Probability Revisited Sampling Exploratory Data Analysis -
Elements of statistics (MATH0487-1) Prof. Dr. Dr. K. Van Steen University of Liège, Belgium November 12, 2012 Introduction to Statistics Basic Probability Revisited Sampling Exploratory Data Analysis -
6.1 Variational representation of f-divergences
 ECE598: Information-theoretic methods in high-dimensional statistics Spring 2016 Lecture 6: Variational representation, HCR and CR lower bounds Lecturer: Yihong Wu Scribe: Georgios Rovatsos, Feb 11, 2016
ECE598: Information-theoretic methods in high-dimensional statistics Spring 2016 Lecture 6: Variational representation, HCR and CR lower bounds Lecturer: Yihong Wu Scribe: Georgios Rovatsos, Feb 11, 2016
Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1. X i, S 2 = 1 n. n 1. X i I(X i < c), T n =
 Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1 1. (a) Let Z i be independent N(0, 1), i = 1, 2,, n. Are Z = 1 n n Z i and S 2 Z = 1 n 1 n (Z i Z) 2 independent? Prove your claim. (b) Let X 1, X 2,, X n be independent identically
Spring 2012 Math 541A Exam 1 1. (a) Let Z i be independent N(0, 1), i = 1, 2,, n. Are Z = 1 n n Z i and S 2 Z = 1 n 1 n (Z i Z) 2 independent? Prove your claim. (b) Let X 1, X 2,, X n be independent identically
March 10, 2017 THE EXPONENTIAL CLASS OF DISTRIBUTIONS
 March 10, 2017 THE EXPONENTIAL CLASS OF DISTRIBUTIONS Abstract. We will introduce a class of distributions that will contain many of the discrete and continuous we are familiar with. This class will help
March 10, 2017 THE EXPONENTIAL CLASS OF DISTRIBUTIONS Abstract. We will introduce a class of distributions that will contain many of the discrete and continuous we are familiar with. This class will help
Theory of Statistics.
 Theory of Statistics. Homework V February 5, 00. MT 8.7.c When σ is known, ˆµ = X is an unbiased estimator for µ. If you can show that its variance attains the Cramer-Rao lower bound, then no other unbiased
Theory of Statistics. Homework V February 5, 00. MT 8.7.c When σ is known, ˆµ = X is an unbiased estimator for µ. If you can show that its variance attains the Cramer-Rao lower bound, then no other unbiased
Final Exam. 1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given.
 1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given. (a) If X and Y are independent, Corr(X, Y ) = 0. (b) (c) (d) (e) A consistent estimator must be asymptotically
1. (6 points) True/False. Please read the statements carefully, as no partial credit will be given. (a) If X and Y are independent, Corr(X, Y ) = 0. (b) (c) (d) (e) A consistent estimator must be asymptotically
STATISTICS/ECONOMETRICS PREP COURSE PROF. MASSIMO GUIDOLIN
 Massimo Guidolin Massimo.Guidolin@unibocconi.it Dept. of Finance STATISTICS/ECONOMETRICS PREP COURSE PROF. MASSIMO GUIDOLIN SECOND PART, LECTURE 2: MODES OF CONVERGENCE AND POINT ESTIMATION Lecture 2:
Massimo Guidolin Massimo.Guidolin@unibocconi.it Dept. of Finance STATISTICS/ECONOMETRICS PREP COURSE PROF. MASSIMO GUIDOLIN SECOND PART, LECTURE 2: MODES OF CONVERGENCE AND POINT ESTIMATION Lecture 2:
f(y θ) = g(t (y) θ)h(y)
 EXAM3, FINAL REVIEW (and a review for some of the QUAL problems): No notes will be allowed, but you may bring a calculator. Memorize the pmf or pdf f, E(Y ) and V(Y ) for the following RVs: 1) beta(δ,
EXAM3, FINAL REVIEW (and a review for some of the QUAL problems): No notes will be allowed, but you may bring a calculator. Memorize the pmf or pdf f, E(Y ) and V(Y ) for the following RVs: 1) beta(δ,
ECE531 Lecture 10b: Maximum Likelihood Estimation
 ECE531 Lecture 10b: Maximum Likelihood Estimation D. Richard Brown III Worcester Polytechnic Institute 05-Apr-2011 Worcester Polytechnic Institute D. Richard Brown III 05-Apr-2011 1 / 23 Introduction So
ECE531 Lecture 10b: Maximum Likelihood Estimation D. Richard Brown III Worcester Polytechnic Institute 05-Apr-2011 Worcester Polytechnic Institute D. Richard Brown III 05-Apr-2011 1 / 23 Introduction So
Limiting Distributions
 We introduce the mode of convergence for a sequence of random variables, and discuss the convergence in probability and in distribution. The concept of convergence leads us to the two fundamental results
We introduce the mode of convergence for a sequence of random variables, and discuss the convergence in probability and in distribution. The concept of convergence leads us to the two fundamental results
ENEE 621 SPRING 2016 DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY THE PARAMETER ESTIMATION PROBLEM
 c 2007-2016 by Armand M. Makowski 1 ENEE 621 SPRING 2016 DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY THE PARAMETER ESTIMATION PROBLEM 1 The basic setting Throughout, p, q and k are positive integers. The setup With
c 2007-2016 by Armand M. Makowski 1 ENEE 621 SPRING 2016 DETECTION AND ESTIMATION THEORY THE PARAMETER ESTIMATION PROBLEM 1 The basic setting Throughout, p, q and k are positive integers. The setup With
February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM
 February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM Abstract. The Rao-Blacwell theorem told us how to improve an estimator. We will discuss conditions on when the Rao-Blacwellization of an estimator
February 26, 2017 COMPLETENESS AND THE LEHMANN-SCHEFFE THEOREM Abstract. The Rao-Blacwell theorem told us how to improve an estimator. We will discuss conditions on when the Rao-Blacwellization of an estimator
Mathematical statistics
 October 4 th, 2018 Lecture 12: Information Where are we? Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Week 10 Week 14 Probability reviews Chapter 6: Statistics and Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter
October 4 th, 2018 Lecture 12: Information Where are we? Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Week 10 Week 14 Probability reviews Chapter 6: Statistics and Sampling Distributions Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter
STAT 512 sp 2018 Summary Sheet
 STAT 5 sp 08 Summary Sheet Karl B. Gregory Spring 08. Transformations of a random variable Let X be a rv with support X and let g be a function mapping X to Y with inverse mapping g (A = {x X : g(x A}
STAT 5 sp 08 Summary Sheet Karl B. Gregory Spring 08. Transformations of a random variable Let X be a rv with support X and let g be a function mapping X to Y with inverse mapping g (A = {x X : g(x A}
 1 of 7 7/16/2009 6:12 AM Virtual Laboratories > 7. Point Estimation > 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. Estimators The Basic Statistical Model As usual, our starting point is a random experiment with an underlying sample
1 of 7 7/16/2009 6:12 AM Virtual Laboratories > 7. Point Estimation > 1 2 3 4 5 6 1. Estimators The Basic Statistical Model As usual, our starting point is a random experiment with an underlying sample
ELEG 5633 Detection and Estimation Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimators (MVUE)
 1 ELEG 5633 Detection and Estimation Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimators (MVUE) Jingxian Wu Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas Outline Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimators (MVUE)
1 ELEG 5633 Detection and Estimation Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimators (MVUE) Jingxian Wu Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas Outline Minimum Variance Unbiased Estimators (MVUE)
Example: An experiment can either result in success or failure with probability θ and (1 θ) respectively. The experiment is performed independently
 Chapter 3 Sufficient statistics and variance reduction Let X 1,X 2,...,X n be a random sample from a certain distribution with p.m/d.f fx θ. A function T X 1,X 2,...,X n = T X of these observations is
Chapter 3 Sufficient statistics and variance reduction Let X 1,X 2,...,X n be a random sample from a certain distribution with p.m/d.f fx θ. A function T X 1,X 2,...,X n = T X of these observations is
Graduate Econometrics I: Unbiased Estimation
 Graduate Econometrics I: Unbiased Estimation Yves Dominicy Université libre de Bruxelles Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management ECARES Yves Dominicy Graduate Econometrics I: Unbiased Estimation
Graduate Econometrics I: Unbiased Estimation Yves Dominicy Université libre de Bruxelles Solvay Brussels School of Economics and Management ECARES Yves Dominicy Graduate Econometrics I: Unbiased Estimation
Problem Selected Scores
 Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part II November 20, 2010 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Selected
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part II November 20, 2010 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Selected
STA 732: Inference. Notes 10. Parameter Estimation from a Decision Theoretic Angle. Other resources
 STA 732: Inference Notes 10. Parameter Estimation from a Decision Theoretic Angle Other resources 1 Statistical rules, loss and risk We saw that a major focus of classical statistics is comparing various
STA 732: Inference Notes 10. Parameter Estimation from a Decision Theoretic Angle Other resources 1 Statistical rules, loss and risk We saw that a major focus of classical statistics is comparing various
Limiting Distributions
 Limiting Distributions We introduce the mode of convergence for a sequence of random variables, and discuss the convergence in probability and in distribution. The concept of convergence leads us to the
Limiting Distributions We introduce the mode of convergence for a sequence of random variables, and discuss the convergence in probability and in distribution. The concept of convergence leads us to the
Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics. https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf
 Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Part 1: Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
A Few Notes on Fisher Information (WIP)
 A Few Notes on Fisher Information (WIP) David Meyer dmm@{-4-5.net,uoregon.edu} Last update: April 30, 208 Definitions There are so many interesting things about Fisher Information and its theoretical properties
A Few Notes on Fisher Information (WIP) David Meyer dmm@{-4-5.net,uoregon.edu} Last update: April 30, 208 Definitions There are so many interesting things about Fisher Information and its theoretical properties
Parameter Estimation
 Parameter Estimation Consider a sample of observations on a random variable Y. his generates random variables: (y 1, y 2,, y ). A random sample is a sample (y 1, y 2,, y ) where the random variables y
Parameter Estimation Consider a sample of observations on a random variable Y. his generates random variables: (y 1, y 2,, y ). A random sample is a sample (y 1, y 2,, y ) where the random variables y
STAT215: Solutions for Homework 2
 STAT25: Solutions for Homework 2 Due: Wednesday, Feb 4. (0 pt) Suppose we take one observation, X, from the discrete distribution, x 2 0 2 Pr(X x θ) ( θ)/4 θ/2 /2 (3 θ)/2 θ/4, 0 θ Find an unbiased estimator
STAT25: Solutions for Homework 2 Due: Wednesday, Feb 4. (0 pt) Suppose we take one observation, X, from the discrete distribution, x 2 0 2 Pr(X x θ) ( θ)/4 θ/2 /2 (3 θ)/2 θ/4, 0 θ Find an unbiased estimator
A General Overview of Parametric Estimation and Inference Techniques.
 A General Overview of Parametric Estimation and Inference Techniques. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan September 11, 2012 The object of statistical inference is to glean information about an underlying
A General Overview of Parametric Estimation and Inference Techniques. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan September 11, 2012 The object of statistical inference is to glean information about an underlying
EIE6207: Estimation Theory
 EIE6207: Estimation Theory Man-Wai MAK Dept. of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University enmwmak@polyu.edu.hk http://www.eie.polyu.edu.hk/ mwmak References: Steven M.
EIE6207: Estimation Theory Man-Wai MAK Dept. of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University enmwmak@polyu.edu.hk http://www.eie.polyu.edu.hk/ mwmak References: Steven M.
1 General problem. 2 Terminalogy. Estimation. Estimate θ. (Pick a plausible distribution from family. ) Or estimate τ = τ(θ).
 Estimation February 3, 206 Debdeep Pati General problem Model: {P θ : θ Θ}. Observe X P θ, θ Θ unknown. Estimate θ. (Pick a plausible distribution from family. ) Or estimate τ = τ(θ). Examples: θ = (µ,
Estimation February 3, 206 Debdeep Pati General problem Model: {P θ : θ Θ}. Observe X P θ, θ Θ unknown. Estimate θ. (Pick a plausible distribution from family. ) Or estimate τ = τ(θ). Examples: θ = (µ,
Chapter 8.8.1: A factorization theorem
 LECTURE 14 Chapter 8.8.1: A factorization theorem The characterization of a sufficient statistic in terms of the conditional distribution of the data given the statistic can be difficult to work with.
LECTURE 14 Chapter 8.8.1: A factorization theorem The characterization of a sufficient statistic in terms of the conditional distribution of the data given the statistic can be difficult to work with.
Mathematics Ph.D. Qualifying Examination Stat Probability, January 2018
 Mathematics Ph.D. Qualifying Examination Stat 52800 Probability, January 2018 NOTE: Answers all questions completely. Justify every step. Time allowed: 3 hours. 1. Let X 1,..., X n be a random sample from
Mathematics Ph.D. Qualifying Examination Stat 52800 Probability, January 2018 NOTE: Answers all questions completely. Justify every step. Time allowed: 3 hours. 1. Let X 1,..., X n be a random sample from
Brief Review on Estimation Theory
 Brief Review on Estimation Theory K. Abed-Meraim ENST PARIS, Signal and Image Processing Dept. abed@tsi.enst.fr This presentation is essentially based on the course BASTA by E. Moulines Brief review on
Brief Review on Estimation Theory K. Abed-Meraim ENST PARIS, Signal and Image Processing Dept. abed@tsi.enst.fr This presentation is essentially based on the course BASTA by E. Moulines Brief review on
Estimation Tasks. Short Course on Image Quality. Matthew A. Kupinski. Introduction
 Estimation Tasks Short Course on Image Quality Matthew A. Kupinski Introduction Section 13.3 in B&M Keep in mind the similarities between estimation and classification Image-quality is a statistical concept
Estimation Tasks Short Course on Image Quality Matthew A. Kupinski Introduction Section 13.3 in B&M Keep in mind the similarities between estimation and classification Image-quality is a statistical concept
ECE534, Spring 2018: Solutions for Problem Set #3
 ECE534, Spring 08: Solutions for Problem Set #3 Jointly Gaussian Random Variables and MMSE Estimation Suppose that X, Y are jointly Gaussian random variables with µ X = µ Y = 0 and σ X = σ Y = Let their
ECE534, Spring 08: Solutions for Problem Set #3 Jointly Gaussian Random Variables and MMSE Estimation Suppose that X, Y are jointly Gaussian random variables with µ X = µ Y = 0 and σ X = σ Y = Let their
McGill University. Faculty of Science. Department of Mathematics and Statistics. Part A Examination. Statistics: Theory Paper
 McGill University Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics Part A Examination Statistics: Theory Paper Date: 10th May 2015 Instructions Time: 1pm-5pm Answer only two questions from Section
McGill University Faculty of Science Department of Mathematics and Statistics Part A Examination Statistics: Theory Paper Date: 10th May 2015 Instructions Time: 1pm-5pm Answer only two questions from Section
Proof In the CR proof. and
 Question Under what conditions will we be able to attain the Cramér-Rao bound and find a MVUE? Lecture 4 - Consequences of the Cramér-Rao Lower Bound. Searching for a MVUE. Rao-Blackwell Theorem, Lehmann-Scheffé
Question Under what conditions will we be able to attain the Cramér-Rao bound and find a MVUE? Lecture 4 - Consequences of the Cramér-Rao Lower Bound. Searching for a MVUE. Rao-Blackwell Theorem, Lehmann-Scheffé
Practice Problems Section Problems
 Practice Problems Section 4-4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 4-7 4-8 4-10 Supplemental Problems 4-1 to 4-9 4-13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 0 4-3, 34, 36, 38 4-47, 49, 5, 54, 55 4-59, 60, 63 4-66, 68, 69, 70, 74 4-79, 81, 84 4-85,
Practice Problems Section 4-4-3 4-4 4-5 4-6 4-7 4-8 4-10 Supplemental Problems 4-1 to 4-9 4-13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 0 4-3, 34, 36, 38 4-47, 49, 5, 54, 55 4-59, 60, 63 4-66, 68, 69, 70, 74 4-79, 81, 84 4-85,
Math 494: Mathematical Statistics
 Math 494: Mathematical Statistics Instructor: Jimin Ding jmding@wustl.edu Department of Mathematics Washington University in St. Louis Class materials are available on course website (www.math.wustl.edu/
Math 494: Mathematical Statistics Instructor: Jimin Ding jmding@wustl.edu Department of Mathematics Washington University in St. Louis Class materials are available on course website (www.math.wustl.edu/
E X A M. Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours. Number of pages incl.
 E X A M Course code: Course name: Number of pages incl. front page: 6 MA430-G Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours Resources allowed: Notes: Pocket calculator,
E X A M Course code: Course name: Number of pages incl. front page: 6 MA430-G Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes Date: December 13, 2016 Duration: 4 hours Resources allowed: Notes: Pocket calculator,
f (1 0.5)/n Z =
 Math 466/566 - Homework 4. We want to test a hypothesis involving a population proportion. The unknown population proportion is p. The null hypothesis is p = / and the alternative hypothesis is p > /.
Math 466/566 - Homework 4. We want to test a hypothesis involving a population proportion. The unknown population proportion is p. The null hypothesis is p = / and the alternative hypothesis is p > /.
Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida
 Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida May 10, 2002, 8:00am - 12:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination. 2. There
Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida May 10, 2002, 8:00am - 12:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination. 2. There
Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics. https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf
 Part : Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
Part : Sample Problems for the Elementary Section of Qualifying Exam in Probability and Statistics https://www.soa.org/files/edu/edu-exam-p-sample-quest.pdf Part 2: Sample Problems for the Advanced Section
STAT 450: Final Examination Version 1. Richard Lockhart 16 December 2002
 Name: Last Name 1, First Name 1 Stdnt # StudentNumber1 STAT 450: Final Examination Version 1 Richard Lockhart 16 December 2002 Instructions: This is an open book exam. You may use notes, books and a calculator.
Name: Last Name 1, First Name 1 Stdnt # StudentNumber1 STAT 450: Final Examination Version 1 Richard Lockhart 16 December 2002 Instructions: This is an open book exam. You may use notes, books and a calculator.
Regression Estimation Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood
 Regression Estimation Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Dr. Frank Wood Frank Wood, fwood@stat.columbia.edu Linear Regression Models Lecture 3, Slide 1 Least Squares Max(min)imization Function to minimize
Regression Estimation Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Dr. Frank Wood Frank Wood, fwood@stat.columbia.edu Linear Regression Models Lecture 3, Slide 1 Least Squares Max(min)imization Function to minimize
Classical Estimation Topics
 Classical Estimation Topics Namrata Vaswani, Iowa State University February 25, 2014 This note fills in the gaps in the notes already provided (l0.pdf, l1.pdf, l2.pdf, l3.pdf, LeastSquares.pdf). 1 Min
Classical Estimation Topics Namrata Vaswani, Iowa State University February 25, 2014 This note fills in the gaps in the notes already provided (l0.pdf, l1.pdf, l2.pdf, l3.pdf, LeastSquares.pdf). 1 Min
10-704: Information Processing and Learning Fall Lecture 24: Dec 7
 0-704: Information Processing and Learning Fall 206 Lecturer: Aarti Singh Lecture 24: Dec 7 Note: These notes are based on scribed notes from Spring5 offering of this course. LaTeX template courtesy of
0-704: Information Processing and Learning Fall 206 Lecturer: Aarti Singh Lecture 24: Dec 7 Note: These notes are based on scribed notes from Spring5 offering of this course. LaTeX template courtesy of
Review Quiz. 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the
 Review Quiz 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the Cramér Rao lower bound (CRLB). That is, if where { } and are scalars, then
Review Quiz 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the Cramér Rao lower bound (CRLB). That is, if where { } and are scalars, then
ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Version Winter 2015
 ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Version Winter 2015 1. (a) Because x i are assumed to be independent realizations of a continuous random variable, it is almost surely (a.s.) 1 the case that x 1 < x 2
ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Version Winter 2015 1. (a) Because x i are assumed to be independent realizations of a continuous random variable, it is almost surely (a.s.) 1 the case that x 1 < x 2
STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I
 STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I (Probability Theory) Definition Classical and axiomatic approaches.laws of total and compound probability, conditional probability, Bayes Theorem. Random variable and its distribution
STATISTICS SYLLABUS UNIT I (Probability Theory) Definition Classical and axiomatic approaches.laws of total and compound probability, conditional probability, Bayes Theorem. Random variable and its distribution
1. Fisher Information
 1. Fisher Information Let f(x θ) be a density function with the property that log f(x θ) is differentiable in θ throughout the open p-dimensional parameter set Θ R p ; then the score statistic (or score
1. Fisher Information Let f(x θ) be a density function with the property that log f(x θ) is differentiable in θ throughout the open p-dimensional parameter set Θ R p ; then the score statistic (or score
Solution. (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic for (θ, β) and give your justification. X i=1. By the factorization theorem, ( n
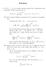 Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
DA Freedman Notes on the MLE Fall 2003
 DA Freedman Notes on the MLE Fall 2003 The object here is to provide a sketch of the theory of the MLE. Rigorous presentations can be found in the references cited below. Calculus. Let f be a smooth, scalar
DA Freedman Notes on the MLE Fall 2003 The object here is to provide a sketch of the theory of the MLE. Rigorous presentations can be found in the references cited below. Calculus. Let f be a smooth, scalar
Part IA Probability. Theorems. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Theorems Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Theorems Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan 11, 2016, 9:00am-1:00pm
 Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan, 06, 9:00am-:00pm Instructions: Provide answers on the supplied pads of paper; write on only one side of each sheet. Complete exactly 5 of the 6 problems.
Statistics GIDP Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Theory Jan, 06, 9:00am-:00pm Instructions: Provide answers on the supplied pads of paper; write on only one side of each sheet. Complete exactly 5 of the 6 problems.
Parameter estimation! and! forecasting! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn!
 Parameter estimation! and! forecasting! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn! Questions?! C. Porciani! Estimation & forecasting! 2! Cosmological parameters! A branch of modern cosmological research focuses
Parameter estimation! and! forecasting! Cristiano Porciani! AIfA, Uni-Bonn! Questions?! C. Porciani! Estimation & forecasting! 2! Cosmological parameters! A branch of modern cosmological research focuses
ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Winter 2018
 ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Winter 2018 1. (a) Because x i are assumed to be independent realizations of a continuous random variable, it is almost surely (a.s.) 1 the case that x 1 < x 2 < < x n Thus,
ECE 275B Homework # 1 Solutions Winter 2018 1. (a) Because x i are assumed to be independent realizations of a continuous random variable, it is almost surely (a.s.) 1 the case that x 1 < x 2 < < x n Thus,
Detection & Estimation Lecture 1
 Detection & Estimation Lecture 1 Intro, MVUE, CRLB Xiliang Luo General Course Information Textbooks & References Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory/Detection Theory, Steven
Detection & Estimation Lecture 1 Intro, MVUE, CRLB Xiliang Luo General Course Information Textbooks & References Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory/Detection Theory, Steven
Parametric Inference
 Parametric Inference Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan April 14, 2004 1 General Discussion The object of statistical inference is to glean information about an underlying population based on a
Parametric Inference Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan April 14, 2004 1 General Discussion The object of statistical inference is to glean information about an underlying population based on a
General Bayesian Inference I
 General Bayesian Inference I Outline: Basic concepts, One-parameter models, Noninformative priors. Reading: Chapters 10 and 11 in Kay-I. (Occasional) Simplified Notation. When there is no potential for
General Bayesian Inference I Outline: Basic concepts, One-parameter models, Noninformative priors. Reading: Chapters 10 and 11 in Kay-I. (Occasional) Simplified Notation. When there is no potential for
Advanced Signal Processing Introduction to Estimation Theory
 Advanced Signal Processing Introduction to Estimation Theory Danilo Mandic, room 813, ext: 46271 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Imperial College London, UK d.mandic@imperial.ac.uk,
Advanced Signal Processing Introduction to Estimation Theory Danilo Mandic, room 813, ext: 46271 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Imperial College London, UK d.mandic@imperial.ac.uk,
p y (1 p) 1 y, y = 0, 1 p Y (y p) = 0, otherwise.
 1. Suppose Y 1, Y 2,..., Y n is an iid sample from a Bernoulli(p) population distribution, where 0 < p < 1 is unknown. The population pmf is p y (1 p) 1 y, y = 0, 1 p Y (y p) = (a) Prove that Y is the
1. Suppose Y 1, Y 2,..., Y n is an iid sample from a Bernoulli(p) population distribution, where 0 < p < 1 is unknown. The population pmf is p y (1 p) 1 y, y = 0, 1 p Y (y p) = (a) Prove that Y is the
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part II November 9, 2002
 Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part II November 9, 2002 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your
Statistics Ph.D. Qualifying Exam: Part II November 9, 2002 Student Name: 1. Answer 8 out of 12 problems. Mark the problems you selected in the following table. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Write your
Interval Estimation. Chapter 9
 Chapter 9 Interval Estimation 9.1 Introduction Definition 9.1.1 An interval estimate of a real-values parameter θ is any pair of functions, L(x 1,..., x n ) and U(x 1,..., x n ), of a sample that satisfy
Chapter 9 Interval Estimation 9.1 Introduction Definition 9.1.1 An interval estimate of a real-values parameter θ is any pair of functions, L(x 1,..., x n ) and U(x 1,..., x n ), of a sample that satisfy
First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida
 First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida August 19, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination.. You must show your
First Year Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida August 19, 010, 8:00 am - 1:00 noon Instructions: 1. You have four hours to answer questions in this examination.. You must show your
Pubh 8482: Sequential Analysis
 Pubh 8482: Sequential Analysis Joseph S. Koopmeiners Division of Biostatistics University of Minnesota Week 7 Course Summary To this point, we have discussed group sequential testing focusing on Maintaining
Pubh 8482: Sequential Analysis Joseph S. Koopmeiners Division of Biostatistics University of Minnesota Week 7 Course Summary To this point, we have discussed group sequential testing focusing on Maintaining
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018
 Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
Statistics & Data Sciences: First Year Prelim Exam May 2018 Instructions: 1. Do not turn this page until instructed to do so. 2. Start each new question on a new sheet of paper. 3. This is a closed book
Detection & Estimation Lecture 1
 Detection & Estimation Lecture 1 Intro, MVUE, CRLB Xiliang Luo General Course Information Textbooks & References Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory/Detection Theory, Steven
Detection & Estimation Lecture 1 Intro, MVUE, CRLB Xiliang Luo General Course Information Textbooks & References Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory/Detection Theory, Steven
13. Parameter Estimation. ECE 830, Spring 2014
 13. Parameter Estimation ECE 830, Spring 2014 1 / 18 Primary Goal General problem statement: We observe X p(x θ), θ Θ and the goal is to determine the θ that produced X. Given a collection of observations
13. Parameter Estimation ECE 830, Spring 2014 1 / 18 Primary Goal General problem statement: We observe X p(x θ), θ Θ and the goal is to determine the θ that produced X. Given a collection of observations
A Handbook to Conquer Casella and Berger Book in Ten Days
 A Handbook to Conquer Casella and Berger Book in Ten Days Oliver Y. Chén Last update: June 25, 2016 Introduction (Casella and Berger, 2002) is arguably the finest classic statistics textbook for advanced
A Handbook to Conquer Casella and Berger Book in Ten Days Oliver Y. Chén Last update: June 25, 2016 Introduction (Casella and Berger, 2002) is arguably the finest classic statistics textbook for advanced
Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida
 Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida May 6, 003, 8:00 am - :00 noon Instructions: You have four hours to answer questions in this examination You must show
Masters Comprehensive Examination Department of Statistics, University of Florida May 6, 003, 8:00 am - :00 noon Instructions: You have four hours to answer questions in this examination You must show
Two hours. To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 21 June :45 11:45
 Two hours MATH20802 To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL METHODS 21 June 2010 9:45 11:45 Answer any FOUR of the questions. University-approved
Two hours MATH20802 To be supplied by the Examinations Office: Mathematical Formula Tables THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER STATISTICAL METHODS 21 June 2010 9:45 11:45 Answer any FOUR of the questions. University-approved
Midterm Examination. STA 215: Statistical Inference. Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm
 Midterm Examination STA 215: Statistical Inference Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm This is an open-book take-home examination. You may work on it during any consecutive 24-hour period you like; please
Midterm Examination STA 215: Statistical Inference Due Wednesday, 2006 Mar 8, 1:15 pm This is an open-book take-home examination. You may work on it during any consecutive 24-hour period you like; please
Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1
 Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1 1. A sample of size n is drawn without replacement from an urn containing N balls, m of which are red and N m are black; the balls are otherwise indistinguishable. Let X denote
Spring 2012 Math 541B Exam 1 1. A sample of size n is drawn without replacement from an urn containing N balls, m of which are red and N m are black; the balls are otherwise indistinguishable. Let X denote
Part IB Statistics. Theorems with proof. Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IB Statistics Theorems with proof Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IB Statistics Theorems with proof Based on lectures by D. Spiegelhalter Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
F & B Approaches to a simple model
 A6523 Signal Modeling, Statistical Inference and Data Mining in Astrophysics Spring 215 http://www.astro.cornell.edu/~cordes/a6523 Lecture 11 Applications: Model comparison Challenges in large-scale surveys
A6523 Signal Modeling, Statistical Inference and Data Mining in Astrophysics Spring 215 http://www.astro.cornell.edu/~cordes/a6523 Lecture 11 Applications: Model comparison Challenges in large-scale surveys
Mathematics Qualifying Examination January 2015 STAT Mathematical Statistics
 Mathematics Qualifying Examination January 2015 STAT 52800 - Mathematical Statistics NOTE: Answer all questions completely and justify your derivations and steps. A calculator and statistical tables (normal,
Mathematics Qualifying Examination January 2015 STAT 52800 - Mathematical Statistics NOTE: Answer all questions completely and justify your derivations and steps. A calculator and statistical tables (normal,
Variations. ECE 6540, Lecture 10 Maximum Likelihood Estimation
 Variations ECE 6540, Lecture 10 Last Time BLUE (Best Linear Unbiased Estimator) Formulation Advantages Disadvantages 2 The BLUE A simplification Assume the estimator is a linear system For a single parameter
Variations ECE 6540, Lecture 10 Last Time BLUE (Best Linear Unbiased Estimator) Formulation Advantages Disadvantages 2 The BLUE A simplification Assume the estimator is a linear system For a single parameter
Monte Carlo Studies. The response in a Monte Carlo study is a random variable.
 Monte Carlo Studies The response in a Monte Carlo study is a random variable. The response in a Monte Carlo study has a variance that comes from the variance of the stochastic elements in the data-generating
Monte Carlo Studies The response in a Monte Carlo study is a random variable. The response in a Monte Carlo study has a variance that comes from the variance of the stochastic elements in the data-generating
Estimation theory. Parametric estimation. Properties of estimators. Minimum variance estimator. Cramer-Rao bound. Maximum likelihood estimators
 Estimation theory Parametric estimation Properties of estimators Minimum variance estimator Cramer-Rao bound Maximum likelihood estimators Confidence intervals Bayesian estimation 1 Random Variables Let
Estimation theory Parametric estimation Properties of estimators Minimum variance estimator Cramer-Rao bound Maximum likelihood estimators Confidence intervals Bayesian estimation 1 Random Variables Let
LECTURE NOTES FYS 4550/FYS EXPERIMENTAL HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS AUTUMN 2013 PART I A. STRANDLIE GJØVIK UNIVERSITY COLLEGE AND UNIVERSITY OF OSLO
 LECTURE NOTES FYS 4550/FYS9550 - EXPERIMENTAL HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS AUTUMN 2013 PART I PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS A. STRANDLIE GJØVIK UNIVERSITY COLLEGE AND UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Before embarking on the concept
LECTURE NOTES FYS 4550/FYS9550 - EXPERIMENTAL HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS AUTUMN 2013 PART I PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS A. STRANDLIE GJØVIK UNIVERSITY COLLEGE AND UNIVERSITY OF OSLO Before embarking on the concept
Estimation Theory Fredrik Rusek. Chapters
 Estimation Theory Fredrik Rusek Chapters 3.5-3.10 Recap We deal with unbiased estimators of deterministic parameters Performance of an estimator is measured by the variance of the estimate (due to the
Estimation Theory Fredrik Rusek Chapters 3.5-3.10 Recap We deal with unbiased estimators of deterministic parameters Performance of an estimator is measured by the variance of the estimate (due to the
Mathematical statistics
 October 18 th, 2018 Lecture 16: Midterm review Countdown to mid-term exam: 7 days Week 1 Chapter 1: Probability review Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Chapter 6: Statistics Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter 8:
October 18 th, 2018 Lecture 16: Midterm review Countdown to mid-term exam: 7 days Week 1 Chapter 1: Probability review Week 2 Week 4 Week 7 Chapter 6: Statistics Chapter 7: Point Estimation Chapter 8:
STA 260: Statistics and Probability II
 Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Winter 2017 1 Properties of Point Estimators and Methods of Estimation 2 3 If you can t explain it simply, you don t understand it well enough Albert Einstein. Definition
Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Winter 2017 1 Properties of Point Estimators and Methods of Estimation 2 3 If you can t explain it simply, you don t understand it well enough Albert Einstein. Definition
ECE 275A Homework 6 Solutions
 ECE 275A Homework 6 Solutions. The notation used in the solutions for the concentration (hyper) ellipsoid problems is defined in the lecture supplement on concentration ellipsoids. Note that θ T Σ θ =
ECE 275A Homework 6 Solutions. The notation used in the solutions for the concentration (hyper) ellipsoid problems is defined in the lecture supplement on concentration ellipsoids. Note that θ T Σ θ =
Lecture 16: UMVUE: conditioning on sufficient and complete statistics
 Lecture 16: UMVUE: coditioig o sufficiet ad complete statistics The 2d method of derivig a UMVUE whe a sufficiet ad complete statistic is available Fid a ubiased estimator of ϑ, say U(X. Coditioig o a
Lecture 16: UMVUE: coditioig o sufficiet ad complete statistics The 2d method of derivig a UMVUE whe a sufficiet ad complete statistic is available Fid a ubiased estimator of ϑ, say U(X. Coditioig o a
5.2 Fisher information and the Cramer-Rao bound
 Stat 200: Introduction to Statistical Inference Autumn 208/9 Lecture 5: Maximum likelihood theory Lecturer: Art B. Owen October 9 Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved
Stat 200: Introduction to Statistical Inference Autumn 208/9 Lecture 5: Maximum likelihood theory Lecturer: Art B. Owen October 9 Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved
