Modeled response of Greenland snowmelt to the presence of biomass burning based absorbing aerosols
|
|
|
- Catherine Pearson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modeled response of Greenland snowmelt to the presence of biomass burning based absorbing aerosols Jamie Ward University of Michigan Climate and Space Science 1
2 Introduction Black carbon (BC): aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of biomass, biofuels, and fossil fuels. BC is highly efficient at absorbing visible radiation. Radiative impacts of BC are very pronounced in the high albedo Arctic environment. Fig. 1: Deposited BC impacts on snow albedo (Brandt et al., 2011) 2
3 Introduction Greenland Ice Sheet (GrIS): largest ice sheet in the northern hemisphere. Entire GrIS melt ~7.4 meters of sea level rise (Hanna et al., 2008). GrIS is a perennial, high albedo surface. July 2012: >97% of the GrIS (Fig. 1) experienced snowmelt (Nghiem et al., 2012). Enhanced biomass burning BC burden in GrIS snow (Keegan et al., 2014). Fig. 2: GrIS melt, July
4 Science Questions What are the relative snowmelt and net surface energy flux effects of suspended and in snow LAAs? For a constant atmospheric LAA burden, to what extent does varying single scattering albedo (SSA) affect Greenland s climate? When we simultaneously perturb atmospheric and deposited LAAs, are the associated climate effects additive? 4
5 Methods: Model Specifications CESM Spatial Resolution: Monthly output over 11 years (first year discarded for spin up) Active, coupled CAM and CLM Prescribed SSTs and sea ice Surface aerosol radiative treatment: Snow and Ice Aerosol Radiation Model (SNICAR) (Flanner and Zender, 2005). Dust are aerosols represented using the Bulk Aerosol Module (BAM). Prescribed 3D aerosols outside of the Greenland region. 5
6 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Strellis et al.,
7 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Strellis et al., 2013 Stohl et al.,
8 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Strellis et al., 2013 Stohl et al.,
9 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Polashenski et al.,
10 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Polashenski et al., 2015 Bory et al., 2003; McConnell et al.,
11 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Polashenski et al., 2015 Bory et al., 2003; McConnell et al.,
12 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA
13 Methods: Greenland specific setup Greenland (Fig. 3): N, W. Greenland Cases (18 total): 1. Atmospheric LAAs only ( AODonly, constant SSA=0.93). 2. In snow BC and dust only ( IN SNOW ). 3. Atmospheric and deposited LAAs ( BOTH ). 4. Changing SSA ( SSA, constant AOD=0.50). Fig. 3: The area over which aerosol perturbations are imposed for each variable simulation AOD BCE (ng/g) SSA Strellis et al.,
14 Methods Compare each of these runs to a control run (CONTROL) AOD=0.0; BCE=0.0ng/g For each variable of interest, determine the impact of the aerosol load for a given case by Difference maps, two sample t test (grid by grid and spatiallyaveraged). 14
15 Results: Snowmelt No significant in the AODonly and SSA runs. Surface dimming and tropospheric warming offset. IN SNOW and BOTH experiments: larger signal. In snow direct aerosol effect. Fig. 4: Spatial plots 15
16 Results: Snowmelt and Net Surface Energy patterns Spatially averaged are similar to snowmelt change. Fig. 5: Surface energy flux and snowmelt changes. 16
17 Results: Snowmelt and Net Surface Energy patterns Spatially averaged are similar to snowmelt change. Surface energy input is the main influence on GrIS snowmelt. Fig. 5: Surface energy flux and snowmelt changes. 17
18 Results: Snowmelt and Net Surface Energy patterns Spatially averaged are similar to snowmelt change. Surface energy input is the main influence on GrIS snowmelt. How do the energy components of net surface energy change for each aerosol experiment? Fig. 5: Surface energy flux and snowmelt changes. 18
19 Results: Net Surface Energy Components 0 for AOD only* and SSA 0 for IN SNOW and BOTH. * 0.09, 0.21 cases: 0 because of cloud burn off, decreasing surface albedo. Fig. 6: Net Surface Energy Components for all experiments 19
20 Results: Net Surface Energy Components 0 due to Stefan Boltzmann response., 0 for AOD only, SSA, and BOTH experiments., 0 for IN SNOW experiment. Fig. 6: Net Surface Energy Components for all experiments 20
21 Conclusions Snowmelt Changes Largest positive changes occur in the IN SNOW experiment. AOD only and SSA cases do not have any significant changes due to offsetting surface dimming and tropospheric warming. BOTH magnitude is smaller than IN SNOW due to the competing atmospheric aerosol effects. Net Surface Energy is largest in the IN SNOW and BOTH scenarios., are more sensitive to atmospheric LAA presence. 21
22 Acknowledgements I would like to thank Dr. Mark Flanner for the excellent advice and assistance he provided throughout the progress of this study. I also received very valuable input from Dr. Amber Soja, Dr. Jack Dibb, Dr. Mike Bergin, Dr. Jennie Thomas, and Dr. Chris Polashenski. This work was partially supported by NASA Grant NNX14AE72G. 22
23 References Bory, A.J. M., Biscaye, P.E., Piotrowski, A.M., & Steffensen, J.P. (2003, December). Regional variability of ice core dust composition and provenance in Greenland. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4(12), doi: /2003gc Brandt, R.E., Warren, S.G., & Clarke, A.D. (2011). A controlled snowmaking experiment testing the relation between black carbon content and reduction of snow albedo. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(D08109), doi: /2010jd Flanner, M.G., & Zender, C.S. (2005). Snowpack radiative heating: Influence on Tibetan Plateau climate. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(L06501), doi: /2004gl Hanna, E., et al. (2008, January). Increased Runoff from Melt from the Greenland Ice Sheet: A Response to Global Warming. Journal of Climate, 21, Keegan, K.M., et al. (2014). Climate change and forest fires synergistically drive widespread melt events of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(22), , doi: /pnas McConnell, J.R. (2007, September). 20th Century Industrial Black Carbon Emissions Altered Arctic Climate Forcing. Science, 317, , doi: /science Nghiem, S.V., et al. (2012). The extreme melt across the Greenland ice sheet in Geophysical Research Letters, 39(L20502), doi: /2012gl Polashenski, C.M, et al. (2015). Neither dust nor black carbon causing apparent albedo decline in Greenland s dry snow zone: Implications for MODIS C5 surface reflectance. Geophysical Research Letters, 42, , doi: /2015gl Stohl, A., et al. (2006). Pan Arctic enhancements of light absorbing aerosol concentrations due to North American boreal forest fires during summer Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(D22214), doi: /2006jd Strellis, B. (2013). Aerosol Radiative Forcing over Central Greenland: Estimates based on Field Measurements. Unpublished master s thesis (submitted), Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia. 23
24 Thank You! Questions? 24
25 Supplementary Information: BCE formula, [BC] is the mixing ratio of BC in the snow. [Dust] is the mixing ratio of dust in the snow for bin i. MAC is the mass absorption cross section the aerosol in question. MAC changes for dust depending on the bin designation. 25
26 Tropospheric Warming 26
27 Snow water Equivalent 27
28 : Spatial Map 28
29 for all runs 29
30 Low Cloud Fraction 30
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols
 Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Arctic climate: Unique vulnerability and complex response to aerosols Mark Flanner November 2, 2011 Santa Fe Conference on Global and Regional Climate Change 1 / 18 Arctic: Unique vulnerability to positive
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle
 Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region
 The third ACAM Workshop in 1 Guangzhou, China (June 5-9, 2017) Theme 2.1 Aerosols and Clouds The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region Faculty of Engineering & Arctic Research Center
The third ACAM Workshop in 1 Guangzhou, China (June 5-9, 2017) Theme 2.1 Aerosols and Clouds The role of snow-darkening effect in the Asian monsoon region Faculty of Engineering & Arctic Research Center
Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles in Snow and Sea Ice in CESM
 Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 30 December 11 Arctic Climate Response to Forcing from Light-Absorbing Particles
Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and
 Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and E. Andrews, T. Berg, J. F. Burkhart, A. M. Fjæraa, C. Forster, A. Herber, S. Hoch, Ø. Hov, D. Kowal, C. Lunder, T. Mefford, W. W. McMillan,
Andreas Stohl Norwegian Institute for Air Research (NILU) and E. Andrews, T. Berg, J. F. Burkhart, A. M. Fjæraa, C. Forster, A. Herber, S. Hoch, Ø. Hov, D. Kowal, C. Lunder, T. Mefford, W. W. McMillan,
Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes
 1 2 3 Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes 4 5 Yun Qian 1*, Hailong Wang 1, Rudong Zhang 2,1,
1 2 3 Black carbon in snow and its radiative forcing over the Arctic and Northern China: uncertainty associated with deposition and in-snow processes 4 5 Yun Qian 1*, Hailong Wang 1, Rudong Zhang 2,1,
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM. Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013
 The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
The Cryosphere Radiative Effect in CESM Justin Perket Mark Flanner CESM Polar Climate Working Group Meeting Wednesday June 19, 2013 Cryosphere Radiative Effect (CrRE) A new diagnostic feature is available
Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow
 Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow Charlie Zender, Mark Flanner, and Jim Randerson Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine Natalie Mahowald,
Present, Past, and Future Climate Effects and Efficacy of Dirty Snow Charlie Zender, Mark Flanner, and Jim Randerson Department of Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine Natalie Mahowald,
Springtime warming and reduced snow cover from carbonaceous particles
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 2481 2497, 29 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/2481/29/ Author(s) 29. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Springtime
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 2481 2497, 29 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/2481/29/ Author(s) 29. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Springtime
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables
 Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
IMPACTS OF A WARMING ARCTIC
 The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
The Earth s Greenhouse Effect Most of the heat energy emitted from the surface is absorbed by greenhouse gases which radiate heat back down to warm the lower atmosphere and the surface. Increasing the
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data
 Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB)
 Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008003, 2007 Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow Mark G. Flanner, 1 Charles S. Zender,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd008003, 2007 Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow Mark G. Flanner, 1 Charles S. Zender,
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1144856/dc1 Supporting Online Material for 20th-Century Industrial Black Carbon Emissions Altered Arctic Climate Forcing Joseph R. McConnell,* Ross Edwards, Gregory
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1144856/dc1 Supporting Online Material for 20th-Century Industrial Black Carbon Emissions Altered Arctic Climate Forcing Joseph R. McConnell,* Ross Edwards, Gregory
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics
 Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
Exploration of California High Resolution Snowpack Modeling with Realistic Surface-Atmospheric Radiation Physics Chaincy Kuo, Alan Rhoades, Daniel Feldman Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory AMS 15th
Arctic Chemistry And Climate
 21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change. Renguang Wu
 The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
The Northern Hemisphere Sea ice Trends: Regional Features and the Late 1990s Change Renguang Wu Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing World Conference on Climate Change
Introduction to Climate Change
 Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
Seasonality of Arctic Black Carbon Processes in the AMAP Multi-Model Ensemble
 Seasonality of Arctic Black Carbon Processes in the AMAP Multi-Model Ensemble R. Mahmood 1,2, K. von Salzen 3, M.G. Flanner 4, M. Sand 5, J. Langner 6, H. Wang 7, and L. Huang 8 1 School of Earth and Ocean
Seasonality of Arctic Black Carbon Processes in the AMAP Multi-Model Ensemble R. Mahmood 1,2, K. von Salzen 3, M.G. Flanner 4, M. Sand 5, J. Langner 6, H. Wang 7, and L. Huang 8 1 School of Earth and Ocean
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System
 Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
Key Feedbacks in the Climate System With a Focus on Climate Sensitivity SOLAS Summer School 12 th of August 2009 Thomas Schneider von Deimling, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Why do Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2
 GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
Two ice cores, identified as D4 and D5, were collected in 2003 from high
 Supporting Online Material Methods Ice core collection and analysis Two ice cores, identified as D4 and D5, were collected in 2003 from high snowfall regions of the west-central Greenland ice sheet (Fig.
Supporting Online Material Methods Ice core collection and analysis Two ice cores, identified as D4 and D5, were collected in 2003 from high snowfall regions of the west-central Greenland ice sheet (Fig.
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Top-of-atmosphere radiative forcing affected by brown carbon in the upper troposphere
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2960 Top-of-atmosphere radiative forcing affected by brown carbon in the upper troposphere Yuzhong Zhang 1,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2960 Top-of-atmosphere radiative forcing affected by brown carbon in the upper troposphere Yuzhong Zhang 1,
Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas
 Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas B. S. Grandey, H. Cheng, and C. Wang December 22, 2015 List of Tables 1 Annual
Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas B. S. Grandey, H. Cheng, and C. Wang December 22, 2015 List of Tables 1 Annual
Earth Science and Climate Change
 Earth Science and Climate Change Dr. Mary L. Cleave February 7, 2007 YOU ARE HERE 3 Land Use Changes Over Time Lingering Doubts on Temperature Trends Have Been Resolved 1st CCSP Synthesis & Assessment
Earth Science and Climate Change Dr. Mary L. Cleave February 7, 2007 YOU ARE HERE 3 Land Use Changes Over Time Lingering Doubts on Temperature Trends Have Been Resolved 1st CCSP Synthesis & Assessment
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM
 The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
The effects of dust emission on the trans- Pacific transport of Asian dust in the CESM Mingxuan Wu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhien Wang, Kang Yang, Chenglai Wu University of Wyoming Kai Zhang, Hailong Wang Pacific
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms
 Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the northern hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008 M. G. Flanner 1 *, K. M. Shell 2, M. Barlage 3, D. K. Perovich 4, & M. A. Tschudi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the northern hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008 M. G. Flanner 1 *, K. M. Shell 2, M. Barlage 3, D. K. Perovich 4, & M. A. Tschudi
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model
 Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Dependence of Radiative Forcing on Mineralogy in the Community Atmosphere Model Rachel Scanza 1, Natalie Mahowald 1, Jasper Kok 2, Steven Ghan 3, Charles Zender 4, Xiaohong Liu 5, Yan Zhang 6 February
Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG
 Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG Benjamin S. Grandey 1, Daniel Rothenberg 2, Alexander Avramov 2,3, Qinjian Jin 2, Hsiang-He Lee 1, Xiaohong Liu 4, Zheng Lu 4,
Effective radiative forcing in the aerosol climate model CAM5.3- MARC-ARG Benjamin S. Grandey 1, Daniel Rothenberg 2, Alexander Avramov 2,3, Qinjian Jin 2, Hsiang-He Lee 1, Xiaohong Liu 4, Zheng Lu 4,
Ice sheet freshwater forcing
 Jan Lenaerts Utrecht University University of Colorado Ice sheet freshwater forcing Photo: Reijmer, 2011 Sea level meeting 5 to ~6 pm, South Bay Goal: Sea level rise and its impacts on coastal populations
Jan Lenaerts Utrecht University University of Colorado Ice sheet freshwater forcing Photo: Reijmer, 2011 Sea level meeting 5 to ~6 pm, South Bay Goal: Sea level rise and its impacts on coastal populations
Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM
 Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM Chaincy Kuo1, Daniel Feldman1, Xianglei Huang2, Mark Flanner2, Ping Yang3, Xiuhong Chen2 1Lawrence Berkeley National
Arctic bias improvements with longwave spectral surface emissivity modeling in CESM Chaincy Kuo1, Daniel Feldman1, Xianglei Huang2, Mark Flanner2, Ping Yang3, Xiuhong Chen2 1Lawrence Berkeley National
2. Fargo, North Dakota receives more snow than Charleston, South Carolina.
 2015 National Tournament Division B Meteorology Section 1: Weather versus Climate Chose the answer that best answers the question 1. The sky is partly cloudy this morning in Lincoln, Nebraska. 2. Fargo,
2015 National Tournament Division B Meteorology Section 1: Weather versus Climate Chose the answer that best answers the question 1. The sky is partly cloudy this morning in Lincoln, Nebraska. 2. Fargo,
2/18/2013 Estimating Climate Sensitivity From Past Climates Outline
 Estimating Climate Sensitivity From Past Climates Outline Zero-dimensional model of climate system Climate sensitivity Climate feedbacks Forcings vs. feedbacks Paleocalibration vs. paleoclimate modeling
Estimating Climate Sensitivity From Past Climates Outline Zero-dimensional model of climate system Climate sensitivity Climate feedbacks Forcings vs. feedbacks Paleocalibration vs. paleoclimate modeling
Aerosols and climate. Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences
 Aerosols and climate Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences What are aerosols? Solid or liquid particles suspended in air Sizes range from a few nm to a few thousand nm Huge range of masses Where do aerosols come
Aerosols and climate Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences What are aerosols? Solid or liquid particles suspended in air Sizes range from a few nm to a few thousand nm Huge range of masses Where do aerosols come
Climate Change in Colorado: Recent Trends, Future Projections and Impacts An Update to the Executive Summary of the 2014 Report
 Climate Change in Colorado: Recent Trends, Future Projections and Impacts An Update to the Executive Summary of the 2014 Report Jeff Lukas, Western Water Assessment, University of Colorado Boulder - Lukas@colorado.edu
Climate Change in Colorado: Recent Trends, Future Projections and Impacts An Update to the Executive Summary of the 2014 Report Jeff Lukas, Western Water Assessment, University of Colorado Boulder - Lukas@colorado.edu
What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
Radiation in the atmosphere
 Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Science of Global Warming and Climate Change
 Science of Global Warming and Climate Change Part 1 Science Dr. David H. Manz, P. Eng. University of Calgary May 2015 Weather vs. Climate Weather happens day to day (moment to moment) best forecast is
Science of Global Warming and Climate Change Part 1 Science Dr. David H. Manz, P. Eng. University of Calgary May 2015 Weather vs. Climate Weather happens day to day (moment to moment) best forecast is
Introduction to HadGEM2-ES. Crown copyright Met Office
 Introduction to HadGEM2-ES Earth System Modelling How the climate will evolve depends on feedbacks Ecosystems Aerosols Chemistry Global-scale impacts require ES components Surface temperature Insolation
Introduction to HadGEM2-ES Earth System Modelling How the climate will evolve depends on feedbacks Ecosystems Aerosols Chemistry Global-scale impacts require ES components Surface temperature Insolation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions
 UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
Second-Order Draft Chapter 10 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
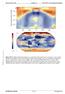 Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Second-Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report Figure... Multi model mean changes in a) zonal mean cloud fraction (in %), shown as a cross section though the atmosphere, and b) total cloud
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis
 Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report Presented by R.K. Pachauri, IPCC Chair and Bubu Jallow, WG 1 Vice Chair Nairobi, 6 February
Xianglei Huang University of Michigan Xiuhong Chen & Mark Flanner (Univ. of Michigan), Ping Yang (Texas A&M), Dan Feldman and Chiancy Kuo (LBL, DoE)
 Incorporating realistic surface LW spectral emissivity into the CESM Model: Impact on simulated climate and the potential sea-ice emissivity feedback mechanism Xianglei Huang University of Michigan Xiuhong
Incorporating realistic surface LW spectral emissivity into the CESM Model: Impact on simulated climate and the potential sea-ice emissivity feedback mechanism Xianglei Huang University of Michigan Xiuhong
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
What is Climate? Climate Change Evidence & Causes. Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing? Is the Climate Changing?
 What is Climate? 1 Climate Change Evidence & Causes Refers to the average environmental conditions (i.e. temperature, precipitation, extreme events) in a given location over many years Climate is what
What is Climate? 1 Climate Change Evidence & Causes Refers to the average environmental conditions (i.e. temperature, precipitation, extreme events) in a given location over many years Climate is what
THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
 ASTRONOMY READER THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT 35.1 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT Overview Planets are heated by light from the Sun. Planets cool off by giving off an invisible kind of light, longwave infrared light.
ASTRONOMY READER THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT 35.1 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT Overview Planets are heated by light from the Sun. Planets cool off by giving off an invisible kind of light, longwave infrared light.
AT350 EXAM #1 September 23, 2003
 AT350 EXAM #1 September 23, 2003 Name and ID: Enter your name and student ID number on the answer sheet and on this exam. Record your answers to the questions by using a No. 2 pencil to completely fill
AT350 EXAM #1 September 23, 2003 Name and ID: Enter your name and student ID number on the answer sheet and on this exam. Record your answers to the questions by using a No. 2 pencil to completely fill
Atmospheric Radiation
 Atmospheric Radiation NASA photo gallery Introduction The major source of earth is the sun. The sun transfer energy through the earth by radiated electromagnetic wave. In vacuum, electromagnetic waves
Atmospheric Radiation NASA photo gallery Introduction The major source of earth is the sun. The sun transfer energy through the earth by radiated electromagnetic wave. In vacuum, electromagnetic waves
Monitoring Climate Change from Space
 Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system
 2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
2nd Workshop on Parameterization of Lakes in Numerical Weather Prediction and Climate Modelling Lake parameters climatology for cold start runs (lake initialization) in the ECMWF forecast system R. Salgado(1),
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002
 Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference)
 Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa
 A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
A new perspective on aerosol direct radiative effects in South Atlantic and Southern Africa Ian Chang and Sundar A. Christopher Department of Atmospheric Science University of Alabama in Huntsville, U.S.A.
Coupling Climate to Clouds, Precipitation and Snow
 Coupling Climate to Clouds, Precipitation and Snow Alan K. Betts akbetts@aol.com http://alanbetts.com Co-authors: Ray Desjardins, Devon Worth Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Shusen Wang and Junhua Li
Coupling Climate to Clouds, Precipitation and Snow Alan K. Betts akbetts@aol.com http://alanbetts.com Co-authors: Ray Desjardins, Devon Worth Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Shusen Wang and Junhua Li
Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects
 Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects GLOBE Pollution Southern Japan TRACE-P, 2001 Dust Antony Clarke, University
Physio-chemical and Optical Characterization of Anthropogenic and Natural Aerosol: Implications for Assessing Global Effects GLOBE Pollution Southern Japan TRACE-P, 2001 Dust Antony Clarke, University
NSF: Natural and Anthropogenic Climate Impacts as Evidenced in Ice Cores
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSF: Natural and Anthropogenic Climate Impacts as Evidenced in Ice Cores Presented by: Dr. Joseph McConnell and Linda Morris May 2, 2012 Natural and Anthropogenic
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSF: Natural and Anthropogenic Climate Impacts as Evidenced in Ice Cores Presented by: Dr. Joseph McConnell and Linda Morris May 2, 2012 Natural and Anthropogenic
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Climate 1: The Climate System
 Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
Impact of Atmoshpheric Brown Clouds (ABCs) on Agriculture. Dr.A.K.Gogoi, ADG(Agro) ICAR, New Delhi- 12
 Impact of Atmoshpheric Brown Clouds (ABCs) on Agriculture Dr.A.K.Gogoi, ADG(Agro) ICAR, New Delhi- 12 What are ABCs Atmospheric Brown Clouds (ABC s ) are regional scale slums of air pollution that consists
Impact of Atmoshpheric Brown Clouds (ABCs) on Agriculture Dr.A.K.Gogoi, ADG(Agro) ICAR, New Delhi- 12 What are ABCs Atmospheric Brown Clouds (ABC s ) are regional scale slums of air pollution that consists
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Radiative effects of desert dust on weather and climate
 UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, DIVISION OF ENVIRONMENT AND METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC MODELING AND WEATHER FORECASTING GROUP Radiative effects of desert dust on weather and climate Christos Spyrou,
UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS SCHOOL OF PHYSICS, DIVISION OF ENVIRONMENT AND METEOROLOGY ATMOSPHERIC MODELING AND WEATHER FORECASTING GROUP Radiative effects of desert dust on weather and climate Christos Spyrou,
Climate Change. April 21, 2009
 Climate Change Chapter 16 April 21, 2009 Reconstructing Past Climates Techniques Glacial landscapes (fossils) CLIMAP (ocean sediment) Ice cores (layering of precipitation) p Otoliths (CaCO 3 in fish sensory
Climate Change Chapter 16 April 21, 2009 Reconstructing Past Climates Techniques Glacial landscapes (fossils) CLIMAP (ocean sediment) Ice cores (layering of precipitation) p Otoliths (CaCO 3 in fish sensory
ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4
 ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4 Atmospheric Sciences 321: Final Examination Study Guide The final examination will consist of similar questions Science of Climate Multiple
ATMS 321: Sci. of Climate Final Examination Study Guide Page 1 of 4 Atmospheric Sciences 321: Final Examination Study Guide The final examination will consist of similar questions Science of Climate Multiple
Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy
 Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy Nicholas Meskhidze & Matthew Johnson First International Workshop on the Long Range Transport and Impacts
Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy Nicholas Meskhidze & Matthew Johnson First International Workshop on the Long Range Transport and Impacts
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Interactive comment on The impact of Saharan dust and black carbon on albedo and long-term glacier mass balance by J. Gabbi et al.
 The Cryosphere Discuss., 9, C553 C564, 2015 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net/9/c553/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. The Cryosphere Discussions
The Cryosphere Discuss., 9, C553 C564, 2015 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net/9/c553/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. The Cryosphere Discussions
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives
 Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Aerosol/Transport issues in VOCALS region
 Aerosol/Transport issues in VOCALS region Phil Rasch Climate Modeling Section National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA With input from Jim Hack, Dani Coleman, Julie Caron, John Truesdale
Aerosol/Transport issues in VOCALS region Phil Rasch Climate Modeling Section National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA With input from Jim Hack, Dani Coleman, Julie Caron, John Truesdale
Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance
 Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance The are three basic snowmelt phases 1) Warming phase: Absorbed energy raises the average snowpack temperature to a point at which the snowpack is isothermal (no vertical
Snow II: Snowmelt and energy balance The are three basic snowmelt phases 1) Warming phase: Absorbed energy raises the average snowpack temperature to a point at which the snowpack is isothermal (no vertical
causes Associate Professor Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University
 Recent climate change and its causes Raymond Najjar Associate Professor Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University Presentation for: Erie County Climate Adaptation Workshop September 1,
Recent climate change and its causes Raymond Najjar Associate Professor Department of Meteorology The Pennsylvania State University Presentation for: Erie County Climate Adaptation Workshop September 1,
Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow
 Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow Heidrun Matthes, Annette Rinke Alfred-Wegener- Institute for Polar and Marine Research photo: Thomas Opel Motivation - Why do we care? Snow
Sensitivity of Present Day Arctic Climate Simulations to Snow Heidrun Matthes, Annette Rinke Alfred-Wegener- Institute for Polar and Marine Research photo: Thomas Opel Motivation - Why do we care? Snow
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Response to Reviewer s comments
 Response to Reviewer s comments (MS Ref. No.: acp-2010-98): Long-term record of aerosol optical properties and chemical composition from a high-altitude site (Manora Peak) in Central Himalaya by K. Ram
Response to Reviewer s comments (MS Ref. No.: acp-2010-98): Long-term record of aerosol optical properties and chemical composition from a high-altitude site (Manora Peak) in Central Himalaya by K. Ram
Arctic Climate Change. Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013
 Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Arctic Climate Change Glen Lesins Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science Dalhousie University Create Summer School, Alliston, July 2013 When was this published? Observational Evidence for Arctic
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions
 Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin
 A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin Pratima Gupta, Ashok Jangid and Ranjit Kumar Department of Chemistry, Faculty of science, Dayalbagh Educational
A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin Pratima Gupta, Ashok Jangid and Ranjit Kumar Department of Chemistry, Faculty of science, Dayalbagh Educational
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview
 Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS
 HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS 1. Introduction: the story so far. 2. Global warming: the last 150 years 3. Is it really warming? 4. Fingerprints: the stratosphere, the hockey sticks Radiance (mw.m
HUMAN FINGERPRINTS (1): OBSERVATIONS 1. Introduction: the story so far. 2. Global warming: the last 150 years 3. Is it really warming? 4. Fingerprints: the stratosphere, the hockey sticks Radiance (mw.m
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Arctic Oxidation Chemistry
 19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
19 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Oxidation Chemistry Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
Our Geologic Backdrop: Ice Age Cycles
 Introduction to Earth s Climate System Our Geologic Backdrop: Ice Age Cycles MODULE 2.4 2.4 Our Geologic Backdrop: Ice Age Cycles Lesson Goals»» Describe Earth s geologic variability over the past million
Introduction to Earth s Climate System Our Geologic Backdrop: Ice Age Cycles MODULE 2.4 2.4 Our Geologic Backdrop: Ice Age Cycles Lesson Goals»» Describe Earth s geologic variability over the past million
A thesis submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Engineering and Physical Science
 To Characterize the Black Carbon Using Single Particle Incandescence Technique: Instrumentation Development, Data Analysis Techniques and Quantitative Measurements A thesis submitted to the University
To Characterize the Black Carbon Using Single Particle Incandescence Technique: Instrumentation Development, Data Analysis Techniques and Quantitative Measurements A thesis submitted to the University
TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS AND GLACIATION. Chris Brierley & Alexey Fedorov
 TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS AND GLACIATION Chris Brierley & Alexey Fedorov Outline Recap on the warm early Pliocene (as we have reconstructed it) Methodology to compare meridional SST gradient impacts and zonal
TEMPERATURE GRADIENTS AND GLACIATION Chris Brierley & Alexey Fedorov Outline Recap on the warm early Pliocene (as we have reconstructed it) Methodology to compare meridional SST gradient impacts and zonal
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida
 Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1
 CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
CLIMATE AND CLIMATE CHANGE MIDTERM EXAM ATM S 211 FEB 9TH 2012 V1 Name: Student ID: Please answer the following questions on your Scantron Multiple Choice [1 point each] (1) The gases that contribute to
Brita Horlings
 Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
Knut Christianson Brita Horlings brita2@uw.edu https://courses.washington.edu/ess431/ Natural Occurrences of Ice: Distribution and environmental factors of seasonal snow, sea ice, glaciers and permafrost
3. Which color of the visible light has the shortest wavelength? A) violet B) green C) yellow D) red
 Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
Name: Topic 6 Test 1. Which process is responsible for the greatest loss of energy from Earth's surface into space on a clear night? A) condensation B) conduction C) radiation D) convection 2. Base your
Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall bywest Asian dust
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2107 Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall bywest Asian dust 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 V Vinoj 1,2, Philip J Rasch 1*, Hailong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2107 Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall bywest Asian dust 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 V Vinoj 1,2, Philip J Rasch 1*, Hailong
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING
 TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING (Start on p 67 in Class Notes) p 67 ENERGY BALANCE (review) Global climate variability and change are caused by changes in the ENERGY BALANCE that are FORCED review FORCING
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING (Start on p 67 in Class Notes) p 67 ENERGY BALANCE (review) Global climate variability and change are caused by changes in the ENERGY BALANCE that are FORCED review FORCING
M. Mielke et al. C5816
 Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 14, C5816 C5827, 2014 www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/14/c5816/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric
Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 14, C5816 C5827, 2014 www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/14/c5816/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Atmospheric
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle
 Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L)
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L)
