Aerosols and climate. Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences
|
|
|
- Reynold Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aerosols and climate Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences
2 What are aerosols? Solid or liquid particles suspended in air Sizes range from a few nm to a few thousand nm Huge range of masses
3 Where do aerosols come from?
4 Estimate of Present-Day Global Emission of Major Aerosol Types (in Tg/year) Present flux Source Low High Best Soil dust (mineral aerosol) Natural Primary 1,000 3,000 1,500 Sea salt 1,000 10,000 1,300 Volcanic dust 4 10, Biological debris Secondary Sulfates from biogenic gases Sulfates from volcanic SO 2 Organic matter from biogenic NMHC * Nitrates from NO x Present flux Source Low High Best Anthropogenic Primary Industrial dust etc Black carbon (soot and charcoal) Secondary Sulphates from SO Biomass burning (w/o black carbon) Nitrates from NO x Organics from anthropogenic NMHC *
5 [nm]
6 Aerosols and light scattering Scattering of solar radiation per unit mass is maximum when particle size is close to solar wavelengths (λ ~ nm) Particles in the size range nm are most efficient scatterers Particle surface area more important than mass Sca attering ef fficiency per mass Particle diameter [nm]
7 Surface area and mass M = (4π/3) ρ r 3 A = 4π r 2 A/M 1/r when r «λ scattering efficiency increases with r 4 r<100 nm particles don t matter Sc cattering efficiency per mass Particle diameter [nm]
8 Aerosols and light scattering If aerosol particle is soluble then size will depend upon water uptake Water uptake depends upon relative humidity (RH) For given number of particles, scattering will increase with RH But with no particles there is no scattering despite what the RH is
9 Size as a function of RH
10 Chemical composition affects growth r/r dry grow wth fa actor r 3 2 marine airmass 1 polluted airmass RH
11 What determines scattering? For particles of size > 200 nm, surface area determines scattering from one particle Multiply this by the number concentration of particles to get overall scattering per unit volume of air A Nr Nr tot 2, M tot 3 A tot N 1/3 M 2/3 Need to know both total aerosol mass and the number concentration
12 Importance of sulfate Sulfate aerosols dominate the scattering over continental regions Anthropogenic sources comparable to natural sources Regionally, this scattering can seriously degrade visibility Globally, this scattering reduces solar radiation entering the climate system by 2 Wm -2 Studies suggest that about W m -2 of this scattering are from anthropogenic aerosols, mostly sulfate ( direct effect of aerosols)
13 Beijing after rain Beijing during dry period
14 Solar radiation reaching the surface
15 Global Sulfur Budget Rates in Tg S yr -1 4 NO 3 18 OH cloud 42 SO4 2- SO 2 OH τ = 3.9d τ = 1.3d 8 H 2 SO 4 (g) (CH 3 ) 2 S (DMS) τ = 10d 1.0d dep 27 dry 20 wet dep 6 dry 44 wet Phytoplankton Volcanoes Combustion/ Smelters
16 Global Sulfur Emission Patterns Chin et al. [2000]
17 SO 2 sources by type
18 Direct effect of aerosols upon solar radiation Aerosols scatter solar radiation More particles more scattering Some scattered radiation returns to space Reduction in amount entering climate system Cooling effect
19 Aerosol optical depth (measure of scattering)
20 How well do we understand human influence? Direct radiative forcing g( (effect of anthropogenic emissions on aerosol scattering) from different models
21 Trends in U.S. NO x AND SO 2 Emissions
22 Aerosol-cloud-climate interactions
23 More aerosol-climate effects
24 Cloud droplets form on aerosol particles For soluble aerosols, particle size increases with RH When a parcel of air rises, it cools and the RH increases When RH>1, the soluble aerosols can activate (grow unstably into much larger cloud droplets) The RH at which an aerosol activates is strongly dependent upon its size Larger aerosols activate first and can consume vapor, preventing the smaller ones from activating The number of cloud droplets is strongly controlled by the number of soluble aerosols
25 What determines N in warm clouds? Cloud con ncentr dropl et ation [cm -3 ] Aerosol concentration (r>0.1 micron) [cm -3 ]
26 Link between number of cloud droplets and cloud albedo Similar arguments as for light scattering due to aerosols For given amount of liquid water, increased N gives smaller average size of droplets Smaller droplets have larger surface area More reflective cloud, more albedo
27
28 Most wellunderstood aerosol-cloud- l climate effects (indirect effects)
29 Global Sulfur Emission Patterns Chin et al. [2000]
30 MODIS, data courtesy of NASA
31 IPCC, 2007
32 Putting it all together
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosol. Challenge: Global Warming. Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio. 1910s. 1950s. 1990s T [Kelvin]
![Aerosol. Challenge: Global Warming. Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio. 1910s. 1950s. 1990s T [Kelvin] Aerosol. Challenge: Global Warming. Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio. 1910s. 1950s. 1990s T [Kelvin]](/thumbs/86/93830655.jpg) Aerosol Challenge: Global Warming 1910s 1950s 1990s 2 1 0 +1 +2 T [Kelvin] Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio Schneider, J. Climate, 2001 1 Aerosols are liquid or solid particles suspended in
Aerosol Challenge: Global Warming 1910s 1950s 1990s 2 1 0 +1 +2 T [Kelvin] Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio Schneider, J. Climate, 2001 1 Aerosols are liquid or solid particles suspended in
Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure
 Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of
Aerosol Basics: Definitions, size distributions, structure Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3152 Week 9, March 8, 2016
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3152 Week 9, March 8, 2016 Hand back Midterm Exams (average = 84) Interaction of atmospheric constituents with light Haze and Visibility Aerosol formation processes (more detail) Haze and
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3152 Week 9, March 8, 2016 Hand back Midterm Exams (average = 84) Interaction of atmospheric constituents with light Haze and Visibility Aerosol formation processes (more detail) Haze and
Slides partly by Antti Lauri and Hannele Korhonen. Liquid or solid particles suspended in a carrier gas Described by their
 Atmospheric Aerosols Slides partly by Antti Lauri and Hannele Korhonen Aerosol particles Liquid or solid particles suspended in a carrier gas Described by their Size Concentration - Number - Surface -
Atmospheric Aerosols Slides partly by Antti Lauri and Hannele Korhonen Aerosol particles Liquid or solid particles suspended in a carrier gas Described by their Size Concentration - Number - Surface -
Why is it difficult to predict climate? Understanding current scientific challenges
 Why is it difficult to predict climate? Understanding current scientific challenges Akua Asa-Awuku October 22, 2009 Global Climate Change (GCC) Workshop University of California - Riverside Bourns College
Why is it difficult to predict climate? Understanding current scientific challenges Akua Asa-Awuku October 22, 2009 Global Climate Change (GCC) Workshop University of California - Riverside Bourns College
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB)
 Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Spatial Variability of Aerosol - Cloud Interactions over Indo - Gangetic Basin (IGB) Shani Tiwari Graduate School of Environmental Studies Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan Email: pshanitiwari@gmail.com
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002
 Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
 1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
1/23 Remote sensing of atmospheric aerosol, clouds and aerosol-cloud interactions. Bremen, 16-19 December 2013 Satellite analysis of aerosol indirect effect on stratocumulus clouds over South-East Atlantic
Aerosols and Climate
 Aerosols and Climate S K Satheesh S K Satheesh is an Assistant Professor at Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests include aerosols,
Aerosols and Climate S K Satheesh S K Satheesh is an Assistant Professor at Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. His research interests include aerosols,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility.
 Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility. Objectives: 1. Attenuation of atmospheric radiation by particulates. 2. Haze and Visibility. Readings:
Lecture 26. Regional radiative effects due to anthropogenic aerosols. Part 2. Haze and visibility. Objectives: 1. Attenuation of atmospheric radiation by particulates. 2. Haze and Visibility. Readings:
7. Aerosols and Climate
 7. Aerosols and Climate I. Scattering 1. When radiation impinges on a medium of small particles, scattering of some of the radiation occurs in all directions. The portion scattered backward is called the
7. Aerosols and Climate I. Scattering 1. When radiation impinges on a medium of small particles, scattering of some of the radiation occurs in all directions. The portion scattered backward is called the
Dust Climate Interactions
 School of Earth and Environment INSTITUTE FOR CLIMATE AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE Dust Climate Interactions Kerstin Schepanski k. schepanski@leeds.ac.uk Dust Impacts Direct and indirect climate forcing Regional
School of Earth and Environment INSTITUTE FOR CLIMATE AND ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE Dust Climate Interactions Kerstin Schepanski k. schepanski@leeds.ac.uk Dust Impacts Direct and indirect climate forcing Regional
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to
 What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, model. Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg
 An AGCM operated at University of Oslo (UiO) Norway Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, 2003 by Kirkevåg; Jón Egill Kristjánsson; ; Trond Iversen Basic: NCAR-CCM3.2 CCM3.2 (Kiehl,et
An AGCM operated at University of Oslo (UiO) Norway Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, 2003 by Kirkevåg; Jón Egill Kristjánsson; ; Trond Iversen Basic: NCAR-CCM3.2 CCM3.2 (Kiehl,et
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Feedbacks & Clouds DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 6: 10-14-13 Feedbacks Climate forcings change global temperatures directly
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Introduction to HadGEM2-ES. Crown copyright Met Office
 Introduction to HadGEM2-ES Earth System Modelling How the climate will evolve depends on feedbacks Ecosystems Aerosols Chemistry Global-scale impacts require ES components Surface temperature Insolation
Introduction to HadGEM2-ES Earth System Modelling How the climate will evolve depends on feedbacks Ecosystems Aerosols Chemistry Global-scale impacts require ES components Surface temperature Insolation
Aerosol type how to use the information from satellites for models???
 Aerosol type how to use the information from satellites for models??? Mian Chin, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center AeroCom/AeroSat workshop, September 2016 What does type mean? Satellite Estimated based
Aerosol type how to use the information from satellites for models??? Mian Chin, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center AeroCom/AeroSat workshop, September 2016 What does type mean? Satellite Estimated based
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions
 UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
Three-dimensional (3-D) radiative transfer codes are mainly used in cloud studies (e.g., LES models) and vegetation studies.
 Lecture 5. Composition and structure of the Earth s atmosphere. Basic properties of gases, aerosols, and clouds that are important for radiative transfer modeling. Objectives: 1. Structure of the Earth
Lecture 5. Composition and structure of the Earth s atmosphere. Basic properties of gases, aerosols, and clouds that are important for radiative transfer modeling. Objectives: 1. Structure of the Earth
EAS1600 Spring 2014 Lab 06 ATMOSPHERIC AEROSOLS
 Objectives EAS1600 Spring 2014 Lab 06 ATMOSPHERIC AEROSOLS During the course of this lab we will investigate some basic connections between aerosols and climate. We will look at the aerosol scattering
Objectives EAS1600 Spring 2014 Lab 06 ATMOSPHERIC AEROSOLS During the course of this lab we will investigate some basic connections between aerosols and climate. We will look at the aerosol scattering
climate change Contents CO 2 (ppm)
 climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 5. OtherGreenhouse Gases (GHGs):
climate change CO 2 (ppm) 2007 Joachim Curtius Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Universität Mainz Contents 1. Summary 2. Background 3. Climate change: observations 4. CO 2 5. OtherGreenhouse Gases (GHGs):
A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation. model. Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan
 A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation model P3.7 Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan Abstract The analysis of solar radiation at the surface
A study of regional and long-term variation of radiation budget using general circulation model P3.7 Makiko Mukai* University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Japan Abstract The analysis of solar radiation at the surface
On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings. Seland,
 On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings Trond Iversen,, Alf Kirkevåg, Øyvind Seland, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Trude Storelvmo,, Jens Debernard Norwegian Meteorological Institute
On-line Aerosols in the Oslo Version of CAM3: Some shortcomings Trond Iversen,, Alf Kirkevåg, Øyvind Seland, Jon Egill Kristjansson, Trude Storelvmo,, Jens Debernard Norwegian Meteorological Institute
Aerosol & Climate. Direct and Indirect Effects
 Aerosol & Climate Direct and Indirect Effects Embedded cooling Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio Schneider, J. Climate, 2001 1 Many Sources / Lifetimes 2 Aerosols are liquid or solid particles
Aerosol & Climate Direct and Indirect Effects Embedded cooling Observed warming during 20 th century, Tapio Schneider, J. Climate, 2001 1 Many Sources / Lifetimes 2 Aerosols are liquid or solid particles
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms
 Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Lecture 9: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Mechanisms Basic radiative feedbacks (Plank, Water Vapor, Lapse-Rate Feedbacks) Ice albedo & Vegetation-Climate feedback Cloud feedback Biogeochemical feedbacks
Marine stratocumulus clouds
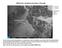 Marine stratocumulus clouds E. Pacific E. Atlantic Subtropical high-p regions Typical cold sea surface temperatures, in conjunc6on with the subsidence associated with the subtropical high, are responsible
Marine stratocumulus clouds E. Pacific E. Atlantic Subtropical high-p regions Typical cold sea surface temperatures, in conjunc6on with the subsidence associated with the subtropical high, are responsible
1. Weather and climate.
 Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era.
 2002 Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era. Figure 1. Reconstructed surface temperature record. Strong warming in the first and late part of the century. El Ninos and major volcanic eruptions are
2002 Recent Climate History - The Instrumental Era. Figure 1. Reconstructed surface temperature record. Strong warming in the first and late part of the century. El Ninos and major volcanic eruptions are
Outline. December 14, Applications Scattering. Chemical components. Forward model Radiometry Data retrieval. Applications in remote sensing
 in in December 4, 27 Outline in 2 : RTE Consider plane parallel Propagation of a signal with intensity (radiance) I ν from the top of the to a receiver on Earth Take a layer of thickness dz Layer will
in in December 4, 27 Outline in 2 : RTE Consider plane parallel Propagation of a signal with intensity (radiance) I ν from the top of the to a receiver on Earth Take a layer of thickness dz Layer will
Chapter 14: The Changing Climate
 Chapter 14: The Changing Climate Detecting Climate Change Natural Causes of Climate Change Anthropogenic Causes of Climate Change Possible Consequences of Global Warming Climate Change? -Paleo studies
Chapter 14: The Changing Climate Detecting Climate Change Natural Causes of Climate Change Anthropogenic Causes of Climate Change Possible Consequences of Global Warming Climate Change? -Paleo studies
Major climate change triggers
 Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
Major climate change triggers Variations in solar output Milankovitch cycles Elevation & distribution of continents Ocean interactions Atmospheric composition change (CO 2 and other volcanic gasses) Biological
Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers OUTLINE
 Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers The Hydrosphere Rain and rivers OUTLINE 1 Generalizations (non-political conservatism) Conservative (not affected) and Non-Conservative (affected) Ions Distinction: whether
Hydrological Cycle Rain and rivers The Hydrosphere Rain and rivers OUTLINE 1 Generalizations (non-political conservatism) Conservative (not affected) and Non-Conservative (affected) Ions Distinction: whether
Radiation in the atmosphere
 Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Radiation in the atmosphere Flux and intensity Blackbody radiation in a nutshell Solar constant Interaction of radiation with matter Absorption of solar radiation Scattering Radiative transfer Irradiance
Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) Slides from Review Sessions are posted on course website:
 Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) 35% of total grade Format will be all multiple choice (~70 questions) Final exam will cover entire course - material since 2 nd midterm weighted
Final Exam: Monday March 17 3:00-6:00 pm (here in Center 113) 35% of total grade Format will be all multiple choice (~70 questions) Final exam will cover entire course - material since 2 nd midterm weighted
Atmospheric models. Chem Christoph Knote - NCAR Spring 2013
 Atmospheric models Chem 55 - Christoph Knote - NCAR Spring 203 based on: Introduction to Atmospheric Chemistry, D. Jacob, Princeton Press, 999 Prof. Colette Heald s course http://www.atmos.colostate.edu/~heald/teaching.html
Atmospheric models Chem 55 - Christoph Knote - NCAR Spring 203 based on: Introduction to Atmospheric Chemistry, D. Jacob, Princeton Press, 999 Prof. Colette Heald s course http://www.atmos.colostate.edu/~heald/teaching.html
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle
 Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Lecture 8: Climate Modeling
 Lecture 8: Climate Modeling How to Build a Climate Model The climate is governed by many complex physical, chemical, and biological processes and their interactions. Building a climate model needs to consider
Lecture 8: Climate Modeling How to Build a Climate Model The climate is governed by many complex physical, chemical, and biological processes and their interactions. Building a climate model needs to consider
T eff = [F s (1 - A)/(4σ)] ¼ = K.
![T eff = [F s (1 - A)/(4σ)] ¼ = K. T eff = [F s (1 - A)/(4σ)] ¼ = K.](/thumbs/82/85857260.jpg) Lectures 16-18. Sci A-30 8. 10 & 15 April 2008 The Planck function gives the energy emission rate for an object, which is a function of it's temperature. The earth exchanges energy with it's environment
Lectures 16-18. Sci A-30 8. 10 & 15 April 2008 The Planck function gives the energy emission rate for an object, which is a function of it's temperature. The earth exchanges energy with it's environment
Glaciology HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION
 HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback
 Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Lecture 10: Climate Sensitivity and Feedback Human Activities Climate Sensitivity Climate Feedback 1 Climate Sensitivity and Feedback (from Earth s Climate: Past and Future) 2 Definition and Mathematic
Professional English
 Tomsk Polytechnic University Institute of natural recourses Geoecology and Geochemistry Department Professional English Lecture 1 «Basic concept of atmospheric aerosols» Anna V. Talovskaya PhD, Associate
Tomsk Polytechnic University Institute of natural recourses Geoecology and Geochemistry Department Professional English Lecture 1 «Basic concept of atmospheric aerosols» Anna V. Talovskaya PhD, Associate
9/5/16. Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate. Common Forms of Energy Transfer in Climate. Electromagnetic radiation.
 Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Section 3-4: Radiation, Energy, Climate Learning outcomes types of energy important to the climate system Earth energy balance (top of atm., surface) greenhouse effect natural and anthropogenic forcings
Indices of Refraction of Absorptive Aerosol Their Importance and Complexity
 Indices of Refraction of Absorptive Aerosol Their Importance and Complexity Steven T Massie NCAR Earth System Laboratory HITRAN Cambridge, Massachusetts June 16-18, 2010 NCAR is sponsored by the National
Indices of Refraction of Absorptive Aerosol Their Importance and Complexity Steven T Massie NCAR Earth System Laboratory HITRAN Cambridge, Massachusetts June 16-18, 2010 NCAR is sponsored by the National
Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem
 Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem Jan Kazil University of Colorado / NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory WRF/Chem Tutorial, 3 August 2015 (WRF/Chem 3.7) Part I - Introduction Overview of... Aerosol Aerosol
Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem Jan Kazil University of Colorado / NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory WRF/Chem Tutorial, 3 August 2015 (WRF/Chem 3.7) Part I - Introduction Overview of... Aerosol Aerosol
Climate 1: The Climate System
 Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
Climate 1: The Climate System Prof. Franco Prodi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Via P. Gobetti, 101 40129 BOLOGNA SIF, School of Energy, Varenna, July 2014 CLIMATE
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols
 A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
Atmospheric Radiation
 Atmospheric Radiation NASA photo gallery Introduction The major source of earth is the sun. The sun transfer energy through the earth by radiated electromagnetic wave. In vacuum, electromagnetic waves
Atmospheric Radiation NASA photo gallery Introduction The major source of earth is the sun. The sun transfer energy through the earth by radiated electromagnetic wave. In vacuum, electromagnetic waves
Study of the Effects of Acidic Ions on Cloud Droplet Formation Using Laboratory Experiments
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 10 (2014 ) 246 250 ICESD 2014: February 19-21, Singapore Study of the Effects of Acidic Ions on Cloud Droplet Formation Using Laboratory
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 10 (2014 ) 246 250 ICESD 2014: February 19-21, Singapore Study of the Effects of Acidic Ions on Cloud Droplet Formation Using Laboratory
Atmosphere Weather and Climate
 Atmosphere Weather and Climate Weather and Climate Weather Atmospheric conditions at a particular time and place Climate Long-term average of weather conditions Often over decades or centuries Coastal
Atmosphere Weather and Climate Weather and Climate Weather Atmospheric conditions at a particular time and place Climate Long-term average of weather conditions Often over decades or centuries Coastal
Sulfur Biogeochemical Cycle
 Sulfur Biogeochemical Cycle Chris Moore 11/16/2015 http://www.inorganicventures.com/element/sulfur 1 Sulfur Why is it important? 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant
Sulfur Biogeochemical Cycle Chris Moore 11/16/2015 http://www.inorganicventures.com/element/sulfur 1 Sulfur Why is it important? 14 th most abundant element in Earth s crust Sulfate is second most abundant
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change
 Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Clouds, Haze, and Climate Change Jim Coakley College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Earth s Energy Budget and Global Temperature Incident Sunlight 340 Wm -2 Reflected Sunlight 100 Wm -2 Emitted Terrestrial
Climate Variability Natural and Anthropogenic
 Climate Variability Natural and Anthropogenic Jim Renwick NIWA Climate Research j.renwick@niwa.co.nz Climate equilibrium and climate forcings Natural forcings Anthropogenic forcings Feedbacks Natural variability
Climate Variability Natural and Anthropogenic Jim Renwick NIWA Climate Research j.renwick@niwa.co.nz Climate equilibrium and climate forcings Natural forcings Anthropogenic forcings Feedbacks Natural variability
The Greenhouse Effect. Lan Ma
 The Greenhouse Effect Lan Ma What to cover today: How do we calculate the Earth s surface temperature? What makes a gas a greenhouse gas and how does the increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere cause
The Greenhouse Effect Lan Ma What to cover today: How do we calculate the Earth s surface temperature? What makes a gas a greenhouse gas and how does the increasing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere cause
A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin
 A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin Pratima Gupta, Ashok Jangid and Ranjit Kumar Department of Chemistry, Faculty of science, Dayalbagh Educational
A study on characterization, emission and deposition of black carbon over Indo- Gangetic Basin Pratima Gupta, Ashok Jangid and Ranjit Kumar Department of Chemistry, Faculty of science, Dayalbagh Educational
Mon Oct 20. Today: radiation and temperature (cont) sun-earth geometry energy balance >> conceptual model of climate change Tues:
 Mon Oct 20 Announcements: bring calculator to class from now on > in-class activities > midterm and final Today: radiation and temperature (cont) sun-earth geometry energy balance >> conceptual model of
Mon Oct 20 Announcements: bring calculator to class from now on > in-class activities > midterm and final Today: radiation and temperature (cont) sun-earth geometry energy balance >> conceptual model of
Monitoring Climate Change from Space
 Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
Monitoring Climate Change from Space Richard Allan (email: r.p.allan@reading.ac.uk twitter: @rpallanuk) Department of Meteorology, University of Reading Why Monitor Earth s Climate from Space? Global Spectrum
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101
 The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
The Atmosphere. All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010
 The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
The Atmosphere All of it. In one hour. Mikael Witte 10/27/2010 Outline Structure Dynamics - heat transport Composition Trace constituent compounds Some Atmospheric Processes Ozone destruction in stratosphere
CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
The Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Ammonia
 The Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Ammonia Russell Dickerson Dept. Meteorology, The University of Maryland Presented at the National Atmospheric Deposition Program Ammonia Workshop October 23, 2003
The Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics of Ammonia Russell Dickerson Dept. Meteorology, The University of Maryland Presented at the National Atmospheric Deposition Program Ammonia Workshop October 23, 2003
ChArMEx. The Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment. Contact: - Ambient air quality - Chemistry-climate interactions
 ChArMEx The Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment Contact: francois.dulac@cea.fr 1. Main regional stakes - Ambient air quality - Chemistry-climate interactions - Impact on ecosystems 2. Scientific
ChArMEx The Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment Contact: francois.dulac@cea.fr 1. Main regional stakes - Ambient air quality - Chemistry-climate interactions - Impact on ecosystems 2. Scientific
Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
1 NAME Investigation 2 Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? Introduction As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date. Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled?
 Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Name(s) Period Date 1 Introduction Earth s Energy Budget: How Is the Temperature of Earth Controlled? As you learned from the reading, the balance between incoming energy from the sun and outgoing energy
Can a change of single scattering albedo in Amami-Oshima in a low pressure condition be explained by GCM simulations?
 Can a change of single scattering albedo in Amami-Oshima in a low pressure condition be explained by GCM simulations? Daisuke Goto 1, Toshihiko Takemura 2, Nick Schutgens 1, Haruo Tsuruta 1, and Teruyuki
Can a change of single scattering albedo in Amami-Oshima in a low pressure condition be explained by GCM simulations? Daisuke Goto 1, Toshihiko Takemura 2, Nick Schutgens 1, Haruo Tsuruta 1, and Teruyuki
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions. Jim Haywood
 Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Chasing Aerosol Particles Down to Nano Sizes
 Chasing Aerosol Particles Down to Nano Sizes ERC Seminar 13 June 2013 Armin Sorooshian Chemical & Environmental Engineering Atmospheric Sciences University of Arizona Outline of Talk 1. What are aerosol
Chasing Aerosol Particles Down to Nano Sizes ERC Seminar 13 June 2013 Armin Sorooshian Chemical & Environmental Engineering Atmospheric Sciences University of Arizona Outline of Talk 1. What are aerosol
- matter-energy interactions. - global radiation balance. Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book. Outline. - shortwave radiation balance
 (1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
(1 of 12) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - matter-energy interactions - shortwave radiation balance - longwave radiation balance - global radiation balance (2 of 12) Previously, we
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Hygroscopic Growth of Aerosols and their Optical Properties
 Hygroscopic Growth of Aerosols and their Optical Properties Cynthia Randles Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Princeton University V. Ramaswamy and L. M. Russell ! Introduction Presentation Overview! Aerosol
Hygroscopic Growth of Aerosols and their Optical Properties Cynthia Randles Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Princeton University V. Ramaswamy and L. M. Russell ! Introduction Presentation Overview! Aerosol
2. Illustration of Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect with Simple Models
 2. Illustration of Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect with Simple Models In the first lecture, I introduced the concept of global energy balance and talked about the greenhouse effect. Today we will address
2. Illustration of Atmospheric Greenhouse Effect with Simple Models In the first lecture, I introduced the concept of global energy balance and talked about the greenhouse effect. Today we will address
BST 200 Radia+ve forcing and Greenhouse Gases
 BST 200 Radia+ve forcing and Greenhouse Gases Atmospheric Burden and Residence Time suppose a tub holds 100 kg of water (Burden) and Source = Sink = 5 kg/minute Residence +me = 100 kg 5 kg/minute = 20
BST 200 Radia+ve forcing and Greenhouse Gases Atmospheric Burden and Residence Time suppose a tub holds 100 kg of water (Burden) and Source = Sink = 5 kg/minute Residence +me = 100 kg 5 kg/minute = 20
Global modeling of atmospheric deposition of N, P and Fe with TM4- ECPL
 Global modeling of atmospheric deposition of N, P and Fe with TM4- ECPL M. Kanakidou, S. Myriokefalitakis, N. Daskalakis, G. Fanourgakis Environmental Chemical Processes Laboratory Department of Chemistry,
Global modeling of atmospheric deposition of N, P and Fe with TM4- ECPL M. Kanakidou, S. Myriokefalitakis, N. Daskalakis, G. Fanourgakis Environmental Chemical Processes Laboratory Department of Chemistry,
Highlights of last lecture
 Highlights of last lecture Nitrogen chemistry 8 oxidation states => wide range of chemical properties Compounds hydrides, halides, oxides, oxoacids high explosives o difference between fuel and explosive
Highlights of last lecture Nitrogen chemistry 8 oxidation states => wide range of chemical properties Compounds hydrides, halides, oxides, oxoacids high explosives o difference between fuel and explosive
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy
 Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy Nicholas Meskhidze & Matthew Johnson First International Workshop on the Long Range Transport and Impacts
Updated Dust-Iron Dissolution Mechanism: Effects Of Organic Acids, Photolysis, and Dust Mineralogy Nicholas Meskhidze & Matthew Johnson First International Workshop on the Long Range Transport and Impacts
Lecture 8. The Holocene and Recent Climate Change
 Lecture 8 The Holocene and Recent Climate Change Recovery from the last ice age About 15,000 years ago, the earth began to warm and the huge ice sheets covering much of North America and Eurasia began
Lecture 8 The Holocene and Recent Climate Change Recovery from the last ice age About 15,000 years ago, the earth began to warm and the huge ice sheets covering much of North America and Eurasia began
Climate change. understanding, and the need for observations Herman Russchenberg Remote Sensing of the Environment.
 Climate change understanding, and the need for observations Herman Russchenberg Remote Sensing of the Environment 19-11-2011 h.w.j.russchenberg@tudelft.nl Delft University of Technology Challenge the future
Climate change understanding, and the need for observations Herman Russchenberg Remote Sensing of the Environment 19-11-2011 h.w.j.russchenberg@tudelft.nl Delft University of Technology Challenge the future
Aerosol Composition and Radiative Properties
 Aerosol Composition and Radiative Properties Urs Baltensperger Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry Paul Scherrer Institut, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland WMO-BIPM Workshop Geneva, 30 March 1 April 2010
Aerosol Composition and Radiative Properties Urs Baltensperger Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry Paul Scherrer Institut, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland WMO-BIPM Workshop Geneva, 30 March 1 April 2010
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Impact of aerosol on air temperature in Baghdad
 Journal of Applied and Advanced Research 2017, 2(6): 317 323 http://dx.doi.org/10.21839/jaar.2017.v2i6.112 http://www.phoenixpub.org/journals/index.php/jaar ISSN 2519-9412 / 2017 Phoenix Research Publishers
Journal of Applied and Advanced Research 2017, 2(6): 317 323 http://dx.doi.org/10.21839/jaar.2017.v2i6.112 http://www.phoenixpub.org/journals/index.php/jaar ISSN 2519-9412 / 2017 Phoenix Research Publishers
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm 3 next Thursday!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm 3 next Thursday! 1 Previously Habitable Zone Energy Balance Emission Temperature Greenhouse Effect Vibration/rotation bands 2 Recap: Greenhouse gases In order
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm 3 next Thursday! 1 Previously Habitable Zone Energy Balance Emission Temperature Greenhouse Effect Vibration/rotation bands 2 Recap: Greenhouse gases In order
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives
 Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Parameterization for Atmospheric Radiation: Some New Perspectives Kuo-Nan Liou Joint Institute for Regional Earth System Science and Engineering (JIFRESSE) and Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Department
Arctic Chemistry And Climate
 21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
21 July 2016 Connaught Summer Institute 1 Arctic Chemistry And Climate Connaught Summer Institute 2016 William (Bill) Simpson Geophysical Institute and Department of Chemistry, University of Alaska Fairbanks
Aerosols-Cloud-Precipitation Interactions in the Climate System. Meinrat O. Andreae Max Planck Institute for Chemistry Mainz, Germany
 Aerosols-Cloud-Precipitation Interactions in the Climate System Meinrat O. Andreae Max Planck Institute for Chemistry Mainz, Germany The global annual mean Earth s energy budget for 2000-2004 (W m 2 ).
Aerosols-Cloud-Precipitation Interactions in the Climate System Meinrat O. Andreae Max Planck Institute for Chemistry Mainz, Germany The global annual mean Earth s energy budget for 2000-2004 (W m 2 ).
Weather and Climate Change
 Weather and Climate Change What if the environmental lapse rate falls between the moist and dry adiabatic lapse rates? The atmosphere is unstable for saturated air parcels but stable for unsaturated air
Weather and Climate Change What if the environmental lapse rate falls between the moist and dry adiabatic lapse rates? The atmosphere is unstable for saturated air parcels but stable for unsaturated air
Spectrum of Radiation. Importance of Radiation Transfer. Radiation Intensity and Wavelength. Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
Introduction to Climate Change
 Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
C-SOLAS Pacific Cruise Summer 2002
 Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Thanks to: Silvia Kloster, MPI Hamburg, Germany Richard Leaitch, Meteorological Service of Canada Maurice Levasseur,Univ.
Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Thanks to: Silvia Kloster, MPI Hamburg, Germany Richard Leaitch, Meteorological Service of Canada Maurice Levasseur,Univ.
8. Clouds and Climate
 8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Mon April 17 Announcements: bring calculator to class from now on (in-class activities, tests) HW#2 due Thursday
 Mon April 17 Announcements: bring calculator to class from now on (in-class activities, tests) HW#2 due Thursday Today: Fundamentals of Planetary Energy Balance Incoming = Outgoing (at equilibrium) Incoming
Mon April 17 Announcements: bring calculator to class from now on (in-class activities, tests) HW#2 due Thursday Today: Fundamentals of Planetary Energy Balance Incoming = Outgoing (at equilibrium) Incoming
FORCING ANTHROPOGENIC
 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
CLIMATE CHANGE Albedo Forcing ALBEDO FORCING
 ALBEDO FORCING Albedo forcing is the hypothesis that variations in the Earth s reflectance of solar radiation can bring about global climate change. This hypothesis is undeniable in principle; since virtually
ALBEDO FORCING Albedo forcing is the hypothesis that variations in the Earth s reflectance of solar radiation can bring about global climate change. This hypothesis is undeniable in principle; since virtually
