Morphodynamic changes of Lohit River, NE India: GIS-based study
|
|
|
- James Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Morphodynamic changes of Lohit River, NE India: GIS-based study S. Borgohain 1, *, J. Das 2, A. K. Saraf 1, G. Singh 1 and S. S. Baral 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee , India 2 Department of Earthquake Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Roorkee , India The Lohit River is a south bank tributary of the Brahmaputra River. Till 1987, the Lohit River used to meet the Brahmaputra at a place near Bairagi Chapari (27.77 N, E). By 1995, the confluence point had shifted about 20 km downstream. One small channel of the Lohit River captured the Dangori River during the 1988 flood. Gradually the Lohit River started flowing along the captured channel. By 1995, it became the trunk channel of the Lohit River and Dibru Saikhowa region became an island. Banklines of Brahmaputra and Lohit rivers have undergone significant changes near their confluence point within the last few decades. By 1987, the south bank of the Brahmaputra near Rohmoria (27.55 N, E) shifted about 1.6 km southward from its position in Interestingly, within the period the south bank shifted about 4.1 km south. This major shifting was the result of capturing of the Dangori River by the Lohit River. However, migration of the rivers towards the south has stopped after Analysis of SRTM DEM reveals that topographic elevation has played a major role in changing the course of the Lohit River. Keywords: Banklines, confluence point, morphodynamic changes, topographic elevation, trunk channel. THE Lohit River is a major tributary of the Brahmaputra River. It originates in Zayal Chu ranges in eastern Tibet and flows about 460 km before meeting the Dibang River. Before entering India, the river flows about 200 km through Tibet. Major thrusts of Mishmi Hills like Lohit Thrust and Tidding Thrust are prominent on the longitudinal profile of the river. However, the Mishmi Thrust is not clearly reflected by the longitudinal profile. The river has a braiding nature along its alluvial segment. The basin area of the river is about 22,418.6 sq. km. During the 1988 floods, the Lohit River captured the Dangori River, flowing southwest from it. By 1995, the captured channel became a perennial channel of the Lohit River and finally became the trunk channel. Geomorphic and sedimentary responses of alluvial rivers in relation to tectonics have been studied The *For correspondence. ( susantaborgohain@gmail.com) avulsion properties of rivers have also been wellstudied Some attempts have been made to understand the fluvial process response system of the Brahmaputra River and its tributaries 2, There have been significant changes in morphology and planform of the Brahmaputra and its tributaries within the last few decades. The 1897 (12 June) Shillong earthquake and 1950 (15 August) Assam earthquake of magnitude 8.7 and 8.5 respectively caused extensive landslides, liquefaction, sand-vent and ground fissuring in the region 26,27. The Subansiri River and some of its tributaries changed their courses at places after the 1950 earthquake 27. Extensive work has been done on fluvial process and bankline migration of the Brahmaputra River in Assam 24,25, Lahiri and Sinha 22 have described seismotectonic controls on the Brahmaputra River in the Upper Assam region. Kotoky et al. 31 have studied the nature of bank erosion. The present work involves a study of the changing behaviour of the Lohit River within the period in Assam and some parts of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Study area The study area is a part of the alluvial Brahmaputra valley in Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. The area is bounded by E E long. and N N lat. Monsoonal rain is predominant in summer with maximum rainfall of 300 cm (as of 2012). During this period, the maximum temperature rises to 37 C. During winter minimum temperature of the region reaches 2 C (as of 2012). Elevation of the study area ranges between 90 and 7200 m from mean sea level (MSL). Brahmaputra is the major river in the region, with many small and large tributaries. Figure 1 shows the location map of the study area. Seasonal flood caused by monsoonal rainfall is a major natural disaster for the region. Moreover, according to Indian earthquake hazard zoning map, the area is within Zone V with highest risks of earthquake. Earthquake of up to MM intensity IX can be expected in the area. The region has already experienced very high-intensity earthquakes in the past. For example, the Cachar earthquake of M 7.5 on 10 January 1869, the Shillong earthquake of M 8.7 on 12 June 1897, the Assam earthquake of M 8.5 on 1810
2 Figure 1. Location map of the study area showing the basin boundary and significant changes that occurred in morphology of the Lohit River. (DEM) with 30 m spatial resolution (vertical error < 4 m)32. Landsat-1 image with 60 m spatial resolution and Landsat-5 and 7 with 30 m spatial resolution acquired within the period from 1973 to 2001 were obtained from Earth Resources Observation and Science Center, United States Geological Survey. Geo-Tiff format (UTM, WGS-1984, Zone 47N, 46N) imageries and DEM were collected for the study area. Required bands of the imageries were stacked using ERDAS IMAGINE (version 2011) to make standard false colour composite (FCC). The Brahmaputra River and its tributaries have been delineated from Landsat images. The length of the tributaries has been computed from the attribute tables of the vector layers. All the measurements were done from the attribute tables of the vector files using ArcGIS (version 10.0). Seismotectonics Figure 2. Tectonic map of the study area along with epicentres of instrumental earthquakes. Major thrusts within the study area are MBT (Main Boundary Thrust), MFT (Main Frontal Thrust), Mishmi Thrust, Tidding Suture, Lohit Thrust and Naga Thrust (after Narula et al.33). 15 August 1950, etc. Smaller earthquakes magnitudes ranging between M 3.0 and M 5.5 are common in the region. Database and methodology The major data used in this study are Landsat image, ESRI World Imagery and SRTM digital elevation model Moderate earthquakes frequently rock the region. Earthquakes exceeding M 6 are also common in the area. These earthquakes have brought various changes into the Brahmaputra and Barak valleys. Besides, the whole region is characterized by numerous thrusts, faults and folds. The Brahmaputra alluvial plain in Upper Assam is bounded by the Himalayan Frontal Thrust (HFT) to the northwest, Mishmi Thrust to the northeast, Naga Thrust to the southeast and Mikir Hills to the west33. From this tectonic set-up it is evident that the sediments and rocks of the region have experienced compressive forces from time to time. The region has experienced several highmagnitude earthquakes within a short period. Many of 1811
3 Figure 3. Landsat image over Dibru Saikhowa. a, 15 November 1973; b, 28 November Levee deposits (yellow dashed lines in a) of the Lohit River acted as a natural embankment till After erosion of the levees in the 1988 flood, the river started flowing south of the Dibru Saikhowa capturing the Dangori River. Figure 4. Trunk channels of Siang, Dibang and Lohit rivers near Dibru Saikhowa. a, November 1973; b, October 1988; c, November 1995; d, November these earthquakes have genetic relationship with the thrusts and faults in the region. The distribution of earthquake epicentres shows that the Mikir Hills and IndoBurma thrusts are much more active than the Naga Patkai ranges of thrusts. Figure 2 shows tectonic features of the study area along with the epicentres of earthquakes River course dynamics Till 1987, the confluence point of Lohit and Brahmaputra rivers was at a location near Bairagi Chapari (27.77 N, E). During the 1988 floods, the Lohit River overflowed its banks and captured the Dangori River, flowing southwest from it. By 1995, the captured channel became
4 a perennial channel of the Lohit River and finally became the trunk channel (Figures 3 and 4). The banklines of the Brahmaputra and Lohit rivers have undergone significant migration near the confluence point within the last few decades (Figure 5). The south bank of the Brahmaputra near Rohmoria (27.55 N, E) shifted about 1.6 km southward by November 1987 from its position in Interestingly, within the southbank shifted about 4.1 km south. This major shifting was the result of erosion by the new channel of the Lohit River. After this, southward migration of the southbank was limited to only 0.14 km till November The Kundil River originates in the Mishmi Hills and is a tributary of the Lohit River. In 1973, the river had overall sinuosity 1.81 along its alluvial part. The sinuosity decreased to 1.42 till Comparison of Landsat images acquired in 1973 and 1988 shows that a new tributary has joined the river and its morphology has changed significantly (Figure 6). Discussion The Lohit River is characterized by highly braiding nature in its alluvial part. Monsoonal flood is the major natural disaster in the downstream region of the river. The flood level in 1988 was high in the study area. On 20 August the flood level at Dibrugarh (near the study area) reached m, which was the highest recorded till then. Landsat image acquired on 27 October 1988 shows that a small braid branch of the Lohit River got connected with the Dangori River after the 1988 floods. This channel of the Lohit River showed dramatic changes in the later years. The river started to flow along the captured Figure 5. Banklines of Brahmaputra, Siang, Dibang and Lohit rivers near Dibru Saikhowa for six different years. channel to meet the Dangori River, abandoning its older course. By November 1995, the Lohit River totally changed its course and the Dangori River became the trunk channel of the Lohit River (Figure 4). Three topographic profiles extracted from SRTM DEM (Figures 7 and 8) near the confluence point of Siang, Dibang and Lohit rivers show that average topographic elevation near the new channel of the Lohit rivers is less than that of the older channel. Moreover, the channel flowing south of the Dibru Saikhowa Island shows a slight depression in its longitudinal profile in comparison to the northern channel after the divergence point P (Figures 7 and 9). These profiles clearly show that topographic elevation along and near the new channel is m lower than that of the older channel (after the divergence point P, Figures 7 and 9). This variation in gradient between the channels is the major factor in changing the course of the Lohit River. Avulsion is a common geomorphic process associated with the river. Normal hydrological floods are the most common triggers of avulsion if the river is close to the avulsion threshold16. The abnormal high flood level of 1988 (highest recorded till then) might have crossed the avulsion threshold of the Figure 6. Landsat image over Kundil River. The sinuosity of the river has changed from 1.81 to 1.42 due to joining of a new tributary. The new tributary has increased discharge and sediment load of the river. 1813
5 Figure 7. DEM (SRTM, Hillshade) showing the confluence point of Siang, Lohit and Dibang rivers. Transverse elevation profiles have been obtained along A B, C D and E F sections. Longitudinal profiles have been obtained along P Q segment of the Lohit River, both northern and southern channels of the Dibru Saikhowa Island. Figure 8. Topographic profiles extracted from SRTM DEM (vertical error < 4 m)32 along the selected sections (A B, C D and E F in Figure 7) near the confluence point of Siang, Dibang and Lohit rivers. In the E F section, the topographic elevation is lower along and near the new channel compared to the old channel of the Lohit River. 1814
6 Figure 9. Longitudinal profile of a segment of Lohit River (P Q in Figure 7) obtained from SRTM DEM. The blue curve is for the old channel flowing north of the Dibru Saikhowa Island, and the red curve is for the new channel south of the Dibru Saikhowa Island. The depression in the red curve (new channel) after the divergence point P reveals that the new channel is deeper than the old course of the Lohit River. This is the major triggering factor in changing the course of the Lohit River. river and triggered avulsion resulting in the removal of some parts of the levees along the left bank. After removal of the levees, difference in gradient between the channels led to course change of the Lohit River. Although topographic elevation along and near Dangori River (south of Dibru Saikhowa Island) was lower than that of the older channel (north of Dibru Saikhowa) of Lohit River, the levee deposits of the Lohit River prevented it to flow along the Dangori River before the 1988 floods. The levee deposits acted as a natural embankment. Once the embankment was eroded, the river started to follow the deeper channel, i.e. along the Dangori River. Similar avulsion processes of the Baghmati and Kosi rivers have been studied by Jain and Sinha 15, and Sinha et al. 18 respectively. The Baghmati River in North Bihar showed eight major and several smaller avulsions within the period from 1770 to Extreme hydrological variations and sedimentological adjustments have been attributed for avulsive behaviour of the Baghmati River 15. On the other hand, the August 2008 avulsion of the Kosi River was triggered by a normal hydrological flow. Sinha et al. 18 suggested that aggradation of channel belt after construction of embankments and planform dynamics led to avulsion of the Kosi River. Landsat image acquired on 27 October 1988 showed that the Kundil River had developed numerous bars (point and mid channel) after joining the new tributary (Figure 6). It can be interpreted that discharge of the river did not increase sufficiently to transport the increased sediment load after joining the new tributary. This resulted in channel deposition of the sediments and decrease in sinuosity of the river. Moreover, a river needs steeper slope to carry higher amount of sediment flux. This can be achieved by reducing sinuosity. A few subsurface and neotectonic faults have been identified by GSI within the study area 33. Major thrusts of the Himalaya (MBT, MFT), Mishmi Hills (Mishmi Thrust, Lohit Thrust) and Naga Patkai (Naga Thrust) ranges are also present near the study area. However, the role of these faults could not be linked directly with the present morphodynamic changes of the Lohit River. Several palaeo-channels and older alluviums are noticed on the southern side of the Dibru Saikhowa region, implying that the topography of the area has remained relatively stable with gentle slope for a long period. This may indicate that the subsurface faults in this part have not caused any change on the surface for last few decades. However, it may be noticed that the Brahmaputra River exhibits northward shifting near Dibrugarh. This may be caused by landform and terrain slope changes, probably affected by the activities along the MFT. Conclusion It is evident from the present study and interpretations that the rivers in the study area are changing their morphological behaviour. Topographic elevation has played a major role in changing the course of the Lohit River. Avulsion is a common geomorphic process associated with many rivers of the Ganga Brahmaputra plain. Some rivers of the Ganga plain like Baghmati and Kosi have also shown significant avulsion in the last few decades 15,18. Capturing of the Dangori River by the Lohit River was triggered by the abnormal high flood level in 1988, and difference in gradient between the channels led to course change of the Lohit River. SRTM DEMs are used to compare the old as well as new course of the Lohit River, which might have maximum vertical error of 4 m (ref. 32). However, for both the cases the same DEMs are used; hence error becomes common for both the channel areas and comparison will not be affected. By 1995, the Dibru Saikhowa region became an island. After 1995, there has been no significant southward migration of the Brahmaputra and Lohit rivers within the study area. 1. Burbank, D. W. and Anderson, R. S., Tectonic Geomorphology, Wiley-Blackwell, West Sussex, UK, 2012, 2nd edn. 2. Coleman, J. M., Brahmaputra River channel processes and sedimentation. Sediment. Geol., 1969, 3, Gupta, A., Kale, V. S., Owen, L. A. and Singhvi, A. K., Late Quaternary bedrock incision in the Narmada River at Dardi Falls. Curr. Sci., 2007, 93, Holbrook, J. and Schumm, S. A., Geomorphic and sedimentary response of rivers to tectonic deformation: a brief review and critique of a tool for recognizing subtle epeirogenic deformation in modern and ancient settings. Tectonophysics, 1999, 305, Jain, V. and Sinha, R., Response of active tectonics on the alluvial Baghmati River, Himalayan foreland basin, Eastern India. Geomorphology, 2005, 70, Mehta, J. S. and Sanwal, R., Evidence of active tectonics along oblique transverse normal fault in the Kosi River valley around Betalghat, Kumaun Lesser Himalaya, India. Curr. Sci., 2011, 101, Ouchi, S., Response of alluvial rivers to slow active tectonic movement. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 1985, 96,
7 8. Sahu, S., Raju, N. J. and Saha, D., Active tectonics and geomorphology in the Sone Ganga alluvial tract in mid-ganga Basin, India. Quaternary Int., 2010, 227, Schumm, S. A., The Fluvial System, John Wiley, New York, 1977, p Schumm, S. A., Alluvial river response to active tectonics. In Active Tectonics (Studies in Geophysics), National Research Council, Washington, DC, 1986, p Schumm, S. A., Dumont, J. F. and Holbrook, J. M., Active Tectonics and Alluvial Rivers, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000, p Singh, I. B. and Rastogi, S. P., Tectonic framework of Gangetic alluvium, with special reference to Ganga River in Uttar Pradesh. Curr. Sci., 1973, 42, Valdiya, K. S., Why does river Brahmaputra remain untamed? Curr. Sci., 1999, 76, Vishwas, S. K., Sengupta, S., Achyuthan, H. and Jaiswal, M. K., Tectonic controls upon Kaveri River drainage, cratonic Peninsular India: Inferences from longitudinal profiles, morphotectonic indices, hanging valleys and fluvial records. Geomorphology, 2014, 227, Jain, V. and Sinha, R., Hyperavulsive anabranching Baghmati river system, North Bihar plains, Eastern India. Z. Geomorphol., NF, 2003, 47, Jones, L. S. and Schumm, S. A., Causes of avulsion: an overview. In Fluvial Sedimentology VI (eds Smith, N. D. and Rogers, J.), International Association of Sedimentologist, Special Publication, Blackwell Science, Oxford, UK, 1999, pp Phillips, J. D., Universal and local controls of avulsions in southeast Texas Rivers. Geomorphology, 2011, 130, Sinha, R., Sripriyanka, K., Jain, V. and Mukul, M., Avulsion threshold and planform dynamics of the Kosi River in north Bihar (India) and Nepal: a GIS framework. Geomorphology, 2014, 216, Goswami, D. C., Brahmaputra River, Assam, India: physiography, basin denudation and channel aggradation. Water Resour. Res., 1985, 21, Goswami, D. C., Estimation of bed load transport in the Brahmaputra River, Assam. Indian J. Earth Sci., 1989, 15, Goswami, U., Sarma, J. N. and Patgiri, A. D., River channel changes of the Subansiri in Assam, India. Geomorphology, 1999, 30, Lahiri, S. K. and Sinha, R., Tectonic controls on the morphodynamics of the Brahmaputra River system in the upper Assam valley, India. Geomorphology, 2012, , Sarma, J. N., A study on palaeochannels from satellite imagery in a part of Upper Assam. In Proceedings of the National Symposium, Indian Society of Remote Sensing, Guwahati, 1993, pp Sarma, J. N. and Phukan, M. K., Origin and some geomorphological changes of Majuli island of the Brahmaputra River in Assam, India. Geomorphology, 2004, 60, Sarma, J. N., Fluvial process and morphology of the Brahmaputra River in Assam, India. Geomorphology, 2005, 70, Oldham, R. D., Report on the Great Earthquake of 12 June Mem. Geol. Surv. India, 1899, 29, Poddar, M. C., The Assam earthquake of 15 August Indian Miner., 1950, 4, Coleman, J. M., Brahmaputra River channel processes and sedimentation. Sediment. Geol., 1969, 3, Bristow, C. S., Brahmaputra River: channel migration and deposition. In Recent Development in Fluvial Sedimentology (eds Ethridge, F. G. et al.), Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 1987, vol. 39, pp Sarma, J. N. and Acharjee, S., Bank erosion of the Brahmaputra River and neotectonic activity around Rohmoria Assam, India. Comun. Geol., 2012, 99, Kotoky, P., Bezbaruah, D., Baruah, J. and Sarma, J. N., Nature of bank erosion along the Brahmaputra River channel, Assam, India. Curr. Sci., 2005, 88, Rodriguez, E., Morris, C. S., Belz, J. E., Chapin, E. C., Martin, J. M., Daffer, W. and Hensley, S., An assessment of the SRTM topographic products. Jet Propulsion Laboratory Publication, 2005, D-31639, p Narula, P. L., Acharyya, S. K. and Banerjee, J., Seismotectonic Atlas of India and its Environs, Geological Survey of India, 2000, SEISAT ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS. We thank the reviewers for their constructive comments that have helped improve the manuscript. We thank USGS for the Landsat images and digital elevation models. Information on earthquakes has been collected from IMD and USGS earthquake data catalogue. We also thank CSIR, New Delhi and Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee for providing financial and institutional support throughout the study period, and the Flood Control Department of Assam, Guwahati for flood data. Received 26 November 2014; revised accepted 8 December 2015 doi: /cs/v110/i9/
A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI RIVER IN ASSAM USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 01-06 2013 ISSN(e): 2319 1813 ISSN(p): 2319 1805 A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 01-06 2013 ISSN(e): 2319 1813 ISSN(p): 2319 1805 A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI
Geospatial assessment on the occurrences of erosion and pattern of channel migration of river Brahmaputra along the Majuli Island of Assam
 77 Geospatial assessment on the occurrences of erosion and pattern of channel migration of river Brahmaputra along the Majuli Island of Assam Jonali Goswami 1, Dibyajyoti Chutia 1, Stuti Singhania 2, Monidip
77 Geospatial assessment on the occurrences of erosion and pattern of channel migration of river Brahmaputra along the Majuli Island of Assam Jonali Goswami 1, Dibyajyoti Chutia 1, Stuti Singhania 2, Monidip
Temporal changes of Fluvio-Morphological scenario and its impact on Settlement: A GIS based study for Mandia block, Barpeta District, Assam
 Temporal changes of Fluvio-Morphological scenario and its impact on Settlement: A GIS based study for Mandia block, Barpeta District, Assam R.K. Sarmah 1, U. Sarma 2 1,2 Assam Remote Sensing Application
Temporal changes of Fluvio-Morphological scenario and its impact on Settlement: A GIS based study for Mandia block, Barpeta District, Assam R.K. Sarmah 1, U. Sarma 2 1,2 Assam Remote Sensing Application
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT
 Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
Paper presented in the Annual Meeting of Association of American Geographers, Las Vegas, USA, March 2009 ABSTRACT CHANGING GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE KOSI RIVER SYSTEM IN THE INDIAN SUBCONTINENT Nupur Bose,
CHANNEL DYNAMICS AND SETTLEMENT VULNERABILITY: A MICRO STUDY OF DEOHA RIVER, PILIBHIT DISTRICT, UTTAR PRADESH
 CHANNEL DYNAMICS AND SETTLEMENT VULNERABILITY: A MICRO STUDY OF DEOHA RIVER, PILIBHIT DISTRICT, UTTAR PRADESH S. Sanyal and *P. S. Mondal Department of Geography, Banaras Hindu University *Author for Correspondence
CHANNEL DYNAMICS AND SETTLEMENT VULNERABILITY: A MICRO STUDY OF DEOHA RIVER, PILIBHIT DISTRICT, UTTAR PRADESH S. Sanyal and *P. S. Mondal Department of Geography, Banaras Hindu University *Author for Correspondence
A novel approach to calculate braiding of a large alluvial river
 A novel approach to calculate braiding of a large alluvial river Lalit Saikia,3, *, Chandan Mahanta and Suranjana Bhaswati Borah 2 Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati,
A novel approach to calculate braiding of a large alluvial river Lalit Saikia,3, *, Chandan Mahanta and Suranjana Bhaswati Borah 2 Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati,
Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study
 European Water 60: 67-71, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study B. Talukdar *, A. Baid and R. Das Civil
European Water 60: 67-71, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study B. Talukdar *, A. Baid and R. Das Civil
A study of erosion-deposition processes around Majuli Island, Assam
 Open access e-journal Earth Science India, Vol. 3 (IV), October, 2010, pp. 206-216 A study of erosion-deposition processes around Majuli Island, Assam M.K.Dutta 1, Swapnali Barman 2, S.P. Aggarwal 2 1
Open access e-journal Earth Science India, Vol. 3 (IV), October, 2010, pp. 206-216 A study of erosion-deposition processes around Majuli Island, Assam M.K.Dutta 1, Swapnali Barman 2, S.P. Aggarwal 2 1
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal
 Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
A GIS based study on bank erosion by the river Brahmaputra around Kaziranga National Park, Assam, India
 Earth Syst. Dynam. Discuss., 3, 8 16, 12 www.earth-syst-dynam-discuss.net/3/8/12/ doi:.194/esdd-3-8-12 Author(s) 12. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the journal
Earth Syst. Dynam. Discuss., 3, 8 16, 12 www.earth-syst-dynam-discuss.net/3/8/12/ doi:.194/esdd-3-8-12 Author(s) 12. CC Attribution 3.0 License. This discussion paper is/has been under review for the journal
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India
 Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
Geomorphic Evidence of Active Tectonics in the Dhundsir Gad Watershed of Alaknada Basin, Uttarakhand, India Hari Ballabh 1, Devi Datt Chauniyal 1 & Mahendra Singh Lodhi 2, * 1. Department of Geography,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Changing trends of channel pattern
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Changing trends of channel pattern
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, 2014
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Process dynamics and controls in
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 1, 2014 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Process dynamics and controls in
Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING
 SHORT COMMUNICATlON DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING Geological Survey of India, Tripura-Mizoram Division, B.K. Road, Banamalipur, Agartala - 790 001 Email: v+srinivasan_geo
SHORT COMMUNICATlON DECIPNERING DIFFERENTIAL UPLIFT IN SHLLONG PLATEAU USING REMOTE SENSING Geological Survey of India, Tripura-Mizoram Division, B.K. Road, Banamalipur, Agartala - 790 001 Email: v+srinivasan_geo
Complete List of Publications
 Complete List of Publications A. Papers in Refereed Journals 1. Bawa, N. *, Jain, V., Shekhar, S., Kumar, N. *, Jyani, V. * (2014) Controls on Morphological Variability and Role of Stream Power Distribution,
Complete List of Publications A. Papers in Refereed Journals 1. Bawa, N. *, Jain, V., Shekhar, S., Kumar, N. *, Jyani, V. * (2014) Controls on Morphological Variability and Role of Stream Power Distribution,
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70. Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills
 Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Geography Class XI Fundamentals of Physical Geography Section A Total Periods : 140 Total Marks : 70 Sr. No. 01 Periods Topic Subject Matter Geographical Skills Nature and Scope Definition, nature, i)
Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran
 2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
2011, TextRoad Publication ISSN: 2090-4215 Journal of Applied Environmental and Biological Sciences www.textroad.com Active Tectonics of Qezel Ozan River Basin, NW Iran Mehran Arian *, Ph.D.; Vahid Hosseini
Megafans in younger orogens
 Megafans in younger orogens Ralf Dedow 1 1 Institute of Geology, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Germany Abstract. Fluvial megafans are unusually large fan-shaped bodies of sediment, whose formation is primarily
Megafans in younger orogens Ralf Dedow 1 1 Institute of Geology, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, Germany Abstract. Fluvial megafans are unusually large fan-shaped bodies of sediment, whose formation is primarily
Upstream-Downstream Interaction in the context of shared water regime of NE India: Arunachal, Assam
 Upstream-Downstream Interaction in the context of shared water regime of NE India: Arunachal, Assam Partha J Das Water, Climate & Hazard Division Aaranyak-Guwahati Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts
Upstream-Downstream Interaction in the context of shared water regime of NE India: Arunachal, Assam Partha J Das Water, Climate & Hazard Division Aaranyak-Guwahati Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN
 ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS
 EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
EMERGENCY PLANNING IN NORTHERN ALGERIA BASED ON REMOTE SENSING DATA IN RESPECT TO TSUNAMI HAZARD PREPAREDNESS Barbara Theilen-Willige Technical University of Berlin, Institute of Applied Geosciences Department
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
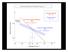 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK GROUND VERTICAL ACCELERATION USING DATA FROM STRONG MOTION ARRAYS IN INDIA
 ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK GROUND VERTICAL ACCELERATION USING DATA FROM STRONG MOTION ARRAYS IN INDIA Mukat L SHARMA 1 SUMMARY An attenuation relationship for peak vertical ground
ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIP FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK GROUND VERTICAL ACCELERATION USING DATA FROM STRONG MOTION ARRAYS IN INDIA Mukat L SHARMA 1 SUMMARY An attenuation relationship for peak vertical ground
RS and GIS based assessment of Bank Erosion in Goalparaa District part of Brahmaputra River, Assam, India
 Short Review Paper International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 RS and GIS based assessment of Bank Erosion in Goalparaa District part of Brahmaputra River, Assam, India Abstract G.
Short Review Paper International Research Journal of Earth Sciences ISSN 2321 2527 RS and GIS based assessment of Bank Erosion in Goalparaa District part of Brahmaputra River, Assam, India Abstract G.
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin
 Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
Morphometric Analysis of Jiya Dhol River Basin Luna Moin Das North-Eastern Hill University, Shillong Abstract: Basin morphometry is an important means of understanding a drainage basin using mathematically
THE DYNAMICS IN CHANNEL SHIFT OF THE BRAHMPUTRA ALONG THE AGYATHURI- SUALKUCHI AREA OF KAMRUP DISTRICT, ASSAM
 THE DYNAMICS IN CHANNEL SHIFT OF THE BRAHMPUTRA ALONG THE AGYATHURI- SUALKUCHI AREA OF KAMRUP DISTRICT, ASSAM Rakesh Chetry, MA Dept. of Geography, Gauhati University, India Abstract Since ages people
THE DYNAMICS IN CHANNEL SHIFT OF THE BRAHMPUTRA ALONG THE AGYATHURI- SUALKUCHI AREA OF KAMRUP DISTRICT, ASSAM Rakesh Chetry, MA Dept. of Geography, Gauhati University, India Abstract Since ages people
Fish diversity and drainage analysis of River Siang, East Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh
 Fish diversity and drainage analysis of River Siang, East Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh Biplab Kumar Das 1*, Prasanna Boruah 2 and Devashish Kar 3 Department of Life Science and Bioinformatics, Assam
Fish diversity and drainage analysis of River Siang, East Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh Biplab Kumar Das 1*, Prasanna Boruah 2 and Devashish Kar 3 Department of Life Science and Bioinformatics, Assam
Geomorphological Manifestations of the Flood Hazard: A Remote Sensing Based Approach
 Geomorphological Manifestations of the Flood Hazard: A Remote Sensing Based Approach Vikrant Jain and R. Sinha Engineering Geosciences Group, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology
Geomorphological Manifestations of the Flood Hazard: A Remote Sensing Based Approach Vikrant Jain and R. Sinha Engineering Geosciences Group, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology
Chapter III DRAINAGE CHARACTERISTICS AND LANDFORMS
 Evolution of Chaliyar River Drainage Basin: Insights from Tectonic Geomorphology Chapter III DRAINAGE CHARACTERISTICS AND LANDFORMS 3.1 Introduction Drainage basin forms natural geomorphic unit and frequently
Evolution of Chaliyar River Drainage Basin: Insights from Tectonic Geomorphology Chapter III DRAINAGE CHARACTERISTICS AND LANDFORMS 3.1 Introduction Drainage basin forms natural geomorphic unit and frequently
Riparian Assessment. Steps in the right direction... Drainage Basin/Watershed: Start by Thinking Big. Riparian Assessment vs.
 Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
Outline. Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring. Introduction. Satellites and their Sensors used for Flood Mapping
 Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
NATURAL RIVER. Karima Attia Nile Research Institute
 NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
NATURAL RIVER CHARACTERISTICS Karima Attia Nile Research Institute NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION NATURAL RIVER DEFINITION Is natural stream of water that flows in channels with ih more or less defined banks.
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION OF SPECTRAL STRONG GROUND MOTION ON BED ROCK IN NORTH EAST INDIA
 4th International Conference on Earthquake Engineering Taipei, Taiwan October 12-13, 2006 Paper No. 015 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION OF SPECTRAL STRONG GROUND MOTION ON BED ROCK
4th International Conference on Earthquake Engineering Taipei, Taiwan October 12-13, 2006 Paper No. 015 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION OF SPECTRAL STRONG GROUND MOTION ON BED ROCK
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
CHAPTER V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS SUMMARY. The evolution of Beas Valley drainage is related with the tectonic history of
 CHAPTER V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS SUMMARY The evolution of Beas Valley drainage is related with the tectonic history of Himalaya. The Great Himalaya were uplifted first and then the mountain building process
CHAPTER V SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS SUMMARY The evolution of Beas Valley drainage is related with the tectonic history of Himalaya. The Great Himalaya were uplifted first and then the mountain building process
Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007
 Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Annotations I. River avulsions and their deposits 2 II. Channel avulsion on alluvial fans
Annotated Bibliography of River Avulsions Pat Dryer Geography 364 5/14/2007 1 Table of Contents Introduction 2 Annotations I. River avulsions and their deposits 2 II. Channel avulsion on alluvial fans
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
Effect of the barrage and embankments on flooding and channel avulsion case study Koshi River, Nepal
 Effect of the barrage and embankments on flooding and channel avulsion case study Koshi River, Nepal Lochan Devkota 1, Alessandra Crosato 2, Sanjay Giri 3 1 Mott MacDonald Singapore Pte Ltd Grange Road,
Effect of the barrage and embankments on flooding and channel avulsion case study Koshi River, Nepal Lochan Devkota 1, Alessandra Crosato 2, Sanjay Giri 3 1 Mott MacDonald Singapore Pte Ltd Grange Road,
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
Geomorphology 216 (2014) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Geomorphology. journal homepage:
 Geomorphology 216 (2014) 157 170 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Geomorphology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/geomorph Avulsion threshold and planform dynamics of the Kosi River in
Geomorphology 216 (2014) 157 170 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Geomorphology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/geomorph Avulsion threshold and planform dynamics of the Kosi River in
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan
 Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
Neotectonic Implications between Kaotai and Peinanshan Abstract Longitudinal Valley was the suture zone between the Philippine Sea plate and the Eurasia plate. Peinanshan was the southest segment of the
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL
 LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
LANDSAT-TM IMAGES IN GEOLOGICAL MAPPING OF SURNAYA GAD AREA, DADELDHURA DISTRICT WEST NEPAL L. N. Rimal* A. K. Duvadi* S. P. Manandhar* *Department of Mines and Geology Lainchaur, Kathmandu, Nepal E-mail:
4.17 Spain. Catalonia
 4.17 Spain Catalonia In Spain, inundation studies are the responsibility of the respective Hydrographic Confederations of each river basin (River Basin Authorities). The actual status of inundation studies
4.17 Spain Catalonia In Spain, inundation studies are the responsibility of the respective Hydrographic Confederations of each river basin (River Basin Authorities). The actual status of inundation studies
ON THE CORRELATION OF SEDIMENTATION AND LANDSLIDES IN WU RIVER CATCHMENT INFLUENCED BY THE 1999 CHI-CHI EARTHQUAKE
 ON THE CORRELATION OF SEDIMENTATION AND LANDSLIDES IN WU RIVER CATCHMENT INFLUENCED BY THE 1999 CHI-CHI EARTHQUAKE Keh-Jian Shou 1*, Li-Yuan Fei 2, Jiin-Fa Lee 2, Cheng-Yueh Wei 2, Chiu-Ching Wu 1, Chia-Yue
ON THE CORRELATION OF SEDIMENTATION AND LANDSLIDES IN WU RIVER CATCHMENT INFLUENCED BY THE 1999 CHI-CHI EARTHQUAKE Keh-Jian Shou 1*, Li-Yuan Fei 2, Jiin-Fa Lee 2, Cheng-Yueh Wei 2, Chiu-Ching Wu 1, Chia-Yue
Groundwater Prospect Evaluation in the Interfluves of the Rivers Brahmaputra and Kolong, Assam Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 207, Volume 6, Issue, pp. 29-257 ISSN 220 02, Crossref: 0.295/cloud.ijarsg.2 Research Article Groundwater Prospect Evaluation
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 207, Volume 6, Issue, pp. 29-257 ISSN 220 02, Crossref: 0.295/cloud.ijarsg.2 Research Article Groundwater Prospect Evaluation
Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from
 Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from 1961-2010 Abong A. A. 1, George A. M. 2, Awhuwhe E. A. 3 1 Department of Physics, Cross River University of Technology, P.M.B 1123, Calabar Nigeria 2 Department
Earthquake Distribution in Northeast India from 1961-2010 Abong A. A. 1, George A. M. 2, Awhuwhe E. A. 3 1 Department of Physics, Cross River University of Technology, P.M.B 1123, Calabar Nigeria 2 Department
Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Configuration in Sadiya Block, Upper Assam, India
 P-225 Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Summary G.K.Ghosh *, S.K.Basha, V.K. Kulshreshth Gravity and magnetic data were collected jointly by National
P-225 Integrated Interpretation of Gravity, Magnetic & Seismic data for delineation of Basement Summary G.K.Ghosh *, S.K.Basha, V.K. Kulshreshth Gravity and magnetic data were collected jointly by National
ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh District, Jharkhand, India
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 2, February-2012 1 ASTER DEM Based Studies for Geological and Geomorphological Investigation in and around Gola block, Ramgarh
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment. Appendix E. River Corridor Delineation Process. VT Agency of Natural Resources. April, E0 - April, 2004
 Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle. Runoff Transpiration
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
UNIT 11 SOUTH ASIA SG 1 - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY & THE ENVIRONMENT I. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY TAKE OUT YOUR PHYSICAL MAP OF SOUTH ASIA A. The Himalayan Mountains form the northern boundary of the region (color
The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido
 Symposium Proceedings of the INTERPRAENENT 2018 in the Pacific Rim The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido Daisuke
Symposium Proceedings of the INTERPRAENENT 2018 in the Pacific Rim The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido Daisuke
WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND. Objectives. The Hydrologic Cycle
 WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND Objectives Define and describe the hydrologic cycle. Identify the basic characteristics of streams. Define drainage basin. Describe how floods occur and what factors may make
WATER ON AND UNDER GROUND Objectives Define and describe the hydrologic cycle. Identify the basic characteristics of streams. Define drainage basin. Describe how floods occur and what factors may make
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Flood risk zone mapping of the
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 1, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Flood risk zone mapping of the
Channel Avulsion Archives and Morphological Readjustment near the Bhagirathi-Mayurakshi Confluence in the Lower Gangatic Plain, West Bengal, India
 Channel Avulsion Archives and Morphological Readjustment near the Bhagirathi-Mayurakshi Confluence in the Lower Gangatic Plain, West Bengal, India Raghunath Pal Centre for the Study of Regional Development,
Channel Avulsion Archives and Morphological Readjustment near the Bhagirathi-Mayurakshi Confluence in the Lower Gangatic Plain, West Bengal, India Raghunath Pal Centre for the Study of Regional Development,
INFLUENCE OF LANDFORM AND GEOMORPHIC PROCESS ON TOPOGRAPHIC EVOLUTION OF A RIVER ISLAND
 INFLUENCE OF LANDFORM AND GEOMORPHIC PROCESS ON TOPOGRAPHIC EVOLUTION OF A RIVER ISLAND BALESHWAR SINGH Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati
INFLUENCE OF LANDFORM AND GEOMORPHIC PROCESS ON TOPOGRAPHIC EVOLUTION OF A RIVER ISLAND BALESHWAR SINGH Associate Professor Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati
Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding Rivers
 6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
Rivers T. Perron
 1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
Landscape Development
 Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Evidences of Neotectonic Activities as Reflected by Drainage Characteristics of the Mahananda River Floodplain and Its Adjoining Areas, Bangladesh
 American Journal of Earth Sciences 2015; 2(4): 61-70 Published online June 20, 2015 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajes) Evidences of Neotectonic Activities as Reflected by Drainage Characteristics
American Journal of Earth Sciences 2015; 2(4): 61-70 Published online June 20, 2015 (http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajes) Evidences of Neotectonic Activities as Reflected by Drainage Characteristics
Figure 1. Map of Feather River Basin in northern California. (A) Region straddles the northwestern Sierra Nevada and Sacramento Valley.
 Figure 1. Map of Feather River Basin in northern California. (A) Region straddles the northwestern Sierra Nevada and Sacramento Valley. (B) Feather River Basin with Yuba and Bear subbasins. Most hydraulic
Figure 1. Map of Feather River Basin in northern California. (A) Region straddles the northwestern Sierra Nevada and Sacramento Valley. (B) Feather River Basin with Yuba and Bear subbasins. Most hydraulic
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA
 2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
2. PHYSICAL FEATURES OF INDIA Question 1: Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. (i) A landmass bound by sea on three sides is referred to as (a) Coast (c) Peninsula (b) Island
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments
 GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Identification and delineation
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Identification and delineation
Durham E-Theses. The eects of dierential uplift and sediment supply on major Himalayan river systems at the mountain front DINGLE, ELIZABETH
 Durham E-Theses The eects of dierential uplift and sediment supply on major Himalayan river systems at the mountain front DINGLE, ELIZABETH How to cite: DINGLE, ELIZABETH (2012) The eects of dierential
Durham E-Theses The eects of dierential uplift and sediment supply on major Himalayan river systems at the mountain front DINGLE, ELIZABETH How to cite: DINGLE, ELIZABETH (2012) The eects of dierential
Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation of Chamshir Dam Site, South West Zagros
 Open Journal of Geology, 2015, 5, 136-143 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2015.53013 Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation
Open Journal of Geology, 2015, 5, 136-143 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2015.53013 Structural Analysis and Tectonic Investigation
Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE
 Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Assam, the eastern most state of
Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Chapter-3 GEOGRAPHICAL LOCATION, CLIMATE AND SOIL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY SITE Assam, the eastern most state of
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Impact of River Bank Erosion on Land Cover in Lower Subansiri River Flood Plain
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 480 Impact of River Bank Erosion on Land Cover in Lower Subansiri River Flood Plain Dr. L.T. Sasang Guite * &
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 5, May 2016 480 Impact of River Bank Erosion on Land Cover in Lower Subansiri River Flood Plain Dr. L.T. Sasang Guite * &
1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces?
 Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
Flood Hazard Mapping in Dikrong Basin of Arunachal Pradesh (India)
 Flood Hazard Mapping in Dikrong Basin of Arunachal Pradesh (India) Aditi Bhadra, Sutapa Choudhury, and Daita Kar Abstract Flood zoning studies have become more efficient in recent years because of the
Flood Hazard Mapping in Dikrong Basin of Arunachal Pradesh (India) Aditi Bhadra, Sutapa Choudhury, and Daita Kar Abstract Flood zoning studies have become more efficient in recent years because of the
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts,
 India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
India is a vast country with varied landforms. Our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands. India is a large landmass formed
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes
 Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Analysis of coarse sediment connectivity in semiarid river channels
 Sediment Transfer tlirongh the Fluviai System (Proceedings of a symposium held in Moscow, August 2004). IAHS Publ. 288, 2004 269 Analysis of coarse sediment connectivity in semiarid river channels J. M.
Sediment Transfer tlirongh the Fluviai System (Proceedings of a symposium held in Moscow, August 2004). IAHS Publ. 288, 2004 269 Analysis of coarse sediment connectivity in semiarid river channels J. M.
Streams. Water. Hydrologic Cycle. Geol 104: Streams
 Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
Streams Why study streams? Running water is the most important geologic agent in erosion, transportation and deposition of sediments. Water The unique physical and chemical properties of water make it
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
IV SEMESTER BACK-PAPER EXAMINATION-2004 Q. [1] [a] Describe internal structure of the earth with a neat sketch. Write down the major land forms and their characteristics on the earth surface. [8] [b] What
Durham E-Theses. Alluvial river response to active tectonics in the Dehradun region, Northwest India: A case study of the Ganga and Yamuna rivers.
 Durham E-Theses Alluvial river response to active tectonics in the Dehradun region, Northwest India: A case study of the Ganga and Yamuna rivers. PICKERING, JACK How to cite: PICKERING, JACK (2010) Alluvial
Durham E-Theses Alluvial river response to active tectonics in the Dehradun region, Northwest India: A case study of the Ganga and Yamuna rivers. PICKERING, JACK How to cite: PICKERING, JACK (2010) Alluvial
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 1, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Hypsometric Analysis of Varattaru
4 th Joint Project Team Meeting for Sentinel Asia 2011
 A Revisit on the Structural Flood Mitigation Measure with the Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in Gin River Basin, Sri Lanka 4 th Joint Project Team Meeting for Sentinel Asia 2011 Geoinformatics Center
A Revisit on the Structural Flood Mitigation Measure with the Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in Gin River Basin, Sri Lanka 4 th Joint Project Team Meeting for Sentinel Asia 2011 Geoinformatics Center
The Overall Objectives of Proposed Study
 Eric Prokocki is currently working on a Ph.D. degree at The University of Illinois. His advisor is Dr. Gary Proctor. His research project is related to Holocene evolution and avulsion dynamics of the lower
Eric Prokocki is currently working on a Ph.D. degree at The University of Illinois. His advisor is Dr. Gary Proctor. His research project is related to Holocene evolution and avulsion dynamics of the lower
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
USE OF SATELLITE DATA FOR TECTONIC INTERPRETATION, NW HIMALAYA
 COVER ARTCLE Photonirvachak Journal of the ndian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 32, No. 3, 2004 USE OF SATELLTE DATA FOR TECTONC NTERPRETATON, NW HMALAYA CHRASHREE MOHANTY, DBYA J. BARAL* AND JAVED N.
COVER ARTCLE Photonirvachak Journal of the ndian Society of Remote Sensing, Vol. 32, No. 3, 2004 USE OF SATELLTE DATA FOR TECTONC NTERPRETATON, NW HMALAYA CHRASHREE MOHANTY, DBYA J. BARAL* AND JAVED N.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Oscillation of meandering
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 5, No 4, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Oscillation of meandering
Global Perspectives on Geography (GPG) Volume 2, 2014
 Global Perspectives on Geography (GPG) Volume 2, 2014 www.as-se.org/gpg The Importance of Geomorphology in Understanding Natural Hazards with Special Reference to Hazards of The Dhansiri River Basin in
Global Perspectives on Geography (GPG) Volume 2, 2014 www.as-se.org/gpg The Importance of Geomorphology in Understanding Natural Hazards with Special Reference to Hazards of The Dhansiri River Basin in
Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India
 Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India by Saurabh Baruah Geoscience Division North-East Institute
Inversion of travel times to estimate Moho depth in Shillong Plateau and Kinematic implications through stress analysis of Northeastern India by Saurabh Baruah Geoscience Division North-East Institute
Bonn, Germany MOUTAZ DALATI. General Organization for Remote Sensing ( GORS ), Syria Advisor to the General Director of GORS,
 Bonn, Germany Early Warning System is needed for Earthquakes disaster mitigation in Syria Case Study: Detecting and Monitoring the Active faulting zones along the Afro-Arabian-Syrian Rift System MOUTAZ
Bonn, Germany Early Warning System is needed for Earthquakes disaster mitigation in Syria Case Study: Detecting and Monitoring the Active faulting zones along the Afro-Arabian-Syrian Rift System MOUTAZ
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010
 Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
Natural hazards in Glenorchy Summary Report May 2010 Contents Glenorchy s hazardscape Environment setting Flood hazard Earthquakes and seismic hazards Hazards Mass movement Summary Glossary Introduction
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
OIL INDIA LIMITED, GEOPHYSICS DEPARTMENT, DULIAJAN, ASSAM.
 J. P. Singh, M. K. Gupta & Akshaya Kumar, Oil India Limited, Duliajan. jpsingh@oilindia.in Summary Oil exploration in Upper Assam commenced with the discovery of the Digboi oilfield more than 100 years
J. P. Singh, M. K. Gupta & Akshaya Kumar, Oil India Limited, Duliajan. jpsingh@oilindia.in Summary Oil exploration in Upper Assam commenced with the discovery of the Digboi oilfield more than 100 years
Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods
 Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods GNAGESWARA RAO Department of Meteorology & Oceanography, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam
Occurrence of heavy rainfall around the confluence line in monsoon disturbances and its importance in causing floods GNAGESWARA RAO Department of Meteorology & Oceanography, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX : GEOGRAPHY TOPIC/CHAPTER: CHAPTER: 2 PHYSICAL FEATURES WORKSHEET NO. 06 Summary:- Tectonic Plate Theory:- This theory is based
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
 General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
Aquifer an underground zone or layer of sand, gravel, or porous rock that is saturated with water.
 Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
