Class XII - Physics Wave Optics Chapter-wise Problems. Chapter 10
|
|
|
- Ralph Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class XII - Physics Wave Optics Chapte-wise Poblems Answes Chapte (c) (a) 3 (a) 4 (c) 5 (d) 6 (a), (b), (d) 7 (b), (d) 8 (a), (b) 9 (a), (b) Yes Spheical Spheical with huge adius as compaed to the eath s adius so that it is almost a plane 3 Sound wave have fequencies Hz to khz The coesponding wavelengths ae 5m and 5mm, espectively iffaction effects ae seen if thee ae slits of width a such that α : Page of 8
2 Fo light waves, wavelengths 7 m Thus diffaction effects will show when 7 a : m wheeas fo sound they will show fo 5mm < a < 5m 4 The linea distance between two dots is l 54 cm ; 84 cm 3 At a distance of Z cm this subtends an angle l 84 cm φ : l / z z : 45 cm 4 φ 58 5 Only in the special cases when the pass axis of (III) is paollel to (I) o (II) thee shall be no light emeging In all othe cases thee shall be light emeging because the pass axis of (II) is no longe pependicula to the pass axis of (III) 6 Polaisation by eflection occus when the angle of incidence is the n Bewste s angle ie tanθ B whee n < n n When light tavels in such a medium the citical angle is whee n < n As tan θ B > sin θ c fo lage angles, θb < θc Thus, polaisation by eflection shall definitely occu n sinθ c n 7 d sin β whee β is the angle subtended by the objective at the object Fo light of 55 A o d 7 55 m sin β Fo electons acceleated though V the deboglie wavelength is h p 7 3nm 3 9 m 3 d ' sin β Page of 8
3 3 d ' sin β d ' 3 : 7 d 55 8 T P + x, T P x 3 S P (S T ) + (PT ) [ + ( x) ] / S P [ + ( + x) ] / Minima will occu when [ + ( + x) ] / [ + ( x) ] / If x ( + 4 ) / (5 ) /, 5 9 Without P: A A + A ω ω φ A A + A A sin( kx t)+a sin( kx t + ) A A + A () () A A [sin( kx wt) + sin( kx ωt + φ] whee A, polaizations Intensity A ae the amplitudes of eithe of the beam in and { + } ( ) A A [sin kx wt (+cos φ + sin φ)+sin ( kx ωt) sin φ] { A } A + (+cos φ ) aveage Page 3 of 8
4 aveage aveage A ( + cos φ)since A A With P: Assume A is blocked: Intensity (A + A ) + (A ) ( cos φ) A A + + Given: I 4 A Intensity without polaise at pincipal maxima Intensity at pincipal maxima with polaise A + 5 I 8 Intensity at fist ima with polaise A A ( ) + I 8 Path diffeence d sin θ + ( µ ) l Fo pincipal maxima, d sinθ + 5l l d sinθ Q l 4d 6 4 OP tan θ 6 Fo the fist ima: d sin θ +5 l ± Page 4 of 8
5 ± / 5 l ± / /8 sin θ ± d 4 6 On the positive side: 3 sinθ + 6 On the negative side: 5 sin θ 6 The fist pincipal maxima on the positive side is at distance + sinθ 3 tanθ + above O sin θ 6 3 In the ve side, the distance will be 5 tanθ below O 6 5 (i) Conside the distubances at R which is a distance d fom A Let the wave at R because of A be Y A a cos ωt The path diffeence of the signal fom A with that fom B is / and hence the phase diffeence is π Thus the wave at R because of B is y a cos( ωt π ) a cos ωt B R The path diffeence of the signal fom C with that fom A is and hence the phase diffeence is π Thus the wave at R because of C is y c a cos ωt The path diffeence between the signal fom with that of A is / / R A B C / d + ( d /) / d + d + 4d / d + d + 8d If d >> the path diffeence is π : and hence the phase diffeence Page 5 of 8
6 y a cosωt Thus, the signal picked up at R is y A + y B + y C + y Let the signal picked up at R fom B be y B a cos ωt The path diffeence between signal at and that at B is / y a cosωt The path diffeence between signal at A and that at B is ( ) + / d + d d d 4d : 8 d The phase diffeence is π π φ : 8 d 4d Hence, y A a cos (ωt-φ) Similaly, y C a cos (ωt-φ) Signal picked up by R is y A + y B + y C + y y a cos (ωt-φ) y 4a cos ( ωt φ) I a Thus R picks up the lage signal (ii) If B is switched off, R picks up y a cos ωt I R a R picks up y a cos ωt IR a Thus R and R pick up the same signal (c) If is switched off R picks up y a cos ωt IR a R picks up y 3a cos ωt IR 9 a Thus R picks up lage signal compaed to R (iv)thus a signal at R indicates B has been switched off and an enhanced signal at R indicates has been switched off Page 6 of 8
7 (i) Suppose the postulate is tue, then two paallel ays would poceed as shown in Fig Assug E shows a wave font then all points on this must have the same phase All points with the same optical path length must have the same phase E i Fig A i B i C ai medium Thus ε µ AE BC ε µ C o BC ε µ ( C AE ) BC >, C > AE As showing that the postulate is easonable If howeve, the light poceeded in the sense it does fo odinay mateial (viz in the fouth quadant, Fig ) Then ε µ AE BC ε µ C A Fig E B C ai medium o, BC ε µ ( C AE ) As AE > C, BC < O showing that this is not possible Hence the postalate is coect (ii) Fom Fig BC AC sin θ i and C-AE AC sin θ : Since ε µ ( AE C) BC n sin θ sin θ i 3 Conside a ay incident at an angle i A pat of this ay is eflected fom the ai-film inteface and a pat efacted inside This is patly eflected at the film-glass inteface and a pat tansmitted A pat of the eflected ay is eflected at the film-ai inteface and a pat tansmitted as paallel to Of couse succesive eflections and tansmissions will keep on deceasing the amplitude of the wave Hence ays and shall doate the behavio If incident light is to be tansmitted though the lens, and should intefee destuctively Both the eflections at A and ae fom lowe to highe efactive index and hence thee is no phase change on eflection The optical path diffeence between and is n (A + C) AB If d is the thickness of the film, then A C d cos AB AC sini AC d tan AC d tan Hence, AB d tan sini Thus the optical path diffeence is Page 7 of 8
8 d n d tan sini cos sini d sin d sini sin cos cos sin d sin sin cos Ai n Film n 38 Glass n 5 i A B i C nd cos Fo these waves to inteefee destuctively this must be / nd cos o nd cos /4 Fo a camea lens, the souces ae in the vetical plane and hence i nd ; 4 55 A d ; 38 4 o o A Page 8 of 8
This brief note explains why the Michel-Levy colour chart for birefringence looks like this...
 This bief note explains why the Michel-Levy colou chat fo biefingence looks like this... Theoy of Levy Colou Chat fo Biefingent Mateials Between Cossed Polas Biefingence = n n, the diffeence of the efactive
This bief note explains why the Michel-Levy colou chat fo biefingence looks like this... Theoy of Levy Colou Chat fo Biefingent Mateials Between Cossed Polas Biefingence = n n, the diffeence of the efactive
The condition for maximum intensity by the transmitted light in a plane parallel air film is. For an air film, μ = 1. (2-1)
 hapte Two Faby--Peot ntefeomete A Faby-Peot intefeomete consists of two plane paallel glass plates A and B, sepaated by a distance d. The inne sufaces of these plates ae optically plane and thinly silveed
hapte Two Faby--Peot ntefeomete A Faby-Peot intefeomete consists of two plane paallel glass plates A and B, sepaated by a distance d. The inne sufaces of these plates ae optically plane and thinly silveed
Waves and Polarization in General
 Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
Waves and Polaization in Geneal Wave means a distubance in a medium that tavels. Fo light, the medium is the electomagnetic field, which can exist in vacuum. The tavel pat defines a diection. The distubance
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 33: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 7 Homewok 6 Due on Oct. 5, 7 by 5: PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii) Review
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 33: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 7 Homewok 6 Due on Oct. 5, 7 by 5: PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii) Review
Maxwell s eqns. r D = ρ ext r B = 0 r r B D = dt r r D r H = + j dt
 D = ρext B = 0 B D = dt D H = + dt j Bounday conditions of EM wave Tangential components of the: - E and H fields (fom Gauss theoem) Nomal components of - D and B fields (fom Stoke s theoem) ( 2 ) (1)
D = ρext B = 0 B D = dt D H = + dt j Bounday conditions of EM wave Tangential components of the: - E and H fields (fom Gauss theoem) Nomal components of - D and B fields (fom Stoke s theoem) ( 2 ) (1)
TRAVELING WAVES. Chapter Simple Wave Motion. Waves in which the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation are called the
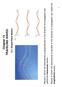 Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
Chapte 15 RAVELING WAVES 15.1 Simple Wave Motion Wave in which the ditubance i pependicula to the diection of popagation ae called the tanvee wave. Wave in which the ditubance i paallel to the diection
2.5 The Quarter-Wave Transformer
 /3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
/3/5 _5 The Quate Wave Tansfome /.5 The Quate-Wave Tansfome Reading Assignment: pp. 73-76 By now you ve noticed that a quate-wave length of tansmission line ( λ 4, β π ) appeas often in micowave engineeing
Chapter 16. Fraunhofer Diffraction
 Chapte 6. Faunhofe Diffaction Faunhofe Appoimation Faunhofe Appoimation ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) λ d d jk U j U ep,, Hugens-Fesnel Pinciple Faunhofe Appoimation : ( ) ( ) ( ) λ π λ d d j U j e e U k j jk ep,,
Chapte 6. Faunhofe Diffaction Faunhofe Appoimation Faunhofe Appoimation ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) λ d d jk U j U ep,, Hugens-Fesnel Pinciple Faunhofe Appoimation : ( ) ( ) ( ) λ π λ d d j U j e e U k j jk ep,,
Phys101 Lectures 30, 31. Wave Motion
 Phys0 Lectues 30, 3 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Tansvese and Longitudinal Mathematical Repesentation of a Taveling Wave The Pinciple of Supeposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: -7,8,9,0,,6,,3,6.
Phys0 Lectues 30, 3 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Tansvese and Longitudinal Mathematical Repesentation of a Taveling Wave The Pinciple of Supeposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: -7,8,9,0,,6,,3,6.
Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Fakultät I Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Institut für Physik Physikalisches Grundpraktikum.
 Mathematisch-Natuwissenschaftliche Fakultät I Humboldt-Univesität zu Belin Institut fü Physik Physikalisches Gundpaktikum Vesuchspotokoll Polaisation duch Reflexion (O11) duchgefüht am 10.11.2009 mit Vesuchspatne
Mathematisch-Natuwissenschaftliche Fakultät I Humboldt-Univesität zu Belin Institut fü Physik Physikalisches Gundpaktikum Vesuchspotokoll Polaisation duch Reflexion (O11) duchgefüht am 10.11.2009 mit Vesuchspatne
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Physics 11 Chapter 3: Vectors and Motion in Two Dimensions. Problem Solving
 Physics 11 Chapte 3: Vectos and Motion in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effot is failue. Souce unknown "We ae what we epeatedly do. Excellence, theefoe, is not an act,
Physics 11 Chapte 3: Vectos and Motion in Two Dimensions The only thing in life that is achieved without effot is failue. Souce unknown "We ae what we epeatedly do. Excellence, theefoe, is not an act,
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination
 E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
E&M poblems Univesity of Illinois at Chicago Depatment of Physics Electicity & Magnetism Qualifying Examination Januay 3, 6 9. am : pm Full cedit can be achieved fom completely coect answes to 4 questions.
Gauss s Law Simulation Activities
 Gauss s Law Simulation Activities Name: Backgound: The electic field aound a point chage is found by: = kq/ 2 If thee ae multiple chages, the net field at any point is the vecto sum of the fields. Fo a
Gauss s Law Simulation Activities Name: Backgound: The electic field aound a point chage is found by: = kq/ 2 If thee ae multiple chages, the net field at any point is the vecto sum of the fields. Fo a
Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions
 Gaphs of Sine and Cosine Functions In pevious sections, we defined the tigonometic o cicula functions in tems of the movement of a point aound the cicumfeence of a unit cicle, o the angle fomed by the
Gaphs of Sine and Cosine Functions In pevious sections, we defined the tigonometic o cicula functions in tems of the movement of a point aound the cicumfeence of a unit cicle, o the angle fomed by the
SEE LAST PAGE FOR SOME POTENTIALLY USEFUL FORMULAE AND CONSTANTS
 Cicle instucto: Moow o Yethiaj Name: MEMORIL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLND DEPRTMENT OF PHYSICS ND PHYSICL OCENOGRPHY Final Eam Phsics 5 Winte 3:-5: pil, INSTRUCTIONS:. Do all SIX (6) questions in section
Cicle instucto: Moow o Yethiaj Name: MEMORIL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLND DEPRTMENT OF PHYSICS ND PHYSICL OCENOGRPHY Final Eam Phsics 5 Winte 3:-5: pil, INSTRUCTIONS:. Do all SIX (6) questions in section
Physics 107 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8
 Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
Physics 07 TUTORIAL ASSIGNMENT #8 Cutnell & Johnson, 7 th edition Chapte 8: Poblems 5,, 3, 39, 76 Chapte 9: Poblems 9, 0, 4, 5, 6 Chapte 8 5 Inteactive Solution 8.5 povides a model fo solving this type
The geometric construction of Ewald sphere and Bragg condition:
 The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
Wave Incidence. Dr. Cruz-Pol. Normal Incidence. Ex.1. Light traveling in air encounters the water; another medium.
 D. Cu-Pol Ex.1. Light taveling in ai encountes the wate; anothe medium. Wave Incidence [Chapte 10 cont, Sadiku] D. Sanda Cu-Pol Electical and Compute Engineeing Dept. UPR-Maagüe Ex.1. Light encountes atmosphee,
D. Cu-Pol Ex.1. Light taveling in ai encountes the wate; anothe medium. Wave Incidence [Chapte 10 cont, Sadiku] D. Sanda Cu-Pol Electical and Compute Engineeing Dept. UPR-Maagüe Ex.1. Light encountes atmosphee,
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
Lecture 2 Date:
 Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
The Laws of Motion ( ) N SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS ! F = ( 6.00) 2 + ( 15.0) 2 N = 16.2 N. Section 4.4. Newton s Second Law The Particle Under a Net Force
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS The Laws of Motion Section 4.3 Mass P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the esultant foce on it must be zeo egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS The Laws of Motion Section 4.3 Mass P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the esultant foce on it must be zeo egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 8. Due: 3 May 2005
 Fields and Waves I Sping 005 Homewok 8 Tansmission Lines Due: 3 May 005. Multiple Choice (6) a) The SWR (standing wave atio): a) is a measue of the match between the souce impedance and line impedance
Fields and Waves I Sping 005 Homewok 8 Tansmission Lines Due: 3 May 005. Multiple Choice (6) a) The SWR (standing wave atio): a) is a measue of the match between the souce impedance and line impedance
Chapter 2 Classical propagation
 Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
Chapte Classical popagation Model: Light: electomagnetic wave Atom and molecule: classical dipole oscillato n. / / t c nz i z t z k i e e c i n k e t z Two popagation paametes: n. Popagation of light in
Galilean Transformation vs E&M y. Historical Perspective. Chapter 2 Lecture 2 PHYS Special Relativity. Sep. 1, y K K O.
 PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
PHYS-2402 Chapte 2 Lectue 2 Special Relativity 1. Basic Ideas Sep. 1, 2016 Galilean Tansfomation vs E&M y K O z z y K In 1873, Maxwell fomulated Equations of Electomagnetism. v Maxwell s equations descibe
Black Body Radiation and Radiometric Parameters:
 Black Body Radiation and Radiometic Paametes: All mateials absob and emit adiation to some extent. A blackbody is an idealization of how mateials emit and absob adiation. It can be used as a efeence fo
Black Body Radiation and Radiometic Paametes: All mateials absob and emit adiation to some extent. A blackbody is an idealization of how mateials emit and absob adiation. It can be used as a efeence fo
Unit 6 Test Review Gravitation & Oscillation Chapters 13 & 15
 A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
A.P. Physics C Unit 6 Test Review Gavitation & Oscillation Chaptes 13 & 15 * In studying fo you test, make sue to study this eview sheet along with you quizzes and homewok assignments. Multiple Choice
Easy. P4.2 Since the car is moving with constant speed and in a straight line, the. resultant force on it must be regardless of whether it is moving
 Chapte 4 Homewok Solutions Easy P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the zeo esultant foce on it must be egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad the ight o the left.
Chapte 4 Homewok Solutions Easy P4. Since the ca is moving with constant speed and in a staight line, the zeo esultant foce on it must be egadless of whethe it is moving (a) towad the ight o the left.
Chapter 3 Optical Systems with Annular Pupils
 Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Chapte 3 Optical Systems with Annula Pupils 3 INTRODUCTION In this chapte, we discuss the imaging popeties of a system with an annula pupil in a manne simila to those fo a system with a cicula pupil The
Solutions. V in = ρ 0. r 2 + a r 2 + b, where a and b are constants. The potential at the center of the atom has to be finite, so a = 0. r 2 + b.
 Solutions. Plum Pudding Model (a) Find the coesponding electostatic potential inside and outside the atom. Fo R The solution can be found by integating twice, 2 V in = ρ 0 ε 0. V in = ρ 0 6ε 0 2 + a 2
Solutions. Plum Pudding Model (a) Find the coesponding electostatic potential inside and outside the atom. Fo R The solution can be found by integating twice, 2 V in = ρ 0 ε 0. V in = ρ 0 6ε 0 2 + a 2
working pages for Paul Richards class notes; do not copy or circulate without permission from PGR 2004/11/3 10:50
 woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
woking pages fo Paul Richads class notes; do not copy o ciculate without pemission fom PGR 2004/11/3 10:50 CHAPTER7 Solid angle, 3D integals, Gauss s Theoem, and a Delta Function We define the solid angle,
Phys 201A. Homework 6 Solutions. F A and F r. B. According to Newton s second law, ( ) ( )2. j = ( 6.0 m / s 2 )ˆ i ( 10.4m / s 2 )ˆ j.
 7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
7. We denote the two foces F A + F B = ma,sof B = ma F A. (a) In unit vecto notation F A = ( 20.0 N)ˆ i and Theefoe, Phys 201A Homewok 6 Solutions F A and F B. Accoding to Newton s second law, a = [ (
Circular Motion & Torque Test Review. The period is the amount of time it takes for an object to travel around a circular path once.
 Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Honos Physics Fall, 2016 Cicula Motion & Toque Test Review Name: M. Leonad Instuctions: Complete the following woksheet. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER. 1. Detemine whethe each statement
Fresnel Diffraction. monchromatic light source
 Fesnel Diffaction Equipment Helium-Neon lase (632.8 nm) on 2 axis tanslation stage, Concave lens (focal length 3.80 cm) mounted on slide holde, iis mounted on slide holde, m optical bench, micoscope slide
Fesnel Diffaction Equipment Helium-Neon lase (632.8 nm) on 2 axis tanslation stage, Concave lens (focal length 3.80 cm) mounted on slide holde, iis mounted on slide holde, m optical bench, micoscope slide
F(r) = r f (r) 4.8. Central forces The most interesting problems in classical mechanics are about central forces.
 4.8. Cental foces The most inteesting poblems in classical mechanics ae about cental foces. Definition of a cental foce: (i) the diection of the foce F() is paallel o antipaallel to ; in othe wods, fo
4.8. Cental foces The most inteesting poblems in classical mechanics ae about cental foces. Definition of a cental foce: (i) the diection of the foce F() is paallel o antipaallel to ; in othe wods, fo
Inverse Square Law and Polarization
 Invese Squae Law and Polaization Objectives: To show that light intensity is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance fom a point light souce and to show that the intensity of the light tansmitted
Invese Squae Law and Polaization Objectives: To show that light intensity is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance fom a point light souce and to show that the intensity of the light tansmitted
PHYS Summer Professor Caillault Homework Solutions. Chapter 5
 PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
PHYS 1111 - Summe 2007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 5 7. Pictue the Poblem: The ball is acceleated hoizontally fom est to 98 mi/h ove a distance of 1.7 m. Stategy: Use equation 2-12 to
Primer Materials Spring
 Pime Mateials ping 07.06.07 Example 8. Calculate the bond stiffness of high puity diamond fom its dielectic constant at low fequencies, ε =5.5. Density of diamond is.55 gm/cm. c 8 m h 6.6 4 Js el.6 9 C
Pime Mateials ping 07.06.07 Example 8. Calculate the bond stiffness of high puity diamond fom its dielectic constant at low fequencies, ε =5.5. Density of diamond is.55 gm/cm. c 8 m h 6.6 4 Js el.6 9 C
Motion in Two Dimensions
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Motion in Two Dimensions Section 3.1 The Position, Velocity, and Acceleation Vectos P3.1 x( m) 0!3 000!1 70!4 70 m y( m)!3 600 0 1 70! 330 m (a) Net displacement x + y 4.87 km at
Physics Tutorial V1 2D Vectors
 Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
Physics Tutoial V1 2D Vectos 1 Resolving Vectos & Addition of Vectos A vecto quantity has both magnitude and diection. Thee ae two ways commonly used to mathematically descibe a vecto. y (a) The pola fom:,
CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE. or by vibratory forces acting directly on the fluid, or by the violent motion of the fluid itself.
 CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE 4.1 POINT SOURCE Sound waves ae geneated by the vibation of any solid body in contact with the fluid medium o by vibatoy foces acting diectly on the fluid,
CHAPTER IV RADIATION BY SIMPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCE 4.1 POINT SOURCE Sound waves ae geneated by the vibation of any solid body in contact with the fluid medium o by vibatoy foces acting diectly on the fluid,
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 32 Electomagnetic Waves PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified P. Lam 8_11_2008 Topics fo Chapte 32 Maxwell s equations
Chapte 32 Electomagnetic Waves PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified P. Lam 8_11_2008 Topics fo Chapte 32 Maxwell s equations
 Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
Page 1 of 6 Physics II Exam 1 155 points Name Discussion day/time Pat I. Questions 110. 8 points each. Multiple choice: Fo full cedit, cicle only the coect answe. Fo half cedit, cicle the coect answe and
3. Electromagnetic Waves II
 Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
Lectue 3 - Electomagnetic Waves II 9 3. Electomagnetic Waves II Last time, we discussed the following. 1. The popagation of an EM wave though a macoscopic media: We discussed how the wave inteacts with
A 1. EN2210: Continuum Mechanics. Homework 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions
 EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homewok 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions School of Engineeing Bown Univesity 1. An ideal fluid with mass density ρ flows with velocity v 0 though a cylindical tube with cosssectional
EN10: Continuum Mechanics Homewok 7: Fluid Mechanics Solutions School of Engineeing Bown Univesity 1. An ideal fluid with mass density ρ flows with velocity v 0 though a cylindical tube with cosssectional
2018 Physics. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 National Qualifications 018 018 Physics Advanced Highe Finalised Making Instuctions Scottish Qualifications Authoity 018 The infomation in this publication may be epoduced to suppot SQA qualifications
National Qualifications 018 018 Physics Advanced Highe Finalised Making Instuctions Scottish Qualifications Authoity 018 The infomation in this publication may be epoduced to suppot SQA qualifications
b) (5) What is the magnitude of the force on the 6.0-kg block due to the contact with the 12.0-kg block?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
COLLISIONLESS PLASMA PHYSICS TAKE-HOME EXAM
 Honou School of Mathematical and Theoetical Physics Pat C Maste of Science in Mathematical and Theoetical Physics COLLISIONLESS PLASMA PHYSICS TAKE-HOME EXAM HILARY TERM 18 TUESDAY, 13TH MARCH 18, 1noon
Honou School of Mathematical and Theoetical Physics Pat C Maste of Science in Mathematical and Theoetical Physics COLLISIONLESS PLASMA PHYSICS TAKE-HOME EXAM HILARY TERM 18 TUESDAY, 13TH MARCH 18, 1noon
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8. Lab 5. Magnetism
 Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lecture 5/6. Comic strip removed for copyright reasons.
 3.12 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 5/6 THE HYDROGEN ATOM Comic stip emoved fo copyight easons. Last Time Metal sufaces and STM Diac notation Opeatos, commutatos, some postulates Homewok fo Mon Oct 3
3.12 Fund of Mat Sci: Bonding Lectue 5/6 THE HYDROGEN ATOM Comic stip emoved fo copyight easons. Last Time Metal sufaces and STM Diac notation Opeatos, commutatos, some postulates Homewok fo Mon Oct 3
The Schwartzchild Geometry
 UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER The Schwatzchild Geomety Byon Osteweil Decembe 21, 2018 1 INTRODUCTION In ou study of geneal elativity, we ae inteested in the geomety of cuved spacetime in cetain special cases
UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER The Schwatzchild Geomety Byon Osteweil Decembe 21, 2018 1 INTRODUCTION In ou study of geneal elativity, we ae inteested in the geomety of cuved spacetime in cetain special cases
GM r. v = For Newton s third law, the forces in the action/reaction pair always act on different objects
 SAT Physics Mechanics The dot poduct of two vectos: A B = AB cos θ The coss poduct of vectos: A B = AB sin θˆn. The magnitude of the coss poduct is equal to the aea of the paallelogam. We use the ight
SAT Physics Mechanics The dot poduct of two vectos: A B = AB cos θ The coss poduct of vectos: A B = AB sin θˆn. The magnitude of the coss poduct is equal to the aea of the paallelogam. We use the ight
Phys 201A. Homework 5 Solutions
 Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
Phys 201A Homewok 5 Solutions 3. In each of the thee cases, you can find the changes in the velocity vectos by adding the second vecto to the additive invese of the fist and dawing the esultant, and by
EFFECTS OF FRINGING FIELDS ON SINGLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS. M. Bassetti and C. Biscari INFN-LNF, CP 13, Frascati (RM), Italy
 Fascati Physics Seies Vol. X (998), pp. 47-54 4 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Wokshop, Fascati, Oct. -5, 997 EFFECTS OF FRININ FIELDS ON SINLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS M. Bassetti and C. Biscai INFN-LNF, CP
Fascati Physics Seies Vol. X (998), pp. 47-54 4 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Wokshop, Fascati, Oct. -5, 997 EFFECTS OF FRININ FIELDS ON SINLE PARTICLE DYNAMICS M. Bassetti and C. Biscai INFN-LNF, CP
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
anubhavclasses.wordpress.com CBSE Solved Test Papers PHYSICS Class XII Chapter : Electrostatics
 CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
CBS Solved Test Papes PHYSICS Class XII Chapte : lectostatics CBS TST PAPR-01 CLASS - XII PHYSICS (Unit lectostatics) 1. Show does the foce between two point chages change if the dielectic constant of
DOING PHYSICS WITH MATLAB COMPUTATIONAL OPTICS
 DOING PHYIC WITH MTLB COMPUTTIONL OPTIC FOUNDTION OF CLR DIFFRCTION THEORY Ian Coope chool of Physics, Univesity of ydney ian.coope@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOD DIRECTORY FOR MTLB CRIPT View document: Numeical
DOING PHYIC WITH MTLB COMPUTTIONL OPTIC FOUNDTION OF CLR DIFFRCTION THEORY Ian Coope chool of Physics, Univesity of ydney ian.coope@sydney.edu.au DOWNLOD DIRECTORY FOR MTLB CRIPT View document: Numeical
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewart, Sections 12.2, 12.3) INTRO: In MATH 1114 vectors were written either as rows (a1, a2,..., an) or as columns a 1 a. ...
 MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
Anyone who can contemplate quantum mechanics without getting dizzy hasn t understood it. --Niels Bohr. Lecture 17, p 1
 Anyone who can contemplate quantum mechanics without getting dizzy hasn t undestood it. --Niels Boh Lectue 17, p 1 Special (Optional) Lectue Quantum Infomation One of the most moden applications of QM
Anyone who can contemplate quantum mechanics without getting dizzy hasn t undestood it. --Niels Boh Lectue 17, p 1 Special (Optional) Lectue Quantum Infomation One of the most moden applications of QM
Exam 3, vers Physics Spring, 2003
 1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
Phys 222 Sp 2009 Exam 1, Wed 18 Feb, 8-9:30pm Closed Book, Calculators allowed Each question is worth one point, answer all questions
 Phys Sp 9 Exam, Wed 8 Feb, 8-9:3pm Closed Book, Calculatos allowed Each question is woth one point, answe all questions Fill in you Last Name, Middle initial, Fist Name You ID is the middle 9 digits on
Phys Sp 9 Exam, Wed 8 Feb, 8-9:3pm Closed Book, Calculatos allowed Each question is woth one point, answe all questions Fill in you Last Name, Middle initial, Fist Name You ID is the middle 9 digits on
Suppose the medium is not homogeneous (gravity waves impinging on a beach,
 Slowly vaying media: Ray theoy Suppose the medium is not homogeneous (gavity waves impinging on a beach, i.e. a vaying depth). Then a pue plane wave whose popeties ae constant in space and time is not
Slowly vaying media: Ray theoy Suppose the medium is not homogeneous (gavity waves impinging on a beach, i.e. a vaying depth). Then a pue plane wave whose popeties ae constant in space and time is not
Chapter 22: Electric Fields. 22-1: What is physics? General physics II (22102) Dr. Iyad SAADEDDIN. 22-2: The Electric Field (E)
 Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
Geneal physics II (10) D. Iyad D. Iyad Chapte : lectic Fields In this chapte we will cove The lectic Field lectic Field Lines -: The lectic Field () lectic field exists in a egion of space suounding a
= 4 3 π( m) 3 (5480 kg m 3 ) = kg.
 CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
CHAPTER 11 THE GRAVITATIONAL FIELD Newton s Law of Gavitation m 1 m A foce of attaction occus between two masses given by Newton s Law of Gavitation Inetial mass and gavitational mass Gavitational potential
Physics 2001 Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
Physics 2001 Poblem Set 5 Solutions Jeff Kissel Octobe 16, 2006 1. A puck attached to a sting undegoes cicula motion on an ai table. If the sting beaks at the point indicated in the figue, which path (A,
PY208 Matter & Interactions Final Exam S2005
 PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
PY Matte & Inteactions Final Exam S2005 Name (pint) Please cicle you lectue section below: 003 (Ramakishnan 11:20 AM) 004 (Clake 1:30 PM) 005 (Chabay 2:35 PM) When you tun in the test, including the fomula
Vectors and 2D Motion. Vectors and Scalars
 Vectos and 2D Motion Vectos and Scalas Vecto aithmetic Vecto desciption of 2D motion Pojectile Motion Relative Motion -- Refeence Fames Vectos and Scalas Scala quantities: equie magnitude & unit fo complete
Vectos and 2D Motion Vectos and Scalas Vecto aithmetic Vecto desciption of 2D motion Pojectile Motion Relative Motion -- Refeence Fames Vectos and Scalas Scala quantities: equie magnitude & unit fo complete
Outline. Classes of polarizing devices Polarization states. Eigen-polarization of crystals. Momentum matching at boundaries Polarization calculations
 Cstal optics lectue C 566 Adv. Optics Lab Outline Classes of polaizing devices Polaization states igen-polaization of cstals Momentum matching at boundaies Polaization calculations Muelle matices Jones
Cstal optics lectue C 566 Adv. Optics Lab Outline Classes of polaizing devices Polaization states igen-polaization of cstals Momentum matching at boundaies Polaization calculations Muelle matices Jones
to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsfn
 Chapte 6 16. (a) In this situation, we take f s to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsf applies, whee μ s = 0.5. pplying ewton s second law to the block of mass
Chapte 6 16. (a) In this situation, we take f s to point uphill and to be equal to its maximum value, in which case f s, max = μsf applies, whee μ s = 0.5. pplying ewton s second law to the block of mass
Phys 774: Ellipsometry
 Dielectic function Phys 774: Ellipsomety Optical vibations (phonons) Fee electons (plasma) Electonic tansitions (valence conduction band) Dielectic function and efactive index ae geneally complex: ε ε
Dielectic function Phys 774: Ellipsomety Optical vibations (phonons) Fee electons (plasma) Electonic tansitions (valence conduction band) Dielectic function and efactive index ae geneally complex: ε ε
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 4. Due 8 March 2005
 Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
Homewok 4 Due 8 Mach 005. Inceasing the Beakdown Voltage: This fist question is a mini design poject. You fist step is to find a commecial cable (coaxial o two wie line) fo which you have the following
cos kd kd 2 cosθ = π 2 ± nπ d λ cosθ = 1 2 ± n N db
 . (Balanis 6.43) You can confim tat AF = e j kd cosθ + e j kd cosθ N = cos kd cosθ gives te same esult as (6-59) and (6-6), fo a binomial aay wit te coefficients cosen as in section 6.8.. Tis single expession
. (Balanis 6.43) You can confim tat AF = e j kd cosθ + e j kd cosθ N = cos kd cosθ gives te same esult as (6-59) and (6-6), fo a binomial aay wit te coefficients cosen as in section 6.8.. Tis single expession
Introduction and Vectors
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Intoduction and Vectos Section 1.1 Standads of Length, Mass, and Time *P1.4 Fo eithe sphee the volume is V = 4! and the mass is m =!V =! 4. We divide this equation fo the lage sphee
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS Intoduction and Vectos Section 1.1 Standads of Length, Mass, and Time *P1.4 Fo eithe sphee the volume is V = 4! and the mass is m =!V =! 4. We divide this equation fo the lage sphee
Advanced Subsidiary GCE (H157) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet
 Advanced Subsidiay GCE (H57) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Fomulae and Relationships Booklet The infomation in this booklet is fo the use of candidates following the Advanced
Advanced Subsidiay GCE (H57) Advanced GCE (H557) Physics B (Advancing Physics) Data, Fomulae and Relationships Booklet The infomation in this booklet is fo the use of candidates following the Advanced
HW #5 Hints. Today. HW #5 Hints. HW #5 Hints. Announcements:
 Today HW #5 Hints Announcements: HW and Exta cedit #3 due 2/25 HW hints + Recap the 2nd law of themodynamics Electic and Magnetic Foces and thei unification the Foce Field concept -1-1) The speed at D
Today HW #5 Hints Announcements: HW and Exta cedit #3 due 2/25 HW hints + Recap the 2nd law of themodynamics Electic and Magnetic Foces and thei unification the Foce Field concept -1-1) The speed at D
3.2 Centripetal Acceleration
 unifom cicula motion the motion of an object with onstant speed along a cicula path of constant adius 3.2 Centipetal Acceleation The hamme thow is a tack-and-field event in which an athlete thows a hamme
unifom cicula motion the motion of an object with onstant speed along a cicula path of constant adius 3.2 Centipetal Acceleation The hamme thow is a tack-and-field event in which an athlete thows a hamme
Current Errata for Electromagnetic Waves
 Cuent Eata fo Electomagnetic Waves Uman S. Inan and Aziz S. Inan August 8, 007 Peface Coections Page xiii: the section on Recommended Couse Content should have no section numbe. Chapte Coections Page 56:
Cuent Eata fo Electomagnetic Waves Uman S. Inan and Aziz S. Inan August 8, 007 Peface Coections Page xiii: the section on Recommended Couse Content should have no section numbe. Chapte Coections Page 56:
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
6.4 Period and Frequency for Uniform Circular Motion
 6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
Lecture 04: HFK Propagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Friday, April 29, 2005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas
 C:\Dallas\0_Couses\0_OpSci_330\0 Lectue Notes\04 HfkPopagation.doc: Page of 9 Lectue 04: HFK Popagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Fiday, Apil 9, 005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas The
C:\Dallas\0_Couses\0_OpSci_330\0 Lectue Notes\04 HfkPopagation.doc: Page of 9 Lectue 04: HFK Popagation Physical Optics II (Optical Sciences 330) (Updated: Fiday, Apil 9, 005, 8:05 PM) W.J. Dallas The
Fundamentals of Photonics Bahaa E. A. Saleh, Malvin Carl Teich
 Fundamentals of Photonics ahaa E. A. Saleh, Malvin Cal Teich 송석호 Physics Depatment (Room #36-4) -93, -4546-93, shsong@hanyang.ac.k http://optics.hanyang.ac.k/~shsong Midtem Exam 3%, Final Exam 3%, Homewok
Fundamentals of Photonics ahaa E. A. Saleh, Malvin Cal Teich 송석호 Physics Depatment (Room #36-4) -93, -4546-93, shsong@hanyang.ac.k http://optics.hanyang.ac.k/~shsong Midtem Exam 3%, Final Exam 3%, Homewok
Physics 313 Practice Test Page 1. University Physics III Practice Test II
 Physics 313 Pactice Test Page 1 Univesity Physics III Pactice Test II This pactice test should give you a ough idea of the fomat and oveall level of the Physics 313 exams. The actual exams will have diffeent
Physics 313 Pactice Test Page 1 Univesity Physics III Pactice Test II This pactice test should give you a ough idea of the fomat and oveall level of the Physics 313 exams. The actual exams will have diffeent
b) (5) What average force magnitude was applied by the students working together?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Physics 4A Chapter 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane
 Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Part V: Closed-form solutions to Loop Closure Equations
 Pat V: Closed-fom solutions to Loop Closue Equations This section will eview the closed-fom solutions techniques fo loop closue equations. The following thee cases will be consideed. ) Two unknown angles
Pat V: Closed-fom solutions to Loop Closue Equations This section will eview the closed-fom solutions techniques fo loop closue equations. The following thee cases will be consideed. ) Two unknown angles
1) Consider a particle moving with constant speed that experiences no net force. What path must this particle be taking?
 Chapte 5 Test Cicula Motion and Gavitation 1) Conside a paticle moving with constant speed that expeiences no net foce. What path must this paticle be taking? A) It is moving in a paabola. B) It is moving
Chapte 5 Test Cicula Motion and Gavitation 1) Conside a paticle moving with constant speed that expeiences no net foce. What path must this paticle be taking? A) It is moving in a paabola. B) It is moving
Basic Interference and. Classes of of Interferometers
 Basic Intefeence and Classes of Intefeometes Basic Intefeence Two plane waves Two spheical waves Plane wave and and spheical wave Classes of of Intefeometes Division of of wavefont Division of of amplitude
Basic Intefeence and Classes of Intefeometes Basic Intefeence Two plane waves Two spheical waves Plane wave and and spheical wave Classes of of Intefeometes Division of of wavefont Division of of amplitude
Static equilibrium requires a balance of forces and a balance of moments.
 Static Equilibium Static equilibium equies a balance of foces and a balance of moments. ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 Eample 1: painte stands on a ladde that leans against the wall of a house at an angle
Static Equilibium Static equilibium equies a balance of foces and a balance of moments. ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 Eample 1: painte stands on a ladde that leans against the wall of a house at an angle
CHEM1101 Worksheet 3: The Energy Levels Of Electrons
 CHEM1101 Woksheet 3: The Enegy Levels Of Electons Model 1: Two chaged Paticles Sepaated by a Distance Accoding to Coulomb, the potential enegy of two stationay paticles with chages q 1 and q 2 sepaated
CHEM1101 Woksheet 3: The Enegy Levels Of Electons Model 1: Two chaged Paticles Sepaated by a Distance Accoding to Coulomb, the potential enegy of two stationay paticles with chages q 1 and q 2 sepaated
kg 2 ) 1.9!10 27 kg = Gm 1
 Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
Section 6.1: Newtonian Gavitation Tutoial 1 Pactice, page 93 1. Given: 1.0 10 0 kg; m 3.0 10 0 kg;. 10 9 N; G 6.67 10 11 N m /kg Requied: Analysis: G m ; G m G m Solution: G m N m 6.67!10 11 kg ) 1.0!100
Lecture 7: Angular Momentum, Hydrogen Atom
 Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Lectue 7: Angula Momentum, Hydogen Atom Vecto Quantization of Angula Momentum and Nomalization of 3D Rigid Roto wavefunctions Conside l, so L 2 2 2. Thus, we have L 2. Thee ae thee possibilities fo L z
Chapter Sixteen: Electric Charge and Electric Fields
 Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chapte Sixteen: Electic Chage and Electic Fields Key Tems Chage Conducto The fundamental electical popety to which the mutual attactions o epulsions between electons and potons ae attibuted. Any mateial
Chem 453/544 Fall /08/03. Exam #1 Solutions
 Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Chem 453/544 Fall 3 /8/3 Exam # Solutions. ( points) Use the genealized compessibility diagam povided on the last page to estimate ove what ange of pessues A at oom tempeatue confoms to the ideal gas law
Circular Motion. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Chapter 5. Applying Newton s Laws. Newton s Laws. r r. 1 st Law: An object at rest or traveling in uniform. 2 nd Law:
 Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
Chapte 5 Applying Newton s Laws Newton s Laws st Law: An object at est o taveling in unifom motion will emain at est o taveling in unifom motion unless and until an extenal foce is applied net ma nd Law:
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) ,
 R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
PHYS Summer Professor Caillault Homework Solutions
 PHYS 1111 - Summe 007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 4 3. Pictue the Poblem: The ca moves up the 5.5 incline with constant acceleation, changing both its hoizontal and vetical displacement
PHYS 1111 - Summe 007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 4 3. Pictue the Poblem: The ca moves up the 5.5 incline with constant acceleation, changing both its hoizontal and vetical displacement
PHY2054 Exam 1 Formula Sheet
 Instucto: Field/Mitselmakhe PHYSICS DPATMNT PHY 54 Final am Apil 3, 6 Name (PINT, last, fist): Signatue: On my hono, I have neithe given no eceived unauthoized aid on this eamination. YOU TST NUMB IS TH
Instucto: Field/Mitselmakhe PHYSICS DPATMNT PHY 54 Final am Apil 3, 6 Name (PINT, last, fist): Signatue: On my hono, I have neithe given no eceived unauthoized aid on this eamination. YOU TST NUMB IS TH
