The Challenge of Weather Prediction
|
|
|
- Rosaline Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Challenge of Weather Prediction 3. Old and Modern Ways of Weather Forecasting B NGoswami Introduction B N Goswami is with the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. After his PhD in Plasma Physics he was attracted to this field by the challenges in weather and climate prediction. His interests include understanding variability and predictability of all tropical phenomena including the monsoon. The previous articles of this series were: 1. The basic driving, November Difficulties in predicting the weather, January In the last two parts we discussed the physical basis for weather forecasting and the practical and conceptual difficulties encountered when one tries to forecast the weather. In this concluding part, we shall trace the history of weather forecasting and describe its current status. Traditional weather forecasting reminds us of meteorologists sitting with the weather charts spread in front of them and making forecasts based on their 'experience'. This experience is the knowledge gathered over years of observations and the background theory on weather. Given a background condition, a particular weather pattern, say a low pressure area, tends to evolve on the average in a certain way. This may be termed as mean or 'climatological' behaviour. Also atmospheric fluctuations have a certain amount of 'persistency'. In other words, once a low pressure is formed, it persists for a while. Forecasts made by meteorologists based on 'climatology' and 'persistence' and empirical knowledge about evolution of weather systems are known as synoptic forecasts. Before the advent of computers, this was the only method of weather forecasting. Upto 12 hours or 24 hours in advance, the meteorologists can actually make very good forecasts based on this technique. But beyond that this type of forecast is not useful. Even with the approximations that must be made, the motion of the air is governed by a set of physical laws as described in Part I of this series. Therefore, if we knew the initial state and we could solve the equations, we could predict the future state. The first problem is that these equations are highly nonlinear coupled ~ R-E~--N-A-N-C-E--I-M-a-r-c-h
2 partial differential equations. It is not possible to arrive at analytic solutions. Thus, the only way to predict is using numerical techniques. The modern concept of numerical weather forecasting was born in the fertile mind of the Quaker mathematician Lewis Fry Richardson ( ) during World War - I. Richardson was attracted by the success of spherical astronomy where the motion of the planets and the timing of the solar eclipse could be predicted years in advance. Although spherical astronomy deals with simple geometrical relations whereas meteorology has to struggle with an enormously complex mechanical and thermodynamical system, Richardson argued that it should be possible to proceed from an initial state of the atmosphere to a final state by a purely mathematical process. Richardson who served with an ambulance unit in France during World War I, worked through long nights and developed a step by step integration method for solving differential equations and in 1922 'published one of the most remarkable books in meteorology, Weather Prediction by Numerical Process. Here he presented a set of equations that he thought described the physical processes governing the atmospheric phenomena together with a method for their approximate solution. Although the example worked out by Richardson in the book was a spectacular failure, this was the beginning of numerical weather forecasting. Richardson, with immense labour using his hand calculator, calculated the change of pressure at the surface over a period of six hours for an area in Europe and obtained an answer which was in error by at least two orders of magnitude. It must have required considerable courage to publish such a ludicrous result. We have reason to be thankful to him for this courage as this example brought to focus some of the intrinsic difficulties in solving meteorological equations! During the next two decades not much progress took place in numerical weather prediction (NWP). In the late 40's Jule Charney (a pioneer of modern meteorology who was later a professor at the Massachussetts Institute of Technology) provided a theoretical basis to overcome the problems faced by Richardson. Lewis Fry Richardson made the first attempt at numerically solving the atmospheric equations make a six hour forecast in 1922 using his hand calculator! His attempt, though a spectacular failure, showed the intrinsic problems in solving the meteorological equations. The group led by Jule Charney at the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, made the first successful numerical weather prediction in April 1950, using the first ever built computer ENIAC. -R-ES-O-N-A-N-C-E--I-M-a-rc-h ~
3 Figure 1 A cart_ian grid for solving thll mefllorologlcal equations. vertical exchange between levels in the atmospheric column wind vectors humidity clouds temperature height fluxes time stepn 30 minutes Meanwhile, the first electronic computer ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was being built at Princeton. Professor John Von Neumann at the Institute of Advanced Studies in Princeton recognised the enormous potential of this machine and organised a group with Jule Charney, R Fjortoft and a few others to conduct numerical forecasts of the atmospheric system. Using the simplified equations proposed by Charney (known as the barotropic vorticity equation) the first successful numerical forecast was produced with the ENIAC in April, 1950 for a level in the middle troposphere (500 hpa) supposed to represent the total behaviour of the atmosphere. Thus the era of numerical weather prediction was finally launched. Although the integration of the barotropic vorticity equation was made in a relatively small domain in the middle latitude (about 5000 Km x 5000 Km) only, a forecast of 24 hours took 36 hours of the computer time! -'n ~ re-s-o-n-a-n-c-e--i-m-a-r-ch
4 CONTROL INITIAL setup Integration and inldal data Figure 2 General/MId flow diagram of a general circulation model. dynamica subrouti calculate rorces dynamical~ such as gravitational, press. gradient & Coriolis. I au points PHYSICS 1lJWIJmC»(. radiative nuxes at each layer AA1?l removes lafle scale precipitation 'Bo'W(1JMl!)' boundary layer nuxes & processes b aupoint.r(~) tuul au l4tltudes (spectral) Filter to maintain numerical stability S~ penetrative convection scheme CLO'l1!J) interactive cloud prediction scheme c test ror which fields, rorm or output & period or averaging OUI'PUT output required results GeneraUy tin IiIM atq " aboul30 minute. b RADIATION ia not alway. ctjlled tjlev'":/ film "ep tja dynamk cluu&ge. are (Gater tlum radigtive cluuag.. c CLOUDS are o~ pracribed rtdinr tlum calculg.t.d In a modem weather forecasting centre such as the one we have in New Delhi (National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts), the basic equations are solved over the entire globe as shown in Figure 1. The method of solving illustrated in this figure is known as finite difference technique in which the equations are solved at a set of equi-spaced points. The other technique, more commonly used in recent times, is known as spectral technique. In this technique the variables are expressed in terms of a set of orthogonal basis functions (spherical harmonics) and equations expressing the evolution of the -R-ES-O-N--A-N-C-E-I--M-a-rc-h ~~ '1
5 WMCs RTHs o RS MCs and N MCs Main Telecommunication network Regional meteorological telecommunication networks Figure 3 The Global Teleconnecf/onSyRem (GTS) (Adopted from WMO Bulletin, Vol. 45, January 1996). amplitudes of these basis functions are solved. The flow chart in Figure 2 shows how this integration is carried out. The grid spacing shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 is somewhat outdated. Most state of the art models now use lox 1 0 grid spacing or better. They divide the atmosphere into 20 layers or more in the vertical. This gives us about 1.3 million points for the seven variables! In addition the calculation of the forcing functions such as radiation and cloud formation and release of latent heat requires very complex calculations. With all these constraints, the forecasts for tomorrow and days beyond must be produced today or else it will not have any value! This is why the weather forecasting centres require super computers. Solving the equations in a super computer is only part of the story. A major effort is required to specify the initial state. The initial state comes from all those weather observations mentioned in Part II of the series. Currently, in addition to about 900 upper air stations, about 10,000 surface meteorological stations, 7000 merchant ships and 600 drifting buoys send their routine weather ~~ R-ES-O-N-A-N-C-E--I-M-a-r-c-h-'9-9-7
6 INTERACTIVE ANALYSIS/FORECAST/ RETRIEVAL SYSTEM Flaure 4 Schemaflc diagram of an Interactive analyslslforecast/refrleval system. INITIAL CONDITIONS PREDICTION SATELLITE L...- SOUNDINGS----- CONVENTIONAL DATA SATELLITE DATA reports. These are passed around the globe through 'hot lines' called the Global Teleconnection System (GTS) as shown in Figure 3. Most NWP centres have facilities to receive these data. In addition to these, weather observations by several aircrafts and satellites are also passed on through the GTS. Since these are different types of information and at non-uniform space and time points with relatively large data void regions, a system has to be evolved to generate data at regular grid points required by the model. This, known as Objective Analysis Scheme uses a certain objective interpolation scheme to fill up the data void regions. In principle, this initial condition must exactly satisfy the governing equations. However, due to observational errors as well as the interpolation over the data void regions, the initial observations normally do not satisfy the governing equations. -R~-~-O-N-4-N-C-~--1 -M-n-rr-n-l-QQ ~ ~
7 Due to tremendous advance in computer technology, better understanding of the physical processes and beher acquisition of data (through conventional means and satellites) have increased the skill in the middle latitude forecasts at least six fold since In contrast, the tropical forecasts have improved by only about two fold since then. This imbalance is seen by the model as an initial error which grows rapidly with the integration of the model. To reduce this initial 'shock' a short forecast by the model is used as the first guess and the differences between the observation and the first guess are minimised using an objective minimisation technique. This procedure generates an initial state for the forecasts that is in approximate balance with the model equations. Before doing all this the system must also carry out some quality control checks on the data. Similarly, getting the meteorological parameters from satellite observations requires a set of calculations called Satellite Retrieval Scheme. A schematic diagram of the interactive analysis/forecast/retrieval system is shown in Figure 4. This procedure is quite involved and requires almost as much, if not more time on the computer as the actual numerical integration of the computer model. NWP has never looked back since the first numerical forecasts in April, The tremendous advance in computer technology allows us to solve more complex models over a global domain. Moreover, specification of initial conditions has steadily improved through better observation, data collection and communication techniques and availability of satellite observations. In addition, our understanding of the physical processes responsible for the weather changes has also steadily improved. As a result, today, operational NWP centres are capable of making successful forecasts of the large scale circulation features in the middle latitude about 6-7 days in advance. By large scale circulation features we refer to wind conditions or temperatures over thousand kilometres or higher spatial scales. However, even in middle latitude, prediction of rainfall is somewhat less successful. Similarly, if we want the forecast for a specific small town, it is less skillful. In the tropics, the skill of the forecast for even the large scale circulation features is currently only about 2-3 days while the skill for precipitation forecasts is even poorer. This is because in the middle latitudes, rainfall is rather passive. The circulation forces upward motion that condenses the moisture and produces ~~ R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C-E-I-M--ar-c-h-'9-9-7
8 rain. In the tropics, rain plays a much more active role. It actually dictates the type of circulation we should have. As a result, to improve the tropical forecasts we must improve our knowledge of how the rains form in the tropics and how they interact with the circulation. The challenge of the day is therefore, to push the skill of tropical forecasts from the present 2-3 days to let us say 5-6 days through better understanding and formulation of the relevant processes. Everyone day improvement in the averaged forecast skill can save us crores of rupees! Better understanding of how clouds are formed and organised in the tropics holds the key to improving the tropical weather forecasts. Before concluding, let me add a few words on climate forecasting. By climate, we refer to the average state of the atmosphere such as the monthly or seasonal mean. Thus, climate forecasts must be made at least one season in advance. From the discussion on the limit to weather forecasts, it is clear that even if we have a 'perfect' model and 'near perfect' observations, the skill of weather forecasts will be limited to about two weeks at best. Does this mean that there is no hope for climate forecasts? Fortunately, the answer to this question is no. This is because, so far we have considered the atmosphere in isolation from the ocean. Oceans have large thermal inertia. On time scales of a season or longer the oceans can modulate the mean condition of the atmosphere. Therefore, even though weather is not predictable beyond two weeks, the climate may be predictable beyond a season! This will be the subject of a future article. Address for Correspondence B N Goswami Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Indian Institute of Science Bangalore , India goswamy@cas.iisc.ernet.in Fax: (080) Suggested Reading Nigel Calder. The Weather Machine. The Viking Press. New York. p 144, John M Wallace and Peter Hobbs. Atmospheric Sciences: An Introductory Survey. Academic Press. San Diego, California. p 467, Richard A Anthes, John J Cahir, A B Fraser and Hans A Panofsky. The Atmosphere. (Third Edition) Charles E Merrill Publishing Company. Colombia, Toronto, London, Sydney. p 532, A Miller, J C Thompson, R E Petterson and DR Harayau.Element.s of Meteorology. Charles E Merrill Publishing Company. Colombia, Toronto, London, Sydney. p 417,1983. J P Peixoto and A H Oort. Physics of Climate. American Institute of Physics. p 520, N Kumar. Deterministic Chaos: Complex Chance Out of Simple Necessity. Universities Press (India) Limited. Hyderabad R -E-S-O-N-A-N--C-E-I-M--a-rc-h ~~
Introduction to Meteorology and Weather Forecasting
 Introduction to Meteorology and Weather Forecasting ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 1 2 040909 ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 1 3 040914 ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting
Introduction to Meteorology and Weather Forecasting ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 1 2 040909 ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting : lecture 1 3 040914 ENVI1400 : Meteorology and Forecasting
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
Computer Models of the Earth s Climate
 Computer Models of the Earth s Climate DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES MATH DAY, 3-25-13 Climate Models Climate Models Climate Models Mathematical model: uses equations to describe
Computer Models of the Earth s Climate DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES MATH DAY, 3-25-13 Climate Models Climate Models Climate Models Mathematical model: uses equations to describe
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Forecasting AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 26 Nov 29, Weather Forecasting
 Forecasting AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Forecasting Lecture 26 Nov 29, 2018 1 Weather Forecasting People have been trying to predict the
Forecasting AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Forecasting Lecture 26 Nov 29, 2018 1 Weather Forecasting People have been trying to predict the
Lecture 1 ATS 601. Thomas Birner, CSU. ATS 601 Lecture 1
 Lecture 1 ATS 601 Thomas Birner, CSU About your Instructor: Thomas Birner Assistant Professor, joined CSU 10/2008 M.Sc. Physics (Condensed Matter Theory), U of Leipzig, Germany Ph.D. Atmospheric Science
Lecture 1 ATS 601 Thomas Birner, CSU About your Instructor: Thomas Birner Assistant Professor, joined CSU 10/2008 M.Sc. Physics (Condensed Matter Theory), U of Leipzig, Germany Ph.D. Atmospheric Science
WEATHER AND CLIMATE PREDICTION
 WEATHER AND CLIMATE PREDICTION ATM S 380, Winter 2017 INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office: ATG 608 E-mail:
WEATHER AND CLIMATE PREDICTION ATM S 380, Winter 2017 INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office: ATG 608 E-mail:
Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence)
 1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
1 Crux of AGW s Flawed Science (Wrong water-vapor feedback and missing ocean influence) William M. Gray Professor Emeritus Colorado State University There are many flaws in the global climate models. But
Chapter 12: Meteorology
 Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
Using Aziz Supercomputer
 The Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research Using Aziz Supercomputer Mansour Almazroui Director, Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research (CECCR) Head, Department of Meteorology King Abdulaziz
The Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research Using Aziz Supercomputer Mansour Almazroui Director, Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research (CECCR) Head, Department of Meteorology King Abdulaziz
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I
 Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380
 Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380 Course web site http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/2013q1/380/ Instructor: Professor Cecilia Bitz PhD in UW atmospheric sciences 1997, masters in
Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380 Course web site http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/2013q1/380/ Instructor: Professor Cecilia Bitz PhD in UW atmospheric sciences 1997, masters in
MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction
 MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction Grid point and spectral models are based on the same set of primitive equations. However, each type formulates and solves the equations
MODEL TYPE (Adapted from COMET online NWP modules) 1. Introduction Grid point and spectral models are based on the same set of primitive equations. However, each type formulates and solves the equations
Exploring and extending the limits of weather predictability? Antje Weisheimer
 Exploring and extending the limits of weather predictability? Antje Weisheimer Arnt Eliassen s legacy for NWP ECMWF is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by 34 states. ECMWF produces
Exploring and extending the limits of weather predictability? Antje Weisheimer Arnt Eliassen s legacy for NWP ECMWF is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by 34 states. ECMWF produces
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
282 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 60, No. 1. A Theory and Method of Long-Range Numerical
 282 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 60, No. 1 A Theory and Method of Long-Range Numerical Weather Forecasts By Chao Jih-Ping, Guo Yu-Fu and Xin Ru-Nan Institute of Atmospheric Physics,
282 Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Vol. 60, No. 1 A Theory and Method of Long-Range Numerical Weather Forecasts By Chao Jih-Ping, Guo Yu-Fu and Xin Ru-Nan Institute of Atmospheric Physics,
Introduction to Climatology. GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1
 Introduction to Climatology GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1 Us Graham Saunders graham.saunders@lakeheadu.ca Jason Freeburn (RC 2004) jtfreebu@lakeheadu.ca Graham Saunders Australian Weather Bureau Environment
Introduction to Climatology GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1 Us Graham Saunders graham.saunders@lakeheadu.ca Jason Freeburn (RC 2004) jtfreebu@lakeheadu.ca Graham Saunders Australian Weather Bureau Environment
A Century of Numerical Weather Prediction
 A Century of Numerical Weather Prediction Peter Lynch School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Royal Meteorological Society, Edinburgh, 10 October, 2008 Outline Prehistory 1890 1920 ENIAC
A Century of Numerical Weather Prediction Peter Lynch School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Royal Meteorological Society, Edinburgh, 10 October, 2008 Outline Prehistory 1890 1920 ENIAC
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 25. Weather Forecasting Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 25 Weather Forecasting Part II NWP s First Baby Steps: Mid-Twentieth Century It wasn t until the development of computers in the 1940s and 1950s that NWP could be even attempted.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 25 Weather Forecasting Part II NWP s First Baby Steps: Mid-Twentieth Century It wasn t until the development of computers in the 1940s and 1950s that NWP could be even attempted.
Introduction to Climatology. GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1
 Introduction to Climatology GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1 Us! Graham Saunders (RC 2006C) graham.saundersl@lakeheadu.ca! Jason Freeburn (RC 2004) jtfreebu@lakeheadu.ca Graham Saunders! Australian Weather Bureau!
Introduction to Climatology GEOG/ENST 2331: Lecture 1 Us! Graham Saunders (RC 2006C) graham.saundersl@lakeheadu.ca! Jason Freeburn (RC 2004) jtfreebu@lakeheadu.ca Graham Saunders! Australian Weather Bureau!
Global Circulation. Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern
 Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
Global Circulation Local weather doesn t come from all directions equally Everyone s weather is part of the global circulation pattern Wind rose shows % frequency of winds around the compass 1 Global Circulation
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS)
 Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
Atmospheric Science-ATS (ATS) 1 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE-ATS (ATS) Courses ATS 150 Science of Global Climate Change Credits: 3 (3-0-0) Physical basis of climate change. Energy budget of the earth, the greenhouse
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN
 MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon
 Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon B. N. Goswami (goswami@tropmet.res.in) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Annual mean Temp. over India 1875-2004 Kothawale, Roopakum
Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon B. N. Goswami (goswami@tropmet.res.in) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Annual mean Temp. over India 1875-2004 Kothawale, Roopakum
EST 5101 Climate Change Science Chapter 5. Climate Models. Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology
 EST 5101 Climate Change Science Chapter 5. Climate Models Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline overview of climate modelling; How Are
EST 5101 Climate Change Science Chapter 5. Climate Models Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline overview of climate modelling; How Are
IV. Atmospheric Science Section
 EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
EAPS 100 Planet Earth Lecture Topics Brief Outlines IV. Atmospheric Science Section 1. Introduction, Composition and Structure of the Atmosphere Learning objectives: Understand the basic characteristics
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
First results from a new observational system over the Indian seas
 PERSPECTIVES ON OCEAN RESEARCH IN INDIA First results from a new observational system over the Indian seas K. Premkumar, M. Ravichandran, S. R. Kalsi*, Debasis Sengupta** and Sulochana Gadgil**, National
PERSPECTIVES ON OCEAN RESEARCH IN INDIA First results from a new observational system over the Indian seas K. Premkumar, M. Ravichandran, S. R. Kalsi*, Debasis Sengupta** and Sulochana Gadgil**, National
Weather and Climate Basics
 Aims of this presentation Weather and Climate Basics To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
Aims of this presentation Weather and Climate Basics To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Weather and Climate Basics
 Weather and Climate Basics Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology Aims of this presentation To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
Weather and Climate Basics Laura Boekel Forecaster at Bureau of Meteorology Aims of this presentation To describe what I do as a forecaster at the Bureau of Meteorology To provide an interesting introduction
Meteorology Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Basic Concepts of Meteorology Unit 2: The Atmosphere in Motion
 Meteorology Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Basic Concepts of Meteorology Unit 2: The Atmosphere in Motion NOTE: Meteorology is a one semester course designed for students interested in understanding the complex
Meteorology Curriculum Maps Unit 1: Basic Concepts of Meteorology Unit 2: The Atmosphere in Motion NOTE: Meteorology is a one semester course designed for students interested in understanding the complex
Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380
 Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380 Course web site http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/2011q1/380/ Instructor: Professor Cecilia Bitz, PhD in UW atmospheric sciences 1997 Lecture notes
Weather and Climate Prediction ATM S 380 Course web site http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/2011q1/380/ Instructor: Professor Cecilia Bitz, PhD in UW atmospheric sciences 1997 Lecture notes
Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Climate & Earth System Science. Atmosphere Ocean Interactions. A: Structure of the Ocean.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Weather Forecasting Principles I
 Weather Forecasting Principles I Isaac Mugume Lecturer Notes MET 2202 April 6, 2017 Isaac Mugume (Mak) Lecture No.02 April 6, 2017 1 / 52 Review of Previous Lecture Isaac Mugume (Mak) Lecture No.02 April
Weather Forecasting Principles I Isaac Mugume Lecturer Notes MET 2202 April 6, 2017 Isaac Mugume (Mak) Lecture No.02 April 6, 2017 1 / 52 Review of Previous Lecture Isaac Mugume (Mak) Lecture No.02 April
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department
 Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
What has ECMWF done for us? David Burridge (ghost of the past) Inspired by Monty Python s sketch What have the Romans done from us?
 What has ECMWF done for us? David Burridge (ghost of the past) Inspired by Monty Python s sketch What have the Romans done from us? REG: All right, but apart from the sanitation, the medicine, education,
What has ECMWF done for us? David Burridge (ghost of the past) Inspired by Monty Python s sketch What have the Romans done from us? REG: All right, but apart from the sanitation, the medicine, education,
The Emergence of Numerical Weather Prediction:
 The Emergence of Numerical Weather Prediction: Fulfilment of a Dream & Realization of a Fantasy Peter Lynch School of Mathematics & Statistics University College Dublin Mathematics of Planet Earth Jamboree
The Emergence of Numerical Weather Prediction: Fulfilment of a Dream & Realization of a Fantasy Peter Lynch School of Mathematics & Statistics University College Dublin Mathematics of Planet Earth Jamboree
Chapter 5: Weather. Only Section 1: What is Weather?
 Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
Chapter 5: Weather Only Section 1: What is Weather? Find the definitions of: Meteorology, meteorologist, weather, climate Not in book? Use the dictionaries **Meteorology - Meteorology is the study of the
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
CHAPTER 13 WEATHER ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The atmosphere is a continuous fluid that envelops the globe, so that weather observation, analysis, and forecasting require international
TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors
 TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts http://www.ecmwf.int Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) 1 ECMWF
TC/PR/RB Lecture 3 - Simulation of Random Model Errors Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts http://www.ecmwf.int Roberto Buizza (buizza@ecmwf.int) 1 ECMWF
ABSTRACT 3 RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION IN BJRUC 3.1 ASSIMILATION STRATEGY OF RADIAL
 REAL-TIME RADAR RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS IN A PRE-OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK IN NORTH CHINA Min Chen 1 Ming-xuan Chen 1 Shui-yong Fan 1 Hong-li Wang 2 Jenny Sun 2 1 Institute of Urban Meteorology,
REAL-TIME RADAR RADIAL VELOCITY ASSIMILATION EXPERIMENTS IN A PRE-OPERATIONAL FRAMEWORK IN NORTH CHINA Min Chen 1 Ming-xuan Chen 1 Shui-yong Fan 1 Hong-li Wang 2 Jenny Sun 2 1 Institute of Urban Meteorology,
Lecture 8. Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall
 Lecture 8 Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall According to the second hypothesis, the monsoon is a manifestation of the seasonal variation of the tropical circulation
Lecture 8 Monsoons and the seasonal variation of tropical circulation and rainfall According to the second hypothesis, the monsoon is a manifestation of the seasonal variation of the tropical circulation
2. Outline of the MRI-EPS
 2. Outline of the MRI-EPS The MRI-EPS includes BGM cycle system running on the MRI supercomputer system, which is developed by using the operational one-month forecasting system by the Climate Prediction
2. Outline of the MRI-EPS The MRI-EPS includes BGM cycle system running on the MRI supercomputer system, which is developed by using the operational one-month forecasting system by the Climate Prediction
Why There Is Weather?
 Lecture 6: Weather, Music Of Our Sphere Weather and Climate WEATHER The daily fluctuations in atmospheric conditions. The atmosphere on its own can produce weather. (From Understanding Weather & Climate)
Lecture 6: Weather, Music Of Our Sphere Weather and Climate WEATHER The daily fluctuations in atmospheric conditions. The atmosphere on its own can produce weather. (From Understanding Weather & Climate)
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models
 ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
WEATHER FORECASTING Acquisition of Weather Information WFO Regions Weather Forecasting Tools Weather Forecasting Tools Weather Forecasting Methods
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 WEATHER FORECASTING Chapter 13 Acquisition of Weather Information 10,000 land-based stations, hundreds of ships and buoys; four times a day, airports hourly Upper level: radiosonde, aircraft,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 WEATHER FORECASTING Chapter 13 Acquisition of Weather Information 10,000 land-based stations, hundreds of ships and buoys; four times a day, airports hourly Upper level: radiosonde, aircraft,
1. Weather and climate.
 Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
WEATHER FORECASTING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 8 Ahrens: Chapters 12 and 13; A&B: Chapters 10 and 13
 WEATHER FORECASTING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 8 Ahrens: Chapters 12 and 13; A&B: Chapters 10 and 13 Assignment 3 Continents cause small-scale circulations (land/sea breezes) due to differential heating. How
WEATHER FORECASTING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 8 Ahrens: Chapters 12 and 13; A&B: Chapters 10 and 13 Assignment 3 Continents cause small-scale circulations (land/sea breezes) due to differential heating. How
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Advanced Hydrology. (Web course)
 Advanced Hydrology (Web course) Subhankar Karmakar Assistant Professor Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering (CESE) Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076 Email: skarmakar@iitb.ac.in
Advanced Hydrology (Web course) Subhankar Karmakar Assistant Professor Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering (CESE) Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076 Email: skarmakar@iitb.ac.in
Logistics. Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Requests for: Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu
 Logistics Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Requests for: Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu Introduction to Numerical Weather Prediction Thanks: Tom Warner, NCAR A bit
Logistics Goof up P? R? Can you log in? Teragrid yes? NCSA no? Requests for: Anders Colberg Syrowski Curtis Rastogi Yang Chiu Introduction to Numerical Weather Prediction Thanks: Tom Warner, NCAR A bit
2) What general circulation wind belt is the place of origin for hurricanes? A) westerlies B) trade winds C) doldrums D) horse latitudes
 Meteo 1010 Homework 6 1) What is the difference between a typhoon and a hurricane? A) A hurricane is a true tropical cyclone, but a typhoon is not. B) A hurricane is stronger than a typhoon. C) They represent
Meteo 1010 Homework 6 1) What is the difference between a typhoon and a hurricane? A) A hurricane is a true tropical cyclone, but a typhoon is not. B) A hurricane is stronger than a typhoon. C) They represent
Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton
 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each & Q. 10 Q. 22 carry two marks each. Q.1 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere among inert gases is (A) Helium (B) Argon (C) Neon (D) Krypton Q.2 The pair of variables that
Weather What is weather? Weather. is the study of our atmosphere. Atmosphere literally means vapor (atmos) of a sphere.
 Weather What is weather? Weather is the study of our atmosphere. Atmosphere literally means vapor (atmos) of a sphere. Our atmosphere is made up of 4 basic layers: The outermost layer is the thermosphere
Weather What is weather? Weather is the study of our atmosphere. Atmosphere literally means vapor (atmos) of a sphere. Our atmosphere is made up of 4 basic layers: The outermost layer is the thermosphere
Steady Flow: rad conv. where. E c T gz L q 2. p v 2 V. Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: rad TOA rad conv surface
 The Three-Dimensional Circulation 1 Steady Flow: F k ˆ F k ˆ VE 0, rad conv where 1 E c T gz L q 2 p v 2 V Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: VE F FF F 0 rad TOA rad conv surface 2 What causes
The Three-Dimensional Circulation 1 Steady Flow: F k ˆ F k ˆ VE 0, rad conv where 1 E c T gz L q 2 p v 2 V Integrate from surface to top of atmosphere: VE F FF F 0 rad TOA rad conv surface 2 What causes
Vertical wind shear in relation to frequency of Monsoon Depressions and Tropical Cyclones of Indian Seas
 Vertical wind shear in relation to frequency of Monsoon Depressions and Tropical Cyclones of Indian Seas Prince K. Xavier and P.V. Joseph Department of Atmospheric Sciences Cochin University of Science
Vertical wind shear in relation to frequency of Monsoon Depressions and Tropical Cyclones of Indian Seas Prince K. Xavier and P.V. Joseph Department of Atmospheric Sciences Cochin University of Science
Computational challenges in Numerical Weather Prediction
 Computational challenges in Numerical Weather Prediction Mike Cullen Oxford 15 September 2008 Contents This presentation covers the following areas Historical background Current challenges Why does it
Computational challenges in Numerical Weather Prediction Mike Cullen Oxford 15 September 2008 Contents This presentation covers the following areas Historical background Current challenges Why does it
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte
 Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
Graduate Courses Meteorology / Atmospheric Science UNC Charlotte In order to inform prospective M.S. Earth Science students as to what graduate-level courses are offered across the broad disciplines of
The WMO Global Basic Observing Network (GBON)
 The WMO Global Basic Observing Network (GBON) A WIGOS approach to securing observational data for critical global weather and climate applications Robert Varley and Lars Peter Riishojgaard, WMO Secretariat,
The WMO Global Basic Observing Network (GBON) A WIGOS approach to securing observational data for critical global weather and climate applications Robert Varley and Lars Peter Riishojgaard, WMO Secretariat,
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate
 Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Tornado Alley (K-12) Virginia Standards of Learning. Kindergarten. Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic. Force, Motion, and Energy
 Kindergarten K.1 The student will conduct investigations in which a) basic properties of objects are identified by direct observation; b) observations are made from multiple positions to achieve different
Kindergarten K.1 The student will conduct investigations in which a) basic properties of objects are identified by direct observation; b) observations are made from multiple positions to achieve different
3/31/17. No CLASS FRIDAY. End of subsidence unit. Next up: SEVERE WEATHER. Video - Severe Weather (Tornadoes) #23 - Weather - Principles I
 No CLASS FRIDAY End of subsidence unit Next up: SEVERE WEATHER Exam 2: Wednesday April 5 th 7:15 PM, 141+151 Loomis Web Exercise #4 (Landslides): Due Today 11:59 PM Writing Assignment Information will
No CLASS FRIDAY End of subsidence unit Next up: SEVERE WEATHER Exam 2: Wednesday April 5 th 7:15 PM, 141+151 Loomis Web Exercise #4 (Landslides): Due Today 11:59 PM Writing Assignment Information will
Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and Production Association "Typhoon" 4 Pobedy Street, , Obninsk, Kaluga Region, Russia.
 DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
EVALUATION OF BROAD SCALE VERTICAL CIRCULATION AND THERMAL INDICES IN RELATION TO THE ONSET OF INDIAN SUMMER MONSOON
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 22: 649 661 (2002) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.742 EVALUATION OF BROAD SCALE VERTICAL CIRCULATION
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 22: 649 661 (2002) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/joc.742 EVALUATION OF BROAD SCALE VERTICAL CIRCULATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE WEATHER FORECAST PROCESS WITH EMPHASIS ON FORECAST UNCERTAINTY. Zoltan Toth
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE WEATHER FORECAST PROCESS WITH EMPHASIS ON FORECAST UNCERTAINTY Zoltan Toth Environmental Modeling Center NOAA/NWS/NCEP USA Acknowledgements: Steve Lord, David Helms, Geoff DiMego,
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE WEATHER FORECAST PROCESS WITH EMPHASIS ON FORECAST UNCERTAINTY Zoltan Toth Environmental Modeling Center NOAA/NWS/NCEP USA Acknowledgements: Steve Lord, David Helms, Geoff DiMego,
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS. Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 1850
 CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
CHAPTER 2 DATA AND METHODS Errors using inadequate data are much less than those using no data at all. Charles Babbage, circa 185 2.1 Datasets 2.1.1 OLR The primary data used in this study are the outgoing
Class Outline, Class #8, 9 February ) Review 2) Today s topics - Climate and Weather forecast models - Dynamical Downscaling 3) Project
 Class Outline, Class #8, 9 February 2017 1) Review 2) Today s topics - Climate and Weather forecast models - Dynamical Downscaling 3) Project Discussion Review Given a column of air, what processes determine
Class Outline, Class #8, 9 February 2017 1) Review 2) Today s topics - Climate and Weather forecast models - Dynamical Downscaling 3) Project Discussion Review Given a column of air, what processes determine
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. In order to make forecasts, meteorologists must gather accurate weather
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 4, Day 1 1 Outcomes for Today PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. In order to make forecasts, meteorologists must gather accurate weather
4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explore this Phenomena. The same sun shines on the entire Earth. Explain why these two areas have such different climates.
 Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather. David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder
 Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder Quick overview of climate and weather models Weather models
Possible Applications of Deep Neural Networks in Climate and Weather David M. Hall Assistant Research Professor Dept. Computer Science, CU Boulder Quick overview of climate and weather models Weather models
Analyzing/Forecasting Weather
 Analyzing/Forecasting Weather Focus Question Dude Its wind. It blows everywhere. Meteorologist to Nicholas Cage in The Weatherman VA SOL SOL 3 The student will investigate and understand how to read and
Analyzing/Forecasting Weather Focus Question Dude Its wind. It blows everywhere. Meteorologist to Nicholas Cage in The Weatherman VA SOL SOL 3 The student will investigate and understand how to read and
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS
 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
Version date 2/10/15. Disciplinary Core Ideas (Framework)
 1 What is Weather? 1 Into the Weather Students delve into the question, What is weather? They view video segments of severe weather, and generate inquiry questions stimulated by the video and discussions.
1 What is Weather? 1 Into the Weather Students delve into the question, What is weather? They view video segments of severe weather, and generate inquiry questions stimulated by the video and discussions.
The Australian Summer Monsoon
 The Australian Summer Monsoon Aurel Moise, Josephine Brown, Huqiang Zhang, Matt Wheeler and Rob Colman Australian Bureau of Meteorology Presentation to WMO IWM-IV, Singapore, November 2017 Outline Australian
The Australian Summer Monsoon Aurel Moise, Josephine Brown, Huqiang Zhang, Matt Wheeler and Rob Colman Australian Bureau of Meteorology Presentation to WMO IWM-IV, Singapore, November 2017 Outline Australian
Status of Indian Satellite Meteorological Programme
 Status of Indian Satellite Meteorological Programme Pradeep K Thapliyal Space Applications Centre (SAC) Indian Space research Organisation (ISRO) Ahmedabad (INDIA) Email: pkthapliyal@sac.isro.gov.in International
Status of Indian Satellite Meteorological Programme Pradeep K Thapliyal Space Applications Centre (SAC) Indian Space research Organisation (ISRO) Ahmedabad (INDIA) Email: pkthapliyal@sac.isro.gov.in International
AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS
 AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS James Hall JHTech PO Box 877 Divide, CO 80814 Email: jameshall@jhtech.com Jeffrey Hall JHTech
AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS James Hall JHTech PO Box 877 Divide, CO 80814 Email: jameshall@jhtech.com Jeffrey Hall JHTech
NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS USING CLOUD MOTION WINDS AT ECMWF GRAEME KELLY. ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading ABSTRACT
 NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS USING CLOUD MOTION WINDS AT ECMWF GRAEME KELLY ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading ABSTRACT Recent monitoring of cloud motion winds (SATOBs) at ECMWF has shown an improvement in quality.
NUMERICAL EXPERIMENTS USING CLOUD MOTION WINDS AT ECMWF GRAEME KELLY ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading ABSTRACT Recent monitoring of cloud motion winds (SATOBs) at ECMWF has shown an improvement in quality.
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR
 CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
CHAPTER 8 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF THE ITCZ OVER THE INDIAN OCEAN AND INDONESIA DURING A NORMAL YEAR AND DURING AN ENSO YEAR In this chapter, comparisons between the model-produced and analyzed streamlines,
Weather and Climate 1. Elements of the weather
 Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Weather and Climate 1 affect = to have an effect on, influence, change altitude = the height of a place above the sea axis = the line around which an object rotates certain = special consist of = to be
Introduction to Data Assimilation
 Introduction to Data Assimilation Alan O Neill Data Assimilation Research Centre University of Reading What is data assimilation? Data assimilation is the technique whereby observational data are combined
Introduction to Data Assimilation Alan O Neill Data Assimilation Research Centre University of Reading What is data assimilation? Data assimilation is the technique whereby observational data are combined
surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight,
 The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
The air that we breathe comes from the atmosphere, a thin gaseous layer that surrounds Earth and protects it somewhat from solar radiation. Like all other matter, air has weight, but this weight varies
Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water Vapor with High and its Impact on Cloud Cover
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V1 PP 06-13 www.iosrjen.org Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 01 (January. 2016), V1 PP 06-13 www.iosrjen.org Change of Dew Point Temperature and Density of Saturated Water
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere
 Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Guided Notes: Atmosphere Layers of the Atmosphere Atmosphere: Absorbs solar radiation, Burns up meteors, transports and recycles water, and other chemicals, and moderates climate Main Components: o Meteorology
Chapter 13: Weather Forecasting
 Chapter 13: Weather Forecasting Forecasting is like driving a car down the road where you are only allowed to look out the back window. - Source unknown Utility of weather forecasts Weather observations
Chapter 13: Weather Forecasting Forecasting is like driving a car down the road where you are only allowed to look out the back window. - Source unknown Utility of weather forecasts Weather observations
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter
 Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of. BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic. Games 2008
 A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic Games 2008 Min Chen 1, Shui-yong Fan 1, Jiqin Zhong 1, Xiang-yu Huang 2, Yong-Run Guo 2, Wei
A WRF-based rapid updating cycling forecast system of BMB and its performance during the summer and Olympic Games 2008 Min Chen 1, Shui-yong Fan 1, Jiqin Zhong 1, Xiang-yu Huang 2, Yong-Run Guo 2, Wei
Suppressed Surface Heating over northwestern parts of the Country and the ensuing Monsoon Rainfall
 Suppressed Surface Heating over northwestern parts of the Country and the ensuing Monsoon Rainfall During this year, the temperatures have been below normal over north and northwestern parts of India.
Suppressed Surface Heating over northwestern parts of the Country and the ensuing Monsoon Rainfall During this year, the temperatures have been below normal over north and northwestern parts of India.
Atmospheric Processes
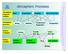 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Implementation of global surface index at the Met Office. Submitted by Marion Mittermaier. Summary and purpose of document
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPAG on DPFS MEETING OF THE CBS (DPFS) TASK TEAM ON SURFACE VERIFICATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND 20-21 OCTOBER 2014 DPFS/TT-SV/Doc. 4.1a (X.IX.2014)
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPAG on DPFS MEETING OF THE CBS (DPFS) TASK TEAM ON SURFACE VERIFICATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND 20-21 OCTOBER 2014 DPFS/TT-SV/Doc. 4.1a (X.IX.2014)
