2014 Penn State Weather Camp
|
|
|
- Patience Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2014 Penn State Weather Camp National Weather Service Presentation N A T I O N A L W E A T H E R S E R V I C E S T A T E C O L L E G E, P A P E T E R J U N G W A R N I N G C O O R D I N A T I O N M E T E O R O L O G I S T P E T E R. J U N N O A A. G O V
2 A little bit about the National Weather Service National Weather Service Our parent agency is NOAA National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration NWS (and NOAA) fall under the Department of Commerce Federal agency Tax-payer supported
3 Does Weather have an Impact? Weather related damages exceed $20 billion per year 70% of all travel delays weather related Economic impact (direct impacts, delays, loss of work, etc.) on the U.S. over $3 trillion per year 97+% of all Presidentially declared disasters are weather related Super snowstorms, Hurricanes (Lee, Irene, Sandy, etc.), Severe thunderstorms and Tornadoes, Flash flooding.
4 The Mission of the National Weather Service Primary Mission: Provide Weather, Hydrologic and Climate Forecasts and Warnings for the Protection of Life and Property Secondary Mission Objectives: Enhance the National Economy Provide a National Information Database which can be used by other government agencies, the private sector, and the Global Community
5 Who is the National Weather Service Organization Local Offices 123 Local Weather Forecast Offices Five offices serve Pennsylvania 13 River Forecast Centers Two serve Pennsylvania 6 Regional Offices Eastern, Central Southern, Western, Alaska and Pacific NWS Headquarters Silver Spring, MD 9 National Centers (NCEP) AWC Aviation Weather Center CPC Climate Prediction Center EMC Environmental Modeling Center NCO NCEP Central Operations NHC National Hurricane Center OPC Ocean Prediction Center SPC Storm Prediction Center SWPC Space Weather Prediction Center WPC Weather Prediction Center
6 Where are all those Local Offices?
7 Pennsylvania Counties and Corresponding National Weather Service Offices YOU ARE HERE
8 A look at the local office Staffing: ~25 persons 10 full-time forecasters 3 interns 5 technicians 5 specialists in science, outreach, observing program and hydrology Open 24x7x365
9 Key Pieces of Equipment Satellite Doppler Radar Remote Sensing Equipment Powerful Computers
10 SkyWarn Spotter Program In addition to all our remote sensing equipment, we use a VOLUNTEER group of TRAINED public citizens that observe and report weather to the NWS to: Supplement remote sensing equipment Provide real-time ground truth reports Add credibility to NWS products and services The SkyWarn program is NOT a storm-chasing network! SkyWarn Spotters act as thousands of eyes and ears out in the field, supporting our forecast and warning program!
11 NWS Products: A Three Tiered Approach Outlooks Time To Event Watches Warnings/ Advisories Confidence in the forecast
12 Weather Definitions and Terms OUTLOOK A long term product (generally 3 to 7 days) Heads-up of something potential on the horizon Our confidence level is about % WATCH Conditions are FAVORABLE for a given weather event to occur, but not imminent Generally 6 hours to as much as 2 days Severe Thunderstorm, Tornado, Flood, High Wind, Snow, etc. Our confidence level is at about %
13 Weather Definitions and Terms OUTLOOK A long term product (generally 3 to 7 days) Heads-up of something potential on the horizon Our confidence level is about 30% WATCH Conditions are FAVORABLE for a given weather event to occur, but not imminent Generally 6 hours to as much as 2 days Severe Thunderstorm, Tornado, Flood, High Wind, Snow, etc. Our confidence level is at about %
14 Weather Definitions and Terms OUTLOOK A long term product (generally 3 to 7 days) Heads-up of something potential on the horizon Our confidence level is about 30% WATCH Conditions are FAVORABLE for a given weather event to occur, but not imminent Generally 6 hours to as much as 2 days Severe Thunderstorm, Tornado, Flood, High Wind, Snow, etc. Our confidence level is at about 50%
15 Weather Definitions and Terms ADVISORY A shorter term product, mainly 0 24 hours High confidence that a weather event will occur, but with limited impacts Lighter snow and ice events, strong (but not severe) wind events, etc. Our confidence level is about % WARNING A shorter term product, mainly 0 to 24 hours High confidence that a significant, high impact, and potentially life threatening condition will take place Severe Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, Flash Floods, Heavy Snow/Ice, etc. Our confidence level is at about %
16 Weather Definitions and Terms ADVISORY A shorter term product, mainly 0 24 hours High confidence that a weather event will occur, but with limited impacts Lighter snow and ice events, strong (but not severe) wind events, etc. Our confidence level is about 80% WARNING A shorter term product, mainly 0 to 24 hours High confidence that a significant, high impact, and potentially life threatening condition will take place Severe Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, Flash Floods, Heavy Snow/Ice, etc. Our confidence level is at about 80%
17 Thunderstorms R E V I E W O F A L I F E C Y C L E O F A T H U N D E R S T O R M
18 Lifecycle of a Thunderstorm Developing Stage Dominated by UPWARD MOVING air Extends vertically to 10,000 to 20,000 ft No Severe Weather at this stage Depending on atmospheric conditions, this may (or may not) develop into a thunderstorm
19 Lifecycle of a Thunderstorm Mature Stage Storm contains UPWARD and DOWNWARD moving air Extends vertically to 40,000 to 60,000 ft Best potential for severe weather including hail at this stage With rotation, this can lead to a tornado
20 Lifecycle of a Thunderstorm Dissipating Stage Storm contains mostly DOWNWARD moving air Supply of warm moist air fuel has been exhausted or cut off Transition from mature to dissipating stages best time for Downbursts to occur
21 Types of Thunderstorms
22 QUIZ Pulse Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
23 QUIZ Pulse Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
24 QUIZ Pulse Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
25 QUIZ Pulse Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
26 QUIZ Pulse Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
27 Types of Thunderstorms Back-Building Storms Characteristics: Multiple Cells...where each cell generates a cold outflow that triggers a gust front Severe potential is higher than pulse storms Good potential Flash Flood producers Cells may propagate (new cells form) different direction from the movement of overall storm system Training Echoes Johnstown Flood
28 Johnstown Area Prone to Devastating Flash Floods May 1889 March 1936 July 1977
29 May 31, fatalities
30 March 17, 1936 St. Patrick s Day Flood - 25 deaths homeless - $50 million in damages - Heavy rain and snowmelt - Water 14 feet deep in downtown Johnstown
31 July 19-20, Over 12 inches of rain from training MCS, eventual failure of the Laurel Run Dam and seven others! - 78 lives lost - 50,000 homeless - $200 million in damages
32 QUIZ Multicell Line or Squall Line Type Characteristics: Multicell Thunderstorm complex in a line Severe potential is higher than pulse storms Best Severe Potential is: Strong Wind Hail Tornadoes Flooding
33 QUIZ Multicell Line or Squall Line Type Characteristics: Multicell Thunderstorm complex in a line Severe potential is higher than pulse storms Best Severe Potential is: Strong Wind Hail Tornadoes Flooding
34 QUIZ Supercell Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
35 QUIZ Supercell Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
36 QUIZ Supercell Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
37 QUIZ Supercell Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds (Downburst) Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
38 QUIZ Supercell Type Characteristics: Average Lifespan:? minutes 1 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours > 6 hours Severe Potential? Low Moderate High Most significant threat? High winds (Downburst) Tornadoes Hail Flooding Wind Shear Environment? Weak Strong
39 Severe Thunderstorms and Damage S T R A I G H T L I N E W I N D S D O W N B U R S T S M I C R O B U R S T S M A C R O B U R S T S T O R N A D O D E R E C H O
40 Severe Thunderstorms Definition: A thunderstorm producing Winds in excess of 58?? mph, structural damage, or large hail greater than?? 1 inch in diameter Lightning, no matter how frequent or deadly is NOT a measure of a Severe Thunderstorm
41 Straight Line Winds Probably the most common wind damage type in Pennsylvania Often the result of a Squall Line Result from a combination of the forward movement of the storm, and transport of high winds aloft down to the surface. Straight line winds may occur ahead of the actual storm at the leading edge (or gust front)
42 Straight Line Winds 35 mph winds at 5000 feet + Cold Front moving at 30 mph = Surface wind gusts of 65 mph
43 Straight Line Winds Straight Line Winds As the name implies...damaging winds produce damage in a unidirectional pattern Not as glamorous as a tornado in name...but can be far more destructive Often covers a large geographic area with many damage reports
44 Straight Line Winds Straight Line Winds Do not be fooled by the extent or intensity of damage, or by the structures the wind affects. Roofs blown off barns/houses, uprooted trees, and even twisted trees are not necessarily an indicator of a tornado Straight Line Winds can easily exceed 100 mph!
45 Radar Loop Straight Line Winds
46 Straight Line Winds
47 Damage shows a clear UNI-DIRECTIONAL pattern STRAIGHT LINE WINDS STRAIGHT LINE WIND fingerprint
48 Downburst Winds The second most common damaging winds in Pennsylvania Unlike straight-line-winds, Downbursts are formed by the outrush of air from aloft brought down by the thunderstorm Damage can be more concentrated than Straight Line Winds Winds can exceed 150 mph...that s the equivalent of an EF3 Tornado!
49 Downburst Downbursts can be as destructive IF NOT MORE destructive than tornadoes Often cover much larger areas than a tornado Are much more common than tornadoes Downbursts, by their nature, are winds diverging on the ground While trees and damage may be oriented in different directions, they show a pattern of emerging outward from a central point These can cause significant tree and structural damage. More often than not, a very large damage path is indicative of a Downburst rather than a Tornado
50 Downburst Damage to NWS Radar We are not Immune! Built to withstand 134 mph winds
51 Downburst / Microburst / Macroburst Downburst: Generic term for downward moving air that spreads out when it reaches the ground Microburst Term for a Downburst less than 2.5 miles in extent Macroburst Term for a Downburst grater than 2.5 miles in extent These terms all describe the same mechanism, and only are differentiated by the size and scope of the damage
52 DOWNBURST
53
54 Central PA Downburst Wind Event (04/19/13) Dauphin County Doppler Reflectivity (around 6:20 pm EDT) showing a fairly straight line of storms.
55 Central PA Downburst Wind Event (04/19/13) Dauphin County Doppler Reflectivity (around 6:37 pm EDT) showing a bowing out segment of the line of storms, a good indicator of accelerating winds and a fingerprint of a Downburst wind event.
56
57 Radar Loop Downburst
58
59 DOWNBURST Damage shows a clear DIVERGING pattern DOWNBURST fingerprint
60 Tornado Very specialized wind event It takes unique conditions aloft in the storm, and very close to the ground, to produce a Tornado 1 in 100 thunderstorms are severe, and on average 1 in 100 severe thunderstorms produce Tornadoes Pennsylvania sees about 15 tornadoes per year. Tornadoes usually produce a very small and defined area of damage (path) THE DEGREE OF DAMAGE DOES NOT INDICATE WHETHER OR NOT THERE WAS A TORNADO!
61
62 Tornadoes
63 A look at a Tornado on Doppler Radar Tornado Winds Much different than Straight Line and Downburst Winds Pattern of Damage shows CONVERGENCE...winds being pulled into the center of the tornado
64 Tornado Is it always that easy? NO! A key is to see where the rotation is, and what is it doing with time! Lots of storms show mid and upper level rotation
65 Tornado Another KEY question: Is the atmosphere near the ground primed for tornadoes? Right conditions of moisture and shear need to be present!
66 Tornadoes Some Terms Wall Cloud Rotating lowering (and often rainfree) section of a thunderstorm. ROTATION IS THE KEY!!!! Sign that conditions within the storm are right for producing a tornado But what are the low level conditions below the storm??? A Wall Cloud, while looking impressive, is not causing damage!
67 Funnel Cloud Funnel Cloud Fast spinning funnel descending from the thunderstorm cloud...but NOT YET REACHING THE GROUND! ROTATION IS THE KEY!!!! Sign that conditions within the storm are right for producing a tornado Again, what about conditions below the storm? A Funnel Cloud, while looking very impressive, is NOT causing damage. It may become a tornado soon!
68 Tornadoes Tornado Tornado Rapidly rotating funnel of air IN CONTACT WITH THE GROUND! ROTATION, STILL, IS THE KEY!!!! Look for Damage: No Damage = No Tornado!
69
70 Campbelltown Tornado July 14, 2004
71 Campbelltown Tornado (SRM)
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86 TORNADO Damage shows a clear CRISS-CROSS pattern TORNADO fingerprint
87 TORNADO Damage shows a clear CONVERGENT pattern TORNADO fingerprint TORNADO fingerprint Damage shows a clear CYCLONIC turning
88 TORNADO Enhanced Fujita Scale Used to Estimate Winds in a tornado Based on after-the-fact damage surveys Expected wind speeds based on engineering studies NOTE: The EF-Scale is a reworking of the F-Scale introduced decades ago Wind Speeds adjusted to reflect more accurate measurements EF- Scale Wind Speed EF EF EF EF EF EF
89 Be wary of Tornado look-a-likes Wall Clouds Make sure they are rotating and connected to the cloud base! Funnel Clouds Again, look for rotation...not just a cloud that looks like a funnel Tornado What damage is it producing Debris! Which way is it moving
90
91 Pennsylvania Tornadoes through the Years
92 COMMON TORNADO MYTHS Myth: Trees laying in different directions must mean tornado damage. The direction trees are laying can be influenced by things like tree type, tree bark, size of tree, amount of foliage, wind load, root structure, and soil conditions. Local terrain can influence the wind direction and change the way trees are blown down. Branches or trunks can lay in different directions if there is tree rot causing weak or failure points. Myth: "Projectiles" automatically suggest a tornado. While projectiles are common from a tornado, straight line wind (especially a downburst) can throw debris down wind and produce projectiles. Myth: A "roaring" sound suggests a tornado. Witnesses often describe a "roaring" or freight train sound with a tornado but that sound can also occur from straight line winds as they pass through trees, forests, or terrain. Those who have been struck by a tornado also describe a high-pitch whine or squeal sound as it hits. Myth: Damage = Tornado! Not all damage is tornado related. More times than not it is simply straight-line wind. The severe thunderstorm that produces a tornado (usually a Supercell) often produces straight line wind damage as well. It is very common to have both types of damage related to the same parent thunderstorm in different areas.
93 COMMON TORNADO MYTHS Myth: Uprooted trees are only caused by Severe Thunderstorms (gusts of 58 mph or higher). Root structure can make a big difference. Shallow roots may allow the tree to topple much easier. Soil type and moisture content can also allow a tree to uproot with winds well below 58 mph. Tree rot can cause branches or entire trees to be toppled with relatively weak wind speeds. Myth: Structures explode in a tornado due to lower pressure. Structures are torn apart in a tornado from the wind or from the impact of debris. Myth: Twisting automatically means a tornado hit. Not true. Houses, for example, are usually impacted by wind in one primary direction due to the size of the tornado. You need to examine the entire area impacted. Another example is stop signs you can see these twist in strong winds even without a tornado.
94 Derecho Derecho Extreme Straight Line Wind (Bow Echo) that covers a huge area 250+ miles long Lasting at least 6 hours May 21, 2004
95 June 30, 2012
96 Derecho Another Look with Velocity
97
98 Portable deck used for concerts was lifted and blown away at Hershey Park 06/29/2012
99 Straight Line (Derecho) Wind Damage near Hershey, PA 06/29/2012
100 Straight Line (Derecho) Wind Damage near Hershey, PA 06/29/2012
101 Hail
102 Hail forms in the region BETWEEN the upward moving air and downward moving air The idealized Supercell
103 Hail Storm May 22, 2014
104 Hail Storm May 22, 2014
105 Flooding R I V E R F L O O D S F L A S H F L O O D S
106 River Flooding Forecasts handled by the River Forecast Center These are for specific, gauged locations along Main Stem Rivers and large tributaries Locations where it takes more than 6 hours for the waterway to respond to heavy rainfall Many streams and creeks are ungauged, and are covered by Flood and Flash Flood products River Forecasts are driven by... Forecast Rainfall Soil conditions Snow Melt Temperatures Time of Year (foliage) Routing of upstream water Reservoir and Dam releases
107 Flash Flooding Rapid Rises on small (ungauged) streams and creeks Mainly driven by... Slow moving, heavy rain producing thunderstorms Repeated rainfall over the same area Dam Breaks Ice Jams These streams and creeks respond in minutes to a few hours after a heavy rain event Major threat to LIFE and PROPERTY
108 Flooding Fatalities
109 Flooding Fatalities
110 Flooding Fatalities
111 Flooding Fatalities
112
113 Is your bus driver crazy enough to do this?
114 A last word about Safety
115 SAFETY TORNADOES Never try and outrun a tornado Immediately get to a sturdy structure...if not...get out of your car! Do not take shelter under bridges or overpasses FLASH FLOODS Turn Around, Don t Drown...Don t drive through flooded roads As little as 18 inches of moving water can carry away most vehicles LIGHTNING Get in a hard-topped vehicle Don t use a corded phone Don t stand under a tall object
116 SAFETY DOWNBURST and HIGH WINDS Keep a firm grip on the steering wheel to maintain control If it can be done safely...point your vehicle into the direction of the wind Be prepared for sudden visibility restrictions In a building, move away from windows HAIL Get in a strong building Hard topped vehicles provide good protection for hail about golf ball sized. Larger hail will damage windshields.
117
HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1. Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266
 HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1 Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266 Violent Weather Thunderstorms Atmospheric turbulence Lightning and thunder Hail Derechos Tornadoes Tornado measurement and science Tropical Cyclones Hurricanes
HAZARDOUS WEATHER 1 Dr. Julie Laity Geography 266 Violent Weather Thunderstorms Atmospheric turbulence Lightning and thunder Hail Derechos Tornadoes Tornado measurement and science Tropical Cyclones Hurricanes
Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona. Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ
 Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ THUNDERSTORM FORMATION All thunderstorms result from the same necessary conditions
Severe Thunderstorm Forecasting and Climatology in Arizona Ken Drozd Warning Coordination Meteorologist NOAA/NWS Tucson, AZ THUNDERSTORM FORMATION All thunderstorms result from the same necessary conditions
Tornadoes. Be able to define what a tornado is. Be able to list several facts about tornadoes.
 Tornadoes Be able to define what a tornado is. Be able to list several facts about tornadoes. 1. Where do tornadoes most U.S. is # 1 occur in the world? Tornadoes are most common in Tornado Alley. Tornado
Tornadoes Be able to define what a tornado is. Be able to list several facts about tornadoes. 1. Where do tornadoes most U.S. is # 1 occur in the world? Tornadoes are most common in Tornado Alley. Tornado
THE IMPACT OF WEATHER
 The United States is the most severe weather prone country in the world. Each year, people in this country cope with an average of 10,000 thunderstorms, 5,000 floods, 1,200 tornadoes and two landfalling
The United States is the most severe weather prone country in the world. Each year, people in this country cope with an average of 10,000 thunderstorms, 5,000 floods, 1,200 tornadoes and two landfalling
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
Unit 4. This unit will enable you to improve coordination and communication with State and local agencies when hazardous weather threatens.
 Unit 4 This unit will enable you to improve coordination and communication with State and local agencies when hazardous weather threatens. In this unit we will discuss the role of Emergency Managers in
Unit 4 This unit will enable you to improve coordination and communication with State and local agencies when hazardous weather threatens. In this unit we will discuss the role of Emergency Managers in
Severe Weather Watches, Advisories & Warnings
 Severe Weather Watches, Advisories & Warnings Tornado Watch Issued by the Storm Prediction Center when conditions are favorable for the development of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes over a larger-scale
Severe Weather Watches, Advisories & Warnings Tornado Watch Issued by the Storm Prediction Center when conditions are favorable for the development of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes over a larger-scale
Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts. Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL
 Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL Why Do We Need Spotters? Radar has limitations, only spotters can provide view
Review of Basic Severe Thunderstorm & Tornado Spotting Concepts Jim Allsopp National Weather Service Chicago/Romeoville, IL Why Do We Need Spotters? Radar has limitations, only spotters can provide view
LECTURE #15: Thunderstorms & Lightning Hazards
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #15: Thunderstorms & Lightning Hazards Date: 1 March 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Severe Weather Hazards focus for next few weeks o somewhat
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #15: Thunderstorms & Lightning Hazards Date: 1 March 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Severe Weather Hazards focus for next few weeks o somewhat
COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM TORNADOES
 Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Severe Thunderstorms. MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms. MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms.
 MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms Damage Swath 1 2 MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Kona Lows Cause more flash floods in Hawaii than any
MET 200 Lecture 24 Severe Thunderstorms Damage Swath 1 2 MET 200 Lecture 24 Flooding in Hawaii and Intro to Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Kona Lows Cause more flash floods in Hawaii than any
Your Task: Read each slide then use the underlined red or underlined information to fill in your organizer.
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Thunderstorms and Lightning S6E4 d. Construct an explanation of the relationship between air pressure, weather fronts, and air masses and meteorological events
Severe Weather. Copyright 2006 InstructorWeb
 Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
Severe Weather People need to know what the weather is going to do. Sometimes severe weather can happen. Severe weather can cause property damage, injuries to people and animals, and even loss of life.
TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst
 THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
THUNDERSTORMS TOPICS: What are Thunderstorms? Ingredients Stages Types Lightning Downburst and Microburst What are Thunderstorms? A storm produced by a cumulonimbus cloud that contains lightning and thunder
Tornadoes. tornado: a violently rotating column of air
 Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
Tornadoes tornado: a violently rotating column of air Tornadoes What is the typical size of a tornado? What are typical wind speeds for a tornado? Five-stage life cycle of a tornado Dust Swirl Stage Tornado
Tornadoes pose a high risk because the low atmospheric pressure, combined with high wind velocity, can:
 Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms and may range in width from several
Chapter 3: Weather Fronts & Storms
 Chapter 3: Weather Fronts & Storms An AIR MASS is a large body of air that has similar characteristics (temperature, humidity) throughout. Air masses can be massively large. Air masses are classified by
Chapter 3: Weather Fronts & Storms An AIR MASS is a large body of air that has similar characteristics (temperature, humidity) throughout. Air masses can be massively large. Air masses are classified by
While all thunderstorms are dangerous, the National Weather Service (NWS) defines a severe thunderstorm as one that:
 While all thunderstorms are dangerous, the National Weather Service (NWS) defines a severe thunderstorm as one that: Produces hail at least three-quarters of an inch in diameter. Has winds of 58 miles
While all thunderstorms are dangerous, the National Weather Service (NWS) defines a severe thunderstorm as one that: Produces hail at least three-quarters of an inch in diameter. Has winds of 58 miles
1st Tornado Photograph
 Lecture 26 Part II Tornados Environment Storm Structure Life Cycle Source of Spin Forecasting Climatology Damage Marilee Thomas of Beaver City, NE took this photograph of her daughter Audra about two miles
Lecture 26 Part II Tornados Environment Storm Structure Life Cycle Source of Spin Forecasting Climatology Damage Marilee Thomas of Beaver City, NE took this photograph of her daughter Audra about two miles
Thunderstorm. Thunderstorms result from the rapid upward movement of warm, moist air.
 Severe Weather Thunderstorm A thunderstorm (aka an electrical storm, a lightning storm, or a thundershower) is a type of storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect, thunder.
Severe Weather Thunderstorm A thunderstorm (aka an electrical storm, a lightning storm, or a thundershower) is a type of storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect, thunder.
Chapter 14 Thunderstorm Fundamentals
 Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Chapter overview: Thunderstorm appearance Thunderstorm cells and evolution Thunderstorm types and organization o Single cell thunderstorms o Multicell thunderstorms o Orographic thunderstorms o Severe
Tornadoes. Tornadoes COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM TORNADOES
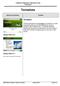 Tornadoes Tornadoes Tell the participants that tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms
Tornadoes Tornadoes Tell the participants that tornadoes are powerful, circular windstorms that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 200 miles per hour. Tornadoes typically develop during severe thunderstorms
10/21/2012. Chapter 10 Thunderstorms. Part II. Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification.
 Chapter 10 Thunderstorms Part I Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification Tornadoes Part II Simplified model depicting the life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm
Chapter 10 Thunderstorms Part I Growth and Development of ordinary Cell Thunderstorms Thunderstorm Electrification Tornadoes Part II Simplified model depicting the life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm
Severe Thunderstorms
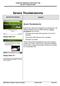 Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Explain that, while all thunderstorms are dangerous, the National Weather Service (NWS) defines a severe thunderstorm as one that: Display Slide Th-0 Produces
Severe Thunderstorms Severe Thunderstorms Explain that, while all thunderstorms are dangerous, the National Weather Service (NWS) defines a severe thunderstorm as one that: Display Slide Th-0 Produces
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather. (Chapt 15)
 Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
Thunderstorms and Severe Weather (Chapt 15) The Big Picture We ve emphasized horizontal transport of energy to balance the planetary energy budget: Hadley Cell Subtropical divergence Midlatitude cyclones
CHAPTER 10. TORNADOES AND WINDSTORMS
 CHAPTER 10. TORNADOES AND WINDSTORMS Wyoming, lying just west of tornado alley, is fortunate to experience less frequent and intense tornadoes than its neighboring states to the east. However, tornadoes
CHAPTER 10. TORNADOES AND WINDSTORMS Wyoming, lying just west of tornado alley, is fortunate to experience less frequent and intense tornadoes than its neighboring states to the east. However, tornadoes
Mark Fox Meteorologist NWS Fort Worth, TX
 Mark Fox Meteorologist NWS Fort Worth, TX Mark Fox Meteorologist NWS Fort Worth, TX What does severe really mean? Heavy Rain? Hail? Flooding? Wind? Lightning? What does severe really mean? Photo: Mike
Mark Fox Meteorologist NWS Fort Worth, TX Mark Fox Meteorologist NWS Fort Worth, TX What does severe really mean? Heavy Rain? Hail? Flooding? Wind? Lightning? What does severe really mean? Photo: Mike
THUNDERSTORMS. Convective heavy rain accompanied by lightning and thunder. Ahrens
 THUNDERSTORMS Convective heavy rain accompanied by lightning and thunder Ahrens Thunderstorms About 1,800 T-storms occur around the world at any instant Where do they occur the most? National Lightning
THUNDERSTORMS Convective heavy rain accompanied by lightning and thunder Ahrens Thunderstorms About 1,800 T-storms occur around the world at any instant Where do they occur the most? National Lightning
Severe Thunderstorms
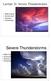 Lecture 26 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 1 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 2 Severe Thunderstorms: NWS Criteria NWS Criteria: to
Lecture 26 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 1 Severe Thunderstorms NWS Criteria Environment Structure Climatology 2 Severe Thunderstorms: NWS Criteria NWS Criteria: to
A guide to thunderstorms and how to stay safe when they strike!
 A guide to thunderstorms and how to stay safe when they strike! Thunderstorms, are a violent example of convection. At any given moment, there are an estimated 1,500 thunderstorms in progress somewhere
A guide to thunderstorms and how to stay safe when they strike! Thunderstorms, are a violent example of convection. At any given moment, there are an estimated 1,500 thunderstorms in progress somewhere
10. Severe Local Storms (Thunderstorms)
 10. Severe Local Storms (Thunderstorms) Hail. Can be larger than softball (10 cm in diameter) Smaller damage ratios, but over large areas In USA causes more than $1 billion crop and property damage each
10. Severe Local Storms (Thunderstorms) Hail. Can be larger than softball (10 cm in diameter) Smaller damage ratios, but over large areas In USA causes more than $1 billion crop and property damage each
Announcements. No office hours tomorrow (Wed. March 30) Homework 5 extra credit:
 Announcements No office hours tomorrow (Wed. March 30) Homework 5 extra credit: Find and plot additional tracks of Hurricane Ivan (after reaching its northeastmost point in U.S) North Dakota Lightning
Announcements No office hours tomorrow (Wed. March 30) Homework 5 extra credit: Find and plot additional tracks of Hurricane Ivan (after reaching its northeastmost point in U.S) North Dakota Lightning
Hurricanes form over warm ocean water.
 KEY CONCEPT Low-pressure systems can become storms. BEFORE, you learned Moving air masses cause changes in weather A low-pressure system brings stormy weather NOW, you will learn How hurricanes develop
KEY CONCEPT Low-pressure systems can become storms. BEFORE, you learned Moving air masses cause changes in weather A low-pressure system brings stormy weather NOW, you will learn How hurricanes develop
Thunderstorms. Thunderstorm Recipe
 Thunderstorms A thunderstorm is a storm with lightning and thunder. It's produced by a cumulonimbus cloud, usually producing gusty winds, heavy rain and sometimes hail. A typical thunderstorm is 15 miles
Thunderstorms A thunderstorm is a storm with lightning and thunder. It's produced by a cumulonimbus cloud, usually producing gusty winds, heavy rain and sometimes hail. A typical thunderstorm is 15 miles
GWINNETT COUNTY GEORGIA AMATEUR RADIO EMERGENCY SERVICE. Operations Plan
 GWINNETT COUNTY GEORGIA AMATEUR RADIO EMERGENCY SERVICE Operations Plan National Weather Service Support Plan 100 (Operation SKYWARN) September 21, 2002 (Revised July 14, 2003) National Weather Service
GWINNETT COUNTY GEORGIA AMATEUR RADIO EMERGENCY SERVICE Operations Plan National Weather Service Support Plan 100 (Operation SKYWARN) September 21, 2002 (Revised July 14, 2003) National Weather Service
We Had No Warning An Overview of Available Forecast Products Before and During Severe Weather Events
 We Had No Warning An Overview of Available Forecast Products Before and During Severe Weather Events Two main sources for severe weather info NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center (SPC) Convective Outlooks
We Had No Warning An Overview of Available Forecast Products Before and During Severe Weather Events Two main sources for severe weather info NOAA/NWS Storm Prediction Center (SPC) Convective Outlooks
Mature Tornado. Tornado funnel and debris cloud. Mature Tornado
 Mature Tornado Tornado funnel and debris cloud 43 Mature Tornado 44 Tornado in Final Rope Stage 45 Source of Spin 46 Source of Spin Updraft Stretches Rotating Column 47 Simulation of Tornado Formation
Mature Tornado Tornado funnel and debris cloud 43 Mature Tornado 44 Tornado in Final Rope Stage 45 Source of Spin 46 Source of Spin Updraft Stretches Rotating Column 47 Simulation of Tornado Formation
SEVERE WEATHER 101. Flood Basics
 SEVERE WEATHER 101 Flood Basics What is flooding? Flooding is an overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry. Floods can happen during heavy rains, when ocean waves come on shore, when snow melts
SEVERE WEATHER 101 Flood Basics What is flooding? Flooding is an overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry. Floods can happen during heavy rains, when ocean waves come on shore, when snow melts
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
Natural Disasters PASSAGE 5
 PASSAGE 5 Name Directions: Read Natural Disasters. Then answer questions 1 8. Natural Disasters Our planet can be a calm place, but weather conditions often change rapidly. Gentle breezes can blow into
PASSAGE 5 Name Directions: Read Natural Disasters. Then answer questions 1 8. Natural Disasters Our planet can be a calm place, but weather conditions often change rapidly. Gentle breezes can blow into
SPEARFISH FIRE DEPARTMENT POLICIES AND PROCEDURES
 SPEARFISH FIRE DEPARTMENT POLICIES AND PROCEDURES Page 1 of 5 Volume: Operation Section: 20.00 Number: 20.09 Subject: Weather Watches, Warnings, Advisory s and Spotter Activation Date Issued: 28 March
SPEARFISH FIRE DEPARTMENT POLICIES AND PROCEDURES Page 1 of 5 Volume: Operation Section: 20.00 Number: 20.09 Subject: Weather Watches, Warnings, Advisory s and Spotter Activation Date Issued: 28 March
TORNADOES. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... Tornadoes can: Rip trees apart. Destroy buildings. Uproot structures and objects.
 TORNADOES Introduce tornadoes by explaining what a tornado is. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... A powerful, circular windstorm that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 250 miles per hour. Tell the participants
TORNADOES Introduce tornadoes by explaining what a tornado is. DISPLAY VISUAL A Tornado Is... A powerful, circular windstorm that may be accompanied by winds in excess of 250 miles per hour. Tell the participants
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms
 Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Section 13-1: Thunderstorms Chapter 13 Main Idea: The intensity and duration of thunderstorms depend on the local conditions that create them. Air-mass thunderstorm Mountain thunderstorm Sea-breeze thunderstorm
Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms. Ordinary Cell Thunderstorms 5/2/11
 A storm containing lightning and thunder; convective storms Chapter 14 Severe thunderstorms: At least one: large hail wind gusts greater than or equal to 50 kt Tornado 1 2 Ordinary Cell Ordinary Cell AKA
A storm containing lightning and thunder; convective storms Chapter 14 Severe thunderstorms: At least one: large hail wind gusts greater than or equal to 50 kt Tornado 1 2 Ordinary Cell Ordinary Cell AKA
SURVIVING THE STORM: A Severe Weather Safety Guide for West Texans
 SURVIVING THE STORM: A Severe Weather Safety Guide for West Texans National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Midland, Texas www.weather.gov/midland Fundamental Definitions WATCH Conditions are favorable
SURVIVING THE STORM: A Severe Weather Safety Guide for West Texans National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office Midland, Texas www.weather.gov/midland Fundamental Definitions WATCH Conditions are favorable
Air Masses, Fronts & Storms
 Air Masses, Fronts & Storms Air Masses and Fronts Bell Work Define Terms (page 130-135) Vocab Word Definition Picture Air Mass A huge body of air that has smilier temperature, humidity and air pressure
Air Masses, Fronts & Storms Air Masses and Fronts Bell Work Define Terms (page 130-135) Vocab Word Definition Picture Air Mass A huge body of air that has smilier temperature, humidity and air pressure
Marine Weather Primer
 1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
1 of 73 Marine Weather Primer Mark A. Thornton LakeErieWX: Marine Weather Education and Forecasting Resources Mark@LakeErieWX.com 2 of 73 3 of 73 Marine Weather Seminars & Workshops Learn a little meteorology
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters
 Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Weather Systems III: Thunderstorms and Twisters Review 1. Definition of airmasses? Bergeron classification of air masses 2. Surface weather analysis: Station model, wind speed code, present weather 3.
Tornado Occurrences. Tornadoes. Tornado Life Cycle 4/12/17
 Chapter 19 Tornadoes Tornado Violently rotating column of air that extends from the base of a thunderstorm to the ground Tornado Statistics Over (100, 1000, 10000) tornadoes reported in the U.S. every
Chapter 19 Tornadoes Tornado Violently rotating column of air that extends from the base of a thunderstorm to the ground Tornado Statistics Over (100, 1000, 10000) tornadoes reported in the U.S. every
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Tornadoes. A. T. Willett/The Image Bank/Getty Images
 Tornadoes A. T. Willett/The Image Bank/Getty Images Created by Chelsea Austin Introduction to Physical Science, EMPACTS Project, Fall 2012 How are Tornadoes related to Hurricanes? Tornadoes are spawned
Tornadoes A. T. Willett/The Image Bank/Getty Images Created by Chelsea Austin Introduction to Physical Science, EMPACTS Project, Fall 2012 How are Tornadoes related to Hurricanes? Tornadoes are spawned
Weather. Weather Patterns
 Weather Weather Patterns What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you
Weather Weather Patterns What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or a D if you
MET Lecture 29 Tornadoes IV
 MET 4300 Lecture 29 Tornadoes IV Outline Definition, life cycle, & climatology of tornadoes Tornado formation within supercells Tornado formation within nonsupercell thunderstorms Fujita scale Tornado
MET 4300 Lecture 29 Tornadoes IV Outline Definition, life cycle, & climatology of tornadoes Tornado formation within supercells Tornado formation within nonsupercell thunderstorms Fujita scale Tornado
NOAA S National Weather Service
 NOAA S National Weather Service Night Spotting Advanced Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2012 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan Weather.gov/milwaukee Problems Spotters Encounter Spotters can only see a
NOAA S National Weather Service Night Spotting Advanced Concepts of Severe Storm Spotting 2012 Rusty Kapela Milwaukee/Sullivan Weather.gov/milwaukee Problems Spotters Encounter Spotters can only see a
Severe Weather. Loulousis
 Severe Weather Loulousis What is severe weather? Weather that causes property damage or loss of life. Types we will study Thunderstorms Tornadoes Hurricanes What is a thunderstorm? A thunderstorm is a
Severe Weather Loulousis What is severe weather? Weather that causes property damage or loss of life. Types we will study Thunderstorms Tornadoes Hurricanes What is a thunderstorm? A thunderstorm is a
CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview
 The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
The Severe Weather Event of 7 August 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Bruce Budd National Weather Service State College, PA 1. INTRODUCTION and Overview A fast moving short-wave (Fig. 1) with -1σ 500 hpa height
Storms. Tropical Cyclone?
 Storms Tropical Cyclone? Tropical Cyclone: low pressure storm forming in the tropics (Start as Thunder Storms). They form around a center, producing heavy winds and rains. Storms What strengthens a Tropical
Storms Tropical Cyclone? Tropical Cyclone: low pressure storm forming in the tropics (Start as Thunder Storms). They form around a center, producing heavy winds and rains. Storms What strengthens a Tropical
SKYWARN Reporting via Ham Radio. MSUARC, April 10, 2018 Bill Call, KJ4W with assistance from Christine Wielgos, NWS
 SKYWARN Reporting via Ham Radio MSUARC, April 10, 2018 Bill Call, KJ4W with assistance from Christine Wielgos, NWS Topics What is SKYWARN? How to Select a Good Vantage Point, if Mobile What Phenomena Are
SKYWARN Reporting via Ham Radio MSUARC, April 10, 2018 Bill Call, KJ4W with assistance from Christine Wielgos, NWS Topics What is SKYWARN? How to Select a Good Vantage Point, if Mobile What Phenomena Are
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Thunderstorms. Stages in the development of a thunderstorm
 Severe Weather Outcomes: S2-4-04 Explain the formation and dynamics of selected severe weather phenomena... S2-4-05 Collect, interpret, and analyze meteorological data related to a severe weather event.
Severe Weather Outcomes: S2-4-04 Explain the formation and dynamics of selected severe weather phenomena... S2-4-05 Collect, interpret, and analyze meteorological data related to a severe weather event.
A bright flash that is produced due to electrical discharge and occurs during a thunderstorm.
 Science Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly Name: KEY Date: Inv.6.1 - That s a Fact: An Introduction to Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, and Hurricanes (pgs.92-97) 1. Define lightning. A bright flash that is produced due to electrical
Science Mr. G/Mrs. Kelly Name: KEY Date: Inv.6.1 - That s a Fact: An Introduction to Thunderstorms, Tornadoes, and Hurricanes (pgs.92-97) 1. Define lightning. A bright flash that is produced due to electrical
FLOODING. Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system.
 CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns. Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 1: Air Masses & Fronts An air mass is a huge body of air that has similar temperature, humidity,
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 6 Content: Severe Weather Notes
 Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Severe weather can pose a risk to you and your property. Meteorologists monitor extreme weather to inform the public about dangerous atmospheric conditions. Thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes are
Advanced Spotter Training Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms
 Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Lesson 4: The Nature of Thunderstorms From Last Time We discussed the different ways to make air rise. We discussed convection, convergence, and the different kinds of fronts.
Advanced Spotter Training Welcome! Lesson 1: Introduction and Why Spotters are Important
 Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Welcome! Lesson 1: Introduction and Why Spotters are Important Introduction This course is intended to advance the basic training given by the National Weather Service (NWS).
Advanced Spotter Training 2009 Welcome! Lesson 1: Introduction and Why Spotters are Important Introduction This course is intended to advance the basic training given by the National Weather Service (NWS).
Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013
 Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Flooding and severe weather affected Pennsylvania on 27 June 2013 (Fig 1). The severe
Flooding and Severe weather of 27 June 2013 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview Flooding and severe weather affected Pennsylvania on 27 June 2013 (Fig 1). The severe
Winter Weather. National Weather Service Buffalo, NY
 Winter Weather National Weather Service Buffalo, NY Average Seasonal Snowfall SNOWFALL = BIG IMPACTS School / government / business closures Airport shutdowns/delays Traffic accidents with injuries/fatalities
Winter Weather National Weather Service Buffalo, NY Average Seasonal Snowfall SNOWFALL = BIG IMPACTS School / government / business closures Airport shutdowns/delays Traffic accidents with injuries/fatalities
Meteorology. Chapter 10 Worksheet 2
 Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
Chapter 10 Worksheet 2 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) Downdrafts totally dominate the in the development of a thunderstorm. a) dissipating stage b) mature
United States Multi-Hazard Early Warning System
 United States Multi-Hazard Early Warning System Saving Lives Through Partnership Lynn Maximuk National Weather Service Director, Central Region Kansas City, Missouri America s s Weather Enterprise: Protecting
United States Multi-Hazard Early Warning System Saving Lives Through Partnership Lynn Maximuk National Weather Service Director, Central Region Kansas City, Missouri America s s Weather Enterprise: Protecting
Tornadoes. The following states are all a part of Tornado Alley:
 Tornadoes Tornadoes are the most dangerous storms that nature creates. It is important that you take these natural disasters very seriously. There are many different levels of severity that a tornado can
Tornadoes Tornadoes are the most dangerous storms that nature creates. It is important that you take these natural disasters very seriously. There are many different levels of severity that a tornado can
Using UAS Technology to Obtain Aerial Storm Damage Imagery. -Mike Sporer NWS Blacksburg
 Using UAS Technology to Obtain Aerial Storm Damage Imagery -Mike Sporer NWS Blacksburg The National Weather Service routinely conducts damage surveys following severe weather events. Observed damage indicators
Using UAS Technology to Obtain Aerial Storm Damage Imagery -Mike Sporer NWS Blacksburg The National Weather Service routinely conducts damage surveys following severe weather events. Observed damage indicators
Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity.
 Section 2 Fronts and Weather Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity. What You Will Learn Differences in pressure, temperature, air movement,
Section 2 Fronts and Weather Key Concept Weather results from the movement of air masses that differ in temperature and humidity. What You Will Learn Differences in pressure, temperature, air movement,
Heavy Rain and Potential for Dangerous Flooding for northeast SC and southeast NC
 US National Weather Service Wilmington NC @NWSWilmingtonNC http://weather.gov/ilm ***Life Threatening Flooding Possible*** Heavy Rain and Potential for Dangerous Flooding for northeast SC and southeast
US National Weather Service Wilmington NC @NWSWilmingtonNC http://weather.gov/ilm ***Life Threatening Flooding Possible*** Heavy Rain and Potential for Dangerous Flooding for northeast SC and southeast
Contents. Chapter 1 Introduction Chapter 2 Cyclones Chapter 3 Hurricanes Chapter 4 Tornadoes... 36
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction.... 4 Chapter 2 Cyclones.... 14 Chapter 3 Hurricanes... 22 Chapter 4 Tornadoes.... 36 Chapter 5 The Perfect Storm... 52 Chapter 6 Hurricane Katrina... 62 Chapter 7 Joplin
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction.... 4 Chapter 2 Cyclones.... 14 Chapter 3 Hurricanes... 22 Chapter 4 Tornadoes.... 36 Chapter 5 The Perfect Storm... 52 Chapter 6 Hurricane Katrina... 62 Chapter 7 Joplin
The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection
 The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection Thunderstorms 1. A thunderstorm is a storm that produces lightning (and therefore thunder) 2. Thunderstorms frequently produce gusty winds, heavy rain, and
The Earth System - Atmosphere III Convection Thunderstorms 1. A thunderstorm is a storm that produces lightning (and therefore thunder) 2. Thunderstorms frequently produce gusty winds, heavy rain, and
Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN
 Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN September 2017 White Paper www.dtn.com / 1.800.610.0777 From flooding to tornados to severe winter storms, the threats to public safety from weather-related
Complete Weather Intelligence for Public Safety from DTN September 2017 White Paper www.dtn.com / 1.800.610.0777 From flooding to tornados to severe winter storms, the threats to public safety from weather-related
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis. Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus
 Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Summer Safety Campaign
 Summer Safety Campaign Author Day Month Year Overall classification of this briefing is. Summer Safety Campaign Key Emphasis Heat Injury Five steps of heat injury risk management Mild and extreme heat
Summer Safety Campaign Author Day Month Year Overall classification of this briefing is. Summer Safety Campaign Key Emphasis Heat Injury Five steps of heat injury risk management Mild and extreme heat
TORNADO PREPAREDNESS AND INFORMATION MANUAL
 TORNADO PREPAREDNESS AND INFORMATION MANUAL What is a Tornado? A tornado is defined as a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. The most violent tornadoes are capable
TORNADO PREPAREDNESS AND INFORMATION MANUAL What is a Tornado? A tornado is defined as a violently rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm to the ground. The most violent tornadoes are capable
Severe Weather. Section
 1 Section 13 3. 2 SC.912.E.7.5: Predict future weather conditions based on present observations and conceptual models and recognize limitations and uncertainties of such predictions. SC.912.E.7.6: Relate
1 Section 13 3. 2 SC.912.E.7.5: Predict future weather conditions based on present observations and conceptual models and recognize limitations and uncertainties of such predictions. SC.912.E.7.6: Relate
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis. Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus
 Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Tornadoes forecasting, dynamics and genesis Mteor 417 Iowa State University Week 12 Bill Gallus Tools to diagnose severe weather risks Definition of tornado: A vortex (rapidly rotating column of air) associated
Wind Events. Flooding Events. T-Storm Events. Awareness Alerts / Potential Alerts / Action Alerts / Immediate Action Alerts / Emergency Alerts.
 Information Updated: February of 2016 Our Alert Terms Definitions * Use exactly as seen below * Wind Events Awareness Alert - Strong Winds Potential Alert - Damaging Winds ACTION Alert - Damaging Winds
Information Updated: February of 2016 Our Alert Terms Definitions * Use exactly as seen below * Wind Events Awareness Alert - Strong Winds Potential Alert - Damaging Winds ACTION Alert - Damaging Winds
Weather Systems. The air around high-pressure weather systems tends to swirl in a clockwise direction, and usually brings clear skies.
 Weather Systems A weather system is a set of temperature, wind, pressure, and moisture conditions for a certain region that moves as a unit for a period of several days. Low-pressure weather systems form
Weather Systems A weather system is a set of temperature, wind, pressure, and moisture conditions for a certain region that moves as a unit for a period of several days. Low-pressure weather systems form
For further information, and additional background on the American Meteorological Society s Education Program, please contact:
 Project ATMOSPHERE This guide is one of a series produced by Project ATMOSPHERE, an initiative of the American Meteorological Society. Project ATMOSPHERE has created and trained a network of resource agents
Project ATMOSPHERE This guide is one of a series produced by Project ATMOSPHERE, an initiative of the American Meteorological Society. Project ATMOSPHERE has created and trained a network of resource agents
MET Lecture 34 Downbursts
 MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
MET 4300 Lecture 34 Downbursts Downbursts A strong downdraft that originates within the lower part of a cumulus cloud or thunderstorms and spreads out at the surface Downbursts do not require strong thunderstorms
Tornadoes. Tornadoes are an interesting topic because as often as they occur in the United
 John Bucaro Environmental Hazards Dr. Scott 9/17/03 Tornadoes Tornadoes are an interesting topic because as often as they occur in the United States scientists still do not know much about them. They occur
John Bucaro Environmental Hazards Dr. Scott 9/17/03 Tornadoes Tornadoes are an interesting topic because as often as they occur in the United States scientists still do not know much about them. They occur
Guided Notes Weather. Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation
 Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
Guided Notes Weather Part 2: Meteorology Air Masses Fronts Weather Maps Storms Storm Preparation The map below shows North America and its surrounding bodies of water. Country borders are shown. On the
IN VEHICLES: Do not try to outrun a tornado. Abandon your vehicle and hide in a nearby ditch or depression and cover your head.
 TORNADO SAFETY TORNADO! The very word strikes fear in many people. While a tornado is perhaps nature's most destructive storm, deaths and injuries can be prevented. By following Tornado Safety Rules, lives
TORNADO SAFETY TORNADO! The very word strikes fear in many people. While a tornado is perhaps nature's most destructive storm, deaths and injuries can be prevented. By following Tornado Safety Rules, lives
Kentucky Weather Hazards: What is Your Risk?
 Kentucky Weather Hazards: What is Your Risk? Stuart A. Foster State Climatologist for Kentucky 2010 Kentucky Weather Conference Bowling Green, Kentucky January 16, 2010 Perspectives on Kentucky s Climate
Kentucky Weather Hazards: What is Your Risk? Stuart A. Foster State Climatologist for Kentucky 2010 Kentucky Weather Conference Bowling Green, Kentucky January 16, 2010 Perspectives on Kentucky s Climate
BROWARD COLLEGE COMMUNITY & INCIDENT COMMAND TEAMS
 BROWARD COLLEGE COMMUNITY & INCIDENT COMMAND TEAMS Types of Severe Weather Communications about Severe Weather Preparedness Actions Initial Response Actions Community & Incident Command Teams Severe Thunderstorms
BROWARD COLLEGE COMMUNITY & INCIDENT COMMAND TEAMS Types of Severe Weather Communications about Severe Weather Preparedness Actions Initial Response Actions Community & Incident Command Teams Severe Thunderstorms
1879-LDG-E. Leader s Guide
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 1879-LDG-E SEVERE WEATHER ALERT: ARE YOU PREPARED? Leader s Guide 2003, ERI Safety Videos SEVERE WEATHER ALERT: ARE YOU PREPARED? This easy-to-use Leader s
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 1879-LDG-E SEVERE WEATHER ALERT: ARE YOU PREPARED? Leader s Guide 2003, ERI Safety Videos SEVERE WEATHER ALERT: ARE YOU PREPARED? This easy-to-use Leader s
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES
 HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
CoCoRaHS. Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, & Snow Network. Ashley Wolf Meteorologist NWS Green Bay Northeast Wisconsin CoCoRaHS Coordinator
 CoCoRaHS Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, & Snow Network Ashley Wolf Meteorologist NWS Green Bay Northeast Wisconsin CoCoRaHS Coordinator What is CoCoRaHS Who, What, Where and Whys of CoCoRaHS What?
CoCoRaHS Community Collaborative Rain, Hail, & Snow Network Ashley Wolf Meteorologist NWS Green Bay Northeast Wisconsin CoCoRaHS Coordinator What is CoCoRaHS Who, What, Where and Whys of CoCoRaHS What?
Our Challenge. It s All Wind 2/16/2017
 2/16/2017 It s All Wind Communicating Damaging Wind & Tornado Threats in an Impact-based Environment Rick Smith - NWS Norman, OK Justin Dougherty Our Challenge Given the history and types of weather threats
2/16/2017 It s All Wind Communicating Damaging Wind & Tornado Threats in an Impact-based Environment Rick Smith - NWS Norman, OK Justin Dougherty Our Challenge Given the history and types of weather threats
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Tornadoes Grab Toto!! TORNADOES Are a low pressure storm that usually forms over land in an average year, 800 tornadoes are reported in the U.S. a tornado is defined
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Tornadoes Grab Toto!! TORNADOES Are a low pressure storm that usually forms over land in an average year, 800 tornadoes are reported in the U.S. a tornado is defined
Extreme Fire Behavior and Weather Conditions
 Extreme Fire Behavior and Weather Conditions Firewhirls A firewhirl is defined as: A spinning vortex of ascending hot air and gases rising from a fire and carrying aloft smoke, debris, and flame. Fire
Extreme Fire Behavior and Weather Conditions Firewhirls A firewhirl is defined as: A spinning vortex of ascending hot air and gases rising from a fire and carrying aloft smoke, debris, and flame. Fire
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes
 Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
Chapter 3 Convective Dynamics 3.4. Bright Bands, Bow Echoes and Mesoscale Convective Complexes Photographs Todd Lindley Bright band associated with stratiform precipitation in a squall line system 1 Bright
The 2015 NWS Spring and Summer Weather Update
 http://weather.gov The 2015 NWS Spring and Summer Weather Update Western North Carolina severe weather climatology Tony Sturey, WCM Greenville/Spartanburg, SC North Carolina Spring and Summer Outlooks
http://weather.gov The 2015 NWS Spring and Summer Weather Update Western North Carolina severe weather climatology Tony Sturey, WCM Greenville/Spartanburg, SC North Carolina Spring and Summer Outlooks
