Statistics 220 Bayesian Data Analysis
|
|
|
- Beverly Elijah Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Statistics 220 Bayesian Data Analysis Mark E. Irwin Department of Statistics Harvard University Spring Term Thursday, February 3, Tuesday, May 17, 2005 Copyright c 2005 by Mark E. Irwin
2 Personnel Instructor: Mark Irwin Office: 611 Science Center Phone: Lectures: Tues, Thurs 10:00-11:30, Science Center 221 Office Hours: Monday & Wednesday, 11:00-12:00 or by appointment Teaching Fellow: Office Hours: Alan Lenarcic To be announced Administration 1
3 Text Book Required Text: Gelman A, Carlin JB, Stern HS, & Rubin DB (2004) Bayesian Data Analysis, 2nd edition. Chapman & Hall/CRC. Available from the COOP and on reserve in Cabot Library Suggested Gilks WR, Richardson S, and Spiegelhalter DJ (1996). References: Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman & Hall / CRC. Liu J (2001). Monte Carlo Strategies in Scientific Computing. Springer-Verlag. Administration 2
4 Computing Many of the computational problems can be done in BUGS (Bayesian inference Using Gibbs Sampling). Windows and Linux (Intel based) versions are available. Familiarity with BUGS is not assumed. R/S-Plus will also be useful. Links to software and other computing resources are available from the course web site or at mirwin/computing/ Administration 3
5 Grading Course grades will be determined based on homework assignments (4 or 5 during the term) and a term project, the exact form of which is to be determined. Administration 4
6 Web Site stat220/ Available on the site: PDF files of the lecture notes Data files used in class, in text format References, with many of the papers available in pdf format. Assignments, solutions, data files for them Class announcements, calendar, etc Administration 5
7 Course Goals 1. Basics of the Bayesian inference: (a) setting up a probability model and the basics of statistical inferences; (b) using the probability theory and the Bayes rule; (c) simple examples: binomial, normal, and exponential families; (d) non-informative priors; (e) exchangeability and modelling; (f) asymptotic normality (informal introduction). 2. Multi-parameter models, normal with unknown mean and variance, the multivariate normal distribution, multinomial models, Dirichlet process models, and examples. Computation and simulation from arbitrary posterior distributions in two parameters. Administration 6
8 3. Inference from large samples and comparison to standard non-bayesian methods. 4. Hierarchical models, estimating several means, estimating population parameters from data, meta analysis, and some examples. Emphasis on statistical thinking for complicated problems. 5. Model checking, comparison to data and prior knowledge, sensitivity analysis, prior and posterior predictive checking, posterior odds ratio, model likelihood. 6. Computation 1 (non-iterative methods): integration, conjugate analysis, normal and Laplace approximations, importance sampling, rejection sampling, sequential imputation. 7. Computation 2 (iterative sampling methods): Metropolis-Hastings algorithms and the Gibbs sampler. Their variations include Metropolized independent sampling, iterative predictive updating, and simulated tempering; etc. Administration 7
9 8. Missing data problems and data augmentation methodology. Latent variable models; Student-t models for robust inference and sensitivity analysis; Bayesian nonparametrics. Administration 8
10 Who is this man? This is reportedly the only known picture of the Reverend Thomas Bayes, F.R.S. 1701? This picture was taken from the 1936 History of Life Insurance (by Terence O Donnell, American Conservation Co., Chicago). As no source is given, the authenticity of this portrait is open to question. So what is the probability that this is actually Reverend Thomas Bayes? However there is some additional information. How does this change our belief about who this is? Introductory material 9
11 Many details about Bayes are sketchy. According to Steve Stigler The date of his birth is not known: Bayes s posterior is better known than his prior. Introductory material 10
12 Actually his date of death isn t that well known either. Its general considered to be April 7, 1761 however it has also be reported as April 17th of the same year. There is some additional information we can get from this picture to help use decide whether this is Bayes or not. 1. The caption under the photo in O Donnell s book was Rev. T. Bayes: Improver of the Columnar Method developed by Barrett. There are some problems with this claim. First Barrett was born in 1752 and would have been about 9 years old when Bayes died. In addition, the method that Bayes allegedly improved was apparently developed between 1788 and 1811 and read to the Royal Society in 1812, long after Bayes death. So there is a problem here, but whether it is a problem with just the caption or the picture as well isn t clear. Introductory material 11
13 2. Bayes was a Nonconformist (Presbyterian) Minister. Does the clothing in the picture match that of a Nonconformist Minister in the 1740 s and 1750 s. The picture has been compared to three other Ministers, Joshua Bayes, Bayes father, Richard Price (portrait dated 1776), the person who read Bayes paper to the Royal Society, and Philip Doddridge, a friend of Bayes brother-in-law. Joshua Bayes Richard Price Philip Doddridge ( ) ( ) ( ) Introductory material 12
14 Two things stand out in the comparisons. (a) No wig. It is likely that Bayes should have been wearing a wig similar to Doddridge s, which was going out of fashion in the 1740 s or similar to Price s, which was coming into style at the time. (b) Bayes appears to be wearing a clerical gown like his father or a larger frock coat with a high collar. On viewing the other two pictures, we can see that the gown is not in the style for Bayes generation and the frock coat with a large collar is definitely anachronistic. (Interpretation of David Bellhouse from IMS Bulletin 17, No. 1, page 49) Introductory material 13
15 Question: How to we incorporate this information to adjust our probability that this is actually a picture of Bayes? Answer: Theorem. P [This is Bayes Data] which can be determined by Bayes P [B Data] = P [B]P [Data B] P [B]P [Data B] + P [B c ]P [Data B c ] Note that this is not easy to do as assigning probabilities here is difficult. For an example of how this can be done, see the paper (available on the course web site) Stigler SM (1983). Who Discovered Bayes s Theorem. American Statistician 37: Introductory material 14
16 In this paper, Stigler examines whether Bayes was the first person to discover what is now known as Bayes Theorem. There is evidence that the result was known in 1749, 12 years before Bayes death and 15 years before Bayes paper was published. In Stigler s analysis P [Bayes 1st discovered Data] = 0.25 P [Saunderson 1st discovered Data] = 0.75 Note that Bayes actually proved a special case of Bayes Theorem involving inference on a Bernoulli success probability. An example where Bayes approach could be used is... Introductory material 15
17 How accurate are Punxsutawney Phil and Wiarton Willie? Punxsutawney Phil Wiarton Willie Shadow in 2005 No Shadow in 2005 So what are the probabilities that Punxsutawney Phil and Wiarton Willie make accurate predictions? Introductory material 16
18 According to the Wiarton Willie website, Willie has been correct 37 times out of 41 years (ˆp = = 0.902). By Bayes approach E[p Data] = = SD(p Data) = Mode(p Data) = = (I suspect their reported results are a bit biased. :) The only numbers I could find for Punxsutawney Phil say he has never been wrong.) Density Posterior Distribution for Wiarton Willie Probilility of Correct Prediction (p) Introductory material 17
19 Statistical Inference Two main approaches Frequentist (Stat 111/211) Model parameters are fixed unknown quantities. data. Randomness only in Estimation - Maximum likelihood, method of moments Confidence intervals Significance testing - p-values Hypothesis testing - Reject/Don t Reject H 0 Introductory material 18
20 Bayesian (Stat 220) Model parameters are random variables. Inference is based on P [θ Data], the posterior distribution given the data. Estimation - Posterior means, modes Credible intervals/sets Posterior probabilities There is also decision theory which tends to be Bayesian in nature (good procedures (e.g Admissible procedures) must be Bayesian with respect to some prior). Introductory material 19
21 Why Should You Use Bayesian Procedures? It is the only the correct form of inference. :) Other inference procedures can be suboptimal or in fact give inconsistent answers. Allows for a consistent method to combine prior beliefs and data for inference procedures. Usually have good frequentist properties. A 95% credibility interval will often have coverage level close to 95%. Can give answers in large, high dimensional problems when frequentist solutions will tend to break down. Introductory material 20
22 Example: Tropical Pacific Sea Surface Temperature Evolution Probabilistic based model involving wind, sea surface temperature, and the Southern Oscillation Index (air pressure measure) data to forecast sea surface temperatures 7 months in the future. A highly complex, hierarchical model was used. In addition to the three sets of input variables into the model, there is a regime component, recognizing that the region goes through periods of below normal, above normal, and typical temperatures. As part of the analysis, we can ask what would temperature field look like conditional on being in a given temperature regime. Introductory material 21
23 Currently there has been 540 months (January 1970 to December 2004) of data analyzed with temperatures forecast on a (= 2520) pixel grid. The forecast map is a summary of the probabilistic model (the posterior mean), which is a weighted average over all possible sea surface temperature maps. As we can determine the likelihood of any temperature field, summary measures of the uncertainty in the forecasts can be determined. The calculation of the posterior distributions was done by Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) based on 1000 imputations with a burn in of 100 imputations (I think). Introductory material 22
24 April 2004 anomaly forecast (top) and observed anomaly (bottom) based on Jan 1970 to September 2003 data. Introductory material 23
25 April 2004 regime specific anomaly forecasts based on Jan 1970 to September 2003 data. Introductory material 24
26 November 2004 anomaly forecast with 25th and 75th percentiles based on Jan 1970 to April 2004 data. Introductory material 25
27 Niño 3.4 Forecast = C Niño 3.4 Observed = C November 2004 anomaly forecast (top) and observed anomaly (bottom) based on Jan 1970 to April 2004 data. This forecast suggests an El Niño this winter. Introductory material 26
28 November 2004 regime specific anomaly forecasts based on Jan 1970 to April 2004 data. Introductory material 27
29 Refs: Berliner, Wikle, and Cressie (2000). Long-Lead Prediction of Pacific SSTs via Bayesian Dynamic Modeling. Journal of Climate, 13, sses/collab enso.php Note that the model used here is only an approximation of reality. This does not include information about the underlying physics of the meteorology. Introductory material 28
Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities
 Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities Statistics 110 Summer 2006 Copyright c 2006 by Mark E. Irwin Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities The three axioms for probability don t discuss how
Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities Statistics 110 Summer 2006 Copyright c 2006 by Mark E. Irwin Joint, Conditional, & Marginal Probabilities The three axioms for probability don t discuss how
Statistics Introduction to Probability
 Statistics 110 - Introduction to Probability Mark E. Irwin Department of Statistics Harvard University Summer Term Monday, June 26, 2006 - Wednesday, August 16, 2006 Copyright 2006 by Mark E. Irwin Personnel
Statistics 110 - Introduction to Probability Mark E. Irwin Department of Statistics Harvard University Summer Term Monday, June 26, 2006 - Wednesday, August 16, 2006 Copyright 2006 by Mark E. Irwin Personnel
Statistics Introduction to Probability
 Statistics 110 - Introduction to Probability Mark E. Irwin Department of Statistics Harvard University Summer Term Monday, June 28, 2004 - Wednesday, August 18, 2004 Personnel Instructor: Mark Irwin Office:
Statistics 110 - Introduction to Probability Mark E. Irwin Department of Statistics Harvard University Summer Term Monday, June 28, 2004 - Wednesday, August 18, 2004 Personnel Instructor: Mark Irwin Office:
Bayesian Inference. Chapter 1. Introduction and basic concepts
 Bayesian Inference Chapter 1. Introduction and basic concepts M. Concepción Ausín Department of Statistics Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Master in Business Administration and Quantitative Methods Master
Bayesian Inference Chapter 1. Introduction and basic concepts M. Concepción Ausín Department of Statistics Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Master in Business Administration and Quantitative Methods Master
PARAMETER ESTIMATION: BAYESIAN APPROACH. These notes summarize the lectures on Bayesian parameter estimation.
 PARAMETER ESTIMATION: BAYESIAN APPROACH. These notes summarize the lectures on Bayesian parameter estimation.. Beta Distribution We ll start by learning about the Beta distribution, since we end up using
PARAMETER ESTIMATION: BAYESIAN APPROACH. These notes summarize the lectures on Bayesian parameter estimation.. Beta Distribution We ll start by learning about the Beta distribution, since we end up using
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation. EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016
 Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016 EPSY 905: Intro to Bayesian and MCMC Today s Class An
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016 EPSY 905: Intro to Bayesian and MCMC Today s Class An
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
Contents. Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1
 Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability
 eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice Edited by W.R. Gilks Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit Cambridge UK S. Richardson French National Institute for Health and Medical Research Vilejuif France
Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice Edited by W.R. Gilks Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit Cambridge UK S. Richardson French National Institute for Health and Medical Research Vilejuif France
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths
 Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
The Bayesian Choice. Christian P. Robert. From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation. Second Edition.
 Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Bayesian Statistical Methods. Jeff Gill. Department of Political Science, University of Florida
 Bayesian Statistical Methods Jeff Gill Department of Political Science, University of Florida 234 Anderson Hall, PO Box 117325, Gainesville, FL 32611-7325 Voice: 352-392-0262x272, Fax: 352-392-8127, Email:
Bayesian Statistical Methods Jeff Gill Department of Political Science, University of Florida 234 Anderson Hall, PO Box 117325, Gainesville, FL 32611-7325 Voice: 352-392-0262x272, Fax: 352-392-8127, Email:
McGill University. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences. Course EPIB-675.
 McGill University Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences Course EPIB-675 Lawrence Joseph Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences EPIB-675 3 credits Instructor:
McGill University Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences Course EPIB-675 Lawrence Joseph Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences EPIB-675 3 credits Instructor:
The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
 Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.3, no.1, 2014, 85-96 ISSN: 2241-0384 (print), 2241-0376 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.3, no.1, 2014, 85-96 ISSN: 2241-0384 (print), 2241-0376 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
Multilevel Statistical Models: 3 rd edition, 2003 Contents
 Multilevel Statistical Models: 3 rd edition, 2003 Contents Preface Acknowledgements Notation Two and three level models. A general classification notation and diagram Glossary Chapter 1 An introduction
Multilevel Statistical Models: 3 rd edition, 2003 Contents Preface Acknowledgements Notation Two and three level models. A general classification notation and diagram Glossary Chapter 1 An introduction
Lecture 14 Bayesian Models for Spatio-Temporal Data
 Lecture 14 Bayesian Models for Spatio-Temporal Data Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 13, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Recap of Bayesian Models 2 Empirical Bayes 3 Case 1: Long-Lead Forecasting of Sea Surface Temperatures
Lecture 14 Bayesian Models for Spatio-Temporal Data Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 13, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Recap of Bayesian Models 2 Empirical Bayes 3 Case 1: Long-Lead Forecasting of Sea Surface Temperatures
Bayesian data analysis in practice: Three simple examples
 Bayesian data analysis in practice: Three simple examples Martin P. Tingley Introduction These notes cover three examples I presented at Climatea on 5 October 0. Matlab code is available by request to
Bayesian data analysis in practice: Three simple examples Martin P. Tingley Introduction These notes cover three examples I presented at Climatea on 5 October 0. Matlab code is available by request to
Doing Bayesian Integrals
 ASTR509-13 Doing Bayesian Integrals The Reverend Thomas Bayes (c.1702 1761) Philosopher, theologian, mathematician Presbyterian (non-conformist) minister Tunbridge Wells, UK Elected FRS, perhaps due to
ASTR509-13 Doing Bayesian Integrals The Reverend Thomas Bayes (c.1702 1761) Philosopher, theologian, mathematician Presbyterian (non-conformist) minister Tunbridge Wells, UK Elected FRS, perhaps due to
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo Hedibert Freitas Lopes Graduate School of Business The University of Chicago 5807 South Woodlawn Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60637 February, 1st 2006 1 Introduction
A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo Hedibert Freitas Lopes Graduate School of Business The University of Chicago 5807 South Woodlawn Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60637 February, 1st 2006 1 Introduction
McGill University. Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics. Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences. Course EPIB-682.
 McGill University Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences Course EPIB-682 Lawrence Joseph Intro to Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences EPIB-682 2 credits
McGill University Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences Course EPIB-682 Lawrence Joseph Intro to Bayesian Analysis for the Health Sciences EPIB-682 2 credits
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics 1
 Introduction to Bayesian Statistics 1 STA 442/2101 Fall 2018 1 This slide show is an open-source document. See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 42 Thomas Bayes (1701-1761) Image from the Wikipedia
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics 1 STA 442/2101 Fall 2018 1 This slide show is an open-source document. See last slide for copyright information. 1 / 42 Thomas Bayes (1701-1761) Image from the Wikipedia
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference
 Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 11, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Bayesian Models 2 Modeling Correlations Using Bayes 3 The Universal Algorithm 4 BUGS 5 Wrapping Up
Lecture 13 Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference Dennis Sun Stats 253 August 11, 2014 Outline of Lecture 1 Bayesian Models 2 Modeling Correlations Using Bayes 3 The Universal Algorithm 4 BUGS 5 Wrapping Up
Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions
 Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions Herbert K. H. Lee University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract: Making good predictions from noisy data is a challenging problem. Methods
Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions Herbert K. H. Lee University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract: Making good predictions from noisy data is a challenging problem. Methods
Subjective and Objective Bayesian Statistics
 Subjective and Objective Bayesian Statistics Principles, Models, and Applications Second Edition S. JAMES PRESS with contributions by SIDDHARTHA CHIB MERLISE CLYDE GEORGE WOODWORTH ALAN ZASLAVSKY \WILEY-
Subjective and Objective Bayesian Statistics Principles, Models, and Applications Second Edition S. JAMES PRESS with contributions by SIDDHARTHA CHIB MERLISE CLYDE GEORGE WOODWORTH ALAN ZASLAVSKY \WILEY-
Bayesian Inference in GLMs. Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence
 Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Probability Review - Bayes Introduction
 Probability Review - Bayes Introduction Statistics 220 Spring 2005 Copyright c 2005 by Mark E. Irwin Advantages of Bayesian Analysis Answers the questions that researchers are usually interested in, What
Probability Review - Bayes Introduction Statistics 220 Spring 2005 Copyright c 2005 by Mark E. Irwin Advantages of Bayesian Analysis Answers the questions that researchers are usually interested in, What
Principles of Bayesian Inference
 Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee University of Minnesota July 20th, 2008 1 Bayesian Principles Classical statistics: model parameters are fixed and unknown. A Bayesian thinks of parameters
Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee University of Minnesota July 20th, 2008 1 Bayesian Principles Classical statistics: model parameters are fixed and unknown. A Bayesian thinks of parameters
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
Parameter Estimation. William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1
 Parameter Estimation William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin bill@bayesrules.net Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1 Elements of Inference Inference problems contain two indispensable elements: Data
Parameter Estimation William H. Jefferys University of Texas at Austin bill@bayesrules.net Parameter Estimation 7/26/05 1 Elements of Inference Inference problems contain two indispensable elements: Data
Stat 451 Lecture Notes Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Ryan Martin UIC
 Stat 451 Lecture Notes 07 12 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Ryan Martin UIC www.math.uic.edu/~rgmartin 1 Based on Chapters 8 9 in Givens & Hoeting, Chapters 25 27 in Lange 2 Updated: April 4, 2016 1 / 42 Outline
Stat 451 Lecture Notes 07 12 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Ryan Martin UIC www.math.uic.edu/~rgmartin 1 Based on Chapters 8 9 in Givens & Hoeting, Chapters 25 27 in Lange 2 Updated: April 4, 2016 1 / 42 Outline
Bayesian Inference. STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan
 Bayesian Inference STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan Bayes Rule...s! Reverend Thomas Bayes Posterior Prior p(θ y) = p(y θ)p(θ)/p(y) Likelihood - Sampling Distribution Normalizing Constant: p(y
Bayesian Inference STA 121: Regression Analysis Artin Armagan Bayes Rule...s! Reverend Thomas Bayes Posterior Prior p(θ y) = p(y θ)p(θ)/p(y) Likelihood - Sampling Distribution Normalizing Constant: p(y
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning
 Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
Who was Bayes? Bayesian Phylogenetics. What is Bayes Theorem?
 Who was Bayes? Bayesian Phylogenetics Bret Larget Departments of Botany and of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison October 6, 2011 The Reverand Thomas Bayes was born in London in 1702. He was the
Who was Bayes? Bayesian Phylogenetics Bret Larget Departments of Botany and of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison October 6, 2011 The Reverand Thomas Bayes was born in London in 1702. He was the
27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain. 1 Recap of MCMC and Naive Parallel Gibbs Sampling
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
Bayesian Phylogenetics
 Bayesian Phylogenetics Bret Larget Departments of Botany and of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison October 6, 2011 Bayesian Phylogenetics 1 / 27 Who was Bayes? The Reverand Thomas Bayes was born
Bayesian Phylogenetics Bret Larget Departments of Botany and of Statistics University of Wisconsin Madison October 6, 2011 Bayesian Phylogenetics 1 / 27 Who was Bayes? The Reverand Thomas Bayes was born
Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression
 When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
(5) Multi-parameter models - Gibbs sampling. ST440/540: Applied Bayesian Analysis
 Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Computational Perception. Bayesian Inference
 Computational Perception 15-485/785 January 24, 2008 Bayesian Inference The process of probabilistic inference 1. define model of problem 2. derive posterior distributions and estimators 3. estimate parameters
Computational Perception 15-485/785 January 24, 2008 Bayesian Inference The process of probabilistic inference 1. define model of problem 2. derive posterior distributions and estimators 3. estimate parameters
an introduction to bayesian inference
 with an application to network analysis http://jakehofman.com january 13, 2010 motivation would like models that: provide predictive and explanatory power are complex enough to describe observed phenomena
with an application to network analysis http://jakehofman.com january 13, 2010 motivation would like models that: provide predictive and explanatory power are complex enough to describe observed phenomena
Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach
 Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach Rating curves what is wanted? A best estimate of the relationship between stage and discharge at a given place in a river. The relationship should be on the
Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach Rating curves what is wanted? A best estimate of the relationship between stage and discharge at a given place in a river. The relationship should be on the
Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model
 UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT SAN ANTONIO Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model Liang Jing April 2010 1 1 ABSTRACT In this paper, common MCMC algorithms are introduced
UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT SAN ANTONIO Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model Liang Jing April 2010 1 1 ABSTRACT In this paper, common MCMC algorithms are introduced
Karl-Rudolf Koch Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Second Edition
 Karl-Rudolf Koch Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Second Edition Karl-Rudolf Koch Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Second, updated and enlarged Edition With 17 Figures Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.-Ing.
Karl-Rudolf Koch Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Second Edition Karl-Rudolf Koch Introduction to Bayesian Statistics Second, updated and enlarged Edition With 17 Figures Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.-Ing.
Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression
 Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression Joop Hox MuLOG, 15 september 2000 mcmc What is Statistics?! Statistics is about uncertainty To err is human, to forgive divine, but to include errors in your design
Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression Joop Hox MuLOG, 15 september 2000 mcmc What is Statistics?! Statistics is about uncertainty To err is human, to forgive divine, but to include errors in your design
Prerequisite: STATS 7 or STATS 8 or AP90 or (STATS 120A and STATS 120B and STATS 120C). AP90 with a minimum score of 3
 University of California, Irvine 2017-2018 1 Statistics (STATS) Courses STATS 5. Seminar in Data Science. 1 Unit. An introduction to the field of Data Science; intended for entering freshman and transfers.
University of California, Irvine 2017-2018 1 Statistics (STATS) Courses STATS 5. Seminar in Data Science. 1 Unit. An introduction to the field of Data Science; intended for entering freshman and transfers.
AMSC/MATH 673, CLASSICAL METHODS IN PDE, FALL Required text: Evans, Partial Differential Equations second edition
 AMSC/MATH 673, CLASSICAL METHODS IN PDE, FALL 2018. MWF 2:00pm - 2:50pm MTH 0407 Instructor: M. Machedon Office: MTH 3311 e-mail: mxm@math.umd.edu Required text: Evans, Partial Differential Equations second
AMSC/MATH 673, CLASSICAL METHODS IN PDE, FALL 2018. MWF 2:00pm - 2:50pm MTH 0407 Instructor: M. Machedon Office: MTH 3311 e-mail: mxm@math.umd.edu Required text: Evans, Partial Differential Equations second
Bayesian inference & Markov chain Monte Carlo. Note 1: Many slides for this lecture were kindly provided by Paul Lewis and Mark Holder
 Bayesian inference & Markov chain Monte Carlo Note 1: Many slides for this lecture were kindly provided by Paul Lewis and Mark Holder Note 2: Paul Lewis has written nice software for demonstrating Markov
Bayesian inference & Markov chain Monte Carlo Note 1: Many slides for this lecture were kindly provided by Paul Lewis and Mark Holder Note 2: Paul Lewis has written nice software for demonstrating Markov
16 : Approximate Inference: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 16 : Approximate Inference: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yuan Yang, Chao-Ming Yen 1 Introduction As the target distribution
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 16 : Approximate Inference: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yuan Yang, Chao-Ming Yen 1 Introduction As the target distribution
F denotes cumulative density. denotes probability density function; (.)
 BAYESIAN ANALYSIS: FOREWORDS Notation. System means the real thing and a model is an assumed mathematical form for the system.. he probability model class M contains the set of the all admissible models
BAYESIAN ANALYSIS: FOREWORDS Notation. System means the real thing and a model is an assumed mathematical form for the system.. he probability model class M contains the set of the all admissible models
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 11 January 7, 2013 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline How to communicate the statistical uncertainty
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 11 January 7, 2013 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline How to communicate the statistical uncertainty
Lecture 5. G. Cowan Lectures on Statistical Data Analysis Lecture 5 page 1
 Lecture 5 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
Lecture 5 1 Probability (90 min.) Definition, Bayes theorem, probability densities and their properties, catalogue of pdfs, Monte Carlo 2 Statistical tests (90 min.) general concepts, test statistics,
A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics
 A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics Niklas Wahlberg Based largely on slides by Paul Lewis (www.eeb.uconn.edu) An Introduction to Bayesian Phylogenetics Bayesian inference in general Markov chain Monte
A Bayesian Approach to Phylogenetics Niklas Wahlberg Based largely on slides by Paul Lewis (www.eeb.uconn.edu) An Introduction to Bayesian Phylogenetics Bayesian inference in general Markov chain Monte
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements
 Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
SAMSI Astrostatistics Tutorial. More Markov chain Monte Carlo & Demo of Mathematica software
 SAMSI Astrostatistics Tutorial More Markov chain Monte Carlo & Demo of Mathematica software Phil Gregory University of British Columbia 26 Bayesian Logical Data Analysis for the Physical Sciences Contents:
SAMSI Astrostatistics Tutorial More Markov chain Monte Carlo & Demo of Mathematica software Phil Gregory University of British Columbia 26 Bayesian Logical Data Analysis for the Physical Sciences Contents:
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes
 Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01
 STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
STAT 499/962 Topics in Statistics Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Jan 2018, Handout 01 Nasser Sadeghkhani a.sadeghkhani@queensu.ca There are two main schools to statistical inference: 1-frequentist
Intro to Bayesian Methods
 Intro to Bayesian Methods Rebecca C. Steorts Bayesian Methods and Modern Statistics: STA 360/601 Lecture 1 1 Course Webpage Syllabus LaTeX reference manual R markdown reference manual Please come to office
Intro to Bayesian Methods Rebecca C. Steorts Bayesian Methods and Modern Statistics: STA 360/601 Lecture 1 1 Course Webpage Syllabus LaTeX reference manual R markdown reference manual Please come to office
BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA
 BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA Intro: Course Outline and Brief Intro to Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA PASI-CIMAT 04/28-30/2010 Marina Vannucci
BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA Intro: Course Outline and Brief Intro to Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA PASI-CIMAT 04/28-30/2010 Marina Vannucci
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CONTENTS. Preface Preface to the First Edition
 Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Precision Engineering
 Precision Engineering 38 (2014) 18 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Precision Engineering j o ur nal homep age : www.elsevier.com/locate/precision Tool life prediction using Bayesian updating.
Precision Engineering 38 (2014) 18 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Precision Engineering j o ur nal homep age : www.elsevier.com/locate/precision Tool life prediction using Bayesian updating.
ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015
 ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015 1 April, Intro; Linear discrete Inverse problems (Aster Ch 1 and 2) Slides 8 April, SVD (Aster ch 2 and 3) Slides 15 April, RegularizaFon (ch
ECE295, Data Assimila0on and Inverse Problems, Spring 2015 1 April, Intro; Linear discrete Inverse problems (Aster Ch 1 and 2) Slides 8 April, SVD (Aster ch 2 and 3) Slides 15 April, RegularizaFon (ch
Sampling Methods (11/30/04)
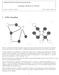 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests
 Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests Use of Bayesian posteriors with informative priors as optimal frequentist tests Christian Bartels Email: h.christian.bartels@gmail.com Allschwil, 5. April 2017
Using prior knowledge in frequentist tests Use of Bayesian posteriors with informative priors as optimal frequentist tests Christian Bartels Email: h.christian.bartels@gmail.com Allschwil, 5. April 2017
NRCSE. Statistics, data, and deterministic models
 NRCSE Statistics, data, and deterministic models Some issues in model assessment Spatiotemporal misalignment Grid boxes vs observations Types of error Measurement error and bias Model error Approximation
NRCSE Statistics, data, and deterministic models Some issues in model assessment Spatiotemporal misalignment Grid boxes vs observations Types of error Measurement error and bias Model error Approximation
Reconstruction of individual patient data for meta analysis via Bayesian approach
 Reconstruction of individual patient data for meta analysis via Bayesian approach Yusuke Yamaguchi, Wataru Sakamoto and Shingo Shirahata Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University Masashi
Reconstruction of individual patient data for meta analysis via Bayesian approach Yusuke Yamaguchi, Wataru Sakamoto and Shingo Shirahata Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University Masashi
Parameter estimation and forecasting. Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn
 Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
Parameter estimation and forecasting Cristiano Porciani AIfA, Uni-Bonn Questions? C. Porciani Estimation & forecasting 2 Temperature fluctuations Variance at multipole l (angle ~180o/l) C. Porciani Estimation
Bayesian inference. Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli. October 3, 2007
 Bayesian inference Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli October 3, 2007 1 Introduction The last few decades has seen a growing interest in Bayesian inference, an alternative approach to statistical inference.
Bayesian inference Fredrik Ronquist and Peter Beerli October 3, 2007 1 Introduction The last few decades has seen a growing interest in Bayesian inference, an alternative approach to statistical inference.
Bayesian philosophy Bayesian computation Bayesian software. Bayesian Statistics. Petter Mostad. Chalmers. April 6, 2017
 Chalmers April 6, 2017 Bayesian philosophy Bayesian philosophy Bayesian statistics versus classical statistics: War or co-existence? Classical statistics: Models have variables and parameters; these are
Chalmers April 6, 2017 Bayesian philosophy Bayesian philosophy Bayesian statistics versus classical statistics: War or co-existence? Classical statistics: Models have variables and parameters; these are
Topic Models. Brandon Malone. February 20, Latent Dirichlet Allocation Success Stories Wrap-up
 Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models
 36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models Taste of MCMC / Bayes for 3 or more levels Brian Junker 132E Baker Hall brian@stat.cmu.edu 1 Outline Practical Bayes Mastery Learning Example A brief taste of JAGS
36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models Taste of MCMC / Bayes for 3 or more levels Brian Junker 132E Baker Hall brian@stat.cmu.edu 1 Outline Practical Bayes Mastery Learning Example A brief taste of JAGS
Ronald Christensen. University of New Mexico. Albuquerque, New Mexico. Wesley Johnson. University of California, Irvine. Irvine, California
 Texts in Statistical Science Bayesian Ideas and Data Analysis An Introduction for Scientists and Statisticians Ronald Christensen University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico Wesley Johnson University
Texts in Statistical Science Bayesian Ideas and Data Analysis An Introduction for Scientists and Statisticians Ronald Christensen University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico Wesley Johnson University
Bayesian Inference: Concept and Practice
 Inference: Concept and Practice fundamentals Johan A. Elkink School of Politics & International Relations University College Dublin 5 June 2017 1 2 3 Bayes theorem In order to estimate the parameters of
Inference: Concept and Practice fundamentals Johan A. Elkink School of Politics & International Relations University College Dublin 5 June 2017 1 2 3 Bayes theorem In order to estimate the parameters of
Departamento de Economía Universidad de Chile
 Departamento de Economía Universidad de Chile GRADUATE COURSE SPATIAL ECONOMETRICS November 14, 16, 17, 20 and 21, 2017 Prof. Henk Folmer University of Groningen Objectives The main objective of the course
Departamento de Economía Universidad de Chile GRADUATE COURSE SPATIAL ECONOMETRICS November 14, 16, 17, 20 and 21, 2017 Prof. Henk Folmer University of Groningen Objectives The main objective of the course
MAS3301 Bayesian Statistics
 MAS3301 Bayesian Statistics M. Farrow School of Mathematics and Statistics Newcastle University Semester, 008-9 1 13 Sequential updating 13.1 Theory We have seen how we can change our beliefs about an
MAS3301 Bayesian Statistics M. Farrow School of Mathematics and Statistics Newcastle University Semester, 008-9 1 13 Sequential updating 13.1 Theory We have seen how we can change our beliefs about an
Answers and expectations
 Answers and expectations For a function f(x) and distribution P(x), the expectation of f with respect to P is The expectation is the average of f, when x is drawn from the probability distribution P E
Answers and expectations For a function f(x) and distribution P(x), the expectation of f with respect to P is The expectation is the average of f, when x is drawn from the probability distribution P E
Spatio-temporal precipitation modeling based on time-varying regressions
 Spatio-temporal precipitation modeling based on time-varying regressions Oleg Makhnin Department of Mathematics New Mexico Tech Socorro, NM 87801 January 19, 2007 1 Abstract: A time-varying regression
Spatio-temporal precipitation modeling based on time-varying regressions Oleg Makhnin Department of Mathematics New Mexico Tech Socorro, NM 87801 January 19, 2007 1 Abstract: A time-varying regression
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods. Arnaud Doucet.
 Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 CS students: don t forget to re-register in CS-535D. Even if you just audit this course, please do register.
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 CS students: don t forget to re-register in CS-535D. Even if you just audit this course, please do register.
Item Parameter Calibration of LSAT Items Using MCMC Approximation of Bayes Posterior Distributions
 R U T C O R R E S E A R C H R E P O R T Item Parameter Calibration of LSAT Items Using MCMC Approximation of Bayes Posterior Distributions Douglas H. Jones a Mikhail Nediak b RRR 7-2, February, 2! " ##$%#&
R U T C O R R E S E A R C H R E P O R T Item Parameter Calibration of LSAT Items Using MCMC Approximation of Bayes Posterior Distributions Douglas H. Jones a Mikhail Nediak b RRR 7-2, February, 2! " ##$%#&
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics
 Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, June 2009
 Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, 14 27 June 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
Topics in Statistical Data Analysis for HEP Lecture 1: Bayesian Methods CERN-JINR European School of High Energy Physics Bautzen, 14 27 June 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University
NONLINEAR APPLICATIONS OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO
 NONLINEAR APPLICATIONS OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO by Gregois Lee, B.Sc.(ANU), B.Sc.Hons(UTas) Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Mathematics
NONLINEAR APPLICATIONS OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO by Gregois Lee, B.Sc.(ANU), B.Sc.Hons(UTas) Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Mathematics
Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference
 PhD School in Statistics cycle XXIX, 2014 Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference Instructors: B. Liseo, L. Pace, A. Salvan (course coordinator), N. Sartori, A. Tancredi, L. Ventura Syllabus Some prerequisites:
PhD School in Statistics cycle XXIX, 2014 Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference Instructors: B. Liseo, L. Pace, A. Salvan (course coordinator), N. Sartori, A. Tancredi, L. Ventura Syllabus Some prerequisites:
Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Markov chain Monte Carlo Karl Oskar Ekvall Galin L. Jones University of Minnesota March 12, 2019 Abstract Practically relevant statistical models often give rise to probability distributions that are analytically
Markov chain Monte Carlo Karl Oskar Ekvall Galin L. Jones University of Minnesota March 12, 2019 Abstract Practically relevant statistical models often give rise to probability distributions that are analytically
CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1
 CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1 An introduction to cosmological parameter estimation and sampling Presenting for the CosmoSIS team: Elise Jennings (Fermilab, KICP) Joe Zuntz (University of Manchester) Vinicius
CosmoSIS Webinar Part 1 An introduction to cosmological parameter estimation and sampling Presenting for the CosmoSIS team: Elise Jennings (Fermilab, KICP) Joe Zuntz (University of Manchester) Vinicius
Forward Problems and their Inverse Solutions
 Forward Problems and their Inverse Solutions Sarah Zedler 1,2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology 2 University of Texas at Austin February, 2013 Outline 1 Forward Problem Example Weather
Forward Problems and their Inverse Solutions Sarah Zedler 1,2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology 2 University of Texas at Austin February, 2013 Outline 1 Forward Problem Example Weather
Plausible Values for Latent Variables Using Mplus
 Plausible Values for Latent Variables Using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén August 21, 2010 1 1 Introduction Plausible values are imputed values for latent variables. All latent variables can
Plausible Values for Latent Variables Using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén August 21, 2010 1 1 Introduction Plausible values are imputed values for latent variables. All latent variables can
Web Appendix for The Dynamics of Reciprocity, Accountability, and Credibility
 Web Appendix for The Dynamics of Reciprocity, Accountability, and Credibility Patrick T. Brandt School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences University of Texas at Dallas E-mail: pbrandt@utdallas.edu
Web Appendix for The Dynamics of Reciprocity, Accountability, and Credibility Patrick T. Brandt School of Economic, Political and Policy Sciences University of Texas at Dallas E-mail: pbrandt@utdallas.edu
Bayesian Phylogenetics:
 Bayesian Phylogenetics: an introduction Marc A. Suchard msuchard@ucla.edu UCLA Who is this man? How sure are you? The one true tree? Methods we ve learned so far try to find a single tree that best describes
Bayesian Phylogenetics: an introduction Marc A. Suchard msuchard@ucla.edu UCLA Who is this man? How sure are you? The one true tree? Methods we ve learned so far try to find a single tree that best describes
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD, SET ESTIMATION, MODEL CRITICISM
 Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD, SET ESTIMATION, MODEL CRITICISM 1. SOMETHING WE SHOULD ALREADY HAVE MENTIONED A t n (µ, Σ) distribution converges, as n, to a N(µ, Σ). Consider the univariate
Eco517 Fall 2004 C. Sims MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD, SET ESTIMATION, MODEL CRITICISM 1. SOMETHING WE SHOULD ALREADY HAVE MENTIONED A t n (µ, Σ) distribution converges, as n, to a N(µ, Σ). Consider the univariate
Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice
 Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice Martyn International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon, France 13 November 2009 The pure approach For a Bayesian purist, all uncertainty is represented
Penalized Loss functions for Bayesian Model Choice Martyn International Agency for Research on Cancer Lyon, France 13 November 2009 The pure approach For a Bayesian purist, all uncertainty is represented
Bayesian Estimation An Informal Introduction
 Mary Parker, Bayesian Estimation An Informal Introduction page 1 of 8 Bayesian Estimation An Informal Introduction Example: I take a coin out of my pocket and I want to estimate the probability of heads
Mary Parker, Bayesian Estimation An Informal Introduction page 1 of 8 Bayesian Estimation An Informal Introduction Example: I take a coin out of my pocket and I want to estimate the probability of heads
Fundamental Probability and Statistics
 Fundamental Probability and Statistics "There are known knowns. These are things we know that we know. There are known unknowns. That is to say, there are things that we know we don't know. But there are
Fundamental Probability and Statistics "There are known knowns. These are things we know that we know. There are known unknowns. That is to say, there are things that we know we don't know. But there are
Quantile POD for Hit-Miss Data
 Quantile POD for Hit-Miss Data Yew-Meng Koh a and William Q. Meeker a a Center for Nondestructive Evaluation, Department of Statistics, Iowa State niversity, Ames, Iowa 50010 Abstract. Probability of detection
Quantile POD for Hit-Miss Data Yew-Meng Koh a and William Q. Meeker a a Center for Nondestructive Evaluation, Department of Statistics, Iowa State niversity, Ames, Iowa 50010 Abstract. Probability of detection
Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Markov chain Monte Carlo Feng Li feng.li@cufe.edu.cn School of Statistics and Mathematics Central University of Finance and Economics Revised on April 24, 2017 Today we are going to learn... 1 Markov Chains
Markov chain Monte Carlo Feng Li feng.li@cufe.edu.cn School of Statistics and Mathematics Central University of Finance and Economics Revised on April 24, 2017 Today we are going to learn... 1 Markov Chains
DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 7: Bayesian Modeling
 DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 7: Bayesian Modeling Due: Tuesday, May 10, 2016, at 6pm (Submit via NYU Classes) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below, including
DS-GA 1003: Machine Learning and Computational Statistics Homework 7: Bayesian Modeling Due: Tuesday, May 10, 2016, at 6pm (Submit via NYU Classes) Instructions: Your answers to the questions below, including
Principles of Bayesian Inference
 Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee and Andrew O. Finley 2 Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. 2 Department of Forestry & Department
Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee and Andrew O. Finley 2 Biostatistics, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. 2 Department of Forestry & Department
