2.4 Hydro-meteorological chain for flood forecasting in the Toce basin: a multi-model comparison
|
|
|
- Clara Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology Hydro-meteorological chain for flood forecasting in the Toce basin: a multi-model comparison A. Ceppi, 1 G. Ravazzani, 1 D. Rabuffetti 2 and M. Mancini 1 1 Politecnico di Milano - D.I.I.A.R., Piazza Leonardo da Vinci, 32, Milano, Italy 2 A.R.P.A. Piemonte - Via Pio VII 9, 10135, Torino, Italy Correspondence to: alessandro.ceppi@mail.polimi.it Abstract This study is part of the international MAP-D-PHASE Project, whose main objective is to demonstrate the benefits in forecasting heavy precipitation and related flood events, by coupling atmospheric and hydrological models. The analysis is focused on the River Toce, a middle-size alpine basin, in North-West of Italy. The hydro-meteorological chain includes both probabilistic forecasts based on ensemble prediction systems with lead time of a few days and short-range forecasts based on high resolution deterministic atmospheric models. The hydrological model used to generate the runoff simulations is the rainfall-runoff distributed FEST-WB model, developed at Politecnico di Milano. The observed data to run the control simulations were supplied by ARPA-Piemonte. A re-analysis for two precipitation events, affecting the Toce river basin at half June and at the end of November 2007, is shown. Introduction In recent years, the interest in the prediction and prevention of natural hazards related to hydrometeorological events has grown, due to the increased frequency of extreme rainstorms (Rabuffetti et al. 2005a). Several research projects have been developed to test hydrometeorological models for flood forecasting, like HYDROPTIMET Project (Rabuffetti et al., 2005b), and AMPHORE Project (Rabuffetti et al., 2008 and Amengual et al., 2008), two recent Interreg IIIB EU Programmes. Despite these improvements, forecasting of highly localized and severe events is still a challenging problem in many areas, particularly where orographic feature and mesoscale structures cannot be properly represented by Global Circulation Model - Ensemble Prediction System (GCM-EPS) because of its coarse horizontal resolution (Federico et al., 2006). For this reason the challenge for numerical weather modelling, in particular for limited area models, is to improve the Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts (QPFs) for hydrological purposes. Following this goal, many research bodies participated during the summer and autumn 2007 at MAP-D-PHASE Project. D-PHASE stands for Demonstration of Probabilistic Hydrological and Atmospheric Simulation of flood
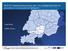
2 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 74 Events in the Alpine region and is a Forecast Demonstration Project (FDP) of the WWRP (World Weather Research Programme of WMO). It aims at demonstrating some of the many achievements of the Mesoscale Alpine Programme (MAP). The MAP FDP will address the entire forecasting chain ranging from limited-area ensemble forecasting, high-resolution atmospheric modelling (km-scale), hydrological modelling and nowcasting to decision making by the end users, i.e., it is foreseen to set up an end-to-end forecasting system. The D- PHASE Operations Period (DOP) was from 1 June to 30 November In this framework two non-hydrostatic meteorological limited area models are used to predict such phenomena at local scale: one with a spatial resolution of 10 km, supported by the powerful ensemble prediction system (Cosmo-Leps model) and the other with a finer grid, but with one deterministic output only (Moloch model). The hydrological model (FEST-WB), developed at Politecnico di Milano, was forced with observed weather data and QPF data coming from the meteorological models used. The state variables of the model are updated daily by A.R.P.A. - Piemonte that runs the same model with weather observations. The aim of this work is to reproduce a hindcast for two precipitation events, affecting the Toce river basin, the Western watershed of Maggiore Lake basin in North-West of Italy, at half June (convective event) and at the end of November 2007 (stratiform event), in order to estimate how the uncertainty of meteorological forecasts influences the quality of hydrological forecasts and the whole hydrometeorological alert system for a midsize catchment. Case study The Toce basin (Figure 2.1) is a midsize watershed located between North-West of Italy (90 %) and South of Switzerland (10 %). The area, closed at Candoglia, covers 1534 km 2 and it is basically an Alpine basin with maximum altitude of 4635 m a.s.l. (East face of Mount Rosa) and minimum altitude of 193 m a.s.l. (height of Maggiore Lake). The lag time of Toce river is about 9 hours. During the MAP-D-PHASE period three warning codes were adopted to highlight different alert thresholds from a meteorological and hydrological point of view. As shown in Figure 2.2 the yellow line points out a discharge (306 m 3 /s) with a return period of at least 60 days, the orange line points out a discharge (694 m 3 /s) with a return period of at least 180 days and the red line a discharge (1588 m 3 /s) with a return period of at least 10 years. Meteorological models The hydrometeorological chain includes both probabilistic forecasts based on ensemble prediction systems with lead time of a few days and short-range forecasts based on high resolution deterministic atmospheric models, in order to predict the QDF (Quantitative Discharge Forecast). The probabilistic forecast was supplied by Cosmo-Leps model (COnsortium
3 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 75 Figure 2.1: Geographical map with the raingauge stations located in the Maggiore Lake basin. The red line bounds the Toce basin. Figure 2.2: Warning codes used for Toce basin at Candoglia during the DPHASE period. for Small-scale Modelling - Limited-Area Ensemble Prediction System) of A.R.P.A. Emilia- Romagna (Marsigli et al., 2005, Montani et al., 2008). The spatial resolution is 10 km (0.09), while the temporal resolution is 3 h, with 40 vertical levels, 16 ensemble members nested on ECMWF EPS (European Centre for Medium Range Forecast - Ensemble Prediction System) and 5 days as lead-time; the run starts every day at 12:00 UTC, while the hydrological simulation begins 12 hours later at 00:00 UTC. The deterministic forecast was supplied by Moloch model of I.S.A.C. - C.N.R. (Davolio et al., 2007). The spatial resolution is 2.2 km (0.02), while the temporal resolution is 1 h, with 50 vertical levels, nested on BOLAM, based on ECMWF and 2 days as lead-time; the run starts every day at 00:00 UTC, at the same time of the hydrological simulation. Hydrological model The hydrological model used to generate the runoff simulations is the rainfall-runoff distributed FEST-WB model, developed at Politecnico di Milano. FEST-WB computes the main process of the hydrological cycle: evapotranspiration, infiltration, surface runoff, flow routing, subsurface flow and snow dynamics. The computation domain is discretized with a mesh of regular square cells, within which water fluxes are calculated. The models needs spatially distributed meteorological forcing. The observed data at ground stations are interpolated to a regular grid using IDW technique, considering the effect of topography such as elevation, aspect and shadow (Rabuffetti et al., 2008). Runoff is computed according to a modified SCS-CN method extended for continuous simulation where the potential maximum retention, S, is updated at the beginning of storm as a linear function of the degree of saturation (Ravazzani et al., 2007). The actual evapotranspiration, ET, is computed as a fraction of the potential rate tuned by a function that, in turn, depends on soil moisture content (Montaldo et al., 2003). The estimation of ETP is computed with Priestley and Taylor
4 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 76 Figure 2.3: Ensemble QDF for Cosmo- Leps model from 14 June to 17 June Figure 2.4: Box-Whisker plot for Cosmo- Leps. The date is referred to the day of the initial hydrological simulation. (1972) equation. The surface and subsurface flow routing is based on the Muskingum-Cunge method in its non-linear form with the time variable celerity (Montaldo et al., 2007). The snow model includes the snow melt and the snow accumulation dynamics. The snow melt simulation is based on the degree day concept (Martinec et al., 1960). The melt rate is proportional to the difference between air temperature and a predefined threshold temperature (Saladin et al., 2004) June 2007 event The synoptic analysis over Europe showed a low depression located South-West of the British Isles with cold air moving eastward over the Po Valley, triggering convective cells on the southern edge of the Alps (about 100 mm of total rain over Toce basin in about 48 hours). The hydrological simulation (green line), done by FEST-WB model, has reached a peak of m 3 /s and it presents 3 hours of delay as peak time error compared to the observed discharge (red line) of m 3 /s. The QPF predicted by Cosmo-Leps model shows a general underestimation in all three days of simulations for all 16 members. This affects the forecasted discharge (Figure 2.4) that has never exceed the second alert threshold as shown in Figure 2.3. The Moloch model, instead, has predicted, one day in advance, the peak discharge, exceeding the second threshold like the observed and simulated discharge, even if there is an evident
5 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 77 Figure 2.5: QDF for Moloch model (light green curve) from 14 June to 15 June Figure 2.6: QDF for Moloch model (light green curve) on 15 June error in time and volume as shown in Figure 2.5. On the contrary, on the same day of the peak event, the QPF was totally underestimated and the discharge has not exceeded even the first alert threshold (Figure 2.6) November 2007 event The synoptic analysis over Europe showed a typical autumn pattern with a deep depression on Atlantic Ocean, bringing moist flow from South-West towards the Italian Alps (about 80 mm of rain on Toce basin, after a long dry period of two months). First of all the FEST-WB discharge simulation with real data has been completely underestimated on 21 (Figure 2.7) and 22 November, due to a not correct initial value of river discharge. Data assimilation of observed discharge, not used in FEST-WB, may provide better results. Therefore, even if Moloch and Cosmo-Leps models have shown a general overestimation of rainfall in terms of volume and intensity, the forecasted discharges remained underestimated. Only on the peak flow day (23 November), after two days of precipitation, a perfect synchrony between the observed and forecasted precipitation (Figure 2.8) and discharges peak is pointed out both for Cosmo-Leps (Figure 2.9) and Moloch model (Figure 2.10). Anyway the observed, simulated and forecasted discharge has never exceeded the first threshold (306 m 3 /s) in any model, i.e. no alert was issued for this event. Conclusions This analysis has shown the results of the hydro-meteorological chain with a multi-model comparison, using the weather models output (Cosmo-Leps and Moloch) as input into the hydrological model (Fest-WB) to predict a QPF (Quantitative Precipitation Forecast) and a QDF (Quantitative Discharge Forecast). The proposed hydro-meteorological forecasting system has been implemented in a real-time configuration, in order to provide useful information concerning the discharge peak (magnitude and timing). High resolution meteorological
6 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 78 Figure 2.7: Observed (red line) vs simulated discharge by FEST-WB model with initial conditions start on 21 November. Figure 2.8: Forecasted mean area accumulated precipitation by Cosmo-Leps model on 21 November. Figure 2.9: QDF for Moloch model (light green curve) on 23 November Figure 2.10: QDF error for Cosmo-Leps ensemble members (black dots) and FEST-WB (dark green dot). model seems to show greater reliability on the prediction of flood on complex topography, but the number of investigated flood events is too small to draw conclusions. Future studies could be addressed to better evaluate the temporal and spatial scale for the total rainfall volume, above all for the convective events. For stratiform events further analyses could be carried out on snow melt temperature which affects the liquid precipitation and therefore the forecasted runoff, like in November event where the snow melt limit was very changeable. Acknowledgments Thanks to ARPA Emilia-Romagna (A. Montani) for his contribute in providing COSMO- LEPS model data and to ISAC-CNR (S. Davolio) for MOLOCH model data. References Amengual, A., Diomede, T., Marsigli, C., Martin, A., Morgillo, A., Romero, R., Papetti, P. and Alonso, S.: A hydrometeorological model intercomparison as a tool to quantify
7 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 79 the forecast uncertainty in a medium size basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, Davolio, S., Buzzi, A., and Malguzzi, P.: High resolution simulations of an intense convective precipitation event. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 95, Federico, S., Avolio, E., Bellucci, C., Colacino, M. and Walko, L.: Application of the LEPS tecnique for a Quantitative Precipitation Forecasting (QPF) in Southern Italy: a preliminary study. Nonlin. Processes Geophys., 13, Marsigli C., Boccanera F., Montani A., Paccagnella T.: The COSMO-LEPS mesoscale ensemble system: validation of the methodology and verification. Nonlin. Proc. Geophys., 12, Martinec, J.: The degree-day factor for snowmelt runoff forecasting, proceedings of general assembly of Helsinki commission on surface waters, IAHS Publ. 51, Montaldo, N., Ravazzani, G. and Mancini, M.: On the prediction of the Toce alpine basin floods with distributed hydrologic models, Hydrol. Processes, 21, Montaldo, N., Toninelli, V., Albertson J. D., Mancini, M. and Troch P. A.: The Effect of Background Hydrometeorological Conditions on the Sensitivity of Evapotranspiration to Model Parameters: Analysis with Measurements from an Italian Alpine Catchment, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 7, Montani, A. Marsigli, C., Paccagnella, T.: Five Years of Limited-Area Ensemble Activities at ARPA- SIM: The COSMO-LEPS system, Cosmo Newsletter n.8. Priestley, C. H. B. and Taylor, R. G.: On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large scale parameters. Mon.Weather Rev., 100, Rabuffetti, D. and Barbero, S.: 2005a. Operational hydro-meteorological warning and real time flood forecasting: the Piemonte Region case study. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 9(4), Rabuffetti, D. and Milelli, M.: 2005b. The hydro-meteorological chain in Piemonte region, North Western Italy - analysis of the HYDROPTIMET test cases. Natural Hazard and Earth System Sciences, 5, Rabuffetti, D., Ravazzani, G., Corbari, C., and Mancini, M.:2008. Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system - the AMPHORE case studies in the upper Po River. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, Ravazzani, G., Mancini, M., Giudici, I., and Amadio, P.: Effects of soil moisture parameterization on a real-time flood forecasting system based on rainfall thresholds, in: Quantification and Reduction of Predictive Uncertainty for Sustainable Water Resources Management, edited by: Boegh, E., Kunstmann, H.,Wagener, T., Hall, A., Bastidas, L.,
8 Fine scale modelling and forecasting in hydrology and meteorology 80 Franks, S., Gupta, H., Rosbjerg, D., and Schaake, J., IAHS Publ. 313, , Salandin, A., Rabuffetti, B., Barbero, S., Cordola, M., Volonte, G. and Mancini, M.: Il lago effimero sul ghiacciaio del Belvedere: monitoraggio e simulazione numerica del fenomeno finalizzata alla previsione e gestione dell emergenza, Neve e Valanghe, 51, 58-65, Tarboton D. G., Chowdhury T. G., Jackson Thomas H.: A Spatially Distributed Energy Balance Snowmelt Model, Utah Water Research Laboratory.
Real-time hydro-meteorological forecasting in the upper Po river basin
 Real-time hydro-meteorological forecasting in the upper Po river basin A. Ceppi 1, G. Ravazzani 1, A. Salandin 2, D. Rabuffetti 2, M. Mancini 1 Roma, 22 Marzo 212 1) Politecnico di Milano D.I.I.A.R. (Dipartimento
Real-time hydro-meteorological forecasting in the upper Po river basin A. Ceppi 1, G. Ravazzani 1, A. Salandin 2, D. Rabuffetti 2, M. Mancini 1 Roma, 22 Marzo 212 1) Politecnico di Milano D.I.I.A.R. (Dipartimento
Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system the AMPHORE case studies in the upper Po River
 Author(s) 8. his work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system
Author(s) 8. his work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Verification of operational Quantitative Discharge Forecast (QDF) for a regional warning system
Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE
 Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE S. Davolio, O. Drofa and P. Malguzzi ISAC - CNR, Bologna, Italy Introduction The Po Valley is an area prone to convective
Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE S. Davolio, O. Drofa and P. Malguzzi ISAC - CNR, Bologna, Italy Introduction The Po Valley is an area prone to convective
Heavy precipitation events over Liguria (Italy): high-resolution hydro-meteorological forecasting and rainfall data assimilation
 Dublin, 08 September 2017 Heavy precipitation events over Liguria (Italy): high-resolution hydro-meteorological forecasting and rainfall data assimilation Silvio Davolio 1, Francesco Silvestro 2, Thomas
Dublin, 08 September 2017 Heavy precipitation events over Liguria (Italy): high-resolution hydro-meteorological forecasting and rainfall data assimilation Silvio Davolio 1, Francesco Silvestro 2, Thomas
Real time probabilistic precipitation forecasts in the Milano urban area: comparison between a physics and pragmatic approach
 Vienna, 18-22 April 16 Session HS4.1/AS4.3/GM9.12/NH1.7 Flash floods and associated hydro-geomorphic processes: observation, modelling and warning Real time probabilistic precipitation forecasts in the
Vienna, 18-22 April 16 Session HS4.1/AS4.3/GM9.12/NH1.7 Flash floods and associated hydro-geomorphic processes: observation, modelling and warning Real time probabilistic precipitation forecasts in the
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
A study on the spread/error relationship of the COSMO-LEPS ensemble
 4 Predictability and Ensemble Methods 110 A study on the spread/error relationship of the COSMO-LEPS ensemble M. Salmi, C. Marsigli, A. Montani, T. Paccagnella ARPA-SIMC, HydroMeteoClimate Service of Emilia-Romagna,
4 Predictability and Ensemble Methods 110 A study on the spread/error relationship of the COSMO-LEPS ensemble M. Salmi, C. Marsigli, A. Montani, T. Paccagnella ARPA-SIMC, HydroMeteoClimate Service of Emilia-Romagna,
LATE REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 LATE REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2016 2018 MEMBER STATE: Italy Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Address: E-mail: Other researchers: Project Title: Valerio Capecchi LaMMA Consortium - Environmental
LATE REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2016 2018 MEMBER STATE: Italy Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Address: E-mail: Other researchers: Project Title: Valerio Capecchi LaMMA Consortium - Environmental
Real-time flood forecasting coupling different postprocessing
 Geosciences ess G Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci.,, 0, 0 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net///0/ doi:0.9/nhess---0 Author(s) 0. CC Attribution.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Atmospheric
Geosciences ess G Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci.,, 0, 0 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net///0/ doi:0.9/nhess---0 Author(s) 0. CC Attribution.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Atmospheric
L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study
 from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
19/11/2008 Real-time demonstration of hydrological ensemble forecasts in MAP D-PHASE
 SHF, Lyon,, 18-19/11/2008 19/11/2008 Real-time demonstration of hydrological ensemble forecasts in MAP D-PHASE Roberto Ranzi, Baldassare Bacchi, University of Brescia, DICATA (I) Alessandro Ceppi, Politecnico
SHF, Lyon,, 18-19/11/2008 19/11/2008 Real-time demonstration of hydrological ensemble forecasts in MAP D-PHASE Roberto Ranzi, Baldassare Bacchi, University of Brescia, DICATA (I) Alessandro Ceppi, Politecnico
DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE
 1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
Sensitivity of COSMO-LEPS forecast skill to the verification network: application to MesoVICT cases Andrea Montani, C. Marsigli, T.
 Sensitivity of COSMO-LEPS forecast skill to the verification network: application to MesoVICT cases Andrea Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy
Sensitivity of COSMO-LEPS forecast skill to the verification network: application to MesoVICT cases Andrea Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy
Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling
 st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
Towards Operational Probabilistic Precipitation Forecast
 5 Working Group on Verification and Case Studies 56 Towards Operational Probabilistic Precipitation Forecast Marco Turco, Massimo Milelli ARPA Piemonte, Via Pio VII 9, I-10135 Torino, Italy 1 Aim of the
5 Working Group on Verification and Case Studies 56 Towards Operational Probabilistic Precipitation Forecast Marco Turco, Massimo Milelli ARPA Piemonte, Via Pio VII 9, I-10135 Torino, Italy 1 Aim of the
Probabilistic high-resolution forecast of heavy precipitation over Central Europe
 Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences () : 315 322 SRef-ID: 168-9981/nhess/--315 European Geosciences Union Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Probabilistic high-resolution forecast of heavy
Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences () : 315 322 SRef-ID: 168-9981/nhess/--315 European Geosciences Union Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Probabilistic high-resolution forecast of heavy
Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands
 Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands Eric Sprokkereef Centre for Water Management Division Crisis Management & Information Supply 2-2-2009 Content The basins Forecasting
Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands Eric Sprokkereef Centre for Water Management Division Crisis Management & Information Supply 2-2-2009 Content The basins Forecasting
COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE
 P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
The D PHASE Operations Period (DOP)
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss The D PHASE Operations Period (DOP) Mathias W Rotach, Marco Arpagaus MeteoSwiss, Zürich, Switzerland Manfred
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss The D PHASE Operations Period (DOP) Mathias W Rotach, Marco Arpagaus MeteoSwiss, Zürich, Switzerland Manfred
Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model
 Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model Giulio Monte, A. Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy OSA 1.6 Session EMS Annual Meeting, 4-8
Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model Giulio Monte, A. Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy OSA 1.6 Session EMS Annual Meeting, 4-8
Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model
 Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model Giulio Monte, A. Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy OSA 1.6 Session EMS Annual Meeting, 4-8
Probabilistic fog forecasting with COSMO model Giulio Monte, A. Montani, C. Marsigli, T. Paccagnella Arpae Emilia-Romagna Servizio IdroMeteoClima, Bologna, Italy OSA 1.6 Session EMS Annual Meeting, 4-8
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s
 C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s Copernicus & Copernicus Services Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu W
C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s Copernicus & Copernicus Services Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu W
Soil moisture perturbations for COSMO in the COTEKINO PP
 Soil moisture perturbations for COSMO in the COTEKINO PP Nicola Loglisci, Riccardo Bonanno ARPA Piemonte Piedmont Regional Agency for Environmental Protection Aim of the task Increase the variability among
Soil moisture perturbations for COSMO in the COTEKINO PP Nicola Loglisci, Riccardo Bonanno ARPA Piemonte Piedmont Regional Agency for Environmental Protection Aim of the task Increase the variability among
Data assimilation in the MIKE 11 Flood Forecasting system using Kalman filtering
 Water Resources Systems Hydrological Risk, Management and Development (Proceedings of symposium IlS02b held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 281. 2003. 75 Data assimilation in the
Water Resources Systems Hydrological Risk, Management and Development (Proceedings of symposium IlS02b held during IUGG2003 al Sapporo. July 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 281. 2003. 75 Data assimilation in the
Preliminary results with very high resolution COSMO model for the forecast of convective events. Antonella Morgillo. Arpa-Simc.
 2 Working Group on Physical Aspects 52 Preliminary results with very high resolution COSMO model for the forecast of convective events. Antonella Morgillo Arpa-Simc amorgillo@arpa.emr.it 1 Introduction
2 Working Group on Physical Aspects 52 Preliminary results with very high resolution COSMO model for the forecast of convective events. Antonella Morgillo Arpa-Simc amorgillo@arpa.emr.it 1 Introduction
PS4a: Real-time modelling platforms during SOP/EOP
 PS4a: Real-time modelling platforms during SOP/EOP Mistral Tramontane Bora Etesian Major sites of dense water formation Major sites of deep water formation influence of coastal waters Chairs: G. Boni,
PS4a: Real-time modelling platforms during SOP/EOP Mistral Tramontane Bora Etesian Major sites of dense water formation Major sites of deep water formation influence of coastal waters Chairs: G. Boni,
A hydrometeorological model intercomparison as a tool to quantify the forecast uncertainty in a medium size basin
 Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, 89 838, 8 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/8/89/8/ Author(s) 8. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Natural Hazards and Earth
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 8, 89 838, 8 www.nat-hazards-earth-syst-sci.net/8/89/8/ Author(s) 8. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Natural Hazards and Earth
Hydrological modelling of snow cover in the large upper Po river basin: winter 2004 results and validation with snow cover estimation from satellite
 Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution II 293 Hydrological modelling of snow cover in the large upper o river basin: winter 2004 results and validation with snow cover estimation from satellite D. Rabuffetti,
Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution II 293 Hydrological modelling of snow cover in the large upper o river basin: winter 2004 results and validation with snow cover estimation from satellite D. Rabuffetti,
Five years of limited-area ensemble activities at ARPA-SIM: the COSMO-LEPS system
 Five years of limited-area ensemble activities at ARPA-SIM: the COSMO-LEPS system Andrea Montani, Chiara Marsigli and Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA-SIM Hydrometeorological service of Emilia-Romagna, Italy 11
Five years of limited-area ensemble activities at ARPA-SIM: the COSMO-LEPS system Andrea Montani, Chiara Marsigli and Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA-SIM Hydrometeorological service of Emilia-Romagna, Italy 11
Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia
 15B.1 RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATES AND NOWCASTS: THE CHALLENGING ROAD FROM RESEARCH TO WARNINGS Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia 1. Introduction Warnings are
15B.1 RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATES AND NOWCASTS: THE CHALLENGING ROAD FROM RESEARCH TO WARNINGS Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia 1. Introduction Warnings are
Matteo Giorcelli 1,2, Massimo Milelli 2. University of Torino, 2 ARPA Piemonte. Eretria, 08/09/2014
 Surface Surface variables variables assimilation assimilation using using FASDAS FASDAS algorithm: algorithm: effects effects on on COSMO-I2 COSMO-I2 RUC RUC forecast forecast Matteo Giorcelli 1,2, Massimo
Surface Surface variables variables assimilation assimilation using using FASDAS FASDAS algorithm: algorithm: effects effects on on COSMO-I2 COSMO-I2 RUC RUC forecast forecast Matteo Giorcelli 1,2, Massimo
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Early Flood Warning for the City of Zurich: Evaluation of real-time Operations since 2010
 EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (EMERGENCY PLANNING, EARLY WARNING, INTERVENTION, RECOVERY) Early Flood Warning for the City of Zurich: Evaluation of real-time Operations since 2010 Katharina Liechti, Dr. 1 ; Matthias
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (EMERGENCY PLANNING, EARLY WARNING, INTERVENTION, RECOVERY) Early Flood Warning for the City of Zurich: Evaluation of real-time Operations since 2010 Katharina Liechti, Dr. 1 ; Matthias
Sensitivity of forecast skill to the parameterisation of moist convection in a limited-area ensemble forecast system
 Sensitivity of forecast skill to the parameterisation of moist convection in a limited-area ensemble forecast system Matteo Vasconi 1,2, Andrea Montani 2, and Tiziana Paccagnella 2 1 Department of Physics
Sensitivity of forecast skill to the parameterisation of moist convection in a limited-area ensemble forecast system Matteo Vasconi 1,2, Andrea Montani 2, and Tiziana Paccagnella 2 1 Department of Physics
Influence of rainfall space-time variability over the Ouémé basin in Benin
 102 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Influence of rainfall space-time variability over
102 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Influence of rainfall space-time variability over
The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic Modelling Outputs
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic
Watershed simulation and forecasting system with a GIS-oriented user interface
 HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 493 Watershed simulation
HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 493 Watershed simulation
Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018
 Flood early warning systems: operational approaches and challenges Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018 Athens, October 31, 2018 Marco Borga University of Padova, Italy
Flood early warning systems: operational approaches and challenges Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018 Athens, October 31, 2018 Marco Borga University of Padova, Italy
Operational Hydrologic Ensemble Forecasting. Rob Hartman Hydrologist in Charge NWS / California-Nevada River Forecast Center
 Operational Hydrologic Ensemble Forecasting Rob Hartman Hydrologist in Charge NWS / California-Nevada River Forecast Center Mission of NWS Hydrologic Services Program Provide river and flood forecasts
Operational Hydrologic Ensemble Forecasting Rob Hartman Hydrologist in Charge NWS / California-Nevada River Forecast Center Mission of NWS Hydrologic Services Program Provide river and flood forecasts
A Strategy for High Resolution Ensemble Prediction
 338 A Strategy for High Resolution Ensemble Prediction Part II: Limited area experiments in four Alpine flood events C Marsigli 1, A Montani 1 F Nerozzi 1, T Paccagnella 1, S. Tibaldi 1, F Molteni 2,3
338 A Strategy for High Resolution Ensemble Prediction Part II: Limited area experiments in four Alpine flood events C Marsigli 1, A Montani 1 F Nerozzi 1, T Paccagnella 1, S. Tibaldi 1, F Molteni 2,3
The hydro-meteorological chain in Piemonte region, North Western Italy - analysis of the HYDROPTIMET test cases
 The hydro-meteorological chain in Piemonte region, North Western Italy - analysis of the HYDROPTIMET test cases D. Rabuffetti, M. Milelli To cite this version: D. Rabuffetti, M. Milelli. The hydro-meteorological
The hydro-meteorological chain in Piemonte region, North Western Italy - analysis of the HYDROPTIMET test cases D. Rabuffetti, M. Milelli To cite this version: D. Rabuffetti, M. Milelli. The hydro-meteorological
The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention
 The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention Muzafar Malikov Space Research Centre Academy of Sciences Republic of Uzbekistan Water H 2 O Gas - Water Vapor
The Importance of Snowmelt Runoff Modeling for Sustainable Development and Disaster Prevention Muzafar Malikov Space Research Centre Academy of Sciences Republic of Uzbekistan Water H 2 O Gas - Water Vapor
European Flooding, Summer 2013
 European Flooding, Summer 2013 Fredrik ikwetterhall Florian Pappenberger, Clement Albergel, Lorenzo Alfieri, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Konrad Bogner, Thomas Haiden, Tim Hewson, Linus Magnusson, Patricia de Rosnay,
European Flooding, Summer 2013 Fredrik ikwetterhall Florian Pappenberger, Clement Albergel, Lorenzo Alfieri, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Konrad Bogner, Thomas Haiden, Tim Hewson, Linus Magnusson, Patricia de Rosnay,
TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP. Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington
 1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
Verification of LAMI (Local Area Model Italy) using non-gts Data over Mountainous Regions
 Verification of LAMI (Local Area Model Italy) using non-gts Data over Mountainous Regions Elena Oberto (*), Stefano Bande (*), Massimo Milelli (*) (*) ARPA Piemonte, Torino, Italy LAMI model Non-hydrostatic
Verification of LAMI (Local Area Model Italy) using non-gts Data over Mountainous Regions Elena Oberto (*), Stefano Bande (*), Massimo Milelli (*) (*) ARPA Piemonte, Torino, Italy LAMI model Non-hydrostatic
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS
 INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center- Hydrologic Modeling System US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center HEC-HMS Uses Schematics Enter properties: watershed, rivers (reaches),
INTRODUCTION TO HEC-HMS Hydrologic Engineering Center- Hydrologic Modeling System US Army Corps of Engineers Hydrologic Engineering Center HEC-HMS Uses Schematics Enter properties: watershed, rivers (reaches),
PROBABILISTIC FORECASTS OF MEDITER- RANEAN STORMS WITH A LIMITED AREA MODEL Chiara Marsigli 1, Andrea Montani 1, Fabrizio Nerozzi 1, Tiziana Paccagnel
 PROBABILISTIC FORECASTS OF MEDITER- RANEAN STORMS WITH A LIMITED AREA MODEL Chiara Marsigli 1, Andrea Montani 1, Fabrizio Nerozzi 1, Tiziana Paccagnella 1, Roberto Buizza 2, Franco Molteni 3 1 Regional
PROBABILISTIC FORECASTS OF MEDITER- RANEAN STORMS WITH A LIMITED AREA MODEL Chiara Marsigli 1, Andrea Montani 1, Fabrizio Nerozzi 1, Tiziana Paccagnella 1, Roberto Buizza 2, Franco Molteni 3 1 Regional
Main characteristics and performance of COSMO LEPS
 Main characteristics and performance of COSMO LEPS Andrea Montani, Chiara Marsigli, Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA Emilia Romagna, Idro Meteo Clima Service Montani Marsigli Paccagnella Stochastic forcing, Ensemble
Main characteristics and performance of COSMO LEPS Andrea Montani, Chiara Marsigli, Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA Emilia Romagna, Idro Meteo Clima Service Montani Marsigli Paccagnella Stochastic forcing, Ensemble
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013
 Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Flood Forecasting Tools for Ungauged Streams in Alberta: Status and Lessons from the Flood of 2013 John Pomeroy, Xing Fang, Kevin Shook, Tom Brown Centre for Hydrology, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS)
 Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
Added Value of Convection Resolving Climate Simulations (CRCS) Prein Andreas, Gobiet Andreas, Katrin Lisa Kapper, Martin Suklitsch, Nauman Khurshid Awan, Heimo Truhetz Wegener Center for Climate and Global
convective parameterization in an
 PANDOWAE (Predictability and Dynamics of Weather Systems in the Atlantic-European Sector) is a research group of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Using the Plant Craig stochastic convective parameterization
PANDOWAE (Predictability and Dynamics of Weather Systems in the Atlantic-European Sector) is a research group of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Using the Plant Craig stochastic convective parameterization
An operational flash-flood forecasting chain applied to the test cases of the EU project HYDROPTIMET
 An operational flash-flood forecasting chain applied to the test cases of the EU project HYDROPTIMET A. C. Taramasso, S. Gabellani, A. Parodi To cite this version: A. C. Taramasso, S. Gabellani, A. Parodi.
An operational flash-flood forecasting chain applied to the test cases of the EU project HYDROPTIMET A. C. Taramasso, S. Gabellani, A. Parodi To cite this version: A. C. Taramasso, S. Gabellani, A. Parodi.
On evaluating the applicability of CRA over small verification domains
 On evaluating the applicability of CRA over small verification domains Stefano Mariani ISPRA Institute for Environmental Protection and Research, Rome, Italy Motivation [ ] it is almost a platitude to
On evaluating the applicability of CRA over small verification domains Stefano Mariani ISPRA Institute for Environmental Protection and Research, Rome, Italy Motivation [ ] it is almost a platitude to
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL
 CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting
 Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
LAM EPS and TIGGE LAM. Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA-SIMC
 DRIHMS_meeting Genova 14 October 2010 Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA-SIMC Ensemble Prediction Ensemble prediction is based on the knowledge of the chaotic behaviour of the atmosphere and on the awareness of
DRIHMS_meeting Genova 14 October 2010 Tiziana Paccagnella ARPA-SIMC Ensemble Prediction Ensemble prediction is based on the knowledge of the chaotic behaviour of the atmosphere and on the awareness of
Surface Hydrology Research Group Università degli Studi di Cagliari
 Surface Hydrology Research Group Università degli Studi di Cagliari Evaluation of Input Uncertainty in Nested Flood Forecasts: Coupling a Multifractal Precipitation Downscaling Model and a Fully-Distributed
Surface Hydrology Research Group Università degli Studi di Cagliari Evaluation of Input Uncertainty in Nested Flood Forecasts: Coupling a Multifractal Precipitation Downscaling Model and a Fully-Distributed
A spatial verification method applied to the evaluation of high-resolution ensemble forecasts
 METEOROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS Meteorol. Appl. 15: 125 143 (2008) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).65 A spatial verification method applied to the evaluation of high-resolution
METEOROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS Meteorol. Appl. 15: 125 143 (2008) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).65 A spatial verification method applied to the evaluation of high-resolution
A HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FLOOD FORECASTING SYSTEM FOR THE RESERVOIR CONTROL IN THE RED RIVER
 COMMISSION INTERNATIONALE DES GRANDS BARRAGES ------ LA 78 EME CONGRES DES GRANDS BARRAGES Hanoi-Vietnam, Mai 21 A HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FLOOD FORECASTING SYSTEM FOR THE RESERVOIR CONTROL IN THE RED RIVER
COMMISSION INTERNATIONALE DES GRANDS BARRAGES ------ LA 78 EME CONGRES DES GRANDS BARRAGES Hanoi-Vietnam, Mai 21 A HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL FLOOD FORECASTING SYSTEM FOR THE RESERVOIR CONTROL IN THE RED RIVER
D. Rabuffetti 1, A. Salandin 1, R. Cremonini 1
 +\GURORJLFDOPRGHOOLQJRIVQRZFRYHULQWKH ODUJHXSSHU3RULYHUEDVLQKHZLQWHU UHVXOWVDQGYDOLGDWLRQZLWKVQRZFRYHU HVWLPDWLRQIURPVDWHOOLWH D. Rabuffetti 1, A. Salandin 1, R. Cremonini 1 $USD3LHPRQWH,WDO\ $EVWUDFW
+\GURORJLFDOPRGHOOLQJRIVQRZFRYHULQWKH ODUJHXSSHU3RULYHUEDVLQKHZLQWHU UHVXOWVDQGYDOLGDWLRQZLWKVQRZFRYHU HVWLPDWLRQIURPVDWHOOLWH D. Rabuffetti 1, A. Salandin 1, R. Cremonini 1 $USD3LHPRQWH,WDO\ $EVWUDFW
Global Flash Flood Guidance System Status and Outlook
 Global Flash Flood Guidance System Status and Outlook HYDROLOGIC RESEARCH CENTER San Diego, CA 92130 http://www.hrcwater.org Initial Planning Meeting on the WMO HydroSOS, Entebbe, Uganda 26-28 September
Global Flash Flood Guidance System Status and Outlook HYDROLOGIC RESEARCH CENTER San Diego, CA 92130 http://www.hrcwater.org Initial Planning Meeting on the WMO HydroSOS, Entebbe, Uganda 26-28 September
The POLIMI forecasting chain for flood and drought predictions
 The POLIMI forecasting chain for flood and drought predictions Politecnico di Milano A. Ceppi 1, G. Ravazzani 1, C. Corbari 1, I. Bocus 1, G. Di Luccio 1, S. Meucci 2, A. Perotto, R. Salerno 3, M. Mancini
The POLIMI forecasting chain for flood and drought predictions Politecnico di Milano A. Ceppi 1, G. Ravazzani 1, C. Corbari 1, I. Bocus 1, G. Di Luccio 1, S. Meucci 2, A. Perotto, R. Salerno 3, M. Mancini
Flood Forecasting. Fredrik Wetterhall European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts
 Flood Forecasting Fredrik Wetterhall (fredrik.wetterhall@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 Flooding a global challenge Number of floods Slide 2 Flooding a global challenge
Flood Forecasting Fredrik Wetterhall (fredrik.wetterhall@ecmwf.int) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 Flooding a global challenge Number of floods Slide 2 Flooding a global challenge
Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting. T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome.
 Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome. The Met Alert Messages by the Watch Office of the Public Safety
Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome. The Met Alert Messages by the Watch Office of the Public Safety
Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project
 3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting
 Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting Enrique R. Vivoni *, Dara Entekhabi *, Rafael L. Bras *, Matthew P. Van Horne *, Valeri Y. Ivanov *, Chris Grassotti + and Ross Hoffman +
Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting Enrique R. Vivoni *, Dara Entekhabi *, Rafael L. Bras *, Matthew P. Van Horne *, Valeri Y. Ivanov *, Chris Grassotti + and Ross Hoffman +
RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF GLACIER CONTRIBUTIONS TO STREAMFLOW IN A CHANGING CLIMATE
 Proceedings of the Second IASTED International Conference WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT August 20-22, 2007, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA ISGN Hardcopy: 978-0-88986-679-9 CD: 978-0-88-986-680-5 RELATIVE IMPORTANCE
Proceedings of the Second IASTED International Conference WATER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT August 20-22, 2007, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA ISGN Hardcopy: 978-0-88986-679-9 CD: 978-0-88-986-680-5 RELATIVE IMPORTANCE
The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review. J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf
 168 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf The Flood-Event During the second half of August 2005 severe floodings
168 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf The Flood-Event During the second half of August 2005 severe floodings
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Improvements in IFS forecasts of heavy precipitation
 from Newsletter Number 144 Suer 215 METEOROLOGY Improvements in IFS forecasts of heavy precipitation cosmin4/istock/thinkstock doi:1.21957/jxtonky This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF
from Newsletter Number 144 Suer 215 METEOROLOGY Improvements in IFS forecasts of heavy precipitation cosmin4/istock/thinkstock doi:1.21957/jxtonky This article appeared in the Meteorology section of ECMWF
Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS Dr. Bogumil Jakubiak Interdisciplinary
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Implementation of Modeling the Land-Surface/Atmosphere Interactions to Mesoscale Model COAMPS Dr. Bogumil Jakubiak Interdisciplinary
Satellite data for hydrological forecasting
 Satellite data for hydrological forecasting Current use at ECMWF and perspective Shopping list! Our current tools does not allow direct use, but could be modified Christel Prudhomme Christel.prudhomme@ecmwf.int
Satellite data for hydrological forecasting Current use at ECMWF and perspective Shopping list! Our current tools does not allow direct use, but could be modified Christel Prudhomme Christel.prudhomme@ecmwf.int
INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework
 INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework Yong Wang ZAMG, Austria This project is implemented through the CENTRAL EUROPE Programme co-financed
INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework Yong Wang ZAMG, Austria This project is implemented through the CENTRAL EUROPE Programme co-financed
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Bolli Pálmason and Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts
1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT
 1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT Enrico Minguzzi 1 Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, and Guido Pirovano 4 1 Hydrometeorological Service of Emilia Romagna (SIM),
1.21 SENSITIVITY OF LONG-TERM CTM SIMULATIONS TO METEOROLOGICAL INPUT Enrico Minguzzi 1 Marco Bedogni 2, Claudio Carnevale 3, and Guido Pirovano 4 1 Hydrometeorological Service of Emilia Romagna (SIM),
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model
 WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
WDS'3 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 8 84, 23. ISBN 978-8-737852-8 MATFYZPRESS Regional Climate Simulations with WRF Model J. Karlický Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: The role of soil moisture and surface- and subsurface water flows on predictability of convection
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: The role of soil moisture and surface- and subsurface water flows on predictability of convection
Assessment of rainfall and evaporation input data uncertainties on simulated runoff in southern Africa
 98 Quantification and Reduction of Predictive Uncertainty for Sustainable Water Resources Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS24 at IUGG27, Perugia, July 27). IAHS Publ. 313, 27. Assessment of rainfall
98 Quantification and Reduction of Predictive Uncertainty for Sustainable Water Resources Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS24 at IUGG27, Perugia, July 27). IAHS Publ. 313, 27. Assessment of rainfall
Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting To cite this article: Ph Stanzel et al
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Modelling snow accumulation and snow melt in a continuous hydrological model for real-time flood forecasting To cite this article: Ph Stanzel et al
STATISTICAL ESTIMATION AND RE- ANALYSIS OF PRECIPITATIONS OVER FRENCH MOUNTAIN RANGES
 STATISTICAL ESTIMATION AND RE- ANALYSIS OF PRECIPITATIONS OVER FRENCH MOUNTAIN RANGES USING WEATHER PATTERNS, WATER BALANCES AND SNOW MEASUREMENTS ASSIMILATION Frederic GOTTARDI EDF frederic.gottardi@edf.fr
STATISTICAL ESTIMATION AND RE- ANALYSIS OF PRECIPITATIONS OVER FRENCH MOUNTAIN RANGES USING WEATHER PATTERNS, WATER BALANCES AND SNOW MEASUREMENTS ASSIMILATION Frederic GOTTARDI EDF frederic.gottardi@edf.fr
Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model
 Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Dara Entekhabi 2 and Ross N. Hoffman 3 1. Department of Earth and Environmental
Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Dara Entekhabi 2 and Ross N. Hoffman 3 1. Department of Earth and Environmental
Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements
 Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements Nergui Nanding, Miguel Angel Rico-Ramirez and Dawei Han Department of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol Queens
Rainfall-runoff modelling using merged rainfall from radar and raingauge measurements Nergui Nanding, Miguel Angel Rico-Ramirez and Dawei Han Department of Civil Engineering, University of Bristol Queens
AMMA-ALMIP-MEM project soil moisture & μwaves Tb
 AMMA-ALMIP-MEM project soil moisture & μwaves Tb P. de Rosnay, A. Boone, M. Drusch, T. Holmes, G. Balsamo, many others ALMIPers (paper submitted to IGARSS) AMMA-ALMIP-MEM first spatial verification of
AMMA-ALMIP-MEM project soil moisture & μwaves Tb P. de Rosnay, A. Boone, M. Drusch, T. Holmes, G. Balsamo, many others ALMIPers (paper submitted to IGARSS) AMMA-ALMIP-MEM first spatial verification of
Multiphysics superensemble forecast applied to Mediterranean heavy precipitation situations
 doi:10.5194/nhess-10-2371-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Multiphysics superensemble forecast applied to Mediterranean heavy precipitation situations
doi:10.5194/nhess-10-2371-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Multiphysics superensemble forecast applied to Mediterranean heavy precipitation situations
INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS, NW GREECE), ON PRECIPITATION, DURING THE WARM PERIOD OF THE YEAR
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Analysis and modeling of a flooding event in the framework of the DRIHM project
 Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: M. Carme Llasat Abstract: In early November 2011 a pertorbation affecting the Mediterranean area led
Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: M. Carme Llasat Abstract: In early November 2011 a pertorbation affecting the Mediterranean area led
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Application and verification of ECMWF products at the Finnish Meteorological Institute
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 2011 at the Finnish Meteorological Institute by Juhana Hyrkkènen, Ari-Juhani Punkka, Henri Nyman and Janne Kauhanen 1. Summary of major highlights ECMWF
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 2011 at the Finnish Meteorological Institute by Juhana Hyrkkènen, Ari-Juhani Punkka, Henri Nyman and Janne Kauhanen 1. Summary of major highlights ECMWF
Application of EPS Weather driven natural hazards
 Application of EPS Weather driven natural hazards J.Thielen EC Joint Research Centre IES/LMU/WDNH Weather driven natural hazards An unexpected or uncontrollable natural event of unusual magnitude that
Application of EPS Weather driven natural hazards J.Thielen EC Joint Research Centre IES/LMU/WDNH Weather driven natural hazards An unexpected or uncontrollable natural event of unusual magnitude that
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods
 Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Limited-area ensembles: finer grids & shorter lead times Susanne Theis COSMO-DE-EPS project leader Deutscher Wetterdienst Thank You Neill Bowler et al. (UK Met Office) Andras Horányi
Deutscher Wetterdienst Limited-area ensembles: finer grids & shorter lead times Susanne Theis COSMO-DE-EPS project leader Deutscher Wetterdienst Thank You Neill Bowler et al. (UK Met Office) Andras Horányi
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Gu rún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2009 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Gu rún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Coupling of high-resolution meteorological and wave models over southern Italy
 Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 9, 1267 1275, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Coupling of high-resolution
Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 9, 1267 1275, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences Coupling of high-resolution
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC
 Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Chiang Rai Province CC Threat overview AAS1109 Mekong ARCC This threat overview relies on projections of future climate change in the Mekong Basin for the period 2045-2069 compared to a baseline of 1980-2005.
Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black Sea coastal area, Northern Caucasus
 Proc. IAHS, 7, 161 165, 215 proc-iahs.net/7/161/215/ doi:1.5194/piahs-7-161-215 Author(s) 215. CC Attribution. License. Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black
Proc. IAHS, 7, 161 165, 215 proc-iahs.net/7/161/215/ doi:1.5194/piahs-7-161-215 Author(s) 215. CC Attribution. License. Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities
 Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
Bill Kappel. Doug Hultstrand. Applied Weather Associates
 Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
Cool-Season PMP/PMF Meteorological Time Series for Snow Melt Calculations Bill Kappel Senior Meteorologist/Vice President Doug Hultstrand Hydrometeorologist Applied Weather Associates www.appliedweatherassociates.com
The indicator can be used for awareness raising, evaluation of occurred droughts, forecasting future drought risks and management purposes.
 INDICATOR FACT SHEET SSPI: Standardized SnowPack Index Indicator definition The availability of water in rivers, lakes and ground is mainly related to precipitation. However, in the cold climate when precipitation
INDICATOR FACT SHEET SSPI: Standardized SnowPack Index Indicator definition The availability of water in rivers, lakes and ground is mainly related to precipitation. However, in the cold climate when precipitation
