Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary layer Clouds
|
|
|
- Felix Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary layer Clouds Bruce Albrecht University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences 4600 Rickenbacker Causeway Miami, FL Award Number: N LONG-TERM GOALS The long term-goal of this project is to provide an improved description and understanding of the effects of aerosol-cloud interactions and drizzle and entrainment processes in boundary layer clouds for the purpose of developing, improving, and evaluating cloud and boundary layer representations in LES, mesoscale and large-scale forecast models. OBJECTIVES The scientific objectives are to: 1) document the structure and characteristics of entrainment circulations in marine stratocumulus and fair-weather-cumuli, 2) characterize the vertical distribution of drizzle and how it relates to cloud and mesoscale circulations; 3) investigate the relative role of cloud thickness, cloud turbulence intensity, and aerosols on precipitation production; 4) study the processing of aerosols by cloud processes; and 5) explore mass, moisture, and aerosol transports across interfacial regions at cloud base and at the capping inversion. APPROACH The observations needed for this study are made using the NAVY CIRPAS Twin Otter research aircraft and includes the use of an FMCW cloud radar to track drizzle and cloud features while making simultaneous in situ measurements of aerosols and cloud characteristics. Further, we use the cloud radar with radar chaff to track air motions in and out of the clouds. Cloud seeding techniques demonstrated in an earlier ONR funded study are extended to study the response of cloud and drizzle processes to the artificial introduction of CCN and giant nuclei under differing aerosol backgrounds. In addition, a set of aerosol and cloud observations in trade wind cumulus clouds using the CIRPAS aircraft with the cloud radar was designed and carried out. The observational components of this study are made in environments where a strong-aerosol-cloud variability was observed. This included observations made during VOCALS (VAMOS Ocean Cloud Atmosphere Land Study) Regional Experiment off the coast of Chile (Oct.-Nov. 2008) where satellite observations indicate strong gradients in cloud properties off the coast. Further from the South Florida area of fair-weather cumulus clouds (Jan. 2008) where clouds with both marine and continental characteristics were observed. This was followed by a set of observations made in 2010 of cumulus clouds in off of Barbados. These studies included the participation of a number of graduate students and a technician/data analyst. For 1
2 the VOCALS study we collaborated with Dr. Carl Friehe and Djmal Khief (U. Calif. Irvine) on turbulence observations from the Twin Otter and with Dr. Patrick Chaung (U. Calif. Santa Cruz) on cloud physics measurements. Dr. Haflidi Jonsson, the chief scientist for the CIRPAS Twin Otter (TO), has been an integral collaborator in all projects involving this research aircraft. WORK COMPLETED From 15 October to Januray-February 2008, the CIPAS Twin Otter was used to study aersosl, cloud, precipitation and turbulence observation in the South Florida area. A total of 15 flights were flown and provided sampling over a wide range of aerosol, cloud and boundary layer conditions. Flights were made over water and over land to provide boundary layer turbulence variations. Substantial boundary layer variations were observed and cloud conditions encountered included nearly solid stratocumulus, shallow non-precipitating cumulus, and shallow precipitating cumulus. Thus a full range of aerosol, cloud, and boundary layer conditions were sampled during the deployment and a rich data set for understaing key physical processes operating in these clouds was obtained. Work is currently in progress to analyze the data that were collected during these aircraft missions and will be compared with the observations made over the open ocean east of the island of Barbados from 15 March to 15 April During these studies 4 University of Miami gaduate students (one funded by this grant ) participated in the aircraft observations. Further, undegradaute meterolgy students from UM toured the Twin Otter facility and received instument tutorials as an enhancement to their meterological intrumentation class during the time the aircraft was in Miami. As part of this research project the CIRPAS Twin Otter (TO) research aircraft was deployed for VAMOS Ocean-Cloud-Atmosphere-Land Study -Regional Experiment (VOCALS-REx) that was undertaken from October to November 2008 over the subtropical southeastern Pacific to investigate physical and chemical processes important for boundary layer and cloud processes in this region. The CIRPAS Twin Otter aircraft made 19 research flights off the coast of Northern Chile during VOCALS- REx from Oct. 15 to Nov. 15. Cloud conditions were excellent during this deployment. The flight strategy involved operations at a fixed point (20 S; 72 W; reference point alpha) that allowed for a definition of the temporal evolution of boundary layer structures, aerosols, and cloud properties. Each flight included 3 to 4 soundings and near-surface, below-cloud, cloud base, in cloud, cloud top, and above inversion observations along fixed-height legs. This study used the aerosol, cloud, boundarylayer thermodynamics and turbulence data from those 18 flights to investigate the boundary layer, and aerosol-cloud-drizzle variations in this region. The Barbados Aerosol Cloud Experiment (BACEX) was planned by our research group and then carried out from 15 March to 15 April The purpose of this field experiment was to observe the time evolution of the cloud and precipitation characteristics of individual oceanic cumulus clouds and to develop statistics on aerosol, cloud, and precipitation under varying aerosol conditions. The principal observing platform for the experiment was the CIRPAS TO that was equipped with aerosol, cloud, and precipitation probes and standard meteorological instrumentation for observing mean and turbulent thermodynamic and wind structures. The highlight of the TO observing package was an upward facing FMCW Doppler 95 GHz radar (designed and fabricated by ProSensing). The use of the FMCW radar, which has a dead zone of less than 50 m, allows for radar observation in close proximity to the in situ probe measurements. The Doppler spectra from the radar proved to be rich in structure that will help deconvolve the contributions to the radar returns from both cloud and rain. The aircraft was used to characterize the structure of shallow to moderately deep (cloud tops less than 2 km) and mostly precipitating marine cumulus clouds. A total of 15 aircraft flights were made just upstream 2
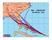
3 from a point on the eastern shore of Barbados (Ragged Point) where surface aerosol measurements (Joe Prospero, University of Miami) were made along with aerosol characterizations from a NASA AERONET tracking sun photometer for aerosol optical depth (AOD) and a micro-pulse LIDAR. Routine rawindsonde observations made daily from the island (by Barbados Meteorological Service) and observations from an S-Band radar (by Caribbean Meteorological Organization) on Barbados were collected in support of BACEX. Cloud radar observations from the CIRPAS Twin Otter were made in support of the TO operations made off the coast of California during July-August 2011 in support of The Eastern Pacific Emitted Aerosol Cloud Experiment (E-PEACE) 2011 that was led by Dr. Lynn Russell and with collaborators John Seinfeld and Armin Sorooshian. The observations from the FMCW radar that was operated by our group are being used to document the cloud structure observed on the flights flown during E- PEACE. A set of experiments where giant (salt) nuclei where intentionally dispersed in solid stratocumulus clouds off the coast was executed. The giant nuclei released during these experiments were milled salt particles (about 3 µm) that were coated to prevent sticking. They were dispersed using a mechanism that auger fed particles into fluidized bed of grit before emitting them to the outside in a pressurized flow. After the particles were dispersed flights were made in the cloud at lower levels where the radar and the in situ probes sampled the air mass that was seeded with the salt particles to see how the cloud and precipitation characteristics of the cloud were modified. RESULTS The observations made during the VOCALS deployment provide a unique characterization of the cloud and aerosol variability in the coastal environment. The marine atmospheric boundary layer structures observed showed relatively little variability and indicated little influence from meso-scale and large-scale systems. The boundary layer structures observed on several of the VOCALS flights were remarkably similar, although the observed aerosol concentrations in the boundary layer and the cloud water content and the liquid water path of the clouds topping the boundary layer varied considerably. On 10 of the flight days, the boundary layer was well mixed, the clouds sampled were non-precipitating, and conditions at the top and the bottom of the mixed layer were very similar. Calculated boundary layer back trajectories for the 72 hours prior to the observations at 20 o N and 72 o W remained mostly over coastal ocean areas and indicate that advective effects were generally small during this time. Thus the boundary layer, cloud and aerosol structures sampled on the individual days were likely to be steady and close to equilibrium. Despite the constancy of the thermodynamic structures of the boundary layers studied on these 10 flights, the subcloud CCN varied substantially and was closely coupled to the cloud droplet concentrations as well. CCN in the boundary layer for these cases ranged from cm -3 in the relatively thin capping clouds. The liquid water path in these clouds ranged from 22 to 73 gm -2 and was positively correlated with the aerosol and cloud droplet concentrations (Fig. 1) as described in a GRL paper (Zheng et al., 2010). Processes that may link the aerosol concentrations and the liquid water path and explain the observed positive correlation are currently under study using satellite observations along low-level trajectories and LES to study the effects of aerosols. 3
4 Figure 1. LWP as a function of sub-cloud CCN concentrations for all flights during VOCALS at Point Alpha. The error bars through these symbols indicate the standard deviation of CCN and estimates of LWP uncertainty. During BACEX the Twin Otter was able to sample many cumulus clouds in various phases of growth during BACEX and under different aerosol loading. Precipitation varied from light to heavy with the convection showing substantial meso-scale organization on several of the flights. Rapidly dissipating clouds (life-times of less than minutes) were probed on several occasions by cloud penetrations starting from cloud top and working downward with time. The time evolution of these strongly precipitating clouds and the relative role of precipitation and evaporation (through entrainment) in explaining these results are under study. The principal variability in the background aerosols observed during these flights was associated with African dust above the boundary layer. On two days when convection was completely suppressed, an African dust event associated with record Aerosol Optical Depths (AODs) for Barbados during this time of the year was observed. The vertical structure of the aerosols and the boundary layer observed during these cases will be documented. The thermodynamic structure and the aerosol structure associated with one of these cases are shown in Figs. 2 and 3. The thermodynamic profiles show a clear layered structure with the SAL layer capping the marine boundary layer. Aerosols in the near-surface mixed layer are relatively mixed with height as are the aerosols in the SAL. The intermediate layer (between the SAL and the surface mixed layer) shows substantial variability in the thermodynamic and the aerosol structures. This variability is most likely linked to convective processing of the aerosol sometime in the history of the intermediate air mass as it moved across the Atlantic. This unique data set is being used to further study aerosol transports and processing during this major African dust event. 4
5 Figure 2. Potential temperature (θ) and mixing ratio profiles obtained on soundings during BACEX on 1 April during an intense African dust event. The Saharan Air Layer (SAL) is observed above the marine boundary layer. The intermediate layer extends from this layer to the top of the subcloud mixed layer. The black data points were obtained on ~10 minute legs flown at a constant altitude and show the spread of θ and mixing ratio at these levels. The dashed lines are extrapolation of the SAL values to the surface. Figure 3. Aerosol concentrations (# per unit mass of dry air) from PCASP (0.1 to 3 µm), CCN (at 0.3 and 0.6 super-saturations), and CN from TO observations. The left and right panels are for two profiles made in the same vicinity but separated by about 2 hours. 5
6 Two new techniques for using an airborne cloud radar for probing air motions in precipitating clouds and tracking circulation in the clear air around and beneath the cloud were demonstrated during BACEX. The first is based on a technique that allows for the retrieval of vertical air motion from an airborne W-Band radar using Mie scattering thumbprints in the radar Doppler spectrum. In cases where raindrops have diameters comparable to the wavelength (3.2 mm) of the 95-GHz radar, Mie scattering explains the oscillation of the backscattering cross section between successive peaks and valleys as a function of the raindrop diameter (Pavlos et al., 2003). The minimum in the Doppler spectrum can then be used to determine the air vertical velocity. At radar wavelengths of 3 mm, the first minimum in the backscattering cross section occurs at a raindrop diameter equal to 1.65 mm. Despite the relatively shallow nature of the convection observed on the BACEX flights (tops at km), raindrops exceeding this diameter were observed on several occasions and allowed us to make a first-ever successful test of this technique from an aircraft. This work was submitted to the J. Appl. Meteor. and Climate. The second technique demonstrated was the use of radar chaff to track motions associated with entrainment and detrainment processes at the top and edges of cumulus clouds the airborne FMCW 95 GHz Doppler radar on the Twin Otter. The chaff used for this experiment was pre-cut metallic coated fibers (cut to 1/4 of the wavelength of the radar) that were dispersed from canisters carried in a pod beneath the wing of the CIRPAS Twin Otter. The fibers have a terminal velocity of about 2 cm/s and follow air motions. The chaff experiments were designed to examine entrainment-detrainment processes and the subsiding shells observed around small cumulus clouds. After the chaff was dispensed near cloud top, the aircraft made penetrations of the cloud at lower levels to observe the chaff clouds above with the radar. Examples of the radar returns from radar chaff above the aircraft flight level are shown in Figs. 4 g and d. In this case chaff was released in a downdraft along the edge of the cloud (Fig. 4a). Here the environmental air above the cloud top descended to the level of equilibrium potential temperature, along the downshear side of out-cloud edges through a downdraft and was subsequently entrained laterally into the cloud at the the lower observational level. This study also provides a more complete picture of the in-cloud flow patterns that have been hypothesized in previous studies and is the first-ever use of a cloud radar to track radar chaff flows in and around cumulus clouds. IMPACT/APPLICATIONS The results from these studies are intended to provide an improved understanding of the physical processes associated with cloud-aerosol-drizzle-turbulence interaction that will lead the way to improved representation of the processes in models operating over a wide range of scale and particularly for mesoscale and large-scale forecast models used in coastal and marine environments. The successful completion of the VOCALS Twin Otter observational period has already produced results that show a positive correlation in the CCN concentration in the boundary layer with the observed LWP. The variations are substantial and the reasons for these changes are under study. The aircraft observations that were obtained during VOCALS have been used for evaluation of the COAMPS real-time forecast (Wang et al., 2011). The air velocity (Mie minimum) retrieval technique that was demonstrated from the BACEX observations has important implications for future observational studies. Using a downward looking cloud radar (95 GHz) one could, for example, retrieve the updraft and downdraft structures in tropical cyclone rainbands in radar sampling volumes extending from the aircraft to the ocean surface. A radar designed to operate at a shorter wavelength (e.g. 1 mm) could be used for retrieving air motion 6
7 associated with smaller raindrops. The demonstration of the use of radar chaff optimally cut for use with a cloud radar provide a unique observational technique for understanding the flows in and around boundary layer clouds and sets the way for future observational studies using this technique. If scanning cloud radars with differential polarization capabilities were used, the returns from cloud and chaff could be separated. Figure 4: Time-height cross sections of (a, d, g) zeroth moment (power/reflectivity), (b, e, h) first moment (vertical velocity) and (c, f, i) second moment (spectrum width) of Doppler spectrum for the chaffed cloud on 29 March 2010 through leg 2 to leg 4 (top-down). The aircraft observations were made at an air speed of about 60 m s -1 and thus cloud widths are approximately 430 to 860 m. Liquid water contents were added as black solid line in panle d. Note that reversed time axes are used for the chaffed cloud at leg 4 (panles g-i) to give a spatial consistency for penetrations made in opposite direction.. REFERENCES Wang, S., O Neill, L. W., Jiang, Q., de Szoeke, S. P., Hong, X., Jin, H., Thompson, W. T., and Zheng, X.: A regional real-time forecast of marine boundary layers during VOCALS-REx, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, , doi: /acp , Kollias, P., B.A. Albrecht, and F. Marks Jr., 2002: Why Mie? Accurate observations of vertical air velocities and raindrops using a cloud radar. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 83(10),
8 PUBLICATIONS Bretherton, C. S., Wood, R., George, R. C., Leon, D., Allen, G., and Zheng, X, 2101: Southeast Pacific stratocumulus clouds, precipitation and boundary layer structure sampled along 20 S, during VOCALS-REx, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10, , doi: /acp , Jung, E., B. Albrecht, P. Kollias, and I. PopStefanija, 2011: The Retrieval of Vertical Air Motion from an Airborne W-Band radar using Mie Scattering. J. of App. Meteor. and Clim. (submitted) Wang, S., O Neill, L. W., Jiang, Q., de Szoeke, S. P., Hong, X., Jin, H., Thompson, W. T., and Zheng, X.: A regional real-time forecast of marine boundary layers during VOCALS-REx, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, , doi: /acp , Wood, R., Bretherton, C. S., Mechoso, C. R., Weller, R. A., Huebert, B., Straneo, F., Albrecht, B. A., Coe, H., Allen, G., Vaughan, G., Daum, P., Fairall, C., Chand, D., Gallardo Klenner, L., Garreaud, R., Grados Quispe, C., Covert, D. S., Bates, T. S., Krejci, R., Russell, L. M., de Szoeke, S., Brewer, A., Yuter, S. E., Springston, S. R., Chaigneau, A., Toniazzo, T., Minnis, P., Palikonda, R., Abel, S. J., Brown, W. O. J., Williams, S., Fochesatto, J., and Brioude, J., 2010: The VAMOS Ocean-Cloud-Atmosphere-Land Study Regional Experiment (VOCALS-REx): goals, platforms, and field operations, Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 10, , doi: /acpd Zheng, X., Albrecht, B. A., Minnis, P., Ayers, K., and Jonsson, H. H., Observed aerosol and liquid water path relationships in marine stratocumulus, Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L17803, doi: /2010gl044095, 2010 Zheng, X., B. Albrecht, B., Jonsson, H. H., Khelif, D., Feingold, G., Minnis, P., Ayers, K., Chuang, P., Donaher, S., Rossiter, D., Ghate, V., Ruiz-Plancarte, J., and Sun-Mack, S., 2011: Observations of the boundary layer, cloud, and aerosol variability in the southeast Pacific coastal marine stratocumulus during VOCALS-REx, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11,
Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary Layer Clouds
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary Layer Clouds Bruce Albrecht University of Miami Rosenstiel School
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary Layer Clouds Bruce Albrecht University of Miami Rosenstiel School
Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary layer Clouds
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary layer Clouds Bruce Albrecht University of Miami Rosenstiel School
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Aerosol-Cloud-Drizzle-Turbulence Interactions in Boundary layer Clouds Bruce Albrecht University of Miami Rosenstiel School
Part 2 Aircraft-based Observations
 Part 2 Aircraft-based Observations NSF C-130 CIRPAS Twin Otter FAAM BAe146 UK NEC Dornier 2028 Measuring microphysical, chemical and optical properties of aerosols aboard the NCAR/NSF C-130 during
Part 2 Aircraft-based Observations NSF C-130 CIRPAS Twin Otter FAAM BAe146 UK NEC Dornier 2028 Measuring microphysical, chemical and optical properties of aerosols aboard the NCAR/NSF C-130 during
A review of VOCALS Hypothesis. VOCALS Science Meeting July 2009 Seattle Washington C. R. Mechoso, UCLA
 A review of VOCALS Hypothesis VOCALS Science Meeting 12-14 July 2009 Seattle Washington C. R. Mechoso, UCLA VOCALS Strategy MODELING Operational Centers, Reseach Institutions, Universities REx AIRBORNE
A review of VOCALS Hypothesis VOCALS Science Meeting 12-14 July 2009 Seattle Washington C. R. Mechoso, UCLA VOCALS Strategy MODELING Operational Centers, Reseach Institutions, Universities REx AIRBORNE
EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS
 EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS Bruce Albrecht 1, Tarah Sharon 1, Haf Jonsson 2, Patrick Minnis 3, J. Kirk Ayers 4, Mandana M.
EVIDENCE FOR NATURAL VARIABILITY IN MARINE STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD PROPERTIES DUE TO CLOUD-AEROSOL INTERACTIONS Bruce Albrecht 1, Tarah Sharon 1, Haf Jonsson 2, Patrick Minnis 3, J. Kirk Ayers 4, Mandana M.
A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S
 A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S Chris Bretherton Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington VOCALS RF05, 72W 20S Work summarized
A synthesis of published VOCALS studies on marine boundary layer and cloud structure along 20S Chris Bretherton Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington VOCALS RF05, 72W 20S Work summarized
Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian,
Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO
 Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO Institutions: University of Miami; University of Colorado; NOAA ETL Investigators: P. Kollias
Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO Institutions: University of Miami; University of Colorado; NOAA ETL Investigators: P. Kollias
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO
 Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius
 In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
In Situ Comparisons with the Cloud Radar Retrievals of Stratus Cloud Effective Radius A. S. Frisch and G. Feingold Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO. Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen
 Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Aircraft Observations for ONR DRI and DYNAMO (NOAA/ONR/NSF) Coupled Air-sea processes: Q. Wang, D. Khelif, L. Mahrt, S. Chen Deep convection/mjo initiation: Dave Jorgensen, S. Chen, R. Houze Aerosol/Cloud
Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO
 Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO Institutions: University of Miami; University of Colorado; NOAA ETL Investigators: P. Kollias
Ship-Based Measurements of Cloud Microphysics and PBL Properties in Precipitating Trade Cumuli During RICO Institutions: University of Miami; University of Colorado; NOAA ETL Investigators: P. Kollias
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models
 Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 (626)
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 (626)
P1.17 SENSITIVITY OF THE RETRIEVAL OF STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD LIQUID WATER AND PRECIPITATION FLUX TO DOPPLER RADAR PARAMETERS
 P1.17 SENSITIVITY OF THE RETRIEVAL OF STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD LIQUID WATER AND PRECIPITATION FLUX TO DOPPLER RADAR PARAMETERS Yefim L. Kogan*, Zena N. Kogan, and David B. Mechem Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale
P1.17 SENSITIVITY OF THE RETRIEVAL OF STRATOCUMULUS CLOUD LIQUID WATER AND PRECIPITATION FLUX TO DOPPLER RADAR PARAMETERS Yefim L. Kogan*, Zena N. Kogan, and David B. Mechem Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale
The Properties of Convective Clouds Over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones
 The Properties of Convective Clouds Over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones Principal Investigator: Dr. Zhaoxia Pu Department of Meteorology, University
The Properties of Convective Clouds Over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones Principal Investigator: Dr. Zhaoxia Pu Department of Meteorology, University
VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme
 VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme Understanding and modeling aerosol indirect effects Is drizzle important to Sc synoptic variability and climatology? IPCC, 2007 AEROSOL-CLOUD-PRECIPITATION HYPOTHESES
VOCALS Cloud-Drizzle-Aerosol Theme Understanding and modeling aerosol indirect effects Is drizzle important to Sc synoptic variability and climatology? IPCC, 2007 AEROSOL-CLOUD-PRECIPITATION HYPOTHESES
Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols
 Authors: Kathryn Sauter, Tristan L'Ecuyer Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols Type of Presentation: Oral Short Abstract: The distribution of mineral dust
Authors: Kathryn Sauter, Tristan L'Ecuyer Title: The Impact of Convection on the Transport and Redistribution of Dust Aerosols Type of Presentation: Oral Short Abstract: The distribution of mineral dust
Global sea surface temperature October 25 th 2007
 The VOCALS Regional Experiment Aerosols, clouds, and precipitation in southeast Pacific stratocumulus Robert Wood Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Global sea surface temperature October 25
The VOCALS Regional Experiment Aerosols, clouds, and precipitation in southeast Pacific stratocumulus Robert Wood Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington Global sea surface temperature October 25
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models. Robert Wood University of Washington
 Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
Warm rain and climate: VOCALS, CloudSat, Models Robert Wood University of Washington Warm rain a missing climatology Image: NASA GSFC Shipboard remote sensing shows frequent precipitation from shallow
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) What processes control
Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties with in-situ measurements over the Southeast Pacific
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 11261 11273, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-11261-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 11261 11273, 2012 doi:10.5194/acp-12-11261-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Comparison of MODIS cloud microphysical properties
The Properties of Convective Clouds over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Properties of Convective Clouds over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Properties of Convective Clouds over the Western Pacific and Their Relationship to the Environment of Tropical Cyclones
NARVAL. North Atlantic Rainfall Validation. Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas
 NARVAL North Atlantic Rainfall Validation Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas Klima Campus Meteorologisches Institut, Universität Hamburg Max-Planck-Institut
NARVAL North Atlantic Rainfall Validation Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas Klima Campus Meteorologisches Institut, Universität Hamburg Max-Planck-Institut
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models
 Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 phone:
Aerosol-Cloud-Radiation Interactions in Atmospheric Forecast Models John H. Seinfeld, Principal Investigator California Institute of Technology 1200 E. California Blvd., M/C 210-41 Pasadena, CA 91125 phone:
Observational and Numerical Studies of the Boundary Layer, Cloud, and Aerosol Variability in the Southeast Pacific Coastal Marine Stratocumulus
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2012-05-01 Observational and Numerical Studies of the Boundary Layer, Cloud, and Aerosol Variability
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2012-05-01 Observational and Numerical Studies of the Boundary Layer, Cloud, and Aerosol Variability
How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate?
 How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate? CloudSat estimated precipitation rate from low clouds Low clouds over the SE Pacific, Nov 11 th 2014 Robert Wood, University of Washington With
How is precipitation from low clouds important for climate? CloudSat estimated precipitation rate from low clouds Low clouds over the SE Pacific, Nov 11 th 2014 Robert Wood, University of Washington With
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes
 Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
Improving Air-Sea Coupling Parameterizations in High-Wind Regimes PI: Dr. Shuyi S. Chen Co-PI: Dr. Mark A. Donelan Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, University of Miami 4600 Rickenbacker
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL. David B. Mechem and Yefim L.
 4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
VOCALS REx: Aerosol Physics at the Ocean Surface On the NOAA RV Ronald H. Brown October, November 2008
 VOCALS REx: Aerosol Physics at the Ocean Surface On the NOAA RV Ronald H. Brown October, November 8 Catherine Hoyle, NOAA PMEL Derek Coffman, NOAA PMEL Tim Bates, NOAA PMEL Trish Quinn, NOAA PMEL Lelia
VOCALS REx: Aerosol Physics at the Ocean Surface On the NOAA RV Ronald H. Brown October, November 8 Catherine Hoyle, NOAA PMEL Derek Coffman, NOAA PMEL Tim Bates, NOAA PMEL Trish Quinn, NOAA PMEL Lelia
Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation
 Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation Adrian Hill Co-authors: Ben Shipway, Ian Boutle, Ryo Onishi UK Met Office Abstract This work discusses
Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation Adrian Hill Co-authors: Ben Shipway, Ian Boutle, Ryo Onishi UK Met Office Abstract This work discusses
Warm Rain Precipitation Processes
 Warm Rain Precipitation Processes Cloud and Precipitation Systems November 16, 2005 Jonathan Wolfe 1. Introduction Warm and cold precipitation formation processes are fundamentally different in a variety
Warm Rain Precipitation Processes Cloud and Precipitation Systems November 16, 2005 Jonathan Wolfe 1. Introduction Warm and cold precipitation formation processes are fundamentally different in a variety
Radar Observations of Updrafts, Downdrafts, and Turbulence in Fair-Weather Cumuli
 1750 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES Radar Observations of Updrafts, Downdrafts, and Turbulence in Fair-Weather Cumuli P. KOLLIAS, B.A.ALBRECHT, R.LHERMITTE, AND A. SAVTCHENKO Division of Meteorology
1750 JOURNAL OF THE ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES Radar Observations of Updrafts, Downdrafts, and Turbulence in Fair-Weather Cumuli P. KOLLIAS, B.A.ALBRECHT, R.LHERMITTE, AND A. SAVTCHENKO Division of Meteorology
EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphe
 EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphere and ocean in this region. Two aircraft, the National
EPIC2001 was conceived as an intensive process study along and near 95 o W during September and October 2001 used to make measurements of the atmosphere and ocean in this region. Two aircraft, the National
Part 3 Selected Modeling and Preliminary Confrontation with VOCALS Hypothesis
 Part 3 Selected Modeling and Preliminary Confrontation with VOCALS Hypothesis Transition to deep convection Shallow convection Transition to shallow convection Coastal clearing Aerosol VOCALS Paradigm
Part 3 Selected Modeling and Preliminary Confrontation with VOCALS Hypothesis Transition to deep convection Shallow convection Transition to shallow convection Coastal clearing Aerosol VOCALS Paradigm
Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Unified Cloud and Mixing Parameterizations of the Marine Boundary Layer: EDMF and PDF-based cloud approaches Joao Teixeira
Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS David B. Mechem Atmospheric
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Improving Mesoscale Prediction of Shallow Convection and Cloud Regime Transitions in NRL COAMPS David B. Mechem Atmospheric
Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian University
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian University
Preliminary Observations of Cloud and Precipitation Characteristics in the Brisbane, Australia Region
 Preliminary Observations of Cloud and Precipitation Characteristics in the Brisbane, Australia Region Sarah Tessendorf April 23, 2008 R. Bruintjes,, J. Wilson, R. Roberts, E. Brandes,, P. May, J. Peter,
Preliminary Observations of Cloud and Precipitation Characteristics in the Brisbane, Australia Region Sarah Tessendorf April 23, 2008 R. Bruintjes,, J. Wilson, R. Roberts, E. Brandes,, P. May, J. Peter,
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land
 Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Lecture 14. Marine and cloud-topped boundary layers Marine Boundary Layers (Garratt 6.3) Marine boundary layers typically differ from BLs over land surfaces in the following ways: (a) Near surface air
Unmanned Aircraft Hurricane Reconnaissance. Pat Fitzpatrick GeoSystems Research Institute Mississippi State University Stennis Space Center branch
 Unmanned Aircraft Hurricane Reconnaissance Pat Fitzpatrick GeoSystems Research Institute Mississippi State University Stennis Space Center branch Outline Motivation Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) [also
Unmanned Aircraft Hurricane Reconnaissance Pat Fitzpatrick GeoSystems Research Institute Mississippi State University Stennis Space Center branch Outline Motivation Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) [also
Understanding Near-Surface and In-Cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-Topped Boundary Layers
 Understanding Near-Surface and In-Cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-Topped Boundary Layers Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831)
Understanding Near-Surface and In-Cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-Topped Boundary Layers Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831)
AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE. SAHEL Conference April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
 AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso The aerosol/precipitation connection Aerosol environment has changed
AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso The aerosol/precipitation connection Aerosol environment has changed
Boundary Layer Structure, Turbulence and Shallow Cumulus Observations During RICO 2005
 Boundary Layer Structure, Turbulence and Shallow Cumulus Observations During RICO 2005 A Thesis Defense By Shaunna Donaher University of Miami, RSMAS April 9 th, 2007 Introduction/ Motivation Previous
Boundary Layer Structure, Turbulence and Shallow Cumulus Observations During RICO 2005 A Thesis Defense By Shaunna Donaher University of Miami, RSMAS April 9 th, 2007 Introduction/ Motivation Previous
Humidity impact on the aerosol effect in warm cumulus clouds
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L17804, doi:10.1029/2008gl034178, 2008 Humidity impact on the aerosol effect in warm cumulus clouds O. Altaratz, 1 I. Koren, 1 and T. Reisin 2 Received 31 March 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L17804, doi:10.1029/2008gl034178, 2008 Humidity impact on the aerosol effect in warm cumulus clouds O. Altaratz, 1 I. Koren, 1 and T. Reisin 2 Received 31 March 2008;
Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean
 Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean Outline: Overview of VOCALS Dudley B. Chelton Oregon State University Overview of the oceanographic component of VOCALS Preliminary analysis
Oceanic Eddies in the VOCALS Region of the Southeast Pacific Ocean Outline: Overview of VOCALS Dudley B. Chelton Oregon State University Overview of the oceanographic component of VOCALS Preliminary analysis
P1.6 Simulation of the impact of new aircraft and satellite-based ocean surface wind measurements on H*Wind analyses
 P1.6 Simulation of the impact of new aircraft and satellite-based ocean surface wind measurements on H*Wind analyses Timothy L. Miller 1, R. Atlas 2, P. G. Black 3, J. L. Case 4, S. S. Chen 5, R. E. Hood
P1.6 Simulation of the impact of new aircraft and satellite-based ocean surface wind measurements on H*Wind analyses Timothy L. Miller 1, R. Atlas 2, P. G. Black 3, J. L. Case 4, S. S. Chen 5, R. E. Hood
Curriculum Vitae: Chunsong Lu
 Curriculum Vitae: Chunsong Lu PERSONAL INFORMATION Address Room 1005, Qixiang Bldg, No. 219, Ningliu Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China 210044 Email luchunsong110@163.com; luchunsong110@gmail.com Cell Phone
Curriculum Vitae: Chunsong Lu PERSONAL INFORMATION Address Room 1005, Qixiang Bldg, No. 219, Ningliu Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China 210044 Email luchunsong110@163.com; luchunsong110@gmail.com Cell Phone
Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions. Photo: Mingxi Zhang
 Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions Robert Wood, Universityof Washington with help and data from Louise Leahy (UW), Matt Lebsock (JPL),
Warm rain variability and its association with cloud mesoscalestructure t and cloudiness transitions Robert Wood, Universityof Washington with help and data from Louise Leahy (UW), Matt Lebsock (JPL),
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET
 2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers
 Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) fax: (304)
Cloud Structure and Entrainment in Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layers David C. Lewellen MAE Dept., PO Box 6106, West Virginia University Morgantown, WV, 26506-6106 phone: (304) 293-3111 (x2332) fax: (304)
A new look at statistical evaluations of cloud seeding experiments WMA Meeting 9-12 April 2013 San Antonio, Texas
 A new look at statistical evaluations of cloud seeding experiments WMA Meeting 9-12 April 2013 San Antonio, Texas Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Mike Dixon, Sarah Tessendorf, Courtney Weeks, DuncanAxisa,
A new look at statistical evaluations of cloud seeding experiments WMA Meeting 9-12 April 2013 San Antonio, Texas Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Mike Dixon, Sarah Tessendorf, Courtney Weeks, DuncanAxisa,
A comparative study of the response of modeled non-drizzling stratocumulus to meteorological and aerosol perturbations
 Manuscript prepared for J. Name with version 2.2 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 21 January 2013 A comparative study of the response of modeled non-drizzling stratocumulus to meteorological
Manuscript prepared for J. Name with version 2.2 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: 21 January 2013 A comparative study of the response of modeled non-drizzling stratocumulus to meteorological
The Interaction of Water and Aerosols in the Marine Boundary Layer: A Study of Selected Processes Impacting Radiative Transfer and Cloudiness
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Interaction of Water and Aerosols in the Marine Boundary Layer: A Study of Selected Processes Impacting Radiative Transfer
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Interaction of Water and Aerosols in the Marine Boundary Layer: A Study of Selected Processes Impacting Radiative Transfer
Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology,
Measurements are infrequent in this region due to difficulty in making both ship- and air-based measurements Natural pristine region far removed from
 PLANNED OBSERVATIONAL CAMPAIGNS OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEANS FOR DETERMINING THE ROLES OF CLOUDS, AEROSOLS AND RADIATION IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM: SOCRATES, MARCUS & MICRE G. McFarquhar, U. Illinois C. Bretherton,
PLANNED OBSERVATIONAL CAMPAIGNS OVER THE SOUTHERN OCEANS FOR DETERMINING THE ROLES OF CLOUDS, AEROSOLS AND RADIATION IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM: SOCRATES, MARCUS & MICRE G. McFarquhar, U. Illinois C. Bretherton,
REQUEST FOR C-130 and WCR SUPPORT DYCOMS II ADDENDUM NCAR/ATD - October 2000 OFAP Meeting
 REQUEST FOR C-130 and WCR SUPPORT DYCOMS II ADDENDUM NCAR/ATD - October 2000 OFAP Meeting Submitted July 6, 2000. Corresponding Principal Investigator Name: Gabor Vali Institution: University of Wyoming
REQUEST FOR C-130 and WCR SUPPORT DYCOMS II ADDENDUM NCAR/ATD - October 2000 OFAP Meeting Submitted July 6, 2000. Corresponding Principal Investigator Name: Gabor Vali Institution: University of Wyoming
Understanding Near-Surface and In-cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-topped Boundary Layers
 Understanding Near-Surface and In-cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-topped Boundary Layers Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831)
Understanding Near-Surface and In-cloud Turbulent Fluxes in the Coastal Stratocumulus-topped Boundary Layers Qing Wang Meteorology Department, Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 Phone: (831)
ERAD Enhancement of precipitation by liquid carbon dioxide seeding. Proceedings of ERAD (2002): c Copernicus GmbH 2002
 Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 150 154 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Enhancement of precipitation by liquid carbon dioxide seeding K. Nishiyama 1, K. Wakimizu 2, Y. Suzuki 2, H. Yoshikoshi 2, and N. Fukuta
Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 150 154 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Enhancement of precipitation by liquid carbon dioxide seeding K. Nishiyama 1, K. Wakimizu 2, Y. Suzuki 2, H. Yoshikoshi 2, and N. Fukuta
Measurements of the Aerosol Light-Scattering Coefficient at Ambient and 85% Relative Humidity on the ONR Pelican During ACE-2
 Measurements of the Aerosol Light-Scattering Coefficient at Ambient and 85% Relative Humidity on the ONR Pelican During ACE-2 Dean A. Hegg University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Box
Measurements of the Aerosol Light-Scattering Coefficient at Ambient and 85% Relative Humidity on the ONR Pelican During ACE-2 Dean A. Hegg University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Box
Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET
 CSET RF11, near Hawaii Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET Robert Wood, University of Washington Paquita Zuidema, Chris Bretherton, Kuan Ting (Andy) O, Hans Mohrmann, Isabel McCoy,
CSET RF11, near Hawaii Ultra clean layers and low albedo ( grey ) clouds in CSET Robert Wood, University of Washington Paquita Zuidema, Chris Bretherton, Kuan Ting (Andy) O, Hans Mohrmann, Isabel McCoy,
Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken during DYNAMO
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1. By Tsutomu Takahashi
 February 1977 T. Takahashi 121 Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1 By Tsutomu Takahashi Cloud Physics Observatory, Department of Meteorology, University of Hawaii Hilo, Hawaii 96720 (Manuscript received 4 September
February 1977 T. Takahashi 121 Rainfall at Hilo, Hawaii1 By Tsutomu Takahashi Cloud Physics Observatory, Department of Meteorology, University of Hawaii Hilo, Hawaii 96720 (Manuscript received 4 September
The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China
 The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China Lei Li, 1 Pak Wai Chan, 2 Honglong Yang, 1 Rong Zong, 1 Xia Mao, 1 Yin Jiang 1 and Hongbo Zhuang
The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China Lei Li, 1 Pak Wai Chan, 2 Honglong Yang, 1 Rong Zong, 1 Xia Mao, 1 Yin Jiang 1 and Hongbo Zhuang
On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties. Science Systems and Applications, Inc., Hampton, Virginia 2
 JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
JP1.10 On the Satellite Determination of Multilayered Multiphase Cloud Properties Fu-Lung Chang 1 *, Patrick Minnis 2, Sunny Sun-Mack 1, Louis Nguyen 1, Yan Chen 2 1 Science Systems and Applications, Inc.,
Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), Boulder CO USA
 J12.1 AEROSOL - CLOUD INTERACTIONS OVER ISTANBUL, TURKEY AND CENTRAL SAUDI ARABIA Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR),
J12.1 AEROSOL - CLOUD INTERACTIONS OVER ISTANBUL, TURKEY AND CENTRAL SAUDI ARABIA Duncan Axisa*, Amit Teller, Roelof Bruintjes, Dan Breed, Roelof Burger National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR),
EUREC 4 A. A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020
 EUREC 4 A A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020 Felix Ament, Sandrine Bony, Susanne Crewell, Bernhard Mayer, Markus Rapp, Bjorn Stevens,
EUREC 4 A A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020 Felix Ament, Sandrine Bony, Susanne Crewell, Bernhard Mayer, Markus Rapp, Bjorn Stevens,
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions
 Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and Michael M. Bell. Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California, USA
 Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic
 On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
On Surface fluxes and Clouds/Precipitation in the Tropical Eastern Atlantic Chris Fairall, NOAA/ESRL Paquita Zuidema, RSMAS/U Miami with contributions from Peter Minnett & Erica Key AMMA Team Meeting Leeds,
Tropical Cyclone Intensity and Structure Changes in relation to Tropical Cyclone Outflow
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Tropical Cyclone Intensity and Structure Changes in relation to Tropical Cyclone Outflow Patrick A. Harr Department of
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Tropical Cyclone Intensity and Structure Changes in relation to Tropical Cyclone Outflow Patrick A. Harr Department of
Some comments on weather modification and its science base
 Some comments on weather modification and its science base Woods Hole -- July 31, 2002 Gabor Vali University of Wyoming Collaborators: R.D. Kelly, D. Leon, S. Haimov, S. Gill 1 BASC - WxMod Jul 31, 2002
Some comments on weather modification and its science base Woods Hole -- July 31, 2002 Gabor Vali University of Wyoming Collaborators: R.D. Kelly, D. Leon, S. Haimov, S. Gill 1 BASC - WxMod Jul 31, 2002
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
Steven Greco* and George D. Emmitt Simpson Weather Associates, Charlottesville, VA. 2. Experiments
 3.3 INVESTIGATION OF FLOWS WITHIN COMPLEX TERRAIN AND ALONG COASTLINES USING AN AIRBORNE DOPPLER WIND LIDAR: OBSERVATIONS AND MODEL COMPARISONS Steven Greco* and George D. Emmitt Simpson Weather Associates,
3.3 INVESTIGATION OF FLOWS WITHIN COMPLEX TERRAIN AND ALONG COASTLINES USING AN AIRBORNE DOPPLER WIND LIDAR: OBSERVATIONS AND MODEL COMPARISONS Steven Greco* and George D. Emmitt Simpson Weather Associates,
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China
 Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Impact of different cumulus parameterizations on the numerical simulation of rain over southern China P.W. Chan * Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China 1. INTRODUCTION Convective rain occurs over southern
Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing, China
 Meteorology Volume 2010, Article ID 412024, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/412024 Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing,
Meteorology Volume 2010, Article ID 412024, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/412024 Research Article Direct Evidence of Reduction of Cloud Water after Spreading Diatomite Particles in Stratus Clouds in Beijing,
PRECIPITATION PROCESSES
 PRECIPITATION PROCESSES Loknath Adhikari This summary deals with the mechanisms of warm rain processes and tries to summarize the factors affecting the rapid growth of hydrometeors in clouds from (sub)
PRECIPITATION PROCESSES Loknath Adhikari This summary deals with the mechanisms of warm rain processes and tries to summarize the factors affecting the rapid growth of hydrometeors in clouds from (sub)
SANDRINE BONY AND BJORN STEVENS
 EUREC 4 A, THE FIELD STUDY: A DRAFT WHITE PAPER SANDRINE BONY AND BJORN STEVENS This draft white paper is meant to sketch out developing plans for the 2019-2020 EUREC 4 A field study. A more complete document
EUREC 4 A, THE FIELD STUDY: A DRAFT WHITE PAPER SANDRINE BONY AND BJORN STEVENS This draft white paper is meant to sketch out developing plans for the 2019-2020 EUREC 4 A field study. A more complete document
Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2214 Satellite-based estimate of global aerosol-cloud radiative forcing by marine warm clouds Y.-C. Chen, M. W. Christensen, G. L. Stephens, and J. H. Seinfeld
7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES
 7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES William R. Cotton, Gustavo G. Carrio, and S Herbener Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Previous
7.6 AEROSOL IMPACTS ON TROPICAL CYCLONES William R. Cotton, Gustavo G. Carrio, and S Herbener Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION Previous
Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters
 Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters P.W. Chan * and K.K. Hon Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China Abstract: The fixed-wing aircraft
Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters P.W. Chan * and K.K. Hon Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China Abstract: The fixed-wing aircraft
S. de Szoeke (NOAA), M. Kohler (ECMWF), T. Toniazzo (U. Reading, UK), and many others
 R. Wood (U. Wash., Rex-PI), C. R. Mechoso (UCLA, Chair), C. Bretherton (U. Wash.), R. Weller (WHOI), C. Fairall (NOAA), H. Coe (Manchester U., UK), F. Straneo (WHOI), C. Grados (IMARPE, Peru), R. Garreaud
R. Wood (U. Wash., Rex-PI), C. R. Mechoso (UCLA, Chair), C. Bretherton (U. Wash.), R. Weller (WHOI), C. Fairall (NOAA), H. Coe (Manchester U., UK), F. Straneo (WHOI), C. Grados (IMARPE, Peru), R. Garreaud
Convective scheme and resolution impacts on seasonal precipitation forecasts
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 20, 2078, doi:10.1029/2003gl018297, 2003 Convective scheme and resolution impacts on seasonal precipitation forecasts D. W. Shin, T. E. LaRow, and S. Cocke Center
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 30, NO. 20, 2078, doi:10.1029/2003gl018297, 2003 Convective scheme and resolution impacts on seasonal precipitation forecasts D. W. Shin, T. E. LaRow, and S. Cocke Center
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II
 P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
CuPIDO flight strategy
 CuPIDO flight strategy an update based on the July 2004 UWKA facility request Bart Geerts, Rick Damiani, Jeff French Flight schedule: The facility request says that the flights are generally between 7
CuPIDO flight strategy an update based on the July 2004 UWKA facility request Bart Geerts, Rick Damiani, Jeff French Flight schedule: The facility request says that the flights are generally between 7
Report on Spring 2017 Sabbatical: Upper-Division and Graduate Coursework in Atmospheric Science
 Report on Spring 2017 Sabbatical: Upper-Division and Graduate Coursework in Atmospheric Science Division of Natural Sciences El Camino College August 2017 1 Overview During Spring 2017, I was granted sabbatical
Report on Spring 2017 Sabbatical: Upper-Division and Graduate Coursework in Atmospheric Science Division of Natural Sciences El Camino College August 2017 1 Overview During Spring 2017, I was granted sabbatical
Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1
 Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 University of Sao Paulo, Brazil Objectives
Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 University of Sao Paulo, Brazil Objectives
Chapter Introduction. Weather. Patterns. Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Describing Weather Weather Patterns Weather Forecasts Chapter Wrap-Up How do scientists describe and predict weather? What do you think? Before you begin,
Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Influence of Organic-Containing Aerosols on Marine Boundary Layer Processes John H. Seinfeld California Institute of Technology
Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Understanding the Nature of Marine Aerosols and Their Effects in the Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere System Armin Sorooshian,
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity
 Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Correspondence to: C. N. Franklin
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 6557 6570, 2014 doi:10.5194/acp-14-6557-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. The effects of turbulent collision coalescence on precipitation formation and precipitation-dynamical
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 6557 6570, 2014 doi:10.5194/acp-14-6557-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. The effects of turbulent collision coalescence on precipitation formation and precipitation-dynamical
Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology. National Report To
 Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology National Report To Panel on Tropical Cyclones in the Bay of Bengal And Arabian Sea 43rd Session, India
Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology National Report To Panel on Tropical Cyclones in the Bay of Bengal And Arabian Sea 43rd Session, India
THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION
 J12.2 THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION Amit Teller*, Duncan Axisa, Daniel Breed, and Roelof Bruintjes
J12.2 THE EFFECTS OF GIANT CCN ON CLOUDS AND PRECIPITATION: A CASE STUDY FROM THE SAUDI ARABIA PROGRAM FOR THE ASSESSMENT OF RAINFALL AUGMENTATION Amit Teller*, Duncan Axisa, Daniel Breed, and Roelof Bruintjes
The HIAPER Cloud Radar Performance and Observations During Winter Storm Observations of a Nor easter
 The HIAPER Cloud Radar Performance and Observations During Winter Storm Observations of a Nor easter S. Ellis 1*, R. Rauber 2, P. Tsai 1, J. Emmett 1, E. Loew 1, C. Burghart 1, M. Dixon 1, J. Vivekanandan
The HIAPER Cloud Radar Performance and Observations During Winter Storm Observations of a Nor easter S. Ellis 1*, R. Rauber 2, P. Tsai 1, J. Emmett 1, E. Loew 1, C. Burghart 1, M. Dixon 1, J. Vivekanandan
MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES
 MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES 4 TH International Workshop on Weather Modification 3 rd Workshop on Cloud Physics 21-22 October 2010 Daegu, Korea Projects Current
MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES 4 TH International Workshop on Weather Modification 3 rd Workshop on Cloud Physics 21-22 October 2010 Daegu, Korea Projects Current
Precipitation Processes
 Precipitation Processes Dave Rahn Precipitation formation processes may be classified into two categories. These are cold and warm processes, where cold processes can only occur below 0 C and warm processes
Precipitation Processes Dave Rahn Precipitation formation processes may be classified into two categories. These are cold and warm processes, where cold processes can only occur below 0 C and warm processes
Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Examination #3 Wednesday, 28 November 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please be sure to read each question CAREFULLY
