R' = 0.7 [cot h ( h Kdir Kdift- ( h) Krefl,
|
|
|
- Egbert Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASSESSMENT OR SOLAR RADIATION ABSORBED BY MAN BASED ON SIMPLE hieteorological PARAMETERS Krzyszlof Blazejczyk Institute of Geography and Spatial Organization, Polish Academy o Sciences, I(rakows1ue Przedmiescie 30, Warszawa, Poland INTRODUCTION Solar radiation is a very important factor influencing human lieat balance outdoors. Many dserent methods are in use or calculation of its value, measured in the liorizontal plane, for the reference person (1). The most realistic values of absorbed solar radiation are obtained assuming an ellipsoid as an analogue model of man (2). However, in practical applications tliere is still a problem concerning the actual input data of solar radiation Tlie aim ofllie paper is to present a simplified method for the estimation of solar radiation absorbed by nude man. The method bases on the simple meteorological (amount and type of a cloud cover) as well as astronomical (Sun altitude) parameters. MATERIALS and METHODS Solar radiation data were collected during numerous climatological investigations carried out in various cloud scenarios as well as in different climatic zones and seasons. Solar altitudes (h) ranged from 5 to 85". A1 data were gathered into thee groups depending on cloud coverage. Solar radiation intensity, measured in the horizontal plane, was recalculated for the intensity o solar radiation absorbed by nude, standing man (R') with the use of the following formula (2): R' = 0.7 [cot h ( h Kdir Kdift- ( h) Krefl, (W/m2) Kdir, Kdif, Kref represent intensity of solar radiation: direct, diffuse and reflected (in W/m2). The calculations were made using the human lieat balance model MENEX (3). RESULTS The R' values, calculated with the use of above formula, were correlated with Sun altitude. Tlie functions describing relationships between R' and h values have dserent runs depending on the type and amount of cloud cover (Fig. 1). Correlation coefficients vary from 0.85 to 0.94, and the regression equations have Uie following forms: 190
2 - h --- N E 150 = loo ' IO I I I I I I I I I h (") Fig. 1 Relationships between Sun altitude (h) and solar radiation absorbed by nude man (R') in different cloud scenarios: a - clear sky (no clouds) or CirruslAltocumulus (covering up to 90% of the sky) or AltostratuslCumulus (covering up to 50% oflhe sky), b - CumuluslAltostratus (covering 51-90% of the sky) or StratocumulusIStratus~imbostratus (covering up to 70% of the sky), c - others clouds scenarios 191
3 R* = (In h - 1.1)/0.015, - for the clear sky or Cirrus and Altocumulus clouds (covering up to 90% of the sky) as well as for Altostratus and Cumulus clouds (covering up to 50% of the sky), R* = exp(0.05 h ) - for Cumulus and Altostratus clouds (covering 51-90% of the sky) as well as for Stratocumulus, Stratus and Nimbostratus clouds (covering up to 70% of the sky), R* = 2.21 h for others clouds scenarios. R* values estimated with the use of above regression equations were compared with R' values calculated for an ellipsoid model of man (Fig. 2) m E 200 ik Fig. 2 Relationships between calculated (R') and estimated (R*) values of solar radiation absorbed by nude man; 1 - regression line, 2 - line of identity 192
4 Figure 2 shows the great similarity between calculated and estimated values of solar radiation absorbed by nude man. Tlie correlation coeficient between compared values is 0.92 (for n=75, p=0.05). Tlie slope of Uie regression line and tlie identity line are very similar. The data oi solar radiation and cloud cover taken for above comparison represent various Sun altitudes (0-85') and Mereiit climatic zones (tropical, subl.ropical, temperate, polar). CONCLUSIONS Because of lligli correlation coefficient between R' and R* values it seems Ihat regression equations of R* can be recommended for the calculations of absorbed solar radialion. They can be applied in studies of human heat balance outdoors in various climatic zones. The accuracy of present method as well as its ease of data collection afford possibilities for its wider use in human heat balance models in outdoor conditions. The clouing factor is needed in adaptations of this metliod for various models. REFERENCES 1. Blazejczyk K., Nilsson H., Holm& I., 1993, Solar heat load on man (review of merent methods of estimation). Int.J.Bioinet., 37, Blazejczyk K., Holm& I., Nilsson H., 1992, A modified equation for tlie calculation of solar heat load in man. in WALotens, G.Havenith (eds), Proc. Fzj7h hf. Coi$Eizviron. Ergon, Maastricht, , Blazejczyk IC, 1994, New climatological-and-physiological model of the human heat balance outdoor (MENEX) and its applications in bioclimatological studies in merent scales. in K.Blazejczjrk, B.Krawczyk, Bioclimatic research ofthe liuman lieat balance, Zeszyfy IGiPZ PAN, 28,
5
8. Clouds and Climate
 8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
8. Clouds and Climate 1. Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few
Unit 4 Lesson 2 Clouds and Cloud Formation. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Head in the Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a collection of small water droplets or ice crystals that are suspended in the air. Clouds are visible because water droplets and ice crystals reflect light.
Head in the Clouds What are clouds? A cloud is a collection of small water droplets or ice crystals that are suspended in the air. Clouds are visible because water droplets and ice crystals reflect light.
Polar regions Temperate Regions Tropics High ( cirro ) 3-8 km 5-13 km 6-18 km Middle ( alto ) 2-4 km 2-7 km 2-8 km Low ( strato ) 0-2 km 0-2 km 0-2 km
 Clouds and Climate Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few cm/sec.
Clouds and Climate Clouds (along with rain, snow, fog, haze, etc.) are wet atmospheric aerosols. They are made up of tiny spheres of water from 2-100 m which fall with terminal velocities of a few cm/sec.
Global Energy and Water Budgets
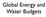 Global Energy and Water Budgets 1 40 10 30 Pressure (hpa) 100 Pure radiative equilibrium Dry adiabatic adjustment 20 Altitude (km) 6.5 C/km adjustment 10 1000 0 180 220 260 300 340 Temperature (K)
Global Energy and Water Budgets 1 40 10 30 Pressure (hpa) 100 Pure radiative equilibrium Dry adiabatic adjustment 20 Altitude (km) 6.5 C/km adjustment 10 1000 0 180 220 260 300 340 Temperature (K)
Objectives: S.W.B.A.T.
 Objectives: S.W.B.A.T. Describe basic cloud formation Define condensation nucleus, fog, Identify 3 basic cloud forms Understand that clouds are based on shape and altitude location in troposphere. Activities:
Objectives: S.W.B.A.T. Describe basic cloud formation Define condensation nucleus, fog, Identify 3 basic cloud forms Understand that clouds are based on shape and altitude location in troposphere. Activities:
Importance of clouds. climate. ocean. radiation. life. hydrological cycle. latent heat + loading. clouds & precip + aerosols.
 Importance of clouds climate life ocean radiation hydrological cycle clouds & precip + aerosols latent heat + loading dynamics electricity aqueous chemistry Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH) Physics and Dynamics
Importance of clouds climate life ocean radiation hydrological cycle clouds & precip + aerosols latent heat + loading dynamics electricity aqueous chemistry Ulrike Lohmann (IACETH) Physics and Dynamics
Name Class Date. Water molecules condense around the salt crystal. More water molecules condense around the original small droplet.
 CHAPTER 20 2 Clouds and Fog SECTION Water in the Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What conditions are necessary for clouds to form? What are the four processes
CHAPTER 20 2 Clouds and Fog SECTION Water in the Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What conditions are necessary for clouds to form? What are the four processes
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Water vapor's role in the Earth's weather is major. Its the product of evaporation. It is lifted up, condenses and forms clouds. It is also a greenhouse
Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time. It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the
 Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Weather Notes Weather Weather is the of the Earth s atmosphere at a place and time It is the movement of through the atmosphere o Energy comes from the The sun is the force that weather The sun s energy
Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J.
 Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, 1954-2008 Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J. Hahn Clouds Over the Ocean The ocean is cloudy, more-so than land Cloud
Changes in Cloud Cover and Cloud Types Over the Ocean from Surface Observations, 1954-2008 Ryan Eastman Stephen G. Warren Carole J. Hahn Clouds Over the Ocean The ocean is cloudy, more-so than land Cloud
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
References: Cloud Formation. ESCI Cloud Physics and Precipitation Processes Lesson 1 - Cloud Types and Properties Dr.
 ESCI 34 - Cloud Physics and Precipitation Processes Lesson 1 - Cloud Types and Properties Dr. DeCaria References: Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd ed., American Meteorological Society A Short Course in Cloud
ESCI 34 - Cloud Physics and Precipitation Processes Lesson 1 - Cloud Types and Properties Dr. DeCaria References: Glossary of Meteorology, 2nd ed., American Meteorological Society A Short Course in Cloud
24.2 Cloud Formation 2/3/2014. Orographic Lifting. Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
 2/3/2014 Orographic Lifting Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging A front is the boundary between two adjoining air masses having contrasting characteristics. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
2/3/2014 Orographic Lifting Processes That Lift Air Frontal Wedging A front is the boundary between two adjoining air masses having contrasting characteristics. Convergence and Localized Convective Lifting
Bell Ringer. 1. What is humidity? 2. What kind of clouds are there outside right now? 3. What happens to air when it gets colder?
 Bell Ringer 1. What is humidity? 2. What kind of clouds are there outside right now? 3. What happens to air when it gets colder? Cloud Notes What are clouds? A cloud is made up of tiny water droplets and/or
Bell Ringer 1. What is humidity? 2. What kind of clouds are there outside right now? 3. What happens to air when it gets colder? Cloud Notes What are clouds? A cloud is made up of tiny water droplets and/or
Mapping of UTCI in local scale (the case of Warsaw) Krzysztof BłaŜejczyk
 Prace i Studia Geograficzne WGSR UW, 47, 2011, p. 275-283 Mapping of UTCI in local scale (the case of Warsaw) Krzysztof BłaŜejczyk Faculty of Geography and Regional Studies, University of Warsaw, Poland
Prace i Studia Geograficzne WGSR UW, 47, 2011, p. 275-283 Mapping of UTCI in local scale (the case of Warsaw) Krzysztof BłaŜejczyk Faculty of Geography and Regional Studies, University of Warsaw, Poland
Cloud detection and classification with the use of whole-sky ground-based images
 Sky Camera Workshop 2014 Processing techniques for the detection of atmospheric constituents and the estimation and forecasting of solar irradiance from all sky images 24 25 June 2014, Patras, Greece Cloud
Sky Camera Workshop 2014 Processing techniques for the detection of atmospheric constituents and the estimation and forecasting of solar irradiance from all sky images 24 25 June 2014, Patras, Greece Cloud
The following ten types of clouds, named using the above terms, are to be used when reporting the cloud type for your area: High Clouds.
 Observing Cloud Type There are five descriptive terms for the various types of clouds: CIRRO or high clouds ALTO or middle clouds CUMULUS or white puffy clouds STRATUS or layered clouds NIMBUS or clouds
Observing Cloud Type There are five descriptive terms for the various types of clouds: CIRRO or high clouds ALTO or middle clouds CUMULUS or white puffy clouds STRATUS or layered clouds NIMBUS or clouds
Most of the earth s weather occurs in the troposphere
 66 Atmosphere and Climate R E A D I N G Most of the earth s weather occurs in the troposphere (TROH-poh-sfeer). In Activity 58, The Causes of Climate, you learned that the ocean has currents that move
66 Atmosphere and Climate R E A D I N G Most of the earth s weather occurs in the troposphere (TROH-poh-sfeer). In Activity 58, The Causes of Climate, you learned that the ocean has currents that move
Keep Your Eye on the Sky - Clouds and Weather Student Worksheet #1: The Clouds Below
 Student Worksheet #1: The Clouds Below How do meteorologists predict and forecast our weather? Meteorologists use weather instruments to measure weather factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed
Student Worksheet #1: The Clouds Below How do meteorologists predict and forecast our weather? Meteorologists use weather instruments to measure weather factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed
NATS 1750 Lecture. Wednesday 28 th November Pearson Education, Inc.
 NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
Weather Notes. Chapter 16, 17, & 18
 Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Weather Notes Chapter 16, 17, & 18 Weather Weather is the condition of the Earth s atmosphere at a particular place and time Weather It is the movement of energy through the atmosphere Energy comes from
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Chapter 6. Cloud Development and Forms
 Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Cloud Formation Chapter 6 Cloud Development and Forms Condensation (i.e. clouds,fog) results from: Diabatic cooling (important for fog) Adiabatic cooling (important for clouds) Clouds form due to adiabatic
Unit: Weather Study Guide
 Name: Period: Unit: Weather Study Guide Define each vocabulary word on a separate piece of paper or index card. Weather Climate Temperature Wind chill Heat index Sky conditions UV index Visibility Wind
Name: Period: Unit: Weather Study Guide Define each vocabulary word on a separate piece of paper or index card. Weather Climate Temperature Wind chill Heat index Sky conditions UV index Visibility Wind
Clouds. How Clouds Form. Humidity. Determining Relative Humidity
 a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air. and Clouds Relative humidity the percentage of water vapor that is actually in the air compared to the
a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air. and Clouds Relative humidity the percentage of water vapor that is actually in the air compared to the
Evaporation - Water evaporates (changes from a liquid to a gas) into water vapor due to heat from the Sun.
 Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
Erin Kathryn 2016 Weather is the conditions of Earth s atmosphere at a certain time and place. For example, sunshine, rain, hurricanes, and storms are all examples of weather. Weather is different at different
Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350
 Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350 T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor ~12/42~29% POLAR
Condensation: Dew, Fog and Clouds AT350 T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor T=30 C Water vapor pressure=12mb What is Td? What is the sat. water vapor ~12/42~29% POLAR
Really Good Stuff Activity Guide Clouds 10-in-1 Poster Set
 Clouds 10-in-1 Poster Set Congratulations on your purchase of the Really Good Stuff 10-in-1 Poster Set! This Really Good Stuff product includes: One 19" x 24" laminated poster Ten 7 1 2" x 11" x mini posters
Clouds 10-in-1 Poster Set Congratulations on your purchase of the Really Good Stuff 10-in-1 Poster Set! This Really Good Stuff product includes: One 19" x 24" laminated poster Ten 7 1 2" x 11" x mini posters
Clouds. Naming/Classifying Clouds. Cloud Heights. Height above ground level Shape
 Clouds Textbook Section 18.2 Irondale High School Earth Science Clouds are collections of billions of ice crystals, water droplets, or combination of the two At temperatures above freezing, a cloud consists
Clouds Textbook Section 18.2 Irondale High School Earth Science Clouds are collections of billions of ice crystals, water droplets, or combination of the two At temperatures above freezing, a cloud consists
Observing Climate - Upper Air
 Observing Climate - Upper Air 3-1 Water (Con t) Clouds Types - Classification Base height Coverage Science Concepts Definition The Earth System (Kump, Kastin & Crane) Chap. 3 (pp. 48-49) 3-2 What do we
Observing Climate - Upper Air 3-1 Water (Con t) Clouds Types - Classification Base height Coverage Science Concepts Definition The Earth System (Kump, Kastin & Crane) Chap. 3 (pp. 48-49) 3-2 What do we
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 11. Clouds
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 11 Clouds Cloud Classification Luke Howard (English naturalist) developed a system in 1803 that employed Latin words to describe clouds as they appear to a ground observer.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 11 Clouds Cloud Classification Luke Howard (English naturalist) developed a system in 1803 that employed Latin words to describe clouds as they appear to a ground observer.
9 Condensation. Learning Goals. After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE
 CHAPTER Y ou have already learnt that the air contains water vapour. It varies from zero to four per cent by volume of the atmosphere and plays an important role in the weather phenomena. Water is present
CHAPTER Y ou have already learnt that the air contains water vapour. It varies from zero to four per cent by volume of the atmosphere and plays an important role in the weather phenomena. Water is present
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types:
 Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Interannual Variations of Arctic Cloud Types: Relationships with Sea Ice and Surface Temperature Ryan Eastman Stephen Warren University of Washington Department of Atmospheric Sciences Changes in Arctic
Lesson 2 / page 1. Lesson 2
 Lesson 2 / page 1 Lesson 2 M i s s i o n A r l i n g t o n M i s s i o n M e t r o p l ex S u m m e r C u r r i c u l u m Lesson 2 Day 2 of Creation Lesson 2 / page 2 Sky Memory Verses For great is your
Lesson 2 / page 1 Lesson 2 M i s s i o n A r l i n g t o n M i s s i o n M e t r o p l ex S u m m e r C u r r i c u l u m Lesson 2 Day 2 of Creation Lesson 2 / page 2 Sky Memory Verses For great is your
6.2 Meteorology. A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather.
 Water and Weather 6.2 Meteorology A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather. 6.2 Water in the Atmosphere Dew point is the temperature
Water and Weather 6.2 Meteorology A meteorologist is a person who uses scientific principles to explain, understand, observe, or forecast Earth s weather. 6.2 Water in the Atmosphere Dew point is the temperature
What does a raindrop look like as it is falling? A B C
 What does a raindrop look like as it is falling? A B C As the raindrop falls, it bumps into air molecules, flattening out the bottom of the drop! Force or air resistance Force of gravity Water can be in
What does a raindrop look like as it is falling? A B C As the raindrop falls, it bumps into air molecules, flattening out the bottom of the drop! Force or air resistance Force of gravity Water can be in
Sample file. Stratus clouds are like a blanket of clouds. They carry steady rain or drizzle. Sometimes they drop to the ground and it becomes fog.
 CUT APART THE CARDS ON PAGES 2-9. FOUR CARDS BELONG TO A SET. THE FOUR STEPS ARE TO BE COMPLETED ON FOUR SEPARATE DAYS. Cumulus clouds are puffy, white clouds. They are flat on the bottom and domed shape
CUT APART THE CARDS ON PAGES 2-9. FOUR CARDS BELONG TO A SET. THE FOUR STEPS ARE TO BE COMPLETED ON FOUR SEPARATE DAYS. Cumulus clouds are puffy, white clouds. They are flat on the bottom and domed shape
Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE
 Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE Why is the atmosphere divided into 5 different layers? The atmosphere is divided into five different layers because the atmosphere is not uniform, its properties
Atmosphere L AY E RS O F T H E AT MOSPHERE Why is the atmosphere divided into 5 different layers? The atmosphere is divided into five different layers because the atmosphere is not uniform, its properties
CIRROCUMULUS CIRROSTRATUS
 Ten Basic Clouds Based on his observations, Luke Howard suggested there were modifications (or combinations) of the core four clouds between categories. He noticed that clouds often have features of two
Ten Basic Clouds Based on his observations, Luke Howard suggested there were modifications (or combinations) of the core four clouds between categories. He noticed that clouds often have features of two
Clouds. What they tell us about the weather
 Clouds What they tell us about the weather Spring funnel cloud over Willard, Utah 2003 Cloud coverage 581-586 How to show Cloud Coverage On a weather map meteorologists use circles shaded differently to
Clouds What they tell us about the weather Spring funnel cloud over Willard, Utah 2003 Cloud coverage 581-586 How to show Cloud Coverage On a weather map meteorologists use circles shaded differently to
Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises. Vertical Thermal Structure. Three Things Need To Be Explained
 Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises Air expands as it rises Air cools as it expands Air pressure Lapse rates Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Sunlight heats the atmosphere from below Convection occurs and
Lecture 7: Air cools when it rises Air expands as it rises Air cools as it expands Air pressure Lapse rates Why Is the Mountain Peak Cold? Sunlight heats the atmosphere from below Convection occurs and
1. CLIMATOLOGY: 2. ATMOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY:
 What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
What is meteorology? A. METEOROLOGY: an atmospheric science that studies the day to day changes in the atmosphere 1. ATMOSPHERE: the blanket of gas that surrounds the surface of Earth; the air 2. WEATHER:
Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture
 Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
Chapter 1: Properties of Atmosphere Temperature Pressure Wind Moisture Thickness of the Atmosphere (from Meteorology Today) 90% 70% The thickness of the atmosphere is only about 2% of Earth s thickness
ISSUED BY KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA - DOWNLOADED FROM
 CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
CHAPTER -11 WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE This chapter deals with Humidity, types of humidity, relative humidity, absolute humidity, specific humidity, dew point, condensation, saturated air, types of precipitation
GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds
 Joint COSMIC Tenth Data Users Workshop and IROWG-6 Meeting GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds Xiaolei Zou Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center (ESSIC) University of Maryland, USA September
Joint COSMIC Tenth Data Users Workshop and IROWG-6 Meeting GPS RO Retrieval Improvements in Ice Clouds Xiaolei Zou Earth System Science Interdisciplinary Center (ESSIC) University of Maryland, USA September
Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and
 Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and You have 50 minutes to complete and revise this test. 1. Do not turn this page until you are told to do so. 2. Write your team name and
Meteorology Division B Team Name: Team Number: Student Names: and You have 50 minutes to complete and revise this test. 1. Do not turn this page until you are told to do so. 2. Write your team name and
CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS
 Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Funding provided by NOAA Sectoral Applications Research Project CLOUDS & THUNDERSTORMS Basic Climatology Oklahoma Climatological Survey How are clouds made? Clouds form when air is cooled to its dewpoint
Final Weather Unit Study Guide
 Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
Name: Atmospheric Composition and Layers Altitude Atmosphere Composition Troposphere Air Pressure Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere Ionosphere Sample Questions: Final Weather Unit Study Guide
Appendix. Atmosphere Investigation Data Work Sheet. Ozone Data Work Sheet. Atmospheric Haze Data Work Sheet. Clouds 7 Measurement Data Work Sheet
 Appendix Atmosphere Investigation Data Work Sheet Ozone Data Work Sheet Atmospheric Haze Data Work Sheet Clouds 7 Measurement Data Work Sheet GLOBE 2000 Appendix - 1 Atmosphere Atmosphere Investigation
Appendix Atmosphere Investigation Data Work Sheet Ozone Data Work Sheet Atmospheric Haze Data Work Sheet Clouds 7 Measurement Data Work Sheet GLOBE 2000 Appendix - 1 Atmosphere Atmosphere Investigation
Due to the Coriolis effect, prevailing winds are: 0-30 N - trade winds (trade winds blow toward the equator) N N - (fig 14.
 1 CD2 Factors that Influence the Earth s Climate Meteorology Meteorology is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and weather systems. The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surround the Earth which extends
1 CD2 Factors that Influence the Earth s Climate Meteorology Meteorology is the study of the Earth's atmosphere and weather systems. The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surround the Earth which extends
CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR
 CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
CHAPTER 7 CLOUDS, PRECIPITATION, AND WEATHER RADAR MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The activation temperature of most ice-forming nuclei is 0 C. a. above b. about c. well below 2. Hygroscopic nuclei water
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH
 INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
INTRODUCTION TO METEOROLOGY PART ONE SC 213 MAY 21, 2014 JOHN BUSH WEATHER PATTERNS Extratropical cyclones (low pressure core) and anticyclones (high pressure core) Cold fronts and warm fronts Jet stream
The Earth s Radiation Balance
 The Earth s Radiation Balance Incoming Energy = Outgoing Energy (absorbed sunshine)(area) = (thermal loss)(area) S(1-a)pr 2 = s T 4 (4 pr 2 ) Solve for T T = -18 C; (0 F) The radiative equilibrium temperature
The Earth s Radiation Balance Incoming Energy = Outgoing Energy (absorbed sunshine)(area) = (thermal loss)(area) S(1-a)pr 2 = s T 4 (4 pr 2 ) Solve for T T = -18 C; (0 F) The radiative equilibrium temperature
Fluid Circulation Review. Vocabulary. - Dark colored surfaces absorb more energy.
 Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Fluid Circulation Review Vocabulary Absorption - taking in energy as in radiation. For example, the ground will absorb the sun s radiation faster than the ocean water. Air pressure Albedo - Dark colored
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition
 Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition Air is a combination of many gases, each with its own unique characteristics. About 99 percent of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen, with the
Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds. Chapter 5
 Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased
Condensation: Dew, Fog, & Clouds Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased
PROJECT REPORT (ASL 720) CLOUD CLASSIFICATION
 PROJECT REPORT (ASL 720) CLOUD CLASSIFICATION SUBMITTED BY- PRIYANKA GUPTA 2011CH70177 RINI KAPOOR 2011CH70179 INDIVIDUAL CONTRIBUTION- Priyanka Gupta- analysed data of region considered in India (West:80,
PROJECT REPORT (ASL 720) CLOUD CLASSIFICATION SUBMITTED BY- PRIYANKA GUPTA 2011CH70177 RINI KAPOOR 2011CH70179 INDIVIDUAL CONTRIBUTION- Priyanka Gupta- analysed data of region considered in India (West:80,
LE Accumulation, Net Radiation, and Drying with Tipped Sensors
 LE Accumulation, Net Radiation, and Drying with Tipped Sensors Three different situations were examined, where the influence that the deployment angle of the sensor has on the accumulation of latent heat
LE Accumulation, Net Radiation, and Drying with Tipped Sensors Three different situations were examined, where the influence that the deployment angle of the sensor has on the accumulation of latent heat
Next quiz: this Friday, questions. Plus more on Wednesday.
 Next quiz: this Friday, 10-20 questions from Plus more on Wednesday. Chapter 19: 1, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 29, 20, 21, 27, 42, 46 Chapter 20: 1, 2, 7, 13, 14, 16, 19, 20, 34, 37, 40, 41, 42, 43, 47,
Next quiz: this Friday, 10-20 questions from Plus more on Wednesday. Chapter 19: 1, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 15, 16, 29, 20, 21, 27, 42, 46 Chapter 20: 1, 2, 7, 13, 14, 16, 19, 20, 34, 37, 40, 41, 42, 43, 47,
Cloud Formation and Classification
 Cloud Formation and Classification Cloud Formation clouds form when air above the surface cools below the dew point condensation nuclei small particles in the atmosphere around which water droplets can
Cloud Formation and Classification Cloud Formation clouds form when air above the surface cools below the dew point condensation nuclei small particles in the atmosphere around which water droplets can
Altocumulus Clouds Occasionally altocumulus clouds show vertical development and produce tower-like extensions. These altocumulus clouds are in the
 This presentation is a classroom resource from Windows to the Universe with funding from the Center for Multi-Scale Modeling of Atmospheric Processes (CMMAP) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research
This presentation is a classroom resource from Windows to the Universe with funding from the Center for Multi-Scale Modeling of Atmospheric Processes (CMMAP) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research
9/22/14. Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation. The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th.
 Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! A cloud is a visible
Chapter 5: Forms of Condensation and Precipitation The Atmosphere: An Introduction to Meteorology, 12 th Lutgens Tarbuck Lectures by: Heather Gallacher, Cleveland State University! A cloud is a visible
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume.
 The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
The most abundant gas in the atmosphere by volume is. This gas comprises 78% of the Earth atmosphere by volume. A. Oxygen B. Water Vapor C. Carbon Dioxide D. Nitrogen An isobar is a line of constant. A.
Wind direction measures in degrees Occasion described with codes, when is calm or variable wind. Explanation
 Introduction The searching results explanations of meteorological data Depending on the parameter, the instrumental measuring or visual observation method is used for the meteorological observations. Instrumentally
Introduction The searching results explanations of meteorological data Depending on the parameter, the instrumental measuring or visual observation method is used for the meteorological observations. Instrumentally
5.04 Clouds and Fog. References: FTGU pages , 147. Meteorology
 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Types and Recognition Associated Precipitation Fog Formation and Types Cloud Classification
5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Types and Recognition Associated Precipitation Fog Formation and Types Cloud Classification
I d e n t i f i c a t i o n
 SKY WATCHERS GUIDE TO Cloud I d e n t i f i c a t i o n For more information on weather and additional teaching resources, please visit www.on.ec.gc.ca/skywatchers Clouds themselves will give you clues
SKY WATCHERS GUIDE TO Cloud I d e n t i f i c a t i o n For more information on weather and additional teaching resources, please visit www.on.ec.gc.ca/skywatchers Clouds themselves will give you clues
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Chapter 04 Lecture 07. Peter Lynch VIS WATER IN THE ATMOSPHERE MAPH 10050
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Clouds By Patti Hutchison
 Clouds By Patti Hutchison 1 Bows and flows of angel hair, And ice cream castles in the air, And feather canyons everywhere I've looked at clouds that way. But now they only block the sun, They rain and
Clouds By Patti Hutchison 1 Bows and flows of angel hair, And ice cream castles in the air, And feather canyons everywhere I've looked at clouds that way. But now they only block the sun, They rain and
Influence of cloudiness on sunshine duration
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 32: 27 36 (2012) Published online 3 June 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:.02/joc.2370 Influence of cloudiness on sunshine
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 32: 27 36 (2012) Published online 3 June 2011 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI:.02/joc.2370 Influence of cloudiness on sunshine
777 GROUNDSCHOOL Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms
 777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
777 GROUNDSCHOOL 2018 Temperature, Stability, Fronts, & Thunderstorms The Atmosphere Heating Transfer of heat occurs thru Radiation Advection Convection Matter changes states due to the amount of heat
Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity,
 Climate Change I m Supposed To Know What That Is? Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity, http://www.climatechangenorth.ca Overview: Students often confuse global warming and the depletion
Climate Change I m Supposed To Know What That Is? Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity, http://www.climatechangenorth.ca Overview: Students often confuse global warming and the depletion
Chapter 7. Water and Atmospheric Moisture. Water on Earth Unique Properties of Water Humidity Atmospheric Stability Clouds and Fog
 Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Chapter 7 Water and Atmospheric Moisture Robert W. Christopherson Charlie Thomsen Water kept both the terrestrial and marine ecosystems closely linked with the atmosphere. (1) Air carries water vapor and
Basic cloud Interpretation using Satellite Imagery
 Basic cloud Interpretation using Satellite Imagery Introduction Recall that images from weather satellites are actually measurements of energy from specified bands within the Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum.
Basic cloud Interpretation using Satellite Imagery Introduction Recall that images from weather satellites are actually measurements of energy from specified bands within the Electromagnetic (EM) spectrum.
Meteorology Clouds and Fog. Cloud Classification MTPs: Height. Shape. and. Clouds are classified by:
 Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Associated Precipitation Clouds are classified by: Cloud Classification Height Shape and
Meteorology 5.04 Clouds and Fog References: FTGU pages 124-126, 147 5.04 Clouds and Fog MTPs: Cloud Classification Associated Precipitation Clouds are classified by: Cloud Classification Height Shape and
Transient/Eddy Flux. Transient and Eddy. Flux Components. Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Why transients/eddies matter to zonal and time means?
 Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Lecture 7: Disturbance (Outline) Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies (From Weather & Climate) Flux Components (1) (2) (3) Three components contribute
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Oklahoma Weather. Adaptable for 4 th -5 th Grade. by Allison Cassady, Ph.D. Brought to you by:
 Oklahoma Weather Brought to you by: by Allison Cassady, Ph.D. Adaptable for 4 th -5 th Grade 4 th -5 th Grade Weather Unit Resources National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration - http://www.srh.noaa.gov/srh/jetstream/clouds/cloudwise/types.html
Oklahoma Weather Brought to you by: by Allison Cassady, Ph.D. Adaptable for 4 th -5 th Grade 4 th -5 th Grade Weather Unit Resources National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration - http://www.srh.noaa.gov/srh/jetstream/clouds/cloudwise/types.html
Cloudscape. Purpose. Materials. Overview. Student Outcomes. Time. Level. A Learning Activity for Do You Know That Clouds Have Names?
 Purpose Cloudscape To help students identify some of the characteristics of clouds. To enable students to observe clouds, describe them in a common vocabulary, and compare their descriptions with the official
Purpose Cloudscape To help students identify some of the characteristics of clouds. To enable students to observe clouds, describe them in a common vocabulary, and compare their descriptions with the official
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. weather 1 1. Sharon woke up on a sunny morning and ate breakfast. Then she looked outside and saw tall, quickly forming clouds. The clouds looked ready to rain.
Water Cycle and Weather Study Guide
 Name: Date: Water Cycle and Weather Study Guide 1. Which symbol would be used to represent this front on a weather map? a. b. c. d. 1 of 14 2. The table shows the relative humidity for a location during
Name: Date: Water Cycle and Weather Study Guide 1. Which symbol would be used to represent this front on a weather map? a. b. c. d. 1 of 14 2. The table shows the relative humidity for a location during
The troposphere is the layer closest to Earth s surface. Extends from 9-16 km above Earth s Surface It contains most of the mass of the atmosphere.
 Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Chapter 11 The atmosphere is the blanket of gases surrounding Earth that contains about 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases such as argon, carbon dioxide, and water vapor The atmosphere is classified
Cloud Analysis Image: Product Guide
 Cloud Analysis Image: Product Guide Doc.No. : EUM/TSS/MAN/15/795729 EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Issue : v1c Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Date : 19 February 2015 http://www.eumetsat.int
Cloud Analysis Image: Product Guide Doc.No. : EUM/TSS/MAN/15/795729 EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Issue : v1c Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Date : 19 February 2015 http://www.eumetsat.int
The influence of nebulosity on the air pollution in the area of Slatina city
 Vol. 1, No.1, June, 2014, pp. 7 14 E-ISSN: 2313-769X 2014 HRMARS www.hrmars.com The influence of nebulosity on the air pollution in the area of Slatina city 1 Dana Maria (Oprea) Constantin, 2 Elena Cofas
Vol. 1, No.1, June, 2014, pp. 7 14 E-ISSN: 2313-769X 2014 HRMARS www.hrmars.com The influence of nebulosity on the air pollution in the area of Slatina city 1 Dana Maria (Oprea) Constantin, 2 Elena Cofas
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations. S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences.
 The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
The Climatology of Clouds using surface observations S.G. Warren and C.J. Hahn Encyclopedia of Atmospheric Sciences Gill-Ran Jeong Cloud Climatology The time-averaged geographical distribution of cloud
GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY
 GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY YEAR 1, PART 1 www.vicensvives.es Contents 01 Our planet Earth 02 The representation of the Earth: maps 03 The Earth s relief 04 Rivers and seas 05 Weather and climate 06 Climates
GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY YEAR 1, PART 1 www.vicensvives.es Contents 01 Our planet Earth 02 The representation of the Earth: maps 03 The Earth s relief 04 Rivers and seas 05 Weather and climate 06 Climates
Thursday, June 5, Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation
 Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Thursday, June 5, 2014 Chapter 5: Condensation & Precipitation Chapter 5: Condensation and Precipitation Formation of Condensation Saturated Air Condensation Nuclei Results of Condensation Clouds Fog Dew
Production of electricity using photovoltaic panels and effects of cloudiness
 Production of electricity using photovoltaic panels and effects of cloudiness PAVEL CHROBÁK, JAN SKOVAJSA AND MARTIN ZÁLEŠÁK The Department of Automation and Control Engineering Tomas Bata University in
Production of electricity using photovoltaic panels and effects of cloudiness PAVEL CHROBÁK, JAN SKOVAJSA AND MARTIN ZÁLEŠÁK The Department of Automation and Control Engineering Tomas Bata University in
Earth and Space Science. Teacher s Guide
 Earth and Space Science Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher............................................................. vi Classroom Management....................................................
Earth and Space Science Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher............................................................. vi Classroom Management....................................................
Identify and describe clouds in the low, middle, and upper levels of the atmosphere. Relate these to specific types of weather.
 5. Cloud Types. Identify and describe clouds in the low, middle, and upper levels of the atmosphere. Relate these to specific types of weather. Clouds and Preciipitation CIRRUS 32.800 FEET CIRROCUMULUS
5. Cloud Types. Identify and describe clouds in the low, middle, and upper levels of the atmosphere. Relate these to specific types of weather. Clouds and Preciipitation CIRRUS 32.800 FEET CIRROCUMULUS
Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation
 Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Cloud Formation visible aggregate of water droplets, ice crystals, or both adiabatic cooling Classifying and Naming of clouds Processes responsible for
Chapter 5 Forms of Condensation and Precipitation Cloud Formation visible aggregate of water droplets, ice crystals, or both adiabatic cooling Classifying and Naming of clouds Processes responsible for
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
ATM 10. Severe and Unusual Weather. Prof. Richard Grotjahn.
 ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
ATM 10 Severe and Unusual Weather Prof. Richard Grotjahn http://atm.ucdavis.edu/~grotjahn/course/atm10/index.html Moisture Mixing ratio Vapor pressure Relative humidity Lecture topics: Saturation vapor
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Name: 1) What is the primary reason New York State is warmer in July than in February? A) The altitude of the noon Sun is greater in February. B) The insolation in New York is greater in July. C) The Earth
Condensation Nuclei. Condensation Nuclei 2/10/11. Hydrophobic Water-repelling Oils, gasoline, paraffin Resist condensation, even above 100% RH
 Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased radiative cooling White
Chapter 5 The Formation of Dew & Frost Dew forms on objects near the ground surface when they cool below the dew point temperature. More likely on clear nights due to increased radiative cooling White
vis = 74 visibility = vis - 50, for 56 vis 80
 ATSC 201 Fall 2018 Assignment 11 Answer Key Total marks out of 69 Chapter 9: A1h, A7a, A8h, A10all Chapter 12: A1h, A7h, A8h, A11g, E21, E23 Chapter 9 A1h) Find the pressure "reduced to sea level" using
ATSC 201 Fall 2018 Assignment 11 Answer Key Total marks out of 69 Chapter 9: A1h, A7a, A8h, A10all Chapter 12: A1h, A7h, A8h, A11g, E21, E23 Chapter 9 A1h) Find the pressure "reduced to sea level" using
2. The spectrum of visible light bounds the region of intensity of light emitted by the Sun. a. maximum b. minimum
 CHAPTER 14 LIGHT AND SOUND IN THE ATMOSPHERE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. As the Sun s rays travel through the atmosphere, they are by cloud droplets or ice crystals, or by raindrops. a. scattered b. reflected
CHAPTER 14 LIGHT AND SOUND IN THE ATMOSPHERE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. As the Sun s rays travel through the atmosphere, they are by cloud droplets or ice crystals, or by raindrops. a. scattered b. reflected
Clouds and Atmospheric convection
 Clouds and Atmospheric convection Caroline Muller carolinemuller123@gmail.com E406 L3 ENS A Year of Weather 2013 This visualisation, comprised of imagery from the geostationary satellites of EUMETSAT,
Clouds and Atmospheric convection Caroline Muller carolinemuller123@gmail.com E406 L3 ENS A Year of Weather 2013 This visualisation, comprised of imagery from the geostationary satellites of EUMETSAT,
a. Air is more dense b. Associated with cold air (more dense than warm air) c. Associated with sinking air
 Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
Meteorology 1. Air pressure the weight of air pressing down on Earth 2. Temperature and altitude determine air pressure 3. The more air particles are present, the more air density or pressure exists 4.
