REAL-TIME NATION-WIDE PRODUCTION OF 3D WIND AND REFLECTIVITY FIELDS IN FRANCE: SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND APPLICATIONS
|
|
|
- Gladys Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REAL-TIME NATION-WIDE PRODUCTION OF 3D WIND AND REFLECTIVITY FIELDS IN FRANCE: SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND APPLICATIONS Antoine Kergomard*, Pascale Dupuy, Pierre Tabary and Olivier Bousquet Centre de Météorologie Radar, Météo-France, Toulouse, France 1. Introduction From November 006 to September 008, realtime analysis of multiple-doppler data collected by the French operational radar network have been performed and evaluated over the greater Paris area using the well-established MUSCAT (multiple-doppler synthesis and continuity adjustment technique) algorithm initially proposed by Bousquet and Chong (1998). Since the results of this experiment were convincing (Bousquet 008), it has been envisaged to extend the retrieval domain to the whole of France, using the 4 French radars. This paper presents the different experiments that were conducted in order to validate the real-time reflectivity and wind products over such a large area. Different sensitivity tests to the interpolation parameters and to the compositing algorithms were carried. Given high-resolution 3D reflectivity and wind fields as a reference, the reflectivity and radial velocity PPIs of all radars were simulated, taking into account the operational scanning strategy. Comparing the retrieved field to the reference enabled to assess the efficiency of the retrieval and to optimize the parameters used in the retrieval algorithm. In order to limit the computing time, the national domain has been divided into 4 overlapping sub-domains. The final product, available in real-time every 15 minutes with a horizontal resolution of.5 km and a vertical resolution of 500 m, is a 3D grid giving the interpolated reflectivity, wind field (u, v and w) and divergence values, all together with some quality indicator. An experimentation is currently being held with the forecasters to assess the benefit of the product in monitoring the realism of the wind structures depicted by the mesoscale numerical model (AROME).. The French radar network The French operational weather radar network, named ARAMIS (Application Radar a la Météorologie Infra-Synoptique), was initially built for rain detection purposes. In 00, an upgrade program, called Programme Aramis Nouvelles Technologies en Hydrometeorologie Extension et Renouvellement (PANTHERE), was initiated in partnership with the French Ministry of Environment to complete and extend this network (Parent et al. 003) and implement Doppler and dual-polarimetry capabilities. As of today, 7 new Doppler radars have been installed, have been replaced, and a numerical receiver has been developed to dopplerize the older radars. Figure 1: Map of the French radar network as of August 009. Circles show the 100 km range of measurement. Colors indicate the kind of radars (Doppler or not) The network comprises Doppler radars (Figure 1) covering about 95 % of the French territory with radar baselines ranging from ~180 km in the northern part of the country down to less than 60 km in the south east of France. The triple-prt scheme proposed by Tabary et al. (006) is operationally deployed. It is being revised (Augros, 009) in order to decrease the number of spurious echoes and to limit the rate of aliased velocities, keeping the useful range up to 50 km. 3. Current configuration of real time 3D chain All radars perform a complete volume scan in 15 minutes (a supercycle) according to the operational modes showed in Table 1. The current scanning strategy consists in 3 to 5 elevation angles every 5 minutes and is radar specific. Input data are operational PPIs of Doppler velocity and reflectivity projected on a 1 km Cartesian grid (same data as for assimilation into the mesoscale model AROME). They are synchronized with respect to the ending time of the current 15 supercycle to account for the non-simultaneity of measurements. Spurious reflectivity and radial velocity data are removed using a threshold on the pulse-to-pulse fluctuation of the reflectivity and a 5x5 km² median filter, respectively. *Corresponding author address: antoine.kergomard@meteo.fr
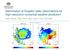
2 PPI Abbeville 0,4 1,1 0,4 Arcis 4 1,1 0,4 3 1,1 0,4 1,1 0,4 Avesnes ,6 1 0, ,6 1 0, ,6 1 0,4 Blaisy 3,6,6 1,6 1 0,5 Bollene 6,4 1,8 1, 0,8 0,4 4,8,4 1,8 1, 0,8 0,4 3,6,4 1,8 1, 0,8 0,4 Bordeaux 9 1,5 0,4 Bourges 3,, 1,3 0,7 4,, 1,3 0,7 5,, 1,3 0,7 Cherves 0,4,6 1,6 1 0,4 0,4 3,6 1,6 1 0,4 0,4 4,6 1,6 1 0,4 Collobrieres 4,8 3,6, 1,4 0,4 0,8 6 3,6, 1,4 0,4 0,8 7, 3,6, 1,4 0,4 0,8 Falaise 1,6 1,1 0,4 Grezes,6 1,6 1 0,4 Momuy 90 5,6,6 1,6 1 0,4 7,6 4,6,6 1,6 1 0,4 6,6 3,6,6 1,6 1 0,4 Montancy 90 5, 1, 0,7 0,4 7 3,9, 1, 0,7 0,4 6 3, 1, 0,7 0,4 Montclar 90 5,5,5 1,6 1 0,4 7,5 4,5,5 1,6 1 0,4 6,5 3,5,5 1,6 1 0,4 Nancy,5 1,9 1,3 0,7 Nimes 8 3,5,4 1,8 1, 0,6 9,5 5,4 1,8 1, 0,6 90 6,5,4 1,8 1, 0,6 Opoul 3 1,4 1 0,6 Plabennec 3 0,8 0,4 Sembadel 4 1, 0,8 0,4 3 1, 0,8 0,4 1, 0,8 0,4 StNizier 4 1,6 1 0,4 3 1,6 1 0,4, 1,6 1 0,4 Toulouse 90 8,5 5,5,5 1,5 0,8 10,5 7,5 4,5,5 1,5 0,8 9,5 6,5 3,5,5 1,5 0,8 Trappes 90 7,5 0,8 1,5 4,5 0,4 9,5 6,5 0,8 1,5 3,5 0,4 8,5 5,5 0,8 1,5,5 0,4 Treillieres,1 1,5 0,8 0,4 3 1,5 0,8 0,4 4 1,5 0,8 0,4 Table 1: scanning strategy of the 3 radars covering the France. A super cycle (18 tilts) is composed of three 5 cycles (6 tilts). Once pre-processed, data are interpolated into the retrieval Cartesian grid using a fixed horizontal influence radius of the Cressman weighting function R H of 3 km and a variable vertical radius of influence R V equal to 1 (beamwidth of the ARAMIS radars). In this configuration, R V varies as a function of range so that the search for data points extends farther out at long range compared to short range. At long range, this also allows to indirectly take into account the lost of resolution resulting from beam broadening. Once interpolated, data are ingested in the MUSCAT analysis (Bousquet and Chong 1998; Chong and Bousquet 001). The national retrieval domain is a Cartesian domain measuring 1000 km x 1100 km x 1 km, covering the whole country (except Corsica). The vertical resolution is set to 500 m. The horizontal resolution is set to.5 km to be consistent with unavoidable smoothing inherent to radar beamwidths and baselines of ~1 and ~180 km, respectively. With simulated PPIs corresponding to the different elevations used operationally for each radar (see Table1), it is possible to calculate the wind and reflectivity coverage. The interpolation parameters used for the simulation are those described before (R H=3km, R V equal to 1, minimum number of data inside the Cressman ellipsoid set to 5). The best coverage is encountered between the altitudes of 3000 and 6000 m (Figure ). At 1000 m, the coverage is quite poor. In practice, it is even poorer due to orography, which is not taken into account in the simulation. 1000m 5000m 3000m 11000m Figure : Doppler radar overlapping at various heights within the national domain shown in Fig. 1
3 To challenge the computing time, the national domain is divided into 4 overlapping domains, measuring 510 km x 56 km x 1 km, as shown in Figure 3. Working with 4 sub-domains, on a 4 processors machine, divides the computing time up to 4, in the case of widespread precipitations. A linear interpolation is used to obtain wind and reflectivity fields at the junction areas. Thus, the final product is ready at worst 15 minutes after all input data are available, instead of up to 1 hour with only one big domain. The following algorithm has finally been chosen, that takes into account the distance from the contributing radars: dradar pixel ω = exp R with R max = 50 radar max Figure 4 shows a vertical latitudinal retrieved reflectivity cross-section over France compared with the reference field. The retrieved field is in line with the reference up to 10 km. Figure 4 : Latitudinal Vertical cross-section of reflectivity (left reference, right retrieved) Figure 3. Reflectivity and wind-field for each retrieval sub-domain, on 4 january at 03:30, at level 000m. 4. Testing the algorithm performances and defining a quality flag It has been chosen to use horizontally uniform reference fields, vertically defined as follow. Reflectivity vertically decreases from 50 dbz at a rate of 3dB/km until 10km, at a rate of 1dB/km above. Wind rotates with altitude. The two horizontal components are given by: π z u = 0 sin( ) π z v = 0 cos( ) z 3000m z 0 There is no vertical component. PPIs have been simulated from these reference fields in accordance with the operational scanning strategy, and next used as input of the 3D retrieval algorithm on the national domain. The first reflectivity composites have been obtained using the maximum reflectivity algorithm, defined as follow: Z pixel ( mosaic) = max( Z pixel( radar)) radar It has been then noted that the reflectivity retrieved field was overestimated at high altitudes, because of the influence of the increasing with range vertical Cressman radius. Decreasing this radius (to 0.5 ) leads to lessen the coverage; furthermore, the quality of the final product is degraded, due to the decrease of the number of radar data available. z 0 A quality flag has been defined, which takes into account the distance between one pixel and the radars contributing to this pixel. For each pixel and for each radar, the following parameter is computed, and then composited with the same method as for reflectivity: Z = Z0 + a. d d with Z0= 3dBZ, a = 3 and d0= 50km The comparison between the retrieved and the reference reflectivity field shows that this quality flag seems to slightly overestimate the uncertainty, but is correctly spatially distributed. Figure 5 shows the same vertical crosssection as above for the norm of the latitudinal component of the wind. Figure 5 : Latitudinal Vertical cross-section of wind (left reference, right retrieved) The wind field is correctly retrieved, wit no major shift along the vertical. It is foreseen to develop a quality indicator for wind, with the same idea than for reflectivity, giving a kind of uncertainty of the retrieved value. 0
4 5. Examples of 3D wind and reflectivity real time retrievals 5.1 Klaus storm This paragraph presents some results from the 3D real-time retrieval algorithm. The first example is the severe storm Klaus which hit France on 4 th January TU As shown in Figure 6, the location of the center of the low analyzed by the ALADIN model (red cross) is in good agreement with the retrieved wind field. Figure 7: La Ferté-Vidame wind-profiler data, during Klaus storm 0600 TU 0900 TU The only other altitude observations available during the Klaus storm are the data from the windprofiler in La Ferté Vidame, which is located 70km southwest of Paris. Although this wind-profiler is north of the maximum wind area, the comparison with the 3D retrieved wind shows a good agreement (Figure 7). At 0300 and 0600 UTC, the wind at an altitude of 000m is south and around 5m.s -1. At 0900TU, both the 3D wind and the wind measured by the profiler have turned east, and strengthened. 5. Hail event The 3D retrieved reflectivity allows computing a derivate probability of hail, using the following formula (Delobbe and Holleman, 006): POH = ( Altiiso 45dBZ Altiiso 0 C) Figure 6: reflectivity and wind at 000m, at 03, 06 and 09 UTC during Klaus storm, on 4 th January 009. The red star is the location of the low-pressure area center at 000m analyzed by ALADIN model. The black point locates La Ferté Vidame wind-profiler. The iso-0 C altitude is taken from ALADIN model analysis. Figure 8 shows the POH calculated every 15 minutes on the 15 May 008 from 1700 (black) to 030 UTC (orange). The red crosses represent the hailpads where hailstones (with diameters greater than 5 mm) were observed, the white crosses the hailpads where no hail was reported. The trajectories of the two cells that gave hail are well detected by the radar. The number of false alarms from the radar is rather high. Some studies are at the present conducted to optimize the hail detection, taking advantage of the dual polarization when available (Tabary, 009).
5 product on a 1 km resolution grid, and applying the obtained VPR to the D reflectivity high resolution image (Le Henaff, 007) References Figure 8: hail imprints on the 1(May 008. The crosses are the hailpads, in red when hail was reported 6. Conclusions It has been demonstrated that running a real time 3D chain was feasible over the whole of France, with a computing time of 10 to 15 minutes. The results were validated using simulated data and on some severe weathers cases. The product is now being evaluated in real time by the forecasters. Many improvements are expected by next year. The wind retrieval coverage should increase with the radars of Plabennec and Grezes being dopplerized in 010. Quality flags will be added to wind parameters. Changes in the projection of the retrieval grid (not to re-project as now from Lambert initial projection to Polar Stereographic projection) will permit to gain time. By computing the reflectivity field first apart from the wind, it should be possible to have the reflectivity mosaic available much sooner as it is now. Tests have already been done, and show that the reflectivity mosaic could be available at H+5, instead of H+10 to H+15 in the current real-time chain. Taking orography into account is another way to improve the current interpolation algorithm. To complete the current product and in order to synthesize the 3D information, it is foreseen to add D fields such as VIL (vertically integrated liquid content), Zmax, altitude of Zmax, EchoTop, with a higher resolution (1 km ) and a frequency of 5 minutes. Those products will be used as an input for nowcasting applications. Those products will be computed by advecting and extrapolating the 3D Augros C, Tabary P, 009: Improvements of the French operational triple-prt Doppler scheme, 34 th Radar Conference, 5-9 october, Williamsburg, VA, USA Delobbe, L., and I. Holleman, 006 : Uncertainties in radar echo top heights used for hail detection, /Meterol. Appl./, *13*, Bousquet O., and M. Chong, 1998: A multiple Doppler and continuity adjustment technique (MUSCAT) to recover wind components from Doppler radar measurements. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 15, Bousquet O., P. Tabary, and J. Parent du Châtelet, 007: On the value of operationally synthesized multiple-doppler wind fields. Geophys. Res. Letter, Accepted pending minor revisions. Browning K., A., and R. Wexler, 1968: The determination of kinematic properties of a wind field using Doppler radar, J. Appl. Meteorol., 7, Chong, M., and O. Bousquet, 001: On the application of Muscat to a ground-based dual-doppler radar system. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 78, Doviak and Zrnic, 1993: Doppler radar and weather observations (second edition), Academic Press, Inc. Parent-du-Chatelet, J., M. Guimera, and P. Tabary, 003: The PANTHERE Project of Meteo-France: Extension and upgrade of the French radar network. Preprints, 31st Int. Conf. on Radar Meteorology, Seattle, WA, Amer. Meteor. Soc., Tabary, P., F. Guibert, L. Perier, and J. Parent-du-chatelet, 006: An operational triple-prt scheme for the French radar network. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol.,3, Bousquet O., Tabary P and Parent du Châtelet J., 007,Operationnal Multiple Doppler Wind Retrieval Inferred from Lon-Range Radial Velocity Measurement, Journal Of Applied Meteorology and Climatology 47. Le Henaff A., 007, Produit radar multi-couches pour DPREVI/PI dans le cadre de FLYSAFE, internal document, Météo France Tabary P., Fradon B., Dupuy P., Ilingworth.J. and Vulpiani G., Hail detection and quantification with a C-band polarimetric radar : Challenge and promises, 34 th Radar Conference, 5-9 october, Williamsburg, VA, USA
9A.2 Real-time multiple-doppler wind fields from RHYTMME and ARAMIS radars with implications for data assimilation within AROME for southeast France
 9A.2 Real-time multiple-doppler wind fields from RHYTMME and ARAMIS radars with implications for data assimilation within AROME for southeast France Jeffrey Beck Olivier Bousquet Mathieu Nuret Météo France,
9A.2 Real-time multiple-doppler wind fields from RHYTMME and ARAMIS radars with implications for data assimilation within AROME for southeast France Jeffrey Beck Olivier Bousquet Mathieu Nuret Météo France,
Development of a nationwide real-time 3-D wind and reflectivity radar composite in France
 Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 611 625, January 2014 B Development of a nationwide real-time 3-D wind and reflectivity radar composite in France Olivier
Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 140: 611 625, January 2014 B Development of a nationwide real-time 3-D wind and reflectivity radar composite in France Olivier
Development of a Nationwide, Low-Level Wind Shear Mosaic in France
 OCTOBER 2013 A U G R O S E T A L. 1241 Development of a Nationwide, Low-Level Wind Shear Mosaic in France CLOTILDE AUGROS, PIERRE TABARY, ADRIEN ANQUEZ, JEAN-MARC MOISSELIN, PASCAL BROVELLI, AND OLIVIER
OCTOBER 2013 A U G R O S E T A L. 1241 Development of a Nationwide, Low-Level Wind Shear Mosaic in France CLOTILDE AUGROS, PIERRE TABARY, ADRIEN ANQUEZ, JEAN-MARC MOISSELIN, PASCAL BROVELLI, AND OLIVIER
P4.2 TOWARDS THE ASSIMILATION OF RADAR REFLECTIVITIES: IMPROVING THE OBSERVATION OPERATOR BY APPLYING BEAM BLOCKAGE INFORMATION
 P4.2 TOWARDS THE ASSIMILATION OF RADAR REFLECTIVITIES: IMPROVING THE OBSERVATION OPERATOR BY APPLYING BEAM BLOCKAGE INFORMATION Günther Haase (1), Joan Bech (2), Eric Wattrelot (3), Uta Gjertsen (4) and
P4.2 TOWARDS THE ASSIMILATION OF RADAR REFLECTIVITIES: IMPROVING THE OBSERVATION OPERATOR BY APPLYING BEAM BLOCKAGE INFORMATION Günther Haase (1), Joan Bech (2), Eric Wattrelot (3), Uta Gjertsen (4) and
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction
 Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements
 Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements Edouard Goudenhoofdt, Maarten Reyniers and Laurent Delobbe Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, 1180
Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements Edouard Goudenhoofdt, Maarten Reyniers and Laurent Delobbe Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, 1180
THE DETECTABILITY OF TORNADIC SIGNATURES WITH DOPPLER RADAR: A RADAR EMULATOR STUDY
 P15R.1 THE DETECTABILITY OF TORNADIC SIGNATURES WITH DOPPLER RADAR: A RADAR EMULATOR STUDY Ryan M. May *, Michael I. Biggerstaff and Ming Xue University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 1. INTRODUCTION The
P15R.1 THE DETECTABILITY OF TORNADIC SIGNATURES WITH DOPPLER RADAR: A RADAR EMULATOR STUDY Ryan M. May *, Michael I. Biggerstaff and Ming Xue University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 1. INTRODUCTION The
RANGE EXTENSION OF DOPPLER RADAR BY COMBINED USE OF LOW-PRF AND PHASE DIVERSITY PROCESSED DUAL-PRF OBSERVATIONS
 P7.5 RANGE EXTENSION OF OPPLER RAAR BY COMBINE USE OF LOW-PRF AN PHASE IVERSITY PROCESSE UAL-PRF OBSERVATIONS Hiroshi Yamauchi* and Osamu Suzuki Meteorological Research Institute, Tsukuba, Japan Kenji
P7.5 RANGE EXTENSION OF OPPLER RAAR BY COMBINE USE OF LOW-PRF AN PHASE IVERSITY PROCESSE UAL-PRF OBSERVATIONS Hiroshi Yamauchi* and Osamu Suzuki Meteorological Research Institute, Tsukuba, Japan Kenji
Empirical Estimation of Attenuation from Differential Propagation Phase Measurements at C Band
 306 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 46 Empirical Estimation of Attenuation from Differential Propagation Phase Measurements at C Band JONATHAN J.
306 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 46 Empirical Estimation of Attenuation from Differential Propagation Phase Measurements at C Band JONATHAN J.
Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars
 Proceedings of ERAD (4): 35 4 c Copernicus GmbH 4 ERAD 4 Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars Y. K. Goh and A. R. Holt Department of Mathematical Sciences, University
Proceedings of ERAD (4): 35 4 c Copernicus GmbH 4 ERAD 4 Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars Y. K. Goh and A. R. Holt Department of Mathematical Sciences, University
OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information
 OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information ALADIN-HIRLAM workshop, Toulouse Maud Martet 26-28 April 2016 OPERA: An EUMETNET Project EUMETNET: EIG of 31 European National
OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information ALADIN-HIRLAM workshop, Toulouse Maud Martet 26-28 April 2016 OPERA: An EUMETNET Project EUMETNET: EIG of 31 European National
ERAD Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany. Proceedings of ERAD (2002): c Copernicus GmbH 2002
 Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 195 199 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany M. Hagen 1, K. Friedrich 1, and J. Seltmann 2 1 Institut
Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 195 199 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany M. Hagen 1, K. Friedrich 1, and J. Seltmann 2 1 Institut
Warning procedures for extreme events in the Emilia-Romagna Region
 Warning procedures for extreme events in the Emilia-Romagna Region Anna Fornasiero, Miria Celano, Roberta Amorati, Virginia Poli and Pier Paolo Alberoni Arpa Emilia-Romagna Hydro-Meteo-Climate Service,
Warning procedures for extreme events in the Emilia-Romagna Region Anna Fornasiero, Miria Celano, Roberta Amorati, Virginia Poli and Pier Paolo Alberoni Arpa Emilia-Romagna Hydro-Meteo-Climate Service,
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE. A Formulation of the Continuity Equation of MUSCAT for either Flat or Complex Terrain
 1556 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 17 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE A Formulation of the Continuity Equation of MUSCAT for either Flat or Complex Terrain MICHEL CHONG Centre National
1556 JOURNAL OF ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC TECHNOLOGY VOLUME 17 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE A Formulation of the Continuity Equation of MUSCAT for either Flat or Complex Terrain MICHEL CHONG Centre National
P13A.7 Multi-pass objective analyses of radar data: Preliminary results
 P13A.7 Multi-pass objective analyses of radar data: Preliminary results MARIO MAJCEN, PAUL MARKOWSKI, AND YVETTE RICHARDSON Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
P13A.7 Multi-pass objective analyses of radar data: Preliminary results MARIO MAJCEN, PAUL MARKOWSKI, AND YVETTE RICHARDSON Department of Meteorology, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar
 ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic
 Submitted for the 12 th Conf. on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteor. 29 Jan. 2 Feb. 2006. Atlanta, GA. P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic Hongping Yang 1, Jian
Submitted for the 12 th Conf. on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteor. 29 Jan. 2 Feb. 2006. Atlanta, GA. P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic Hongping Yang 1, Jian
Weather radar refractivity variability in the boundary layer of the atmosphere
 Weather radar refractivity variability in the boundary layer of the atmosphere Ruben Hallali, Jacques Parent Du Châtelet, Francis Dalaudier, Gilles Guillemin, Alain Moreau To cite this version: Ruben Hallali,
Weather radar refractivity variability in the boundary layer of the atmosphere Ruben Hallali, Jacques Parent Du Châtelet, Francis Dalaudier, Gilles Guillemin, Alain Moreau To cite this version: Ruben Hallali,
WMO Aeronautical Meteorology Scientific Conference 2017
 Session 1 Science underpinning meteorological observations, forecasts, advisories and warnings 1.1 En route phenomena 1.1.1 Ice crystal icing, and airframe icing research Signatures of supercooled liquid
Session 1 Science underpinning meteorological observations, forecasts, advisories and warnings 1.1 En route phenomena 1.1.1 Ice crystal icing, and airframe icing research Signatures of supercooled liquid
Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003.
 SAFIR WARNING : Expected risk Radar-based Probability of Hail 0915 0930 0945 1000 Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003. Lightning
SAFIR WARNING : Expected risk Radar-based Probability of Hail 0915 0930 0945 1000 Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003. Lightning
APPLICATION OF SPECTRAL POLARIMETRY TO A HAILSTORM AT LOW ELEVATION ANGLE
 13A.3 1 APPLICATION OF SPECTRAL POLARIMETRY TO A HAILSTORM AT LOW ELEVATION ANGLE T.-Y. Yu 1,2,3,, H. Le 1,2, Y. Wang 4,5, A. Ryzhkov 3,4,5, and M. Kumjian 6 1 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
13A.3 1 APPLICATION OF SPECTRAL POLARIMETRY TO A HAILSTORM AT LOW ELEVATION ANGLE T.-Y. Yu 1,2,3,, H. Le 1,2, Y. Wang 4,5, A. Ryzhkov 3,4,5, and M. Kumjian 6 1 School of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
IMPROVEMENTS OF POLARIMETRIC RADAR ECHO CLASSIFICATIONS. Ronald Hannesen* Selex-Gematronik, Neuss, Germany
 P13.14 IMPROVEMENTS OF POLARIMETRIC RADAR ECHO CLASSIFICATIONS Ronald Hannesen* Selex-Gematronik, Neuss, Germany 1. INTRODUCTION A two-step radar echo classification is applied on polarimetric radar data:
P13.14 IMPROVEMENTS OF POLARIMETRIC RADAR ECHO CLASSIFICATIONS Ronald Hannesen* Selex-Gematronik, Neuss, Germany 1. INTRODUCTION A two-step radar echo classification is applied on polarimetric radar data:
Precipitation estimate of a heavy rain event using a C-band solid-state polarimetric radar
 Precipitation estimate of a heavy rain event using a C-band solid-state polarimetric radar Hiroshi Yamauchi 1, Ahoro Adachi 1, Osamu Suzuki 2, Takahisa Kobayashi 3 1 Meteorological Research Institute,
Precipitation estimate of a heavy rain event using a C-band solid-state polarimetric radar Hiroshi Yamauchi 1, Ahoro Adachi 1, Osamu Suzuki 2, Takahisa Kobayashi 3 1 Meteorological Research Institute,
Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom
 2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
5.3 THREE BODY SCATTER SIGNATURE PRODUCING UNCERTAINTIES IN DOPPLER RADIAL VELOCITY STRUCTURES
 5.3 THREE BODY SCATTER SIGNATURE PRODUCING UNCERTAINTIES IN DOPPLER RADIAL VELOCITY STRUCTURES Aurora Stan-Sion *, D. V. Carbunaru and B. Antonescu National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romanian
5.3 THREE BODY SCATTER SIGNATURE PRODUCING UNCERTAINTIES IN DOPPLER RADIAL VELOCITY STRUCTURES Aurora Stan-Sion *, D. V. Carbunaru and B. Antonescu National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romanian
DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE
 DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE H. Kyznarová 1 and P. Novák 2 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, kyznarova@chmi.cz 2 Czech Hydrometeorological
DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE H. Kyznarová 1 and P. Novák 2 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, kyznarova@chmi.cz 2 Czech Hydrometeorological
Validation Report for Precipitation products from Cloud Physical Properties (PPh-PGE14: PCPh v1.0 & CRPh v1.0)
 Page: 1/26 Validation Report for Precipitation SAF/NWC/CDOP2/INM/SCI/VR/15, Issue 1, Rev. 0 15 July 2013 Applicable to SAFNWC/MSG version 2013 Prepared by AEMET Page: 2/26 REPORT SIGNATURE TABLE Function
Page: 1/26 Validation Report for Precipitation SAF/NWC/CDOP2/INM/SCI/VR/15, Issue 1, Rev. 0 15 July 2013 Applicable to SAFNWC/MSG version 2013 Prepared by AEMET Page: 2/26 REPORT SIGNATURE TABLE Function
EDWARD A. BRANDES* Research Applications Program National Center for Atmospheric Research. and ALEXANDER V. RYZHKOV
 P5.10 HAIL DETECTION WITH POLARIMETRIC RADAR EDWARD A. BRANDES* Research Applications Program National Center for Atmospheric Research and ALEXANDER V. RYZHKOV Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
P5.10 HAIL DETECTION WITH POLARIMETRIC RADAR EDWARD A. BRANDES* Research Applications Program National Center for Atmospheric Research and ALEXANDER V. RYZHKOV Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
Impact of Observation Operators on Low-Level Wind Speed Retrieved by Variational Multiple-Doppler Analysis
 215 Impact of Observation Operators on Low-Level Wind Speed Retrieved by Variational Multiple-Doppler Analysis Ken-ichi Shimose, Shingo Shimizu, Takeshi Maesaka, Ryohei Kato, Kaori Kieda, and Koyuru Iwanami
215 Impact of Observation Operators on Low-Level Wind Speed Retrieved by Variational Multiple-Doppler Analysis Ken-ichi Shimose, Shingo Shimizu, Takeshi Maesaka, Ryohei Kato, Kaori Kieda, and Koyuru Iwanami
Using Gap-Filling Radars in Mountainous Regions to Complement a National Radar Network: Improvements in Multiple-Doppler Wind Syntheses
 1836 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 52 Using Gap-Filling Radars in Mountainous Regions to Complement a National Radar Network: Improvements in
1836 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 52 Using Gap-Filling Radars in Mountainous Regions to Complement a National Radar Network: Improvements in
3D radar reflectivity mosaics based on a variational method
 ERAD 1 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN ONFERENE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY 3D radar reflectivity mosaics based on a variational method Jordi Roca-Sancho, Marc erenguer, Daniel Sempere-Torres entre de
ERAD 1 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN ONFERENE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY 3D radar reflectivity mosaics based on a variational method Jordi Roca-Sancho, Marc erenguer, Daniel Sempere-Torres entre de
Estimating the Impact of a 3-dB Sensitivity Loss on WSR-88D Data
 P12R.9 Estimating the Impact of a 3-dB Sensitivity Loss on WSR-88D Data Kevin A. Scharfenberg*, Kim L. Elmore, Eddie Forren, and Valery Melnikov Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorology Studies,
P12R.9 Estimating the Impact of a 3-dB Sensitivity Loss on WSR-88D Data Kevin A. Scharfenberg*, Kim L. Elmore, Eddie Forren, and Valery Melnikov Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorology Studies,
19B.2 QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION USING SPECIFIC DIFFERENTIAL PROPAGATION PHASE IN TYPHOON SYSTEMS IN TAIWAN
 19B.2 QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION USING SPECIFIC DIFFERENTIAL PROPAGATION PHASE IN TYPHOON SYSTEMS IN TAIWAN Yadong Wang* 1, Jian Zhang 1,2, Alexander V. Ryzhkov 1, Lin Tang 1, Kenneth W. Howard
19B.2 QUANTITATIVE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATION USING SPECIFIC DIFFERENTIAL PROPAGATION PHASE IN TYPHOON SYSTEMS IN TAIWAN Yadong Wang* 1, Jian Zhang 1,2, Alexander V. Ryzhkov 1, Lin Tang 1, Kenneth W. Howard
RODGER A. BROWN NOAA/National Severe Storms Laboratory, Norman, OK
 Preprints, 25th Intern. Conf. on Interactive Information and Processing Systems, Phoenix, AZ, Amer. Meteor. Soc., January 2009 9B.3 Progress Report on the Evolutionary Characteristics of a Tornadic Supercell
Preprints, 25th Intern. Conf. on Interactive Information and Processing Systems, Phoenix, AZ, Amer. Meteor. Soc., January 2009 9B.3 Progress Report on the Evolutionary Characteristics of a Tornadic Supercell
P. N. Gatlin 1, Walter. A. Petersen 2, Lawrence. D. Carey 1, Susan. R. Jacks Introduction
 P14.21 34 th Conference on Radar Meteorology Williamsburg, VA, 4-9 Oct 2009 The NEXRAD Rainfall Estimation Processing System: A radar tool to improve rainfall estimation across the Tennessee River Valley
P14.21 34 th Conference on Radar Meteorology Williamsburg, VA, 4-9 Oct 2009 The NEXRAD Rainfall Estimation Processing System: A radar tool to improve rainfall estimation across the Tennessee River Valley
Single-Doppler EnKF assimilation of high-resolution data from the 29 May 2004 OKC supercell: Comparisons with dual-doppler analyses.
 Single-Doppler assimilation of high-resolution data from the 29 May 2004 OKC supercell: Comparisons with dual-doppler analyses. Lou Wicker NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab, Norman OK With lots of help from:
Single-Doppler assimilation of high-resolution data from the 29 May 2004 OKC supercell: Comparisons with dual-doppler analyses. Lou Wicker NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab, Norman OK With lots of help from:
2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA
 2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA Alessandro M. Hering* 1, Stéphane Sénési 2, Paolo Ambrosetti 1, and Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 2 1 MeteoSwiss, ML, Locarno-Monti, Switzerland
2.14 NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORMS IN COMPLEX CASES USING RADAR DATA Alessandro M. Hering* 1, Stéphane Sénési 2, Paolo Ambrosetti 1, and Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 2 1 MeteoSwiss, ML, Locarno-Monti, Switzerland
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar
 Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf 1, H. Leijnse 1, A. Dokter 2, J. Shamoun-Baranes 2, H. van Gasteren 3, J. Koistinen 4, and W. Bouten 2 1 Royal Netherlands Meteorological
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf 1, H. Leijnse 1, A. Dokter 2, J. Shamoun-Baranes 2, H. van Gasteren 3, J. Koistinen 4, and W. Bouten 2 1 Royal Netherlands Meteorological
Preliminary results. Leonardo Calvetti, Rafael Toshio, Flávio Deppe and Cesar Beneti. Technological Institute SIMEPAR, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil
 HIGH RESOLUTION WRF SIMULATIONS FOR WIND GUST EVENTS Preliminary results Leonardo Calvetti, Rafael Toshio, Flávio Deppe and Cesar Beneti Technological Institute SIMEPAR, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil 3 rd WMO/WWRP
HIGH RESOLUTION WRF SIMULATIONS FOR WIND GUST EVENTS Preliminary results Leonardo Calvetti, Rafael Toshio, Flávio Deppe and Cesar Beneti Technological Institute SIMEPAR, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil 3 rd WMO/WWRP
TIFS DEVELOPMENTS INSPIRED BY THE B08 FDP. John Bally, A. J. Bannister, and D. Scurrah Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
 P13B.11 TIFS DEVELOPMENTS INSPIRED BY THE B08 FDP John Bally, A. J. Bannister, and D. Scurrah Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 1. INTRODUCTION This paper describes the developments
P13B.11 TIFS DEVELOPMENTS INSPIRED BY THE B08 FDP John Bally, A. J. Bannister, and D. Scurrah Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 1. INTRODUCTION This paper describes the developments
22B.5 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF THE DPR RAINFALL PRODUCTS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA ACCORDING TO THE H-SAF VALIDATION PROTOCOL
 22B.5 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF THE RAINFALL PRODUCTS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA ACCORDING TO THE H-SAF VALIDATION PROTOCOL Marco Petracca *, Silvia Puca, Stefano Sebastianelli, Gianfranco Vulpiani Department
22B.5 LONG-TERM ASSESSMENT OF THE RAINFALL PRODUCTS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN AREA ACCORDING TO THE H-SAF VALIDATION PROTOCOL Marco Petracca *, Silvia Puca, Stefano Sebastianelli, Gianfranco Vulpiani Department
Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project
 ERAD 2012 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project Kalogiros J. 1, Anagnostou
ERAD 2012 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Measurements of a network of mobile radars during the experimental campaign of the HydroRad project Kalogiros J. 1, Anagnostou
Non-negative K DP Estimation by Monotone Increasing Φ DP Assumption below Melting Layer
 on-negative K DP Estimation by Monotone Increasing Φ DP Assumption below Melting Layer Takeshi Maesaka 1, Koyuru Iwanami 1 and Masayuki Maki 1 1 ational Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster
on-negative K DP Estimation by Monotone Increasing Φ DP Assumption below Melting Layer Takeshi Maesaka 1, Koyuru Iwanami 1 and Masayuki Maki 1 1 ational Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster
11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA
 11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA Svetlana Bachmann* and Dusan Zrnic Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA Svetlana Bachmann* and Dusan Zrnic Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
Application of Radar Wind Observations for Low-Level NWP Wind Forecast Validation
 1362 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 50 Application of Radar Wind Observations for Low-Level NWP Wind Forecast Validation KIRSTI SALONEN, SAMI NIEMELÄ,
1362 J O U R N A L O F A P P L I E D M E T E O R O L O G Y A N D C L I M A T O L O G Y VOLUME 50 Application of Radar Wind Observations for Low-Level NWP Wind Forecast Validation KIRSTI SALONEN, SAMI NIEMELÄ,
Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of Sciences, San Sebastian, Spain University of the Basque Country, Spain. Hosted by
 Analysis of weather radar data in the context of bird migration STSM-2016 Cost Action ES1305-European Network for the Radar surveillance of Animal Movement (ENRAM) Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of
Analysis of weather radar data in the context of bird migration STSM-2016 Cost Action ES1305-European Network for the Radar surveillance of Animal Movement (ENRAM) Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of
TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP. Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington
 1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
1.1 TWO CASES OF HEAVY RAIN ON THE MEDITERRANEAN SIDE OF THE ALPS IN MAP Robert Houze 1 and Socorro Medina University of Washington Matthias Steiner Princeton University 1. INTRODUCTION The Mesoscale Alpine
On the Influence of Assumed Drop Size Distribution Form on Radar-Retrieved Thunderstorm Microphysics
 FEBRUARY 2006 B R A N D E S E T A L. 259 On the Influence of Assumed Drop Size Distribution Form on Radar-Retrieved Thunderstorm Microphysics EDWARD A. BRANDES, GUIFU ZHANG, AND JUANZHEN SUN National Center
FEBRUARY 2006 B R A N D E S E T A L. 259 On the Influence of Assumed Drop Size Distribution Form on Radar-Retrieved Thunderstorm Microphysics EDWARD A. BRANDES, GUIFU ZHANG, AND JUANZHEN SUN National Center
Update on CoSPA Storm Forecasts
 Update on CoSPA Storm Forecasts Haig August 2, 2011 This work was sponsored by the Federal Aviation Administration under Air Force Contract No. FA8721-05-C-0002. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions,
Update on CoSPA Storm Forecasts Haig August 2, 2011 This work was sponsored by the Federal Aviation Administration under Air Force Contract No. FA8721-05-C-0002. Opinions, interpretations, conclusions,
results, azimuthal over-sampling and rapid update Y. Umemoto 1, 2, T. Lei 3, T. -Y. Yu 1, 2 and M. Xue 3, 4
 P9.5 Examining the Impact of Spatial and Temporal Resolutions of Phased-Array Radar on EnKF Analysis of Convective Storms Using OSSEs - Modeling Observation Errors Y. Umemoto, 2, T. Lei 3, T. -Y. Yu, 2
P9.5 Examining the Impact of Spatial and Temporal Resolutions of Phased-Array Radar on EnKF Analysis of Convective Storms Using OSSEs - Modeling Observation Errors Y. Umemoto, 2, T. Lei 3, T. -Y. Yu, 2
Preliminary result of hail detection using an operational S-band polarimetric radar in Korea
 Preliminary result of hail detection using an operational S-band polarimetric radar in Korea Mi-Young Kang 1, Dong-In Lee 1,2, Cheol-Hwan You 2, and Sol-Ip Heo 3 1 Department of Environmental Atmospheric
Preliminary result of hail detection using an operational S-band polarimetric radar in Korea Mi-Young Kang 1, Dong-In Lee 1,2, Cheol-Hwan You 2, and Sol-Ip Heo 3 1 Department of Environmental Atmospheric
Enhancing information transfer from observations to unobserved state variables for mesoscale radar data assimilation
 Enhancing information transfer from observations to unobserved state variables for mesoscale radar data assimilation Weiguang Chang and Isztar Zawadzki Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Faculty
Enhancing information transfer from observations to unobserved state variables for mesoscale radar data assimilation Weiguang Chang and Isztar Zawadzki Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Faculty
Asymmetry in Wind Field of Typhoon 0115 analyzed by Triple Doppler Radar Observation
 Asymmetry in Wind Field of Typhoon 115 analyzed by Triple Doppler Radar Observation Hiroshi YAMAUCHI*, Osamu SUZUKI (Meteorological Research Institute Kenji AKAEDA (Japan Meteorological Agency 1. Introduction
Asymmetry in Wind Field of Typhoon 115 analyzed by Triple Doppler Radar Observation Hiroshi YAMAUCHI*, Osamu SUZUKI (Meteorological Research Institute Kenji AKAEDA (Japan Meteorological Agency 1. Introduction
DATA FUSION NOWCASTING AND NWP
 DATA FUSION NOWCASTING AND NWP Brovelli Pascal 1, Ludovic Auger 2, Olivier Dupont 1, Jean-Marc Moisselin 1, Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 1, Philippe Cau 1, Adrien Anquez 1 1 Météo-France Forecasting Department
DATA FUSION NOWCASTING AND NWP Brovelli Pascal 1, Ludovic Auger 2, Olivier Dupont 1, Jean-Marc Moisselin 1, Isabelle Bernard-Bouissières 1, Philippe Cau 1, Adrien Anquez 1 1 Météo-France Forecasting Department
3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL
 3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL Q. Zhao 1*, J. Cook 1, Q. Xu 2, and P. Harasti 3 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey,
3.23 IMPROVING VERY-SHORT-TERM STORM PREDICTIONS BY ASSIMILATING RADAR AND SATELLITE DATA INTO A MESOSCALE NWP MODEL Q. Zhao 1*, J. Cook 1, Q. Xu 2, and P. Harasti 3 1 Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey,
P14R.11 INFERENCE OF MEAN RAINDROP SHAPES FROM DUAL-POLARIZATION DOPPLER SPECTRA OBSERVATIONS
 P14R.11 INFERENCE OF MEAN RAINDROP SHAPES FROM DUAL-POLARIZATION DOPPLER SPECTRA OBSERVATIONS Dmitri N. Moisseev and V. Chandrasekar Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO 1. INTRODUCTION Direct observations
P14R.11 INFERENCE OF MEAN RAINDROP SHAPES FROM DUAL-POLARIZATION DOPPLER SPECTRA OBSERVATIONS Dmitri N. Moisseev and V. Chandrasekar Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO 1. INTRODUCTION Direct observations
Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals. From Airborne Doppler Radar
 Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals From Airborne Doppler Radar Shannon L. McElhinney and Michael M. Bell University of Hawaii at Manoa Recent studies have highlighted the importance
Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals From Airborne Doppler Radar Shannon L. McElhinney and Michael M. Bell University of Hawaii at Manoa Recent studies have highlighted the importance
Evolution of the assimilation of radar data in the AROME model at convective scale
 Evolution of the assimilation of radar data in the AROME model at convective scale Eric WATTRELOT 1, Thibaut MONTMERLE 1, Carlos Geijo GUERRERO 2 1 CNRM/GAME (Météo-France/CNRS), 42 avenue Coriolis, France,
Evolution of the assimilation of radar data in the AROME model at convective scale Eric WATTRELOT 1, Thibaut MONTMERLE 1, Carlos Geijo GUERRERO 2 1 CNRM/GAME (Météo-France/CNRS), 42 avenue Coriolis, France,
5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR
 5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR Howard B. Bluestein * and Michael French University of Oklahoma, Norman Ivan Popstefanija ProSensing, Inc., Amherst, Massachusetts
5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR Howard B. Bluestein * and Michael French University of Oklahoma, Norman Ivan Popstefanija ProSensing, Inc., Amherst, Massachusetts
Meteorology 311. RADAR Fall 2016
 Meteorology 311 RADAR Fall 2016 What is it? RADAR RAdio Detection And Ranging Transmits electromagnetic pulses toward target. Tranmission rate is around 100 s pulses per second (318-1304 Hz). Short silent
Meteorology 311 RADAR Fall 2016 What is it? RADAR RAdio Detection And Ranging Transmits electromagnetic pulses toward target. Tranmission rate is around 100 s pulses per second (318-1304 Hz). Short silent
The impact of wet radome on the quality of polarimetric measurements. January 5, 2010
 The impact of wet radome on the quality of polarimetric measurements 1. Introduction January 5, 2010 It is well known that wet radome causes attenuation of microwave radiation. Such a transmission loss
The impact of wet radome on the quality of polarimetric measurements 1. Introduction January 5, 2010 It is well known that wet radome causes attenuation of microwave radiation. Such a transmission loss
Errors in surface rainfall rates retrieved from radar due to wind-drift
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 6: 71 77 (2) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/asl.96 Errors in surface rainfall rates retrieved from radar due to
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 6: 71 77 (2) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI:.2/asl.96 Errors in surface rainfall rates retrieved from radar due to
P5.4 WSR-88D REFLECTIVITY QUALITY CONTROL USING HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL REFLECTIVITY STRUCTURE
 P5.4 WSR-88D REFLECTIVITY QUALITY CONTROL USING HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL REFLECTIVITY STRUCTURE Jian Zhang 1, Shunxin Wang 1, and Beth Clarke 1 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
P5.4 WSR-88D REFLECTIVITY QUALITY CONTROL USING HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL REFLECTIVITY STRUCTURE Jian Zhang 1, Shunxin Wang 1, and Beth Clarke 1 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
USING GRIDDED MOS TECHNIQUES TO DERIVE SNOWFALL CLIMATOLOGIES
 JP4.12 USING GRIDDED MOS TECHNIQUES TO DERIVE SNOWFALL CLIMATOLOGIES Michael N. Baker * and Kari L. Sheets Meteorological Development Laboratory Office of Science and Technology National Weather Service,
JP4.12 USING GRIDDED MOS TECHNIQUES TO DERIVE SNOWFALL CLIMATOLOGIES Michael N. Baker * and Kari L. Sheets Meteorological Development Laboratory Office of Science and Technology National Weather Service,
A new operational convection-permitting NWP system for tropical cyclone forecasting in the SW Indian Ocean
 A new operational convection-permitting NWP system for tropical cyclone forecasting in the SW Indian Ocean Olivier BOUSQUET, Soline BIELLI, David BARBARY, Marie-Dominique LEROUX, Christelle BARTHE, Dominique
A new operational convection-permitting NWP system for tropical cyclone forecasting in the SW Indian Ocean Olivier BOUSQUET, Soline BIELLI, David BARBARY, Marie-Dominique LEROUX, Christelle BARTHE, Dominique
Ecography. Supplementary material
 Ecography ECOG-04028 Dokter, A. M., Desmet, P., Spaaks, J. H., van Hoey, S., Veen, L., Verlinden, L., Nilsson, C., Haase, G., Leijnse, H., Farnsworth, A., Bouten, W. and Shamoun-Baranes, J. 2019. biorad:
Ecography ECOG-04028 Dokter, A. M., Desmet, P., Spaaks, J. H., van Hoey, S., Veen, L., Verlinden, L., Nilsson, C., Haase, G., Leijnse, H., Farnsworth, A., Bouten, W. and Shamoun-Baranes, J. 2019. biorad:
7 WSR-88D OBSERVATIONS OF AN EXTREME HAIL EVENT IMPACTING ABILENE, TX ON 12 JUNE 2014
 28TH CONFERENCE ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS 7 WSR-88D OBSERVATIONS OF AN EXTREME HAIL EVENT IMPACTING ABILENE, TX ON 12 JUNE 2014 ARTHUR WITT * NOAA/National Severe Storms Laboratory, Norman, OK MIKE JOHNSON
28TH CONFERENCE ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS 7 WSR-88D OBSERVATIONS OF AN EXTREME HAIL EVENT IMPACTING ABILENE, TX ON 12 JUNE 2014 ARTHUR WITT * NOAA/National Severe Storms Laboratory, Norman, OK MIKE JOHNSON
BY REAL-TIME ClassZR. Jeong-Hee Kim 1, Dong-In Lee* 2, Min Jang 2, Kil-Jong Seo 2, Geun-Ok Lee 2 and Kyung-Eak Kim 3 1.
 P2.6 IMPROVEMENT OF ACCURACY OF RADAR RAINFALL RATE BY REAL-TIME ClassZR Jeong-Hee Kim 1, Dong-In Lee* 2, Min Jang 2, Kil-Jong Seo 2, Geun-Ok Lee 2 and Kyung-Eak Kim 3 1 Korea Meteorological Administration,
P2.6 IMPROVEMENT OF ACCURACY OF RADAR RAINFALL RATE BY REAL-TIME ClassZR Jeong-Hee Kim 1, Dong-In Lee* 2, Min Jang 2, Kil-Jong Seo 2, Geun-Ok Lee 2 and Kyung-Eak Kim 3 1 Korea Meteorological Administration,
Monitoring bird migration by weather radar
 Monitoring bird migration by weather radar Adriaan Dokter and Iwan Holleman Introduction Weather and bird migration are intimately related. Evolution has shaped the migration strategies of birds such that
Monitoring bird migration by weather radar Adriaan Dokter and Iwan Holleman Introduction Weather and bird migration are intimately related. Evolution has shaped the migration strategies of birds such that
Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia
 15B.1 RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATES AND NOWCASTS: THE CHALLENGING ROAD FROM RESEARCH TO WARNINGS Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia 1. Introduction Warnings are
15B.1 RADAR RAINFALL ESTIMATES AND NOWCASTS: THE CHALLENGING ROAD FROM RESEARCH TO WARNINGS Aurora Bell*, Alan Seed, Ross Bunn, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, Australia 1. Introduction Warnings are
Fundamentals of Radar Display. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
P4.11 SINGLE-DOPPLER RADAR WIND-FIELD RETRIEVAL EXPERIMENT ON A QUALIFIED VELOCITY-AZIMUTH PROCESSING TECHNIQUE
 P4.11 SINGLE-DOPPLER RADAR WIND-FIELD RETRIEVAL EXPERIMENT ON A QUALIFIED VELOCITY-AZIMUTH PROCESSING TECHNIQUE Yongmei Zhou and Roland Stull University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Robert
P4.11 SINGLE-DOPPLER RADAR WIND-FIELD RETRIEVAL EXPERIMENT ON A QUALIFIED VELOCITY-AZIMUTH PROCESSING TECHNIQUE Yongmei Zhou and Roland Stull University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Robert
THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DROP SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS OF CLOUD TYPES USING GUDUCK WEATHER RADAR, BUSAN, KOREA
 THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DROP SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS OF CLOUD TYPES USING GUDUCK WEATHER RADAR, BUSAN, KOREA Dong-In Lee 1, Min Jang 1, Cheol-Hwan You 2, Byung-Sun Kim 2, Jae-Chul Nam 3 Dept.
THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DROP SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS AND CLASSIFICATIONS OF CLOUD TYPES USING GUDUCK WEATHER RADAR, BUSAN, KOREA Dong-In Lee 1, Min Jang 1, Cheol-Hwan You 2, Byung-Sun Kim 2, Jae-Chul Nam 3 Dept.
Current Limited Area Applications
 Current Limited Area Applications Nils Gustafsson SMHI Norrköping, Sweden nils.gustafsson@smhi.se Outline of talk (contributions from many HIRLAM staff members) Specific problems of Limited Area Model
Current Limited Area Applications Nils Gustafsson SMHI Norrköping, Sweden nils.gustafsson@smhi.se Outline of talk (contributions from many HIRLAM staff members) Specific problems of Limited Area Model
THE IMPACT OF DIFFERENT DATA FIELDS ON STORM-SSCALE DATA ASSIMILATION
 JP1J.3 THE IMPACT OF DIFFERENT DATA FIELDS ON STORM-SSCALE DATA ASSIMILATION Guoqing Ge 1,2,*, Jidong Gao 1, Kelvin Droegemeier 1,2 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms, University of Oklahoma,
JP1J.3 THE IMPACT OF DIFFERENT DATA FIELDS ON STORM-SSCALE DATA ASSIMILATION Guoqing Ge 1,2,*, Jidong Gao 1, Kelvin Droegemeier 1,2 Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms, University of Oklahoma,
A Climatology of supercells in Romania
 A Climatology of supercells in Romania Bogdan Antonescu, Daniel Carbunaru, Monica Sasu, Sorin Burcea, and Aurora Bell National Meteorological Administration, Sos. Bucuresti-Ploiesti 97, Bucharest-013686,
A Climatology of supercells in Romania Bogdan Antonescu, Daniel Carbunaru, Monica Sasu, Sorin Burcea, and Aurora Bell National Meteorological Administration, Sos. Bucuresti-Ploiesti 97, Bucharest-013686,
7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR
 7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR David Priegnitz 1, S. M. Torres 1 and P. L. Heinselman 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR David Priegnitz 1, S. M. Torres 1 and P. L. Heinselman 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars.
 Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars. R. Kaltenboeck 1 and A. Ryzhkov 2 1 Austrocontrol - Aviation Weather Service, Vienna and Institute
Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars. R. Kaltenboeck 1 and A. Ryzhkov 2 1 Austrocontrol - Aviation Weather Service, Vienna and Institute
THUNDERSTORM LIGHTNING DATA
 THUNDERSTORM EVOLUTION ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION USING RADAR AND TOTAL LIGHTNING DATA Jianhua Dai 1,2 *, Yuan Wang 1, Lei Chen 2, Lan Tao 2, Hong Lin 2 1. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Key Laboratory
THUNDERSTORM EVOLUTION ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION USING RADAR AND TOTAL LIGHTNING DATA Jianhua Dai 1,2 *, Yuan Wang 1, Lei Chen 2, Lan Tao 2, Hong Lin 2 1. Department of Atmospheric Sciences, Key Laboratory
P5.16 OBSERVED FAILURE MODES OF THE WSR-88D VELOCITY DEALIASING ALGORITHM DURING SEVERE WEATHER OUTBREAKS
 P5.16 OBSERVED FAILURE MODES OF THE WSR-88D VELOCITY DEALIASING ALGORITHM DURING SEVERE WEATHER OUTBREAKS Donald W. Burgess * Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies, The University
P5.16 OBSERVED FAILURE MODES OF THE WSR-88D VELOCITY DEALIASING ALGORITHM DURING SEVERE WEATHER OUTBREAKS Donald W. Burgess * Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies, The University
P7.1 STUDY ON THE OPTIMAL SCANNING STRATEGIES OF PHASE-ARRAY RADAR THROUGH ENSEMBLE KALMAN FILTER ASSIMILATION OF SIMULATED DATA
 P7.1 STUDY ON THE OPTIMAL SCANNING STRATEGIES OF PHASE-ARRAY RADAR THROUGH ENSEMBLE KALMAN FILTER ASSIMILATION OF SIMULATED DATA Ting Lei 1, Ming Xue 1,, Tianyou Yu 3 and Michihiro Teshiba 3 1 Center for
P7.1 STUDY ON THE OPTIMAL SCANNING STRATEGIES OF PHASE-ARRAY RADAR THROUGH ENSEMBLE KALMAN FILTER ASSIMILATION OF SIMULATED DATA Ting Lei 1, Ming Xue 1,, Tianyou Yu 3 and Michihiro Teshiba 3 1 Center for
ERAD Czech weather radar data utilization for precipitation nowcasting. Proceedings of ERAD (2004): c Copernicus GmbH 2004
 Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 459 463 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Czech weather radar data utilization for precipitation nowcasting P. Novák Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Radar Department, Na
Proceedings of ERAD (2004): 459 463 c Copernicus GmbH 2004 ERAD 2004 Czech weather radar data utilization for precipitation nowcasting P. Novák Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Radar Department, Na
and hydrological applications
 Overview of QPE/QPF techniques and hydrological applications Siriluk Chumchean Department of Civil Engineering Mahanakorn University of Technology Typhoon Committee Roving Seminar 2011, Malaysia (20-23
Overview of QPE/QPF techniques and hydrological applications Siriluk Chumchean Department of Civil Engineering Mahanakorn University of Technology Typhoon Committee Roving Seminar 2011, Malaysia (20-23
Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2. Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway
 4.11 RADAR DATA QUALITY THE CHALLENGE OF BEAM BLOCKAGES AND PROPAGATION CHANGES Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway 2 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological
4.11 RADAR DATA QUALITY THE CHALLENGE OF BEAM BLOCKAGES AND PROPAGATION CHANGES Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway 2 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological
Operational Implementation of the 1D13D-Var Assimilation Method of Radar Reflectivity Data in the AROME Model
 Operational Implementation of the 1D13D-Var Assimilation Method of Radar Reflectivity Data in the AROME Model Eric Wattrelot, Olivier Caumont, Jean-Francois Mahfouf To cite this version: Eric Wattrelot,
Operational Implementation of the 1D13D-Var Assimilation Method of Radar Reflectivity Data in the AROME Model Eric Wattrelot, Olivier Caumont, Jean-Francois Mahfouf To cite this version: Eric Wattrelot,
24 TH CONFERENCE ON SEVERE LOCAL STORMS, OCTOBER 2008, SAVANNAH, GEORGIA
 P9.13 SUPER-RESOLUTION POLARIMETRIC OBSERVATIONS OF A CYCLIC TORNADIC SUPERCELL MATTHEW R. KUMJIAN*, ALEXANDER V. RYZHKOV, AND VALERY M. MELNIKOV Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
P9.13 SUPER-RESOLUTION POLARIMETRIC OBSERVATIONS OF A CYCLIC TORNADIC SUPERCELL MATTHEW R. KUMJIAN*, ALEXANDER V. RYZHKOV, AND VALERY M. MELNIKOV Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
ERAD THE SIXTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 Radar and lightning data based classification scheme for the severity of convective cells Pekka Rossi 1, Kalle Halmevaara 2, Antti Mäkelä 1, Jarmo Koistinen 1, Vesa Hasu 2 1. Finnish Meteorological Institute,
Radar and lightning data based classification scheme for the severity of convective cells Pekka Rossi 1, Kalle Halmevaara 2, Antti Mäkelä 1, Jarmo Koistinen 1, Vesa Hasu 2 1. Finnish Meteorological Institute,
DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers
 DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers M. Thurai 1, W. A. Petersen 2, and L. D. Carey 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers M. Thurai 1, W. A. Petersen 2, and L. D. Carey 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
ERAD THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 ERAD 2014 - THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Microphysical interpretation of coincident simultaneous and fast alternating horizontal and vertical polarization transmit
ERAD 2014 - THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Microphysical interpretation of coincident simultaneous and fast alternating horizontal and vertical polarization transmit
Real time mitigation of ground clutter
 Real time mitigation of ground clutter John C. Hubbert, Mike Dixon and Scott Ellis National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder CO 1. Introduction The identification and mitigation of anomalous propagation
Real time mitigation of ground clutter John C. Hubbert, Mike Dixon and Scott Ellis National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder CO 1. Introduction The identification and mitigation of anomalous propagation
Identification of Convective Hotspots in Mountainous Terrain
 Identification of Convective Hotspots in Mountainous Terrain Martin Hagen, Leslie Grebe, Joël van Baelen, Evelyne Richard DLR Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Université de Clermont-Ferrand, France Observatoire
Identification of Convective Hotspots in Mountainous Terrain Martin Hagen, Leslie Grebe, Joël van Baelen, Evelyne Richard DLR Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Université de Clermont-Ferrand, France Observatoire
Lei Feng Ben Jong-Dao Jou * T. D. Keenan
 P2.4 CONSIDER THE WIND DRIFT EFFECTS IN THE RADAR-RAINGAUGE COMPARISONS Lei Feng Ben Jong-Dao Jou * T. D. Keenan National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction, Taipei County, R.O.C National
P2.4 CONSIDER THE WIND DRIFT EFFECTS IN THE RADAR-RAINGAUGE COMPARISONS Lei Feng Ben Jong-Dao Jou * T. D. Keenan National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction, Taipei County, R.O.C National
AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM
 AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM Koji Yamashita Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1-3-4, Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
AN OBSERVING SYSTEM EXPERIMENT OF MTSAT RAPID SCAN AMV USING JMA MESO-SCALE OPERATIONAL NWP SYSTEM Koji Yamashita Japan Meteorological Agency / Numerical Prediction Division 1-3-4, Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku,
ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL
 JP2.9 ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL Patrick T. Marsh* and David J. Karoly School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and
JP2.9 ASSESMENT OF THE SEVERE WEATHER ENVIROMENT IN NORTH AMERICA SIMULATED BY A GLOBAL CLIMATE MODEL Patrick T. Marsh* and David J. Karoly School of Meteorology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK and
Improving real time observation and nowcasting RDT. E de Coning, M Gijben, B Maseko and L van Hemert Nowcasting and Very Short Range Forecasting
 Improving real time observation and nowcasting RDT E de Coning, M Gijben, B Maseko and L van Hemert Nowcasting and Very Short Range Forecasting Introduction Satellite Application Facilities (SAFs) are
Improving real time observation and nowcasting RDT E de Coning, M Gijben, B Maseko and L van Hemert Nowcasting and Very Short Range Forecasting Introduction Satellite Application Facilities (SAFs) are
ERAD THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 Multi-beam raindrop size distribution retrieals on the oppler spectra Christine Unal Geoscience and Remote Sensing, TU-elft Climate Institute, Steinweg 1, 68 CN elft, Netherlands, c.m.h.unal@tudelft.nl
Multi-beam raindrop size distribution retrieals on the oppler spectra Christine Unal Geoscience and Remote Sensing, TU-elft Climate Institute, Steinweg 1, 68 CN elft, Netherlands, c.m.h.unal@tudelft.nl
NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORM HAZARDS FOR FLIGHT OPERATIONS: THE CB WIMS APPROACH IN FLYSAFE
 26 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORM HAZARDS FOR FLIGHT OPERATIONS: THE CB WIMS APPROACH IN FLYSAFE A. Tafferner*, C. Forster*, S. Sénési**, Y. Guillou**, P.
26 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES NOWCASTING THUNDERSTORM HAZARDS FOR FLIGHT OPERATIONS: THE CB WIMS APPROACH IN FLYSAFE A. Tafferner*, C. Forster*, S. Sénési**, Y. Guillou**, P.
118 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS
 8 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS Shinju Park, Marc Berenguer Centre de Recerca Aplicada en Hidrometeorologia, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (BarcelonaTech), Barcelona, Spain..
8 RECONSTRUCTION OF RADAR RFLECTIVITY IN CLUTTER AREAS Shinju Park, Marc Berenguer Centre de Recerca Aplicada en Hidrometeorologia, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (BarcelonaTech), Barcelona, Spain..
Backscatter differential phase. Estimation and variability.
 Backscatter differential phase. Estimation and variability. S. Trömel 1, M. Kumjian 2, A. Ryzhkov 2, C. Simmer 3, A. Tokay 4, J.-B. Schroer 3 1 Hans-Ertel-Centre for Weather Research, Atmospheric Dynamics
Backscatter differential phase. Estimation and variability. S. Trömel 1, M. Kumjian 2, A. Ryzhkov 2, C. Simmer 3, A. Tokay 4, J.-B. Schroer 3 1 Hans-Ertel-Centre for Weather Research, Atmospheric Dynamics
Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley
 EASTERN REGION TECHNICAL ATTACHMENT NO. 98-9 OCTOBER, 1998 Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley Nicole M. Belk and Lyle
EASTERN REGION TECHNICAL ATTACHMENT NO. 98-9 OCTOBER, 1998 Using Cell-Based VIL Density to Identify Severe-Hail Thunderstorms in the Central Appalachians and Middle Ohio Valley Nicole M. Belk and Lyle
