Monitoring bird migration by weather radar
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Monitoring bird migration by weather radar Adriaan Dokter and Iwan Holleman Introduction Weather and bird migration are intimately related. Evolution has shaped the migration strategies of birds such that they optimally respond to and make use of weather conditions during their long distance travels between breeding and wintering grounds. Both wind and precipitation strongly determine the day-to-day timing of migration and altitude use by birds. 5 EUMETNET/OPERA Radar Network Trappes Den Helder De Bilt Wideumont Kilometers [dbz] 55 7 Spatiotemporal information on bird migration is of invaluable use to scientists and society alike, but so far no sensor networks have been established that can monitor bird movement continuously over large areas. In aviation bird migration information is important for improving flight safety. Especially military low level flying has a high risk of en-route bird strikes and spatial bird migration information is essential for generating reliable flight warnings to pilots. Comprehensive monitoring of bird migration at continental scales can also provide insight into migration patterns and the impact on migratory flight of synoptic scale factors like weather and orography. As part of an international project by the European Space Agency (ESA) aimed at reducing collisions between aircrafts and birds, we have explored the potential of operational Doppler weather radar as a bird migration sensor. Observing bird migration by Doppler weather radar Operational weather radar networks exist in e.g. Europe and the United States for meteorological applications. These networks have a large spatial coverage as illustrated in Figure, showing part of the European 5 55 Figure. Map of operational weather radars for part of Western Europe. Radar sites are indicated by bullets, the weather radars used in this study are labelled and coloured red. The OPERA reflectivit y composite is overlaid for 9 April 8 9. UTC. 5 network OPERA (Operational Programme for the Exchange of weather Radar information) ). Although weather radars are used primarily for precipitation monitoring, also biological scatterers can be observed by these systems. Boundary layer clear-air weather radar echoes are caused nearly exclusively by arthropods (mostly insects) and flying birds. Weather radars are therefore a promising sensor for providing bird migration information. A bird migration quantification algorithm needs to automatically distinguish bird-scattered signals from all other echoes detected by weather radar. Bird echoes and other clear-air signals tend to be considerably weaker than meteorologically relevant signals from hydrometeors. Birds, insects and hydrometeors give rise to signals in an Triennial Scientific Report
2 overlapping reflectivity regime, which makes it challenging to distinguish them. Doppler weather radars provide information on the radial velocity of scatterers, which we use to select out echoes related to bird migration. Figure shows weather radar images during intense bird migration (top row) and during a case with convective showers (bottom row). Bird migration gives rise to a characteristically high spatial variability of the radial velocity scan data, which is not observed for echoes from precipitation or insects. Unlike precipitation and insects, birds perform active flight which varies in speed and direction per individual, causing a higher variability in the Doppler velocity Figure. Radar displays for reflectivity factor (left) and radial velocity (right) during a bird migration event (top rectangular box in green) and an event with weak convective showers (bottom rectangular box in blue). The displays show the. degree elevation scan for a circular area of 5 km radius around the weather radar in De Bilt. Contiguous areas of echoes identified by the algorithm are indicated within the reflectivity displays by red borders. For the precipitation case (bottom) these areas removed from the data based on a low spatial variance of the radial velocities, while for the bird migration case (top) these areas are retained based on a high spatial variance of radial velocities. After removing precipitation echoes average bird densities are calculated from the remaining reflectivity data. Triennial Scientific Report 5
3 We developed a bird detection algorithm, ) based on existing wind-profiling algorithms for Doppler weather radars, using the Volume Velocity Profiling (VVP) technique 5). A target identification scheme was developed to filter out non-bird echoes from the radar volume data, based on an analysis of the local variance in radial velocity. The filtered reflectivity data is used to construct a bird density altitude profile, and an analysis of the radial velocity data yields the average bird speed and direction. Reflectivity was converted to bird density by assuming a constant bird radar cross section of cm, which we found to be an adequate approximation during nocturnal migration over Western Europe, which is strongly dominated by passerines (small song-birds). Bird radar field campaigns for validation In corporation with the Swiss Ornithological Institute we used a dedicated bird radar of the type Superfledermaus (see Figure ) to validate the weather radar observations of bird migration. The dedicated radar is capable of detecting the wingbeat pattern for individual radar targets 6) (see Figure ). Based on these echo signatures, insects, birds and hydrometeors can be distinguished with a high selectivity. The mobile tracking radar is therefore a state-of-the-art reference for validating the weather radar bird observations 7). Three field campaigns were organized to validate the weather radar bird observations. The bird radar has Weather radar can be used as a reliable sensor for bird migration quantification Figure. The bird radar Superfledermaus equipped with a camera mounted parallel to the radar antenna. Figure. Wingbeat pattern of a small songbird with regular phases of wingbeats (frequency around 5 Hz) and pauses as recorded by the Superfledermaus bird radar. The single wingbeats are clearly visible. The envelope of increasing and decreasing amplitude (vertical axis) of the signal along the time axis (horizontal axis) reflects the bird s flight entering the radar beam at one edge, flying through the centre and leaving at the other edge. been stationed within the measurement volume of the weather radar in De Bilt, the Netherlands from 9 Aug - 6 Sep 7, in Wideumont, Belgium from 8 Sep - Oct 7 and in Trappes, France from Mar - 9 May 8, thus covering a full autumn and spring migration season. In Figure 5 the bird densities altitude profiles detected by bird radar (top panel) and weather radar (middle panel) are displayed for the period of -6 October 7, when the bird radar was stationed in Trappes. We find a remarkable correspondence in the detected bird densities by the two sensors during all field campaigns. The altitude distributions and absolute number of detected birds match quantitatively. Weather radar can thus be used as a reliable sensor for bird migration quantification. The effect of wind on bird migration The effect of the environmental wind on flight altitudes becomes evident by comparing the weather radar bird density profile (Figure 5 middle panel) with the wind profiles calculated by the HIRLAM numerical weather prediction model (Figure 5 bottom panel). We find that birds adjust their flight altitude to make optimal use of tail winds along the predominant (south-westerly) migratory direction. For example, the HIRLAM wind profile (bottom panel Figure 5) shows that on October wind conditions at high altitude were unfavourable, where strong westerly winds cause negative wind effects. Migration therefore does not extend above km (see middle panel Figure 5). On the other hand, on October 6 tail winds are most favourable above km and as a result a large fraction of migration takes place at high altitude. Bird migration patterns observed at single sites can strongly depend on weather conditions elsewhere. This applies particularly to northern temperate climate, where frequent passages of high and low pressure s ystems cause a large spatial variability in weather. Using four weather radars (see Figure ) we 5 Triennial Scientific Report
4 Bird radar Height agl [km] Height agl [km] -Oct-7 -Oct-7 -Oct-7 5-Oct-7 6-Oct-7 7-Oct-7 Weather radar Reflectivity factor [dbz] Density [Birds / km ] Bird density [birds/km ] 5 5 -Oct-7 -Oct-7 -Oct-7 5-Oct-7 6-Oct-7 7-Oct-7 Height-integrated bird density and wind profile -Oct-7 -Oct-7 -Oct-7 5-Oct-7 6-Oct-7 7-Oct-7 Time Height agl [km] Figure 5. Comparison of the bird densities altitude profiles determined by bird radar (top panel) and weather radar (middle panel). Integrated bird densities over all height layers are displayed in the lower panel for both weather radar (red) and bird radar (blue) (left vertical axis). The period between sunset and sunrise is shaded in grey. Wind barbs in the lower panel show the wind profile from the HIRLAM numerical weather prediction model (right vertical axis). Wind barbs in the middle panel indicate the bird speed and direction as retrieved by the weather radar algorithm. Each half flag represents km/h and each full flag km/h. monitored the bird migration flyway at several sites simultaneously. Weather radar bird observations for the night of 9- April 8 are depicted in Figure 6. For this night the OPERA reflectivity composite is overlaid on Figure to give an impression of the large scale weather conditions. At each site, the timing and altitude profile of bird migration is observed to be influenced by weather conditions at locations passed earlier during a migratory flight. As an example, migration at the most southern site (Trappes) is characterized by strong departure and ascent to high altitudes around.5 km, where birds experience favourable tail winds along the preferred migratory direction (NE in spring). Low altitude migration is avoided because of unfavourable easterly low level winds. At one radar site north-east of Wideumont, we observe the appearance of a migration layer centred around km height after UTC. This migration layer appears after hours of flight time, which corresponds with a measured bird ground speed of 7 km/h to birds having travelled over a distance of about 8 km towards Triennial Scientific Report 5
5 Height AGL [km] bird density [birds/km ] Den Helder 8: : : : : : 6: 8: : 8: : : : : : 6: 8: : 8: : : : : : 6: 8: : 5 De Bilt Wideumont 8: : : : : : 6: 8: : Trappes 5 Reflectivity factor [dbz] Density [Birds / km ] Den Helder De Bilt Wideumont Trappes 9-Apr-8 8: -Apr-8 : -Apr-8 6: Time [UTC] Figure 6. Bird densities as a function of time and altitude at different weather radar sites (see Figure ) for the night of 9 April 8. The wind barbs represent the measured bird ground speed and direction. The lower panel shows the height integrated bird densities over.- km altitude. The period between sunset and sunrise is shaded in grey and civil twilight is shaded in light grey. The pink boxed inset on the right hand side of each panel shows the HIRLAM wind profile at UTC. Around UTC a double layered bird density profile is observed in Wideumont. We attribute the top band to birds that departed in the vicinity of Trappes, while the lower band results from birds departed at closer distance. band closely matches the cruising altitude after departure near Trappes. Birds have thus maintained a constant flight altitude during their migratory flight with respect to sea level. The altitude profile observed in Wideumont is clearly affected by the particular wind conditions at the more southern site of Trappes. In De Bilt, north of Wideumont, no birds depart in the early night. This is explained by the weak occlusion front slightly south of De Bilt, which blocks most migration. With this front weakening in activity, migration conditions became more favourable over the course of the night, and after UTC we do observe the passage and arrival of migrating birds. No migration is observed on the most northerly located weather radar in Den Helder. The extent to which birds are able to adapt their flight altitudes in response to changing meteorological conditions will be topic of future research. Conclusion We find that Doppler weather radar is highly successful in determining quantitative bird densities and average flight speeds and directions as a function of altitude. We find that weather radar reflectivity can be quantitatively correlated to the bird-densities determined independently by bird radar. The developed methods for bird detection and quantification can be easily extended to full operational weather radar networks. With the establishment of the OPERA data centre for radar data within the coming two years ) the establishment of a continent-wide bird migration sensor network in Europe is within reach. Such a network can enable important applications both in flight safety, health (avian disease spread) and environmental impact assessments. north-east. These birds must therefore have departed in the vicinity of Trappes in northern France, where birds chose a flight altitude of.5 km. Since Wideumont is located 5 m above mean sea level, the km altitude The establishment of a continent-wide bird migration sensor network in Europe is within reach 5 Triennial Scientific Report
6 References ) Holleman I., L. Delobbe and A. Zgonc, 8. Update on the european weather radar network (OPERA). Proc. Fifth European Conf. on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, June-July 8, Helsinki, Finland, 5pp ) Holleman, I., H. van Gasteren and W. Bouten, 8. Quality assessment of weather radar wind profiles during bird migration. J. Atm. Oceanic Technol., 5, 88-98, htpp://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/pdf/.75/8jtecha67. ) Dokter, A.M., F. Liechti, H. Stark, L. Delobbe, P. Tabary and I. Holleman,. Bird migration flight altitudes studied by a network of operational weather radars. J. R. Soc. Interface 7, doi:-98/rsif..6 ) Gasteren, H. van, I. Holleman, W. Bouten, E. van Loon, and J. Shamoun-Baranes, 8. Extracting bird migration information from C-band weather radars. Ibis, 5, ) Waldteufel, P. and H. Corbin, 979. On the analysis of single doppler radar data. J. Appl. Meteor., 8, ) Zaugg, S., G. Saporta, E. van Loon, H. Schmaljohann and F. Liechti, 8. Automatic identification of bird targets with radar via patterns produced by wing flapping. J. Royal Soc. Interface, 5, -5. 7) Schmaljohann, H., F. Liechti, E. Bächler, T. Steuri, and B. Bruderer, 8. Quantification of bird migration by radar - a detection probability problem. Ibis, 5, -55. Triennial Scientific Report 55
Bird detection by operational weather radar
 Bird detection by operational weather radar Adriaan M. Dokter 1,2, Felix Liechti 3, Laurent Delobbe 4, Pierre Tabary 5, Hans Beekhuis 6 and Iwan Holleman 2 1 Institute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics,
Bird detection by operational weather radar Adriaan M. Dokter 1,2, Felix Liechti 3, Laurent Delobbe 4, Pierre Tabary 5, Hans Beekhuis 6 and Iwan Holleman 2 1 Institute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics,
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar
 Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf 1, H. Leijnse 1, A. Dokter 2, J. Shamoun-Baranes 2, H. van Gasteren 3, J. Koistinen 4, and W. Bouten 2 1 Royal Netherlands Meteorological
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf 1, H. Leijnse 1, A. Dokter 2, J. Shamoun-Baranes 2, H. van Gasteren 3, J. Koistinen 4, and W. Bouten 2 1 Royal Netherlands Meteorological
Combining radar systems to get a 3D - picture of the bird migration Liechti, F.; Dokter, A.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.Z.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Holleman, I.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combining radar systems to get a 3D - picture of the bird migration Liechti, F.; Dokter, A.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.Z.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Holleman, I. Published in:
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combining radar systems to get a 3D - picture of the bird migration Liechti, F.; Dokter, A.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.Z.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Holleman, I. Published in:
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using
 Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf, H. Leijnse, A. Dokter, J. Shamoun-Baranes, H. van Gasteren, J. Koistinen, and W. Bouten 7th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology
Bird migration monitoring across Europe using weather radar M. de Graaf, H. Leijnse, A. Dokter, J. Shamoun-Baranes, H. van Gasteren, J. Koistinen, and W. Bouten 7th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology
Ecography. Supplementary material
 Ecography ECOG-04028 Dokter, A. M., Desmet, P., Spaaks, J. H., van Hoey, S., Veen, L., Verlinden, L., Nilsson, C., Haase, G., Leijnse, H., Farnsworth, A., Bouten, W. and Shamoun-Baranes, J. 2019. biorad:
Ecography ECOG-04028 Dokter, A. M., Desmet, P., Spaaks, J. H., van Hoey, S., Veen, L., Verlinden, L., Nilsson, C., Haase, G., Leijnse, H., Farnsworth, A., Bouten, W. and Shamoun-Baranes, J. 2019. biorad:
Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements
 Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements Edouard Goudenhoofdt, Maarten Reyniers and Laurent Delobbe Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, 1180
Long term analysis of convective storm tracks based on C-band radar reflectivity measurements Edouard Goudenhoofdt, Maarten Reyniers and Laurent Delobbe Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium, 1180
The FlySafe project: How weather radars can improve the en-route bird strike warning system.
 The FlySafe project: How weather radars can improve the en-route bird strike warning system. Hans van Gasteren 1,2, Arie Dekker 2, Judy Shamoun-Baranes 1, Hidde Leijnse 3, Michael Kemp 1, Martin de Graaf
The FlySafe project: How weather radars can improve the en-route bird strike warning system. Hans van Gasteren 1,2, Arie Dekker 2, Judy Shamoun-Baranes 1, Hidde Leijnse 3, Michael Kemp 1, Martin de Graaf
Quality of clear-air radar radial velocity data: Do insects matter?
 Quality of clear-air radar radial velocity data: Do insects matter? Ronald Hannesen, Sebastian Kauczok and André Weipert Selex ES GmbH, Raiffeisenstr. 10, 41470 Neuss, Germany (Dated: 15 July 2014) Ronald
Quality of clear-air radar radial velocity data: Do insects matter? Ronald Hannesen, Sebastian Kauczok and André Weipert Selex ES GmbH, Raiffeisenstr. 10, 41470 Neuss, Germany (Dated: 15 July 2014) Ronald
Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of Sciences, San Sebastian, Spain University of the Basque Country, Spain. Hosted by
 Analysis of weather radar data in the context of bird migration STSM-2016 Cost Action ES1305-European Network for the Radar surveillance of Animal Movement (ENRAM) Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of
Analysis of weather radar data in the context of bird migration STSM-2016 Cost Action ES1305-European Network for the Radar surveillance of Animal Movement (ENRAM) Nadja Weisshaupt Aranzadi - Society of
Fundamentals of Radar Display. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
Fundamentals of Radar Display Outline Fundamentals of Radar Display Scanning Strategies Basic Geometric Varieties WSR-88D Volume Coverage Patterns Classic Radar Displays and Signatures Precipitation Non-weather
Quality assessment of weather radar wind profiles during bird migration Holleman, I.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Bouten, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Quality assessment of weather radar wind profiles during bird migration Holleman, I.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Bouten, W. Published in: Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Quality assessment of weather radar wind profiles during bird migration Holleman, I.; van Gasteren, J.R.; Bouten, W. Published in: Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic
Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology. National Report To
 Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology National Report To Panel on Tropical Cyclones in the Bay of Bengal And Arabian Sea 43rd Session, India
Government of Sultanate of Oman Public Authority of Civil Aviation Directorate General of Meteorology National Report To Panel on Tropical Cyclones in the Bay of Bengal And Arabian Sea 43rd Session, India
FLYSAFE Bird strike risk mitigation in aviation
 FLYSAFE Bird strike risk mitigation in aviation Arie Dekker Command Mission Support Branche Nature Bureau Serge Sorbi Belgian Air Force Aviation Safety Directorate Wildlife Hazard Management Integrated
FLYSAFE Bird strike risk mitigation in aviation Arie Dekker Command Mission Support Branche Nature Bureau Serge Sorbi Belgian Air Force Aviation Safety Directorate Wildlife Hazard Management Integrated
How birds weather the weather: avian migration in the mid-latitudes Kemp, M.U.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) How birds weather the weather: avian migration in the mid-latitudes Kemp, M.U. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kemp, M. U. (2012). How birds
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) How birds weather the weather: avian migration in the mid-latitudes Kemp, M.U. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kemp, M. U. (2012). How birds
Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003.
 SAFIR WARNING : Expected risk Radar-based Probability of Hail 0915 0930 0945 1000 Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003. Lightning
SAFIR WARNING : Expected risk Radar-based Probability of Hail 0915 0930 0945 1000 Figure 5: Comparison between SAFIR warning and radar-based hail detection for the hail event of June 8, 2003. Lightning
Mode-S EHS data usage in the meteorological domain:
 Mode-S EHS data usage in the meteorological domain: derivation of Wind and Temperature observations; and assimilation of these observations in a numerical weather prediction model. Jan Sondij, MBA Senior
Mode-S EHS data usage in the meteorological domain: derivation of Wind and Temperature observations; and assimilation of these observations in a numerical weather prediction model. Jan Sondij, MBA Senior
WIND PROFILER NETWORK OF JAPAN METEOROLOGICAL AGENCY
 WIND PROFILER NETWORK OF JAPAN METEOROLOGICAL AGENCY Masahito Ishihara Japan Meteorological Agency CIMO Expert Team on Remote Sensing Upper-Air Technology and Techniques 14-17 March, 2005 Geneva, Switzerland
WIND PROFILER NETWORK OF JAPAN METEOROLOGICAL AGENCY Masahito Ishihara Japan Meteorological Agency CIMO Expert Team on Remote Sensing Upper-Air Technology and Techniques 14-17 March, 2005 Geneva, Switzerland
Channelling effect of the coastline and radar observed insect migration
 Channelling effect of the coastline and radar observed insect migration Matti Leskinen 1, Hannu Savijärvi 2, Susanna Lautaportti 2, Kauri Mikkola 3 1 Department of Physics University of Helsinki, P.O.Box
Channelling effect of the coastline and radar observed insect migration Matti Leskinen 1, Hannu Savijärvi 2, Susanna Lautaportti 2, Kauri Mikkola 3 1 Department of Physics University of Helsinki, P.O.Box
and SUMMARY preliminary parameters. 1.1 MET/14-IP/ /15 In line 1.2 WORLD INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION 2/6/14 English only
 INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION Meteorology (MET) Divisional Meeting (2014) WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Commission for Aeronautical Meteorology Fifteenth Session MET/14-IP/ /15 2/6/14 English
INTERNATIONAL CIVIL AVIATION ORGANIZATION Meteorology (MET) Divisional Meeting (2014) WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Commission for Aeronautical Meteorology Fifteenth Session MET/14-IP/ /15 2/6/14 English
Reprint 797. Development of a Thunderstorm. P.W. Li
 Reprint 797 Development of a Thunderstorm Nowcasting System in Support of Air Traffic Management P.W. Li AMS Aviation, Range, Aerospace Meteorology Special Symposium on Weather-Air Traffic Management Integration,
Reprint 797 Development of a Thunderstorm Nowcasting System in Support of Air Traffic Management P.W. Li AMS Aviation, Range, Aerospace Meteorology Special Symposium on Weather-Air Traffic Management Integration,
ADL110B ADL120 ADL130 ADL140 How to use radar and strike images. Version
 ADL110B ADL120 ADL130 ADL140 How to use radar and strike images Version 1.00 22.08.2016 How to use radar and strike images 1 / 12 Revision 1.00-22.08.2016 WARNING: Like any information of the ADL in flight
ADL110B ADL120 ADL130 ADL140 How to use radar and strike images Version 1.00 22.08.2016 How to use radar and strike images 1 / 12 Revision 1.00-22.08.2016 WARNING: Like any information of the ADL in flight
Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and Michael M. Bell. Department of Meteorology, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California, USA
 Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
Latent heating rate profiles at different tropical cyclone stages during 2008 Tropical Cyclone Structure experiment: Comparison of ELDORA and TRMM PR retrievals Myung-Sook Park, Russell L. Elsberry and
Mobile, phased-array, X-band Doppler radar observations of tornadogenesis in the central U. S.
 Mobile, phased-array, X-band Doppler radar observations of tornadogenesis in the central U. S. Howard B. Bluestein 1, Michael M. French 2, Ivan PopStefanija 3 and Robert T. Bluth 4 Howard (Howie Cb ) B.
Mobile, phased-array, X-band Doppler radar observations of tornadogenesis in the central U. S. Howard B. Bluestein 1, Michael M. French 2, Ivan PopStefanija 3 and Robert T. Bluth 4 Howard (Howie Cb ) B.
ERAD Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany. Proceedings of ERAD (2002): c Copernicus GmbH 2002
 Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 195 199 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany M. Hagen 1, K. Friedrich 1, and J. Seltmann 2 1 Institut
Proceedings of ERAD (2002): 195 199 c Copernicus GmbH 2002 ERAD 2002 Wind-field observations with the operational Doppler radar network in Germany M. Hagen 1, K. Friedrich 1, and J. Seltmann 2 1 Institut
TIME EVOLUTION OF A STORM FROM X-POL IN SÃO PAULO: 225 A ZH-ZDR AND TITAN METRICS COMPARISON
 TIME EVOLUTION OF A STORM FROM X-POL IN SÃO PAULO: 225 A ZH-ZDR AND TITAN METRICS COMPARISON * Roberto V Calheiros 1 ; Ana M Gomes 2 ; Maria A Lima 1 ; Carlos F de Angelis 3 ; Jojhy Sakuragi 4 (1) Voluntary
TIME EVOLUTION OF A STORM FROM X-POL IN SÃO PAULO: 225 A ZH-ZDR AND TITAN METRICS COMPARISON * Roberto V Calheiros 1 ; Ana M Gomes 2 ; Maria A Lima 1 ; Carlos F de Angelis 3 ; Jojhy Sakuragi 4 (1) Voluntary
Analyzing the impact of wind turbines on operational weather radar products
 Analyzing the impact of wind turbines on operational weather radar products Günther Haase 1, Daniel Johnson 1 and Kjell-Åke Eriksson 2 1 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, S-60176 Norrköping,
Analyzing the impact of wind turbines on operational weather radar products Günther Haase 1, Daniel Johnson 1 and Kjell-Åke Eriksson 2 1 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, S-60176 Norrköping,
Use of lightning data to improve observations for aeronautical activities
 Use of lightning data to improve observations for aeronautical activities Françoise Honoré Jean-Marc Yvagnes Patrick Thomas Météo_France Toulouse France I Introduction Aeronautical activities are very
Use of lightning data to improve observations for aeronautical activities Françoise Honoré Jean-Marc Yvagnes Patrick Thomas Météo_France Toulouse France I Introduction Aeronautical activities are very
Verification and performance measures of Meteorological Services to Air Traffic Management (MSTA)
 Verification and performance measures of Meteorological Services to Air Traffic Management (MSTA) Background Information on the accuracy, reliability and relevance of products is provided in terms of verification
Verification and performance measures of Meteorological Services to Air Traffic Management (MSTA) Background Information on the accuracy, reliability and relevance of products is provided in terms of verification
OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information
 OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information ALADIN-HIRLAM workshop, Toulouse Maud Martet 26-28 April 2016 OPERA: An EUMETNET Project EUMETNET: EIG of 31 European National
OPERA: Operational Programme for the Exchange of Weather Radar Information ALADIN-HIRLAM workshop, Toulouse Maud Martet 26-28 April 2016 OPERA: An EUMETNET Project EUMETNET: EIG of 31 European National
P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic
 Submitted for the 12 th Conf. on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteor. 29 Jan. 2 Feb. 2006. Atlanta, GA. P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic Hongping Yang 1, Jian
Submitted for the 12 th Conf. on Aviation, Range, and Aerospace Meteor. 29 Jan. 2 Feb. 2006. Atlanta, GA. P1.10 Synchronization of Multiple Radar Observations in 3-D Radar Mosaic Hongping Yang 1, Jian
Convective Structures in Clear-Air Echoes seen by a Weather Radar
 Convective Structures in Clear-Air Echoes seen by a Weather Radar Martin Hagen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Weather Radar Weather radar are normally used to locate
Convective Structures in Clear-Air Echoes seen by a Weather Radar Martin Hagen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany Weather Radar Weather radar are normally used to locate
Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters
 Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters P.W. Chan * and K.K. Hon Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China Abstract: The fixed-wing aircraft
Wind data collected by a fixed-wing aircraft in the vicinity of a typhoon over the south China coastal waters P.W. Chan * and K.K. Hon Hong Kong Observatory, Hong Kong, China Abstract: The fixed-wing aircraft
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Chapter 05 SOME OBSERVING INSTRUMENTS. Instrument Enclosure.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction
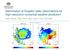 Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site
 Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
P474 SYDNEY AIRPORT WIND SHEAR ENCOUNTER - 15 APRIL 2007
 P474 SYDNEY AIRPORT WIND SHEAR ENCOUNTER - 15 APRIL 2007 Rodney Potts* 1, Barry Hanstrum 2 and Peter Dunda 2 1. CAWCR, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 2. Bureau of Meteorology, Sydney,
P474 SYDNEY AIRPORT WIND SHEAR ENCOUNTER - 15 APRIL 2007 Rodney Potts* 1, Barry Hanstrum 2 and Peter Dunda 2 1. CAWCR, Bureau of Meteorology, Melbourne, VIC, Australia 2. Bureau of Meteorology, Sydney,
AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER ABSTRACT
 AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER Christoph Münkel 1, Reijo Roininen 1 Vaisala GmbH, Schnackenburgallee 1d, 55 Hamburg, Germany Phone +9 89 1, Fax +9 89 11, E-mail christoph.muenkel@vaisala.com
AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER Christoph Münkel 1, Reijo Roininen 1 Vaisala GmbH, Schnackenburgallee 1d, 55 Hamburg, Germany Phone +9 89 1, Fax +9 89 11, E-mail christoph.muenkel@vaisala.com
Inter-comparison of X-band radar and lidar low-level wind measurement for air traffic control (ATC)
 Inter-comparison of X-band radar and lidar low-level wind measurement for air traffic control (ATC) Thomas Ernsdorf 1, Bernd Stiller 2, Björn-Rüdiger Beckmann 1, André Weipert 3, Sebastian Kauczok 3 and
Inter-comparison of X-band radar and lidar low-level wind measurement for air traffic control (ATC) Thomas Ernsdorf 1, Bernd Stiller 2, Björn-Rüdiger Beckmann 1, André Weipert 3, Sebastian Kauczok 3 and
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection
 Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
Aviation Hazards: Thunderstorms and Deep Convection TREND Diagnosis of thunderstorm hazards using imagery Contents Satellite imagery Visible, infrared, water vapour Basic cloud identification Identifying
P13A.4 THE AIR FRANCE 358 INCIDENT OF 2 AUGUST 2005 AT TORONTO INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT. Paul Joe
 P13A.4 THE AIR FRANCE 358 INCIDENT OF 2 AUGUST 2005 AT TORONTO INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT Paul Joe Environment Canada, 4905 Dufferin St., Toronto, Ontario, CANADA M3H 5T4 email: paul.joe@ec.gc.ca tel: 416 739
P13A.4 THE AIR FRANCE 358 INCIDENT OF 2 AUGUST 2005 AT TORONTO INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT Paul Joe Environment Canada, 4905 Dufferin St., Toronto, Ontario, CANADA M3H 5T4 email: paul.joe@ec.gc.ca tel: 416 739
A tail strike event of an aircraft due to terrain-induced wind shear at the Hong Kong International Airport
 METEOROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS Meteorol. Appl. 21: 504 511 (2014) Published online 14 March 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/met.1303 A tail strike event of an aircraft due
METEOROLOGICAL APPLICATIONS Meteorol. Appl. 21: 504 511 (2014) Published online 14 March 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/met.1303 A tail strike event of an aircraft due
an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar
 ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
ERAD 12 - THE SEVENTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY RAINSCANNER@Barcelona: an experiment to assess the hydrological value of a portable X-band radar Marc Berenguer1, Shinju
Renewable Energy Development and Airborne Wildlife Conservation
 Whitepaper ECHOTRACK TM RADAR ACOUSTIC TM SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Renewable Energy Development and Airborne Wildlife Conservation Renewable energy developers must meet regulatory requirements to mitigate for
Whitepaper ECHOTRACK TM RADAR ACOUSTIC TM SURVEILLANCE SYSTEM Renewable Energy Development and Airborne Wildlife Conservation Renewable energy developers must meet regulatory requirements to mitigate for
The Avian Hazard Advisory System
 101 The Avian Hazard Advisory System T. Adam Kelly a, Ronald Merritt a, Maj Thomas J. Donalds b and Ronald L. White a a 3160 Airport Rd, Suite 22-A, Panama City, FL, 32405 b 4th Wing, Seymour Johnson AFB,
101 The Avian Hazard Advisory System T. Adam Kelly a, Ronald Merritt a, Maj Thomas J. Donalds b and Ronald L. White a a 3160 Airport Rd, Suite 22-A, Panama City, FL, 32405 b 4th Wing, Seymour Johnson AFB,
Chapter 12: Meteorology
 Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
Chapter 12: Meteorology Section 1: The Causes of Weather 1. Compare and contrast weather and climate. 2. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. 3. Describe how and where
The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China
 The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China Lei Li, 1 Pak Wai Chan, 2 Honglong Yang, 1 Rong Zong, 1 Xia Mao, 1 Yin Jiang 1 and Hongbo Zhuang
The first tropospheric wind profiler observations of a severe typhoon over a coastal area in South China Lei Li, 1 Pak Wai Chan, 2 Honglong Yang, 1 Rong Zong, 1 Xia Mao, 1 Yin Jiang 1 and Hongbo Zhuang
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
SPECIAL PROJECT PROGRESS REPORT Progress Reports should be 2 to 10 pages in length, depending on importance of the project. All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Reporting year
Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals. From Airborne Doppler Radar
 Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals From Airborne Doppler Radar Shannon L. McElhinney and Michael M. Bell University of Hawaii at Manoa Recent studies have highlighted the importance
Improved Tropical Cyclone Boundary Layer Wind Retrievals From Airborne Doppler Radar Shannon L. McElhinney and Michael M. Bell University of Hawaii at Manoa Recent studies have highlighted the importance
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017 Finnish Meteorological Institute compiled by Weather and Safety Centre with help of several experts 1. Summary of major highlights FMI s forecasts are
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2017 Finnish Meteorological Institute compiled by Weather and Safety Centre with help of several experts 1. Summary of major highlights FMI s forecasts are
Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide
 Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide Seasons 1. Know what is responsible for the change in seasons on Earth. 2. Be able to determine seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres given the position
Seasons, Global Wind and Climate Study Guide Seasons 1. Know what is responsible for the change in seasons on Earth. 2. Be able to determine seasons in the northern and southern hemispheres given the position
Reprint 850. Within the Eye of Typhoon Nuri in Hong Kong in C.P. Wong & P.W. Chan
 Reprint 850 Remote Sensing Observations of the Subsidence Zone Within the Eye of Typhoon Nuri in Hong Kong in 2008 C.P. Wong & P.W. Chan 8 th International Symposium on Tropospheric Profiling: Integration
Reprint 850 Remote Sensing Observations of the Subsidence Zone Within the Eye of Typhoon Nuri in Hong Kong in 2008 C.P. Wong & P.W. Chan 8 th International Symposium on Tropospheric Profiling: Integration
WMO Aeronautical Meteorology Scientific Conference 2017
 Session 1 Science underpinning meteorological observations, forecasts, advisories and warnings 1.1 En route phenomena 1.1.1 Ice crystal icing, and airframe icing research Signatures of supercooled liquid
Session 1 Science underpinning meteorological observations, forecasts, advisories and warnings 1.1 En route phenomena 1.1.1 Ice crystal icing, and airframe icing research Signatures of supercooled liquid
Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data
 Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data Tim Böhme 1 1 Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany (Dated: 29 August 2014) Tim Böhme 1. Introduction
Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data Tim Böhme 1 1 Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany (Dated: 29 August 2014) Tim Böhme 1. Introduction
P4.10. Kenichi Kusunoki 1 * and Wataru Mashiko 1 1. Meteorological Research Institute, Japan
 P4. DOPPLER RADAR INVESTIGATIONS OF THE INNER CORE OF TYPHOON SONGDA (24) Polygonal / elliptical eyewalls, eye contraction, and small-scale spiral bands. Kenichi Kusunoki * and Wataru Mashiko Meteorological
P4. DOPPLER RADAR INVESTIGATIONS OF THE INNER CORE OF TYPHOON SONGDA (24) Polygonal / elliptical eyewalls, eye contraction, and small-scale spiral bands. Kenichi Kusunoki * and Wataru Mashiko Meteorological
Hazard assessment based on radar-based rainfall nowcasts at European scale The HAREN project
 Hazard assessment based on radar-based rainfall nowcasts at European scale The HAREN project Marc Berenguer, Daniel Sempere-Torres 3 OPERA radar mosaic OPERA radar mosaic: 213919 133 Precipitation observations
Hazard assessment based on radar-based rainfall nowcasts at European scale The HAREN project Marc Berenguer, Daniel Sempere-Torres 3 OPERA radar mosaic OPERA radar mosaic: 213919 133 Precipitation observations
1. Introduction. 2. Verification of the 2010 forecasts. Research Brief 2011/ February 2011
 Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
Research Brief 2011/01 Verification of Forecasts of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific and Number of Tropical Cyclones Making Landfall in South China and the Korea and Japan region
A Voyage to Africa by Mr Swift
 Geolocation using light levels Niklas Wahlström 1 Fredrik Gustafsson 1 Susanne Åkesson 2 1 Division of Automatic Control Linköping University 2 Centre for Animal Movement Research Department of Biology
Geolocation using light levels Niklas Wahlström 1 Fredrik Gustafsson 1 Susanne Åkesson 2 1 Division of Automatic Control Linköping University 2 Centre for Animal Movement Research Department of Biology
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation
 NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
NAVIGATION THEORY QUESTIONS Basics of Navigation Q610065 look at it The angle between the plane of the ecliptic and the plane of equator is approx? 23.5 degrees In which two months of the year is the difference
ERAD THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 ERAD 2014 - THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Microphysical interpretation of coincident simultaneous and fast alternating horizontal and vertical polarization transmit
ERAD 2014 - THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY Microphysical interpretation of coincident simultaneous and fast alternating horizontal and vertical polarization transmit
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia
 Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
DETECTION OF BIRDS AND INSECTS USING POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION
 P5.3 DETECTION OF BIRDS AND INSECTS USING POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION Pengfei Zhang *, Alexander Ryzhkov, and Dusan Zrnic 2 CIMMS, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 2 NOAA/National Severe Storms
P5.3 DETECTION OF BIRDS AND INSECTS USING POLARIMETRIC RADAR OBSERVATION Pengfei Zhang *, Alexander Ryzhkov, and Dusan Zrnic 2 CIMMS, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 2 NOAA/National Severe Storms
Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2. Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway
 4.11 RADAR DATA QUALITY THE CHALLENGE OF BEAM BLOCKAGES AND PROPAGATION CHANGES Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway 2 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological
4.11 RADAR DATA QUALITY THE CHALLENGE OF BEAM BLOCKAGES AND PROPAGATION CHANGES Uta Gjertsen 1 and Günther Haase 2 1 Norwegian Meteorological Institute, Oslo, Norway 2 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological
Plan for operational nowcasting system implementation in Pulkovo airport (St. Petersburg, Russia)
 Plan for operational nowcasting system implementation in Pulkovo airport (St. Petersburg, Russia) Pulkovo airport (St. Petersburg, Russia) is one of the biggest airports in the Russian Federation (150
Plan for operational nowcasting system implementation in Pulkovo airport (St. Petersburg, Russia) Pulkovo airport (St. Petersburg, Russia) is one of the biggest airports in the Russian Federation (150
Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events. Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist
 Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist Physical Geography, Department of Earth Sciences, Göteborg University Box 460, SE-405 30 Göteborg,
Regional influence on road slipperiness during winter precipitation events Marie Eriksson and Sven Lindqvist Physical Geography, Department of Earth Sciences, Göteborg University Box 460, SE-405 30 Göteborg,
Radar Analysis of Second Wave of UFO Sightings Near Stephenville, Texas. October 21 and 23, 2008
 Radar Analysis of Second Wave of UFO Sightings Near Stephenville, Texas Background October 21 and 23, 2008 A wave of UFO sightings occurred in the Stephenville-Dublin, Texas area on January 8, 2008 [1-3].
Radar Analysis of Second Wave of UFO Sightings Near Stephenville, Texas Background October 21 and 23, 2008 A wave of UFO sightings occurred in the Stephenville-Dublin, Texas area on January 8, 2008 [1-3].
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II
 P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
P6.10 COMPARISON OF SATELLITE AND AIRCRAFT MEASUREMENTS OF CLOUD MICROPHYSICAL PROPERTIES IN ICING CONDITIONS DURING ATREC/AIRS-II Louis Nguyen*, Patrick Minnis NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA,
J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER
 J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER Khalil. A. Ahmad* PSGS/NOAA/NESDIS/StAR, Camp Springs, MD Joseph Sienkiewicz NOAA/NWS/NCEP/OPC,
J16.1 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT OF ASCAT OCEAN SURFACE VECTOR WIND (OSVW) RETRIEVALS AT NOAA OCEAN PREDICTION CENTER Khalil. A. Ahmad* PSGS/NOAA/NESDIS/StAR, Camp Springs, MD Joseph Sienkiewicz NOAA/NWS/NCEP/OPC,
SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF DAYTIME BIRD MIGRATION IN ISRAEL: RADAR MONITORING DATA
 THE RING 30, 1/2 (2008) DOI 10.2478/v10050-008-0002-5 SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF DAYTIME BIRD MIGRATION IN ISRAEL: RADAR MONITORING DATA Leonid Dinevich and Yossi Leshem ABSTRACT Dinevich L., Leshem Y. 2008.
THE RING 30, 1/2 (2008) DOI 10.2478/v10050-008-0002-5 SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF DAYTIME BIRD MIGRATION IN ISRAEL: RADAR MONITORING DATA Leonid Dinevich and Yossi Leshem ABSTRACT Dinevich L., Leshem Y. 2008.
4.3.2 Configuration. 4.3 Ensemble Prediction System Introduction
 4.3 Ensemble Prediction System 4.3.1 Introduction JMA launched its operational ensemble prediction systems (EPSs) for one-month forecasting, one-week forecasting, and seasonal forecasting in March of 1996,
4.3 Ensemble Prediction System 4.3.1 Introduction JMA launched its operational ensemble prediction systems (EPSs) for one-month forecasting, one-week forecasting, and seasonal forecasting in March of 1996,
AIR TRAFFIC INCIDENT REPORT FORM
 Address: Rannsóknarnefnd samgönguslysa Flugvallarvegur 7, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland Telephone: +354 511 6500 Telefax: +354 511 6501 E-mail: RNSA@RNSA.is AIR TRAFFIC INCIDENT REPORT FORM For use when submitting
Address: Rannsóknarnefnd samgönguslysa Flugvallarvegur 7, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland Telephone: +354 511 6500 Telefax: +354 511 6501 E-mail: RNSA@RNSA.is AIR TRAFFIC INCIDENT REPORT FORM For use when submitting
Objectives. Vocabulary
 The Causes of Weather Objectives Compare and contrast weather and climate. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. Describe how and where air masses form. Vocabulary meteorology
The Causes of Weather Objectives Compare and contrast weather and climate. Analyze how imbalances in the heating of Earth s surface create weather. Describe how and where air masses form. Vocabulary meteorology
INCA-CE achievements and status
 INCA-CE achievements and status Franziska Strauss Yong Wang Alexander Kann Benedikt Bica Ingo Meirold-Mautner INCA Central Europe Integrated nowcasting for the Central European area This project is implemented
INCA-CE achievements and status Franziska Strauss Yong Wang Alexander Kann Benedikt Bica Ingo Meirold-Mautner INCA Central Europe Integrated nowcasting for the Central European area This project is implemented
NIWA Outlook: March-May 2015
 March May 2015 Issued: 27 February 2015 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland, Auckland,
March May 2015 Issued: 27 February 2015 Hold mouse over links and press ctrl + left click to jump to the information you require: Overview Regional predictions for the next three months: Northland, Auckland,
Automated Thunderstorm Alert Service (ATSAS) User Guide
 Automated Thunderstorm Alert Service (ATSAS) User Guide November 2016 Table of Contents 1 ATSAS System...2 1.1.1 Background Map... 3 1.1.2 Thunderstorm Cell and Trac k... 3 1.1.3 Legend... 4 1.1.4 ATSAS
Automated Thunderstorm Alert Service (ATSAS) User Guide November 2016 Table of Contents 1 ATSAS System...2 1.1.1 Background Map... 3 1.1.2 Thunderstorm Cell and Trac k... 3 1.1.3 Legend... 4 1.1.4 ATSAS
Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars
 Proceedings of ERAD (4): 35 4 c Copernicus GmbH 4 ERAD 4 Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars Y. K. Goh and A. R. Holt Department of Mathematical Sciences, University
Proceedings of ERAD (4): 35 4 c Copernicus GmbH 4 ERAD 4 Analysis of three-dimensional wind fields from two operational doppler radars Y. K. Goh and A. R. Holt Department of Mathematical Sciences, University
Translating Meteorological Observations into Air Traffic Impacts in Singapore Flight Information Region (FIR)
 Translating Meteorological Observations into Air Traffic Impacts in Singapore Flight Information Region (FIR) Michael Robinson The MITRE Corporation Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited.
Translating Meteorological Observations into Air Traffic Impacts in Singapore Flight Information Region (FIR) Michael Robinson The MITRE Corporation Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited.
SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2011/2012. ACM Synoptic Meteorology II
 SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2011/2012 ACM 40540 Synoptic Meteorology II External examiner: Professor Peter A Clark Head of School: Dr Patrick Murphy Lecturer: Professor Peter Lynch Time Allowed: 2 hours Instructions
SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2011/2012 ACM 40540 Synoptic Meteorology II External examiner: Professor Peter A Clark Head of School: Dr Patrick Murphy Lecturer: Professor Peter Lynch Time Allowed: 2 hours Instructions
Attribution of Estonian phyto-, ornitho- and ichtyophenological trends with parameters of changing climate
 Attribution of Estonian phyto-, ornitho- and ichtyophenological trends with parameters of changing climate Rein Ahas*, Anto Aasa, Institute of Geography, University of Tartu, Vanemuise st 46, Tartu, 51014,
Attribution of Estonian phyto-, ornitho- and ichtyophenological trends with parameters of changing climate Rein Ahas*, Anto Aasa, Institute of Geography, University of Tartu, Vanemuise st 46, Tartu, 51014,
Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars.
 Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars. R. Kaltenboeck 1 and A. Ryzhkov 2 1 Austrocontrol - Aviation Weather Service, Vienna and Institute
Comparison of polarimetric radar signatures in hailstorms simultaneously observed by C-band and S-band radars. R. Kaltenboeck 1 and A. Ryzhkov 2 1 Austrocontrol - Aviation Weather Service, Vienna and Institute
CHARACTERISATION OF STORM SEVERITY BY USE OF SELECTED CONVECTIVE CELL PARAMETERS DERIVED FROM SATELLITE DATA
 CHARACTERISATION OF STORM SEVERITY BY USE OF SELECTED CONVECTIVE CELL PARAMETERS DERIVED FROM SATELLITE DATA Piotr Struzik Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, Satellite Remote Sensing Centre
CHARACTERISATION OF STORM SEVERITY BY USE OF SELECTED CONVECTIVE CELL PARAMETERS DERIVED FROM SATELLITE DATA Piotr Struzik Institute of Meteorology and Water Management, Satellite Remote Sensing Centre
7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR
 7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR David Priegnitz 1, S. M. Torres 1 and P. L. Heinselman 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
7 AN ADAPTIVE PEDESTAL CONTROL ALGORITHM FOR THE NATIONAL WEATHER RADAR TESTBED PHASED ARRAY RADAR David Priegnitz 1, S. M. Torres 1 and P. L. Heinselman 2 1 Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological
Lab 6 Radar Imagery Interpretation
 Lab 6 Radar Imagery Interpretation Background Weather radar (radio detection and ranging) is another very useful remote sensing tool used in meteorological forecasting. Microwave radar was developed in
Lab 6 Radar Imagery Interpretation Background Weather radar (radio detection and ranging) is another very useful remote sensing tool used in meteorological forecasting. Microwave radar was developed in
Heathrow Community Noise and Track-keeping Report: Chertsey
 Heathrow Community Noise and Track-keeping Report: Chertsey This document reports on an 98-day period of continuous noise monitoring from 9 June 211 to 14 September 211 using a Larson Davies LD 87 sound
Heathrow Community Noise and Track-keeping Report: Chertsey This document reports on an 98-day period of continuous noise monitoring from 9 June 211 to 14 September 211 using a Larson Davies LD 87 sound
IDENTIFICATION OF BIOLOGICAL AND ANOMALOUS PROPAGATION ECHOES IN WEATHER RADAR OBSERVATIONS AN IMAGING PROCESSING APPROACH
 IDENTIFICATION OF BIOLOGICAL AND ANOMALOUS PROPAGATION ECHOES IN WEATHER RADAR OBSERVATIONS AN IMAGING PROCESSING APPROACH P11.123 Lin Tang* 1, Jian Zhang 1, 2, Yadong Wang 1, and Kenneth W. Howard 1,
IDENTIFICATION OF BIOLOGICAL AND ANOMALOUS PROPAGATION ECHOES IN WEATHER RADAR OBSERVATIONS AN IMAGING PROCESSING APPROACH P11.123 Lin Tang* 1, Jian Zhang 1, 2, Yadong Wang 1, and Kenneth W. Howard 1,
1. INTRODUCTION 3. VERIFYING ANALYSES
 1.4 VERIFICATION OF NDFD GRIDDED FORECASTS IN THE WESTERN UNITED STATES John Horel 1 *, Bradley Colman 2, Mark Jackson 3 1 NOAA Cooperative Institute for Regional Prediction 2 National Weather Service,
1.4 VERIFICATION OF NDFD GRIDDED FORECASTS IN THE WESTERN UNITED STATES John Horel 1 *, Bradley Colman 2, Mark Jackson 3 1 NOAA Cooperative Institute for Regional Prediction 2 National Weather Service,
DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers
 DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers M. Thurai 1, W. A. Petersen 2, and L. D. Carey 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
DSD characteristics of a cool-season tornadic storm using C-band polarimetric radar and two 2D-video disdrometers M. Thurai 1, W. A. Petersen 2, and L. D. Carey 3 1 Colorado State University, Fort Collins,
The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting
 The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting Erik Andersson Slide 1 ECMWF European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 ECMWF s global forecasting system High resolution forecast
The benefits and developments in ensemble wind forecasting Erik Andersson Slide 1 ECMWF European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Slide 1 ECMWF s global forecasting system High resolution forecast
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia
 ID: 0030 Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia M. Benko Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute (SHMI), Jeséniova 17, 83315 Bratislava, Slovakia Corresponding author s E-mail: martin.benko@shmu.sk ABSTRACT
ID: 0030 Road weather forecasts and MDSS in Slovakia M. Benko Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute (SHMI), Jeséniova 17, 83315 Bratislava, Slovakia Corresponding author s E-mail: martin.benko@shmu.sk ABSTRACT
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound
 8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
METEOROLOGY. 1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km
 1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km 2 In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature A is almost constant B decreases with altitude C increases
1 The average height of the tropopause at 50 N is about A 14 km B 16 km C 11 km D 8 km 2 In the lower part of the stratosphere the temperature A is almost constant B decreases with altitude C increases
New applications using real-time observations and ECMWF model data
 New applications using real-time observations and ECMWF model data 12 th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems Wim van den Berg [senior meteorological researcher, project coordinator] Overview
New applications using real-time observations and ECMWF model data 12 th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems Wim van den Berg [senior meteorological researcher, project coordinator] Overview
5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR
 5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR Howard B. Bluestein * and Michael French University of Oklahoma, Norman Ivan Popstefanija ProSensing, Inc., Amherst, Massachusetts
5B.1 OBSERVATIONS OF TORNADOGENESIS USING A MOBILE, PHASED-ARRAY, DOPPLER RADAR Howard B. Bluestein * and Michael French University of Oklahoma, Norman Ivan Popstefanija ProSensing, Inc., Amherst, Massachusetts
An operational model predicting autumn bird migration. intensities for flight safety. J. VAN BELLE,* J. SHAMOUN-BARANES,* E. VAN LOON* and W.
 2007 An operational model predicting autumn bird migration Publishing Ltd intensities for flight safety J. VAN BELLE,* J. SHAMOUN-BARANES,* E. VAN LOON* and W. BOUTEN* *Computational Biogeography and Physical
2007 An operational model predicting autumn bird migration Publishing Ltd intensities for flight safety J. VAN BELLE,* J. SHAMOUN-BARANES,* E. VAN LOON* and W. BOUTEN* *Computational Biogeography and Physical
INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE Amsterdam, April 2000
 INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE IBSC25/WP-RS5 Amsterdam, 17-21 April 2000 THE AVIAN HAZARD ADVISORY SYSTEM (AHAS): OPERATIONAL USE OF WEATHER RADAR FOR REDUCING BIRD STRIKE RISK IN NORTH AMERICA. T
INTERNATIONAL BIRD STRIKE COMMITTEE IBSC25/WP-RS5 Amsterdam, 17-21 April 2000 THE AVIAN HAZARD ADVISORY SYSTEM (AHAS): OPERATIONAL USE OF WEATHER RADAR FOR REDUCING BIRD STRIKE RISK IN NORTH AMERICA. T
11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA
 11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA Svetlana Bachmann* and Dusan Zrnic Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
11B.3 ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUE TO EXTRACT INTRINSIC INSECTS BACKSCATTER DIFFERENTIAL PHASE FROM POLARIMETRIC SPECTRA Svetlana Bachmann* and Dusan Zrnic Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies,
DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE
 DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE H. Kyznarová 1 and P. Novák 2 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, kyznarova@chmi.cz 2 Czech Hydrometeorological
DEVELOPMENT OF CELL-TRACKING ALGORITHM IN THE CZECH HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL INSTITUTE H. Kyznarová 1 and P. Novák 2 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, kyznarova@chmi.cz 2 Czech Hydrometeorological
Description of the case study
 Description of the case study During the night and early morning of the 14 th of July 011 the significant cloud layer expanding in the West of the country and slowly moving East produced precipitation
Description of the case study During the night and early morning of the 14 th of July 011 the significant cloud layer expanding in the West of the country and slowly moving East produced precipitation
