rkids.o rg/2005/01/black-ho le-jo urney-2/
|
|
|
- Diana Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 scie nce ne wsf o rkids.o rg rkids.o rg/2005/01/black-ho le-jo urney-2/ Black Hole Journey By Emily Sohn / January 25, 2005 There are all sorts of holes: big ones and little ones, deep ones and shallow ones. T here are swimming holes and buttonholes, cheese holes and bullet holes. T hen, there are black holes. These mysterious, bizarre objects pack a huge mass into a tiny volume. Their gravity is so strong that they gobble up anything that comes near them, even stars, gas, and light. They re invisible. They re like cracks in space, and they lurk all over the universe. An invisible, massive, spinning black hole may lie at the center of this galaxy, as shown in an artist s illustration. The black hole would pull in material from a swirling disk of nearby gas and stars. The extremely high temperatures and pressures produc Dana Berry, Space Telescope Science Institute If you were to jump into a black hole (something that no one has yet f igured out how to do), you d be stretched f rom head to toe and squeezed f rom side to side into a long string of human spaghetti. Finally, you d get pulverized into the tiniest bits imaginable. If you were to f all in, what remains of you would eventually come out as light and other particles, says Tom Banks. He s a physicist who spends a lot of his time thinking about black holes and trying to understand them. There wouldn t be much of you that we could recognize, Banks says. It would be as if we had burned you up in a f ire. Everything in the body would come out as nothing more than radiation and ashes. Both scientists and nonscientists f ind black holes f ascinating. The whole idea sounds crazy, and it can be hard to wrap your head around something that seems like it should be impossible. Nevertheless, new observations and thought experiments are shining light into the darkness.
2 Astronomers now suspect that there s a black hole at the center of just about every galaxy in the universe. Some researchers even suggest that the universe was once a big ball of black holes, bef ore there were any stars or planets. This image taken by the Chandra X-ray Observatory, shows a region at the center of our own Milky Way galaxy that appears to host a supermassive black hole. NASA/CXC/MIT/F.K.Baganoff et al. Further research on black holes might eventually help explain how the universe began, Banks says. He works at Rutgers University in New Brunswick, N.J., and at the University of Calif ornia, Santa Cruz. One of the questions we ask ourselves is, What happened in the very, very earliest moments of the universe? he says. Supernovas and gravity A century ago, Albert Einstein s theory of gravitation predicted that black holes might exist. But no one wanted to believe it, including Einstein himself. Astronomers f inally began to detect signs of black holes in the 1980s. Scientists now are pretty sure that a black hole can f orm when a huge star reaches the end of its lif e and runs out of f uel. First, the inner part of the star collapses. Then there s an enormous explosion called a supernova, sending light and matter into space. Eventually, the entire mass of what s lef t of the star gets squeezed into the tiniest space imaginable f orming a black hole.
3 This artist s illustration shows a black hole, together with its whirling disk of matter, hurtling like a cannonball through the disk of our own galaxy. Astronomers say that such a black hole, only several times more massive than the sun, is created when ESA, NASA, and Felix Mirabel The more mass an object has, the more gravity it has. So, black holes have a lot of gravity. Black holes f ormed in a supernova may be only a f ew times the mass of our sun. On the other hand, black holes at the centers of galaxies may have a billion times as much mass as the sun, all crammed into a very small space. Earth s gravity keeps us on the ground; a black hole s gravity sucks things in. Its pull is so strong that not even light can escape. That s why it looks black as if there s nothing there. A black hole s size is def ined by an invisible boundary called an event horizon. Anything you, atoms, or light that gets sucked in and crosses the boundary can never get back out again. The event horizon is the boundary between a black hole and the rest of the universe. Any matter that spirals in toward the black hole and crosses the event horizon disappears. Ann Feild, Space Telescope Science Institute The more you think about black holes, the harder it is to imagine how they could possibly exist. That s what most interests many people, Banks says. When he was a kid, Banks always wanted to know about extremes the tallest building in the world, the deepest part of the ocean, the most of anything. In that sense, black holes are the ultimate extreme, he
4 says. That s also what intrigues many scientists about black holes. It s the ultimate limit on how much you can squeeze stuf f together, Banks says. T his suggests that black holes tell us something about the f undamental theory of what matter or the universe looks like in its most extreme condition. Data and theory Because black holes are so weird (not to mention invisible), they can be dif f icult to study. Scientists tackle this problem in two ways. Some use telescopes to make observations, staring into the sky and looking f or signs of radiation that signal the presence of a black hole. Others use mathematics and computers to develop theories about black holes and explore the behavior of equations that describe such objects. T hey do thought experiments. Black holes can be detected only by their effects on matter surrounding them. This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a rapidly rotating disk of material at the core of a galaxy known as M87. The existence of such a disk of hot, spinning material suggests Holland Ford, Space Telescope Science Institute/Johns Hopkins University, et al., NASA Theorists, such as Banks, look at data and try to understand observations made by astronomers. They attempt to put it all together to explain how the universe came to look the way it does now. For example, astronomers observe many dif f erent kinds of galaxies. At the same time, theorists develop equations that link the shapes of galaxies to how they f ormed and evolved. Researchers can then compare what the f ormulas predict to what s actually seen in the sky. You continually go back and f orth between observations and theory, Banks says. If the theory doesn t work, you change it a little bit until you get something that works better. T his type of thinking has led some theorists to propose that entire galaxies can actually collapse into black holes.
5 Our own Milky Way galaxy may look like this spiral galaxy known as M100. NASA, Space Telescope Science Institute A complicated set of ideas called string theory has also led some physicists to suggest that the universe once held a whole bunch of black holes, all scrunched together. Eventually, these black holes grew and separated, and each one f ormed a galaxy around itself. It s possible that every galaxy visible today has a massive black hole at its center. But the equations developed so f ar by theorists provide only part of the picture. The rest is still a work in progress. With string theory and other ideas, scientists hope eventually to come up with a grand explanation f or how everything came to be. But, even if researchers do get all the numbers to work, black holes and the history of the universe might always remain something of a mystery. We weren t there at the beginning of the universe, Banks says. We can t go look. We make theories to predict what we see today. We don t yet have a good enough theory to pin it all down. Ready to jump in? Going Deeper: Word Find: Black Holes Additional Inf ormation Questions about the Article
7. How many black holes do scientists think are in the Milky Way galaxy?
 Name: Block: Date: Science News for Students Black Hole Mysteries https://student.societyforscience.org/article/black-hole-mysteries 1. Is a black hole really a hole? Explain. 2. Why can't anything escape
Name: Block: Date: Science News for Students Black Hole Mysteries https://student.societyforscience.org/article/black-hole-mysteries 1. Is a black hole really a hole? Explain. 2. Why can't anything escape
Introduction. The Mystery of our universe today, is Dark Matter. Dark Matter is the heart of our
 Introduction The Mystery of our universe today, is Dark Matter. Dark Matter is the heart of our galaxy, and it keeps the planets and stars from flying away or moving positions. Dark Matter is the pitch
Introduction The Mystery of our universe today, is Dark Matter. Dark Matter is the heart of our galaxy, and it keeps the planets and stars from flying away or moving positions. Dark Matter is the pitch
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE AND BLACK HOLES WHAT IS COSMOGONY? Cosmogony (or cosmogeny) is any model explaining the origin of the universe. Cosmogony = Coming into existence WHAT IS COSMOLOGY Cosmology
Einstein s Gravity. Understanding space-time and the gravitational effects of mass
 Einstein s Gravity Understanding space-time and the gravitational effects of mass Albert Einstein (1879-1955) One of the iconic figures of the 20 th century, Einstein revolutionized our understanding of
Einstein s Gravity Understanding space-time and the gravitational effects of mass Albert Einstein (1879-1955) One of the iconic figures of the 20 th century, Einstein revolutionized our understanding of
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
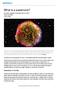 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
A Galaxy Full of Black Holes. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origins Education Forum - STScI 1 Navigator Public Engagement Program - JPL
 A Galaxy Full of Black Holes Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origins Education Forum - STScI 1 Navigator Public Engagement Program - JPL 1915: Einstein s Theory of Gravity predicted the possibility
A Galaxy Full of Black Holes Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Origins Education Forum - STScI 1 Navigator Public Engagement Program - JPL 1915: Einstein s Theory of Gravity predicted the possibility
Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way
 GALAXIES Lesson 2 Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way The Milky Way appears to be curved when we view it but in reality it is a straight line. It is curved due to the combination of pictures taken
GALAXIES Lesson 2 Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way The Milky Way appears to be curved when we view it but in reality it is a straight line. It is curved due to the combination of pictures taken
Review of Lecture 15 3/17/10. Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath
 Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
Lecture 15: Dark Matter and the Cosmic Web (plus Gamma Ray Bursts) Prof. Tom Megeath A2020 Disk Component: stars of all ages, many gas clouds Review of Lecture 15 Spheroidal Component: bulge & halo, old
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It s called a spiral galaxy because if you could
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY BACKGROUND READING FOR MIDDLE AND HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It s called a spiral galaxy because if you could
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Galaxies. Objectives. How did find out about other galaxies What are their characteristics How do galaxies evolve How does dark matter come into play?
 Galaxies Objectives How did find out about other galaxies What are their characteristics How do galaxies evolve How does dark matter come into play? Nebula Early astronomers saw lots of fuzzy things across
Galaxies Objectives How did find out about other galaxies What are their characteristics How do galaxies evolve How does dark matter come into play? Nebula Early astronomers saw lots of fuzzy things across
Name: Space Questions. Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s:
 Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Chapter 26: Cosmology
 Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
Chapter 26: Cosmology Cosmology means the study of the structure and evolution of the entire universe as a whole. First of all, we need to know whether the universe has changed with time, or if it has
What is a supernova? They Outshine Their Entire Galaxy. By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on Word Count 675 Level 840L
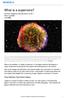 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 675 Level 840L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
ASTRO 114 Lecture 55 1 Okay. We re now gonna continue discussing and conclude discussing the entire universe. So today we re gonna learn about everything, everything that we know of. There s still a lot
o Terms to know o Big Bang Theory o Doppler Effect o Redshift o Universe
 Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Standard 1: Students will understand the scientific evidence that supports theories that explain how the universe and the solar system developed. They will compare Earth to other objects in the solar system.
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system?
 What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.19.17 Word Count 819 Level 970L An image of the Milky Way galaxy taken In celebration of the International
What is the difference between a galaxy and a solar system? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.19.17 Word Count 819 Level 970L An image of the Milky Way galaxy taken In celebration of the International
Accretion Disks. Review: Stellar Remnats. Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath 2/25/10. Review: Creating Stellar Remnants
 Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Neutron Stars. Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes. Neutron Stars. What s holding it up? The Lighthouse Model of Pulsars
 Neutron Stars Form from a 8-20 M Sun star Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes Leftover 1.4-3 M Sun core after supernova Neutron Stars consist entirely of neutrons (no protons) Neutron Star (tennis
Neutron Stars Form from a 8-20 M Sun star Chapter 14: Neutron Stars and Black Holes Leftover 1.4-3 M Sun core after supernova Neutron Stars consist entirely of neutrons (no protons) Neutron Star (tennis
HOST: Welcome to Astronomy Behind the Headlines, a podcast by the Astronomical
 ASTRONOMY BEHIND THE HEADLINES A podcast for Informal Science Educators from the Astronomical Society of the Pacific with Dr. Shep Doeleman, MIT s Haystack Observatory Written by Carolyn Collins Petersen
ASTRONOMY BEHIND THE HEADLINES A podcast for Informal Science Educators from the Astronomical Society of the Pacific with Dr. Shep Doeleman, MIT s Haystack Observatory Written by Carolyn Collins Petersen
Module 3: Astronomy The Universe Topic 1 Content: Cosmology Presentation Notes
 Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy?
 Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
Ch 14: Mysteries of the Milky Way How does the galaxy rotate and keep the spiral arms together? And what really lies at the center of the galaxy? The Structure of the Galaxy We know that our galaxy has
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe. Galactic rotation curves
 Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
Chapter 23: Dark Matter, Dark Energy & Future of the Universe Galactic rotation curves Orbital speed as a function of distance from the center: rotation_of_spiral_galaxy.htm Use Kepler s Third Law to get
ASTRO 114 Lecture gonna be talking about individual galaxies, but we re gonna be talking about the whole
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 53 1 Okay. We re now going to turn our attention to the entire universe. We re not just gonna be talking about individual galaxies, but we re gonna be talking about the whole thing. I
ASTRO 114 Lecture 53 1 Okay. We re now going to turn our attention to the entire universe. We re not just gonna be talking about individual galaxies, but we re gonna be talking about the whole thing. I
and Universe Awareness
 Brought to you by s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Universe wareness Light Looking up at the night sky, you might think that space is dull, with lots of black, some white dots and just a hint of red if
Brought to you by s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Universe wareness Light Looking up at the night sky, you might think that space is dull, with lots of black, some white dots and just a hint of red if
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 2: Our Home: The Milky Way
 Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 2: Our Home: The Milky Way The Milky Way is our home galaxy. It s a collection of stars, gas and dust. (1) What holds it together? Its self-gravity. (2) What did the last slide
Arvind Borde / AST 10, Week 2: Our Home: The Milky Way The Milky Way is our home galaxy. It s a collection of stars, gas and dust. (1) What holds it together? Its self-gravity. (2) What did the last slide
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. White Dwarfs. What is a white dwarf? Size of a White Dwarf White Dwarfs
 Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Chapter 18 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 18.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf? White Dwarfs White
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Black Holes and Beyond Modeling a Black Hole
 Black Holes and Beyond Modeling a Black Hole Subject: Science Grade Level: 6 th 8 th Materials: (For a class of 28 working in pairs) 14 small round balloons 14 basic calculators 14 pieces of string in
Black Holes and Beyond Modeling a Black Hole Subject: Science Grade Level: 6 th 8 th Materials: (For a class of 28 working in pairs) 14 small round balloons 14 basic calculators 14 pieces of string in
Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS /30/11 The Big Bang Theory
 Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long God had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long God had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
u Today I will look for key ideas in the text to support the role gravity has on the formation of the planets.
 Space SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.4: Explore the Law of Universal Gravitation by explaining the role that gravity plays in the formation of planets, stars, and solar systems, and determining their motions Game
Space SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.4: Explore the Law of Universal Gravitation by explaining the role that gravity plays in the formation of planets, stars, and solar systems, and determining their motions Game
What s the longest single-shot exposure ever recorded of any object or area of space by Hubble?
 Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
The Universe and Galaxies. Adapted from:
 The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
The Universe and Galaxies Adapted from: http://www.west-jefferson.k12.oh.us/earthandspacescience.aspx Astronomy The study of objects and matter outside the Earth s atmosphere and of their physical and
Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All
 Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All IPods off and headphones out of your ears Hats off
Sit in your appropriate seat quietly Have all necessary materials out All back packs on the floor All cell phones on silent and away in backpacks All IPods off and headphones out of your ears Hats off
Relativity and Black Holes
 Relativity and Black Holes Post-MS Evolution of Very High Mass (>15 M Θ ) Stars similar to high mass except more rapid lives end in Type II supernova explosions main difference: mass of iron core at end
Relativity and Black Holes Post-MS Evolution of Very High Mass (>15 M Θ ) Stars similar to high mass except more rapid lives end in Type II supernova explosions main difference: mass of iron core at end
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
25.2 Stellar Evolution. By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star.
 25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
25.2 Stellar Evolution By studying stars of different ages, astronomers have been able to piece together the evolution of a star. Star Birth The birthplaces of stars are dark, cool interstellar clouds,
Directed Reading A. Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS THE LIFE CYCLE OF SUNLIKE STARS A TOOL FOR STUDYING STARS.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Relative Sizes of Stars. Today Exam#3 Review. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Blackbody Radiation
 Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Today Exam#3 Review Exam #3 is Thursday April 4th in this room, BPS 40; Extra credit is due 8:00 am Tuesday April 9 Final Exam is 3:00pm Monday April 8 in BPS 40 The exam is 40 multiple choice questions.
Galaxies. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book. Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps:
 FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
FOCUS Book Galaxies Make a model that helps demonstrate how the universe is expanding. Follow these steps: 1 Use markers to make dots on the outside of an uninflated balloon to represent galaxies full
Neutron Stars. But what happens to the super-dense core? It faces two possible fates:
 Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
Neutron Stars When a massive star runs out of fuel, its core collapses from the size of the Earth to a compact ball of neutrons just ten miles or so across. Material just outside the core falls onto this
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet
 Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Gravity simplest. fusion
 Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09. Astronomy 101
 High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
High Mass Stars and then Stellar Graveyard 7/16/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Something Cool Betelgeuse Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Something
What is a Black Hole?
 What is a Black Hole? Robert H. Gowdy Virginia Commonwealth University December 2016 Bob G (VCU) Black Holes December 2016 1 / 29 Black Holes Bob G (VCU) Black Holes December 2016 2 / 29 Overview Spacetime
What is a Black Hole? Robert H. Gowdy Virginia Commonwealth University December 2016 Bob G (VCU) Black Holes December 2016 1 / 29 Black Holes Bob G (VCU) Black Holes December 2016 2 / 29 Overview Spacetime
Today. life the university & everything. Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations
 life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
life the university & everything Phys 2130 Day 41: Questions? The Universe Reminders: Review Wed & Fri Eyes to the web Final Exam Tues May 3 Check in on accomodations Today Today: - how big is the universe?
Assignment 9. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
Assignment 9 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The astrophysicist who first calculated the highest mass that a dying star can
GAMMA RAYS. 1 P a g e
 GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
GAMMA RAYS 1 P a g e 2 P a g e 3 P a g e Death Stars Do the most powerful blasts of energy in the universe threaten Earth? You don't want to be anywhere near a giant star when it dies. In just a few seconds,
Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
what scientist believe happened to form the universe, and it is called the Big Bang Theory.
 Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long god had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long god had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th
 Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Active Galaxies and Galactic Structure Lecture 22 April 18th FINAL Wednesday 5/9/2018 6-8 pm 100 questions, with ~20-30% based on material covered since test 3. Do not miss the final! Extra Credit: Thursday
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Protostars on the HR Diagram. Lifetimes of Stars. Lifetimes of Stars: Example. Pressure-Temperature Thermostat. Hydrostatic Equilibrium
 Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
Protostars on the HR Diagram Once a protostar is hot enough to start, it can blow away the surrounding gas Then it is visible: crosses the on the HR diagram The more the cloud, the it will form stars Lifetimes
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. We re gonna continue our discussion today on galaxies and quasars, and
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 52 1 Okay. We re gonna continue our discussion today on galaxies and quasars, and all the strange objects that are out there in the universe. I wanted to mention a little bit more about
ASTRO 114 Lecture 52 1 Okay. We re gonna continue our discussion today on galaxies and quasars, and all the strange objects that are out there in the universe. I wanted to mention a little bit more about
How Did the Universe Begin?
 How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
 Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
Lecture Outline Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard 14.1 White Dwarfs Our goals for learning: What is a white dwarf? What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? What is a white dwarf?
Galaxy Classification
 Galaxies Galaxies are collections of billons of stars; our home galaxy, the Milky Way, is a typical example. Stars, gas, and interstellar dust orbit the center of the galaxy due to the gravitational attraction
Galaxies Galaxies are collections of billons of stars; our home galaxy, the Milky Way, is a typical example. Stars, gas, and interstellar dust orbit the center of the galaxy due to the gravitational attraction
Chapter 13 2/19/2014. Lecture Outline Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars and Black Holes Neutron Stars. Units of Chapter
 13.1 Neutron Stars Lecture Outline Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and After a Type I supernova, little or nothing remains of the original star. After a Type II supernova, part of the core may survive. It is
13.1 Neutron Stars Lecture Outline Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and After a Type I supernova, little or nothing remains of the original star. After a Type II supernova, part of the core may survive. It is
The interpretation is that gravity bends spacetime and that light follows the curvature of space.
 7/8 General Theory of Relativity GR Two Postulates of the General Theory of Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same in all frames of reference. 2. The principle of equivalence. Three statements
7/8 General Theory of Relativity GR Two Postulates of the General Theory of Relativity: 1. The laws of physics are the same in all frames of reference. 2. The principle of equivalence. Three statements
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley Lecture 38
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 15 1 Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve been spending a lot of time talking about laws. We ve talked about gravitational laws, we ve talked
ASTRO 114 Lecture 15 1 Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve been spending a lot of time talking about laws. We ve talked about gravitational laws, we ve talked
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars
 Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars Finding Black Holes "Yesterday upon the stair I met a man who wasn't there. He wasn't there again today. I wish that man would go away." Hughes Mearns (1875-1965)
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars Finding Black Holes "Yesterday upon the stair I met a man who wasn't there. He wasn't there again today. I wish that man would go away." Hughes Mearns (1875-1965)
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
ANSWER KEY. Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe. Telescopes Guided Reading and Study. Characteristics of Stars Guided Reading and Study
 Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
Stars, Galaxies, a the Universe Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Telescopes Use Target Reading Skills Check student definitions for accuracy. 1. Electromagneticradiationisenergythatcan travel through
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS
 STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 22. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 22 Neutron Stars and Black Holes Units of Chapter 22 22.1 Neutron Stars 22.2 Pulsars 22.3 Neutron-Star Binaries 22.4 Gamma-Ray
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued
 Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Neutron Stars, Pulsars, Magnetars, and Black Holes the corpses of high-mass stars
 Neutron Stars, Pulsars, Magnetars, and Black Holes the corpses of high-mass stars Combination X-ray & visible light image of the Crab Nebula Pulsar From Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope
Neutron Stars, Pulsars, Magnetars, and Black Holes the corpses of high-mass stars Combination X-ray & visible light image of the Crab Nebula Pulsar From Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope
Astronomy 102, Fall September 2009
 Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
Today in Astronomy 102: prologue in outer space, continued Visit 10 9 M, 10 13 M and 45 M black holes Image: mid infrared picture of Centaurus A, probably the nearest galaxy with a billionsolar-mass central
TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify This star is in the last stage of its life cycle. What is that stage?
 CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
Today. Announcements. Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black holes
 Today Announcements HW #8 due Friday (tomorrow) 8am Test #2 average was 31/40 not as bad as it first appeared (several answer sheets were put in the wrong pile) Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black
Today Announcements HW #8 due Friday (tomorrow) 8am Test #2 average was 31/40 not as bad as it first appeared (several answer sheets were put in the wrong pile) Big Bang theory cont d Introduction to black
The State of the Universe
 The State of the Universe Harry Ringermacher, PhD General Electric Research Center Adj. Prof. of Physics, U. of S. Mississippi State of the Universe Universe is still going strong! - At least 100,000,000,000
The State of the Universe Harry Ringermacher, PhD General Electric Research Center Adj. Prof. of Physics, U. of S. Mississippi State of the Universe Universe is still going strong! - At least 100,000,000,000
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 24 BLACK HOLES AND CURVED SPACETIME PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 24 BLACK HOLES AND CURVED SPACETIME PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 24.1 Stellar Mass Black Hole. On the left, a visible-light image shows a region of the sky in the constellation of
ASTRONOMY Chapter 24 BLACK HOLES AND CURVED SPACETIME PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 24.1 Stellar Mass Black Hole. On the left, a visible-light image shows a region of the sky in the constellation of
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline. The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) Inflationary Model Added. (10^-35 to 10^-33 Of A Second)
 The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System The Universe pp
 Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System 25.3 The Universe pp 715-721 The Milky Way Galaxy On a clear and moonless night, away from city lights, you might see a a band of light in the sky. This band is The
Chapter 25: Beyond our Solar System 25.3 The Universe pp 715-721 The Milky Way Galaxy On a clear and moonless night, away from city lights, you might see a a band of light in the sky. This band is The
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
The Universe. But first, let s talk about light! 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
The Universe But first, let s talk about light! Light is fast! The study of light All forms of radiation travel at 300,000,000 meters (186,000 miles) per second Since objects in space are so far away,
Beyond the Black Hole
 Middle Grades Science Beyond the Black Hole Modeling an Imploding Star MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP balance string calculator aluminum foil meter stick balloon push pin ABOUT THIS LESSON This lesson
Middle Grades Science Beyond the Black Hole Modeling an Imploding Star MATERIALS AND RESOURCES EACH GROUP balance string calculator aluminum foil meter stick balloon push pin ABOUT THIS LESSON This lesson
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Figure 19.19: HST photo called Hubble Deep Field.
 19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
19.3 Galaxies and the Universe Early civilizations thought that Earth was the center of the universe. In the sixteenth century, we became aware that Earth is a small planet orbiting a medium-sized star.
The Death of Stars. Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages ) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars
 The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
The Death of Stars Today s Lecture: Post main-sequence (Chapter 13, pages 296-323) How stars explode: supernovae! White dwarfs Neutron stars White dwarfs Roughly the size of the Earth with the mass of
Stars and Galaxies. The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold
 Stars and Galaxies The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold Big Bang Our universe starts from a Big Bang The early universe was simple, with little structure A thin mist of H & He atoms + photons
Stars and Galaxies The Big History of our Planet The 2nd threshold Big Bang Our universe starts from a Big Bang The early universe was simple, with little structure A thin mist of H & He atoms + photons
A100H Exploring the Universe: Quasars, Dark Matter, Dark Energy. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the :, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 19, 2016 Read: Chaps 20, 21 04/19/16 slide 1 BH in Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at
A100H Exploring the :, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 19, 2016 Read: Chaps 20, 21 04/19/16 slide 1 BH in Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at
