a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions are just right c) the ocean is calm d) the ocean is wavy e) motion of the Moon
|
|
|
- Aleesha Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question 26.1 When watching the Moon over the ocean, you often see a long streak of light on the surface of the water. This occurs because: Reflection a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions are just right c) the ocean is calm d) the ocean is wavy e) motion of the Moon
2 Question 26.1 When watching the Moon over the ocean, you often see a long streak of light on the surface of the water. This occurs because: Reflection a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions are just right c) the ocean is calm d) the ocean is wavy e) motion of the Moon When the water surface changes, the angle of incidence also changes. Thus, different spots on the water can reflect the Moon into your eyes at different times. Follow-up: Where else does this occur?
3 Question 26.2a Mirror I An observer at point O is facing a mirror and observes a light source S. Where does the observer perceive the mirror image of the source to be located? O S mirror a b c d
4 Question 26.2a Mirror I An observer at point O is facing a mirror and observes a light source S. Where does the observer perceive the mirror image of the source to be located? O S mirror a b c Trace the light rays from the object to the mirror to the eye. Since the brain assumes that light travels in a straight line, simply extend the rays back behind the mirror to locate the image. d Follow-up: What happens when the observer starts moving toward the mirror?
5 Question 26.2b Mirror II You stand in front of a mirror. How tall does the mirror have to be so that you can see yourself entirely? a) same as your height b) less than your full height but more than half your height c) half your height d) less than half your height e) any size will do
6 Question 26.2b Mirror II You stand in front of a mirror. How tall does the mirror have to be so that you can see yourself entirely? a) same as your height b) less than your full height but more than half your height c) half your height d) less than half your height e) any size will do Trace the light rays from the image s foot to the mirror and then to the eye. Since we know that q i = q r, you need a mirror only half your size.
7 Question 26.2c Mirror III Does this depend on your distance from the mirror? a) no b) yes c) depends on the mirror d) depends on the person
8 Question 26.2c Mirror III Does this depend on your distance from the mirror? a) no b) yes c) depends on the mirror d) depends on the person The farther you step back, the smaller the incident and reflected angles will be. But the rays will still be reflected at the same points, so the ray from the foot will still be reflected at midheight.
9 Question 26.3 All Smoke and Mirrors You hold a hand mirror 0.5 m in a) 0.5 m front of you and look at your b) 1.0 m reflection in a full-length mirror 1 m behind you. How far in back of the c) 1.5 m big mirror do you see the image of d) 2.0 m your face? e) 2.5 m 1.0 m 0.5 m
10 Question 26.3 All Smoke and Mirrors You hold a hand mirror 0.5 m in a) 0.5 m front of you and look at your b) 1.0 m reflection in a full-length mirror 1 m behind you. How far in back of the c) 1.5 m big mirror do you see the image of d) 2.0 m your face? e) 2.5 m The image of the face reflected in the 1.0 m 0.5 m small mirror appears 0.5 m behind the small mirror. This image (which is the object for the big mirror) is 2.0 m away from the big mirror. The final image is 2.0 m behind the big mirror.
11 Question 26.4a Parallel light rays cross interfaces from air into two different media, 1 and 2, as shown in the figures below. In which of the media is the light traveling faster? Refraction I a) medium 1 b) medium 2 c) both the same air air 1 2
12 Question 26.4a Refraction I Parallel light rays cross interfaces from air into two different media, 1 and 2, as shown in the figures below. In which of the media is the light traveling faster? a) medium 1 b) medium 2 c) both the same The greater the difference in the speed of light between the two media, the greater the bending of the light rays. 1 air 2 air Follow-up: How does the speed in air compare to that in #1 or #2?
13 Question 26.4b Refraction II Parallel light rays cross interfaces from medium 1 into medium 2 and then into medium 3. What can we say about the relative sizes of the index of refraction of these media? a) n 1 > n 2 > n 3 b) n 3 > n 2 > n 1 c) n 2 > n 3 > n 1 d) n 1 > n 3 > n 2 e) none of the above 1 2 3
14 Question 26.4b Refraction II Parallel light rays cross interfaces from medium 1 into medium 2 and then into medium 3. What can we say about the relative sizes of the index of refraction of these media? a) n 1 > n 2 > n 3 b) n 3 > n 2 > n 1 c) n 2 > n 3 > n 1 d) n 1 > n 3 > n 2 e) none of the above The rays are bent toward the normal when crossing into #2, so n 2 > n 1. But rays are bent away from the normal when going into #3, so n 3 < n 2. How to find the relationship between #1 and #3? Ignore medium #2! So the rays are bent away from the normal if they would pass from #1 directly into #3. Thus, we have: n 2 > n 1 > n
15 Question 26.5a To shoot a fish with a gun, should you aim directly at the image, slightly above, or slightly below? Gone Fishin I a) aim directly at the image b) aim slightly above c) aim slightly below
16 Question 26.5a To shoot a fish with a gun, should you aim directly at the image, slightly above, or slightly below? Gone Fishin I a) aim directly at the image b) aim slightly above c) aim slightly below Due to refraction, the image will appear higher than the actual fish, so you have to aim lower to compensate.
17 Question 26.5b To shoot a fish with a laser gun, should you aim directly at the image, slightly above, or slightly below? Gone Fishin II a) aim directly at the image b) aim slightly above c) aim slightly below
18 Question 26.5b To shoot a fish with a laser gun, should you aim directly at the image, slightly above, or slightly below? Gone Fishin II a) aim directly at the image b) aim slightly above c) aim slightly below The light from the laser beam will also bend when it hits the air-water interface, so aim directly at the fish.
19 Question 26.6 An observer views two closely spaced lines through an angled piece of glass. To the observer, the lines appear: Parallel Lines a) shifted to the right b) shifted to the left c) spaced farther apart d) spaced closer together e) no change same as before
20 Question 26.6 An observer views two closely spaced lines through an angled piece of glass. To the observer, the lines appear: Parallel Lines a) shifted to the right b) shifted to the left c) spaced farther apart d) spaced closer together e) no change same as before The light rays get refracted twice, so they remain parallel, but they shift to the left, as seen in the figure. Their relative spacing does not change, just the overall position. Follow-up: What happens when the top glass moves toward the bottom glass?
Quest Chapter 29. turned back think bounce. Reread the definition of the law of reflection on page 444.
 1 A wave is turned back when it meets the boundary of the medium in which it is traveling. The wave is said to have undergone 1. interference. 2. diffraction. 3. reflection. 4. refraction. 2 What is the
1 A wave is turned back when it meets the boundary of the medium in which it is traveling. The wave is said to have undergone 1. interference. 2. diffraction. 3. reflection. 4. refraction. 2 What is the
School. Team Number. Optics
 School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
University of Maryland Department of Physics
 Spring 2002 University of Maryland Department of Physics Laura Lising Physics 122 April 24, 2003 Exam #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions. Just the answer counts for these. (8 points each) 1) Suppose
Spring 2002 University of Maryland Department of Physics Laura Lising Physics 122 April 24, 2003 Exam #2 Solutions Multiple choice questions. Just the answer counts for these. (8 points each) 1) Suppose
L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light
![L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light](/thumbs/74/70673315.jpg) L 31 Light and Optics [1] Measurements of the speed of light: 186,000 miles per second (1 foot per nanosecond) light propagating through matter transparent vs. opaque materials colors, why is an orange
L 31 Light and Optics [1] Measurements of the speed of light: 186,000 miles per second (1 foot per nanosecond) light propagating through matter transparent vs. opaque materials colors, why is an orange
0.4 s 0.8 s 1.5 s. 2.5 s. 2. A beam of light from a ray box spreads out as shown in the diagram and strikes a plane mirror.
 1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference
 Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference Phys 2435: Chap. 35, Pg 1 Geometrical Optics Assumption: the dimensions
Some properties of waves: Huygens principle Superposition Coherence Interference Young s double-slit experiment Thin-film interference Phys 2435: Chap. 35, Pg 1 Geometrical Optics Assumption: the dimensions
Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors
 Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Physics 102 recent lectures Light as a wave Lecture 14 EM waves Lecture 15 Polarization Lecture 20 & 21 Interference & diffraction
Physics 102: Lecture 16 Introduction to Mirrors Physics 102: Lecture 16, Slide 1 Physics 102 recent lectures Light as a wave Lecture 14 EM waves Lecture 15 Polarization Lecture 20 & 21 Interference & diffraction
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced)
 The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
PHYS 102 Exams. PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A)
 PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
PHYS 102 Exams PHYS 102 Exam 3 PRINT (A) The next two questions pertain to the situation described below. A metal ring, in the page, is in a region of uniform magnetic field pointing out of the page as
Physics 208 Exam 1 Oct. 3, 2007
 1 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 1 Oct. 3, 2007 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed
1 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 1 Oct. 3, 2007 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed
Waves ~ Learning Guide
 Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves. Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com
 Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom
 Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom Introduction: This series of demonstrations will illustrate a number of optical phenomena. Using different light sources and a tank of water, you
Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom Introduction: This series of demonstrations will illustrate a number of optical phenomena. Using different light sources and a tank of water, you
CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES
 Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
TA/TI survey. Phy Phy
 TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6
 Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version
 Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
Projectiles: Target Practice Student Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
sun focus image of sun
 These are slightly modified book questions. They do NOT represent the entire subject material of the test. Moreover, I have not fully vetted these questions or the supplied answers. They are supplied as
These are slightly modified book questions. They do NOT represent the entire subject material of the test. Moreover, I have not fully vetted these questions or the supplied answers. They are supplied as
LIGHT. A beam is made up of several rays. It maybe parallel, diverging (spreading out) or converging (getting narrower). Parallel Diverging Converging
 LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
LIGHT Light is a form of energy. It stimulates the retina of the eye and produces the sensation of sight. We see an object when light leaves it and enters the eye. Objects such as flames, the sum and stars
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light
 Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Waves ~ Learning Guide
 Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Waves ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
MHS. Physics. Sample Questions. Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11
 MHS Physics Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11 Sample Questions 1. non-luminous source of light is one which: 1. emits light by itself 2. carries light inside 3. reflects light coming from other objects
MHS Physics Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11 Sample Questions 1. non-luminous source of light is one which: 1. emits light by itself 2. carries light inside 3. reflects light coming from other objects
Hubble Space Telescope
 Before the first telescopes were invented at the beginning of the 17th century, people looked up at the stars with their naked eyes. The first refracting telescope that Galileo developed in 1609 was likely
Before the first telescopes were invented at the beginning of the 17th century, people looked up at the stars with their naked eyes. The first refracting telescope that Galileo developed in 1609 was likely
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination
 Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination This exam has two parts: Part A contains 25 multiple choice questions. Complete the bubbles for your name and student number on the multiple
Simon Fraser University 2000 April 18 Physics 100 Final Examination This exam has two parts: Part A contains 25 multiple choice questions. Complete the bubbles for your name and student number on the multiple
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated.
 Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated. 1 An electromagnetic wave has an electric field with peak value 250 N/C, What is the
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated. 1 An electromagnetic wave has an electric field with peak value 250 N/C, What is the
Intensity of Light and Heat. The second reason that scientists prefer the word intensity is Well, see for yourself.
 IDS 102 Intensity of Light and Heat When talking about a light source, most people are more comfortable with the word brightness than they are with the word intensity. Scientists generally prefer the word
IDS 102 Intensity of Light and Heat When talking about a light source, most people are more comfortable with the word brightness than they are with the word intensity. Scientists generally prefer the word
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER
 SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
SECTION 3 & 4 LIGHT WAVES & INFORMATION TRANSFER Light Waves Light is a type of energy that travels as waves. Light is different than other waves because it does not need matter to travel. Light waves
Name (LAST, First):, Block (circle): Date: / /
 Name (LAST, First):, Block (circle): 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Date: / / MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A new car manufacturer advertises
Name (LAST, First):, Block (circle): 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Date: / / MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A new car manufacturer advertises
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
The Challenge of Light
 Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
PHY 205 Final Exam 6/24/2009 Second Semester2008 Part 1.
 Part 1. Please read each question carefully. Each question worth s 1 point. or the following questions, please circle the correct answer. 1. Which one of the following statements concerning the index of
Part 1. Please read each question carefully. Each question worth s 1 point. or the following questions, please circle the correct answer. 1. Which one of the following statements concerning the index of
Physics 010 Midterm #2
 Physics 010 Midterm #2 Thursday April 2, 8:30 10:00am This midterm is closed book. No books or notes allowed. Calculators are allowed There are 10 questions on this midterm, with marks noted beside each
Physics 010 Midterm #2 Thursday April 2, 8:30 10:00am This midterm is closed book. No books or notes allowed. Calculators are allowed There are 10 questions on this midterm, with marks noted beside each
Name Date Class. Electromagnetic Spectrum. Colors
 b e n c h m a r k t e s t : p h y s i c a l s c i e n c e Multiple Choice Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio waves A B C D Gamma rays Long Wavelength
b e n c h m a r k t e s t : p h y s i c a l s c i e n c e Multiple Choice Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio waves A B C D Gamma rays Long Wavelength
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
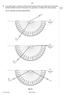 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING
 Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Reviewing Key Terms Use a key term from the list below to fill in the blanks in statements 1 to 5. mirage shimmering
 Goal To review the concepts from Chapter 11. Reviewing Key Terms Use a key term from the list below to fill in the blanks in statements 1 to 5. critical angle dispersion index of refraction mirage shimmering
Goal To review the concepts from Chapter 11. Reviewing Key Terms Use a key term from the list below to fill in the blanks in statements 1 to 5. critical angle dispersion index of refraction mirage shimmering
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
SPECTRUM. Dispersion. This phenomenon can be observed in a lab environment using a
 SPECTRUM Dispersion The phenomenon due to which a polychromatic light, like sunlight, splits into its component colours, when passed through a transparent medium like a glass prism, is called dispersion
SPECTRUM Dispersion The phenomenon due to which a polychromatic light, like sunlight, splits into its component colours, when passed through a transparent medium like a glass prism, is called dispersion
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Name Class Date. a. Light is a wave. 2. Empedocles. b. Light consists of tiny 3. Euclid
 Exercises 27.1 Early Concepts of (page 533) Scientist Idea About 1. Einstein a. is a wave. 2. Empedocles b. consists of tiny 3. Euclid particles. 4. Huygens c. Vision results from streamers or filaments
Exercises 27.1 Early Concepts of (page 533) Scientist Idea About 1. Einstein a. is a wave. 2. Empedocles b. consists of tiny 3. Euclid particles. 4. Huygens c. Vision results from streamers or filaments
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 7. Light
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 7 Light Introduction Light is hard to study because you can't see it, you only see it's effects. Newton tried to explain the energy in a light beam as the KE of a particle
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 7 Light Introduction Light is hard to study because you can't see it, you only see it's effects. Newton tried to explain the energy in a light beam as the KE of a particle
FORM 3 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hrs
 ST.FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY SPECIMEN PAPER. FORM 3 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hrs Name: Class: Answer all questions on the exam paper. In calculations show all steps in your working. The use of scientific
ST.FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY SPECIMEN PAPER. FORM 3 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hrs Name: Class: Answer all questions on the exam paper. In calculations show all steps in your working. The use of scientific
Test 3 results B A. Grades posted in Learn
 Test 3 results Grades posted in Learn D C B A End of the Semester approaches - make sure that your test, clicker and homework grades are what you think they should be on Learn F Clicker Question: What
Test 3 results Grades posted in Learn D C B A End of the Semester approaches - make sure that your test, clicker and homework grades are what you think they should be on Learn F Clicker Question: What
Lecture 2 - Length Contraction
 Lecture 2 - Length Contraction A Puzzle We are all aware that if you jump to the right, your reflection in the mirror will jump left. But if you raise your hand up, your reflection will also raise its
Lecture 2 - Length Contraction A Puzzle We are all aware that if you jump to the right, your reflection in the mirror will jump left. But if you raise your hand up, your reflection will also raise its
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves
 Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Wave Motion and Sound
 Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
λ Fig. 2 Name: y direction. In what c) in the + y direction d) in the y direction e) in the x direction
 Name: Exam #3 D#: Physics 140 Section #: hoose the best answer for each of Questions 1-19 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a # pencil. (5.6 pts each) 1. At a certain instant in time,
Name: Exam #3 D#: Physics 140 Section #: hoose the best answer for each of Questions 1-19 below. Mark your answer on your scantron form using a # pencil. (5.6 pts each) 1. At a certain instant in time,
VISIBLE LIGHT. L 32 Light and Optics [2] Seeing through the window. Windows behaving as mirrors. Seeing through a window
![VISIBLE LIGHT. L 32 Light and Optics [2] Seeing through the window. Windows behaving as mirrors. Seeing through a window VISIBLE LIGHT. L 32 Light and Optics [2] Seeing through the window. Windows behaving as mirrors. Seeing through a window](/thumbs/86/94409665.jpg) L 32 Light and Optics [2] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky and red sunsets Mirrors
L 32 Light and Optics [2] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky and red sunsets Mirrors
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Tools of Modern Astronomy
 Tools of Modern Astronomy Are Those Stars Really a Group? 1. Cut ten pieces of thread to different lengths between 5 cm and 25 cm. Tape a 1- cm plastic foam ball to the end of each piece of thread. 2.
Tools of Modern Astronomy Are Those Stars Really a Group? 1. Cut ten pieces of thread to different lengths between 5 cm and 25 cm. Tape a 1- cm plastic foam ball to the end of each piece of thread. 2.
2 nd Term Worksheet [ ] Subject Physics Class VIII Name : Sec. :
![2 nd Term Worksheet [ ] Subject Physics Class VIII Name : Sec. : 2 nd Term Worksheet [ ] Subject Physics Class VIII Name : Sec. :](/thumbs/95/124418031.jpg) 1 phy (viii) 2 nd Term Worksheet [2018 19] Subject Physics Class VIII Name : Sec. : Check Point: Chapter 4 [Energy] [A] Answer the following questions: [53] 1. In physics, when is work said to be done?
1 phy (viii) 2 nd Term Worksheet [2018 19] Subject Physics Class VIII Name : Sec. : Check Point: Chapter 4 [Energy] [A] Answer the following questions: [53] 1. In physics, when is work said to be done?
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument
 Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
Universal Gravitation W.S.
 Universal Gravitation W.S. 1. Paint spray travels radially away from the nozzle of the can in straight lines. Like gravity, the strength (intensity) of the spray obeys an inverse-square law. distance area
Universal Gravitation W.S. 1. Paint spray travels radially away from the nozzle of the can in straight lines. Like gravity, the strength (intensity) of the spray obeys an inverse-square law. distance area
Grade Level 11 (9-12) Activity Dependency Time Required: 10 minutes Group Size: 2 to 4 persons Expendable Cost per Group US $0.80
 Make it invisible! Subject Area(s) Physical science, Chemistry Associated Unit Associated Lesson The science of invisibility Activity Title Make it invisible! Image 1 ADA Description: This image shows
Make it invisible! Subject Area(s) Physical science, Chemistry Associated Unit Associated Lesson The science of invisibility Activity Title Make it invisible! Image 1 ADA Description: This image shows
Test 4 Preparation Questions
 Test 4 Preparation Questions A1. One joule of work is required to move a one-coulomb point charge from point A to point B in a uniform electric field. This indicates that (A) the resistance between points
Test 4 Preparation Questions A1. One joule of work is required to move a one-coulomb point charge from point A to point B in a uniform electric field. This indicates that (A) the resistance between points
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test. Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy. Name. Date
 McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy Name Date Use the text, illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 4. The illustration shows
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy Name Date Use the text, illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 4. The illustration shows
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay
 96 R E A D I N G The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay in orbit. The planets in the Solar System could not continue to orbit the Sun without the force of gravity. Astronauts
96 R E A D I N G The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay in orbit. The planets in the Solar System could not continue to orbit the Sun without the force of gravity. Astronauts
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test
 Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Chapter 26: Properties of Light
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
Lecture Outline Chapter 26: Properties of Light This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent Materials Opaque Materials Seeing Light The Eye Electromagnetic
RED LASER POINTER ITEM # LIGHT AND COLOR
 T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
PHYSICS. Ray Optics. Mr Rishi Gopie
 Ray Optics Mr Rishi Gopie Ray Optics Nature of light Light is a form of energy which affects the human eye in such a way as to cause the sensation of sight. Visible light is a range of electromagnetic
Ray Optics Mr Rishi Gopie Ray Optics Nature of light Light is a form of energy which affects the human eye in such a way as to cause the sensation of sight. Visible light is a range of electromagnetic
Where is the shadow?
 Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
RELEASED. Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC s Common Exams
 Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh, North
Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Physics RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction Raleigh, North
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Light.notebook May 03, 2016
 Unit 4 Light LIGHT.1 Describe the ray model of light. 16.1 LIGHT.2 Predict the effect of distance on light s illuminance. 16.1 LIGHT.3 Explain polarization and the Doppler effect. 16.2 LIGHT.4 Describe
Unit 4 Light LIGHT.1 Describe the ray model of light. 16.1 LIGHT.2 Predict the effect of distance on light s illuminance. 16.1 LIGHT.3 Explain polarization and the Doppler effect. 16.2 LIGHT.4 Describe
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
Ch Guided Reading Sound and Light
 Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Name Date Hour Chapter 15 Answer Key Ch.15-18 Guided Reading Sound and Light 1. Compare the speed of sound as it travels within a liquid, a solid, and a gas. Why does the speed of sound differ? Sound travels
Practice Final Name. m 3 /s b) 8.75 x 10 4 c) 8.21 x 10 4 d) 7.45 x 10 4 e) 7.21 x 10 4 Ans: a
 I included more than 35 problems only for practice purposes. In the final you will have 35 problems, as I stated during the last class meeting on Thursday, December 7, 2006. Practice Final Name 1) In a
I included more than 35 problems only for practice purposes. In the final you will have 35 problems, as I stated during the last class meeting on Thursday, December 7, 2006. Practice Final Name 1) In a
Your Comments. I was not sure about the angle at which the beam reflects from a concave mirror.
 Your Comments This pre-lecture was almost a "mirror" image o the last one! This stu makes sense!!! Yay!!! I was not sure about the angle at which the beam relects rom a concave mirror. Keeping all these
Your Comments This pre-lecture was almost a "mirror" image o the last one! This stu makes sense!!! Yay!!! I was not sure about the angle at which the beam relects rom a concave mirror. Keeping all these
HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
 HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES The Human Eye: The human eye is a sensitive sense organ and acts like a camera, which enable us to capture the colourful picture of
HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES The Human Eye: The human eye is a sensitive sense organ and acts like a camera, which enable us to capture the colourful picture of
Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM A Winter 2009
 Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM A Winter 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book exam. You may consult four (twosided) 8 1/2" 11" sheets of paper of personal notes. However, you may not collaborate and/or
Physics 5B PRACTICE FINAL EXAM A Winter 2009 INSTRUCTIONS: This is a closed book exam. You may consult four (twosided) 8 1/2" 11" sheets of paper of personal notes. However, you may not collaborate and/or
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory)
 The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources
Note on Posted Slides. History of Light. History of Light
 Note on Posted Slides These are the slides that I intended to show in class on Wed. Mar. 27, 2013. They contain important ideas and questions from your reading. Due to time constraints, I was probably
Note on Posted Slides These are the slides that I intended to show in class on Wed. Mar. 27, 2013. They contain important ideas and questions from your reading. Due to time constraints, I was probably
Downloaded from
 Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Question 10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index
Fluids density Pascal s principle (pressure vs. depth) Equation of continuity Buoyant force Bernoulli s (pressure, velocity, depth)
 Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
Final Exam All Finals week in the testing center. 50 multiple choice questions. Equations on the back of the test. Calculators are allowed on the test. There is a practice test in the packet. Exam 1 Review
TELESCOPES POWERFUL. Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book POWERFUL TELESCOPES Why do we need telescopes in order to observe stars that are very far away? Why do stars look bright in the sky while most galaxies, which have billions of stars, are too
FOCUS Book POWERFUL TELESCOPES Why do we need telescopes in order to observe stars that are very far away? Why do stars look bright in the sky while most galaxies, which have billions of stars, are too
Fresnel Equations cont.
 Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Lecture 11 Chapter 4 Fresnel quations cont. Total internal reflection and evanescent waves Optical properties of metals Familiar aspects of the interaction of light and matter Fresnel quations: phases
Level 2 Physics, 2004
 For Supervisor s 2 9 0 2 5 4 Level 2 Physics, 2004 90254 Demonstrate understanding of wave phenomena Credits: Four 2.00 pm Thursday 18 November 2004 Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your
For Supervisor s 2 9 0 2 5 4 Level 2 Physics, 2004 90254 Demonstrate understanding of wave phenomena Credits: Four 2.00 pm Thursday 18 November 2004 Check that the National Student Number (NSN) on your
Physics 234 Homework Chapter 35 Q3, P3, P24, P32, P55, P81, P91. air
 Physics 34 Homework Chapter 35 Q3, P3, P4, P3, P55, P8, P9 Q a) r = r a r b = 5d 3d = d. b) r = /. c) / = d = r. Also, r = 3(/), 5(/), etc., works. d) / = d so d = /4. P3) (a) We take the phases of both
Physics 34 Homework Chapter 35 Q3, P3, P4, P3, P55, P8, P9 Q a) r = r a r b = 5d 3d = d. b) r = /. c) / = d = r. Also, r = 3(/), 5(/), etc., works. d) / = d so d = /4. P3) (a) We take the phases of both
Decomposing white light into its components:
 Decomposing white light into its components: a. Look through a spectroscope at a white light from within the lab (if possible a fluorescent bulb output as well as a regular incandescent bulb) and the natural
Decomposing white light into its components: a. Look through a spectroscope at a white light from within the lab (if possible a fluorescent bulb output as well as a regular incandescent bulb) and the natural
Your Comments. Nutcracker
 Nutcracker Your Comments I don't understand the pressure differences in different sized pipes. To me, I would think that a pipe with a larger diameter has the smaller pressure and a skinnier pipe has a
Nutcracker Your Comments I don't understand the pressure differences in different sized pipes. To me, I would think that a pipe with a larger diameter has the smaller pressure and a skinnier pipe has a
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1, Version D
 PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1, Version D Tue. Feb. 4, 2014, 11:00am-12:15am This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam, but you are permitted to bring and use a clean copy of the official Formula Sheet for
PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1, Version D Tue. Feb. 4, 2014, 11:00am-12:15am This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam, but you are permitted to bring and use a clean copy of the official Formula Sheet for
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5545678956* PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Core October/November 2008 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *5545678956* PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Core October/November 2008 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Physics 25 Exam #4 December 2, 2008 Dr. Alward Page 1
 1. Light with a wavelength of 589 nm in a vacuum strikes the surface of an unknown liquid at an angle of 31.2 with respect to the normal to the surface. If the light travels at a speed of 1.97 10 8 m/s
1. Light with a wavelength of 589 nm in a vacuum strikes the surface of an unknown liquid at an angle of 31.2 with respect to the normal to the surface. If the light travels at a speed of 1.97 10 8 m/s
PAP Physics Spring Exam Review
 Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Class: Date: PAP Physics Spring Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. A container of gas is at a pressure of.3 0 5 Pa
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020
 Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
Multiple Choice Review for Final Exam ~ Physics 1020 1. You are throwing a ball straight up in the air. At the highest point, the ball s a) velocity and acceleration are zero b) velocity is nonzero, but
Polarized Light. Nikki Truss. Abstract:
 Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A
 Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Projectiles: Target Practice Teacher Advanced Version
 Projectiles: Target Practice Teacher Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
Projectiles: Target Practice Teacher Advanced Version In this lab you will shoot a chopstick across the room with a rubber band and measure how different variables affect the distance it flies. You will
An Analysis of a Sunset Photo
 Robert J. Vanderbei The Earth Is N An Analysis of a Sunset Photo Can a photo of the sunset over Lake Michigan reveal the shape of our planet? 34 OPN November 2008 1047-6938/08/0??/0034/6-$15.00 OSA www.osa-opn.org
Robert J. Vanderbei The Earth Is N An Analysis of a Sunset Photo Can a photo of the sunset over Lake Michigan reveal the shape of our planet? 34 OPN November 2008 1047-6938/08/0??/0034/6-$15.00 OSA www.osa-opn.org
BEFORE YOU READ. Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion STUDY TIP. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
Last Name: First Name:. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science. APRIL 2013 EXAMINATION version 2 PHY 205H1S
 Last Name: First Name:. Student Number: UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2013 EXAMINATION version 2 PHY 205H1S This examination has 9 pages and should take no longer than 2 hours.
Last Name: First Name:. Student Number: UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2013 EXAMINATION version 2 PHY 205H1S This examination has 9 pages and should take no longer than 2 hours.
download instant at
 download instant at https://testbanksolution.net CHAPTER, FORM A TRIGONOMETRY NAME DATE For Problems 1-10, do not use a calculator. 1. Write sin 9 in terms of its cofunction. 1.. Find cos A, sec A, and
download instant at https://testbanksolution.net CHAPTER, FORM A TRIGONOMETRY NAME DATE For Problems 1-10, do not use a calculator. 1. Write sin 9 in terms of its cofunction. 1.. Find cos A, sec A, and
