Reviewing Key Terms Use a key term from the list below to fill in the blanks in statements 1 to 5. mirage shimmering
|
|
|
- Karen Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Goal To review the concepts from Chapter 11. Reviewing Key Terms Use a key term from the list below to fill in the blanks in statements 1 to 5. critical angle dispersion index of refraction mirage shimmering 1. The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium is the of the medium. (11.1) 2. is the separation of white light into its colours. (11.1) 3. The angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction is 90 is called the. (11.2) 4. is the apparent movement of objects seen through hot air over objects and surfaces. (11.3) 5. When you think that you are seeing an object but it is not really there, you are seeing a. (11.3) 6. Label the following in this diagram: incident ray, normal, refracted ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence, angle of refraction, and angle of reflection.
2 Knowledge and Understanding Fill in the blanks to complete the statements in questions 7 to When light goes from air into water at an angle, the speed of the light and the light refracts the normal. 8. In a given medium, the speed of each of light is different. For this reason, indices of refraction are measured using a pure light with a wavelength of 589 nm. 9. a. When light crosses into a medium with a lesser index of refraction, the angle of refraction will be than the angle of incidence. b. When light crosses into a medium with a greater index of refraction, the angle of refraction will be than the angle of incidence. 10. Two factors that can affect the index of refraction of a given substance are and. 11. When light crosses the boundary between two substances that have different indices of refraction, the of determines the proportion that is reflected. 12. A light ray is travelling from a medium with a larger index of refraction to a medium with a smaller index of refraction. If the angle of incidence increases from 0, of the incident light is refracted. When the angle of incidence becomes greater than the critical angle, of the incident light is reflected. 13. White light can be dispersed into a spectrum of colours because each colour has a wavelength, travels at a different speed, and is refracted at a different. 14. Rainbows are produced by a combination of reflection and refraction in, while sundogs are a result of in. 15. While standing in the shallow end of a swimming pool, you see a coin on the bottom of the pool several metres ahead of you. This coin is the surface of the water than it appears.
3 Thinking and Investigation 16. A clear plastic cube is submerged in a container of water. Why would the cube be difficult to see if the plastic has exactly the same index of refraction as water? 17. a. The speed of light in a solid is m/s. Calculate the index of refraction for the solid. b. Calculate the speed of light in diamond, which has an index of refraction of c. Calculate the speed of light in ethyl alcohol, which has an index of refraction of at 20 C. d. The speed of light in a solid is m/s. Calculate the index of refraction. Then, use the data in Table 11.1 to help identify the solid (see page 454 of your textbook).
4 18. Why is a small critical angle desirable for optical fibres? What problem could a larger critical angle cause? 19. The beaker in this diagram contains water and cooking oil. The oil has a higher index of refraction than the water. Draw the refracted ray in the oil and in the water. 20. Some of the astronauts who landed on the Moon placed retroreflectors there. The distance between Earth and the Moon can be determined by measuring the time it takes for a pulse of a laser light to reach the reflector and then return to Earth. What properties of light would you have to know in order to calculate the distance between Earth and the Moon? 21. Review Investigation 11-D in your textbook. The method you used to determine the critical angle of water only works for some liquids. Describe how you could determine the critical angle of a flat piece of glass. Communication 22. Describe how society has benefited from the development of a. optical fibres b. retroreflectors
5 23. Using a sketch, explain the daytime and nighttime settings for a prism-type rearview mirror. 24. Complete this ray diagram to show how a retroreflector reverses the direction of incident light rays. 25. Imagine that you and a friend are hiking across a hot desert. Your map shows no sources of water in the area. However, your friend is sure he can see a pool of water off to one side, and wants to turn toward it. Explain how hot temperatures change the index of refraction of air and create the effect that your friend mistakes for water.
6 26. The following diagram shows wave fronts of light travelling across the boundary between air and water. a. Explain the significance of the change in spacing of the wave fronts as the light passes from air into water. b. Beside this diagram, draw a similar diagram, but with an angle of incidence of 0, so that the wave fronts are parallel to the boundary. Describe what happens when the light crosses the boundary. 27. Review your observations for Activity 11-1, The Re-appearing Coin, on page 447 of your textbook. Explain these observations in terms of what you have learned about refraction in this chapter. Application 28. Identify two careers related to the optics described in this chapter. 29. Astronomers can learn a lot about stars by studying the wavelengths of the light that they emit. Some of the early instruments used to analyze starlight contained prisms. What do you think the function of these prisms is?
Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours are shown.
 Name Q9.Visible white light consists of several different colours. Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours
Name Q9.Visible white light consists of several different colours. Figure 1 shows white light passing through a triangular glass prism. The white light splits up into different colours. Two of the colours
Year 9- Physics First Term Revision
 Year 9- Physics First Term Revision All objects EMIT and ABSORB infrared radiation The hotter the obect, the more infrared radiation it emits (gives off) Dark/Matte surfaces are good absorbers of infrared
Year 9- Physics First Term Revision All objects EMIT and ABSORB infrared radiation The hotter the obect, the more infrared radiation it emits (gives off) Dark/Matte surfaces are good absorbers of infrared
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
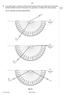 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
Sun Building Activity 2 The Signature of the Stars
 Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
Sun Building The Signature of the Stars Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours
UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION
 UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION S C I E N C E 9 1 Science 9 Unit E Section 3.0 OPTICAL TELESCOPES, RADIO TELESCOPES, AND OTHER TECHNOLOGIES ADVANCE OUR UNDERSTANDING OF SPACE SECTI ON 3.0 Science 9 Unit E Section
UNIT E: SPACE EXPLORATION S C I E N C E 9 1 Science 9 Unit E Section 3.0 OPTICAL TELESCOPES, RADIO TELESCOPES, AND OTHER TECHNOLOGIES ADVANCE OUR UNDERSTANDING OF SPACE SECTI ON 3.0 Science 9 Unit E Section
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light
 Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
Physics 30: Chapter 5 Exam Wave Nature of Light Name: Date: Mark: /33 Numeric Response. Place your answers to the numeric response questions, with units, in the blanks at the side of the page. (1 mark
CHAPTER 9. Knowledge. (d) 3 2 l
 CHAPTER 9 Review K/U Knowledge/Understanding T/I Thinking/Investigation C Communication A Application Knowledge For each question, select the best answer from the four alternatives. 1. Water waves splash
CHAPTER 9 Review K/U Knowledge/Understanding T/I Thinking/Investigation C Communication A Application Knowledge For each question, select the best answer from the four alternatives. 1. Water waves splash
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2939187014* PHYSICS 0625/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) October/November 2017 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *2939187014* PHYSICS 0625/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) October/November 2017 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument
 Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
PHYSICS 11. Review What is the critical angle for a glass that has an index of refraction of 1.52?
 Waves Review 4 1. Explain, with the help of a sketch, what each of these terms means with respect to waves: (a) crest; (b) trough; (c) wavelength; (d) frequency; (e) amplitude. 2. A dog wags its tail 50
Waves Review 4 1. Explain, with the help of a sketch, what each of these terms means with respect to waves: (a) crest; (b) trough; (c) wavelength; (d) frequency; (e) amplitude. 2. A dog wags its tail 50
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
UNIT-5 EM WAVES UNIT-6 RAY OPTICS
 UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
Light and motion. = v c
 Light and motion This means that if you know what wavelength some radiation was emitted at (as you would for, say, a hydrogen Balmer line), then the observed wavelength tells you the velocity of the object
Light and motion This means that if you know what wavelength some radiation was emitted at (as you would for, say, a hydrogen Balmer line), then the observed wavelength tells you the velocity of the object
Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity. Gennady Sokolov, Vitali Sokolov gennadiy@vtmedicalstaffing.com The interference experiment with moving water
Fizeau s Interference Experiment with Moving Water Contradicts the Special Theory of Relativity. Gennady Sokolov, Vitali Sokolov gennadiy@vtmedicalstaffing.com The interference experiment with moving water
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory)
 The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Introductory) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources
Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics. 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below.
 Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics SP1 & SP2: Motion & Forces 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below. a) Find out John's speed for
Grade 10 First Term Examination (Revision) Physics SP1 & SP2: Motion & Forces 1. A part of travel graph of John's journey from his house to the shops and back is shown below. a) Find out John's speed for
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Quest Chapter 29. turned back think bounce. Reread the definition of the law of reflection on page 444.
 1 A wave is turned back when it meets the boundary of the medium in which it is traveling. The wave is said to have undergone 1. interference. 2. diffraction. 3. reflection. 4. refraction. 2 What is the
1 A wave is turned back when it meets the boundary of the medium in which it is traveling. The wave is said to have undergone 1. interference. 2. diffraction. 3. reflection. 4. refraction. 2 What is the
CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING
 Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6
 Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced)
 The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
The Nature of Light Student Question Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project Introduction This worksheet contains questions and activities which will test your knowledge and
GRADE 9: Physical processes 4. UNIT 9P.4 6 hours. The electromagnetic spectrum. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 9: Physical processes 4 The electromagnetic spectrum UNIT 9P.4 6 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of seven units on physical processes for Grade 9. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 9: Physical processes 4 The electromagnetic spectrum UNIT 9P.4 6 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of seven units on physical processes for Grade 9. The unit is designed to guide your
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at January 2016
 Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision January 2016 Paper 1P (Higher Tier) Model Answers Level Edexcel Subject Physics Exam Board IGCSE Year January 2016 Paper Paper 1P (Double Award) Tier Higher Tier Booklet
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
 Light as Waves Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 41! In the previous chapter we discussed light as rays! These rays traveled in a straight line except when they were reflected
Light as Waves Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 41! In the previous chapter we discussed light as rays! These rays traveled in a straight line except when they were reflected
How does your eye form an Refraction
 Astronomical Instruments and : Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the of light Eye uses refraction
Astronomical Instruments and : Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the of light Eye uses refraction
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics
 PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics Hot Radiating Objects Imagine a piece of metal placed in a hot furnace. At first, the metal becomes warm, although its visual appearance doesn't change. As it
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics Hot Radiating Objects Imagine a piece of metal placed in a hot furnace. At first, the metal becomes warm, although its visual appearance doesn't change. As it
P H Y S I C S Half Yearly Exam Specimen Paper
 P H Y S I C S Half Yearly Exam Specimen Paper Form 3 Time: 2 hrs Name: Class: Answer all questions on the exam paper. In calculations you are advised to show all steps in your working. The use of scientific
P H Y S I C S Half Yearly Exam Specimen Paper Form 3 Time: 2 hrs Name: Class: Answer all questions on the exam paper. In calculations you are advised to show all steps in your working. The use of scientific
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated.
 Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated. 1 An electromagnetic wave has an electric field with peak value 250 N/C, What is the
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03 (with solutions) All questions are worth 5 points unless otherwise stated. 1 An electromagnetic wave has an electric field with peak value 250 N/C, What is the
RED LASER POINTER ITEM # LIGHT AND COLOR
 T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
T E A C H E G U I R D S E RED LASER POINTER ITEM # 5135-00 LIGHT AND COLOR While it excels at its traditional purpose of drawing attention to a particular object from a distance, the humble laser pointer
Being a Chemist. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
School. Team Number. Optics
 School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
School Team Number Optics Physical Optics (30%) Proceed to the laser shoot (40%) when your team number is called. 1. What are the four colors used in the CMYK color model? (2 points) 2. Muscae Volitantes
PHYSICS PAST PAPERS PHYSICS PAPER Suppose the handle bars of the wheelbarrow in question 2 were extended, which force(s) would
 PHYSICS PAST PAPERS PHYSICS PAPER 1 1995 1. Name the instrument that would be most suitable for measuring the thickest of one sheet of this question paper. Figure 1 shows a worker ready to lift a load
PHYSICS PAST PAPERS PHYSICS PAPER 1 1995 1. Name the instrument that would be most suitable for measuring the thickest of one sheet of this question paper. Figure 1 shows a worker ready to lift a load
Atmospheric Optics - II
 Atmospheric Optics - II First midterm exam is this Friday! The exam will be in-class, during our regular lecture this Friday September 28 at 9:30 am The exam will be CLOSED BOOK No textbooks No calculators
Atmospheric Optics - II First midterm exam is this Friday! The exam will be in-class, during our regular lecture this Friday September 28 at 9:30 am The exam will be CLOSED BOOK No textbooks No calculators
What can laser light do for (or to) me?
 What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
What can laser light do for (or to) me? Phys 1020, Day 15: Questions? Refection, refraction LASERS: 14.3 Next Up: Finish lasers Cameras and optics 1 Eyes to web: Final Project Info Light travels more slowly
Being a Physicist Unit 5. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
Telescopes (Chapter 6)
 Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions are just right c) the ocean is calm d) the ocean is wavy e) motion of the Moon
 Question 26.1 When watching the Moon over the ocean, you often see a long streak of light on the surface of the water. This occurs because: Reflection a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions
Question 26.1 When watching the Moon over the ocean, you often see a long streak of light on the surface of the water. This occurs because: Reflection a) the Moon is very large b) atmospheric conditions
CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES
 Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
Name Period CHAPTERS: 9.1, 10.1 AND 10.2 LIGHT WAVES PROPERTIES ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT WAVES FOLDABLE (blue, green & yellow completely filled in.) /30 /30 2. WS READING GUIDE FOR
How does your eye form an Refraction
 Astronomical Instruments Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the bending of light
Astronomical Instruments Eyes and Cameras: Everyday Light Sensors How does your eye form an image? How do we record images? How does your eye form an image? Refraction Refraction is the bending of light
Space Physics Questions CfE
 Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
Space Physics Questions CfE 1) Write down the definitions of the following: a) Moon b) Planet c) Sun d) Star e) Solar System f) Exoplanet g) Galaxy h) Universe. 2) What is cosmology the study of? 3) a)
13 + Entrance Examination
 13 + Entrance Examination Paper 1 Physics - Level 2 Total marks: 60 Time allowed: 40 minutes Calculators may be used Full name. 1. Circle the correct answer for each of the following questions: a. On Earth
13 + Entrance Examination Paper 1 Physics - Level 2 Total marks: 60 Time allowed: 40 minutes Calculators may be used Full name. 1. Circle the correct answer for each of the following questions: a. On Earth
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Advanced)
 The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources or
The Nature of Light Answer Sheet (Advanced) Author: Sarah Roberts - Faulkes Telescope Project What is light? 1. Arrange the following objects in the table below according to whether they are sources or
KCSE 2009 PHYSICS PAPER 2
 KCSE 2009 PHYSICS PAPER 2 SECTION A (25 MARKS) Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided 1. State the number of images formed when an object is between two plane mirror placed in
KCSE 2009 PHYSICS PAPER 2 SECTION A (25 MARKS) Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided 1. State the number of images formed when an object is between two plane mirror placed in
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014. SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN
 KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN NAME : CLASS : INDEX NO : Track 2 Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the
KULLEGG MARIA REGINA BOYS SECONDARY MOSTA HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2013/2014 SUBJECT: PHYSICS Form 4 TIME: 1 HR 30 MIN NAME : CLASS : INDEX NO : Track 2 Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided on the
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating
 P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp)
 You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp) Introduction Astronomy is a unique science because unlike many of the other sciences, the
You Are the Spectrometer! A Look Inside Astronomy's Essential Instrument (Robert B. Friedman & Matthew K. Sharp) Introduction Astronomy is a unique science because unlike many of the other sciences, the
Properties of Waves. Before You Read. What are the features of a wave?
 Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
Properties of Waves Textbook pages 134 143 Before You Read Section 4.1 Summary In this section, you will find out about waves, such as water waves, sound waves, and radio waves. On the lines below, list
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
E. Physics: The Characteristics of Electricity (Grades 9)
 E. Physics: The Characteristics of Electricity (Grades 9) Overall Expectations E1. assess some of the costs and benefits associated with the production of electrical energy from renewable and non renewable
E. Physics: The Characteristics of Electricity (Grades 9) Overall Expectations E1. assess some of the costs and benefits associated with the production of electrical energy from renewable and non renewable
Particles and Waves Homework One (Target mark 13 out of 15)
 Particles and Waves Homework One (Target mark 13 out of 15) Display all answers to 2 significant figures. 1. A car covers a distance of 170m in a time of 18s. Calculate the average speed of the car. 2.
Particles and Waves Homework One (Target mark 13 out of 15) Display all answers to 2 significant figures. 1. A car covers a distance of 170m in a time of 18s. Calculate the average speed of the car. 2.
The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts. 13+ Entrance Examination 2015 PHYSICS
 The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts 13+ Entrance Examination 2015 PHYSICS Please follow these instructions The Science paper is divided into three sections (Biology, Chemistry and Physics).
The Haberdashers' Aske's Boys School Elstree, Herts 13+ Entrance Examination 2015 PHYSICS Please follow these instructions The Science paper is divided into three sections (Biology, Chemistry and Physics).
Why does a hot air balloon rise up in the air? Record your ideas on the lines below. Why are gases less dense than liquids?
 Fluids and Density Before You Read Why does a hot air balloon rise up in the air? Record your ideas on the lines below. What are fluids? A fluid is any form of matter that can flow. Liquids and gases are
Fluids and Density Before You Read Why does a hot air balloon rise up in the air? Record your ideas on the lines below. What are fluids? A fluid is any form of matter that can flow. Liquids and gases are
GOZO COLLEGE. Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
 GOZO COLLEGE Track 3 Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools 2011 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
GOZO COLLEGE Track 3 Half Yearly Examinations for Secondary Schools 2011 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Answer all questions. All working must be shown. The use of a calculator is allowed.
Grade 5. Practice Test. What is Light? How Light Behaves. Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com
 Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
Name Date Grade 5 What is Light? How Light Behaves Photo Credits (in order of appearance): Alexandr Mitiuc/Dreamstime.com Today you will read two passages. Read these sources carefully to gather information
1) What do all waves transport from one place to another?
 Pre Quiz 1) What do all waves transport from one place to another? 2) In which of the following scenarios would the Doppler effect be present? a) A police car, with its siren sounding, speeds past you
Pre Quiz 1) What do all waves transport from one place to another? 2) In which of the following scenarios would the Doppler effect be present? a) A police car, with its siren sounding, speeds past you
National 3 Waves and Radiation
 What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
What is a wave? National 3 Waves and Radiation 1. Wave Properties The basic definition Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We
and the radiation from source 2 has the form. The vector r points from the origin to the point P. What will the net electric field be at point P?
 Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Grade 7 Physical Pretest
 Grade 7 Physical Pretest Select the best answer to each question. 1. Energy from the sun arrives as electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Of the four wave types listed,
Grade 7 Physical Pretest Select the best answer to each question. 1. Energy from the sun arrives as electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Of the four wave types listed,
Lecture 7. Outline. ASTR 111 Section 002. Discuss Quiz 5 Light. Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s
 Lecture 7 ASTR 111 Section 002 Outline Discuss Quiz 5 Light Suggested reading: Chapter 5.1-5.2 and 5.6-5.8 of textbook Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s In 1676, Danish astronomer
Lecture 7 ASTR 111 Section 002 Outline Discuss Quiz 5 Light Suggested reading: Chapter 5.1-5.2 and 5.6-5.8 of textbook Light travels through empty space at a speed of 300,000 km/s In 1676, Danish astronomer
Higher Physics. Particles and Waves
 Perth Academy Physics Department Higher Physics Particles and Waves Particles and Waves Homework Standard Model 1 Electric Fields and Potential Difference 2 Radioactivity 3 Fusion & Fission 4 The Photoelectric
Perth Academy Physics Department Higher Physics Particles and Waves Particles and Waves Homework Standard Model 1 Electric Fields and Potential Difference 2 Radioactivity 3 Fusion & Fission 4 The Photoelectric
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature. Topic 6. Transferring Energy. pp WORKBOOK. Name:
 Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual
 Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual Fall 2006 Dr. Keith Mon 5:30-8:30 Wed 2:30-5:30 Thurs 5:30-8:30 Text by R. Thompson, J. Christensen, T. Bykov, and W. Keith, and for the Virtual
Physics 1401 Introduction to Astronomy Laboratory Manual Fall 2006 Dr. Keith Mon 5:30-8:30 Wed 2:30-5:30 Thurs 5:30-8:30 Text by R. Thompson, J. Christensen, T. Bykov, and W. Keith, and for the Virtual
Light and Geometric Optics
 By the end of this week I will be able to... label a diagram of a wave Solve word problems using the wave equation identify the types of radiation on the EM spectrum explain how light behaves like a wave
By the end of this week I will be able to... label a diagram of a wave Solve word problems using the wave equation identify the types of radiation on the EM spectrum explain how light behaves like a wave
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light
![L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light L 31 Light and Optics [1] Galileo s result. Galileo and the speed of light. The speed of light inside matter. Measurement of the speed of light](/thumbs/74/70673315.jpg) L 31 Light and Optics [1] Measurements of the speed of light: 186,000 miles per second (1 foot per nanosecond) light propagating through matter transparent vs. opaque materials colors, why is an orange
L 31 Light and Optics [1] Measurements of the speed of light: 186,000 miles per second (1 foot per nanosecond) light propagating through matter transparent vs. opaque materials colors, why is an orange
Physics 25 Exam #4 December 2, 2008 Dr. Alward Page 1
 1. Light with a wavelength of 589 nm in a vacuum strikes the surface of an unknown liquid at an angle of 31.2 with respect to the normal to the surface. If the light travels at a speed of 1.97 10 8 m/s
1. Light with a wavelength of 589 nm in a vacuum strikes the surface of an unknown liquid at an angle of 31.2 with respect to the normal to the surface. If the light travels at a speed of 1.97 10 8 m/s
hf = E 1 - E 2 hc = E 1 - E 2 λ FXA 2008 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA
 1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
1 Candidates should be able to : EMISSION LINE SPECTRA Explain how spectral lines are evidence for the existence of discrete energy levels in isolated atoms (i.e. in a gas discharge lamp). Describe the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *6297016693* PHYSICS 5054/21 Paper 2 Theory October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *6297016693* PHYSICS 5054/21 Paper 2 Theory October/November 2013 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer
Current Score: 0/20. Due: Tue Apr :15 PM EDT. Question Points. 0/1 0/1 0/3 0/3 0/1 0/3 0/2 0/2 0/2 0/2 Total 0/20.
 1 of 8 4/10/2010 3:38 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Tue Apr 20 2010 10:15 PM EDT Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0/1 0/1 0/3 0/3 0/1 0/3 0/2 0/2 0/2 0/2 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth
1 of 8 4/10/2010 3:38 PM Current Score: 0/20 Due: Tue Apr 20 2010 10:15 PM EDT Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0/1 0/1 0/3 0/3 0/1 0/3 0/2 0/2 0/2 0/2 Total 0/20 Description This assignment is worth
FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management Educational Assessment Unit Track 3 Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2016 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management Educational Assessment Unit Track 3 Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2016 FORM 4 PHYSICS TIME: 1h 30min
The Challenge of Light
 Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
Thomas Alva Edison The Challenge of Light We have been studying light for years Do we know everything about it? Absolutely not! Greeks & Chinese have been using light for years with no real concept of
Core Concept. PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e. Chapter 7 Light. New Symbols for this Chapter 3/29/2011
 PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e Chapter 7 Light Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Core Concept Light is electromagnetic radiation
PowerPoint Lectures to accompany Physical Science, 8e Chapter 7 Light Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Core Concept Light is electromagnetic radiation
2011 Assessment Report. Physics Level 1
 National Certificate of Educational Achievement 2011 Assessment Report Physics Level 1 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 90938 Demonstrate understanding of aspects
National Certificate of Educational Achievement 2011 Assessment Report Physics Level 1 90937 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of electricity and magnetism 90938 Demonstrate understanding of aspects
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
What is mechanical energy? How do we use it? Energy Energy
 You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L (P.520-525) Wave Nature of Light Not only did Young s double-slit experiment demonstrate the wave nature of light, it also paved the way for applications
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L (P.520-525) Wave Nature of Light Not only did Young s double-slit experiment demonstrate the wave nature of light, it also paved the way for applications
Astron 104 Laboratory #10 Solar Energy and the Habitable Zone
 Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #10 Solar Energy and the Habitable Zone Introduction The Sun provides most of the energy available in the solar system. Sunlight warms the planet and helps create
Name: Date: Section: Astron 104 Laboratory #10 Solar Energy and the Habitable Zone Introduction The Sun provides most of the energy available in the solar system. Sunlight warms the planet and helps create
PHYSICS. Ray Optics. Mr Rishi Gopie
 Ray Optics Mr Rishi Gopie Ray Optics Nature of light Light is a form of energy which affects the human eye in such a way as to cause the sensation of sight. Visible light is a range of electromagnetic
Ray Optics Mr Rishi Gopie Ray Optics Nature of light Light is a form of energy which affects the human eye in such a way as to cause the sensation of sight. Visible light is a range of electromagnetic
Lecture 2: Basic Astronomical Optics. Prisms, Lenses, and Mirrors
 Lecture 2: Basic Astronomical Optics Prisms, Lenses, and Mirrors Basic Optical Elements Refraction (Lenses) No longer used for large telescopes Widely used for instrument optics Reflection (mirrors) Widely
Lecture 2: Basic Astronomical Optics Prisms, Lenses, and Mirrors Basic Optical Elements Refraction (Lenses) No longer used for large telescopes Widely used for instrument optics Reflection (mirrors) Widely
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Physics/Science Unit P1: Universal Physics Wednesday 9 November 2011 Morning Time: 1 hour You must have: Calculator, ruler Candidate
Physics Assessment Unit AS 2
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2014 Physics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Waves, Photons and Medical Physics AY121 [AY121]
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY (AS) General Certificate of Education January 2014 Physics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Waves, Photons and Medical Physics AY121 [AY121]
General Physics II PHYS 102 Final Exam Spring st May 2011
 Qatar University Arts and Sciences College Mathematics and Physics Department General Physics II PHYS 102 Final Exam Spring 2011 31 st May 2011 Student Name: ID Number: 60 Please read the following carefully
Qatar University Arts and Sciences College Mathematics and Physics Department General Physics II PHYS 102 Final Exam Spring 2011 31 st May 2011 Student Name: ID Number: 60 Please read the following carefully
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
Welcome to Class 5: Earth Geology. Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room
 Welcome to Class 5: Earth Geology Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What s going to happen today? 1. You will learn: Sublime is more than a dead heroin addict s band. 2. You will better
Welcome to Class 5: Earth Geology Remember: sit only in the first 10 rows of the room What s going to happen today? 1. You will learn: Sublime is more than a dead heroin addict s band. 2. You will better
Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum!
 Earth Science Zimmerman Name: Period: Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum! HOOK: An astronomer discovers a new galaxy. How can the Doppler Effect be applied to determine if that galaxy
Earth Science Zimmerman Name: Period: Reading for Meaning and the Electromagnetic Spectrum! HOOK: An astronomer discovers a new galaxy. How can the Doppler Effect be applied to determine if that galaxy
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Problem 8.0 Make Your Own Exam Problem for Midterm II by April 13
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Problem Set 8: Electromagnetic Waves at Boundaries
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.007 Electromagnetic Energy: From Motors to Lasers Spring 2011 Problem Set 8: Electromagnetic Waves at Boundaries
Sparks CH301. WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid? UNIT 3 Day 7
 Sparks CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid? UNIT 3 Day 7 What are we going to do today? Discuss types of intermolecular forces. Compare intermolecular forces for different molecules.
Sparks CH301 WHY IS EVERYTHING SO DIFFERENT? Gas, Liquid or Solid? UNIT 3 Day 7 What are we going to do today? Discuss types of intermolecular forces. Compare intermolecular forces for different molecules.
Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope
 Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope Subject Area: Physical Sciences Grade Level: 9 12 Overview In this activity students will build a spectroscope to analyze the composition of light. Our scope is inexpensive,
Build and Use a Simple Spectroscope Subject Area: Physical Sciences Grade Level: 9 12 Overview In this activity students will build a spectroscope to analyze the composition of light. Our scope is inexpensive,
Hubble Space Telescope
 Before the first telescopes were invented at the beginning of the 17th century, people looked up at the stars with their naked eyes. The first refracting telescope that Galileo developed in 1609 was likely
Before the first telescopes were invented at the beginning of the 17th century, people looked up at the stars with their naked eyes. The first refracting telescope that Galileo developed in 1609 was likely
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A
 Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1252 Sec.A Exam #1A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 1112, Exam 3 Section 1 Version 1 December 6, 2004 Total Weight: 100 points 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting.
Discussion Review Test #2. Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
 Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Planetary Science: Investigations 9-10 I-Check Quiz STUDY GUIDE- ANSWER KEY Name HR Date
 1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
1. How are different types of radiation arranged along the electromagnetic spectrum? A. By how fast they travel incorrect answer B. By their sources incorrect answer C. By the amount of energy they carry
