A shocking group! Turbulent dissipation and star formation in Stephan s Quintet
|
|
|
- Scott Singleton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics of Groups, IAP, Dec A shocking group! Turbulent dissipation and star formation in Stephan s Quintet Pierre Guillard, P. Appleton, F. Boulanger, M. Cluver, P. Lesaffre, G. Pineau des Forêts, E. Falgarone, U. Lisenfeld, K. Alatalo, T. Bitsakis, A. Gusdorf, K. Xu.
2 Physics of Groups, IAP, Dec Details* matter! * gastrophysics: turbulence, shocks, mixing exchange of momentum, mass and energy between gas phases, conduction, chemistry, dust processing
3 Outline Stephan s Quintet: observational evidence for a multiphase, highly turbulent intergalactic medium What are the tracers of turbulent dissipation? How (well) can models constrain gas heating/cooling rates and physical scales of dissipation? 4. What do we learn about feedback / regulation of star formation?
4 Stephan s Quintet: a galaxy collision shocking the IGM V=6700 km/s Giant Shock T X = K V shock =600 km/s 40 kpc V=5700 km/s X-rays (Chandra): blue Optical: CFHT
5 Stephan s Quintet: a galaxy collision shocking the IGM NGC 7318b is crashing into the rest of the group at V ~ 800 km/s : interloper VLA Observations (20 cm) Hα + Chandra contours VLA Observations (HI line) WARM MOLECULAR HYDROGEN SEEN HERE 20 cm Radio emission from between galaxies suggested an intergalactic shock (Allen & Hartzuiker 1972) Hot X-ray gas indicating a 600 km/s shock wave (Trinchieri et al. 2003) Neutral hydrogen Observations show gap in HI where the shock is observed
6 Isolating the physics of turbulent dissipation against the dark sky! Pure H 2 spectrum! Image: Visible (Hubble) BLUE=H 2 gas (Spitzer) L(H 2 ) = 3 L(X-rays) M(H 2 ) = M Appleton et al. 2006, Guillard et al. 2009; Guillard et al. 2012b; Cluver et al SFR < 0.07 M /yr 6
7 One example amongst other SF-suppressed HCGs (cf. Katey s talk + Ute s poster) Stephan s Quintet updated from Alatalo et al. Guillard et al. 2012b, Cluver et al. 2013; Alatalo et al. 2014b, 2015c
8 The energy of the galaxy collision is not thermalized Stephan s Quintet BLUE=H 2 gas (Spitzer) Discovery of extremely turbulent CO and [CII] Image: Visible (Hubble) Guillard et al. 2009; Guillard et al. 2012b Appleton, Guillard et al t diss =10 8 yrs >> t dyn = yrs 8
9 Large CO complexes along the ridge Guillard et al. 2017
10 Detection of Ly-α with COS/HST dynamically coupled gas phases at all scales! cf. Phil Appleton s talk and Benoit Epinat s poster for more examples! See Thodoris and Phil s talk for optical diagnostics Lyα (COS) C+ [158µm] OIII 5007A
11 Modelling H2 formation and excitation Guillard et al
12 Paris-Durham MHD shock model Flower+03,+15, Guillard+09, Lesaffre+13 12
13 H 2 emission from shocks H 2 mid-ir lines are the main cooling lines of shocked molecular for 5 < V s < 40 km/s Cooling of MHD shocks in H 2 gas Shocks trigger the formation of H 2 gas if the gas is initially atomic provided that there is dust (Bergin+2007, Guillard +2009) 1D models of shocks within diffuse irradiated gas (Flower+15, Lesaffre+13) 13 16
14 Modeling of H 2 shows that mechanical energy is cascading from large (40 kpc) to small scales (<0.1pc) Guillard et al. 2009, Appleton et al
15 Modelling the H 2 excitation diagram constrains the distribution of turbulence dissipation structures chi 2 values (6 H 2 lines are fitted simultaneously) Lesaffre et al
16 Probability Distribution Function (PDF) of shock velocities Driven turbulence Decaying turbulence power-law PDF exponential PDF Subsonic wind tunnel experiments: Mouri & Hori 2008 Smith, Mac Low & Heitsch 2000 Compressible supersonic turbulence: Pety & Falgarone 2000 "16
17 Change of shocked gas properties across the IGM Appleton et al
18 Riding the turbulent energy cascade L Re=2300 L L k Large-scale cutoff Energy injection Inertial subrange 1/L Energy flow (Cascade) Dissipation: - Friction - Compression - Ambipolar diff. - Magnetic diff. SF, AGN, interactions, gravity Energy conserved in cascade 1/L k Heating, chemistry (molecular) emission lines Log 1/L 18
19 Let s shake a small box of ISM gas. 19
20 Dissipation in decaying MHD turbulence Isothermal 3D MHD, (Mach 4, ABC) n H ~ 100cm 3 <u 2 >~<b 2 /ρ> Re =LU/ν ~ Heating sources: Rem=LU/η Red = Ohmic Green = viscous shear Blue - viscous compression RAMSES simulations with careful treatment of viscous and resistive dissipation: DUMSES (Momferratos, PhD) pixels 20
21 Coupling chemistry and MHD CHEMSES = RAMSES + DUMSES ACTUAL viscous dissipation cm 32 species, 7 H 2 levels Uniform Irradiation: G 0 =1, Av=0.1 n H ~ 100/cm 3 => molecular, but without CO pixels Map of H2 v=0, J=3 21
22 Production of molecules and H 2 excitation by dissipation of turbulence G 0 =1 Av=0.1 22
23 Lessons learned From line luminosities and energy balance arguments: Molecular cooling rate can be higher than X-ray cooling Gas cooling is controlled by the dissipation of turbulent energy Turbulent dissipation time >> dynamical time From kinematics: Mechanical energy >> thermal energy The gas has to cool dynamically (not only thermally). The different gas phases are kinematically coupled From shock models and simulations: Turbulence is supersonic in the dense phase Amplitude of turbulence is beyond what is explored in current models/simulations of star formation Large dynamical range of spatial scales: ~100 kpc 0.01pc 23
24 Merci! 24
Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST
 Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST Pierre Guillard Institut d Astrophysique de Paris Université Pierre et Marie Curie he Warm H 2 with JWST Outline and take-home messages 1. Observations
Warm Molecular Hydrogen at high redshift with JWST Pierre Guillard Institut d Astrophysique de Paris Université Pierre et Marie Curie he Warm H 2 with JWST Outline and take-home messages 1. Observations
AGN-driven turbulence revealed by extreme [CII]158µm line cooling in radio-galaxies
![AGN-driven turbulence revealed by extreme [CII]158µm line cooling in radio-galaxies AGN-driven turbulence revealed by extreme [CII]158µm line cooling in radio-galaxies](/thumbs/81/83115490.jpg) AGN-driven turbulence revealed by extreme [CII]158µm line cooling in radio-galaxies Pierre Guillard CNES Fellow Intitut d Astrophysique Spatiale, Orsay, France The Universe Explored by Herschel, ESTEC,
AGN-driven turbulence revealed by extreme [CII]158µm line cooling in radio-galaxies Pierre Guillard CNES Fellow Intitut d Astrophysique Spatiale, Orsay, France The Universe Explored by Herschel, ESTEC,
The formation of super-stellar clusters
 The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
The formation of super-stellar clusters François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Cynthia Herrera, Edith Falgarone, Pierre Guillard, Nicole Nesvadba, Guillaume Pineau des Forets Outline How
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds. Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame
 Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
The Interstellar Medium
 The Interstellar Medium Fall 2014 Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium 528 doney@strw.leidenuniv.nl Class Schedule
The Interstellar Medium Fall 2014 Lecturer: Dr. Paul van der Werf Oortgebouw 565, ext 5883 pvdwerf@strw.leidenuniv.nl Assistant: Kirstin Doney Huygenslaboratorium 528 doney@strw.leidenuniv.nl Class Schedule
Cold Clouds in Cool Cores
 Becky Canning NGC 1275, Perseus Cluster Cold Clouds in Cool Cores 1 Snowcluster 2015 Cold Clouds in Cool Cores Excitation mechanisms of the multi-phase cool/cold gas Why should we care? Heard that X-ray
Becky Canning NGC 1275, Perseus Cluster Cold Clouds in Cool Cores 1 Snowcluster 2015 Cold Clouds in Cool Cores Excitation mechanisms of the multi-phase cool/cold gas Why should we care? Heard that X-ray
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm
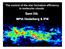 ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm M ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)?! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud? dn
! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm M ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)?! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud? dn
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
68 Star Formation Laws in LITTLE THINGS Dwarfs: The case of DDO133 and DDO168. Dana Ficut-Vicas
 68 Star Formation Laws in LITTLE THINGS Dwarfs: The case of DDO133 and DDO168 Dana Ficut-Vicas Little Things Project LITTLE: Local Irregulars That Trace Luminosity Extremes THINGS: The HI Nearby Galaxy
68 Star Formation Laws in LITTLE THINGS Dwarfs: The case of DDO133 and DDO168 Dana Ficut-Vicas Little Things Project LITTLE: Local Irregulars That Trace Luminosity Extremes THINGS: The HI Nearby Galaxy
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
The Impact of the Galactic Center Arches Cluster: Radio & X-ray Observations
 The Impact of the Galactic Center Arches Cluster: Radio & X-ray Observations Cornelia C. Lang University of Iowa GC region (Sagittarius) is obscured by ~30 visual magnitudes of extinction no optical, UV;
The Impact of the Galactic Center Arches Cluster: Radio & X-ray Observations Cornelia C. Lang University of Iowa GC region (Sagittarius) is obscured by ~30 visual magnitudes of extinction no optical, UV;
Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of ngvla Working Group 2
 Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Next Generation Very Large Array Working Group 2 HI in M74: Walter+ 08 CO in M51: Schinnerer+ 13 Continuum in M82: Marvil & Owen Galaxy Ecosystems Adam Leroy (OSU), Eric Murphy (NRAO/IPAC) on behalf of
Maria Cunningham, UNSW. CO, CS or other molecules?
 Maria Cunningham, UNSW CO, CS or other molecules? Wide field Surveys at mm wavelengths: pu8ng the whole picture together Follow chemical abundances through the whole ISM. Follow energy transfer through
Maria Cunningham, UNSW CO, CS or other molecules? Wide field Surveys at mm wavelengths: pu8ng the whole picture together Follow chemical abundances through the whole ISM. Follow energy transfer through
Physical Processes in Astrophysics
 Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
Physical Processes in Astrophysics Huirong Yan Uni Potsdam & Desy Email: hyan@mail.desy.de 1 Reference Books: Plasma Physics for Astrophysics, Russell M. Kulsrud (2005) The Physics of Astrophysics, Frank
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium
 Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Chapter 10 The Interstellar Medium Guidepost You have begun your study of the sun and other stars, but now it is time to study the thin gas and dust that drifts through space between the stars. This chapter
Astronomy. Astrophysics. H 2 formation and excitation in the Stephan s Quintet galaxy-wide collision
 A&A 502, 515 528 (2009) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200811263 c ESO 2009 Astronomy & Astrophysics H 2 formation and excitation in the Stephan s Quintet galaxy-wide collision P. Guillard 1, F. Boulanger 1, G.
A&A 502, 515 528 (2009) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200811263 c ESO 2009 Astronomy & Astrophysics H 2 formation and excitation in the Stephan s Quintet galaxy-wide collision P. Guillard 1, F. Boulanger 1, G.
Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs. Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics
 Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics Outline Turbulence inhibits star formation, but slowly Interplay between turbulence
Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics Outline Turbulence inhibits star formation, but slowly Interplay between turbulence
Cinthya Herrera (NAOJ)
 Cinthya Herrera (NAOJ) ASTE/ALMA Development Workshop 2014, June 18th, 2014 Galaxies interactions... Key in hierarchical model of galaxy formation and evolution (e.g., Kauffmann et al. 1993) Most massive
Cinthya Herrera (NAOJ) ASTE/ALMA Development Workshop 2014, June 18th, 2014 Galaxies interactions... Key in hierarchical model of galaxy formation and evolution (e.g., Kauffmann et al. 1993) Most massive
AGN winds and outflows
 AGN winds and outflows BAL QSOs (10-40% of all QSOs) Two problems: Fast winds with velocity up to a fraction of c are observed in the central regions of AGNs; they likely originate from the acceleration
AGN winds and outflows BAL QSOs (10-40% of all QSOs) Two problems: Fast winds with velocity up to a fraction of c are observed in the central regions of AGNs; they likely originate from the acceleration
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 11 26 / Colloquium University of Victoria Outline 1 Cosmic
Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies
 Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies Helen Russell Brian McNamara Alastair Edge Robert Main Adrian Vantyghem Francoise Combes Andy Fabian Philippe Salomé Outline Introduction Radiative
Molecular gas & AGN feedback in brightest cluster galaxies Helen Russell Brian McNamara Alastair Edge Robert Main Adrian Vantyghem Francoise Combes Andy Fabian Philippe Salomé Outline Introduction Radiative
Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM
 Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM P. Hily-Blant IPAG April 14th, 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Introduction to turbulence 3 Turbulent Cascade 4 Structures 5 Dissipation 6 Flavors 7 Perspectives failed to catch
Turbulence in the (Cold) ISM P. Hily-Blant IPAG April 14th, 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Introduction to turbulence 3 Turbulent Cascade 4 Structures 5 Dissipation 6 Flavors 7 Perspectives failed to catch
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift
 Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift Dawn Erb (CfA) Kennicutt-Schmidt Workshop, UCSD December 19, 2006 Overview Properties of star-forming galaxies
Gas Masses and Gas Fractions: Applications of the Kennicutt- Schmidt Law at High Redshift Dawn Erb (CfA) Kennicutt-Schmidt Workshop, UCSD December 19, 2006 Overview Properties of star-forming galaxies
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
A World of Dust. Bare-Eye Nebula: Orion. Interstellar Medium
 Interstellar Medium Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 10 Learning Outcomes: A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of
Interstellar Medium Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 10 Learning Outcomes: A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies.
 Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Multi-wavelength analysis of Hickson Compact Groups of Galaxies. Thodoris Bitsakis Department of Physics, University of Crete Paper: Bitsakis T., Charmandaris V., da Cunha E., Diaz-Santos T., Le Floc h
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063
 A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy
 Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy Dipanjan Mukherjee Universita di Torino with Geoff Bicknell Alex Wagner Ralph Sutherland AGN feedback and galaxy AGN feedback crucial to match
Impact of relativistic jets on the ISM of their host galaxy Dipanjan Mukherjee Universita di Torino with Geoff Bicknell Alex Wagner Ralph Sutherland AGN feedback and galaxy AGN feedback crucial to match
The Excited and Exciting ISM in Galaxies: PDRs, XDRs and Shocks as Probes and Triggers
 The Excited and Exciting ISM in Galaxies: PDRs, XDRs and Shocks as Probes and Triggers Marco Spaans (Groningen) Rowin Meijerink (Groningen), Paul van der Werf (Leiden), Juan Pablo Pérez Beaupuits (Bonn),
The Excited and Exciting ISM in Galaxies: PDRs, XDRs and Shocks as Probes and Triggers Marco Spaans (Groningen) Rowin Meijerink (Groningen), Paul van der Werf (Leiden), Juan Pablo Pérez Beaupuits (Bonn),
Models of Stephan s Quintet: hydrodynamic constraints on the group s evolution
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 419, 1780 1794 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19847.x Models of Stephan s Quintet: hydrodynamic constraints on the group s evolution Jeong-Sun Hwang, 1,2 Curtis Struck, 1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 419, 1780 1794 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19847.x Models of Stephan s Quintet: hydrodynamic constraints on the group s evolution Jeong-Sun Hwang, 1,2 Curtis Struck, 1
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^
 Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Star Formation In this lecture we discuss the formation of stars. After describing the structure
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Star Formation In this lecture we discuss the formation of stars. After describing the structure
Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM
 Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM Dieter Breitschwerdt Collaborators Miguel de Avillez (Evora, Portugal) Verena Baumgartner (Vienna, Austria) Jan Bolte (TU Berlin, Germany) Jenny
Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM Dieter Breitschwerdt Collaborators Miguel de Avillez (Evora, Portugal) Verena Baumgartner (Vienna, Austria) Jan Bolte (TU Berlin, Germany) Jenny
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline A galaxy is a collection of 100 billion stars! Our Milky Way Galaxy (1)Components - HII regions, Dust Nebulae, Atomic Gas (2) Shape & Size (3) Rotation of
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Spatially-Resolved Molecular Gas, Dust and Star Formation in Early-Types
 Spatially-Resolved Molecular Gas, Dust and Star Formation in Early-Types CO (Katey Alatalo, Leo Blitz, Francoise Combes, Alison Crocker, Timothy Davis, Lisa Young) Optical (SAURON + Atlas 3D teams) Plans:
Spatially-Resolved Molecular Gas, Dust and Star Formation in Early-Types CO (Katey Alatalo, Leo Blitz, Francoise Combes, Alison Crocker, Timothy Davis, Lisa Young) Optical (SAURON + Atlas 3D teams) Plans:
Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer
 Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer Matthew Palotti palotti@astro.wisc.edu University of Wisconsin Center for Magnetic Self Organization Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin
Structure Formation and Particle Mixing in a Shear Flow Boundary Layer Matthew Palotti palotti@astro.wisc.edu University of Wisconsin Center for Magnetic Self Organization Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era. François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale
 Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Galactic dust in the Herschel and Planck era François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale Motivation Dust emission Dust models Dust life cycle Planck early results Dust polarisation Outline Dust
Lecture 2: Introduction to stellar evolution and the interstellar medium. Stars and their evolution
 Lecture 2: Introduction to stellar evolution and the interstellar medium Stars and their evolution The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram (Color-Magnitude Diagram) Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes; Dust
Lecture 2: Introduction to stellar evolution and the interstellar medium Stars and their evolution The Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) Diagram (Color-Magnitude Diagram) Apparent and Absolute Magnitudes; Dust
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview. Ulrike Kuchner
 STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
Studying Galaxy Evolution with FIRI. A Far-InfraRed Interferometer for ESA. Dimitra Rigopoulou Oxford/RAL-STFC
 Studying Galaxy Evolution with FIRI A Far-InfraRed Interferometer for ESA Dimitra Rigopoulou Oxford/RAL-STFC The FIR gap from Wild & Helmich SPIE 2008 From MaE Griffin from Wild & Helmich SPIE 2008 The
Studying Galaxy Evolution with FIRI A Far-InfraRed Interferometer for ESA Dimitra Rigopoulou Oxford/RAL-STFC The FIR gap from Wild & Helmich SPIE 2008 From MaE Griffin from Wild & Helmich SPIE 2008 The
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era
 2015. 11. 3. SKA Meeting HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era Bon-Chul Koo (SNU, KIAS) Supernova Explosions SN explosions play a major role in the ecology and evolution of galaxies by supplying
2015. 11. 3. SKA Meeting HI 21-cm Study of Supernova Remnants in SKA Era Bon-Chul Koo (SNU, KIAS) Supernova Explosions SN explosions play a major role in the ecology and evolution of galaxies by supplying
The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs)
 The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, N. Schneider, B. Mookerjea, Z. Makai, O. Ricken, P. Pilleri, Y. Okada, M. Gerin Page 1 Main question: What happens here? Impact
The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, N. Schneider, B. Mookerjea, Z. Makai, O. Ricken, P. Pilleri, Y. Okada, M. Gerin Page 1 Main question: What happens here? Impact
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium
 The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
The Physics of the Interstellar Medium Ulrike Heiter Contact: 471 5970 ulrike@astro.uu.se www.astro.uu.se Matter between stars Average distance between stars in solar neighbourhood: 1 pc = 3 x 1013 km,
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud Thomas G. Bisbas
![The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud Thomas G. Bisbas The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud Thomas G. Bisbas](/thumbs/95/126074993.jpg) The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud Thomas G. Bisbas tbisbas@gmail.com University of Virginia Outline of the presentation 1. Introduction 2.
The Inception of Star Cluster Formation Revealed by [CII] Emission Around an Infrared Dark Cloud Thomas G. Bisbas tbisbas@gmail.com University of Virginia Outline of the presentation 1. Introduction 2.
What FIREs Up Star Formation? The Emergence of Kennicutt- Schmidt from Feedback
 What FIREs Up Star Formation? The Emergence of Kennicutt- Schmidt from Feedback SFDE7, Quy Nhon, Vietnam August, 7 Matt Orr Ph.D. Advisor: Dr. Philip F. Hopkins TAPIR California Institute of Technology
What FIREs Up Star Formation? The Emergence of Kennicutt- Schmidt from Feedback SFDE7, Quy Nhon, Vietnam August, 7 Matt Orr Ph.D. Advisor: Dr. Philip F. Hopkins TAPIR California Institute of Technology
- AGN feedback in action?
 Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
Gas outflows and star formation in type 2 AGNs - AGN feedback in action? Jong-Hak Woo (Seoul National Univ.) & Hyun-Jin Bae, Donghoon Son, Marios Karouzos Muse view of OIII outflows in NGC 7582 (Juneau+16
Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium. Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro
 Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro This course consists of three components: Lectures Exercises Seminar [Wed., 2-4] [Thu., 4-5]
Physics and chemistry of the interstellar medium Lecturers: Simon Glover, Rowan Smith Tutor: Raquel Chicharro This course consists of three components: Lectures Exercises Seminar [Wed., 2-4] [Thu., 4-5]
molecular cloud and a
 A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations
 Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light! ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light! ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G.
 Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G. Dumas, E. Schinnerer (MPIA), J. M. Mazzarella, J. H.
Junfeng Wang, G. Fabbiano, G. Risaliti, M. Elvis, M. Karovska, A. Zezas (Harvard CfA/SAO), C. G. Mundell (Liverpool John Moores University, UK), G. Dumas, E. Schinnerer (MPIA), J. M. Mazzarella, J. H.
Understanding Submillimetre Galaxies: Lessons from Low Redshifts
 #SMG20 Durham 2017 Understanding Submillimetre Galaxies: Lessons from Low Redshifts Paul van der Werf Leiden: Marissa Rosenberg Rowin Meijerink Saskia van den Broek Edo Loenen Kirsty Butler Cardiff/ESO:Padelis
#SMG20 Durham 2017 Understanding Submillimetre Galaxies: Lessons from Low Redshifts Paul van der Werf Leiden: Marissa Rosenberg Rowin Meijerink Saskia van den Broek Edo Loenen Kirsty Butler Cardiff/ESO:Padelis
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy
 Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Halo Gas Velocities Using Multi-slit Spectroscopy Cat Wu Thesis Proposal, Fall 2009 Astronomy Department New Mexico State University Outline Diffuse ionized gas; galaxy halos Origin of halo galactic fountain
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM
 Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
Magnetic field structure from Planck polarization observations of the diffuse Galactic ISM François Boulanger Institut d Astrophysique Spatiale on behalf of the Planck Consortium Outline The Planck data
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies We observe star-gas-star cycle operating in Milky Way s disk using many different wavelengths of light Infrared light reveals stars whose visible light
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds
 Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
The Schmidt Law at Sixty. Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University
 The Schmidt Law at Sixty Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University Log (SFR surface density) Maarten Schmidt conjecture (1959, 1963): - volume/surface densities of star formation scale
The Schmidt Law at Sixty Robert Kennicutt University of Arizona Texas A&M University Log (SFR surface density) Maarten Schmidt conjecture (1959, 1963): - volume/surface densities of star formation scale
Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation
 Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Norm Murray, Jackson Debuhr, Phil Hopkins... Spitzer s view of Carina Outline Feedback: What is it good for? Absolutely
Feedback from Radiation Pressure during Galaxy Formation Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Norm Murray, Jackson Debuhr, Phil Hopkins... Spitzer s view of Carina Outline Feedback: What is it good for? Absolutely
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Galactic Neighborhood and (Chandra-enabled) X-ray Astrophysics
 Galactic Neighborhood and (Chandra-enabled) X-ray Astrophysics Q. Daniel Wang (University of Massachusetts) Frontier Science Galactic Neighborhood Panel Members: Leo Blitz, Julianne Dalcanton, Bruce Draine,
Galactic Neighborhood and (Chandra-enabled) X-ray Astrophysics Q. Daniel Wang (University of Massachusetts) Frontier Science Galactic Neighborhood Panel Members: Leo Blitz, Julianne Dalcanton, Bruce Draine,
C+ and Methylidyne CH+ Mapping with HIFI
 C and H Reactives in Orion KL C+ and Methylidyne CH+ Mapping with HIFI Pat Morris, NHSC (IPAC/Caltech) J. Pearson, D. Lis, T. Phillips and the HEXOS team and HIFI Calibration team Outline Orion KL nebula
C and H Reactives in Orion KL C+ and Methylidyne CH+ Mapping with HIFI Pat Morris, NHSC (IPAC/Caltech) J. Pearson, D. Lis, T. Phillips and the HEXOS team and HIFI Calibration team Outline Orion KL nebula
Observations of jet dissipation. Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford)
 Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA
 Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
Magnetic Fields in Evolving Spiral Galaxies and their Observation with the SKA Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn & SKA Science Working Group Fundamental magnetic questions When and how were the first fields generated?
II- Molecular clouds
 2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
2. II- Molecular clouds 3. Introduction 4. Observations of MC Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 218 / 290 3. Introduction 3. Introduction Pierre Hily-Blant (Master2) The ISM 2012-2013 219 /
Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure
 Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory
Dissipation Scales & Small Scale Structure Ellen Zweibel zweibel@astro.wisc.edu Departments of Astronomy & Physics University of Wisconsin, Madison and Center for Magnetic Self-Organization in Laboratory
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau
 Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
Orianne ROOS CEA-Saclay Collaborators : F. Bournaud, J. Gabor, S. Juneau Bachelor of Physics, Master of Astrophysics Université de Strasbourg PhD, Université Paris-Diderot Observatoire de Strasbourg Les
The importance of galactic fountain in galaxy evolution
 The importance of galactic fountain in galaxy evolution Federico Marinacci in collaboration with: L. Armillotta, A. Marasco, F. Fraternali, J. Binney, L. Ciotti & C. Nipoti Sydney, 4 November 214 Galactic
The importance of galactic fountain in galaxy evolution Federico Marinacci in collaboration with: L. Armillotta, A. Marasco, F. Fraternali, J. Binney, L. Ciotti & C. Nipoti Sydney, 4 November 214 Galactic
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3
 Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Enrico Fermi School Varenna Cool Cores and Mergers in Clusters Lecture 3 Craig Sarazin Dept. of Astronomy University of Virginia A85 Chandra (X-ray) Cluster Merger Simulation Cool Cores in Clusters Central
Hydra A (x-ray) Perseus ` (optical)
 The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
The Biermann Lectures: Adventures in Theoretical Astrophysics I: The Physics of Galaxy Cluster Plasmas Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Mike McCourt, Ian Parrish, Prateek Sharma Perseus ` (optical) Hydra
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
The Magnetic Field of GMCs. Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona)
 The Magnetic Field of GMCs Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona) Two different views of the magnetic field in MCs: 1. The old view (Shu et al. 1987) Strong mean
The Magnetic Field of GMCs Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona) Two different views of the magnetic field in MCs: 1. The old view (Shu et al. 1987) Strong mean
Observational Evidence of AGN Feedback
 10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
10 de maio de 2012 Sumário Introduction AGN winds Galaxy outflows From the peak to the late evolution of AGN and quasars Mergers or secular evolution? The AGN feedback The interaction process between the
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18)
 The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
The Interaction of Jets with the Interstellar Medium of Radio Galaxies
 The Interaction of Jets with the Interstellar Medium of Radio Galaxies Geoff Bicknell, Ralph Sutherland, Vicky Safouris Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Australian National University Ravi Subrahmanyan,
The Interaction of Jets with the Interstellar Medium of Radio Galaxies Geoff Bicknell, Ralph Sutherland, Vicky Safouris Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics Australian National University Ravi Subrahmanyan,
Lecture 18 - Photon Dominated Regions
 Lecture 18 - Photon Dominated Regions 1. What is a PDR? 2. Physical and Chemical Concepts 3. Molecules in Diffuse Clouds 4. Galactic and Extragalactic PDRs References Tielens, Ch. 9 Hollenbach & Tielens,
Lecture 18 - Photon Dominated Regions 1. What is a PDR? 2. Physical and Chemical Concepts 3. Molecules in Diffuse Clouds 4. Galactic and Extragalactic PDRs References Tielens, Ch. 9 Hollenbach & Tielens,
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies. Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
 X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
HI clouds near the Galactic Center:
 PHISCC 217 February 7th, Pune HI clouds near the Galactic Center: Possible tracers for a Milky-Way nuclear wind? Enrico Di Teodoro Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics Australian National University
PHISCC 217 February 7th, Pune HI clouds near the Galactic Center: Possible tracers for a Milky-Way nuclear wind? Enrico Di Teodoro Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics Australian National University
Interstellar shocks:! The contribution of SOFIA/GREAT!
 1! Interstellar shocks:! The contribution of SOFIA/GREAT! Antoine Gusdorf,!!!!!! LERMA, Paris, France! Claudio Codella,!!!!!!!!!!INAF Firenze, Italy! Rolf Güsten,!!!!!!!!! MPIfR, Bonn, Germany! Sibylle
1! Interstellar shocks:! The contribution of SOFIA/GREAT! Antoine Gusdorf,!!!!!! LERMA, Paris, France! Claudio Codella,!!!!!!!!!!INAF Firenze, Italy! Rolf Güsten,!!!!!!!!! MPIfR, Bonn, Germany! Sibylle
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars. Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004
 Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Probing the End of Dark Ages with High-redshift Quasars Xiaohui Fan University of Arizona Dec 14, 2004 High-redshift Quasars and the End of Cosmic Dark Ages Existence of SBHs at the end of Dark Ages BH
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring
 Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
The Evolution of Spiral Galaxies in a Cluster Environment
 The Evolution of Spiral Galaxies in a Cluster Environment ESA/ESAC, XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre In collaboration with: M. Weżgowiec 1,2, R.-J. Dettmar 1, B. Vollmer 3, M. Soida 2, K.T. Chyży 2,
The Evolution of Spiral Galaxies in a Cluster Environment ESA/ESAC, XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre In collaboration with: M. Weżgowiec 1,2, R.-J. Dettmar 1, B. Vollmer 3, M. Soida 2, K.T. Chyży 2,
Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations. Hugo Martel Université Laval
 Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations Hugo Martel Université Laval Leiden, June 19, 2013 GALACTIC OUTFLOWS Optical image of galaxy (Hubble Space Telescope)
Implementing sub-grid treatments of galactic outflows into cosmological simulations Hugo Martel Université Laval Leiden, June 19, 2013 GALACTIC OUTFLOWS Optical image of galaxy (Hubble Space Telescope)
THE INFLUENCE OF MAGNETIC FIELD ON THE CNM MASS FRACTION AND ITS ALIGNMENT WITH DENSITY STRUCTURES.
 THE INFLUENCE OF MAGNETIC FIELD ON THE CNM MASS FRACTION AND ITS ALIGNMENT WITH DENSITY STRUCTURES. MARCO A. VILLAGRAN* Colaborator: Adriana Gazol *m.villagran@irya.unam.mx INTRODUCTION: CNM MASS FRACTION
THE INFLUENCE OF MAGNETIC FIELD ON THE CNM MASS FRACTION AND ITS ALIGNMENT WITH DENSITY STRUCTURES. MARCO A. VILLAGRAN* Colaborator: Adriana Gazol *m.villagran@irya.unam.mx INTRODUCTION: CNM MASS FRACTION
4/6/17. SEMI-WARM stuff: dust. Tour of Galaxies. Our Schedule
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Super-bubble blowout in NGC 3709 Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 22 Thur 6 Apr 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Tour of Galaxies Look at complex
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations. simulations of galaxy and structure formation
 Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Cosmic ray feedback in hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy and structure formation Canadian Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics, Toronto April, 13 26 / Workshop Dark halos, UBC Vancouver Outline 1
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters
 Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
Magnetic Fields (and Turbulence) in Galaxy Clusters Dongsu Ryu (UNIST, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Korea) with Hyesung Kang (Pusan Nat. U, Korea), Jungyeon Cho (Chungnam Nat. U.),
The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations
 The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations Alex S. Hill University of Wisconsin-Madison Collaborators: Robert A. Benjamin, Grzegorz Kowal, Ronald J. Reynolds, L. Matthew Haffner, Alex Lazarian
The Turbulent WIM: Distribution and MHD Simulations Alex S. Hill University of Wisconsin-Madison Collaborators: Robert A. Benjamin, Grzegorz Kowal, Ronald J. Reynolds, L. Matthew Haffner, Alex Lazarian
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe
 Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
