! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm
|
|
|
- Alban Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm M
4 ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)?! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud? dn /dm M
5 ! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud?! Do they form in a single cluster (monolitically) or from the coalescence of sub-clusters?! what is the fraction of stars that are in binary/triple/multiple systems?
6 Final value of the SFE In real observations SFE in a molecular cloud SFE(t) " SFE f = [SFE(t exp ),1] " SFE f " M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) # % % $ M ( cluster t ) exp M ( gas,initial +M gas,acc t ),1 exp # M & % cluster ( " [0.01 ) 0.5] $ M gas,present + M cluster ' & ( ( ' Lada & Lada (2003)
7 Molecular Cloud Properties ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ M~ M! R ~10-30 parsecs T ~10-30 K, c s ~ km s -1 Number densities n ~100 cm -3 Ma=!/c s ~ 5-10 B ~ Gauss Free-fall time: t ff ~(3 "/32 G #) 1/2 =(3 " N A / 32 G µ n) 1/2 ~1-5*10 6 yrs t cr ~R/!~5*10 6 yrs
8 The Star Formation Paradigm ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ The star formation rate: SFR = SFE M H 2 # % $ " SF Mass of molecular hydrogen in the Galaxy (CO map converted to H 2 ): M H 2 = 2 "10 9 M sol & ( ' Dame et al. (1987, 2001) If : " SF # " ff then SFR "1000M sol yr #1 or SFR "10 #100M sol yr #1 with SFE " 0.01 # 0.1 Observations, from counting protostars (with the Spitzer space telescope) indicate that the Galactic value is SFR "1.5M sol yr #1 Robitaille & Whitney (2010)
9 The Star Formation Paradigm ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Galactic SFR value is SFR "1.5M sol This implies that molecular clouds are long lived " SF # 20" ff And that the SFE is low ~0.01 It also implies that turbulence in the clouds must be replenished. What What What controls stabilizes processes the the low the drive clouds galactic the star star against formation turbulence gravitational rates in & the efficiencies clouds? collapse??
10 Supersonic Turbulence? Galactic differential Gravity rotation? Stellar Feedback? Magnetic Fields?
11 The role of supersonic turbulence ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Supersonic in molecular clouds Possesses a certain injection scale, (or a multitude of them) Decays on a crossing time Cascades towards smaller scales following a given power spectrum Main Consequences * without gravity: generates the a lognormal distrubution of the density field. In the presence of gravity: lognormal + power at the high density end * Localized star formation sites in the overdensities in which t ff,local << t ff,cloud
12 The role of supersonic turbulence ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Simulations 3D grids: 256 3, 512 3, resolutions Periodic boundary conditions MHD, Isothermal self-gravity driven turbulence (or decaying) on large scales (perturbation with wav numbers in the range k=1-2) Ma= 10, J=L 0 /L J =4 Vazquez-Semadeni et al. (2005), Dib et al. (2007,2008) L 0 = 4pc, n 0 = 500 cm -3, T=11.4 K, c s =0.2 km s -1
13 The role of supersonic turbulence ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ PDF of density field: Isothermal gas PDF of density field: multiphase gas Dib Kritsuk & Burkert et al
14 The role of supersonic turbulence ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ SFE dependence on the turbulence properties Jeans Mass M J " c s 3 n # 1 2 Turbulent Jeans mass 3 M J " c s,eff n # 1 2 with 2 c s,eff = c s 2 + "2 3 Klessen et al. 2000
15 Influence of the magnetic fields Mass-to magnetic flux ratio µc= (M/!)c/ (M/!)cr!c=" Bm Rc 2 Bm is the the Mean Magnetic field µc < 1 : magnetic support, µc > 1 no magnetic support. We used µc=0.9 (B=4.5 microg), 2.8 (B=14.5 microg), 8.8 (B=45 microg)
16 Influence of the magnetic fields µ c = 8.8 CFE ff = 0.33 Dib et al µ c = 2.8 CFE ff = 0.06
17 Influence of the magnetic fields Price & Bate 2008
18 Influence of Stellar Feedback Effects of feedback on the clouds evolution Injects energy and momentum into the cloud Re-distributes matter in the cloud Maintains the turbulence Heats the gas " change the Jeans mass Eventually disperses the gas and destroys the clouds
19 Influence of Stellar Feedback Effects of protostellar outflows Wang et al Li & Nakamura 2007
20 Influence of Stellar Feedback Feedback from massive stars Ionization and heating of the gas Stellar winds Dale & Bonnell 2008 Dale et al 2005
21 Influence of Stellar Feedback A semi-analytical model for feedback from massive stars Protocluster forming molecular cloud Mass~ M sol time
22 Influence of Stellar Feedback Feedback model: Stellar Winds Stellar mass loss rate Terminal wind velocity " $ # dm dt v " % ' & ( Energy cumulated in winds E wind = t " =t * t " =0 $ 2 N(m)(dM /dt) " (m)v # ' * & dm) dt " % 2 ( m =80M sol m =5M sol Fraction of wind energy that counters gravity E k,wind = "E wind k <1
23 Power of stellar wind - Calculate main sequence models of OB stars (! 5 M! ) (using CESAM) - (T eff, L *, R * ) # Stellar atmosphere model (Vink et al.) # Ṁ Ṁ v " 2 Dib et al. 2011
24 Influence of Stellar Feedback Gas expulsion Dib et al. 2011,2013
25 Influence of Stellar Feedback Comparison to observations: massive clusters Dib et al. (2013)
26 Influence of Stellar Feedback Dependence on metallicity: Galactic SFEs Dib et al. (2011)
27 Influence of Shear results from numerical simulations Models of clouds with similar masses (10 6 M sol ), sizes (50 pc), but different angular velocities. Increasing shear Weidner et al. (2010)
28 Influence of Shear Correlation between shear and the distribution of molecular clouds and stars Galaxies have differential rotation " shear Application to HI gas Critial surface density beyong which shear is inefficient " gravity wins This defines a shear parameter S = " cr " = # A$ A %G" with A = " 1 2 R d# dr = " 1 2 Gas is supported by shear if S>1 $ & % V R " dv ' ) dr ( Elson et al. (2012)
29 Influence of Shear Is shear (really) regulating the SFE on cloud scales? Data from the Galactic Ring Survey ( 13 CO 1-0 line) masses [ ] M sol, sizes [0.5-70] pc Roman-Duval et al. (2012)
30 Influence of Shear Is shear (really) regulating the SFE on cloud scales? Measuring the shear parameter on molecular cloud scales Dib et al. (2012)
31 Influence of Shear Is shear (really) regulating the SFE on cloud scales? correlation between S and the YSOs Luminosities (RMS survey) L bol M " SFE Dib et al. (2012)
32 Conclusions! The SFE in Giant Molecular clouds: ~ 1-10 %! In protocluster forming regions: ~ 5-70 %! Many processus participate & eventually compete in setting the SFE in molecular clouds! magnetic fields:! turbulence:! stellar feedback! shear: X * Effet of external disruptions/compressions/triggering (e.g., interaction with a shock, cloud-cloud collisions, tidal effects)
33 !,- )*+& '( #$%&!"
SFEs in clusters. Final value of the SFE. For an isolated clump SFE exp. (t exp. = SFE(t exp. M ( cluster. t ) exp M clump. (t) M gas,i.
 SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
SFEs in clusters. Final value of the SFE. For an isolated clump SFE exp. (t exp. = SFE(t exp. M ( cluster. t ) exp M clump. (t) M gas,i.
 SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
SFEs in clusters SFE(t) Final value of the SFE M cluster (t) M gas,i + M gas,acc (t) SFE exp = SFE(t exp ) M cluster (t exp ) M gas,i + M gas,acc ( t ) exp For an isolated clump SFE exp M ( cluster t )
Fundamental Issues in Star Formation
 Fundamental Issues in Star Formation - Formation and statistical properties of dense molecular cloud cores (mass function of cores, scaling relations, gravitational boundedness, rotational properties)
Fundamental Issues in Star Formation - Formation and statistical properties of dense molecular cloud cores (mass function of cores, scaling relations, gravitational boundedness, rotational properties)
The Formation of Star Clusters
 The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
The Formation of Star Clusters Orion Nebula Cluster (JHK) - McCaughrean Jonathan Tan University of Florida & KITP In collaboration with: Brent Buckalew (ERAU), Michael Butler (UF u-grad), Jayce Dowell
An overview of star formation
 An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm
 Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm Shantanu Basu The University of Western Ontario Collaborators: Glenn Ciolek (RPI), Takahiro Kudoh (NAOJ), Wolf Dapp,
Molecular Cloud Support, Turbulence, and Star Formation in the Magnetic Field Paradigm Shantanu Basu The University of Western Ontario Collaborators: Glenn Ciolek (RPI), Takahiro Kudoh (NAOJ), Wolf Dapp,
The Competitive Accretion Debate
 The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs. Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics
 Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics Outline Turbulence inhibits star formation, but slowly Interplay between turbulence
Turbulence, kinematics & galaxy structure in star formation in dwarfs Mordecai-Mark Mac Low Department of Astrophysics Outline Turbulence inhibits star formation, but slowly Interplay between turbulence
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation
 The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
The Effects of Radiative Transfer on Low-Mass Star Formation Stella Offner NSF Fellow, ITC Dense Cores in Dark Clouds Oct 23 2009 Collaborators: Chris McKee (UC Berkeley), Richard Klein (UC Berkeley; LLNL),
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation
 Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni. Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México
 Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Collaborators: CRyA UNAM: Abroad: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Pedro Colín Gilberto Gómez Recent PhDs: Alejandro González
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Collaborators: CRyA UNAM: Abroad: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Pedro Colín Gilberto Gómez Recent PhDs: Alejandro González
ISM Structure: Order from Chaos
 ISM Structure: Order from Chaos Philip Hopkins with Eliot Quataert, Norm Murray, Lars Hernquist, Dusan Keres, Todd Thompson, Desika Narayanan, Dan Kasen, T. J. Cox, Chris Hayward, Kevin Bundy, & more The
ISM Structure: Order from Chaos Philip Hopkins with Eliot Quataert, Norm Murray, Lars Hernquist, Dusan Keres, Todd Thompson, Desika Narayanan, Dan Kasen, T. J. Cox, Chris Hayward, Kevin Bundy, & more The
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^
 Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Galaxy Simulators Star Formation for Dummies ^ Mark Krumholz UC Santa Cruz HIPACC Summer School August 6, 2010 The Challenge of Star Formation ~10 pc ~10 pc ~10 pc Like stars, star formation involves impossibly
Observational Programme in Kent
 Observational Programme in Kent ASTRO-F, WFCAM, SCUBA-2, SALT UKIRT: individual protostellar outflows SAO/MMT/LBT: individual high- mass protostars NTT/Calar Alto + SEST: rho Ophiuchus 2MASS/NTT: Rosette
Observational Programme in Kent ASTRO-F, WFCAM, SCUBA-2, SALT UKIRT: individual protostellar outflows SAO/MMT/LBT: individual high- mass protostars NTT/Calar Alto + SEST: rho Ophiuchus 2MASS/NTT: Rosette
The Initial Mass Function Elisa Chisari
 The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
The Initial Mass Function AST 541 Dec 4 2012 Outline The form of the IMF Summary of observations Ingredients of a complete model A Press Schechter model Numerical simulations Conclusions The form of the
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Star Formation In this lecture we discuss the formation of stars. After describing the structure
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 16: Star Formation Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Star Formation In this lecture we discuss the formation of stars. After describing the structure
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds
 Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
Lec 22 Physical Properties of Molecular Clouds 1. Giant Molecular Clouds 2. Orion s Clouds 3. Correlations of Observed Properties 4. The X-Factor References Origins of Stars & Planetary Systems eds. Lada
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
 The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
The dependence of star cluster formation on initial conditions Matthew Bate University of Exeter Stellar properties do not greatly depend on initial conditions constellation Little evidence for variation
Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations
 Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations Robi Banerjee Hamburg University Collaborators: Thomas Peters (Zurich), Daniel Seifried (Hamburg), Philipp Girichidis (MPA), Roberto Galvan-Madrid (UNAM,
Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations Robi Banerjee Hamburg University Collaborators: Thomas Peters (Zurich), Daniel Seifried (Hamburg), Philipp Girichidis (MPA), Roberto Galvan-Madrid (UNAM,
Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation
 Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation Robi Banerjee 1, @ 1 : Hamburg Sternewarte, University of Hamburg Gojenbergsweg 112 21209 Hamburg - Germany Jets and outflows are
Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation Robi Banerjee 1, @ 1 : Hamburg Sternewarte, University of Hamburg Gojenbergsweg 112 21209 Hamburg - Germany Jets and outflows are
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise
 Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
Early Stages of (Low-Mass) Star Formation: The ALMA Promise Philippe André, CEA/SAp Saclay Outline Introduction: Prestellar cores and the origin of the IMF Identifying proto-brown dwarfs Bate et al. 1995
A shocking group! Turbulent dissipation and star formation in Stephan s Quintet
 Physics of Groups, IAP, Dec 12-15 A shocking group! Turbulent dissipation and star formation in Stephan s Quintet Pierre Guillard, P. Appleton, F. Boulanger, M. Cluver, P. Lesaffre, G. Pineau des Forêts,
Physics of Groups, IAP, Dec 12-15 A shocking group! Turbulent dissipation and star formation in Stephan s Quintet Pierre Guillard, P. Appleton, F. Boulanger, M. Cluver, P. Lesaffre, G. Pineau des Forêts,
The role of magnetic fields during massive star formation
 The role of magnetic fields during massive star formation Wouter Vlemmings Chalmers University of Technology / Onsala Space Observatory / Nordic ALMA Regional Center with: Gabriele Surcis, Kalle Torstensson,
The role of magnetic fields during massive star formation Wouter Vlemmings Chalmers University of Technology / Onsala Space Observatory / Nordic ALMA Regional Center with: Gabriele Surcis, Kalle Torstensson,
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni. Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México
 Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 2 Collaborators: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes
Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 1 Javier Ballesteros-Paredes Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México 2 Collaborators: Javier Ballesteros-Paredes
Accretion Mechanisms
 Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
Massive Protostars Accretion Mechanism Debate Protostellar Evolution: - Radiative stability - Deuterium shell burning - Contraction and Hydrogen Ignition Stahler & Palla (2004): Section 11.4 Accretion
Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation
 Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation Javier Ballesteros-Paredes1, Ralf Klessen2, MordecaiMark Mac Low3, Enrique Vazquez-Semadeni1 1UNAM Morelia, Mexico, 2AIP, Potsdam, Germany, 3AMNH New York,
Molecular Cloud Turbulence and Star Formation Javier Ballesteros-Paredes1, Ralf Klessen2, MordecaiMark Mac Low3, Enrique Vazquez-Semadeni1 1UNAM Morelia, Mexico, 2AIP, Potsdam, Germany, 3AMNH New York,
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG)
 SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
SAM GEEN (ITA/ZAH HEIDELBERG) WITH PATRICK HENNEBELLE JUAN SOLER AND RALF KLESSEN Credit: Lost Valley Observatory Star formation is self regulating HII HII regions, regions, supernovae supernovae Molecular
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay)
 Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Formation of massive stars: a review
 Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
Star Cluster Formation
 Star Cluster Formation HST Colin Hill Princeton Astrophysics 4 December 2012 Trapezium VLT Outline Star Clusters: Background + Observations The Life of a Cluster - Fragmentation - Feedback Effects - Mass
Star Cluster Formation HST Colin Hill Princeton Astrophysics 4 December 2012 Trapezium VLT Outline Star Clusters: Background + Observations The Life of a Cluster - Fragmentation - Feedback Effects - Mass
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies?
 Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
molecular cloud and a
 A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
A molecular cloud and a Stop me if you ve heard this one before star cluster walk into a bar... Florent Renaud Lund Observatory with E. Emsellem, N. Guillard et al. A complex scale-coupling environment
Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds 1. Stability of Cloud Cores 2. Collapse and Fragmentation of Clouds 3. Applying the Virial Theorem References Myers, Physical Conditions in Molecular Clouds in
Lecture 22 Stability of Molecular Clouds 1. Stability of Cloud Cores 2. Collapse and Fragmentation of Clouds 3. Applying the Virial Theorem References Myers, Physical Conditions in Molecular Clouds in
Widespread star formation throughout the Galactic center cloud Sgr B2
 Widespread star formation throughout the Galactic center cloud Sgr B2 and its implications for SF theory Adam Ginsburg Adam Ginsburg, 1, 2 John Bally, 3 Ashley Barnes, 4 Nate Bastian, 4 Cara Battersby,
Widespread star formation throughout the Galactic center cloud Sgr B2 and its implications for SF theory Adam Ginsburg Adam Ginsburg, 1, 2 John Bally, 3 Ashley Barnes, 4 Nate Bastian, 4 Cara Battersby,
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview. Ulrike Kuchner
 STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
STAR FORMATION RATES observational overview Ulrike Kuchner Remember, remember.. Outline! measurements of SFRs: - techniques to see what the SF rate is - importance of massive stars and HII regions - the
From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective
 From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective NRAO Filaments. Oct. 10-11, 2014 Ralph E. Pudritz Origins Institute, McMaster U. Collaborators McMaster: Mikhail Klassen, Corey Howard, (Ph.D.s) Helen
From Filaments to Stars: a Theoretical Perspective NRAO Filaments. Oct. 10-11, 2014 Ralph E. Pudritz Origins Institute, McMaster U. Collaborators McMaster: Mikhail Klassen, Corey Howard, (Ph.D.s) Helen
The Magnetic Field of GMCs. Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona)
 The Magnetic Field of GMCs Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona) Two different views of the magnetic field in MCs: 1. The old view (Shu et al. 1987) Strong mean
The Magnetic Field of GMCs Paolo Padoan (ICREA & Institute of Cosmos Sciences - University of Barcelona) Two different views of the magnetic field in MCs: 1. The old view (Shu et al. 1987) Strong mean
Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved
 Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Outline Stellar Populations: Resolved vs. unresolved Individual stars can be analyzed Applicable for Milky Way star clusters and the most nearby galaxies Integrated spectroscopy / photometry only The most
Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) Coordinated by Frédérique Motte, Annie Zavagno, and Sylvain Bontemps
 Cloud structure and high-mass star formation in HOBYS, the Herschel imaging survey of OB Young Stellar objects Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) http://hobys-herschel.cea.fr
Cloud structure and high-mass star formation in HOBYS, the Herschel imaging survey of OB Young Stellar objects Frédérique Motte and Nicola Schneider (AIM Paris-Saclay, Obs. Bordeaux) http://hobys-herschel.cea.fr
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds. Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame
 Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
Direct Evidence for Two Fluid Effects in Molecular Clouds Dinshaw Balsara & David Tilley University of Notre Dame 1 Outline Introduction earliest stages of star formation Theoretical background Magnetically
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales
 Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
Star Formation in Disk Galaxies: From Kiloparsec to Giant Molecular Cloud Scales Suzanne N. Shaske1 and Dr. Jonathan C. Tan2 1 2 Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Florida Departments of
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
igure 4 of McMullin et al McMullin et al Testi & Sargent 1998 Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998:
 igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
igure 4 of McMullin et al. 1994. Figure 1 of Testi & Sargent 1998: McMullin et al. 1994 BIMA with (only!) three elements Eight configurationsàcoverage of 2 kλ to 30 kλ Naturally wtd. Beam of 11" x 6" (for
Where do Stars Form?
 Where do Stars Form? Coldest spots in the galaxy: T ~ 10 K Composition: Mainly molecular hydrogen 1% dust EGGs = Evaporating Gaseous Globules ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1995/95-190.txt Slide
Where do Stars Form? Coldest spots in the galaxy: T ~ 10 K Composition: Mainly molecular hydrogen 1% dust EGGs = Evaporating Gaseous Globules ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/pressrel/1995/95-190.txt Slide
Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud
 Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Origin of high-mass protostars in Cygnus-X
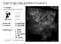 T. Csengeri Service d Astrophysique, CEA-Saclay Supervisor: Co-advisor: Collaborators: S. Bontemps N. Schneider F. Motte F. Gueth P. Hennebelle S. Dib Ph. André 7. April 2010 - From stars to Galaxies,
T. Csengeri Service d Astrophysique, CEA-Saclay Supervisor: Co-advisor: Collaborators: S. Bontemps N. Schneider F. Motte F. Gueth P. Hennebelle S. Dib Ph. André 7. April 2010 - From stars to Galaxies,
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties. Matthew Bate University of Exeter
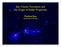 Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
Star Cluster Formation and the Origin of Stellar Properties Matthew Bate University of Exeter Typical molecular cloud (Bate et al. 2003) Denser cloud (Bate & Bonnell 2005) Jeans mass 1 M, Opacity limit
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Sep 2013 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 30 Sep 2013](/thumbs/78/78646713.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2009) Printed 1 October 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Feedback-regulated star formation: II. dual constraints on the SFE and the age spread of stars in massive clusters
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2009) Printed 1 October 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Feedback-regulated star formation: II. dual constraints on the SFE and the age spread of stars in massive clusters
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 5 Jun 2008](/thumbs/75/72265232.jpg) Draft version December 15, 2017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 08/13/06 DRIVEN AND DECAYING TURBULENCE SIMULATIONS OF LOW-MASS STAR FORMATION: FROM CLUMPS TO CORES TO PROTOSTARS Stella
Draft version December 15, 2017 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 08/13/06 DRIVEN AND DECAYING TURBULENCE SIMULATIONS OF LOW-MASS STAR FORMATION: FROM CLUMPS TO CORES TO PROTOSTARS Stella
Spiral Density waves initiate star formation
 Spiral Density waves initiate star formation A molecular cloud passing through the Sagittarius spiral arm Spiral arm Gas outflows from super supernova or O/B star winds Initiation of star formation Supernova
Spiral Density waves initiate star formation A molecular cloud passing through the Sagittarius spiral arm Spiral arm Gas outflows from super supernova or O/B star winds Initiation of star formation Supernova
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations
 Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Modelling star formation in galaxy formation simulations Vadim Semenov (U.Chicago) Andrey Kravtsov University of Chicago Carving through the codes Davos, Switzerland 16 February, 2017 Nick Gnedin (Fermilab)
Formation of massive stars : a review
 Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
Low mass star formation. Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...
 Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
Low mass star formation Mark Thompson (with contributions from Jennifer Hatchell, Derek Ward-Thompson, Jane Greaves, Larry Morgan...) The observational state of play Multiwavelength surveys are bringing
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 1 Apr 2008](/thumbs/71/65799928.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 3 December 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The star formation efficiency and its relation to variations in the initial mass function arxiv:0803.4053v2
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 3 December 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The star formation efficiency and its relation to variations in the initial mass function arxiv:0803.4053v2
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation
 Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
Superbubble Feedback in Galaxy Formation Ben Keller (McMaster University) James Wadsley, Samantha Benincasa, Hugh Couchman Paper: astro-ph/1405.2625 (Accepted MNRAS) Keller, Wadsley, Benincasa & Couchman
Old pre-main-sequence stars
 Old pre-main-sequence stars and a second chance for planet formation Peter Scicluna Uni Kiel & ESO, Garching 9th September 2014 Giovanni Rosotti (MPE, USM, IoA) Leonardo Testi (ESO, INAF) Jim Dale (Excellence
Old pre-main-sequence stars and a second chance for planet formation Peter Scicluna Uni Kiel & ESO, Garching 9th September 2014 Giovanni Rosotti (MPE, USM, IoA) Leonardo Testi (ESO, INAF) Jim Dale (Excellence
An Evolutionary Model of Massive Star Formation and Radiation Transfer
 An Evolutionary Model of Massive Star Formation and Radiation Transfer Yichen Zhang Universidad de Chile Collaborators: Jonathan Tan (UF), Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley), Takashi Hosokawa (U. Tokyo),
An Evolutionary Model of Massive Star Formation and Radiation Transfer Yichen Zhang Universidad de Chile Collaborators: Jonathan Tan (UF), Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley), Takashi Hosokawa (U. Tokyo),
The turbulent formation of stars
 The turbulent formation of stars Christoph Federrath Citation: Physics Today 71, 6, 38 (2018); doi: 10.1063/PT.3.3947 View online: https://doi.org/10.1063/pt.3.3947 View Table of Contents: http://physicstoday.scitation.org/toc/pto/71/6
The turbulent formation of stars Christoph Federrath Citation: Physics Today 71, 6, 38 (2018); doi: 10.1063/PT.3.3947 View online: https://doi.org/10.1063/pt.3.3947 View Table of Contents: http://physicstoday.scitation.org/toc/pto/71/6
Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring
 Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
Snow Cluster 2018 Suppressing the Cooling Flows in Massive Galaxies with Turbulent Stirring Kung-Yi Su TAPIR, California Institute of Technology Collaborators Prof. Philip F. Hopkins Chris Hayward Prof.
The nature of the velocity field in molecular clouds I. The non-magnetic case
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 390, 769 780 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13778.x The nature of the velocity field in molecular clouds I. The non-magnetic case Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni, 1 Ricardo F. González,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 390, 769 780 (2008) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13778.x The nature of the velocity field in molecular clouds I. The non-magnetic case Enrique Vázquez-Semadeni, 1 Ricardo F. González,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation. Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan)
 Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Recent Progress in Modeling of Galaxy Formation Oleg Gnedin (University of Michigan) In current simulations, galaxies look like this: 10 kpc Disk galaxy at z=3: stars, molecular gas, atomic gas (Zemp,
Star Formation and Protostars
 Stellar Objects: Star Formation and Protostars 1 Star Formation and Protostars 1 Preliminaries Objects on the way to become stars, but extract energy primarily from gravitational contraction are called
Stellar Objects: Star Formation and Protostars 1 Star Formation and Protostars 1 Preliminaries Objects on the way to become stars, but extract energy primarily from gravitational contraction are called
Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web
 Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web Andreas Burkert (University of Munich & MPE) Bigiel et al. Properties of the Hubble Sequence Halpha imaging surveys (galaxy assembly in the great wall) (Gavazzi+
Connecting Galaxy Formation to the Cosmic Web Andreas Burkert (University of Munich & MPE) Bigiel et al. Properties of the Hubble Sequence Halpha imaging surveys (galaxy assembly in the great wall) (Gavazzi+
Gravity or Turbulence?
 Gravity or Turbulence? On the dynamics of Molecular Clouds Javier Ballesteros-Paredes On Sabbatical at Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik, University of Heidelberg Instituto de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica,
Gravity or Turbulence? On the dynamics of Molecular Clouds Javier Ballesteros-Paredes On Sabbatical at Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik, University of Heidelberg Instituto de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica,
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation! Star Formation Efficiency!
 Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Theoretical ideas About Galaxy Wide Star Formation Theoretical predictions are that galaxy formation is most efficient near a mass of 10 12 M based on analyses of supernova feedback and gas cooling times
Sound. References: L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol. 2, Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8
 References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
References: Sound L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz: Fluid Mechanics, Chapter VIII F. Shu: The Physics of Astrophysics, Vol., Gas Dynamics, Chapter 8 1 Speed of sound The phenomenon of sound waves is one that
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS. η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith)
 THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee Institute for Astronomy November 2, 2011 with Andrew Cunningham Edith Falgarone Richard
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee Institute for Astronomy November 2, 2011 with Andrew Cunningham Edith Falgarone Richard
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 5 Oct 2016](/thumbs/80/82309556.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2016) Printed 6 October 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The roles of stellar feedback and galactic environment in star forming molecular clouds arxiv:1610.01371v1 [astro-ph.ga]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2016) Printed 6 October 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The roles of stellar feedback and galactic environment in star forming molecular clouds arxiv:1610.01371v1 [astro-ph.ga]
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas
 N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
N-body Dynamics in Stellar Clusters Embedded in Gas Matthew Bate, University of Exeter Kurosawa, Harries, Bate & Symington (2004) Collaborators: Ian Bonnell, St Andrews Volker Bromm, Texas Star Formation
Gravitational collapse of gas
 Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
Gravitational collapse of gas Assume a gas cloud of mass M and diameter D Sound speed for ideal gas is c s = γ P ρ = γ nkt ρ = γ kt m Time for sound wave to cross the cloud t sound = D == D m c s γ kt
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF. Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation. G.
 Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
Revealing and understanding the low-mass end of the IMF Low-mass part of the Initial Mass Function Star, brown dwarf formation G. Chabrier Field: Resolved objects IMF down to the HB limit Salpeter Kroupa
Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation
 Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation Gabriella De Lucia Astronomical Observatory of Trieste Outline: ü Observational properties of galaxies ü Galaxies and Cosmology ü Gas
Galaxy formation and evolution II. The physics of galaxy formation Gabriella De Lucia Astronomical Observatory of Trieste Outline: ü Observational properties of galaxies ü Galaxies and Cosmology ü Gas
Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind
 Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind Karel Schrijver July 3, 203 Stratification of a static atmosphere within a force-free magnetic field Problem: Write down the general MHD force-balance equation
Problem set: solar irradiance and solar wind Karel Schrijver July 3, 203 Stratification of a static atmosphere within a force-free magnetic field Problem: Write down the general MHD force-balance equation
Stellar structure and evolution. Pierre Hily-Blant April 25, IPAG
 Stellar structure and evolution Pierre Hily-Blant 2017-18 April 25, 2018 IPAG pierre.hily-blant@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr, OSUG-D/306 10 Protostars and Pre-Main-Sequence Stars 10.1. Introduction 10 Protostars
Stellar structure and evolution Pierre Hily-Blant 2017-18 April 25, 2018 IPAG pierre.hily-blant@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr, OSUG-D/306 10 Protostars and Pre-Main-Sequence Stars 10.1. Introduction 10 Protostars
!"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+! #"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;<(&"-+
 !"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+!3444+567+ 18#"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;
!"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+!3444+567+ 18#"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;
The First Stars. Simone Ferraro Princeton University. Sept 25, 2012
 The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
The First Stars Simone Ferraro Princeton University Sept 25, 2012 Outline Star forming minihalos at high z Cooling physics and chemistry Gravitational Collapse and formation of protostar Magnetic fields
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation?
 What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
What Doesn t Quench Galaxy Formation? Phil Hopkins Dusan Keres, Claude Faucher-Giguere, Jose Onorbe, Freeke van de Voort, Sasha Muratov, Xiangcheng Ma, Lena Murchikova, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, James
The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars
 Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars Daniel J. Price and Matthew R. Bate c Springer-Verlag
Astrophysics and Space Science DOI 10.1007/sXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-X The effect of magnetic fields on the formation of circumstellar discs around young stars Daniel J. Price and Matthew R. Bate c Springer-Verlag
coronal gas (10 6 K)! high T radiates inefficiently (no ion states, only free-free)!! once gas is hot, stays hot for 10 6 yrs!
 Global Models of ISM! relationship between phases of ISM! phases of ISM : HII : 10 4, 10 6 K! HI : 100, 10 3 K! H 2 : 10 K!? s! 1) stationary or transient! e.g. is HI at 10 3 K, just HII cooling to 100K!
Global Models of ISM! relationship between phases of ISM! phases of ISM : HII : 10 4, 10 6 K! HI : 100, 10 3 K! H 2 : 10 K!? s! 1) stationary or transient! e.g. is HI at 10 3 K, just HII cooling to 100K!
Is the IMF a probability density distribution function or is star formation a self-regulated process?
 Is the IMF a probability density distribution function or is star formation a self-regulated process? Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg 25th of September 2015 Pavel Kroupa Helmholtz-Institut fuer
Is the IMF a probability density distribution function or is star formation a self-regulated process? Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg 25th of September 2015 Pavel Kroupa Helmholtz-Institut fuer
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS. η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith)
 THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS η Carina (NASA, ESA, N. Smith) THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STARS Christopher F. McKee HIPACC, UCSC August 8, 2013 with Andrew Cunningham Richard Klein Mark Krumholz Andrew Myers
Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation
 Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
Astrophysical Dynamics, VT 010 Gravitational Collapse and Star Formation Susanne Höfner Susanne.Hoefner@fysast.uu.se The Cosmic Matter Cycle Dense Clouds in the ISM Black Cloud Dense Clouds in the ISM
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The distribution of shock waves in driven supersonic turbulence
 Astron. Astrophys. 362, 333 341 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The distribution of shock waves in driven supersonic turbulence M.D. Smith 1, M.-M. Mac Low 2, and F. Heitsch 3 1 Armagh Observatory, College
Astron. Astrophys. 362, 333 341 (2000) ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS The distribution of shock waves in driven supersonic turbulence M.D. Smith 1, M.-M. Mac Low 2, and F. Heitsch 3 1 Armagh Observatory, College
The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds
 The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of Barcelona Christoph Federrath Monash University Gilles Chabrier Ecole Normale Suprieure de Lyon Neal J. Evans II The University of
The Star Formation Rate of Molecular Clouds Paolo Padoan University of Barcelona Christoph Federrath Monash University Gilles Chabrier Ecole Normale Suprieure de Lyon Neal J. Evans II The University of
Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM
 Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM Dieter Breitschwerdt Collaborators Miguel de Avillez (Evora, Portugal) Verena Baumgartner (Vienna, Austria) Jan Bolte (TU Berlin, Germany) Jenny
Detailed Study of a Turbulent multiphase multicomponent ISM Dieter Breitschwerdt Collaborators Miguel de Avillez (Evora, Portugal) Verena Baumgartner (Vienna, Austria) Jan Bolte (TU Berlin, Germany) Jenny
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Mar 2006
 The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam arxiv:astro-ph/0603447v1 17 Mar 2006
The Origin of the Initial Mass Function Ian A. Bonnell University of St Andrews Richard B. Larson Yale University Hans Zinnecker Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam arxiv:astro-ph/0603447v1 17 Mar 2006
THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS
 THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS Diego Falceta-Gonçalves, Marcelo C. de Juli & Vera Jatenco-Pereira Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e C. Atmosféricas Universidade
THE ROLE OF DUST-CYCLOTRON DAMPING OF ALFVÉN WAVES IN STAR FORMATION REGIONS Diego Falceta-Gonçalves, Marcelo C. de Juli & Vera Jatenco-Pereira Instituto de Astronomia, Geofísica e C. Atmosféricas Universidade
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Oct 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 29 Oct 2008](/thumbs/80/81600070.jpg) STAR FORMATION TRIGGERED BY SNR 1 STAR FORMATION TRIGGERED BY SNR IMPACT INTO MAGNETIZED NEUTRAL CLOUDS M. R. M. Leão, 1,5 E. M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, 1,6 D. Falceta-Gonçalves, 2,3,7 C. Melioli, 4,8 F.
STAR FORMATION TRIGGERED BY SNR 1 STAR FORMATION TRIGGERED BY SNR IMPACT INTO MAGNETIZED NEUTRAL CLOUDS M. R. M. Leão, 1,5 E. M. de Gouveia Dal Pino, 1,6 D. Falceta-Gonçalves, 2,3,7 C. Melioli, 4,8 F.
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO
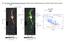 21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
21. The Green Bank Ammonia Survey: Dense Cores Under Pressure in Orion A Kirk+ ApJ in press GAS Herschel YSO Spitzer YSO JCMT prestellar core prestellar core JCMT protostellar core protostellar core surface
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION
 MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
Turbulence simulations with ENZO and FLASH3
 Turbulence simulations with ENZO and FLASH3... not yet Adaptive-mesh simulations with FLASH Christoph Federrath Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics Heidelberg Collaborators: Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee,
Turbulence simulations with ENZO and FLASH3... not yet Adaptive-mesh simulations with FLASH Christoph Federrath Institute for Theoretical Astrophysics Heidelberg Collaborators: Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee,
