The LHC beam collimation
|
|
|
- Egbert Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 39 th ICFA Advance Beam dynamics Workshop High Intensity High Brightness Hadron Beams - HB 2006 Tsukuba, May 29 th - June 2 nd, 2006 The LHC beam collimation Stefano Redaelli, AB department on behalf of the CERN LHC Collimation Project CERN, CH-1211 Geneva
2 LHC proton collimation people Project leader: R. Assmann (AB department) Synergy among many CERN departments: AB - TS - AT - SC People involved: O. Aberle, R. Assmann, I. Baishev, A. Bertarelli, C. Bracco, H. Braun, M. Brugger, S. Calatroni, E. Chiaveri, A. Dallocchio, F. Decorvet, B. Dehning, A. Ferrari, D. Forkel-Wirth, A. Grudiev, E.B. Holzer, J.B. Jeanneret, M. Jimenez, M. Jonker, Y. Kadi, V. Kain, M. Lamont, R. Losito, M. Magistris, A. Masi, M. Mayer, E. Métral, R. Perret, L. Ponce, C. Rathjen, S. Redaelli, G. Robert-Demolaize, S. Roesler, F. Ruggiero, M. Santana Leitner, L. Sarchiapone, R. Schmidt, D. Schulte, G. Spiezia, P. Sievers, M. Sobczak, K. Tsoulou, V. Vlachoudis, T. Weiler, J. Wenninger,... Inputs from many CERN working groups: Injection, protection, dump,... Additional support for beam tests: G. Arduini, T. Bohl, H. Burkhardt, F. Caspers, M. Gasior, B. Goddard, L. Jensen, R. Jones, T. Kroyer, R. Steinhagen, J. Uythoven, H. Vincke, F. Zimmermann Outside collaborations with TRIUMF (optics design - completed) IHEP (IR3 energy deposition studies) Kurchatov Institute (radiation effects on C-C jaws) SLAC, BNL, FNAL (phase 2 R&D, tertiary collimators and material studies) S. Redaelli, HB2006 2
3 Outline Introduction LHC collimation system layout Mechanical design of the collimator Achieved cleaning performance System limitations and upgrades Conclusions S. Redaelli, HB2006 3
4 Introduction x 200!! Eb = 7 TeV - Ib = 3.4x10 14 Stored energy ~ 2 x 360 MJ Quench limit ~ 10 mj / cm 3 Damage (metal) ~ 50 kj / mm 2 Cleaning Protection LHC enters in a new territory for handling ultra-intense beams in a super-conducting environment! Control losses 1000 time better than the state-of-the-art! Need collimation at all machine states: injection, ramp, squeeze, physics Important role in machine protection (no details here) S. Redaelli, HB2006 4
5 Some numbers High stored beam energy (melt 500 kg Cu, required for cm -2 s -1 luminosity) ~ 360 MJ/beam Large transverse energy density (beam is destructive, 3 orders beyond Tevatron/HERA) 1 GJ/mm 2 High required cleaning efficiency (clean lost protons to avoid SC magnet quenches) Activation of collimation insertions (good reliability required, very restricted access) Small spot sizes at high energy (small 7 TeV emittance, no large beta in restricted space) Collimation close to beam (available mechanical aperture is at ~10 σ) Small collimator gaps (impedance problem, tight tolerances: ~ 10 μm) Big and distributed system (coupled with mach. protection / dump) % (~10-5 p/m) ~ 1-15 msv/h ~ 200 μm 6-7 σ < 3 mm (at 7 TeV) ~100 locations ~500 deg. of freedom Quench Damage Heating Activation Stability Impedance Precision How can we meet all these challenging (and sometimes conflicting) requirements? S. Redaelli, HB2006 5
6 Phased approach: path towards nominal performance Ncoll Imax Phase I % Transfer lines (Carbon) Phase I 88 40% Robustness (mostly Carbon-based) Phase II 30 > 40% Low-impedance (metal) Phase III > 50% of nominal luminosity Phase IV % Ultimate cleaning performance This talk Focused on Phase I system: Final configuration at startup! Ensures required performance for commissioning and first years Already very challenging: 100 collimators = 500 deg. of freedom But we don t forget the upgrades: Required ring locations are reserved R&D for the Phase II collimators has started When needed, we will be ready for nominal intensity! S. Redaelli, HB2006 6
7 Outline Introduction Collimation system layout Phase I collimation layout Multi-stage collimation LHC aperture and collimator settings Mechanical design of the collimator Achieved cleaning performance System limitations and upgrades Conclusions S. Redaelli, HB2006 7
8 Layout of the LHC collimation system Multi-stage halo cleaning Two warm cleaning insertions IR3: Momentum cleaning 1 primary (H) TCP [C] 4 secondary (H,S) TCS [C] 4 shower abs. (H,V) TCLA [W] IR7: Betatron cleaning 3 primary (H,V,S) 11 secondary (H,V,S) 5 shower abs. (H,V) Local cleaning at triplets 8 tertiary (2 per IP) TCT [W] Passive absorbers for warm magnets Physics debris absorbers [ Cu ] 2 TCLP s (IP1/IP5) Transfer lines 13 collimators TCDI [ C ] Protection (injection/dump) 10 elements TCLI/TCDQ [ C ] >100 collimators for the Phase I system! S. Redaelli, HB2006 8
9 Layout of the LHC collimation system How do we want to use all these collimators? S. Redaelli, HB2006 Picture by C. Bracco 9
10 Detailed tables for the records Phase Acronym Material Length Number Locations INJ TOP Purpose [m] Scrapers 1 TCHS tbd tbd 6 IR3, IR7 Beam scraping 2 TCHS tbd tbd 2 IR3, IR7 Skew beam scraping Collimators 1 TCP C-C IR3, IR7 Y Y Primary collimators 1 TCSG C-C IR3, IR7 Y Y Secondary collimators 1 TCSG C-C IR6 Y Y Help for TCDQ set-up 2 TCSM tbd tbd 30 IR3, IR7 Hybrid secondary collimators 4 TCS4 tbd tbd 10 IR7 Phase 4 collimators Diluters 1 TDI Sandwich IR2, IR8 Y Injection protection 1 TCLI C IR2, IR8 Y Injection protection 1 TCDI C TI2, TI8 Y Injection collimation 1 TCDQ C-C IR6 Y Y Dump protection Movable Absorbers 1 TCT Cu/W IR1, IR2, Y Tertiary collimators IR5, IR8 1 TCLA Cu IR3, IR7 Y Y Showers from collimators 1 TCL/TCLP Cu IR1, IR5 Y Secondaries from IP 3 TCL/TCLP Cu IR1, IR5 Y Secondaries from IP How do we want to use all these collimators? S. Redaelli, HB
11 Principle of multi-stage cleaning (illustrative scheme) Cold aperture Primary collimator Secondary collimators Shower absorbers Tertiary collimators SC Triplet Protection devices Primary beam halo Secondary beam halo + hadronic showers Tertiary beam halo + hadronic showers Circulating beam Cleaning insertion Arc(s) IP The available cold aperture sets the scale! S. Redaelli, HB2006 R. Assmann 11
12 LHC aperture and collimator settings (Detailed worked out in Chamonix2005) 5.7σ 6.7σ 10.0σ ~30σ out Injection ARC Beam halo ARC IP and Triplets ARC ±7.5 σ 6.0σ 7.0σ 10.0σ 8.5σ 10.0σ 7 TeV ARC Beam halo ARC IP & Triplets ARC ±8.5 σ Primary (robust) Secondary (robust) Absorber (W metal) Tertiary (W metal) Physics absorbers (Cu metal) Similar normalized settings at injection (arc) and at 7 TeV (triplet). Canonical settings: ATCP = 6σ / ATCS = 7σ (σ= βiε). S. Redaelli, HB
13 Collimator gaps at injection - IR7 ATCP = 5.7 σ ATCS = 6.7 σ ATCLA = 10 σ Gapmin = ± 4.6 mm Collimator gaps [ mm ] IP7 3σy 3σx Cold S. Redaelli, HB Longitudinal coordinate, [ km ] Cold 13
14 Collimator gaps at 7 TeV - IR7 20 ATCP = 6 σ ATCS = 7 σ ATCLA = 10 σ Collimator gaps [ mm ] Gapmin = ± 1.2 mm 3σx IP7 3σy ~ 2 mm Can we fit 360 MJ in these collimator gaps?? S. Redaelli, HB Longitudinal coordinate, [ km ] 14
15 Outline Introduction Collimation system layout Mechanical design of the collimator Design criteria and challenges Mechanical design Beam test results Achieved cleaning performance System limitations and upgrades Conclusions S. Redaelli, HB
16 Challenges of the design requirements Mechanical tolerance 40 μm surface flatness over L=1m σb = 200 μm at 7 TeV/c 10 μm positioning accuracy Heat load (7 TeV) Up to 30 kw at top energy Minimum lifetime: τmin 0.2h Keep T < 50 o C Failure scenarios [Robustness!] Full injection batch 288 bunches 2 MJ (7.2 μsec) 8 nominal bunches at 7 TeV/c 8 bunches 1 MJ (0.2 μsec) High radiation environment Radiation hardness of components ~10 16 protons per years! E.g.: stepping motors: 10 MGy/year Cooling Robustness Maintainability Precision High absorption Radiation hardness Phase I addresses successfully most of these challenges! Here: review main design features S. Redaelli, HB
17 The collimator assembly Main design features: Two jaws (position and angle) Concept of spare surface Different azimuthal angles (H,V,S) External reference of jaw position Auto-retraction RF fingers Jaw cooling Beam EPAC04 + PAC05, A. Bertarelli et al. S. Redaelli, HB
18 External measurements of jaw position S. Redaelli, HB
19 A real collimator Vacuum tank Beam Quick plug-in system Support Bellows Motors position survey system A. Bertarelli, A. Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
20 A look inside the vacuum tank Vacuum tank Jaw (Carbon) RF contact Longitudinal strip (Cu-Be) What the beam sees! Beam A. Bertarelli, A. Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
21 Dealing with different azimuthal angles Same support and quick plug-in system for different orientations Whole vacuum tank can be rotated to match the beam requirements (horizontal, vertical or skew) A. Bertarelli, A. Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
22 The LHC collimator jaw Collimating Jaw (C/C composite) Main support beam (Glidcop) Cooling-circuit (Cu-Ni pipes) Counter-plates (Stainless steel) Preloaded springs (Stainless steel) Clamping plates (Glidcop) Carbon jaw (10cm tapering for RF contact) Special sandwich design with different layers designed to minimize the thermal deformations: Steady (~5 kw) < 30 μm Transient (~30 kw) ~ 110 μm Beam A. Bertarelli, A. Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
23 3D integration in the LHC tunnel Water Connections Vacuum pumping Modules (TS-MME & AT-VAC) Collimator Tank (water cooled) Quick connection flanges Beam 2 BLM Soon a picture will be available... A. Bertarelli, A Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
24 Highlights of lab and beam tests Many crucial laboratory tests: Temperature transmission for cooling Contact resistance of RF fingers Material property measurements Positioning accuracy (~10 μm) Flatness measurements ( 40-60μm) Vacuum, bake-out, outgassing... Circulating beam of 270 GeV with collimator gap of ~2 mm Major milestones: Beam tests in 2004 (SPS) Mechanical functionality with circulating beam Centering around beam with 50 μm accuracy (see talk on Thr.) Robustness test with extracted beam at 450 GeV Collimator survived at worst injection failure case! S. Redaelli, HB
25 Robustness test with 450 GeV p beams No damage of the Carbon and Graphite blocks Permanent deformation of the Copper plate behind the jaw Inconel plate solved the problem! 250 μm Collimator jaws AFTER impacts of 450 GeV LHC injection batch (288x , 7.2 μs, ~2 MJ) Carbon/ carbon jaw Graphite jaw Sound: A. Bertarelli, A Dallocchio S. Redaelli, HB
26 Outline Introduction Collimation system layout Mechanical design of the collimator Achieved cleaning performance Simulation tools Beam loss patterns Energy deposition studies System limitations and upgrades Conclusions S. Redaelli, HB
27 LHC loss map simulations Accurate tracking of halo particles 6D dynamics, chromatic effects, δp/p, high order field errors,... Scattering routine Track protons inside collimator materials Detailed collimator geometry Implement all collimators and protection devices, treat any azimuthal angle, tilt/flatness errors Detailed aperture model Precisely find the locations of losses SixTrack K2 BeamLossPattern Aperture / beam position [ m ] IR7 Trajectory of a halo particle IR s [ km ] Magnet locations : s 100m Interpolation: s=10cm ( points!) See G. Robert-Demolaize et al., A new version of SixTrack for collimation studies, PAC05 S. Redaelli, HB
28 Cleaning performance at 7 TeV Beam Losses in collimators Losses in cold apert. Black = okay Controlled losses at the collimators Blue = BAD! Losses in cold aperture quench Beam Only a few loss locations outside the collimators (perfect machine) S. Redaelli, HB
29 Comparison with the previous system without shower absorbers and tertiary collimators (two-stage cleaning) Full system with TCT s + absorbers IP2 IP3 IP4 IP5 IP6 IP7 IP8 IP1 TCLA + TCT Significant improvement in the IR s 2 stage cleaning in IR7 (as of Jan. 2005) Before many losses outside collimators! Beam There are still losses above the quench limit! S. Redaelli, HB
30 Losses downstream of the betatron cleaning Warm betatron cleaning Cold disp. suppr. Arc Loss rate per unit length [ p/m/s ] IP7 Warm Cold Assumed quench limit Particles with large δp/p and small β kick escape from the collimators! s [ km ] With nominal intensity, the quench limit is reached. Intrinsic limitation of the Carbon based system (low absorption)! S. Redaelli, HB
31 Energy deposition studies Inelastic impacts inside collimators input for energy deposition studies Impact distribution at the TCP Courtesy of V. Vlachoudis Energy deposition studies play a major role in the system design! Energy in the super-conducting magnets versus quench limit Estimate life time of warm magnets/electronics (passive absorbers) Optimize layout of insertion (e.g. chicane design) Quantify does to personnel (implications on the collimator design) and impact on the environment S. Redaelli, HB
32 Dose along the betatron cleaning COLD WARM COLD 5 orders of magnitude!! K. Tsoulou et al IR7 Radiation is basically confined within the warm insertions! S. Redaelli, HB
33 Outline Introduction Collimation system layout Mechanical design of the collimator Achieved cleaning performance System limitations and upgrades Conclusions S. Redaelli, HB
34 Limitations of the Phase I collimation Loss rate per unit length [ p/m/s ] The proposed robust system (low Z) cannot achieve the Inom: Reduced efficiency (poor absorption of Carbon) Losses downstream of IR7 close to quench limit for perfect machine Large impedance (small gaps + large resistivity) Severe beam instabilities at nominal intensity IP7 Warm Cold Quench limit reached with perfect machine! Assumed quench limit Inom collective tune shift outside stability region!! With collimators Inom Unstable Imax 40% Inom Stable Without coll s [ km ] Courtesy of E. Métral, CERN-AB-ABP Solution: use high-z collimator material (metals)!! S. Redaelli, HB
35 Studies for system upgrades ~50 space reservations in the LHC for additional collimators R&D for the Phase II Hybrid collimators has started! US-LARP program to build metallic consumable collimators! European program recently started to fund new studies The proposal aims at significantly extending the present state-of-theart in high power and high efficiency collimators.... extending the state of the art by another factor 5-10 beyond LHC phase 1 collimation, reaching the 1 GJ/mm 2 regime with ultra-high efficiency collimation. The proposal includes phase 2 of LHC collimation but extends beyond by including novel concepts like crystals and R&D for overcoming specific limitations for ion operation. Who wants to work with us on this challenging research topics? S. Redaelli, HB
36 US-LARP: LHC consumable collimator Consumable rotary collimator for the NLC Updated design to meet the LHC requirements! Be am m a e B Be am Courtesy of T. Markiewicz et al., SLAC Time line: FY 2004: (approved by DOE) FY 2005: FY 2006: FY 2007: FY 2008: FY 2009: FY 2010: FY 2011: S. Redaelli, HB Introduction to project Phase II CDR and set up of a collimator lab at SLAC Design, construction & testing of a mechanical prototype Design, construction & no-beam testing of a beam test prototype Ship, Install, Beam Tests of beam test prototype in the LHC Final drawing package for CERN Await production & installation by CERN Commissioning support 36
37 Conclusions LHC enters a new territory of hadron beam collimation! Phased approach = path towards ultimate LHC performance Robustness is the keyword for the Phase I system Multi-stage cleaning based on (mostly) Carbon collimators Mechanical design thoroughly assessed (beam + lab. tests) Expected cleaning inefficiency performance: 10-4! Impedance and cleaning limit the Phase I to < 1/2 Inom We are confident that we will handle the ~100 MJ regime! Another step forward is needed to successfully tackle the GJ/mm 2 regime of nominal and ultimate LHC performance! S. Redaelli, HB
Commissioning of the LHC collimation system S. Redaelli, R. Assmann, C. Bracco, M. Jonker and G. Robert-Demolaize CERN, AB department
 39 th ICFA Advance Beam dynamics Workshop High Intensity High Brightness Hadron Beams - HB 2006 Tsukuba, May 29 th - June 2 nd, 2006 Commissioning of the LHC collimation system S. Redaelli, R. Assmann,
39 th ICFA Advance Beam dynamics Workshop High Intensity High Brightness Hadron Beams - HB 2006 Tsukuba, May 29 th - June 2 nd, 2006 Commissioning of the LHC collimation system S. Redaelli, R. Assmann,
Collimators and Cleaning, Could this Limit the LHC Performance?
 Collimators and Cleaning, Could this Limit the LHC Performance? R. Assmann, CERN-AB/ABP Chamonix XII March 2003 Answer is easy: You bet, collimation and cleaning can limit us! The question we are considering:
Collimators and Cleaning, Could this Limit the LHC Performance? R. Assmann, CERN-AB/ABP Chamonix XII March 2003 Answer is easy: You bet, collimation and cleaning can limit us! The question we are considering:
LHC Collimation and Loss Locations
 BLM Audit p. 1/22 LHC Collimation and Loss Locations BLM Audit Th. Weiler, R. Assmann, C. Bracco, V. Previtali, S Redaelli Accelerator and Beam Department, CERN BLM Audit p. 2/22 Outline Introduction /
BLM Audit p. 1/22 LHC Collimation and Loss Locations BLM Audit Th. Weiler, R. Assmann, C. Bracco, V. Previtali, S Redaelli Accelerator and Beam Department, CERN BLM Audit p. 2/22 Outline Introduction /
Simulations and measurements of collimation cleaning with 100MJ beams in the LHC
 The 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference, IPAC13 May 13 th -17 th, 2013 Shanghai, China Simulations and measurements of collimation cleaning with 100MJ beams in the LHC R. Bruce, R.W. Assmann,
The 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference, IPAC13 May 13 th -17 th, 2013 Shanghai, China Simulations and measurements of collimation cleaning with 100MJ beams in the LHC R. Bruce, R.W. Assmann,
Status of the LHC Beam Cleaning Study Group
 Status of the LHC Beam Cleaning Study Group R. Assmann, SL BI Review 19.11.2001 BI Review 19.11.01, R. Assmann 1 LHC Beam Cleaning Study Group: Mandate: Study beam dynamics and operational issues for the
Status of the LHC Beam Cleaning Study Group R. Assmann, SL BI Review 19.11.2001 BI Review 19.11.01, R. Assmann 1 LHC Beam Cleaning Study Group: Mandate: Study beam dynamics and operational issues for the
Beam losses versus BLM locations at the LHC
 Geneva, 12 April 25 LHC Machine Protection Review Beam losses versus BLM locations at the LHC R. Assmann, S. Redaelli, G. Robert-Demolaize AB - ABP Acknowledgements: B. Dehning Motivation - Are the proposed
Geneva, 12 April 25 LHC Machine Protection Review Beam losses versus BLM locations at the LHC R. Assmann, S. Redaelli, G. Robert-Demolaize AB - ABP Acknowledgements: B. Dehning Motivation - Are the proposed
Simulations of HL halo loss and IR losses. R. Bruce, F. Cerutti, R. de Maria, A. Marsili, S. Redaelli
 Simulations of HL halo loss and IR losses R. Bruce, F. Cerutti, R. de Maria, A. Marsili, S. Redaelli 1 Outline Introduction: SixTrack Halo: ATS results Comparison with 7TeV nominal Debris tracking Halo
Simulations of HL halo loss and IR losses R. Bruce, F. Cerutti, R. de Maria, A. Marsili, S. Redaelli 1 Outline Introduction: SixTrack Halo: ATS results Comparison with 7TeV nominal Debris tracking Halo
Beam Cleaning and Collimation Systems
 Published by CERN in the Proceedings of the Joint International Accelerator School: Beam Loss and Accelerator Protection, Newport Beach, US, 5 14 November 2014, edited by R. Schmidt, CERN-2016-002 (CERN,
Published by CERN in the Proceedings of the Joint International Accelerator School: Beam Loss and Accelerator Protection, Newport Beach, US, 5 14 November 2014, edited by R. Schmidt, CERN-2016-002 (CERN,
HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study. Deliverable Report SIMULATION MODELS FOR ENERGY DEPOSITION
 CERN-ACC-2013-011 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report SIMULATION MODELS FOR ENERGY Redaelli, Stefano (CERN) 20 November 2012 The HiLumi LHC Design Study
CERN-ACC-2013-011 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report SIMULATION MODELS FOR ENERGY Redaelli, Stefano (CERN) 20 November 2012 The HiLumi LHC Design Study
LHC Commissioning in 2008
 LHC Commissioning in 2008 Mike Lamont AB/OP Schedule slides c/o Lyn Evans (MAC 14/6/07) Status: Installation & equipment commissioning LHC commissioning - CMS June 07 2 Procurement problems of remaining
LHC Commissioning in 2008 Mike Lamont AB/OP Schedule slides c/o Lyn Evans (MAC 14/6/07) Status: Installation & equipment commissioning LHC commissioning - CMS June 07 2 Procurement problems of remaining
LHC APERTURE AND COMMISSIONING OF THE COLLIMATION SYSTEM
 LHC APERTURE AND COMMISSIONING OF THE COLLIMATION SYSTEM S. Redaelli, R. Aßmann, G. Robert-Demolaize, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The design LHC aperture and its dependence on various optics imperfections
LHC APERTURE AND COMMISSIONING OF THE COLLIMATION SYSTEM S. Redaelli, R. Aßmann, G. Robert-Demolaize, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The design LHC aperture and its dependence on various optics imperfections
TRANSVERSE IMPEDANCE OF LHC COLLIMATORS
 Contributed talk WEOAC03 (12 + 3 min, 14 slides) TRANSVERSE IMPEDANCE OF LHC COLLIMATORS Elias Métral Work in collaboration with G. Arduini,, R. Assmann,, A. Boccardi,, T. Bohl, F. Caspers,, M. Gasior,,
Contributed talk WEOAC03 (12 + 3 min, 14 slides) TRANSVERSE IMPEDANCE OF LHC COLLIMATORS Elias Métral Work in collaboration with G. Arduini,, R. Assmann,, A. Boccardi,, T. Bohl, F. Caspers,, M. Gasior,,
EuCARD-2 Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development. Conference/Workshop Paper
 CERN-ACC-6-6 EuCARD- Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development Conference/Workshop Paper Cleaning Studies with Advanced Collimator Materials for HL-LHC Valloni, A. (CERN, University
CERN-ACC-6-6 EuCARD- Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development Conference/Workshop Paper Cleaning Studies with Advanced Collimator Materials for HL-LHC Valloni, A. (CERN, University
Gianluigi Arduini CERN - Beams Dept. - Accelerator & Beam Physics Group
 Gianluigi Arduini CERN - Beams Dept. - Accelerator & Beam Physics Group Acknowledgements: O. Brüning, S. Fartoukh, M. Giovannozzi, G. Iadarola, M. Lamont, E. Métral, N. Mounet, G. Papotti, T. Pieloni,
Gianluigi Arduini CERN - Beams Dept. - Accelerator & Beam Physics Group Acknowledgements: O. Brüning, S. Fartoukh, M. Giovannozzi, G. Iadarola, M. Lamont, E. Métral, N. Mounet, G. Papotti, T. Pieloni,
Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS
 HB2012 - Beijing - 18 September 2012 Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS Simone Montesano (CERN) for the UA9 collaboration Silicon strip crystal Outline Crystal
HB2012 - Beijing - 18 September 2012 Status and Results of the UA9 Crystal Collimation Experiment at the CERN-SPS Simone Montesano (CERN) for the UA9 collaboration Silicon strip crystal Outline Crystal
LHC Luminosity and Energy Upgrade
 LHC Luminosity and Energy Upgrade Walter Scandale CERN Accelerator Technology department EPAC 06 27 June 2006 We acknowledge the support of the European Community-Research Infrastructure Activity under
LHC Luminosity and Energy Upgrade Walter Scandale CERN Accelerator Technology department EPAC 06 27 June 2006 We acknowledge the support of the European Community-Research Infrastructure Activity under
Machine Protection Systems
 Machine Protection Systems Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operations group Special CERN CAS, Feb. 2009 Introduction Beam induced damage CERN accelerators risks Beam dumps Passive protection Failure
Machine Protection Systems Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operations group Special CERN CAS, Feb. 2009 Introduction Beam induced damage CERN accelerators risks Beam dumps Passive protection Failure
The TESLA Dogbone Damping Ring
 The TESLA Dogbone Damping Ring Winfried Decking for the TESLA Collaboration April 6 th 2004 Outline The Dogbone Issues: Kicker Design Dynamic Aperture Emittance Dilution due to Stray-Fields Collective
The TESLA Dogbone Damping Ring Winfried Decking for the TESLA Collaboration April 6 th 2004 Outline The Dogbone Issues: Kicker Design Dynamic Aperture Emittance Dilution due to Stray-Fields Collective
ASPECTS OF MACHINE INDUCED BACKGROUND IN THE LHC EXPERIMENTS
 ASPECTS OF MACHINE INDUCED BACKGROUND IN THE LHC EXPERIMENTS Abstract G.Corti and V.Talanov Λ, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland In our report we review different aspects of the LHC Machine Induced Background
ASPECTS OF MACHINE INDUCED BACKGROUND IN THE LHC EXPERIMENTS Abstract G.Corti and V.Talanov Λ, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland In our report we review different aspects of the LHC Machine Induced Background
Case study: Energy deposition in superconducting magnets in IR7
 Case study: Energy deposition in superconducting magnets in IR7 AMT Workshop A.Ferrari, M.Magistris, M.Santana, V.Vlachoudis CERN Fri 4/3/2005 Overview Motivation Geometry and Simulation setup Studies:
Case study: Energy deposition in superconducting magnets in IR7 AMT Workshop A.Ferrari, M.Magistris, M.Santana, V.Vlachoudis CERN Fri 4/3/2005 Overview Motivation Geometry and Simulation setup Studies:
SPPC Study and R&D Planning. Jingyu Tang for the SPPC study group IAS Program for High Energy Physics January 18-21, 2016, HKUST
 SPPC Study and R&D Planning Jingyu Tang for the SPPC study group IAS Program for High Energy Physics January 18-21, 2016, HKUST Main topics Pre-conceptual design study Studies on key technical issues R&D
SPPC Study and R&D Planning Jingyu Tang for the SPPC study group IAS Program for High Energy Physics January 18-21, 2016, HKUST Main topics Pre-conceptual design study Studies on key technical issues R&D
MACHINE PROTECTION ISSUES AND STRATEGIES FOR THE LHC
 MACHINE PROTECTION ISSUES AND STRATEGIES FOR THE LHC R. Schmidt and J. Wenninger for the Working Group on Machine Protection, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract For nominal beam parameters at 7 TeV/c,
MACHINE PROTECTION ISSUES AND STRATEGIES FOR THE LHC R. Schmidt and J. Wenninger for the Working Group on Machine Protection, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract For nominal beam parameters at 7 TeV/c,
INJECTION AND DUMP CONSIDERATIONS FOR A 16.5 TEV HE-LHC
 INJECTION AND DUMP CONSIDERATIONS FOR A 16.5 TEV HE-LHC B. Goddard, M. Barnes, W. Bartmann, J. Borburgh, C. Bracco, L. Ducimetière, V. Kain, M. Meddahi, V. Mertens, V. Senaj, J. Uythoven, CERN, Geneva,
INJECTION AND DUMP CONSIDERATIONS FOR A 16.5 TEV HE-LHC B. Goddard, M. Barnes, W. Bartmann, J. Borburgh, C. Bracco, L. Ducimetière, V. Kain, M. Meddahi, V. Mertens, V. Senaj, J. Uythoven, CERN, Geneva,
AFP - TCL collimator studies
 AFP - TCL collimator studies LHC Collimation Study Group, 24-Aug-2009 F. Roncarolo The University of Manchester/Cockcroft Institute CERN BE/ABP/LCU Many thanks to C. Bracco, K.Potter, R.Appleby and R.
AFP - TCL collimator studies LHC Collimation Study Group, 24-Aug-2009 F. Roncarolo The University of Manchester/Cockcroft Institute CERN BE/ABP/LCU Many thanks to C. Bracco, K.Potter, R.Appleby and R.
Elias Métral, LHC Collimation Working Group Meeting, 15/03/ /31
 Answers to Jeff and Liling concerning the simulations of trapped modes of the SLAC Phase 2 collimator, and news on impedance for the Phase 1 and 2 at CERN Reminder on the trapped modes simulations performed
Answers to Jeff and Liling concerning the simulations of trapped modes of the SLAC Phase 2 collimator, and news on impedance for the Phase 1 and 2 at CERN Reminder on the trapped modes simulations performed
Merlin scattering models for the HL-LHC collimation system
 Merlin scattering models for the HL-LHC collimation system S. Tygier 12, R.B. Appleby 12, R.J.Barlow 3, H. Rafique 12, and S.Rowan 3 1 University of Manchester 2 Cockcroft Institute 3 University of Huddesfield
Merlin scattering models for the HL-LHC collimation system S. Tygier 12, R.B. Appleby 12, R.J.Barlow 3, H. Rafique 12, and S.Rowan 3 1 University of Manchester 2 Cockcroft Institute 3 University of Huddesfield
Collimation strategy for the high-β Special Physics run at injection
 Collimation strategy for the high-β Special Physics run at injection Hector Garcia-Morales 1,2, Roderik Bruce 2, Stefano Redaelli 2 Acknowledgements to H.Burkhardt 1 Royal Holloway University of London
Collimation strategy for the high-β Special Physics run at injection Hector Garcia-Morales 1,2, Roderik Bruce 2, Stefano Redaelli 2 Acknowledgements to H.Burkhardt 1 Royal Holloway University of London
Electron Cloud Studies made at CERN in the SPS
 Electron Cloud Studies made at CERN in the SPS J.M. Jimenez On behalf of the Electron Cloud Study Team, a Collaboration between AT and AB Departments Main Topics Introduction LHC Injectors SPS Running
Electron Cloud Studies made at CERN in the SPS J.M. Jimenez On behalf of the Electron Cloud Study Team, a Collaboration between AT and AB Departments Main Topics Introduction LHC Injectors SPS Running
LHC Run 2: Results and Challenges. Roderik Bruce on behalf of the CERN teams
 LHC Run 2: Results and Challenges Roderik Bruce on behalf of the CERN teams Acknowledgements A big thanks to all colleagues involved across various teams! Special thanks for material and discussions G.
LHC Run 2: Results and Challenges Roderik Bruce on behalf of the CERN teams Acknowledgements A big thanks to all colleagues involved across various teams! Special thanks for material and discussions G.
HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study. Deliverable Report. Conceptual Design of IR Collimation
 CERN-ACC-2014-0293 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report Conceptual Design of IR Collimation Bruce, Roderick (CERN) et al 28 November 2014 The HiLumi LHC
CERN-ACC-2014-0293 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report Conceptual Design of IR Collimation Bruce, Roderick (CERN) et al 28 November 2014 The HiLumi LHC
Beam. RF antenna. RF cable
 Status of LEP2 J. Wenninger, SL Operation for the SL division LEPC September 1998 Outline Optics and RF for 1998 Beam current limitations Injection and ramp Performance at high energy Conclusions LEPC/15-09-98
Status of LEP2 J. Wenninger, SL Operation for the SL division LEPC September 1998 Outline Optics and RF for 1998 Beam current limitations Injection and ramp Performance at high energy Conclusions LEPC/15-09-98
Beam Optics & Dynamics Studies for LHC
 Beam Optics & Dynamics Studies for LHC Alexander Koschik ETH Zurich, Integrated Systems Laboratory (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich) SLAC, Aug. 2010 0 Background Information Master s degree
Beam Optics & Dynamics Studies for LHC Alexander Koschik ETH Zurich, Integrated Systems Laboratory (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich) SLAC, Aug. 2010 0 Background Information Master s degree
The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC. G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory
 The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory RHIC accelerator complex: IPAC'15 - May 3-8, 2015 - Richmond, VA, USA 2 The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) aims
The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory RHIC accelerator complex: IPAC'15 - May 3-8, 2015 - Richmond, VA, USA 2 The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) aims
LHC commissioning. 22nd June Mike Lamont LHC commissioning - CMS 1
 LHC commissioning Mike Lamont AB-OP nd June 005.06.05 LHC commissioning - CMS 1 Detailed planning for 7-87 8 and 8-18 005 006 Short Circuit Tests CNGS/TI8/IT1 HWC LSS.L8.06.05 LHC commissioning - CMS Sector
LHC commissioning Mike Lamont AB-OP nd June 005.06.05 LHC commissioning - CMS 1 Detailed planning for 7-87 8 and 8-18 005 006 Short Circuit Tests CNGS/TI8/IT1 HWC LSS.L8.06.05 LHC commissioning - CMS Sector
Lattice Design and Performance for PEP-X Light Source
 Lattice Design and Performance for PEP-X Light Source Yuri Nosochkov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory With contributions by M-H. Wang, Y. Cai, X. Huang, K. Bane 48th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop
Lattice Design and Performance for PEP-X Light Source Yuri Nosochkov SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory With contributions by M-H. Wang, Y. Cai, X. Huang, K. Bane 48th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop
OTHER MEANS TO INCREASE THE SPS 25 ns PERFORMANCE TRANSVERSE PLANE
 OTHER MEANS TO INCREASE THE SPS 25 ns PERFORMANCE TRANSVERSE PLANE H. Bartosik, G. Arduini, A. Blas, C. Bracco, T. Bohl, K. Cornelis, H. Damerau, S. Gilardoni, S. Hancock, B. Goddard, W. Höfle, G. Iadarola,
OTHER MEANS TO INCREASE THE SPS 25 ns PERFORMANCE TRANSVERSE PLANE H. Bartosik, G. Arduini, A. Blas, C. Bracco, T. Bohl, K. Cornelis, H. Damerau, S. Gilardoni, S. Hancock, B. Goddard, W. Höfle, G. Iadarola,
Sources of machine-induced background in the ATLAS and CMS detectors at the CERN Large Hadron Collider
 CERN-ACC-214-21 214-1-16 roderik.bruce@cern.ch Sources of machine-induced background in the ATLAS and CMS detectors at the CERN Large Hadron Collider R. Bruce a,*, R.W. Assmann b,1, V. Boccone a, G. Bregliozzi
CERN-ACC-214-21 214-1-16 roderik.bruce@cern.ch Sources of machine-induced background in the ATLAS and CMS detectors at the CERN Large Hadron Collider R. Bruce a,*, R.W. Assmann b,1, V. Boccone a, G. Bregliozzi
The LHC: the energy, cooling, and operation. Susmita Jyotishmati
 The LHC: the energy, cooling, and operation Susmita Jyotishmati LHC design parameters Nominal LHC parameters Beam injection energy (TeV) 0.45 Beam energy (TeV) 7.0 Number of particles per bunch 1.15
The LHC: the energy, cooling, and operation Susmita Jyotishmati LHC design parameters Nominal LHC parameters Beam injection energy (TeV) 0.45 Beam energy (TeV) 7.0 Number of particles per bunch 1.15
1.1 Electron-Cloud Effects in the LHC
 11 1.1 Electron-Cloud Effects in the LHC F. Zimmermann, E. Benedetto 1 mail to: frank.zimmermann@cern.ch CERN, AB Department, ABP Group 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 1.1.1 Introduction The LHC is the first
11 1.1 Electron-Cloud Effects in the LHC F. Zimmermann, E. Benedetto 1 mail to: frank.zimmermann@cern.ch CERN, AB Department, ABP Group 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland 1.1.1 Introduction The LHC is the first
Collimation method studies for next-generation hadron colliders
 Collimation method studies for next-generation hadron colliders Jian-Quan Yang, 1,2 Ye Zou, 3 and Jing-Yu Tang 1,4* 1 Institute of High Energy Physics, CAS, Yuquan Road 19B, Beijing 100049, People s Republic
Collimation method studies for next-generation hadron colliders Jian-Quan Yang, 1,2 Ye Zou, 3 and Jing-Yu Tang 1,4* 1 Institute of High Energy Physics, CAS, Yuquan Road 19B, Beijing 100049, People s Republic
Plans for 2016 and Run 2
 Plans for 2016 and Run 2 Mike Lamont An attempt at synthesis Acknowledgements all round After LS1 It s going to be like after a war Serge Claudet Evian 2012 Where are we? 1/2 6.5 TeV, 2*80 cm, 2*levelled
Plans for 2016 and Run 2 Mike Lamont An attempt at synthesis Acknowledgements all round After LS1 It s going to be like after a war Serge Claudet Evian 2012 Where are we? 1/2 6.5 TeV, 2*80 cm, 2*levelled
Higgs Factory Magnet Protection and Machine-Detector Interface
 Higgs Factory Magnet Protection and Machine-Detector Interface Nikolai Mokhov Fermilab MAP Spring Workshop May 27-31, 2014 Outline MDI Efforts Building Higgs Factory Collider, Detector and MDI Unified
Higgs Factory Magnet Protection and Machine-Detector Interface Nikolai Mokhov Fermilab MAP Spring Workshop May 27-31, 2014 Outline MDI Efforts Building Higgs Factory Collider, Detector and MDI Unified
BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
 JINR BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM W.Höfle, G.Kotzian, E.Montesinos, M.Schokker, D.Valuch (CERN) V.M. Zhabitsky (JINR) XXII Russian Particle Accelerator Conference 27.9-1.1. 21, Protvino
JINR BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM W.Höfle, G.Kotzian, E.Montesinos, M.Schokker, D.Valuch (CERN) V.M. Zhabitsky (JINR) XXII Russian Particle Accelerator Conference 27.9-1.1. 21, Protvino
2008 JINST 3 S Main machine layout and performance. Chapter Performance goals
 Chapter 2 Main machine layout and performance 2.1 Performance goals The aim of the LHC is to reveal the physics beyond the Standard Model with centre of mass collision energies of up to 14 TeV. The number
Chapter 2 Main machine layout and performance 2.1 Performance goals The aim of the LHC is to reveal the physics beyond the Standard Model with centre of mass collision energies of up to 14 TeV. The number
LHC status & 2009/2010 operations. Mike Lamont
 LHC status & 2009/2010 operations Mike Lamont Contents 7-9-09 LHC status - CMS week 2 Consolidation brief recall Splices Operational energies Potential performance Present status Plans for 2009-2010 Consolidation
LHC status & 2009/2010 operations Mike Lamont Contents 7-9-09 LHC status - CMS week 2 Consolidation brief recall Splices Operational energies Potential performance Present status Plans for 2009-2010 Consolidation
The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System
 The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System A.I. Drozhdin, N.V. Mokhov, A.A. Sery, Fermilab, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL 65 USA INTRODUCTIONS Even in good operational conditions, a finite fraction
The Very Large Hadron Collider Beam Collimation System A.I. Drozhdin, N.V. Mokhov, A.A. Sery, Fermilab, P.O. Box 5, Batavia, IL 65 USA INTRODUCTIONS Even in good operational conditions, a finite fraction
Beam Loss Monitors, Specification
 H.Burkhardt, BI Review, Mon. 19/11/2001 Beam Loss Monitors, Specification BLM main scope and challenges types of BLM Collimation, Special, Arc Sensitivity and Time Resolution Summary largely based on work
H.Burkhardt, BI Review, Mon. 19/11/2001 Beam Loss Monitors, Specification BLM main scope and challenges types of BLM Collimation, Special, Arc Sensitivity and Time Resolution Summary largely based on work
Overview of LHC Accelerator
 Overview of LHC Accelerator Mike Syphers UT-Austin 1/31/2007 Large Hadron Collider ( LHC ) Outline of Presentation Brief history... Luminosity Magnets Accelerator Layout Major Accelerator Issues U.S. Participation
Overview of LHC Accelerator Mike Syphers UT-Austin 1/31/2007 Large Hadron Collider ( LHC ) Outline of Presentation Brief history... Luminosity Magnets Accelerator Layout Major Accelerator Issues U.S. Participation
Interface with Experimental Detector in the High Luminosity Run
 Chapter 5 Interface with Experimental Detector in the High Luminosity Run H. Burkhardt CERN, BE Department, Genève 23, CH-1211, Switzerland This chapter describes the upgrade of the interaction regions
Chapter 5 Interface with Experimental Detector in the High Luminosity Run H. Burkhardt CERN, BE Department, Genève 23, CH-1211, Switzerland This chapter describes the upgrade of the interaction regions
ULTIMATE LHC BEAM. G. Arduini, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland
 Abstract The present status of the nominal LHC beam in the LHC injector complex and the limitations towards the achievement of the ultimate brightness are outlined. ULTIMATE LHC BEAM G. Arduini, CERN,
Abstract The present status of the nominal LHC beam in the LHC injector complex and the limitations towards the achievement of the ultimate brightness are outlined. ULTIMATE LHC BEAM G. Arduini, CERN,
LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future
 LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future Moriond Workshop La Thuile March 2016 Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operation group / LHC For the LHC commissioning and operation teams 1 Moriond
LHC operation in 2015 and prospects for the future Moriond Workshop La Thuile March 2016 Jörg Wenninger CERN Beams Department Operation group / LHC For the LHC commissioning and operation teams 1 Moriond
LHC Upgrade Plan and Ideas - scenarios & constraints from the machine side
 LHC Upgrade Plan and Ideas - scenarios & constraints from the machine side Frank Zimmermann LHCb Upgrade Workshop Edinburgh, 11 January 2007 Frank Zimmermann, LHCb Upgrade Workshop time scale of LHC upgrade
LHC Upgrade Plan and Ideas - scenarios & constraints from the machine side Frank Zimmermann LHCb Upgrade Workshop Edinburgh, 11 January 2007 Frank Zimmermann, LHCb Upgrade Workshop time scale of LHC upgrade
HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study. Deliverable Report BEAM HALO SIMULATIONS
 CERN-ACC-2013-008 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report Bruce, Roderik (CERN) et al 14 June 2013 The HiLumi LHC Design Study is included in the High Luminosity
CERN-ACC-2013-008 HiLumi LHC FP7 High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider Design Study Deliverable Report Bruce, Roderik (CERN) et al 14 June 2013 The HiLumi LHC Design Study is included in the High Luminosity
Modeling of beam-induced damage of the LHC tertiary collimators
 PHYSICAL REVIEW ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 20, 091002 (2017) Modeling of beam-induced damage of the LHC tertiary collimators E. Quaranta, * A. Bertarelli, R. Bruce, F. Carra, F. Cerutti, A. Lechner, S. Redaelli,
PHYSICAL REVIEW ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 20, 091002 (2017) Modeling of beam-induced damage of the LHC tertiary collimators E. Quaranta, * A. Bertarelli, R. Bruce, F. Carra, F. Cerutti, A. Lechner, S. Redaelli,
STATUS OF LHC COMMISSIONING
 Proceedings of PAC9, Vancouver, BC, Canada MO1BCI3 STATUS OF LHC COMMISSIONING J. Wenninger, CERN, Geneva Abstract Beam commissioning of the LHC started with injection tests in August 28, and a circulating
Proceedings of PAC9, Vancouver, BC, Canada MO1BCI3 STATUS OF LHC COMMISSIONING J. Wenninger, CERN, Geneva Abstract Beam commissioning of the LHC started with injection tests in August 28, and a circulating
LHC Commissioning and First Operation
 LHC Commissioning and First Operation PPC 2010, July 12, 2010, Turin, Italy Steve Myers Director for Accelerators and Technology, CERN Geneva (On behalf of the LHC team and international collaborators)
LHC Commissioning and First Operation PPC 2010, July 12, 2010, Turin, Italy Steve Myers Director for Accelerators and Technology, CERN Geneva (On behalf of the LHC team and international collaborators)
The MD was done at 450GeV using beam 2 only. An MD focussing on injection of bunches with nominal emittance was done in parallel on beam 1.
 CERN-ATS-Note-2011-065 MD 2011-08-08 Tobias.Baer@cern.ch MKI UFOs at Injection Tobias BAER, Mike BARNES, Wolfgang BARTMANN, Chiara BRACCO, Etienne CARLIER, Christophe CHANAVAT, Lene Norderhaug DROSDAL,
CERN-ATS-Note-2011-065 MD 2011-08-08 Tobias.Baer@cern.ch MKI UFOs at Injection Tobias BAER, Mike BARNES, Wolfgang BARTMANN, Chiara BRACCO, Etienne CARLIER, Christophe CHANAVAT, Lene Norderhaug DROSDAL,
SC magnets for Future HEHIHB Colliders
 SC magnets for Future HEHIHB Colliders presented by L. Bottura WAMS, Archamps, March 22-23,2004 Overview Few selected examples of drivers for R&D in the next 10 years LHC upgrades scenarios (why? how?)
SC magnets for Future HEHIHB Colliders presented by L. Bottura WAMS, Archamps, March 22-23,2004 Overview Few selected examples of drivers for R&D in the next 10 years LHC upgrades scenarios (why? how?)
Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators
 Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators W.S. Graves July, 2011 MIT W.S. Graves July, 2011 1.Introduction to Accelerator Physics 2.Three Big Machines Large Hadron Collider (LHC) International Linear Collider
Tools of Particle Physics I Accelerators W.S. Graves July, 2011 MIT W.S. Graves July, 2011 1.Introduction to Accelerator Physics 2.Three Big Machines Large Hadron Collider (LHC) International Linear Collider
Daniel Wollmann, CERN
 LHC parameters for Machine Protection Failure time scales and Machine Protection Systems LHC Operation a machine protection view Machine Protection studies for the future Cold diode qualification Sc. strand
LHC parameters for Machine Protection Failure time scales and Machine Protection Systems LHC Operation a machine protection view Machine Protection studies for the future Cold diode qualification Sc. strand
BETATRON SQUEEZE: STATUS, STRATEGY AND ISSUES
 BETATRON SQUEEZE: STATUS, STRATEGY AND ISSUES M. Lamont, G. Müller, S. Redaelli, M. Strzelczyk CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The betatron squeeze will be one of the most critical manipulation of the
BETATRON SQUEEZE: STATUS, STRATEGY AND ISSUES M. Lamont, G. Müller, S. Redaelli, M. Strzelczyk CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract The betatron squeeze will be one of the most critical manipulation of the
(4) vacuum pressure & gas desorption in the IRs ( A.
 Electron Cloud Effects in the LHC Frank Zimmermann,, SL/AP (1) heat load on the beam screen inside the s.c. magnets (4 20 K) (2) heat load on the cold bore (1.9 K) (3) beam instability at injection (4)
Electron Cloud Effects in the LHC Frank Zimmermann,, SL/AP (1) heat load on the beam screen inside the s.c. magnets (4 20 K) (2) heat load on the cold bore (1.9 K) (3) beam instability at injection (4)
Simulations and Measurements of Secondary Electron Emission Beam Loss Monitors for LHC
 Simulations and Measurements of Secondary Electron Emission Beam Loss Monitors for LHC Daniel Kramer,, Eva Barbara Holzer,, Bernd Dehning, Gianfranco Ferioli, Markus Stockner CERN AB-BI BI 4.10.2006 IPRD06,
Simulations and Measurements of Secondary Electron Emission Beam Loss Monitors for LHC Daniel Kramer,, Eva Barbara Holzer,, Bernd Dehning, Gianfranco Ferioli, Markus Stockner CERN AB-BI BI 4.10.2006 IPRD06,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF
 ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
(Lead) Ions in the LHC
 (Lead) Ions in the LHC Large Hadrons in the Large Hadron Collider John Jowett BE-ABP J.M. Jowett, LHC Performance Workshop, Chamonix, 6/2/2009 1 Plan of talk n Simplified survey of parameter space Energy,
(Lead) Ions in the LHC Large Hadrons in the Large Hadron Collider John Jowett BE-ABP J.M. Jowett, LHC Performance Workshop, Chamonix, 6/2/2009 1 Plan of talk n Simplified survey of parameter space Energy,
LHC Upgrade (accelerator)
 LHC Upgrade (accelerator) Time scale of LHC luminosity upgrade Machine performance limitations Scenarios for the LHC upgrade Phase 0: no hardware modifications Phase 1: Interaction Region upgrade Phase
LHC Upgrade (accelerator) Time scale of LHC luminosity upgrade Machine performance limitations Scenarios for the LHC upgrade Phase 0: no hardware modifications Phase 1: Interaction Region upgrade Phase
Why are particle accelerators so inefficient?
 Why are particle accelerators so inefficient? Philippe Lebrun CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Workshop on Compact and Low-Consumption Magnet Design for Future Linear and Circular Colliders CERN, 9-12 October
Why are particle accelerators so inefficient? Philippe Lebrun CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Workshop on Compact and Low-Consumption Magnet Design for Future Linear and Circular Colliders CERN, 9-12 October
Main aim: Preparation for high bunch intensity operation with β*=3.5 m and crossing angle (-100 µrad in IR1 and +100 µrad in IR5)
 Week 24 Main aim: Preparation for high bunch intensity operation with β*=3.5 m and crossing angle (-100 µrad in IR1 and +100 µrad in IR5) Commission systems required for guaranteeing beam stability as
Week 24 Main aim: Preparation for high bunch intensity operation with β*=3.5 m and crossing angle (-100 µrad in IR1 and +100 µrad in IR5) Commission systems required for guaranteeing beam stability as
Status and Outlook of the LHC
 Status and Outlook of the LHC Enrico Bravin - CERN BE-BI J-PARC visit seminar 6 July 2017 Outlook Overview of LHC Objectives for run2 Parameters for 2016/2017 and differences w.r.t. 2015 Summary of commissioning
Status and Outlook of the LHC Enrico Bravin - CERN BE-BI J-PARC visit seminar 6 July 2017 Outlook Overview of LHC Objectives for run2 Parameters for 2016/2017 and differences w.r.t. 2015 Summary of commissioning
ANSWERS TO NICOLAAS KOS FOR HIS PAPER Cold Beam Vacuum System for the LHC IR Upgrade Phase-1
 ANSWERS TO NICOLAAS KOS FOR HIS PAPER Cold Beam Vacuum System for the LHC IR Upgrade Phase-1 Maximum acceptable width for the pumping slots for a new beam screen wall thickness of 1.5 mm (SS only, and
ANSWERS TO NICOLAAS KOS FOR HIS PAPER Cold Beam Vacuum System for the LHC IR Upgrade Phase-1 Maximum acceptable width for the pumping slots for a new beam screen wall thickness of 1.5 mm (SS only, and
Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun
 Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun JLEIC Collaboration Meeting October 6, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Magnetized Cooling JLEIC bunched magnetized
Update on Development of High Current Bunched Electron Beam from Magnetized DC Photogun JLEIC Collaboration Meeting October 6, 2016 Riad Suleiman and Matt Poelker Magnetized Cooling JLEIC bunched magnetized
TRANSVERSE DAMPER. W. Höfle, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland. Abstract INTRODUCTION AND HIGHLIGHTS IN Controlled Transverse Blow-up
 TRANSVERSE DAMPER W. Höfle, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract Plans for the operation of the transverse damper in 2012 at bunch spacings of 50 ns and 25 ns and at increased collision energy will be reviewed.
TRANSVERSE DAMPER W. Höfle, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract Plans for the operation of the transverse damper in 2012 at bunch spacings of 50 ns and 25 ns and at increased collision energy will be reviewed.
BEAM SCREEN ISSUES (with 20 T dipole magnets instead of 8.3 T)
 BEAM SCREEN ISSUES (with 20 T dipole magnets instead of 8.3 T) Introduction and current LHC beam screen Magneto-Resistance (MR) What was done in the past (approx. of the approx. Kohler s rule) Exact and
BEAM SCREEN ISSUES (with 20 T dipole magnets instead of 8.3 T) Introduction and current LHC beam screen Magneto-Resistance (MR) What was done in the past (approx. of the approx. Kohler s rule) Exact and
Tobias Baer February, 9 th 2012
 UFOs Will they take over? Chamonix Workshop 2012 Tobias Baer February, 9 th 2012 Acknowledgements: W. Bartmann, M. Barnes, C. Bracco, F. Cerutti, B. Dehning, L. Ducimetière, A. Ferrari, N. Fuster Martinez,
UFOs Will they take over? Chamonix Workshop 2012 Tobias Baer February, 9 th 2012 Acknowledgements: W. Bartmann, M. Barnes, C. Bracco, F. Cerutti, B. Dehning, L. Ducimetière, A. Ferrari, N. Fuster Martinez,
HL-LHC: parameter space, constraints & possible options
 HL-LHC: parameter space, constraints & possible options Many thanks to R. Assmann, C. Bhat, O. Brüning, R. Calaga, R. De Maria, S. Fartoukh, J.-P. Koutchouk, S. Myers, L. Rossi, W. Scandale, E. Shaposhnikova,
HL-LHC: parameter space, constraints & possible options Many thanks to R. Assmann, C. Bhat, O. Brüning, R. Calaga, R. De Maria, S. Fartoukh, J.-P. Koutchouk, S. Myers, L. Rossi, W. Scandale, E. Shaposhnikova,
arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Oct 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.acc-ph] 21 Oct 2014](/thumbs/89/99419860.jpg) SIX-DIMENSIONAL WEAK STRONG SIMULATIONS OF HEAD-ON BEAM BEAM COMPENSATION IN RHIC arxiv:.8v [physics.acc-ph] Oct Abstract Y. Luo, W. Fischer, N.P. Abreu, X. Gu, A. Pikin, G. Robert-Demolaize BNL, Upton,
SIX-DIMENSIONAL WEAK STRONG SIMULATIONS OF HEAD-ON BEAM BEAM COMPENSATION IN RHIC arxiv:.8v [physics.acc-ph] Oct Abstract Y. Luo, W. Fischer, N.P. Abreu, X. Gu, A. Pikin, G. Robert-Demolaize BNL, Upton,
Simulation of the ILC Collimation System using BDSIM, MARS15 and STRUCT
 Simulation of the ILC Collimation System using BDSIM, MARS5 and STRUCT J. Carter, I. Agapov, G. A. Blair, L. Deacon, A. I. Drozhdin, N. V. Mokhov, Y. Nosochkov, A. Seryi August, 006 Abstract The simulation
Simulation of the ILC Collimation System using BDSIM, MARS5 and STRUCT J. Carter, I. Agapov, G. A. Blair, L. Deacon, A. I. Drozhdin, N. V. Mokhov, Y. Nosochkov, A. Seryi August, 006 Abstract The simulation
ACHIEVABLE SPACE-CHARGE TUNE SHIFT WITH LONG LIFETIME IN THE CERN PS & SPS
 Contributed talk (15 + 5 min, 30 slides) ACHIEVABLE SPACE-CHARGE TUNE SHIFT WITH LONG LIFETIME IN THE CERN PS & SPS Elias Métral Elias Métral, HB2008 workshop, Nashville, Tennessee, USA, August 25-29,
Contributed talk (15 + 5 min, 30 slides) ACHIEVABLE SPACE-CHARGE TUNE SHIFT WITH LONG LIFETIME IN THE CERN PS & SPS Elias Métral Elias Métral, HB2008 workshop, Nashville, Tennessee, USA, August 25-29,
Machine Protection. Lars Fröhlich DESY. CERN Accelerator School on FELs and ERLs June 9, 2016
 Machine Protection Lars Fröhlich DESY CERN Accelerator School on FELs and ERLs June 9, 2016 Overview What & Why? Interaction of Beams with Matter Damage to Permanent Magnets Photo: Wikimedia Commons, CC
Machine Protection Lars Fröhlich DESY CERN Accelerator School on FELs and ERLs June 9, 2016 Overview What & Why? Interaction of Beams with Matter Damage to Permanent Magnets Photo: Wikimedia Commons, CC
Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project:
 Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project: The Shielding World s for Leading the Hard X-ray Light Source Advanced Photon Source - Upgrade Bradley J. Micklich Radiation Physicist Argonne National
Advanced Storage Photon Ring Source Upgrade Project: The Shielding World s for Leading the Hard X-ray Light Source Advanced Photon Source - Upgrade Bradley J. Micklich Radiation Physicist Argonne National
ELIC Design. Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators. Jefferson Lab. Second Electron-Ion Collider Workshop Jefferson Lab March 15-17, 2004
 ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
e + e Factories M. Sullivan Presented at the Particle Accelerator Conference June 25-29, 2007 in Albuquerque, New Mexico e+e- Factories
 e + e Factories M. Sullivan Presented at the Particle Accelerator Conference June 25-29, 2007 in Albuquerque, New Mexico 1 Outline Factory Running KEKB PEP-II DAFNE CESR-c BEPCII 2 Summary Factory Running
e + e Factories M. Sullivan Presented at the Particle Accelerator Conference June 25-29, 2007 in Albuquerque, New Mexico 1 Outline Factory Running KEKB PEP-II DAFNE CESR-c BEPCII 2 Summary Factory Running
Open Issues from the SPS Long-Range Experiments
 Open Issues from the SPS Long-Range Experiments Frank Zimmermann US-LARP Beam-Beam Workshop SLAC, 2007 Gerard Burtin, Ulrich Dorda, Gijs de Rijk, Jean-Pierre Koutchouk, Yannis Papaphilippou, Tannaji Sen,
Open Issues from the SPS Long-Range Experiments Frank Zimmermann US-LARP Beam-Beam Workshop SLAC, 2007 Gerard Burtin, Ulrich Dorda, Gijs de Rijk, Jean-Pierre Koutchouk, Yannis Papaphilippou, Tannaji Sen,
US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping
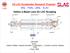 US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping Jeff Smith SLAC Vladmir Shiltsev, Shasha Drozhdin, V. Kuznetsov, L. Vorobiev and Alex Valishev FNAL 2 April,
US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping Jeff Smith SLAC Vladmir Shiltsev, Shasha Drozhdin, V. Kuznetsov, L. Vorobiev and Alex Valishev FNAL 2 April,
Electron Cloud Studies
 Electron Cloud Studies Tom Kroyer, Edgar Mahner,, Fritz Caspers, CERN LHC MAC, 7. December 2007 Agenda Introduction to electron cloud effects Overview over possible remedies surface coatings rough surfaces
Electron Cloud Studies Tom Kroyer, Edgar Mahner,, Fritz Caspers, CERN LHC MAC, 7. December 2007 Agenda Introduction to electron cloud effects Overview over possible remedies surface coatings rough surfaces
Beam-induced heat loads on the beam screens of the inner triplets for the HL-LHC
 CERN-ACC-2018-0009 Galina.Skripka@cern.ch Beam-induced heat loads on the beam screens of the inner triplets for the HL-LHC G. Skripka and G. Iadarola CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Keywords: LHC, HL-LHC, heat
CERN-ACC-2018-0009 Galina.Skripka@cern.ch Beam-induced heat loads on the beam screens of the inner triplets for the HL-LHC G. Skripka and G. Iadarola CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Keywords: LHC, HL-LHC, heat
Injection: Hadron Beams
 Proceedings of the CAS CERN Accelerator School: Beam Injection, Extraction and Transfer, Erice, Italy, 10-19 March 2017, edited by B. Holzer, CERN Yellow Reports: School Proceedings, Vol. 5/2018, CERN-2018-008-SP
Proceedings of the CAS CERN Accelerator School: Beam Injection, Extraction and Transfer, Erice, Italy, 10-19 March 2017, edited by B. Holzer, CERN Yellow Reports: School Proceedings, Vol. 5/2018, CERN-2018-008-SP
Transverse beam stability and Landau damping in hadron colliders
 Work supported by the Swiss State Secretariat for Educa6on, Research and Innova6on SERI Transverse beam stability and Landau damping in hadron colliders C. Tambasco J. Barranco, X. Buffat, T. Pieloni Acknowledgements:
Work supported by the Swiss State Secretariat for Educa6on, Research and Innova6on SERI Transverse beam stability and Landau damping in hadron colliders C. Tambasco J. Barranco, X. Buffat, T. Pieloni Acknowledgements:
LHC accelerator status and prospects. Frédérick Bordry Higgs Hunting nd September Paris
 LHC accelerator status and prospects 2 nd September 2016 - Paris LHC (Large Hadron Collider) 14 TeV proton-proton accelerator-collider built in the LEP tunnel Lead-Lead (Lead-proton) collisions 1983 :
LHC accelerator status and prospects 2 nd September 2016 - Paris LHC (Large Hadron Collider) 14 TeV proton-proton accelerator-collider built in the LEP tunnel Lead-Lead (Lead-proton) collisions 1983 :
Results of UFO dynamics studies with beam in the LHC
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Results of UFO dynamics studies with beam in the LHC To cite this article: B Lindstrom et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1067 022001 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Results of UFO dynamics studies with beam in the LHC To cite this article: B Lindstrom et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1067 022001 View the article
Longitudinal Dynamics
 Longitudinal Dynamics F = e (E + v x B) CAS Bruges 16-25 June 2009 Beam Dynamics D. Brandt 1 Acceleration The accelerator has to provide kinetic energy to the charged particles, i.e. increase the momentum
Longitudinal Dynamics F = e (E + v x B) CAS Bruges 16-25 June 2009 Beam Dynamics D. Brandt 1 Acceleration The accelerator has to provide kinetic energy to the charged particles, i.e. increase the momentum
Experimental Results of a LHC Type Cryogenic Vacuum System Subjected to an Electron Cloud
 Experimental Results of a LHC Type Cryogenic Vacuum System Subjected to an Electron Cloud V. Baglin, B. Jenninger CERN AT-VAC, Geneva 1. Introduction LHC & Electron Cloud LHC cryogenic vacuum system 2.
Experimental Results of a LHC Type Cryogenic Vacuum System Subjected to an Electron Cloud V. Baglin, B. Jenninger CERN AT-VAC, Geneva 1. Introduction LHC & Electron Cloud LHC cryogenic vacuum system 2.
HL-LHC OPERATIONAL SCENARIOS
 CERN-ACC-NOTE-2015-0009 2015-05-19 Elias.Metral@cern.ch HL-LHC OPERATIONAL SCENARIOS G. Arduini, N. Biancacci, O. Brüning, R. De Maria, M. Giovannozzi, W. Höfle, K. Li, E. Métral, J.E. Muller, Y. Papaphilippou,
CERN-ACC-NOTE-2015-0009 2015-05-19 Elias.Metral@cern.ch HL-LHC OPERATIONAL SCENARIOS G. Arduini, N. Biancacci, O. Brüning, R. De Maria, M. Giovannozzi, W. Höfle, K. Li, E. Métral, J.E. Muller, Y. Papaphilippou,
LHC Status and CERN s future plans. Lyn Evans
 LHC Status and CERN s future plans Lyn Evans Machine layout L. Evans EDMS document no. 859415 2 Cryodipole overview 1250 1000 Equivalent dipoles 750 500 250 0 01-Jan-01 01-Jan-02 01-Jan-03 01-Jan-04 01-Jan-05
LHC Status and CERN s future plans Lyn Evans Machine layout L. Evans EDMS document no. 859415 2 Cryodipole overview 1250 1000 Equivalent dipoles 750 500 250 0 01-Jan-01 01-Jan-02 01-Jan-03 01-Jan-04 01-Jan-05
EuCARD-2 Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development. Conference/Workshop Paper
 CERN-ACC-2017-0020 EuCARD-2 Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development Conference/Workshop Paper Upgrade of the CERN SPS Extraction Protection Elements TPS Borburgh, Jan (CERN)
CERN-ACC-2017-0020 EuCARD-2 Enhanced European Coordination for Accelerator Research & Development Conference/Workshop Paper Upgrade of the CERN SPS Extraction Protection Elements TPS Borburgh, Jan (CERN)
US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping
 US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping Jeff Smith SLAC Vladmir Shiltsev, Shasha Drozhdin FNAL 9 April, 2009 1 Motivation As of now, there are no
US LHC Accelerator Research Program BNL - FNAL- LBNL - SLAC Hollow e-beam Lens for LHC Scraping Jeff Smith SLAC Vladmir Shiltsev, Shasha Drozhdin FNAL 9 April, 2009 1 Motivation As of now, there are no
WHAT CAN THE SSC AND THE VLHC STUDIES TELL US FOR THE HE-LHC?
 WHAT CAN THE SSC AND THE VLHC STUDIES TELL US FOR THE HE-LHC? U. Wienands Λ Stanford Linear Accelerator Center; Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA ABSTRACT In the SSC and the VLHC machine designs a number of accelerator
WHAT CAN THE SSC AND THE VLHC STUDIES TELL US FOR THE HE-LHC? U. Wienands Λ Stanford Linear Accelerator Center; Menlo Park, CA 94025, USA ABSTRACT In the SSC and the VLHC machine designs a number of accelerator
Electron cloud experiments, and cures in RHIC
 Electron cloud experiments, and cures in RHIC Wolfram Fischer M. Blaskiewicz, H.-C. Hseuh, H. Huang, U. Iriso, V. Ptitsyn, T. Roser, P. Thieberger, D. Trbojevic, J. Wei, S.Y. Zhang PAC 07 Albuquerque,
Electron cloud experiments, and cures in RHIC Wolfram Fischer M. Blaskiewicz, H.-C. Hseuh, H. Huang, U. Iriso, V. Ptitsyn, T. Roser, P. Thieberger, D. Trbojevic, J. Wei, S.Y. Zhang PAC 07 Albuquerque,
Beam-induced heating in the TOTEM Roman Pot detectors at the LHC
 CERN-TOTEM-NOTE-2012-001 02 April 2012 Beam-induced heating in the TOTEM Roman Pot detectors at the LHC F. Ravotti CERN PH-DT, Geneva, Switzerland CERN-TOTEM-NOTE-2012-001 02/04/2012 Abstract During 2011,
CERN-TOTEM-NOTE-2012-001 02 April 2012 Beam-induced heating in the TOTEM Roman Pot detectors at the LHC F. Ravotti CERN PH-DT, Geneva, Switzerland CERN-TOTEM-NOTE-2012-001 02/04/2012 Abstract During 2011,
DYNAMIC APERTURE STUDIES FOR HL-LHC V1.0 *
 SLAC PUB 17366 December 2018 DYNAMIC APERTURE STUDIES FOR HL-LHC V1.0 * Y. Cai, R. De Maria, M. Giovannozzi, Y. Nosochkov, F.F. Van der Veken ;1 CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland SLAC National Accelerator
SLAC PUB 17366 December 2018 DYNAMIC APERTURE STUDIES FOR HL-LHC V1.0 * Y. Cai, R. De Maria, M. Giovannozzi, Y. Nosochkov, F.F. Van der Veken ;1 CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland SLAC National Accelerator
