Amsterdam Class 8. AMST (DVD 3) Counter Time: AMST (DVD 4) Counter Time: Questions and Answers
|
|
|
- Hester Cook
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Amsterdam Class 8 AMST (DVD 3) Counter Time: AMST (DVD 4) Counter Time: Questions and Answers 1. What is meant by the 15 Days of 1 st Creation? The next Gestation Cycle after the SEda Cycle is the one in which the Rasha Body Structure is born, simultaneously with the Tauren Cycle (1 st Day) which eventually births the Diad (2 nd Day). The first 9 Structures of the Inner Light Body, each formed after a Takeyon Cycle, are counted as 9 Days The Starborn Cycle. Simultaneously 6 Outer Light Body Structures birth, counted as 6 Days. Together these are the 15 Days of 1 st Creation. Inner Light Body Structures: Outer Light Body Structures: Day 1: The Tauren births with: The YunasA (Rosetta Sun) on Day 9 Day 2: The Diad births with: The Eukatharaista Body on Day 10 Day 3: The Miad births with: The 4 Eckasha-A on Day 11 Day 4: The Monad births with: The 24 Eckashas on Day 12 Day 5: The AmOrA Hub Cell births with: The Ecka-Vecas on Day 13 Day 6: The Adon births with: The E-Luman-yana on Day 14 Day 7: The Edon births with: The ELuman-aeri on Day 15 Day 8: The Aton (Rashallah) 2. What are the Harmonic Key Cycles, or, what is the Takeyon Cycle? After the Tauren is born at the center of the ELum-Eiradhona it goes through a Takeyon Cycle, which is a Pulse Phase Cycle with 12 Harmonic Key Cycles where sparks are made along the Allurean Lines to build enough quantum to hit the Takeyon Flash Point. After 12 Takeyon Cycles the critical mass is reached all the quantum comes together, pulls through as the Backflow through the Creation Point, and then gets a Backflow Return that is an increase of quantum plus the original quantum itself. The 1 st Flash Point is where the Tauren goes in to replicate its quantum. The Tauren comes back out as itself, but also has the Diad with it that has 6 Partiki. Harmonic Key Generation: a spark quantum building and replication Cycle. Harmonic Key Assembly: Sparks assemble in groups to form 12 Harmonic Keys Base Tone Keys with EirA energy and Overtone Keys with ManA energy. Key Resolution: By resolving the difference of their quantum, Keys form Prana. Key Ordenation: Every 3 rd Harmonic Key Cycle in a Takeyon Cycle (12 Harmonic Key Cycles) phases to build more quantum. 1
2 3. Why do the Ring and Span Tones activate not only our Rasha Body but also our Light Body and Physical Manifest Body? The structure of the PartikE of the Tauren is based on the larger structure of the ELum-Eiradhona with the huge 15 Geleziac Layers. The Rasha Body Dark Matter Template came from this structure of the PartikE and has the same 15 layers as the Light Body Base Shield structures. So when you are activating your Rasha Body with the Ring and Span Tones, you are activating the other as well. The Span Tones activate the bands in between, and the Ring Tones go with the Geleziac Radiation Levels. It brings the entire Rasha structure and Spiritual Body connection faster into the Matter structures. 4. Where do the Ethos and Eiros Grids come from? The Ethos and Eiros Grids that we phase in the Pillar of Power are part of the structure of the 4 Vecas plus the 2 (Ecka) E-Luman-yana Density Spirit Bodies. These Ethos-Eiros E-Luman-yana Density Spirit Bodies are behind the Radial Bodies called E-Luman-ata that we were activating with the Flame Body Activation Techniques. 5. What are the E-Luman-aeri (Density Time Vector Spirit Bodies)? In each Density E-Luman-yana and Radial Body E-Luman-ata you have 12 -Cell Probability Clusters: E-Luman-aeri Density Time Vector Spirit Bodies. Different probabilities come from the same main events. You have different probabilities depending on your Base Pulse Rhythm. You can end up seeing that probability as your manifest reality field rather than others. Technically you have a Probable Self in every one of the 12 Probabilities. The process of bringing yourself together is accreting all of the 12 different frequencies. First you bring in the lowest frequencies that run the Number 1 Allurean Chamber and then you experience the Number 2 Probability, then the Number 3 Probability, until you pulled yourself all together and get back to the middle Probability and then do another Cycle of them. In each Ecka-Veca, Eckasha, Eckasha-A and Eckasha-Aah are sets of 12 of these. 6. How are the 2 Krystal Spirals formed and what happens when they merge? After the Aton Cluster of 20,736 Partiki is born and before the YunasA is born, all the Inner Light Cells (the Tauren, Diad, Miad, Monad, AmOrA Hub Cell, Adon, Edon and Aton) that grow before, start opening their Spark Currents. These currents birth a Krystal Spiral. This happens on both the AdorA and EtorA sides. Both Krystal Spirals birth and meet each other on the Zero Point Axis (see Schedule with 8 Axes). They merge and then the Flame Shift Cycle occurs. The Inner Flame and Core Flame are formed within the Seed Atom of the Inner Domain the Yunasai. (See Flame Images.) The Aton Activation and Akashic Record Imprinting also occur during this period (between Days 8 and 9). 2
3 7. What is the Aton Activation and Akashic Record Imprinting? During the Flame Shift Cycle, the Krystal Spiral Inner Light Body Currents eventually merge their EtorA and AdorA Elemental Adjugate Twin Spark Currents. This activates not only the Inner and Core Flames but also the 20,736 Partiki Cells of the Aton. There is a whole process in which everything that was created so far, the Aton included, pulls in to the Hall of Records 8-Cell Cluster. Through activation of the Flame Cycle and bringing together these currents from the AdorA and the EtorA side, the encryption of that entire particular part of the Rasha Body and Light Body of that Creation Cycle is imprinted into the Spirit Body in the Akashic and Ecoushic Records of the 1 st Cell, literally recording it and putting it in a permanent record. 8. What is the relationship between the Cosmic YunasA and the Domains? On Day 9 the Cosmic YunasA 30-Cell Cluster births after a Flame Cycle, simultaneously with the birth of the ELum-Eiradhona and the Tauren on Day 1, after the first SEda Cycle. Before the Birth of the YunasA, the NavE-Na Cycles (Day 6 and Day 7) and the SEda Cycles (Day 8) of the smaller Domains started. The Spirit Domain Bodies phase into the HaRA Krysta Body, pull in through the DhaLA-LUma Doorway, and then birth out with the Cosmic Yunasun Cluster (the Cosmic YunasA or Rosetta Sun). This Cosmic YunasA creates all of the Seed Atoms for the Inner, the Middle, the Outer Domains and also the Adashi Domains. The Light Body and the Spirit Body of those smaller Domains fill themselves out, each creating a Eukatharaista Structure with its Spirit Body. 9. What has the YunasA to do with the Rosetta Flows? The Cosmic YunasA 30-Cell Light Body Elemental Command Cluster, also called the Rosetta Sun, births with the Inner Light Body Rosetta Cluster. The 9 layers of the Rosetta Cluster are formed from those different sets of Cell Structures that birth on the first 9 Days of Creation. (From the Tauren, the Diad, the Miad, the Monad, the AmOrA Hub Cell, the Adon, the Edon to the Aton.) They form the Rosetta Core Currents (the AdorA and EtorA Krystal Spirals). The Rosetta Flows open the Akashic and Ecoushic Record 1 st Cells. The Rosetta Flows draw the 144 manifest Elemental Adjugate Twins into the 12 Allurean Chambers of the Cosmic Spirit Body. By opening these 12 Cosmic ELum-Eiradhona Currents into the Cosmic and Domain Allurean Chambers, the Core LaVa and Rosetta Flows merge with the Spirit Body Currents. In the LUma Eturna level of the Spirit Body, the Elemental Adjugate Twins open the NaVA-Ho Core Flows, which are shaped like 8s. These NaVA-Ho Core Flows run between the LUma Eturna, the Hall of Records 8-Cells, the Akashic, Ecoushic Record 1 st Cells, the Rasha Dark Matter Body, and the Inner and Outer Light Bodies. 3
4 The Rosetta Flows also form the 9 Kundalini Flows when entering the Allurean Chambers of the smaller Domain Spirit Bodies. 10. Why are the HaRA Krysta Lines important? When the currents of the YunasA open up, they form the HaRA Lines. The Rosetta Flows open into the Allurean Chambers Cosmic and Domain Levels, creating the Core LaVa Flows and the 9 Rosetta Currents combined, to form the Core Cosmic HaRA Krysta Lines in the Domains and Cosmic Allurean Chambers. There are 12 HaRA Krysta Lines, which run the Allurean Chambers. They open into the whole structure of the Akashic Record and the Ecoushic Record and the Halls, right into the Creation Point and the Spirit Body. The 12 HaRA Krysta Lines directly link the Light Body through the Rasha Body through the Spirit Body so the flows can begin. They put everything on line with the Cosmic Time Matrix and the Living Body of God-Source. 11. What are Foils and how are they created? The Elemental Current fission and fusion begins at the core of the Cosmic Rasha Prana Seed, forming the 144 Base Elemental Currents of Eiradonis Atomic Matter and releasing the Atomic-Eiradonis Currents into the Light Body for Matter accretion. Atomic Elemental Currents are Eiradonis Adjugate Spirit Currents that form the Base Accretion Templates of Matter forms the Eiradonis Templates or Foils. Light Body Spark Currents accrete upon, and form a crystalline membrane over, the Atomic-Eiradonis Armature Foil. Underneath the Light Body is this living Eiradonis level that is considered the core of the Atomic level. 12. What are the Axi-A-Tonal Lines and Meridian Lines supposed to run? In the manifest natural EtorA System, Axi-A-Tonal Lines are supposed to run the Akashic Currents, which are the EtorA Matter Eiradonis Currents flowing from the Allurean Chambers and Akashic Record AdorA 1 st Cell. The substance is referred to as Hydrolase. These Akashic Currents form the Akashic Body EtorA Matter Foil natural Meridian Lines. These Meridian Lines are positive lines running EtorA Light Body Currents (Rosetta Currents) from the Allurean Chambers and the YunasA Rosetta Cluster. These EtorA Light Body Currents (Rosetta Currents) form the EtorA crystallized light-skin membrane over the Akashic Body Eiradonis Geleziac Foil. 4
5 Vocabulary 1. Creation Cycle: The Creation process starts from the first Partiki and includes the NaVE-Na Cycle (Fertilization), the SEda Cycle (Birth of the ELum-Eiradhona), the Lightborn Cycle (Birth of the Tauren), the Starborn Cycle (Birth of the Rosetta + Seed Atom), the Life Born Cycle (Birth of the Rasha), and the God Born Cycle (Birth of the 7 Inner Suns Hub + the Outer Eukatharaista Body). All the stages are shown on a schedule with 8 axes. 2. Prana Joule: The Prana Joule is the part of the Overtone ManA Key that is taken away to bond with the Base Tone EirA Key during the Key Resolution process. 3. Mana: After Key Resolution, the part of the Overtone ManA Key that remains after the same amount of the Base Tone EirA Key has been subtracted is called Mana. 4. NaVE-Na Cycle: Before the SEda Cycle there is first the NaVA-na Cycle with the birth of Partiki 1, then the NuVA-Na Cycle with the birth of Partiki 2. Together these are called the NaVE-Na Cycle. 5. Adjugate Twins: During the Flame Shift Cycle, the Krystal Spiral Inner Light Body Currents eventually merge their EtorA and AdorA Elemental Adjugate Twin Spark Currents. Adjugate Twins are associated with each of the Allurean Chambers. Where an Allurean Chamber crosses through a Span, it creates a specific type of Element Encryption. These Chambers function as cross-vectors where the two different (EtorA and AdorA) Elemental Currents combine to form the transient element Celestalline. 6. Natural Periodic Table: The Natural Periodic Table is associated with the 12 Allurean Chambers. They are actually responsible for making a specific encryption for specific elements that have to do with Adjugate Twins. Bringing the Adjugate Currents together is bringing Elemental Currents together from the AdorA and EtorA side. Every combination of these Adjugate Currents forms Celestalline, a transient element. 7. Kundalini Flows: The Rosetta Flows form the 9 Kundalini Flows, which enter the Allurean Chambers of the smaller Domain Spirit Bodies. 8. Akashic Currents: The EtorA Matter Eiradonis Currents are called the Akashic Currents and flow into EtorA Matter from the Akashic Record AdorA 1 st Cell. The substance is referred to as Hydrolase. 5
6 9. Ecoushic Currents: The AdorA Matter Eiradonis Currents are called the Ecoushic Currents and flow into AdorA Matter from the Ecoushic Record EtorA 1 st Cell. The substance is referred to as Hydrolase. 10. Hydrolase Currents: The Eiradonis Atomic Adjugate Spirit Currents are Hydrolase Currents. The substance is referred to as Hydrolase. It is part EirA and part Prana. 11. HaRA Krysta Line: The currents coming from the YunasA open up the Hara Lines. These 12 HaRA Krysta Lines, which run the Allurean Chambers, open into the whole structure of the Akashic Record and the Ecoushic Record and the Halls, right into the Creation Point and the Spirit Body. They link the Light Body through the Rasha Body through the Spirit Body, so the flows can begin. 12. The Reuzhetta Starlight Code: The Reuzhetta Starlight Code is the 15 Geleziac Template of the Base Shield Planes of the Light Bodies, showing the rotational expansion that starts with the Tauren all the way up to the Diad, Miad, Monad, AmOrA Hub Cell, Edon, Adon and Aton. These layers correspond with the 15 Geleziac Layers of the Rasha Body. Multiple Choice 1. What birthed on Day 1 with the Tauren Light Seed and the YunasA? (a) The Aton. (b) The Eckasha. (c) The Halls of REisha-TA. (d) The ELum-Eiradhona. 2. What are the 15 Geleziac Layers within the PartikE of the Tauren called? (a) The Ovum of Living Light. (b) The Dark Matter Templates. (c) The Halls of REisha-TA. (d) The ELum-Eiradhona. 3. What was formed in the Zero Point Cycle before the 15 Days of 1 st Creation? (a) The Diad, when the 2 Eckasha-Aahs are created the Eukatharaista Body. (b) The Triad, when Partiki 1 was split by Partiki 2 the start of the SEda Cycle. (c) The Seed Atoms of the Inner, Middle and Outer Domains. (d) The Inner Light Body Rosetta Cluster. 6
7 4. How many Harmonic Key Cycles and Key Ordenations are there in 1 Takeyon? (a) 1 Takeyon has 4 Harmonic Key Cycles and 12 Key Ordenations. (b) 1 Takeyon has 48 Harmonic Key Cycles and 4 Key Ordenations. (c) 1 Takeyon has 12 Harmonic Key Cycles and 12 Key Ordenations. (d) 1 Takeyon has 12 Harmonic Key Cycles and 4 Key Ordenations. 5. What are the numbers of Partiki quantum building times 2 replication? (a) The Tauren: 6; Diad: 12; Miad: 24; Monad: 48; and AmOrA Hub: 96 Partiki. (b) The Tauren: 12; Diad: 24; Miad: 48; Monad: 96; and AmOrA Hub: 192 Partiki. (c) The Tauren: 3; Diad: 6; Miad: 24; Monad: 144; and AmOrA Hub: 1728 Partiki. (d) The Tauren: 3; Diad: 6; Miad: 12; Monad: 24; and AmOrA Hub: 48 Partiki. 6. What are the numbers of Partiki quantum building times 3 and 12 replication? (a) The Adon: 144; the Edon: 1728; and the Aton: 20,736 Partiki. (b) The Adon: 24; the Edon: 72; and the Aton: 216 Partiki. (c) The Adon: 48; the Edon: 1728; and the Aton: 20,736 Partiki. (d) The Adon: 48; the Edon: 144; and the Aton: 432 Partiki. 7. What are the parts of the Eukatharaista Body? (a) The 2 Eckasha-Aahs, 1 referring to the AdorA side and 1 to the EtorA side. (b) The 4 Eckasha-As, each having a set of 4 Vecas and 2 Eckas. (c) The 24 Eckashas, 16 visible ones and 8 in the center of the Eckasha-As. (d) The 4 Vecas and 2 Eckas. 8. Which Grids are part of the 2 (Ecka) E-Luman-yana Density Spirit Bodies? (a) The E-Luman-aeri Grids, which we phase with the Pillar of Power. (b) The E-Luman-ata Grids, which we phase with the Pillar of Power. (c) The Ethos and Eiros Grids, which we phase with the Pillar of Power. (d) The Adon and Edon Grids, which we phase with the Pillar of Power. 9. What is the 12-Cell Probability Cluster called? (a) The E-Luman-aeri. (b) The E-Luman-yana. (c) The E-Luman-ata. (d) The ELum-Eiradhona. 10. What births the Seed Atoms of the Inner, Middle and Outer Domain? (a) The Cosmic YunasA 30-Cell Cluster. (b) The Yunasai 15-Cell Cluster. (c) The Tauren. (d) The ELum-Eiradhona. 7
8 11. What are the names of the Seed Atoms of the Inner, Middle and Outer Domains? (a) YunasA, Yon-A-Sa and UmShadEi. (b) UmShadEi, Yunasai and YunasA. (c) Yunasai, UmShadEi and Yon-A-Sa. (d) UmShadEi, Yunasai and Yon-A-Sa. 12. What births on Day 10 with the Diad and the Eukatharaista Body? (a) A Baby. (b) The Big Bang. (c) The Reuzhetta. (d) All of the above. Multiple Choice Answers: 1.D, 2.A, 3.B, 4.D, 5.D, 6.A, 7.A, 8.C, 9.A, 10.A, 11.C, 12.D. The dynamics of the emerging MCEO materials involve the reality that the detailed understanding of major topics is under continuous development; therefore, the contents, and level of detail herein, are as advanced as possible UP TO the date of the workshop recording. 8
Amsterdam Class 5. AMST DVD 3 Counter Time: Questions and Answers
 Amsterdam Class 5 AMST DVD 3 Counter Time: 0.38 1.31 Questions and Answers 1. How does the Rasha Dark Matter Body connect the EtorA and AdorA sides? The Rasha Dark Matter Body and its structure connect
Amsterdam Class 5 AMST DVD 3 Counter Time: 0.38 1.31 Questions and Answers 1. How does the Rasha Dark Matter Body connect the EtorA and AdorA sides? The Rasha Dark Matter Body and its structure connect
Amenti Class 1. Amenti DVDs Counter Time: (DVD1) 0:00 00:40 min. Questions and Answers
 Amenti Class 1 Amenti DVDs Counter Time: (DVD1) 0:00 00:40 min. Questions and Answers 1. Ash describes the Science of Keylonta in detail. What points does she use to characterize, or describe it with?
Amenti Class 1 Amenti DVDs Counter Time: (DVD1) 0:00 00:40 min. Questions and Answers 1. Ash describes the Science of Keylonta in detail. What points does she use to characterize, or describe it with?
SSC Class 8. SSC DVD 4 Counter Time: 00:00 01:15. Questions and Answers
 SSC Class 8 SSC DVD 4 Counter Time: 00:00 01:15 Questions and Answers 1. In the Heliographic Re-programming Technique, where is the corrected personal Merkabic Density Disc finally anchored? The personal
SSC Class 8 SSC DVD 4 Counter Time: 00:00 01:15 Questions and Answers 1. In the Heliographic Re-programming Technique, where is the corrected personal Merkabic Density Disc finally anchored? The personal
Search Results. Summary
 Search Results Summary Searched for : cluster In index(es) : H:\KS_Scan_Library\MasterIndex.pdx Results : 63 document(s) with 631 instance(s) Saved on : 7/8/2017 11:35:38 PM File : 1999-09_EvolutionaryPathClass_scan.pdf
Search Results Summary Searched for : cluster In index(es) : H:\KS_Scan_Library\MasterIndex.pdx Results : 63 document(s) with 631 instance(s) Saved on : 7/8/2017 11:35:38 PM File : 1999-09_EvolutionaryPathClass_scan.pdf
3/1/18. Things to do. Topics for Today
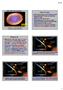 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Spirograph Planetary Nebula Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 14 Thur 1 Mar 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today Revisit birth of stars
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Spirograph Planetary Nebula Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 14 Thur 1 Mar 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Topics for Today Revisit birth of stars
Star Formation. Stellar Birth
 Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
The Evolution of Consciousness to Matter
 The Evolution of Consciousness to Matter Jere Rivera-Dugenio, Ph.D. Quantum Spanner Research Reno, Nevada USA Copyright: 2017 Rivera- Dugenio. This is an open- access article distributed under the terms
The Evolution of Consciousness to Matter Jere Rivera-Dugenio, Ph.D. Quantum Spanner Research Reno, Nevada USA Copyright: 2017 Rivera- Dugenio. This is an open- access article distributed under the terms
Nucleus Hydrogen nucleus. hydrogen. helium
 1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
1. (a) Once formed, a star can have a stable life for billions of years. Describe the two main forces at work in the star during this period of stability. 1.... 2.... What happens to a star once this stable
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun
 Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Life of stars, formation of elements
 Life of stars, formation of elements Recap life of sun Life of massive stars Creation of elements Formation of stars Profs. Jack Baldwin & Horace Smith will teach course for the remainder of the term to
Life of stars, formation of elements Recap life of sun Life of massive stars Creation of elements Formation of stars Profs. Jack Baldwin & Horace Smith will teach course for the remainder of the term to
The Universe. Unit 3 covers the following framework standards: ES 8 and 12. Content was adapted the following:
 Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Unit 3 The Universe Chapter 4 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 1 ~ The Scale of the Universe o Section 2 ~ The Formation of the Universe o Section 3 ~ The Future of the Universe Chapter 5 ~ Galaxies
Chapter 17 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Stuff Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
Chapter 17 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Stuff Star Stuff 17.1 Lives in the Balance Our goals for learning: How does a star's mass affect nuclear fusion? How does a star's mass affect
M42 (The Orion Nebula) and M43
 3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 The H-R Diagram review So far: AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies - Stars on Main Sequence (MS) - Pre MS (Star Birth) Next: - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Evolution of Low
The H-R Diagram review So far: AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies - Stars on Main Sequence (MS) - Pre MS (Star Birth) Next: - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Evolution of Low
TA feedback forms are online!
 1 Announcements TA feedback forms are online! find the link at the class website. Please take 5 minutes to tell your TAs your opinion. In case you did not notice, the Final is set for 03/21 from 12:00-3:00
1 Announcements TA feedback forms are online! find the link at the class website. Please take 5 minutes to tell your TAs your opinion. In case you did not notice, the Final is set for 03/21 from 12:00-3:00
December 2 nd through December 22 nd
 Phase I March 8 to March 22 Phase II March 22 to Phase III to May 4 December 2 nd through December 22 nd Photograph by Karyl Jackson True inner self sets the coordinates for this 2018 journey Mercury retrograde
Phase I March 8 to March 22 Phase II March 22 to Phase III to May 4 December 2 nd through December 22 nd Photograph by Karyl Jackson True inner self sets the coordinates for this 2018 journey Mercury retrograde
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Birth & Death of Stars
 Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
Birth & Death of Stars Objectives How are stars formed How do they die How do we measure this The Interstellar Medium (ISM) Vast clouds of gas & dust lie between stars Diffuse hydrogen clouds: dozens of
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
1 The Life Cycle of a Star
 CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
How do we measure properties of a star? Today. Some Clicker Questions - #1. Some Clicker Questions - #1
 Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Today Announcements: HW#8 due Friday 4/9 at 8:00 am. The size of the Universe (It s expanding!) The Big Bang Video on the Big Bang NOTE: I will take several questions on exam 3 and the final from the videos
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System 25.1 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies The H-R Diagram review So far: Stars on Main Sequence (MS) Next: - Pre MS (Star Birth) - Post MS: Giants, Super Giants, White dwarfs Star Birth We start
Section 25.1 Exploring the Solar System (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 25 The Solar System Section 25.1 Exploring the Solar System (pages 790 794) This section explores early models of our solar system. It describes the components of the solar system
Name Class Date Chapter 25 The Solar System Section 25.1 Exploring the Solar System (pages 790 794) This section explores early models of our solar system. It describes the components of the solar system
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS
 STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department. Space. Pupil Notes Name:
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Formation of the Universe
 A. The Universe 1. 2. 3. How did the universe begin? Only one exists or are there more? Composed of space and 100 billion galaxies A galaxy is a grouping of millions or billions of stars kept together
A. The Universe 1. 2. 3. How did the universe begin? Only one exists or are there more? Composed of space and 100 billion galaxies A galaxy is a grouping of millions or billions of stars kept together
Physics 311 General Relativity. Lecture 18: Black holes. The Universe.
 Physics 311 General Relativity Lecture 18: Black holes. The Universe. Today s lecture: Schwarzschild metric: discontinuity and singularity Discontinuity: the event horizon Singularity: where all matter
Physics 311 General Relativity Lecture 18: Black holes. The Universe. Today s lecture: Schwarzschild metric: discontinuity and singularity Discontinuity: the event horizon Singularity: where all matter
10/26/ Star Birth. Chapter 13: Star Stuff. How do stars form? Star-Forming Clouds. Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud. Gravity Versus Pressure
 10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
10/26/16 Lecture Outline 13.1 Star Birth Chapter 13: Star Stuff How do stars form? Our goals for learning: How do stars form? How massive are newborn stars? Star-Forming Clouds Stars form in dark clouds
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture
 (Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
(Astronomy for Dummies) remark : apparently I spent more than 1 hr giving this lecture A.D. 125? Ptolemy s geocentric model Planets ( ) wander among stars ( ) For more info: http://aeea.nmns.edu.tw/aeea/contents_list/universe_concepts.html
Implications of the Hubble Law: - it is not static, unchanging - Universe had a beginning!! - could not have been expanding forever HUBBLE LAW:
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe. Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is changing (getting bigger!) - it is not static, unchanging
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Today + Become a Learning Assistant! Info Session (Tomorrow) Wed March 5, 6-8pm6 MCD Biology Interactive Classroom
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Kyle Augustson Lecture 15 Tues 4 Mar 08 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre MID-POINT LECTURE Etched Hourglass Nebula Today + Discuss
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Kyle Augustson Lecture 15 Tues 4 Mar 08 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre MID-POINT LECTURE Etched Hourglass Nebula Today + Discuss
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B.
 Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion 1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B. Draw a line to link each description in List A to its correct name
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion 1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B. Draw a line to link each description in List A to its correct name
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small. Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction
 The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction 1 Galaxies lie at the crossroads of astronomy The study of galaxies brings together nearly all astronomical disciplines:
The Universe of Galaxies: from large to small Physics of Galaxies 2012 part 1 introduction 1 Galaxies lie at the crossroads of astronomy The study of galaxies brings together nearly all astronomical disciplines:
Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
2) On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars? A) upper right B) lower right C) upper left D) lower left
 Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Multiple choice test questions 2, Winter Semester 2015. Based on parts covered after mid term. Essentially on Ch. 12-2.3,13.1-3,14,16.1-2,17,18.1-2,4,19.5. You may use a calculator and the useful formulae
Stellar Evolution: Outline
 Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Stellar Evolution: Outline Interstellar Medium (dust) Hydrogen and Helium Small amounts of Carbon Dioxide (makes it easier to detect) Massive amounts of material between 100,000 and 10,000,000 solar masses
Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics Starting a different area of physics called thermodynamics Thermodynamics focuses on energy rather than
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics Starting a different area of physics called thermodynamics Thermodynamics focuses on energy rather than
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary. Chapter 1 The Setting
 How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
How to Build a Habitable Planet Summary Chapter 1 The Setting The universe as we know it began about 15 billion years ago with an explosion that is called the big bang. There is no record of any prior
Chapter 16: Ionizing Radiation
 Chapter 6: Ionizing Radiation Goals of Period 6 Section 6.: To discuss unstable nuclei and their detection Section 6.2: To describe the sources of ionizing radiation Section 6.3: To introduce three types
Chapter 6: Ionizing Radiation Goals of Period 6 Section 6.: To discuss unstable nuclei and their detection Section 6.2: To describe the sources of ionizing radiation Section 6.3: To introduce three types
Learning Objectives: Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars. AST 2010: Chapter 13. AST 2010 Descriptive Astronomy
 Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
Chapter 13, Part 1: Lower Main Sequence Stars Define red dwarf, and describe the internal dynamics and later evolution of these low-mass stars. Appreciate the time scale of late-stage stellar evolution
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
October 4 th through October 25 th
 Phase I Sept 15 Oct 4 Phase II Oct 4 Oct 25 Phase III Oct 25 Nov 10 PHASE I: Mercury will collect the issues from September 15th through October 4th as events culminate. Mercury reaches the furthest forward
Phase I Sept 15 Oct 4 Phase II Oct 4 Oct 25 Phase III Oct 25 Nov 10 PHASE I: Mercury will collect the issues from September 15th through October 4th as events culminate. Mercury reaches the furthest forward
According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a. Chapter 34: Cosmology. Cosmology: How the Universe Works
 Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Chapter 34: Cosmology According to the currents models of stellar life cycle, our sun will eventually become a a) Cloud of hydrogen gas b) Protostar c) Neutron star d) Black hole e) White dwarf id you
Page 2. Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun.
 Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun. (a) (i) What is the relationship between the masses of the dust and gas in the cloud in Stage 2 and the force of
Q1. The diagram shows part of the life cycle of a star which is much bigger than the Sun. (a) (i) What is the relationship between the masses of the dust and gas in the cloud in Stage 2 and the force of
Low mass stars. Sequence Star Giant. Red. Planetary Nebula. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. White Dwarf. Interstellar Cloud. Planetary Nebula.
 Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Interstellar Cloud Main Sequence Star Red Giant Planetary Nebula White Dwarf Low mass stars Interstellar Cloud
Card #1/28. Card #2/28. Science Revision P2. Science Revision P2. Science Revision P2. Card #4/28. Topic: F = ma. Topic: Resultant Forces
 Card #1/28 Card #2/28 Topic: Resultant Forces Topic: F = ma Topic: Distance-TIme Graphs Card #3/28 Card #4/28 Topic: Velocity-Time Graphs Card #2/28 Card #1/28 Card #4/28 Card #3/28 Card #5/28 Card #6/28
Card #1/28 Card #2/28 Topic: Resultant Forces Topic: F = ma Topic: Distance-TIme Graphs Card #3/28 Card #4/28 Topic: Velocity-Time Graphs Card #2/28 Card #1/28 Card #4/28 Card #3/28 Card #5/28 Card #6/28
TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify This star is in the last stage of its life cycle. What is that stage?
 CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
Questions on Universe
 Questions on Universe 1. The Doppler shift may be used in the study of distant galaxies. Explain what is meant by a Doppler shift and how it is used to deduce the motion of distant galaxies. You may be
Questions on Universe 1. The Doppler shift may be used in the study of distant galaxies. Explain what is meant by a Doppler shift and how it is used to deduce the motion of distant galaxies. You may be
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
Study Guide Chapter 2
 Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Module 3: Astronomy The Universe Topic 1 Content: Cosmology Presentation Notes
 Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Pretend that you have been given the opportunity to travel through time to explore cosmology. Cosmology is the study of how the universe formed and what will happen to it. Watch through your viewport as
Esoteric Astrology as the Highest Science
 The Morya Federation Esoteric Astrology as the Highest Science - The needed main subjects to work with esoteric astrology as the highest science - Birgitte Rasmussen Classic astrology is occupied with
The Morya Federation Esoteric Astrology as the Highest Science - The needed main subjects to work with esoteric astrology as the highest science - Birgitte Rasmussen Classic astrology is occupied with
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 27 What s Next?
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 27 What s Next? The origin of the elements Apart from the expansion of the universe and the cosmic microwave background radiation, the Big Bang theory makes another important set of
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation!
 AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
AST-1002 Section 0459 Review for Final Exam Please do not forget about doing the evaluation! Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the scantrons
Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars.
 1 (a) Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars. (i) Explain briefly the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
1 (a) Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars. (i) Explain briefly the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Astronomy. Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe.
 Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
Astronomy Study of objects in space such as the Sun, stars, planets, comets, gas, & galaxies. *Also, the Earth s place in the universe. Universe = everything that exists Disclaimer: Astrology is NOT science!!!
17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star
 17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Our goals for learning: What are the life stages of a high-mass star? How do high-mass stars make the elements necessary for life? How does a high-mass star die? What are
17.3 Life as a High-Mass Star Our goals for learning: What are the life stages of a high-mass star? How do high-mass stars make the elements necessary for life? How does a high-mass star die? What are
Some stars will finish their life cycle as a black dwarf and other stars as a black hole.
 Q1.Stars go through a life cycle. Some stars will finish their life cycle as a black dwarf and other stars as a black hole. (a) The table below gives the mass, relative to the Sun, of three stars, J, K
Q1.Stars go through a life cycle. Some stars will finish their life cycle as a black dwarf and other stars as a black hole. (a) The table below gives the mass, relative to the Sun, of three stars, J, K
Learning Outcomes 2. Key Concepts 2. Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3. Vocabulary 4. Lesson and Content Overview 5
 UNIT 3 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 3 GUIDE 1 Unit 3 Stars and
UNIT 3 GUIDE Table of Contents Learning Outcomes 2 Key Concepts 2 Misconceptions and Teaching Challenges 3 Vocabulary 4 Lesson and Content Overview 5 BIG HISTORY PROJECT / UNIT 3 GUIDE 1 Unit 3 Stars and
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life
 Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Quiz Unless otherwise noted, all pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 The presence of
Joy of Science Experience the evolution of the Universe, Earth and Life Review Introduction Main contents Quiz Unless otherwise noted, all pictures are taken from wikipedia.org Review 1 The presence of
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Potter Name: Date: Hour: Earth Science Unit 2: Astronomy
 Unit 2: Astronomy #1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. Yes I can 1. Can you roughly explain how
Unit 2: Astronomy #1 LT 2.1 Galaxy Formation: I am able to describe the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy and our solar system and model earth s position in each. Yes I can 1. Can you roughly explain how
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
The Formation of the Solar System
 Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
Earth and the Solar System The Formation of the Solar System Write a number beside each picture to rank each from the oldest (1) to the youngest (4). The universe includes everything that exists: all matter,
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The dying sun/ creation of elements
 The dying sun/ creation of elements Homework 6 is due Thurs, 2 April at 6:00am OBAFGKM extra credit Angel: Lessons>Extra Credit Due 11:55pm, 31 March Final exam (new, later time) 6 May, 3:00-5:00, BPS
The dying sun/ creation of elements Homework 6 is due Thurs, 2 April at 6:00am OBAFGKM extra credit Angel: Lessons>Extra Credit Due 11:55pm, 31 March Final exam (new, later time) 6 May, 3:00-5:00, BPS
SSC Class 11. SSC DVD 5 Counter Time: 00:45 02:00. Questions and Answers
 SSC Class 11 SSC DVD 5 Counter Time: 00:45 02:00 Questions and Answers 1. The anchoring of the BeaST machine in our planetary grids began with the creation of an unnatural "patrol station" that included
SSC Class 11 SSC DVD 5 Counter Time: 00:45 02:00 Questions and Answers 1. The anchoring of the BeaST machine in our planetary grids began with the creation of an unnatural "patrol station" that included
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Chapter 14: The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard Assignments 2 nd Mid-term to be held Friday Nov. 3 same basic format as MT1 40 mult. choice= 80 pts. 4 short answer = 20 pts. Sample problems on web page Origin
Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein
 Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein Part 1: The Untold Physics Chapter 5: Concept of Black Holes In order to understand the concept of atoms, planets, galaxies and stars as all having
Crossing the Event Horizon Presented by Nassim Haramein Part 1: The Untold Physics Chapter 5: Concept of Black Holes In order to understand the concept of atoms, planets, galaxies and stars as all having
Name: Space Questions. Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s:
 Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
AP5301/ Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions.
 Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
Review Problems on Optical Microscopy AP5301/8301-2015 1. Name the major parts of an optical microscope and state their functions. 2. Compare the focal lengths of two glass converging lenses, one with
The Secrets behind the Origin of Our Galaxy (Hypothesis)
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 3 Ver. I (May - Jun. 2015), PP 17-21 www.iosrjournals.org The Secrets behind the Origin of
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 3 Ver. I (May - Jun. 2015), PP 17-21 www.iosrjournals.org The Secrets behind the Origin of
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015
 Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Astro 1050 Fri. Apr. 10, 2015 Today: Continue Ch. 13: Star Stuff Reading in Bennett: For Monday: Finish Chapter 13 Star Stuff Reminders: Ch. 12 HW now on Mastering Astronomy, due Monday. Ch. 13 will be
Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System
 Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System The Andromeda Galaxy One of hundreds of billions of galaxies, each with hundreds of billions of stars A warped spiral galaxy, 150 MLY away and 100,000
Outline 8: History of the Universe and Solar System The Andromeda Galaxy One of hundreds of billions of galaxies, each with hundreds of billions of stars A warped spiral galaxy, 150 MLY away and 100,000
Organization of Detail
 Organization of Detail For the chronology and points of detail within the chronology, a numbering system has been employed. Each detail is assigned a number containing several decimal points. The numbering
Organization of Detail For the chronology and points of detail within the chronology, a numbering system has been employed. Each detail is assigned a number containing several decimal points. The numbering
Introduction to Cosmology
 Introduction to Cosmology Subir Sarkar CERN Summer training Programme, 22-28 July 2008 Seeing the edge of the Universe: From speculation to science Constructing the Universe: The history of the Universe:
Introduction to Cosmology Subir Sarkar CERN Summer training Programme, 22-28 July 2008 Seeing the edge of the Universe: From speculation to science Constructing the Universe: The history of the Universe:
A Star Becomes a Star
 A Star Becomes a Star October 28, 2002 1) Stellar lifetime 2) Red Giant 3) White Dwarf 4) Supernova 5) More massive stars Review Solar winds/sunspots Gases and Dust Molecular clouds Protostars/Birth of
A Star Becomes a Star October 28, 2002 1) Stellar lifetime 2) Red Giant 3) White Dwarf 4) Supernova 5) More massive stars Review Solar winds/sunspots Gases and Dust Molecular clouds Protostars/Birth of
Chapter 5. Periodic Law.
 Chapter 5 Periodic Law http://www.sciencedump.com/content/new-periodic-table-song Chapter 5.1 History of the Periodic Table 5.1 Objectives Explain the roles of Mendeleev and Moseley in the development
Chapter 5 Periodic Law http://www.sciencedump.com/content/new-periodic-table-song Chapter 5.1 History of the Periodic Table 5.1 Objectives Explain the roles of Mendeleev and Moseley in the development
g = Gm / r 2 The Big Idea
 The Big Idea Over 2500 years ago Aristotle proposed two laws of physics governing motion. One for Earthly bodies (objects on Earth) that states objects naturally go in straight lines and one for Heavenly
The Big Idea Over 2500 years ago Aristotle proposed two laws of physics governing motion. One for Earthly bodies (objects on Earth) that states objects naturally go in straight lines and one for Heavenly
21/11/ /11/2017 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8
 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing;
 Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Q. Describe, in as much detail as you can: the evidence that the size of the observable Universe is changing; the evidence that, billions of years ago, all the matter in the Universe was tightly packed
Stars and Galaxies. Content Outline for Teaching
 Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
Section 1 Stars A. Patterns of stars - constellations 1. Ancient cultures used mythology or everyday items to name constellations 2. Modern astronomy studies 88 constellations 3. Some constellations are
Lecture 12 Cosmology III. Inflation The beginning?
 Lecture 12 Cosmology III Inflation The beginning? Unsolved issues in the standard model Horizon problem: Why is the CMB so smooth? The flatness problem: Why is Ω~1? Why is the universe flat? The structure
Lecture 12 Cosmology III Inflation The beginning? Unsolved issues in the standard model Horizon problem: Why is the CMB so smooth? The flatness problem: Why is Ω~1? Why is the universe flat? The structure
CHAPTER 4 STARS, GALAXIES & THE UNIVERSE
 CHAPTER 4 STARS, GALAXIES & THE UNIVERSE LESSON 1: TELESCOPES ALL TYPES OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION TRAVEL AT THE SPEED OF LIGHT 186,000 miles per second!! Electromagnetic Radiation = energy that travels
CHAPTER 4 STARS, GALAXIES & THE UNIVERSE LESSON 1: TELESCOPES ALL TYPES OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION TRAVEL AT THE SPEED OF LIGHT 186,000 miles per second!! Electromagnetic Radiation = energy that travels
Name... Class... Date...
 Radiation and temperature Specification reference: P6.3 Black body radiation (physics only) Aims This is an activity that has been designed to help you improve your literacy skills. In this activity you
Radiation and temperature Specification reference: P6.3 Black body radiation (physics only) Aims This is an activity that has been designed to help you improve your literacy skills. In this activity you
Abstracts of Powerpoint Talks - newmanlib.ibri.org - The Cosmos. Robert C. Newman
 The Cosmos Robert C. Newman The Cosmos Carl Sagan said: "The cosmos is all that is, or ever was, or ever will be." If Christianity is true, Sagan is mistaken. But we can perhaps define the cosmos as "All
The Cosmos Robert C. Newman The Cosmos Carl Sagan said: "The cosmos is all that is, or ever was, or ever will be." If Christianity is true, Sagan is mistaken. But we can perhaps define the cosmos as "All
Era of Atoms 5/3/18. Our Schedule and Topics
 5/3/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Cosmic Web Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 30 Thur 3 May 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule and Topics Final Exam on Wed May
5/3/18 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Cosmic Web Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 30 Thur 3 May 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Our Schedule and Topics Final Exam on Wed May
Star Stuff. Star Formation. Star Formation. Stars form in the interstellar medium
 Star Stuff Star Formation Stars form in the interstellar medium Nebula in Scorpius Star Formation Stars form in the interstellar medium This contains very cold, dark clouds of dusty molecular gas Pillars
Star Stuff Star Formation Stars form in the interstellar medium Nebula in Scorpius Star Formation Stars form in the interstellar medium This contains very cold, dark clouds of dusty molecular gas Pillars
Test 2 Result: Sec 1. To see the scantron & problem set, contact the TA: Mr. He Gao
 Test 2 Result: Sec 1 Column Statistics for: Test2 Count: 103 Average: 31.4 Median: 32.0 Maximum: 46.0 Minimum: 10.0 Standard Deviation: 7.94 To see the scantron & problem set, contact the TA: Mr. He Gao
Test 2 Result: Sec 1 Column Statistics for: Test2 Count: 103 Average: 31.4 Median: 32.0 Maximum: 46.0 Minimum: 10.0 Standard Deviation: 7.94 To see the scantron & problem set, contact the TA: Mr. He Gao
