Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation?
|
|
|
- Melinda Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation? Marcella Brusa Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik Garching, Germany XMM view of the COSMOS field The Starburst-AGN connection under the multiwavelength limelight ESAC (Villafranca de Castilla) / September 14-16, 2011
2 Observational evidences of a mutual Star formation (SF) relationship (1) AGN 1) traces growth of stellar mass 2) all galaxies assembled their masses through episodes of SF (starbursts) 1) traces growth of BH mass (>10 6 M sun ) 2) all SMBH assembled their mass through accretion during AGN phase (SMBH are present in almost all galaxies) all galaxies went through an AGN phase
3 Observational evidences of a mutual Star formation (SF) relationship (1) AGN 1) traces growth of stellar mass 2) all galaxies assembled their masses through episodes of SF (starbursts) 1) traces growth of BH mass (>10 6 M sun ) 2) all SMBH assembled their mass through accretion during AGN phase (SMBH are present in almost all galaxies) all galaxies went through an AGN phase First evidence of Starburst-AGN connection: BH mass depends on stellar mass (local scaling relations) see also Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al Haering&Rix 2004, Greene et al Gultekin et al (but see Jahnke & Maccio 2011, Cen 2011)
4 Observational evidences of a mutual adapted from Silverman+2008 relationship (2) (integral) SMBH growth traces (integral) SFR SMBH growth = from XLF of AGN (modulo uncertainties in N H distribution vs. z and Compton Thick sources) SF growth = from deep NIR and optical surveys (data: Hopkins & Beacon 2006) See e.g. Merloni 2004; Marconi et al. 2004; Shankar et al. 2007; Merloni & Heinz 2008
5 Observational evidences of a mutual SF downsizing relationship (3) AGN downsizing Thomas et al De Lucia+2006 La Franca et al Cosmic downsizing the larger the faster (Cowie et al. 1996):.. galaxy formation took place in downsizing, with more massive galaxies forming at higher redshift.. Fiore,Brusa+2003 (HELLAS2XMM) Ueda+03; Barger+05; Hasinger+05; Silverman+05, Bongiorno+07, Della Ceca+08, Ebrero+09 etc. - but see Aird et al more luminous AGN had the peak of activity at earlier redshifts
6 Observational evidences of a mutual relationship (4) correlation between AGN and FIR luminosity (e.g.netzer+2007, Lutz +2008, Netzer 2010) correlation between AGN luminosity and PAH strength (e.g. Schweitzer +2006, Lutz et al. 2008) We observe simultaneous SF and AGN activity in bright local AGN and QSO (e.g. some well-known objects studied in details, e.g. NGC 1068, NGC 6240, Mrk231,Arp299, Circinus...) [posters and talks all over the workshop]
7 mergers scenario Hopkins et al (ULIRGs-QSO sequence) Early on Mergers between gas rich galaxies drive gas which fuel both SF and BH activity; Compton Thick BH Growth INFRARED Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY unobscured QSO OPTICAL Violent starbursts episodes (ULIRGS); Heavily obscured BH growth When galaxies coalesce Accretion peaks; SMBH becomes X-ray and optically visible QSO phase follow, AGN winds blow out gas (e.g. Sanders et al. 1988, Silk & Rees 1998, Granato et al. 2004, Di Matteo et al. 2005, Hopkins et al , Croton et al. 2006, Fontanot et al. 2006, De Lucia et al. 2006, Sijacki et al. 2007, Menci et al. 2008, Marulli et al. 2009) Later times SF & BH accretion quenched; Dead quasars in red galaxies (passive evolution) AGN co-evolutionary models vs. Unified models (definition of obscured AGN: time critical vs. orientation ) BH growth and SF simultaneous --> feedback from AGN
8 Is this valid for all systems? (Starburst-AGN sequence) A population of galaxies evolved without mergers does clearly exist (disks are observed at z~2; e.g. Genzel+2006, 2008; see also yesterday ESA/Herschel press release: Elbaz+11, Rodighiero+11) Kormendy et al no correlation between M BH and disk or pseudobulge properties (Kormendy et al. 2011; see also Graham et al. 2010) Stochastic/secular accretion can explain some classes of low-l AGN (NLS1) observed at low-z (see also Davies talk) Dichotomy in formation history of galaxies mergers vs. secular (weak) activity driven stochastically by local processes (galaxies encounters, inflow, disks/bars instabilities etc.; Croton+2006, Ciotti&Ostriker, Cen 2011, Bournaud+2011, Di Matteo+2011) NGC 1068
9 Expectations and key tests/observable 1) Correlation SFR - AGN luminosity? expected in mergers scenarios - AGN regulate the SB (see Lutz and Mullaney talks friday!) not expected if SB and AGN are nocoeval (Cen 2011) 2) enhanced SFR in AGN hosts? (and AGN colors) expected in mergers scenarios, but it is time--dependent (expected pre and during the merger, not post-merger); luminosity dependence? 3) AGN hosts morphologies should be different in the merger (elliptical or disturbed systems) or secular (disks) scenarios 4) Difference in SFR between Type 2 and Type 1 obscured AGN at high-z are expected to be more starforming than unobscured AGN (see tomorrow morning session!) 5) are we able to disentangle among positive (enhance SF) and negative (stop SF) AGN feedback? Evolution effects? AGN power may be greater than binding energy of host galaxies and may provide necessary feedback to stop star formation; crucial role of mm/alma observations (see Maiolino talk and friday session!)
10 Expectations and key tests/observable 1) Correlation SFR - AGN luminosity? expected in mergers scenarios - AGN regulate the SB (see Lutz and Mullaney talks friday!) not expected if SB and AGN are nocoeval (Cen 2011) 2) enhanced SFR in AGN hosts? (and AGN colors) expected in mergers scenarios, but it is time--dependent (expected pre and during the merger, not post-merger); luminosity dependence? 3) AGN hosts morphologies should be different in the merger (elliptical or disturbed systems) or secular (disks) scenarios 4) Difference in SFR between Type 2 and Type 1 obscured AGN at high-z are expected to be more starforming than unobscured AGN (see tomorrow morning session!) 5) are we able to disentangle among positive (enhance SF) and negative (stop SF) AGN feedback? Evolution effects? AGN power may be greater than binding energy of host galaxies and may provide necessary feedback to stop star formation; crucial role of mm/alma observations (see Maiolino talk and friday session!)
11 Tools: (hard) X-ray surveys most complete (modulo Compton Thick sources) least contaminated (normal galaxies and stars emerge only in deepest exposures) COSMOS field, 2 deg 2 (Scoville+07) XMM 1.55 Ms (Hasinger+07, Cappelluti+09, Brusa+10) Chandra 1.8 Ms (Elvis+09, Civano+in prep) down to ~1e-15 cgs, ~1800 objects soft kev medium kev hard kev catch AGN in blowout and QSO phase Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY obs/unobs QSO X-ray/OPTICAL Multiwavelength coverage to assure identification, redshift determination, SED studies, host galaxy properties, and alternative AGN selection (e.g. Compton Thick census; see Donley/Vignali talks) Ony two among the many (~40) XMM & Chandra surveys in russian-doll style All wavelengths, very deep coverage available CDFS Chandra 1-2-4Ms XMM 3 Ms ~0.1 deg2, ~4e-17 cgs objects (Giacconi+2002, Alexander +2003, Luo+ 2008,10, Xue +2011, Comastri+2011)
12 Star formation in AGN hosts Brusa et al. (2009) - obscured AGN in CDFS loglx ~43 Lusso et al. (2011) - Type 2 AGN in COSMOS loglx~43.5 Mainieri et al. (2011) - QSO2 in COSMOS loglx > 44 Xue et al. (2010) - AGN in GOODS fields loglx>42 Santini et al. (2011) - PEP/Herschel data of GOODS+COSMOS AGN
13 Host/AGN decomposition Full XMM-COSMOS sample (~1600 objects, Brusa+2010) (particularly) important for moderate & high-lum obscured QSO and unobs AGN (all lum) Lusso+2011 (Type2) Bongiorno+in prep (full XMM) see also Merloni+2010 (BL AGN) Bongiorno et al (full XMM) Pozzi+2007,2010; Gruppioni+2010; Santini see Feltre talk! (adapted from Hao+2010) Most of the SEDs can be explained as a combination of a pure AGN, extinct and/or contaminated by the host galaxy Fact: (Without Herschel information) Multiple components SED fitting needed (AGN + host galaxy) to get the physical parameters
14 Obscured AGN: colors Brusa+2009 (obscured AGN in CDFS, <Lx>~43) Xue+2010 (obscured AGN in CDFS, <Lx>~43) Lx range: Red >43, Blue < 43 Green contours: Field population (Santini+2009) Importance of mass-matched parent samples: AGN have expected colors of galaxies of their mass (see also Cardamone+2009, Lusso+2011) Field galaxies: Two distinct populations: red sequence and blue cloud (early type and SF galaxies) AGN: (X-ray selected) AGN populate the green valley or red sequence (see Kauffmann+03, Nandra +05, Silverman+08, Schawinski+10) at almost all z they are red, optically luminous and massive Fact: obscured AGN are RED, but not particularly redder or luminous than inactive galaxies of same mass
15 Obscured AGN: SFR Brusa+2009 (obscured AGN in CDFS. <Lx>~43) Lusso+2011 (Type2 AGN in COSMOS, <Lx>~43.5) Blue <43, Red > 43 Masses and SFR from Santini+09 Fact: 50% X-ray selected obscured AGN are actively forming stars (>20 Msun/year or 1/SSFR<t_Hubble), at almost all redshifts but they are not (all) ULIRGS/Starbursts galaxies
16 Obscured QSO: SFR Same level of starformation for active (AGN) and inactive (SF) galaxies QSO2 hosts follow the tight correlation between SFR and M * of blue star-forming galaxies (e.g. Noeske+07; Daddi+07; Elbaz+07; Rodighiero+10 / Herschel) Mainieri et al (QSO2 in COSMOS, Lx>44) Rodighiero+10 Passive population also present Fact: Obscured AGN associated to SF galaxies do not scatter significantly off the main sequence of SF galaxies Daddi+07 See Vincenzo Mainieri talk on Friday!
17 Enhanced SFR in AGN hosts? Santini+2011 (GOODS & COSMOS) Evidence for enhancement: - GOODS (low-lx): SFR in AGN hosts broadly consistent with that observed in inactive galaxies (modest) enhancement observed only in low-mass samples - COSMOS (high-lx): SFR in AGN hosts ~0.6 dex higher than in inactive galaxies, at all z/masses (see also Silverman+2009, Xue+2010, Mullaney+2011) see Lutz & Mullaney talks tomorrow! Fact: different enhancements at low and at high-l consistent with two different modes of SF and BH growth high-l: major mergers low-l: smooth accretion (or mergers with delay in SB and AGN phases)
18 SF vs. AGN luminosity Shao et al [Herschel / GOODS-N X-ray AGN] Rosario+in prep [Herschel / GOOS+COSMOS X-ray AGN] at L(AGN)>45 (Lx>43.5) correlation is observed, as expected in mergers models at L(AGN)<45 (Lx<43.5) no correlation between AGN and SF at z>0.2 and in local X-ray selected samples See Lutz and Mullaney talks! see also Netzer+2007; Netzer2009; Lutz+2010
19 SF vs. AGN luminosity Shao et al [Herschel / GOODS-N X-ray AGN] Rosario+in prep [Herschel / GOOS+COSMOS X-ray AGN] at L(AGN)>45 (Lx>43.5) secular local AGN mergers correlation is observed, as expected in mergers models at L(AGN)<45 (Lx<43.5) no correlation between AGN and SF at z>0.2 and in local X-ray selected samples See Lutz and Mullaney talks! see also Netzer+2007; Netzer2009; Lutz+2010
20 During or Post? Most luminous, obscured X-ray selected sources at z>1 are red --> effect of (negative) feedback efficient in stopping star formation, or AGN is in dusty environment? Evidences for both! --> different phases/timescales are sampled evidence of SF both in FIR and optical spectra (see e.g. Del Moro, Mateos, Sani, Page, Symeonidis talks) ULIRG-QSO2 Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY obs/unobs QSO X-ray/OPTICAL passive ellipticals/early type spectra without any sign of SF (see also Mignoli+2004, Brusa+2005, Daddi ) QSO2 Severgnini et al outflow of ~300 km/s Very short phase (<< 1Gyr): need large & bright samples (RARE OBJECTS!!) Cyan points: PACS 100 & 160 μm Courtesy D. Lutz/PEP Brusa et al see also Mainieri+05, Vignali+10 Importance of X-ray selection, prospects for large area X-ray surveys (SWIRE/XMM-XXL/ erosita) Ideal targets for WFC3/ X shooter/ ALMA/JWST follow-up and deep spectroscopy Silverman et al. 2010
21 AGN hosts morphologies Cisternas et al. (2010) - z~1 AGN hosts morphologies in COSMOS (HST/ACS) Kocevski et al. (2011) - z~2 AGN hosts morphologies in CDFS (HST/WFC3)
22 Morphologies of AGN hosts Sanders+1988 (QSO): local QSO/ULIRGs hosted in highly disturbed systems, evidence for mergers Cisternas+10 (AGN at z<1): >85% of AGN host galaxies do not show strong distortions; no enhancement in mergers fraction among AGN morphologies wrt normal galaxy population (see also Grogin+03, Pierce+07, Georgakakis+09, Gabor+2009) --> no major merger AGN connection Brusa et al., in prep morphological classification from ZEST (Scarlata et al. 2007) Kocevski+11, Schawinski+2011 (AGN at z=1-3): NO significant excess of distorted morphologies; large fraction reside in late-type galaxies, fueled by stochastic accretion of cold-gas Lx dependence: low-l = mostly disks high-l = mostly ellipticals/relaxed systems (but see results from Manieri+2011) Fact: high disk fraction (and no distortion) at odds with predictions that merger driven accretion is the dominant AGN fueling mode
23 Combining results from SFR & morphologies 1) SF in AGN hosts is only slightly enhanced (ULIRG in only a small fraction of hosts, even at the highest L) and morphologies of AGN do not show strong distortions 2) Luminosity effect is observed (both in SFR enhancement and morphologies) Time delay between AGN activity, SF and merger? (predicted in simulations involving AGN feedback, e.g. Hopkins+2006, Wild+2010) --> can explain the SFR enhancement observed in low-lx/low-mass systems but not the disky morphologies... Secular evolution / smooth accretion fit better both observed morphologies and SFR --> major mergers model crisis also for moderate/high-l (Di Matteo et al. 2011, Bournaud et al. 2011) Merger path NOT the rule (timescale problem)... or...
24 Cen Scenario : NO AGN feedback NO causal relation Cen 2011 SF and BH growth are self regulated and independent Starformation starts through mergers or secular processes (not important) (timescales involved are much longer with respect to Hopkins et al. 2008!)
25 Summary
26 Summary Evidence of Starburst-AGN connection: local scaling relations and SF/AGN downsizing Dichotomy in formation history of galaxies mergers vs. secular Fact: obscured AGN are RED, but not particularly redder or luminous than inactive galaxies of same mass Fact: Obscured AGN associated to SF galaxies do not scatter significantly off the main sequence of SF galaxies) Fact: high disk fraction (and no distortion) at odds with predictions that merger driven accretion is the dominant AGN fueling mode Fact: 50% X-ray selected obscured AGN are actively forming stars (>20 Msun/year or 1/SSFR<t_Hubble) at almost all redshifts Fact: different enhancements at low and at high-l consistent with two different modes of SF and BH growth...or no causal relation at all (no AGN feedback)
27 Importance of combined X-ray/FIR coverage to isolate obscured accreting black holes at high-z and study host galaxies properties Essential role of Herschel in disentangling starburst component... essential role of XMM/Chandra in revealing AGN! (multiwavelength limelight) Thanks! (Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC/PEP teams)
Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations)
 Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations) Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna
Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations) Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs
 Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
The search for. COSMOS and CDFS. Marcella Brusa
 The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College
 AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not?
 Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity
 Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
What s the fuss about AGN?
 What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
A Herschel view on star formation in high
 A Herschel view on star formation in high redshift AGN hosts Dieter Lutz Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik + PEP Herschel GTO survey team Massive Galaxies over Cosmic Time 3 Tucson, November
A Herschel view on star formation in high redshift AGN hosts Dieter Lutz Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik + PEP Herschel GTO survey team Massive Galaxies over Cosmic Time 3 Tucson, November
Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR
 Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR With: D. H. Weinberg, J. Miralda-Escudé, M. Bernardi, L. Ferrarese, J. Moreno, R. K. Sheth, Y. Shen,
Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR With: D. H. Weinberg, J. Miralda-Escudé, M. Bernardi, L. Ferrarese, J. Moreno, R. K. Sheth, Y. Shen,
The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature
 The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature Ji Hoon Kim Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Along with Myungshin Im, Dohyeong
The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature Ji Hoon Kim Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Along with Myungshin Im, Dohyeong
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback
 Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution
 Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution Philip Hopkins Arizona 11/29/07 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Adam Lidz, Gordon Richards, Alison Coil, Adam Myers, Paul Martini, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson,
Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution Philip Hopkins Arizona 11/29/07 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Adam Lidz, Gordon Richards, Alison Coil, Adam Myers, Paul Martini, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson,
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS)
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity?
 Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity? Carolin Villforth University of Bath! Timothy Hamilton (Schawnee State), M. Pawlik, T. Hewlett, K. Rowlands (St Andrews),
Unhidden monsters: Are unobscured quasars the late stages of obscured quasar activity? Carolin Villforth University of Bath! Timothy Hamilton (Schawnee State), M. Pawlik, T. Hewlett, K. Rowlands (St Andrews),
AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift
 AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift Andrea Merloni (EXC, MPE) A. Bongiorno (MPE), COSMOS + zcosmos teams Outline Co-evolution of stellar
AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift Andrea Merloni (EXC, MPE) A. Bongiorno (MPE), COSMOS + zcosmos teams Outline Co-evolution of stellar
X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION
 1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies
 The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material
 Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es
 Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations
 Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
Obscured AGN. I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations
 Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations (ESO, Germany) (see Harrison 2017) Overview Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations 1.
Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations (ESO, Germany) (see Harrison 2017) Overview Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations 1.
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey
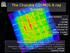 The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation
 BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation Dieter Lutz MPE Torus 2018 The many faces of AGN obscuration Puerto Varas, December 12, 2018 What is the size and structure of star formation (or cold gas) in
BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation Dieter Lutz MPE Torus 2018 The many faces of AGN obscuration Puerto Varas, December 12, 2018 What is the size and structure of star formation (or cold gas) in
AGN feedback and the connection to triggering
 AGN feedback and the connection to triggering Ryan C. Hickox Dartmouth College The Triggering Mechanisms for Active Galactic Nuclei Lorentz Center, Leiden 26 July 2013 Illustration courtesy NASA Outline
AGN feedback and the connection to triggering Ryan C. Hickox Dartmouth College The Triggering Mechanisms for Active Galactic Nuclei Lorentz Center, Leiden 26 July 2013 Illustration courtesy NASA Outline
The quest for early Black Holes
 The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North
 Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird. University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester)
 Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
Active Galactic Alexander David M Nuclei
 d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models. Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11
 Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
44 JAXA Special Publication JAXA-SP E Lutz Figure 2. The cosmic far-infrared background as seen by direct measurements and as resolved by Hersch
 From Exoplanets to Distant Galaxies : SPICA's New Window 43 Far-infrared Galaxy Evolution Surveys with Herschel Dieter Lutz 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Germany ABSTRACT The 2009-2013
From Exoplanets to Distant Galaxies : SPICA's New Window 43 Far-infrared Galaxy Evolution Surveys with Herschel Dieter Lutz 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Germany ABSTRACT The 2009-2013
THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT. F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3
 1 THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3 1 Instituto de Física de Cantabria, Avenida de los Castros, 39005 Santander, Spain
1 THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3 1 Instituto de Física de Cantabria, Avenida de los Castros, 39005 Santander, Spain
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey
 The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
The physical state of radio-mode, low- luminosity AGN
 The physical state of radio-mode, low- luminosity AGN Andrea Merloni Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik 5GHz, VLA image of Cyg A by R. Perley PhiGN start-up workshop, 14/12/2007 Parallel
The physical state of radio-mode, low- luminosity AGN Andrea Merloni Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik 5GHz, VLA image of Cyg A by R. Perley PhiGN start-up workshop, 14/12/2007 Parallel
Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes?
 Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes? Knud Jahnke Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie Katherine Inskip, Dading Nugroho, Mauricio Cisternas, Hans-Walter Rix, Chien Y. Peng, COSMOS (Mara Salvato, Jonathan
Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes? Knud Jahnke Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie Katherine Inskip, Dading Nugroho, Mauricio Cisternas, Hans-Walter Rix, Chien Y. Peng, COSMOS (Mara Salvato, Jonathan
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes. R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams
 The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt
 X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure. Mark Dickinson (NOAO)
 Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Mark Dickinson (NOAO) Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Past Mark Dickinson (NOAO) IRAS FIDEL 60μm MIPS 160μm 70μm
Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Mark Dickinson (NOAO) Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Past Mark Dickinson (NOAO) IRAS FIDEL 60μm MIPS 160μm 70μm
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD
 The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history
 The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history A&A, 574, A105 (2015) A&A, 579, A132 (2015) A. Biviano, INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Introduction The cosmic z-dependent Star
The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history A&A, 574, A105 (2015) A&A, 579, A132 (2015) A. Biviano, INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Introduction The cosmic z-dependent Star
Quasars, Feedback, and Galaxy Interactions
 Quasars, Feedback, and Galaxy Interactions Philip Hopkins 09/24/08 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson, Paul Martini, Adam Lidz, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh
Quasars, Feedback, and Galaxy Interactions Philip Hopkins 09/24/08 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Dusan Keres, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson, Paul Martini, Adam Lidz, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh
Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS
 Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS Bruno Altieri Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Garching PACS Team, PACS GT extragalactic survey (PEP) Team PI: Dieter Lutz PEP in a
Extragalactic Surveys: Prospects from Herschel-PACS Bruno Altieri Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Garching PACS Team, PACS GT extragalactic survey (PEP) Team PI: Dieter Lutz PEP in a
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies
 Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation
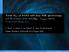 Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
High-z star formation the Herschel view
 High-z star formation the Herschel view Dieter Lutz for the PACS Evolutionary Probe (PEP) team Galaxies in the Distant Universe, Schloß Ringberg May 18, 2010 The deepest Herschel-PACS blank fields taken
High-z star formation the Herschel view Dieter Lutz for the PACS Evolutionary Probe (PEP) team Galaxies in the Distant Universe, Schloß Ringberg May 18, 2010 The deepest Herschel-PACS blank fields taken
The Origins & Evolution of the Quasar Luminosity Function
 The Origins & Evolution of the Quasar Luminosity Function Philip Hopkins 07/14/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, Gordon Richards, T. J. Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Sukanya Chakrabarti
The Origins & Evolution of the Quasar Luminosity Function Philip Hopkins 07/14/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, Gordon Richards, T. J. Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Sukanya Chakrabarti
Vivienne Wild. Timing the starburst AGN connection
 Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
Vivienne Wild Timing the starburst AGN connection There are many theories successful in explaining the observed correlations between black holes and their host galaxies. In turn, these theories play a
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback
 A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 10/05/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, TJ Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh Younger Motivation QUASARS
Quasars, Mergers, and the Buildup of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 10/05/06 Lars Hernquist, Volker Springel, TJ Cox, Brant Robertson, Tiziana Di Matteo, Yuexing Li, Josh Younger Motivation QUASARS
THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED
 ESLAB 2013 04/04/2013 Noordwijk THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED Material at http://irfu.cea.fr/sap/phocea/page/index.php?id=537 Matthieu Béthermin In
ESLAB 2013 04/04/2013 Noordwijk THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED Material at http://irfu.cea.fr/sap/phocea/page/index.php?id=537 Matthieu Béthermin In
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey. R. Della Ceca. INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan
 The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova
 ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova Starlight, HII & AGN Dust & Molecules Where we stand and looking in perspective The current generation of ground & space telescopes are
ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova Starlight, HII & AGN Dust & Molecules Where we stand and looking in perspective The current generation of ground & space telescopes are
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx
 X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations
 The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
The Hot and Energetic Universe
 The Hot and Energetic Universe An Athena+ supporting paper Understanding the build-up of supermassive black holes and galaxies at the heyday of the Universe Authors and contributors A. Georgakakis, F.
The Hot and Energetic Universe An Athena+ supporting paper Understanding the build-up of supermassive black holes and galaxies at the heyday of the Universe Authors and contributors A. Georgakakis, F.
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
Hunting for Monsters. Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016
 Hunting for Monsters Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016 Ryan Hickox Dartmouth College Mike DiPompeo Christopher Carroll
Hunting for Monsters Selecting and Characterizing Obscured Quasars with WISE Kevin Hainline Hidden Monsters Dartmouth College August 2016 Ryan Hickox Dartmouth College Mike DiPompeo Christopher Carroll
Compton-thick AGN. SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects
 Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects A. S. Evans (Stony Brook) J. A. Surace & D. T. Frayer (Caltech) D. B. Sanders (Hawaii) Luminous Infrared Galaxies Properties
Molecular Gas and the Host Galaxies of Infrared-Excess Quasi-Stellar Objects A. S. Evans (Stony Brook) J. A. Surace & D. T. Frayer (Caltech) D. B. Sanders (Hawaii) Luminous Infrared Galaxies Properties
PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME
 THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering. Alison Coil UCSD
 What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
What Can We Learn from Galaxy Clustering 1: Why Galaxy Clustering is Useful for AGN Clustering Alison Coil UCSD Talk Outline 1. Brief review of what we know about galaxy clustering from observations 2.
Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies
 Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies Luis C. Ho ( 何子山 ) The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Ho 2008, ARA&A Nuclear Activity in Nearby Galaxies Kormendy &
Coevolution (Or Not) of Supermassive Black Holes and Galaxies Luis C. Ho ( 何子山 ) The Observatories of the Carnegie Institution for Science Ho 2008, ARA&A Nuclear Activity in Nearby Galaxies Kormendy &
Black Holes in the local Universe
 Outline 1. AGN evolution and the history of accretion 2. From AGN SED to AGN physics Accretion discs and X-ray coronae in AGN 3. Do AGN reveal accretion mode changes? The fundamental plane of BH activity
Outline 1. AGN evolution and the history of accretion 2. From AGN SED to AGN physics Accretion discs and X-ray coronae in AGN 3. Do AGN reveal accretion mode changes? The fundamental plane of BH activity
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers
 Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers Yuexing Li et al Presentation by: William Gray Definitions and Jargon QUASAR stands for QUASI-stellAR radio source Extremely bright and active
Lecture 11: SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio. Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS
 Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 4, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture : SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio Large Surveys at Many Wavelengths SDSS: UV-IR five-band
Astr 598: Astronomy with SDSS Spring Quarter 4, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture : SDSS Sources at Other Wavelengths: From X rays to radio Large Surveys at Many Wavelengths SDSS: UV-IR five-band
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019](/thumbs/94/119592941.jpg) Draft version February 12, 2019 Typeset using L A TEX preprint2 style in AASTeX61 MULTI-WAVELENGTH PROPERTIES OF TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2 AGN HOST GALAXIES IN THE CHANDRA-COSMOS LEGACY SURVEY arxiv:1902.03244v1
Draft version February 12, 2019 Typeset using L A TEX preprint2 style in AASTeX61 MULTI-WAVELENGTH PROPERTIES OF TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2 AGN HOST GALAXIES IN THE CHANDRA-COSMOS LEGACY SURVEY arxiv:1902.03244v1
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN
 Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0<z 2.5
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2015) Printed February 11, 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2015) Printed February 11, 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0
20x increase from z = 0 to 2!
 black hole accretion (AGN) & star formation (SF) 20x increase from z = 0 to 2! due to more gas (initial supply or accretion) or higher efficiency gas è stars, AGN starbursts merging? ALMA survey of ISM
black hole accretion (AGN) & star formation (SF) 20x increase from z = 0 to 2! due to more gas (initial supply or accretion) or higher efficiency gas è stars, AGN starbursts merging? ALMA survey of ISM
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012](/thumbs/93/111700682.jpg) Draft version May 10, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE HIDDEN AGN MAIN SEQUENCE : EVIDENCE FOR A UNIVERSAL BLACK HOLE ACCRETION TO STAR FORMATION RATE RATIO SINCE z 2
Draft version May 10, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE HIDDEN AGN MAIN SEQUENCE : EVIDENCE FOR A UNIVERSAL BLACK HOLE ACCRETION TO STAR FORMATION RATE RATIO SINCE z 2
Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing?
 Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing? Mauricio Cisternas Ins:tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias, Spain + Nacho Trujillo Jürgen Fliri Johan Knapen dagalnetwork.eu ESO San:ago,
Underneath the Monster: In which galaxies are black holes growing? Mauricio Cisternas Ins:tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias, Spain + Nacho Trujillo Jürgen Fliri Johan Knapen dagalnetwork.eu ESO San:ago,
The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz
 The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz David R. Ballantyne Center for Relativistic Astrophysics, School of Physics, Georgia Tech The Cosmic Backgrounds
The Contribution of Active Galactic Nuclei to the Excess Cosmic Radio Background at 1.4 GHz David R. Ballantyne Center for Relativistic Astrophysics, School of Physics, Georgia Tech The Cosmic Backgrounds
The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8
 The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8 Mauricio Cisternas Ins(tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias The Triggering Mechanisms for AGN, Leiden, July 24, 2013 What is triggering most AGN?
The Rela(on Between Bars and AGN locally and at high redshi8 Mauricio Cisternas Ins(tuto de Astrofisica de Canarias The Triggering Mechanisms for AGN, Leiden, July 24, 2013 What is triggering most AGN?
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN
 The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
Optical colours of AGN in the extended Chandra deep field South: obscured black holes in early type galaxies ABSTRACT. 2. Data
 A&A 475, 115 120 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077651 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Optical colours of AGN in the extended Chandra deep field South: obscured black holes in early type galaxies
A&A 475, 115 120 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20077651 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics Optical colours of AGN in the extended Chandra deep field South: obscured black holes in early type galaxies
Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies
 Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231 Gemini Press Release February 2011 (Rupke & SV 2011) QUEST: Quasar and ULIRG Evolution
Massive Neutral and Molecular Winds in Nearby Galaxies S. Veilleux (U. Maryland) Powerful wide-angle outflow in Mrk 231 Gemini Press Release February 2011 (Rupke & SV 2011) QUEST: Quasar and ULIRG Evolution
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister
 The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
FEEDBACK IN GALAXY FORMATION
 FEEDBACK IN GALAXY FORMATION Disks SMBH growth AGN and star formation Joe Silk IAP/JHU/Oxford Collaborators: Vincenzo Antonnucio-Deloglou, Volker Gaibler, Sadegh Khochfar Feedback is needed t cool t dyn
FEEDBACK IN GALAXY FORMATION Disks SMBH growth AGN and star formation Joe Silk IAP/JHU/Oxford Collaborators: Vincenzo Antonnucio-Deloglou, Volker Gaibler, Sadegh Khochfar Feedback is needed t cool t dyn
The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function:
 The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function: towards the high-mass end at high redshifts Helena Domínguez Sánchez Jordi Cepa (IAC), Miguel Sánchez Portal (ESAC), Andrea Cimatti (UniBo), Francesca
The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function: towards the high-mass end at high redshifts Helena Domínguez Sánchez Jordi Cepa (IAC), Miguel Sánchez Portal (ESAC), Andrea Cimatti (UniBo), Francesca
GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies. (Affiliations can be found after the references)
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219880 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies A. Del Moro 1, D. M. Alexander 1, J.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219880 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies A. Del Moro 1, D. M. Alexander 1, J.
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA
 ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings
 A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings Andrea Biviano Andrea Biviano INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Outline: mid-ir & multiwavelength observations
A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings Andrea Biviano Andrea Biviano INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Outline: mid-ir & multiwavelength observations
SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY
 Lecture #4 SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY Observational facts Olivier Le Fèvre ON Rio de Janeiro School 2014 Putting it all together Clear survey strategies Instrumentation and observing
Lecture #4 SURVEYS: THE MASS ASSEMBLY AND STAR FORMATION HISTORY Observational facts Olivier Le Fèvre ON Rio de Janeiro School 2014 Putting it all together Clear survey strategies Instrumentation and observing
MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY
 1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
SOFIA/HAWC+ Detection of a Gravitationally Lensed Starburst Galaxy at z = 1.03
 SOFIA/HAWC+ Detection of a Gravitationally Lensed Starburst Galaxy at z = 1.03 Jingzhe Ma University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Asantha Cooray, Arianna Brown, Hooshang Nayyeri, Hugo Messias,
SOFIA/HAWC+ Detection of a Gravitationally Lensed Starburst Galaxy at z = 1.03 Jingzhe Ma University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Asantha Cooray, Arianna Brown, Hooshang Nayyeri, Hugo Messias,
Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM
 Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM The History of Nuclear Black Holes in Galaxies Harvard University, May 18, 2006 WMAP mm Sky Backgrounds
Radiation Backgrounds Observations across the Electromagnetic Spectrum Günther Hasinger, MPE Garching & TUM The History of Nuclear Black Holes in Galaxies Harvard University, May 18, 2006 WMAP mm Sky Backgrounds
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests
 Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory November 15, 2009 Research Interests My recent research projects study galaxy evolution with emphasis on star formation histories, gas accretion and outflow, and galaxy
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback
 Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
Empirical Evidence for AGN Feedback Christy Tremonti MPIA (Heidelberg) / U. Wisconsin-Madison Aleks Diamond-Stanic (U. Arizona), John Moustakas (NYU) Much observational and theoretical evidence supports
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us?
 The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies
 Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 11/02/06 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson Gordon Richards (JHU), Kevin Bundy (Caltech), Rachel Somerville
Quasars, Mergers, and the Formation of Elliptical Galaxies Philip Hopkins 11/02/06 Lars Hernquist, TJ Cox, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson Gordon Richards (JHU), Kevin Bundy (Caltech), Rachel Somerville
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community
 Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey
 An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey Marco Bondi, INAF-IRA AGN selected using different techniques/wavelengths represent separate populations, with differences in host galaxies, environments
An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey Marco Bondi, INAF-IRA AGN selected using different techniques/wavelengths represent separate populations, with differences in host galaxies, environments
Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows
![Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows](/thumbs/83/87306418.jpg) Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Natalie Christopher, University of Oxford Dr Verma and Professor Roche, University of Oxford And the SHINING team, Lead by E. Sturm,
Outflows in local ULIRGS: [CII] 158 Broad Components and OH outflows Natalie Christopher, University of Oxford Dr Verma and Professor Roche, University of Oxford And the SHINING team, Lead by E. Sturm,
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts
 Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift
 Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift Yicheng Guo University of Massachusetts Collaborator: Mauro Giavalisco (UMASS), Paolo Cassata (Marseille), Henry
Assembly of Galaxies Across Cosmic Time: Formaton of te Hubble Sequence at High Redshift Yicheng Guo University of Massachusetts Collaborator: Mauro Giavalisco (UMASS), Paolo Cassata (Marseille), Henry
