Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations)
|
|
|
- Emerald Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Obscured QSOs in the golden epoch of AGN-galaxy evolution placing objects in the mergers sequence (with NIR and mm observations) Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna 3) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany (major) credits: A. Bongiorno, V. Mainieri
2 MAIN ARGUMENTS: Active Galactic Nuclei in a cosmological framework 1) AGN trace (accreting) SMBH SMBH (M>10 6 M ) are powering Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Source of power: accretion of material onto the SMBH through an accretion disc
3 MAIN ARGUMENTS: Active Galactic Nuclei in a cosmological framework 1) AGN trace (accreting) SMBH 2) (non active) SMBH are ubiquitous in nearby galaxies Chandra, HST, VLA/VLBI surveys of Palomar sample, AMUSE-VIRGO (Elvis & Keel 84; Ho, Filippenko, Nagar, Wilson, Gallo etc ) à AGN transient phase
4 MAIN ARGUMENTS: Active Galactic Nuclei in a cosmological framework 1) AGN trace (accreting) SMBH 2) (non active) SMBH are ubiquitous in nearby galaxies 3) Large scale galaxies properties strongly depend on BH mass tight correlation between M BH and bulge properties (e.g. Magorrian+1998, Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al. 2000, Marconi & Hunt 2003, Haring & Rix 2004, Greene et al. 2007, Gultekin et al. 2009, van de Boesch et al. 2012)
5 MAIN ARGUMENTS: Active Galactic Nuclei in a cosmological framework 1) AGN trace (accreting) SMBH 2) (non active) SMBH are ubiquitous in nearby galaxies 3) Large scale galaxies properties strongly depend on BH mass tight correlation between M BH and bulge properties (e.g. Magorrian+1998, Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al. 2000, Marconi & Hunt 2003, Haring & Rix 2004, Greene et al. 2007, Gultekin et al. 2009, van de Boesch et al. 2012)
6 MAIN ARGUMENTS: Active Galactic Nuclei in a cosmological framework 1) AGN trace (accreting) SMBH 2) (non active) SMBH are ubiquitous in nearby galaxies 3) Large scale galaxies properties strongly depend on BH mass tight correlation between M BH and bulge properties (e.g. Magorrian+1998, Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al. 2000, Marconi & Hunt 2003, Haring & Rix 2004, Greene et al. 2007, Gultekin et al. 2009, van de Boesch et al. 2012) à AGN play a key role in galaxy evolution: Feedback
7 AGN-galaxy coevolution paths MERGERS SCENARIO: (last decade paradigm) Major mergers can trigger SF and BH activity (Silk & Rees 1998, Granato et al. 2004, Di Matteo et al. 2005, Croton et al. 2006, Fontanot et al. 2006, De Lucia et al. 2006, Sijacki et al. 2007, Menci et al. 2008, Hopkins et al. 2008, Marulli et al. 2009) strong correlation between M BH and bulge properties (e.g. Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al. 2000, Marconi & Hunt 2003, Haring & Rix 2004, Greene et al. 2007, Gultekin et al. 2009) Q S O - U L I R G S connection (e.g. Sanders et al. 1988,) Alexander & Hickox 2012 SECULAR SCENARIO: (this decade novelty) (weak) activity driven stochastically by local processes (inflow, disks/bars instabilities; Croton+2006, Ciotti&Ostriker 2007, Cen 2011, Bournaud+2011, Di Matteo+2011) no correlation between M BH and disk or pseudobulge properties (Kormendy et al. 2011; see also Graham et al. 2010) A population of galaxies evolved without mergers does clearly exist (disks are observed at z~2; e.g. Genzel +2006, 2008) also in AGN hosts (Cisternas+2011, Kocevski +2012)
8 AGN-galaxy coevolution paths MERGERS SCENARIO: (last decade paradigm) Major mergers can trigger SF and BH activity (Silk & Rees 1998, Granato et al. 2004, Di Matteo et al. 2005, Croton et al. 2006, Fontanot et al. 2006, De Lucia et al. 2006, Sijacki et al. 2007, Menci et al. 2008, Hopkins et al. 2008, Marulli et al. 2009) strong correlation between M BH and bulge properties (e.g. Ferrarese & Merritt 2000, Gebhardt et al. 2000, Marconi & Hunt 2003, Haring & Rix 2004, Greene et al. 2007, Gultekin et al. 2009) Q S O - U L I R G S NEED AREA connection (e.g. Sanders et al. 1988,) Alexander & Hickox 2012 Luminosity dependence? SECULAR SCENARIO: (this decade novelty) (weak) activity driven stochastically by local processes (inflow, disks/bars instabilities; Croton+2006, Ciotti&Ostriker 2007, Cen 2011, Bournaud+2011, Di Matteo+2011) no correlation between M BH and disk or pseudobulge properties (Kormendy et al. 2011; see also Graham et al. 2010) A population of galaxies evolved without mergers does clearly exist (disks are observed at z~2; e.g. Genzel +2006, 2008) also in AGN hosts (Cisternas+2011, Kocevski +2012) NEED RESOLUTION
9 mergers scenario Hopkins et al Compton Thick BH Growth INFRARED Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY unobscured QSO OPTICAL MERGERS MODEL IMPLICATIONS: 1) obscured AGN: time critical 2) BH growth and SF simultaneous 3) feedback (!)
10 mergers scenario Hopkins et al Compton Thick BH Growth INFRARED Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY unobscured QSO OPTICAL MERGERS MODEL IMPLICATIONS: 1) obscured AGN: time critical 2) BH growth and SF simultaneous 3) feedback (!)
11 INTERMEZZO (1) courtesy A.Merloni, S. Bonoli, ESO Graphics AGN emission AGN emission is observed over the entire electromagnetic spectrum Different wavelengths sample different emission processes and emission regions X-ray emission sample the innermost regions (<10-2 pc, <1000 RS)
12 INTERMEZZO (2) Tools: X-ray surveys COSMOS field, 2 deg 2 (Scoville+07) XMM 1.55 Ms (Hasinger+07, Cappelluti+09, Brusa+10) Chandra 1.8 Ms (Elvis+09, Civano+2012) down to ~1e-15 cgs, ~1800 objects soft kev medium kev hard kev most complete (modulo Compton Thick sources - known missing) least contaminated (normal galaxies and stars emerge only in deepest exposures) Multiwavelength coverage to assure identification, redshift determination, SED studies, host galaxy properties, and alternative AGN selection (e.g. Compton Thick census) Ony two among the many (~40) XMM & Chandra surveys in russian-doll style All wavelengths, very deep coverage available CDFS Chandra 1-2-4Ms XMM 3 Ms ~0.1 deg2, ~4e-17 cgs objects (Giacconi+2002, Alexander +2003, Luo+ 2008,10, Xue +2011, Comastri+2011, Ranalli+2013)
13 1) Obscured fraction as a function of z La Franca et al Hasinger 2008 Type 2 AGN fraction is higher at high-z... higher-z, more cold gas available, more obscured Detailed studies of z>3 samples also reveal high fraction (>50%) of obscured objects (e.g. Fiore et al. 2012, Vito et al. 2013)
14 1) Obscured fraction as a function of z COSMOS: Merloni et al. in prep La Franca et al Hasinger 2008 Type 2 AGN fraction is higher at high-z... higher-z, more cold gas available, more obscured Detailed studies of z>3 samples also reveal high fraction (>50%) of obscured objects (e.g. Fiore et al. 2012, Vito et al. 2013)... or not? Result still very debated after ~10 years issues of classifications (X-ray/optical), selection (hard/soft), NH determination, Lx etc.
15 2) Co-eval SF and accretion SF downsizing Downsizing Thomas et al De Lucia+2006 AGN downsizing Cosmic downsizing : the larger the faster (Cowie et al. 1996):.. galaxy formation took place in downsizing, with more massive galaxies forming at higher redshift.. more luminous AGN had the peak of activity at earlier redshifts see also Bongiorno et al z-dependence of specific accretion rate: (1+z) 4.2 at λedd = 10% Edd La Franca et al Fiore,MB+2003, Ueda+03; Barger+05; Hasinger+05; Silverman+05, Della Ceca+08, Ebrero+09 [i.e. like the ssfr evolution in galaxy population, Karim , Pannella+2010]
16 Rosario+2012 PEP / GOODS+COSMOS X-ray AGN 2) Co-eval SF and accretion SF vs. AGN luminosity correlation between Lx and SF does not hold at low- L (see also Shao+2010) evidence for dichotomy...
17 Rosario+2012 PEP / GOODS+COSMOS X-ray AGN 2) Co-eval SF and accretion SF vs. AGN luminosity mergers secular local AGN correlation between Lx and SF does not hold at low- L (see also Shao+2010) evidence for dichotomy...
18 Rosario+2012 PEP / GOODS+COSMOS X-ray AGN 2) Co-eval SF and accretion SF vs. AGN luminosity secular mergers very high L(AGN) > 46 : controversial results and interpretations... 1) at high-z, high-l mergers not important, same secular processes as low-z, low-l are in place 2) SF-AGN synchronization is lost at high-z (Rosario ) local AGN correlation between Lx and SF does not hold at low- L (see also Shao+2010) possible interpretation: effect of feedback in stopping SF evidence for dichotomy...
19 3) Evidence for Feedback? Page+2012 Hermes/ CDFN X--ray AGN Harrison+2012 CDFN/CDFS/COSMOS SFR drops at Lx>44 in CDFN -> evidence for feedback from AGN different results on CDFN (green, drop), CDFS (cyan, increase!) and COSMOS (red, ~constant) Huge cosmic variance problem! N.B.: so far, feedback revealed as molecular outflows (CO broad wings, Feruglio et al. 2010) or ionized outflows (emission line kinematics, Cano-Diaz et al. 2012) only in very bright systems
20 Summary (I) SF and AGN activity co-exist (e.g. same downsizing, same redshift evolution for sssfr and specific accretion rate), but very little knowledge on timescales/delays. They may share the same process of triggering, but there are not evidences yet that they trigger each other. Whatever physical process is responsible for triggering and fueling AGN and SF activity must decrease in frequency with cosmic time. There are evidences for mergers conditions (e.g. obscured fraction increases with z.. to be confirmed!) but no direct evidence for feedback or feedback effects (e.g. no shutdown of SF is proven) in L* objects - except the very brightest, local ones Luminosity effect is clearly in place (e.g. SF vs. Lx), but current surveys do not probe with enough statistics the critical range (loglx=logl*+/-0.5). Huge cosmic variance problem. LUMINOUS OBSCURED QSOs best laboratory...
21 INTERMEZZO (3) HOW to efficiently isolate obscured QSO Use correlations between observables (X/O, R-K, HR, luminosities) for the identified samples to isolate obscured AGN Brusa et al XMM-COSMOS 2-10 kev Most efficient selection to pick up obscured QSO using only 3 bands! Also pure X-ray selection (NH>22 and Lx>44, see Manieri et al. 2011)
22 INTERMEZZO (3) HOW to efficiently isolate obscured QSO Use correlations between observables (X/O, R-K, HR, luminosities) for the identified samples to isolate obscured AGN Brusa et al XMM-COSMOS 2-10 kev X/O correlates with Lx for obscured AGN (proposed by Fiore, MB+03; see also Barger+05, Eckart+06 etc.) Most efficient selection to pick up obscured QSO using only 3 bands! Also pure X-ray selection (NH>22 and Lx>44, see Manieri et al. 2011)
23 INTERMEZZO (3) HOW to efficiently isolate obscured QSO Use correlations between observables (X/O, R-K, HR, luminosities) for the identified samples to isolate obscured AGN Brusa et al XMM-COSMOS 2-10 kev X/O correlates with Lx for obscured AGN (proposed by Fiore, MB+03; see also Barger+05, Eckart+06 etc.) obscured sources are RED (Alexander et al. 2011, Mignoli+2004, Brusa +2005; 2009) Most efficient selection to pick up obscured QSO using only 3 bands! Also pure X-ray selection (NH>22 and Lx>44, see Manieri et al. 2011)
24 INTERMEZZO (3) HOW to efficiently isolate obscured QSO Use correlations between observables (X/O, R-K, HR, luminosities) for the identified samples to isolate obscured AGN Soft Hard Brusa et al XMM-COSMOS 2-10 kev QSO2 X/O correlates with Lx for obscured AGN (proposed by Fiore, MB+03; see also Barger+05, Eckart+06 etc.) BL AGN obscured sources are RED NL AGN (Alexander et al. 2011, Mignoli+2004, Brusa +2005; 2009) OBS AGN Most efficient selection to pick up obscured QSO using only 3 bands! Also pure X-ray selection (NH>22 and Lx>44, see Manieri et al. 2011)
25 How to place objects in the mergers sequence? Most luminous, obscured X-ray selected sources at z>1 are red --> effect of (negative) feedback efficient in stopping star formation, or AGN is in dusty environment? Evidences for both! Same level of starformation for active (AGN) and inactive (SF) outflow of ~300 km/s galaxies (see Bongiorno et al. 2012) Mainieri et al (QSO2 in COSMOS, Lx>44) see also Brusa+2009, Lusso+2011, Rovilos+2012 QSO2 hosts follow the tight correlation between SFR and M * of blue star-forming galaxies (e.g. Noeske+07; Daddi+07; Elbaz+07; Rodighiero+10 / Herschel) Daddi+07 Rodighiero+10 Passive population also present!
26 Merger sequence Compton Thick (not sampled) Coeval SB-AGN X-RAY obs/unobs QSO X-ray/OPTICAL SF QSO2 obscuration = torus and/or galaxy QSO1 (BL AGN) no obscuration passive QSO2 obscuration = torus
27 During or Post? X-ray obscured selection sample different phases/timescales evidence of SF both in FIR and optical spectra passive ellipticals/early type spectra without any sign of SF (see also Mignoli+2004, Brusa+2005, Daddi ) outflow of ~300 km/s Severgnini et al Cyan points: PACS 100 & 160 μm Courtesy D. Lutz/PEP team Brusa et al see also Mainieri+05, Vignali+10
28 How to test models? (1) BH masses zero-th order predictions: 1) unobscured AGN are subsequent phase of obscured QSO --> BH masses of unobscured AGN should be higher than those of X-ray obscured AGN. 2) unobscured AGN are a subsequent phase of **SF** obscured QSOs --> BH masses of unobscured AGN should be higher than those of X-ray obscured **SF** QSOs. (BH masses of passive QSO2 should be higher than those of SF QSO2)
29 How to test models? (1) BH masses zero-th order predictions: 1) unobscured AGN are subsequent phase of obscured QSO --> BH masses of unobscured AGN should be higher than those of X-ray obscured AGN. 2) unobscured AGN are a subsequent phase of **SF** obscured QSOs --> BH masses of unobscured AGN should be higher than those of X-ray obscured **SF** QSOs. (BH masses of passive QSO2 should be higher than those of SF QSO2) BH masses for X-ray obscured AGN at z>1 can be obtained with IR spectroscopy (Halpha redshifted in NIR); some dedicated programs started to exploit NIR spectrograph, such as SINFONI, XSHOOTER, ISAAC, FMOS, LUCIFER etc.
30 How to test models? (1) BH masses unobscured AGN are subsequent phase of obscured AGN --> BH masses of unobscured AGN should be higher than those of X-ray obscured AGN. X-ray Obscured QSOs tend to have a MBH-Mstar ratio consistent with the local one, while BL AGN have a higher ratio (Bongiorno et al. 2013) For a given M*, this is consistent with obscured AGN having a smaller BH mass than unobscured AGN BH masses for ~20 obscured AGN compared to BL AGN (Bongiorno et al. 2013) BUT... the observed lower ratio can be reproduced also with the same BH mass of BL AGN and a larger M* --> same phase as BL AGN, and obscuration is only from the torus (unified model)
31 How to test models? (1) BH masses passive QSO2 are a subsequent phase of SF QSO2--> BH masses of passive QSO2 should be higher than those of SF QSO2 current observations of obscured AGN at z>1 are on (small) sparse samples at different Lx, and other wavelength info is not homogeneous. 15 QSO2 at z~1.5 from XMM-COSMOS to be observed with Xshooter! (SF properties very well constrained from PEP/SED fitting)
32 How to test models? (1) BH masses passive QSO2 are a subsequent phase of SF QSO2--> BH masses of passive QSO2 should be higher than those of SF QSO2 current observations of obscured AGN at z>1 are on (small) sparse samples at different Lx, and other wavelength info is not homogeneous. 10 QSO2 at z~1.5 from XMM-COSMOS observed with Xshooter! (SF properties very well constrained from PEP/SED fitting)
33 X-shooter spectrum of XID 2028 outflow of ~300 km/s Hbeta OIII OIII Halpha
34 How to test models? (2) Cold Gas Mass If mergers scenario hold: Gas mass in SF QSO2 (still available) should be higher than in passive QSO2 (already diminished/exhausted) --> CO luminosities vs. LIR / SFE (IRAM + ALMA programs). Molecular gas kinematics Tacconi et al Polletta et al high SFE (mergers) low SFE (disks) IRAM detection of BzK and SMG gas fraction higher than in local SB. Time to extend these studies to AGN and larger samples --> ALMA! IRAM/ALMA studies so far limited to high-z QSOs and SF systems. Observations of PASSIVE QSO2 key to test (or falsify) merger models
35 Summary SF and AGN activity co-exist (e.g. same downsizing, same redshift evolution for sssfr and specific accretion rate), but very little knowledge on timescales/delays. They may share the same process of triggering, but there are not evidences yet that they trigger each other. Whatever physical process is responsible for triggering and fueling AGN and SF activity must decrease in frequency with cosmic time. There are evidences for mergers conditions (e.g. obscured fraction increases with z) but no direct evidence for feedback or feedback effects (e.g. no shutdown of SF is proven) in L* objects - except the very brightest, local ones Luminosity effect is clearly in place (e.g. SF vs. Lx), but current surveys do not probe with enough statistics the critical range (loglx=logl*+/-0.5). Huge cosmic variance problem. Lot of information already in place, but critical parameters (BH masses, gas masses) for obscured QSOs over a wide range of SF properties still missing. Exciting perspective for NIR spectroscopy and ALMA -> STAY TUNED!!!!!
36 The golden epoch of multi-wavelength synergies Gas mass (CO lines) ALMA/IRAM Stellar mass (SED fitting) Subaru/ CFHT/ Spitzer VLT/ Keck Herschel SFR (FIR fitting) BH mass (broad lines) X-shooter/ Sinfoni/FMOS/ NICS/Lucifer Chandra/ XMM SMBH growth rate (X-ray lum) ACS + WFC3 Morphologies
37 The (next) golden epoch of multi-wavelength synergies Gas mass (CO lines) ALMA/ SKA SPICA SFR (FIR fitting) Stellar mass (SED fitting) LSST/Euclid E-ELT/ Euclid BH mass (broad lines) KMOS/ JWST/Euclid? (erosita) SMBH growth rate (X-ray lum) JWST Morphologies
38 Thanks!
39 Backup
40
41 selection: yellow (+magenta) points z=
42 Comparison of AGN selection inner 0.9 deg2 COSMOS area deeper Chandra and optical data X-ray IR Optical Radio X-ray+IR 24.8% 31.5% 1) largest contribution from X- rays (Civano et al. 2012) 3) Radio provide a good 10% of extra AGN candidates (Smolcic et al. 2008) 9.8% 6.9% 4) most of ONLY Optical sources are NL AGN from BPT diagrams (e..g Bongiorno et al. 2010) 26.9% 2) IRAC color-color diagrams (Donley et al. 2012) relative contribution very sensitive to depth at different wavelengths..
43 Mergers vs. smooth accretion in mm Two families (sequences): low SFE and spatially extended gas reservoirs (disks) high SFE and compact gas reservoirs (mergers) Genzel et al see also Daddi et al. 2010
44 Mergers vs. smooth accretion in mm Two families (sequences): low SFE and spatially Low-L extended AGN gas reservoirs (disks) high SFE and high-l compact AGNgas reservoirs (mergers) Genzel et al see also Daddi et al. 2010
45 Enhanced SFR in AGN hosts? Santini+2012 (GOODS & COSMOS / PEP data) Evidence for enhancement: - GOODS (low-lx): SFR in AGN hosts broadly consistent with that observed in inactive galaxies; (modest) enhancement observed only in low-mass samples - COSMOS (high-lx): average SFR in AGN hosts ~0.6 dex higher than in inactive galaxies, at all z/masses (see also Silverman+2009, Xue+2010, Mullaney+2011) Enhancement is measured... but this does not mean that AGN do preferentially live in strong starbursts. Weighted average of detections and non-detections --> PACS detection rate is higher for AGN than non-agn
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs
 Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Revealing powerful outflows in z~1.5 obscured QSOs Marcella Brusa 1) Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia / Universita di Bologna 2) Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik / Garching, Germany
Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation?
 Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation? Marcella Brusa Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik Garching, Germany XMM view of the COSMOS field The Starburst-AGN connection under the multiwavelength
Starburst-AGN connection: a mutual relation? Marcella Brusa Max-Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik Garching, Germany XMM view of the COSMOS field The Starburst-AGN connection under the multiwavelength
The search for. COSMOS and CDFS. Marcella Brusa
 The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
The search for obscured AGN in COSMOS and CDFS Marcella Brusa MPE - High Energy Group XMM view of the COSMOS field Results obtained in the framework of the COSMOS & CDFS/MUSIC teams: Bongiorno, Brunner,
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not?
 Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
Connection between AGN and Star Formation activities, or not? Y.Sophia Dai ( 戴昱 ) National Astronomical Observatories of China (NAOC) daysophia@gmail.com Close Correlations between SMBH and hosts M SMBH
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey
 The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
The bolometric output of AGN in the XMM-COSMOS survey Elisabeta Lusso Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna-INAF/OABO A. Comastri, C. Vignali, G. Zamorani, M. Brusa, E. Treister, R. Gilli, M.
Feeding the Beast. Chris Impey (University of Arizona)
 Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
Feeding the Beast Chris Impey (University of Arizona) Note: the box is growing due to cosmic expansion but this is factored out. Heirarchical Structure Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) Nuclear activity in
What s the fuss about AGN?
 What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
What s the fuss about AGN? Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan, Italy) 1 Outline What is an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN)? AGN role and importance AGN evolutionary models and feedback Star-formation and AGN
The quest for early Black Holes
 The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
The quest for early Black Holes Andrea Comastri (INAF-Bologna) Roberto Gilli (INAF-Bologna) Cristian Vignali (Bologna University) Marcella Brusa (MPE) and many others Outline High redshift (z > 3) AGN
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es
 Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Radio Quiet AGN: Black Hole & Host Galaxy Proper;es (ESO) Collaborators: V. Mainieri, P. Padovani, P. Rosa6, N. Miller, K. I. Kellermann, P. Tozzi, S. Va>akunnel, A. Bongiorno, + PEP Collaboration Credit:
Obscured AGN. I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
Obscured AGN I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens Talk Outline Rationale: Why obscured AGN are important (especially the Compton-thick AGN) Obscured AGN from X-ray surveys (Chandra, XMM, Swift/BAT,
ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova
 ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova Starlight, HII & AGN Dust & Molecules Where we stand and looking in perspective The current generation of ground & space telescopes are
ISM and Galaxy Evolution the ELT View Alvio Renzini, INAF Padova Starlight, HII & AGN Dust & Molecules Where we stand and looking in perspective The current generation of ground & space telescopes are
X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION
 1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
1 X RAY EMITTING EROS AS TRACERS OF BLACK HOLES-GALAXIES COEVOLUTION M. Brusa 1, A. Comastri 2, E. Daddi 3, M. Mignoli 2, C. Vignali 4, G. Zamorani 2, F. Fiore 5, and L. Pozzetti 2 1 Max Planck Institut
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material
 Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
Active Galactic Nuclei in the infrared: identification, energetic and properties of the obscuring material Mari Polletta (Institut d Astrophysique de Paris) Collaborators: D. Weedman (Cornell U.), S. Hoenig
Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR
 Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR With: D. H. Weinberg, J. Miralda-Escudé, M. Bernardi, L. Ferrarese, J. Moreno, R. K. Sheth, Y. Shen,
Local Scaling Relations of Super-Massive Black Holes: Origin, Evolution, Consequences FRANCESCO SHANKAR With: D. H. Weinberg, J. Miralda-Escudé, M. Bernardi, L. Ferrarese, J. Moreno, R. K. Sheth, Y. Shen,
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback
 A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
A galaxy without its SMBH: implications for feedback Francesca Civano (SAO) M. Elvis, G. Lanzuisi,, L. Blecha, A. Loeb, T. Aldcroft, M. Trichas A. Bongiorno, M. Brusa, A. Comastri, M. Salvato, A. Fruscione,
AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift
 AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift Andrea Merloni (EXC, MPE) A. Bongiorno (MPE), COSMOS + zcosmos teams Outline Co-evolution of stellar
AGN feedback in action: constraints on the scaling relations between BH and galaxy at high redshift Andrea Merloni (EXC, MPE) A. Bongiorno (MPE), COSMOS + zcosmos teams Outline Co-evolution of stellar
Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College
 AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
AGN vs SF 2014 Durham University Obscuration and Star formation in Luminous Quasars Chien-Ting Chen! Dartmouth College In collaboration with: Ryan C. Hickox, Stacey Alberts, David M. Alexander, Roberto
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey
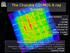 The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
The Chandra COSMOS X-ray Survey Vital Statistics: 1.8 Ms 1/2sq.deg @160 ksec 1761 sources Dec 06-June 07 Catalog in press ApJS Martin Elvis, Francesca Civano, Aldcroft T., Fruscione A., Harvard Smithsonian
The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature
 The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature Ji Hoon Kim Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Along with Myungshin Im, Dohyeong
The symbiotic nature of AGN and SF activities of AGNs probed by the PAH 3.3 micron emission feature Ji Hoon Kim Subaru Telescope National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Along with Myungshin Im, Dohyeong
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies
 Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
Astro2010 Science White Paper: Tracing the Mass Buildup of Supermassive Black Holes and their Host Galaxies Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI) Dan Batcheldor (RIT) Marc Postman (STScI) Rachel Somerville (STScI)
BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation
 BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation Dieter Lutz MPE Torus 2018 The many faces of AGN obscuration Puerto Varas, December 12, 2018 What is the size and structure of star formation (or cold gas) in
BAT AGN prefer circumnuclear star formation Dieter Lutz MPE Torus 2018 The many faces of AGN obscuration Puerto Varas, December 12, 2018 What is the size and structure of star formation (or cold gas) in
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity
 Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
Active Galactic Nuclei SEDs as a function of type and luminosity Mari Polletta (IASF-INAF Milan) Collaborators: L. Chiappetti (IASF-INAF), L. Maraschi, M. Giorgetti, G. Trinchieri (Brera-INAF), B. Wilkes
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN
 The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
The Hard X-Ray Luminosity Function of High-Redshift (z > 3) AGN Fabio Vito Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia - Università di Bologna INAF-OABo F Vito, RGilli, C Vignali, A Comastri, M Brusa, N Cappelluti,
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) AGN10 11/09/12 Outline of review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation Outline of (biased) review talk AGNs in theoretical models of galaxy formation
PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME
 THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
THE MOST LUMINOUS QUASARS: PROBING THE AGN/GALAXY CO-EVOLUTION AT ITS EXTREME Enrico Piconcelli Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma - INAF! A. Bongiorno, F. Fiore, M. Bischetti, L. Zappacosta OA-Roma! C.
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics
 Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Observing the Formation of Dense Stellar Nuclei at Low and High Redshift (?) Roderik Overzier Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics with: Tim Heckman (JHU) GALEX Science Team (PI: Chris Martin), Lee Armus,
Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations
 Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations (ESO, Germany) (see Harrison 2017) Overview Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations 1.
Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations (ESO, Germany) (see Harrison 2017) Overview Evidence for AGN impact on star formation in (unresolved) galaxy populations 1.
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North
 Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
Results from the Chandra Deep Field North Brandt, Alexander, Bauer, Garmire, Hornschemeier, Immler, Lehmer, Schneider, Vignali, Wu, Barger, Cowie, Bautz, Nousek, Sargent, Townsley Chandra Deep Field North
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability. Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida
 Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Multi-wavelength Surveys for AGN & AGN Variability Vicki Sarajedini University of Florida What are Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN)? Galaxies with a source of non-stellar emission arising in the nucleus (excessive
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback
 Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
Luminous radio-loud AGN: triggering and (positive?) feedback Clive Tadhunter University of Sheffield ASA, ESA, NRAO Collaborators: C. Ramos Almeida, D. Dicken," R. Morganti,T. Oosterloo, " R. Oonk, M.
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution. Fabio Fontanot (HITS)
 AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
AGN/Galaxy Co-Evolution Fabio Fontanot (HITS) 21/11/2012 AGN activity in theoretical models of galaxy formation Represents a viable solution for a number of long-standing theoretical problems Properties
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models. Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11
 Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Galaxy Activity in Semi Analytical Models Fabio Fontanot (INAF OATs) Ljubljana 05/04/11 Part I: Theoretical background 1. Baryonic gas falls in the gravitational potential of Dark Matter Halos 2. Baryonic
Compton-thick AGN. SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens
 Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
Compton-thick AGN SWIFT/BAT 70 month survey (+ CDFS 7Ms + models) I. Georgantopoulos National Observatory of Athens A. Akylas, P. Ranalli, A. Corral, G. Lanzuisi Talk Outline Rationale: Why heavily obscured
Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure. Mark Dickinson (NOAO)
 Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Mark Dickinson (NOAO) Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Past Mark Dickinson (NOAO) IRAS FIDEL 60μm MIPS 160μm 70μm
Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Mark Dickinson (NOAO) Galaxy Evolution at High Redshift: The Future Remains Obscure Past Mark Dickinson (NOAO) IRAS FIDEL 60μm MIPS 160μm 70μm
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD
 The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
The Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) The Evolution of the FIR/SMM Luminosity Function and of the Cosmic SFRD Lucia Marchetti University of Padova - Open University Mattia Vaccari - University
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory
 A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs
 Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
Luminous Quasars and AGN Surveys with ELTs Roberto J. Assef Núcleo de Astronomía Universidad Diego Portales This Talk Will focus on two topics: 1. The most luminous (obscured) quasars 2. AGN surveys Big
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey. R. Della Ceca. INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan
 The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
The Bright Side of the X-ray Sky The XMM-Newton Bright Survey T. Maccacaro A. Caccianiga P. Severgnini V. Braito R. Della Ceca INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera,Milan On behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation
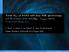 Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
Virial M BH of AGN2 with deep NIR spectroscopy and the measure of the local M BH L 3.6,bul relation 1 Università Roma Tre F. Ricci 1, F. Onori, F. La Franca 1, E. Sani, M. Brusa et al. Hidden Monsters,
The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift. Lidia Tasca & VUDS collaboration
 The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift of massive Large galaxies Programme at 2
The The largest assembly ESO high-redshift of massive Large galaxies Programme at 2
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community
 Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
Scientific cases for Simbol-X of interest of the Italian community Based on the High Energy Astrophysics study: Fields of interest and perspective for the national community ASI 2003-2004 Fabrizio Fiore
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts
 Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
Astrophysics of feedback in local AGN and starbursts A personal view Gabriele Ponti co-chair of swg 2.3 Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (Garching) Outline 1) Why is feedback required?
AGN feedback and the connection to triggering
 AGN feedback and the connection to triggering Ryan C. Hickox Dartmouth College The Triggering Mechanisms for Active Galactic Nuclei Lorentz Center, Leiden 26 July 2013 Illustration courtesy NASA Outline
AGN feedback and the connection to triggering Ryan C. Hickox Dartmouth College The Triggering Mechanisms for Active Galactic Nuclei Lorentz Center, Leiden 26 July 2013 Illustration courtesy NASA Outline
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us?
 The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
The quest for Type 2 quasars: What are the X-ray observations of optically selected QSOs2 telling us? Cristian Vignali Dipartimento di Astronomia, Universita`degli Studi di Bologna In collaboration with
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes. R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams
 The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
The cosmic X ray background: abundance and evolu8on of hidden black holes R. Gilli (INAF OaBologna) with the XMM CDFS, 4Ms CDFS, COSMOS, WFXT teams Cosmic X ray background spectrum = radiamve imprint of
Active Galactic Alexander David M Nuclei
 d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
d.m.alexander@durham.ac.uk Durham University David M Alexander Active Galactic Nuclei The Power Source QuickTime and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. Black hole is one billionth
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations
 Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
Exploring the Origin of the BH Mass Scaling Relations Vardha Nicola Bennert Assistant Professor California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo in collaboration with Tommaso Treu, Chelsea E. Harris
The Hot and Energetic Universe
 The Hot and Energetic Universe An Athena+ supporting paper Understanding the build-up of supermassive black holes and galaxies at the heyday of the Universe Authors and contributors A. Georgakakis, F.
The Hot and Energetic Universe An Athena+ supporting paper Understanding the build-up of supermassive black holes and galaxies at the heyday of the Universe Authors and contributors A. Georgakakis, F.
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA
 ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
ALMA Synergy with ATHENA Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris 9 September 2015 ALMA & Athena: common issues Galaxy formation and evolution, clustering Surveys of galaxies at high and intermediate redshifts
A Herschel view on star formation in high
 A Herschel view on star formation in high redshift AGN hosts Dieter Lutz Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik + PEP Herschel GTO survey team Massive Galaxies over Cosmic Time 3 Tucson, November
A Herschel view on star formation in high redshift AGN hosts Dieter Lutz Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik + PEP Herschel GTO survey team Massive Galaxies over Cosmic Time 3 Tucson, November
The ALMA z=4 Survey (AR4S)
 The ALMA z=4 Survey (AR4S) ALMA studies of massive z~4-5 galaxies Corentin Schreiber Leiden University October 21 2016 In collaboration with: Maurilio Pannella, David Elbaz, Roger Leiton, Tao Wang, and
The ALMA z=4 Survey (AR4S) ALMA studies of massive z~4-5 galaxies Corentin Schreiber Leiden University October 21 2016 In collaboration with: Maurilio Pannella, David Elbaz, Roger Leiton, Tao Wang, and
Multi-wavelength ISM diagnostics in high redshift galaxies
 Multi-wavelength ISM diagnostics in high redshift galaxies Alexandra Pope (UMass Amherst) Transformational Science in the ALMA Era: Multi-Wavelength Studies of Galaxy Evolution Conference Charlottesville,
Multi-wavelength ISM diagnostics in high redshift galaxies Alexandra Pope (UMass Amherst) Transformational Science in the ALMA Era: Multi-Wavelength Studies of Galaxy Evolution Conference Charlottesville,
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies
 Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
Gas Accretion & Outflows from Redshift z~1 Galaxies David C. Koo Kate Rubin, Ben Weiner, Drew Phillips, Jason Prochaska, DEEP2, TKRS, & AEGIS Teams UCO/Lick Observatory, University of California, Santa
A Monster at any other Epoch:
 A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
A Monster at any other Epoch: Are Intermediate Redshift ULIRGs the Progenitors of QSO Host Galaxies? Barry Rothberg Large Binocular Telescope Observatory/George Mason University Co-Is: J. Fischer (NRL),
THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED
 ESLAB 2013 04/04/2013 Noordwijk THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED Material at http://irfu.cea.fr/sap/phocea/page/index.php?id=537 Matthieu Béthermin In
ESLAB 2013 04/04/2013 Noordwijk THE CONNECTION BETWEEN STAR FORMATION AND DARK MATTER HALOS AS SEEN IN THE INFRARED Material at http://irfu.cea.fr/sap/phocea/page/index.php?id=537 Matthieu Béthermin In
PoS(SWIFT 10)153. SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses
 SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses a Fabio La Franca a, Federica Ricci a, Marcella Brusa b, Eleonora Sani c, Roberto Maiolino d,
SWIFT/BAT AGN2 reveal broad emission lines in the NIR: the first virial measure of their black hole masses a Fabio La Franca a, Federica Ricci a, Marcella Brusa b, Eleonora Sani c, Roberto Maiolino d,
The parsec scale of. ac-ve galac-c nuclei. Mar Mezcua. International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics
 The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
The parsec scale of ESO ac-ve galac-c nuclei International Max Planck Research School for Astronomy and Astrophysics COST Ac(on MP0905 - Black Holes in a Violent Universe In collaboration with A. Prieto,
Massively Star-Forming Dusty Galaxies. Len Cowie JCMT Users Meeting
 Massively Star-Forming Dusty Galaxies Len Cowie JCMT Users Meeting The luminous dusty star-formation history: We are using SCUBA-2 to address three questions What fraction of the SF is in luminous dusty
Massively Star-Forming Dusty Galaxies Len Cowie JCMT Users Meeting The luminous dusty star-formation history: We are using SCUBA-2 to address three questions What fraction of the SF is in luminous dusty
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen,W-H Wang and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird. University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester)
 Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
Surveys for high-redshift (z>6) AGN with AXIS (cf. Athena) James Aird University of Cambridge (-> University of Leicester) SMBH seed formation mechanisms Pop III star remnants MBH ~ 100 M z~20-30 Direct
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx
 X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
X-raying High-Redshift AGNs and the First Black Holes: From Chandra to Lynx Niel Brandt, Fabio Vito, the Chandra Deep Fields Team, and the Lynx First Accretion Light Working Group Some Relevant Results
Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011
 Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011 BASIC PARADIGM: Copious energy output from AGN (10 9-10 13 L Θ ) from accretion of material onto a Supermassive Black Hole SMBH ( 10 6-10 9 M Θ ). AGN
Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, 27 Ottobre 2011 BASIC PARADIGM: Copious energy output from AGN (10 9-10 13 L Θ ) from accretion of material onto a Supermassive Black Hole SMBH ( 10 6-10 9 M Θ ). AGN
Disk Building Processes in the local Massive HI LIRG HIZOA J A prototype for disk galaxies at z=1?
 Disk Building Processes in the local Massive HI LIRG HIZOA J0836-43 A prototype for disk galaxies at z=1? Renée C. Kraan-Korteweg Astronomy Department Centre for Astrophysics Cosmology and Gravity, UCT
Disk Building Processes in the local Massive HI LIRG HIZOA J0836-43 A prototype for disk galaxies at z=1? Renée C. Kraan-Korteweg Astronomy Department Centre for Astrophysics Cosmology and Gravity, UCT
Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0<z 2.5
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2015) Printed February 11, 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2015) Printed February 11, 2015 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Mapping the average AGN accretion rate in the SFR M plane for Herschel selected galaxies at 0
Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes?
 Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes? Knud Jahnke Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie Katherine Inskip, Dading Nugroho, Mauricio Cisternas, Hans-Walter Rix, Chien Y. Peng, COSMOS (Mara Salvato, Jonathan
Co-evolution of galaxies and black holes? Knud Jahnke Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie Katherine Inskip, Dading Nugroho, Mauricio Cisternas, Hans-Walter Rix, Chien Y. Peng, COSMOS (Mara Salvato, Jonathan
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 21 Nov 2016](/thumbs/93/113519117.jpg) Astron. Nachr. / AN, No., 1 6 () / DOI please set DOI! X-ray selection of Compton Thick AGN at high redshift G. Lanzuisi 1,2, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Universitá degli studi di Bologna, Via
Astron. Nachr. / AN, No., 1 6 () / DOI please set DOI! X-ray selection of Compton Thick AGN at high redshift G. Lanzuisi 1,2, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Universitá degli studi di Bologna, Via
THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT. F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3
 1 THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3 1 Instituto de Física de Cantabria, Avenida de los Castros, 39005 Santander, Spain
1 THE XMM-NEWTON AND SPITZER VIEW OF GALAXY/AGN FORMATION AT F.J. Carrera, J. Ebrero 1, M.J. Page 2, and J.A. Stevens 3 1 Instituto de Física de Cantabria, Avenida de los Castros, 39005 Santander, Spain
MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY
 1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
1 MULTI-WAVELENGTH OBSERVATIONS OF X-RAY SELECTED AGN: WHAT WE NEED AND WHY M. Polletta 1,2 and D. M. Alexander 3 1 INAF - IASF Milan, via E. Bassini 15, 20133 Milan, Italy 2 Institut d Astrophysique de
The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function:
 The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function: towards the high-mass end at high redshifts Helena Domínguez Sánchez Jordi Cepa (IAC), Miguel Sánchez Portal (ESAC), Andrea Cimatti (UniBo), Francesca
The evolution of the Galaxy Stellar Mass Function: towards the high-mass end at high redshifts Helena Domínguez Sánchez Jordi Cepa (IAC), Miguel Sánchez Portal (ESAC), Andrea Cimatti (UniBo), Francesca
Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti. Lezione 7
 Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti Lezione 7 First hints of BH-galaxy relations Kormendy & Richstone (1995) suggest the existence of a correlation between the total blue magnitude of the
Relazioni di scala tra Buchi Neri e Galassie Ospiti Lezione 7 First hints of BH-galaxy relations Kormendy & Richstone (1995) suggest the existence of a correlation between the total blue magnitude of the
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister
 The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
The Connection between Major Galaxy Mergers, Black Hole Growth and Galaxy Evolution from Multiwavelength Observations Ezequiel Treister P. Universidad Católica Collaborators: Franz Bauer (PUC), George
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN
 Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
Multiwavelength signatures of AGN feedback in local AGN Chiara Feruglio Institut de RadioAstronomie Millimétrique, Grenoble Thanks to: G. FABBIANO (CfA), F. FIORE (INAF) INAF - Bologne, 6 Mai 2013 1 Galaxy
Introduction and Motivation
 1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
1 Introduction and Motivation This last two days at this conference, we ve focused on two large questions regarding the role that AGNs play in galaxy evolution: My research focuses on exploring these questions
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 6 Jun 2012](/thumbs/93/111700682.jpg) Draft version May 10, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE HIDDEN AGN MAIN SEQUENCE : EVIDENCE FOR A UNIVERSAL BLACK HOLE ACCRETION TO STAR FORMATION RATE RATIO SINCE z 2
Draft version May 10, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE HIDDEN AGN MAIN SEQUENCE : EVIDENCE FOR A UNIVERSAL BLACK HOLE ACCRETION TO STAR FORMATION RATE RATIO SINCE z 2
The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history
 The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history A&A, 574, A105 (2015) A&A, 579, A132 (2015) A. Biviano, INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Introduction The cosmic z-dependent Star
The role of massive halos in the cosmic star formation history A&A, 574, A105 (2015) A&A, 579, A132 (2015) A. Biviano, INAF-Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Introduction The cosmic z-dependent Star
An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey
 An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey Marco Bondi, INAF-IRA AGN selected using different techniques/wavelengths represent separate populations, with differences in host galaxies, environments
An AGN census: the contribution of radio survey Marco Bondi, INAF-IRA AGN selected using different techniques/wavelengths represent separate populations, with differences in host galaxies, environments
The growth and evolution of super massive black holes
 The growth and evolution of super massive black holes A white paper submitted to the Decadal Survey Committee Authors: S. Murray 1, R. Gilli 2, P. Tozzi 3, M. Paolillo 4, N. Brandt 8, G. Tagliaferri 9,
The growth and evolution of super massive black holes A white paper submitted to the Decadal Survey Committee Authors: S. Murray 1, R. Gilli 2, P. Tozzi 3, M. Paolillo 4, N. Brandt 8, G. Tagliaferri 9,
A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings
 A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings Andrea Biviano Andrea Biviano INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Outline: mid-ir & multiwavelength observations
A mid and far-ir view of the star formation activity in galaxy systems and their surroundings Andrea Biviano Andrea Biviano INAF/Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste Outline: mid-ir & multiwavelength observations
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang
 The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
The History of Active Galaxies A.Barger, P. Capak, L. Cowie, RFM, A. Steffen, and Y. Yang Active Galaxies (AKA quasars, Seyfert galaxies etc) are radiating massive black holes with L~10 8-10 14 L sun The
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations
 The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
The Evolution of BH Mass Scaling Relations Nicola Bennert UCSB in collaboration with Tommaso Treu (UCSB), Jong-Hak Woo (UCLA), Alexandre Le Bris (UCSB), Matthew A. Malkan (UCLA), Matthew W. Auger (UCSB),
44 JAXA Special Publication JAXA-SP E Lutz Figure 2. The cosmic far-infrared background as seen by direct measurements and as resolved by Hersch
 From Exoplanets to Distant Galaxies : SPICA's New Window 43 Far-infrared Galaxy Evolution Surveys with Herschel Dieter Lutz 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Germany ABSTRACT The 2009-2013
From Exoplanets to Distant Galaxies : SPICA's New Window 43 Far-infrared Galaxy Evolution Surveys with Herschel Dieter Lutz 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Germany ABSTRACT The 2009-2013
Clustering of Star-forming Galaxies and connections with AGN activity
 Clustering of Star-forming Galaxies and connections with AGN activity MANUELA MAGLIOCCHETTI IAPS-INAF Collaborators: Herschel PEP team (D.Lutz, P.Popesso, D.Rosario et al.) & A.Lapi, M.Negrello, G.De Zotti.,
Clustering of Star-forming Galaxies and connections with AGN activity MANUELA MAGLIOCCHETTI IAPS-INAF Collaborators: Herschel PEP team (D.Lutz, P.Popesso, D.Rosario et al.) & A.Lapi, M.Negrello, G.De Zotti.,
Active Galactic Nuclei: Making the Most of the Great Observatories
 Active Galactic Nuclei: Making the Most of the Great Observatories Niel Brandt (Penn State) AGN Spectral Energy Distribution 3.6-160 µm 1150-25000 A 0.3-8 kev Host galaxy Richards et al. (2006) Active
Active Galactic Nuclei: Making the Most of the Great Observatories Niel Brandt (Penn State) AGN Spectral Energy Distribution 3.6-160 µm 1150-25000 A 0.3-8 kev Host galaxy Richards et al. (2006) Active
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 15 Nov 2014](/thumbs/95/125499947.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Perna14_sub c ESO 2018 August 27, 2018 Galaxy-wide outflows in z 1.5 luminous obscured QSOs revealed through NIR slit-resolved spectroscopy M. Perna 1, 2, M. Brusa
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Perna14_sub c ESO 2018 August 27, 2018 Galaxy-wide outflows in z 1.5 luminous obscured QSOs revealed through NIR slit-resolved spectroscopy M. Perna 1, 2, M. Brusa
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies
 The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
The Monster Roars: AGN Feedback & Co-Evolution with Galaxies Philip Hopkins Ø (Nearly?) Every massive galaxy hosts a supermassive black hole Ø Mass accreted in ~couple bright quasar phase(s) (Soltan, Salucci+,
LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi
 LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi in collaboration with I. McHardy, D. Williams, R. Beswick and many others The radio-loud / radio-quiet dichotomy Among the many
LeMMINGs the emerlin radio legacy survey of nearby galaxies Ranieri D. Baldi in collaboration with I. McHardy, D. Williams, R. Beswick and many others The radio-loud / radio-quiet dichotomy Among the many
Star Formation Indicators
 Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
Star Formation Indicators Calzetti 2007 astro-ph/0707.0467 Brinchmann et al. 2004 MNRAS 351, 1151 SFR indicators in general! SFR indicators are defined from the X ray to the radio! All probe the MASSIVE
Black Holes in the local Universe
 Outline 1. AGN evolution and the history of accretion 2. From AGN SED to AGN physics Accretion discs and X-ray coronae in AGN 3. Do AGN reveal accretion mode changes? The fundamental plane of BH activity
Outline 1. AGN evolution and the history of accretion 2. From AGN SED to AGN physics Accretion discs and X-ray coronae in AGN 3. Do AGN reveal accretion mode changes? The fundamental plane of BH activity
Paul Sell. University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti
 A SAMPLE OF EXTREME MERGER-DRIVEN STARBURST GALAXIES AS VIEWED BY THE CHANDRA AND HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPES Paul Sell University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti Collaboration: Aleks Diamond-Stanic,
A SAMPLE OF EXTREME MERGER-DRIVEN STARBURST GALAXIES AS VIEWED BY THE CHANDRA AND HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPES Paul Sell University of Wisconsin-Madison Advisor: Christy Tremonti Collaboration: Aleks Diamond-Stanic,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Feb 2019](/thumbs/94/119592941.jpg) Draft version February 12, 2019 Typeset using L A TEX preprint2 style in AASTeX61 MULTI-WAVELENGTH PROPERTIES OF TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2 AGN HOST GALAXIES IN THE CHANDRA-COSMOS LEGACY SURVEY arxiv:1902.03244v1
Draft version February 12, 2019 Typeset using L A TEX preprint2 style in AASTeX61 MULTI-WAVELENGTH PROPERTIES OF TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2 AGN HOST GALAXIES IN THE CHANDRA-COSMOS LEGACY SURVEY arxiv:1902.03244v1
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay)
 Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
Searching for the dominant mode of galaxy growth! from deep extragalactic Herschel surveys! D.Elbaz (CEA Saclay) Star formation = local process (~pc scale)! How sensitive is SF to larger scales inside
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt
 X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
X ray Survey Results on AGN Physics and Evolution Niel Brandt Chandra XMM Newton Photon statistics Hard response ACIS Best positions Highest sens. < 6 kev 50 250 times sens. of previous missions Good positions
Daichi Kashino Nagoya
 21 Feb. 2014, Hokkaido Univ. The impact of galactic structure on star formation Properties of star-forming galaxies at z~1.6 revealed by FMOS-COSMOS survey Daichi Kashino Nagoya FMOS-COSMOS team J. Silverman
21 Feb. 2014, Hokkaido Univ. The impact of galactic structure on star formation Properties of star-forming galaxies at z~1.6 revealed by FMOS-COSMOS survey Daichi Kashino Nagoya FMOS-COSMOS team J. Silverman
20x increase from z = 0 to 2!
 black hole accretion (AGN) & star formation (SF) 20x increase from z = 0 to 2! due to more gas (initial supply or accretion) or higher efficiency gas è stars, AGN starbursts merging? ALMA survey of ISM
black hole accretion (AGN) & star formation (SF) 20x increase from z = 0 to 2! due to more gas (initial supply or accretion) or higher efficiency gas è stars, AGN starbursts merging? ALMA survey of ISM
GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies. (Affiliations can be found after the references)
 DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219880 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies A. Del Moro 1, D. M. Alexander 1, J.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201219880 c ESO 2012 Astronomy & Astrophysics GOODS-Herschel: radio-excess signature of hidden AGN activity in distant star-forming galaxies A. Del Moro 1, D. M. Alexander 1, J.
AST Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy. Lecture 20. Black Holes Part II
 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Lecture 20 Black Holes Part II 1 AST4320 - Cosmology and extragalactic astronomy Outline: Black Holes Part II Gas accretion disks around black holes, and
Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution
 Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution Philip Hopkins Arizona 11/29/07 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Adam Lidz, Gordon Richards, Alison Coil, Adam Myers, Paul Martini, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson,
Quasars, Mergers, and Spheroid Evolution Philip Hopkins Arizona 11/29/07 Lars Hernquist, T. J. Cox, Adam Lidz, Gordon Richards, Alison Coil, Adam Myers, Paul Martini, Volker Springel, Brant Robertson,
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction
 The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
The Phenomenon of Active Galactic Nuclei: an Introduction Outline Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN): > Why are they special? > The power source > Sources of Continuum Emission > Emission & absorption lines
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies. Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts
 X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
X-raying galactic feedback in nearby disk galaxies Q. Daniel Wang University of Massachusetts Chandra survey of diffuse X-ray emission from 53 edge-on galaxies i > 60 o, D < 30 Mpc (Li, J.-T. & Wang, Q.D.
Quasar Feedback in Galaxies
 Quasar Feedback in Galaxies Philip Hopkins Lars Hernquist, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, Todd Thompson, Dusan Keres, Chris Hayward, Stijn Wuyts, Kevin Bundy, Desika Narayanan, Ryan Hickox, Rachel Somerville,
Quasar Feedback in Galaxies Philip Hopkins Lars Hernquist, Norm Murray, Eliot Quataert, Todd Thompson, Dusan Keres, Chris Hayward, Stijn Wuyts, Kevin Bundy, Desika Narayanan, Ryan Hickox, Rachel Somerville,
