The Los Cabos Lectures
|
|
|
- Bernice Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
2 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 free-streaming cut-off The linear power spectrum in power per octave form Assumes a 100GeV wimp following Green et al (2004)
3 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 free-streaming cut-off Variance of linear density fluctuation within spheres containing mass M, extrapolated to z = 0 As M 0, S(M) 720
4 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 If these Markov random walks are scaled so the maximum variance is 720 and the vertical axis is multiplied by 720, then they represent complete halo assembly histories for random CDM particles. An ensemble of walks thus represents the probability distribution of assembly histories
5 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 Distribution of the masses of the first halos for a random set of dark matter particles The median is 10-2M For 10% of the mass the first halo has M > 107M
6 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 Distribution of the collapse redshifts of the first halos for a random set of dark matter particles The median is z = 13 For 10% of the mass the first halo collapses at z > 34 For 1% at z > 55
7 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 Distribution of the collapse redshifts of the first halos for dark matter particles split by the mass of the first object The high redshift tail is entirely due to matter in small first halos For first halo masses below a solar mass, the median collapse redshift is z = 21
8 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Angulo et al 2009 Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Total mass fraction in halos At z = 0 about 5% (Sph) or 20% (Ell) of the mass is still diffuse Beyond z = 50 almost all the mass is diffuse Only at z < 2 (Sph) or z<0.5 (Ell) is most mass in halos with M > 108M The Ell curve agrees with simulations
9 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 The typical mass element in a Milky Way halo goes through ~5 infall events where its halo falls into a halo bigger than itself. Typically only one of these is as part of a halo with M > 108M
10 EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ = 0.75, n=1, σ8 = 0.9 Angulo et al 2009 The typical mass element in a Milky Way halo goes through ~3 major mergers where the two halos are within a factor of 3 in mass The majority of these occur when the element is part of the larger halo
11 EPS halo assembly: conclusions The typical first halo is much more massive than the free streaming mass First halos typically collapse quite late z ~ 13 Halo growth occurs mainly by accretion of much smaller halos There are rather few generations of accretion/merger events Major mergers are not a major part of the growth of many halos
12 The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al 2001 A 'Milky Way' halo Power et al kpc/h 2.5cm
13 CDM galaxy halos (without galaxies!) Halos extend to ~10 times the 'visible' radius of galaxies and contain ~10 times the mass in the visible regions Halos are not spherical but approximate triaxial ellipsoids -- more prolate than oblate -- axial ratios greater than two are common "Cuspy" density profiles with outwardly increasing slopes -- d ln ϱ / d ln r = with < -2.5 at large r > -1.2 at small r Substantial numbers of self-bound subhalos contain ~10% of the halo's mass and have d N / d M ~ M Most substructure mass is in most massive subhalos
14 Density profiles of dark matter halos Navarro, Frenk & White 1996 The average dark matter density of a dark halo depends on distance from halo centre in a very similar way in halos of all masses at all times -- a universal profile shape -ρ(r)/ρcrit δ rs / r(1 + r/rs)2 More massive halos and halos that form earlier have higher densities (bigger δ) Concentration c = r200 / rs is an alternative density measure Beware variety of definitions!
15 NFW profiles may not be pretty...
16 ...but they work surprisingly well N200 ~ 3 x kpc Navarro et al 2006
17 Milky Way halo z = 1.5 N200 = 3 x 106
18 Milky Way halo z = 1.5 N200 = 94 x 106
19 Milky Way halo z = 1.5 N200 = 750 x 106
20 How well do density profiles converge? Aquarius Project: Springel et al 2008 z=0
21 How well do density profiles converge? Aquarius Project: Springel et al 2008
22 Concentration scatter and trend with M and z Gao et al 2008
23 Concentration trends with M, z and cosmology Zhao et al 2008
24 The Aquarius halos Springel et al 2008
25 The Einasto profile fits the inner cusps Navarro et al 2009 Einasto's (1965) profile: ln ρ(r) /ρ-2 = -2 / α [(r / r-2)α - 1]
26 The Einasto profile fits the inner cusps Navarro et al 2009 Einasto's (1965) profile: ln ρ(r) /ρ-2 = -2 / α [(r / r-2)α - 1]
27 The Einasto profile fits the inner cusps Navarro et al 2009 Einasto's (1965) profile: ln ρ(r) /ρ-2 = -2 / α [(r / r-2)α - 1]
28 The Einasto α varies with mass Gao et al 2008 Results for stacked halos in the Millennium run Einasto's (1965) profile: ln ρ(r) /ρ-2 = -2 / α [(r / r-2)α - 1]
29 Mean profiles to much larger radii Hayashi & White 2008 At large radii, the mean density profile ρ(r) ξlin(r), the linear mass correlation function To a good approximation ρ(r) = max[ ρein(r), b ξlin(r) ]
30 A lensing test of the DM paradigm? Hayashi & White 2008
31 Velocity dispersion profiles Navarro et al 2009 Results are well converged Velocity dispersion and anisotropy peak at intermediate radii
32 Velocity dispersion profiles Navarro et al 2009 Results are well converged Velocity dispersion and anisotropy peak at intermediate radii Profiles vary significantly between halos
33 Pseudo-phase-space density profiles Navarro et al 2009 Shape variations in the density and velocity dispersion profiles compensate to make ρ(r) /σ(r)3 an almost universal power law
34 Halo profiles: conclusions The NFW formula fits spherically averaged profiles of most objects to within 10% out to at least 2 rs The characteristic density (or concentration) varies with mass, redshift and cosmology The Einasto formula fits better its additional shape parameter varies systematically with mass There is no indication of any asymptotic inner power law The scatter among halos is larger than the Einasto-NFW difference Mean profiles change shape dramatically for δ < 10 Velocity dispersion profiles show considerable variation Variations in ρ(r) and σ(r) compensate to give power law ρ/σ3
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
halo merger histories
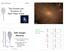 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 25 Jun 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 25 Jun 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 25 Jun 2012](/thumbs/90/104332349.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 17 February 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Phoenix Project: the Dark Side of Rich Galaxy Clusters arxiv:1201.1940v2 [astro-ph.co] 25 Jun 2012
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 17 February 2013 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Phoenix Project: the Dark Side of Rich Galaxy Clusters arxiv:1201.1940v2 [astro-ph.co] 25 Jun 2012
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model. Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik
 Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Dark Matter Halos. They will have a large impact on galaxies
 Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos form through gravitational instability. Density perturbations grow linearly until they reach a critical density, after which they turn around from the expansion of the
Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos form through gravitational instability. Density perturbations grow linearly until they reach a critical density, after which they turn around from the expansion of the
N-body Simulations. Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY
 N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 18 Nov 2009](/thumbs/72/67298474.jpg) Draft version November 22, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE DYNAMICAL STRUCTURE OF DARK MATTER HALOS Andreas Faltenbacher 1,2,3 and Simon D. M. White
Draft version November 22, 2013 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 ASSEMBLY BIAS AND THE DYNAMICAL STRUCTURE OF DARK MATTER HALOS Andreas Faltenbacher 1,2,3 and Simon D. M. White
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies
 The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies
 Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
The Caustic Technique An overview
 The An overview Ana Laura Serra Torino, July 30, 2010 Why the mass of? Small scales assumption of dynamical equilibrium Mass distribution on intermediate scales (1 10 Mpc/h) Large scales small over densities
The An overview Ana Laura Serra Torino, July 30, 2010 Why the mass of? Small scales assumption of dynamical equilibrium Mass distribution on intermediate scales (1 10 Mpc/h) Large scales small over densities
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises
 The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure of Dark Matter Haloes In this lecture we examine the detailed
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure of Dark Matter Haloes In this lecture we examine the detailed
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos
 Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics
 Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
Beyond the spherical dust collapse model
 Beyond the spherical dust collapse model 1.5M 1.0M M=1.66 10 15 M 0.65M 0.4M 0.25M Evolution of radii of different mass shells in a simulated halo Yasushi Suto Department of Physics and RESCEU (Research
Beyond the spherical dust collapse model 1.5M 1.0M M=1.66 10 15 M 0.65M 0.4M 0.25M Evolution of radii of different mass shells in a simulated halo Yasushi Suto Department of Physics and RESCEU (Research
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context
 IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter
 Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
2. What are the largest objects that could have formed so far? 3. How do the cosmological parameters influence structure formation?
 Einführung in die beobachtungsorientierte Kosmologie I / Introduction to observational Cosmology I LMU WS 2009/10 Rene Fassbender, MPE Tel: 30000-3319, rfassben@mpe.mpg.de 1. Cosmological Principles, Newtonian
Einführung in die beobachtungsorientierte Kosmologie I / Introduction to observational Cosmology I LMU WS 2009/10 Rene Fassbender, MPE Tel: 30000-3319, rfassben@mpe.mpg.de 1. Cosmological Principles, Newtonian
The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias. Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
 The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Halo clustering depends on formation history Gao, Springel & White 2005 The 20% of halos with
The halo-galaxy connection KITP, May 2017` Assembly bias Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Halo clustering depends on formation history Gao, Springel & White 2005 The 20% of halos with
The Alexandria Lectures
 March 2006 The Alexandria Lectures Numerical Cosmology: Recreating the Universe in a Supercomputer Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Three-fold Way to Astrophysical Truth OBSERVATION
March 2006 The Alexandria Lectures Numerical Cosmology: Recreating the Universe in a Supercomputer Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Three-fold Way to Astrophysical Truth OBSERVATION
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters. Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009
 The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution
 Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution Simon White & Mark Vogelsberger Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Milky Way halo seen in DM annihilation radiation Aquarius simulation: N200
Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution Simon White & Mark Vogelsberger Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Milky Way halo seen in DM annihilation radiation Aquarius simulation: N200
Dark matter. Anne Green University of Nottingham
 Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM
 Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1
 The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster
 DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
cluster scaling relations and mass definitions
 cluster scaling relations and mass definitions Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS Abell 85 SDSS/ Abell
cluster scaling relations and mass definitions Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS Abell 85 SDSS/ Abell
RHAPSODY: I. HALO PROPERTIES AND FORMATION HISTORY FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF RE-SIMULATED CLUSTER-SIZE HALOS
 Draft version July 24, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 RHAPSODY: I. HALO PROPERTIES AND FORMATION HISTORY FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF RE-SIMULATED CLUSTER-SIZE HALOS Hao-Yi
Draft version July 24, 2012 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 RHAPSODY: I. HALO PROPERTIES AND FORMATION HISTORY FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF RE-SIMULATED CLUSTER-SIZE HALOS Hao-Yi
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way
 Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter. Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC
 Observational Evidence for Dark Matter Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC XXXIX SLAC Summer Institute 28 July 2011 Outline Evidence for dark matter at very different scales Galaxies Clusters of galaxies Universe???
Observational Evidence for Dark Matter Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC XXXIX SLAC Summer Institute 28 July 2011 Outline Evidence for dark matter at very different scales Galaxies Clusters of galaxies Universe???
Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe
 Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe Figures + Tables for Lecture 13 on Tu Mar 18 Lectures 9 to 12 1) Evidence for DM ; CDM vs HDM 2) Surface brightness profile and v/σ of Disks, Bulges,
Astro 358/Spring 2008 (49520) Galaxies and the Universe Figures + Tables for Lecture 13 on Tu Mar 18 Lectures 9 to 12 1) Evidence for DM ; CDM vs HDM 2) Surface brightness profile and v/σ of Disks, Bulges,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 1999
 Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach
 Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach Puerto Vallarta January, 2011 Martin White UC Berkeley/LBNL (http://mwhite.berkeley.edu/talks) Strong non-linearity Martin White UCB/LBNL Limited
Non-linear structure in the Universe Cosmology on the Beach Puerto Vallarta January, 2011 Martin White UC Berkeley/LBNL (http://mwhite.berkeley.edu/talks) Strong non-linearity Martin White UCB/LBNL Limited
THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS
 THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS SURHUD MORE (KAVLI IPMU) Collaborators : Benedikt Diemer, Andrey Kravtsov, Philip Mansfield, Masahiro Takada, Hironao Miyatake, Neal Dalal, Rachel
THE EDGES OF DARK MATTER HALOS: THEORY AND OBSERVATIONS SURHUD MORE (KAVLI IPMU) Collaborators : Benedikt Diemer, Andrey Kravtsov, Philip Mansfield, Masahiro Takada, Hironao Miyatake, Neal Dalal, Rachel
Galaxy population simulations
 Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters
 Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014](/thumbs/88/115103634.jpg) Accepted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECTS OF VARYING COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON HALO SUBSTRUCTURE Gregory A. Dooley 1, Brendan F. Griffen 1, Phillip Zukin 2,3,
Accepted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECTS OF VARYING COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON HALO SUBSTRUCTURE Gregory A. Dooley 1, Brendan F. Griffen 1, Phillip Zukin 2,3,
Dark matter from cosmological probes
 PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 Distant Clusters of Galaxies Ringberg, October, 2005 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Bennett et al 2003 > 105 near-independent 5 temperature
Distant Clusters of Galaxies Ringberg, October, 2005 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Bennett et al 2003 > 105 near-independent 5 temperature
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix
 Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and old stellar populations
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies
 Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies de Vaucouleurs R 1/4 law for ellipticals and bulges A good fit to the light profile of many ellipticals and bulges: (constant such that
Some useful spherically symmetric profiles used to model galaxies de Vaucouleurs R 1/4 law for ellipticals and bulges A good fit to the light profile of many ellipticals and bulges: (constant such that
The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF CLUSTER-SIZE HALOS
 Draft version October 23, 212 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 SLAC-PUB-15314 RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF
Draft version October 23, 212 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 SLAC-PUB-15314 RHAPSODY: II. SUBHALO PROPERTIES AND THE IMPACT OF TIDAL STRIPPING FROM A STATISTICAL SAMPLE OF
Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies
 Chapter 14 Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies Rotation curves of disk galaxies rise steeply in their inner regions and then remain roughly flat out to the last point measured. To explain these observations within
Chapter 14 Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies Rotation curves of disk galaxies rise steeply in their inner regions and then remain roughly flat out to the last point measured. To explain these observations within
Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations-
 Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations- Sinziana Paduroiu University of Geneva / Observatoire de Geneve In memoriam Hector de Vega Chalonge Cosmology Colloquium
Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations- Sinziana Paduroiu University of Geneva / Observatoire de Geneve In memoriam Hector de Vega Chalonge Cosmology Colloquium
PATRICIA B. TISSERA. Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina
 PATRICIA B. TISSERA Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina i Observational motivations Model Results GALAXY FORMATION In the last years, studies of chemical elements obtained in the Local
PATRICIA B. TISSERA Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics Argentina i Observational motivations Model Results GALAXY FORMATION In the last years, studies of chemical elements obtained in the Local
Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter
 Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside TeVPA, August 7, 2017 See Anna Kwa s talk Review for Physics Reports: Sean Tulin, HBY arxiv:
Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside TeVPA, August 7, 2017 See Anna Kwa s talk Review for Physics Reports: Sean Tulin, HBY arxiv:
The imprint of the initial conditions on large-scale structure
 Stars, Planets and Galaxies 2018 Harnack House, Berlin The imprint of the initial conditions on large-scale structure Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Planck map of TCMB the initial
Stars, Planets and Galaxies 2018 Harnack House, Berlin The imprint of the initial conditions on large-scale structure Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Planck map of TCMB the initial
The structure of clusters in a Self-Interacting Dark Matter cosmology
 The structure of clusters in a Self-Interacting Dark Matter cosmology Thejs Ehlert Brinckmann Supervisor: Jesús Zavala Franco Co-supervisor: Steen Harle Hansen Master s thesis, submitted on August 7, 2015
The structure of clusters in a Self-Interacting Dark Matter cosmology Thejs Ehlert Brinckmann Supervisor: Jesús Zavala Franco Co-supervisor: Steen Harle Hansen Master s thesis, submitted on August 7, 2015
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10445 Measuring gravitational redshift of galaxies in clusters The gravitational potential depth in typical galaxy clusters, expressed in terms of the velocity shift, is estimated at
doi:10.1038/nature10445 Measuring gravitational redshift of galaxies in clusters The gravitational potential depth in typical galaxy clusters, expressed in terms of the velocity shift, is estimated at
Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos
 Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos Houjun Mo February 23, 2004 Hierarchical clustering, the matter in the universe condenses to form quasiequilibrium objects (dark halos) of increasing masses in the passage
Lecture 6: Dark Matter Halos Houjun Mo February 23, 2004 Hierarchical clustering, the matter in the universe condenses to form quasiequilibrium objects (dark halos) of increasing masses in the passage
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures.
 CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 May 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 May 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 May 2016](/thumbs/84/90821303.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 11 May 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Mass-Concentration-Redshift Relation of Cold and Warm Dark Matter Halos arxiv:1602624v2 [astro-ph.co] 10
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 11 May 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Mass-Concentration-Redshift Relation of Cold and Warm Dark Matter Halos arxiv:1602624v2 [astro-ph.co] 10
The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data
 Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 13 May 2008
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution
 AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution Darren Croton (University of California Berkeley) Simon White, Volker Springel, et al. (MPA) DEEP2 & AEGIS collaborations (Berkeley & everywhere
AGN feedback and its influence on massive galaxy evolution Darren Croton (University of California Berkeley) Simon White, Volker Springel, et al. (MPA) DEEP2 & AEGIS collaborations (Berkeley & everywhere
Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter)
 Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter) ICC, Durham! with the Eagle collaboration: J Schaye (Leiden), R Crain (Liverpool), R Bower, C Frenk, & M Schaller (ICC)
Hunting for dark matter in the forest (astrophysical constraints on warm dark matter) ICC, Durham! with the Eagle collaboration: J Schaye (Leiden), R Crain (Liverpool), R Bower, C Frenk, & M Schaller (ICC)
Cluster density profiles and orbits of galaxies from dynamical analysis. Andrea Biviano, INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste
 Cluster density profiles and orbits of galaxies from dynamical analysis Andrea Biviano, INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Collaborators & papers: on the observational side: A.B. & M. Girardi 2003, P. Katgert, A.B.
Cluster density profiles and orbits of galaxies from dynamical analysis Andrea Biviano, INAF/Oss.Astr.Trieste Collaborators & papers: on the observational side: A.B. & M. Girardi 2003, P. Katgert, A.B.
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution. Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure
 Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites. Jacqueline Chen
 The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
Homework 1. Astronomy 202a. Fall 2009
 Homework 1 Astronomy 0a Fall 009 Solutions Problems: 1. A galaxy has an integrated blue magnitude of 6.5, a rotation velocity (essentially flat) of 107 km s 1, and is ellptical in overall shape with major
Homework 1 Astronomy 0a Fall 009 Solutions Problems: 1. A galaxy has an integrated blue magnitude of 6.5, a rotation velocity (essentially flat) of 107 km s 1, and is ellptical in overall shape with major
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution. Elliptical Galaxies (II)
 Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Elliptical Galaxies (II) Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics Feb 19: Disk Galaxies
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Elliptical Galaxies (II) Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics Feb 19: Disk Galaxies
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1
 The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
The Distribution of Stellar Mass in Galaxy Clusters since z=1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France Adam Muzzin, Henk Hoekstra, Monique Arnaud, Hervé Aussel, Gabriel Pratt, JeanBaptiste Melin, Sean McGee,
First detection of dark matter How Much Dark Matter is There?
 Galaxies AS7007, 2012 Lecture 3: Dark matter in galaxies Outline I What is dark matter? How much dark matter is there? How do we know it exists? Dark matter candidates The Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model
Galaxies AS7007, 2012 Lecture 3: Dark matter in galaxies Outline I What is dark matter? How much dark matter is there? How do we know it exists? Dark matter candidates The Cold Dark Matter (CDM) model
Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies
 Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies Chung-Pei Ma Onsi Fakhouri James McBride (UC Berkeley) Mike Boylan-Kolchin (MPA --> Southern UC) Claude-Andre Faucher-Giguere Dusan Keres (Harvard
Mergers and Mass Assembly of Dark Matter Halos & Galaxies Chung-Pei Ma Onsi Fakhouri James McBride (UC Berkeley) Mike Boylan-Kolchin (MPA --> Southern UC) Claude-Andre Faucher-Giguere Dusan Keres (Harvard
NYU Nov 5, R isa Wechsler. The Dark Matter and Satellites in the Milky Way and its Twins
 NYU Nov 5, 2010 R isa Wechsler The Dark Matter and Satellites in the Milky Way and its Twins What is the formation history of the Milky Way? Can we understand the population of satellites in the Milky
NYU Nov 5, 2010 R isa Wechsler The Dark Matter and Satellites in the Milky Way and its Twins What is the formation history of the Milky Way? Can we understand the population of satellites in the Milky
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation
 Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Fabrizio Nesti. LNGS, July 5 th w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci. Università dell Aquila, Italy. The Dark Matter density. F.
 Global The Dark Matter Fabrizio Nesti Università dell Aquila, Italy LNGS, July 5 th 2012 w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci Global Dark Matter? A number of indirect supporting evidences Modify Gravity
Global The Dark Matter Fabrizio Nesti Università dell Aquila, Italy LNGS, July 5 th 2012 w/ C.F. Martins, G. Gentile, P. Salucci Global Dark Matter? A number of indirect supporting evidences Modify Gravity
A Universe in Motion: Testing the Cosmological Paradigm with Galaxy Dynamics. John Dubinski, Toronto
 A Universe in Motion: Testing the Cosmological Paradigm with Galaxy Dynamics John Dubinski, Toronto Outline Cosmology and galaxy dynamics Tools of the trade and computational challenges Case Studies: Triaxial
A Universe in Motion: Testing the Cosmological Paradigm with Galaxy Dynamics John Dubinski, Toronto Outline Cosmology and galaxy dynamics Tools of the trade and computational challenges Case Studies: Triaxial
The statistics of ΛCDM halo concentrations
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 381, 1450 1462 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12381.x The statistics of ΛCDM halo concentrations Angelo F. Neto, 1,2 Liang Gao, 2 Philip Bett, 2 Shaun Cole, 2 Julio F. Navarro,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 381, 1450 1462 (2007) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2007.12381.x The statistics of ΛCDM halo concentrations Angelo F. Neto, 1,2 Liang Gao, 2 Philip Bett, 2 Shaun Cole, 2 Julio F. Navarro,
WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER
 1 WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER "Hubble Maps the Cosmic Web of "Clumpy" Dark Matter in 3-D" (Press release). NASA. 7 January 2007. DARK MATTER 2 CONTENTS 1.Relating Mass and Light Tulley-Fisher relation
1 WOLFGANG KLASSEN DARK MATTER "Hubble Maps the Cosmic Web of "Clumpy" Dark Matter in 3-D" (Press release). NASA. 7 January 2007. DARK MATTER 2 CONTENTS 1.Relating Mass and Light Tulley-Fisher relation
The mass of a halo. M. White
 A&A 367, 27 32 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000357 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The mass of a halo M. White Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: mwhite@cfa.harvard.edu
A&A 367, 27 32 (2001) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20000357 c ESO 2001 Astronomy & Astrophysics The mass of a halo M. White Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA e-mail: mwhite@cfa.harvard.edu
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges
 Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Exact potential density pairs for flattened dark haloes
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 3, 1503 1508 00) doi:10.1111/j.1365-66.008.14174.x Exact potential density pairs for flattened dark haloes Maarten Baes Sterrenkundig Observatorium, Universiteit Gent, Krijgslaan
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 3, 1503 1508 00) doi:10.1111/j.1365-66.008.14174.x Exact potential density pairs for flattened dark haloes Maarten Baes Sterrenkundig Observatorium, Universiteit Gent, Krijgslaan
Systematic Uncertainties from Halo Asphericity in Dark Matter Searches
 Systematic Uncertainties from Halo Asphericity in Dark Matter Searches Based on: Nicolas Bernal, Jaime Forero-Romero, RG & Sergio Palomares-Ruiz JCAP 1409 (2014) 004 Raghuveer Garani University of Bonn
Systematic Uncertainties from Halo Asphericity in Dark Matter Searches Based on: Nicolas Bernal, Jaime Forero-Romero, RG & Sergio Palomares-Ruiz JCAP 1409 (2014) 004 Raghuveer Garani University of Bonn
Distinguishing between WDM and CDM by studying the gap power spectrum of stellar streams
 Distinguishing between WDM and CDM by studying the gap power spectrum of stellar streams based on arxiv:1804.04384, JCAP 07(2018)061 Nilanjan Banik Leiden University/GRAPPA, University of Amsterdam In
Distinguishing between WDM and CDM by studying the gap power spectrum of stellar streams based on arxiv:1804.04384, JCAP 07(2018)061 Nilanjan Banik Leiden University/GRAPPA, University of Amsterdam In
Milky Way disc dynamics and kinematics from mock data
 Milky Way disc dynamics and kinematics from mock data Laurent Chemin CNES Postdoctoral Fellow (Lab. Astro. of Bordeaux) DPAC CU6 member: Gaia RVS calibrations and commissioning CU9 member: validation of
Milky Way disc dynamics and kinematics from mock data Laurent Chemin CNES Postdoctoral Fellow (Lab. Astro. of Bordeaux) DPAC CU6 member: Gaia RVS calibrations and commissioning CU9 member: validation of
The local dark matter halo density. Riccardo Catena. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg
 The local dark matter halo density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 17.05.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. To be published in JCAP Riccardo Catena
The local dark matter halo density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 17.05.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. To be published in JCAP Riccardo Catena
Probing Dark Matter Halos with Satellite Kinematics & Weak Lensing
 Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
A novel determination of the local dark matter density. Riccardo Catena. Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg
 A novel determination of the local dark matter density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 28.04.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. Riccardo Catena (ITP)
A novel determination of the local dark matter density Riccardo Catena Institut für Theoretische Physik, Heidelberg 28.04.2010 R. Catena and P. Ullio, arxiv:0907.0018 [astro-ph.co]. Riccardo Catena (ITP)
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
