Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
|
|
|
- Linda Justina Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
2 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does the Milky Way's halo really look like this? Concentration? Shape? Substructure?
3 Observed velocity dispersion versus potential well depth Consider a known (i.e. observed) density distribution of stars (r) in a given (i.e. simulated) potential well (r) For gas in a spherical potential: d p/d r = - d /d r = - V c 2 / r For a spherical stellar distribution d ( r 2 ) / d r + 2 ( r 2 l.o.s. 2 = V c 2 / 3 - t 2 ) / r = - V c 2 / r where... denotes an average over all stars in the dwarf For an isotropic velocity dispersion ( r = t at all r) l.o.s. 2 (r p ) = d r V c 2 (r 2 - r p 2 ) 1/2 /r / d r r / (r 2 - r p 2 ) 1/2
4 Simulations of CDM Milky Way halos Stöhr, White, Tormen & Springel 2002 Circular Velocity Curves Subhalo Counts within R 200 V c R 200 NFW N 200 GA GA GA
5 Circular velocity curves for subhalos Stöhr et al 2002 V c (r) for the 20 most massive subhalos in GA2
6 Predicted velocity dispersion profiles for Draco and Fornax Putting the observed star distributions in the potentials of the 20 largest CDM subhalos
7 A resolution of the substructure "crisis"? The observed kinematics of all eleven of the Milky Way's satellites are consistent with them being embedded in one of the 15 most massive subhalos in the CDM Milky Way There is no contradiction but an excellent agreement! The potential wells of the less massive substructures are too shallow to harbour the observed satellites The outstanding question is why the formation of stars has been so inefficient in these substructure potentials e.g. Draco and Fornax have similar potentials but differ by a factor 60 in luminosity
8 High resolution simulations of subhalo stripping Hayashi et al 2002 Simulations of the tidal stripping of a single NFW subhalo with N ~ 100,000 falling into a rigid NFW Milky Way halo Note the steepening of the inner V c (r) curve
9 A resimulation with 10x better mass resolution Stoehr et al 2003 New simulation with N 200 = 10,089,396, = 240 pc, improved integration for all simulations
10 Satellite circular velocity curves Stoehr et al 2003 constant density main halo NFW Circular velocity curves for 11 of the 30 most massive subhalos in GA3n Only bound particles used The NFW and 'main halo' curves are scaled to the (r m,v m ) of largest subhalo All curves are narrower than NFW or 'main halo' Subhalo profiles approach a constant density core in the inner regions
11 Convergence test for subhalo structure 10 of the 14 most massive subhalos in GA3n can be matched to subhalos in GA2n Structural parameters of the circular velocity curves match well with no systematic trend despite 10 times better resolution log (V c /V max ) = a [log(r/r max )] 2 a values are much larger than the a = 0.17 found for the main halo in both GA2n and GA3n
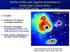
12 -rays from the annihilation of DM particles 270 kpc Stoehr et al 2003 Image of a 'Milky Way' halo in annihilation radiation Distributions of mass and of smooth and subhalo luminosity
13 -rays from the annihilation of DM particles Stoehr et al 2003 J = i m i i summed over all particles in a (sub)halo is L i Convergence of contributions to luminosity with increasing mass resolution in simulation
14 -rays from the annihilation of DM particles The annihilation luminosity is L 2 dv 2 r 2 dr for a spherical system the dominant contribution comes from regions where r -1.5 The simulated CDM Milky Way halo has half its luminosity coming from within 8.6 kpc of the centre The luminosity/mass of substructures is independent of mass extra luminosity comes from most massive substructures The total luminosity exceeds that of a smooth spherical halo with the same V circ (r) by: +25% due to substructure +15% due to flattening + 8% due to unbound substructure Annihilation radiation from R < R sun may be detectable with next generation -ray telescopes
15 Are galaxy halos scaled copies of clusters? Stoehr et al 2003 Moore et al 1999 M halo
16 Gao Liang et al 2003 Universal substructure mass functions? Scaling subhalo mass functions to the mass of the parent halo gives systematics with M halo Counting subhalos per unit parent halo mass without scaling gives much better agreement at low mass + a cut-off at high m sub /M halo
17 Mass fraction in substructure Gao Liang et al x x x x Most of subhalo mass is in the most massive subhalos More massive halos have a larger fraction of their mass in substructure Fraction of halo mass in subhalos less massive than ~ 2 x is the same in all the mass groups
18 Gao Liang et al 2003 The concentration-- substructure relation The concentration of a halo, as measured by V max /V 200, is anticorrelated with the fraction of its mass in substructure. This is true for both cluster and galaxy mass halos
19 Gao Liang et al 2003 Subhalo and halo mass functions The abundance of sub- halos per unit mass within collapsed halos is very similar to the abundance of halos per unit mass in the Universe as a whole, once a correction is made for the differing density at the edge
20 Gao Liang et al 2003 When are subhalos accreted? Most of the subhalos (and most of the mass in subhalos) first became a subhalo at late times 60% after z = % after z = 1.0
21 Gao Liang et al 2003 Mass loss vs Accretion time Subhalos which have lost little mass were accreted recently Subhalos retaining more than half their mass have z acc ~ 0.3 Subhalos retaining <0.1 of their mass have z acc ~ 0.9
22 Gao Liang et al 2003 Density profiles for subhalos The mean radial density profiles of subhalos are shallower than those of the mass in halos of all masses
23 Conclusions Satellite subhalos appear to have softer cores both than their progenitor halos and than isolated halos of similar mass The normalised halo mass function appears to be universal for m sub M halo (1/M halo ) dn(m sub )/dm sub After correction for the differing definitions of (sub)halo edge, this function is close to the Sheth-Tormen halo mass function The concentration of a halo is anticorrelated with the amount of substructure it contains Most z=0 subhalos first became subhalos at low redshift (z < 1) Subhalos with less mass loss were accreted at lower redshift The density profiles for subhalos are shallower than NFW
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals. Jorge Peñarrubia
 Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
Dark Matter Dominated Objects. Louie Strigari Stanford
 Dark Matter Dominated Objects Louie Strigari Stanford Milky Way Circa 2009 Satellite Year Discovered LMC 1519 SMC 1519 Sculptor 1937 Fornax 1938 Leo II 1950 Leo I 1950 Ursa Minor 1954 Draco 1954 Carina
Dark Matter Dominated Objects Louie Strigari Stanford Milky Way Circa 2009 Satellite Year Discovered LMC 1519 SMC 1519 Sculptor 1937 Fornax 1938 Leo II 1950 Leo I 1950 Ursa Minor 1954 Draco 1954 Carina
The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
high density low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) Springel (2010)
 GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos
 Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution
 Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution Simon White & Mark Vogelsberger Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Milky Way halo seen in DM annihilation radiation Aquarius simulation: N200
Ensenada March 2008 Galaxy halos at (very) high resolution Simon White & Mark Vogelsberger Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Milky Way halo seen in DM annihilation radiation Aquarius simulation: N200
The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model. Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik
 Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
UMa II and the Orphan Stream
 UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
Modelling the galaxy population
 Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11. Tidal Debris
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry
 Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry Louie Strigari UC Irvine Center for Cosmology Fermilab, 4.16.2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Juerg Diemand, Manoj Kaplinghat, Michael Kuhlen, Piero
Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry Louie Strigari UC Irvine Center for Cosmology Fermilab, 4.16.2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Juerg Diemand, Manoj Kaplinghat, Michael Kuhlen, Piero
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group
 Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
Galaxy population simulations
 Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context
 IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
IAU Symposium #254, Copenhagen June 2008 Simulations of disk galaxy formation in their cosmological context Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al
Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis. Matthias Steinmetz
 Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis Matthias Steinmetz Can we form disk galaxies? 3 Not really Formation of disks has been notoriously difficult Feedback? Resolution?
Modelling the Milky Way: challenges in scientific computing and data analysis Matthias Steinmetz Can we form disk galaxies? 3 Not really Formation of disks has been notoriously difficult Feedback? Resolution?
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 1999
 Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way
 Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies
 Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias. Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan
 Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan Galaxies are not necessarily test particles Probing dark energy with growth
Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan Galaxies are not necessarily test particles Probing dark energy with growth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM
 Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure
 Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
Galaxy interaction and transformation
 Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter
 Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection
 Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection Kavli Institue for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford,
Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection Kavli Institue for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford,
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix
 Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile,
 Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile, Italy Emmanuel Moulin CTA meeting, Zürich 2009 1 Core-energy
Emmanuel Moulin! on behalf of the CTA Consortium!!! Rencontres de Moriond 2013! Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe! March 9-16, La Thuile, Italy Emmanuel Moulin CTA meeting, Zürich 2009 1 Core-energy
Some like it warm. Andrea V. Macciò
 Some like it warm Andrea V. Macciò MPIA - Heidelberg D. Aderhalden, A. Schneider, B. Moore (Zurich), F. Fontanot (HITS), A. Dutton, J. Herpich, G. Stinson (MPIA), X. Kang (PMO) CDM problems, hence WDM
Some like it warm Andrea V. Macciò MPIA - Heidelberg D. Aderhalden, A. Schneider, B. Moore (Zurich), F. Fontanot (HITS), A. Dutton, J. Herpich, G. Stinson (MPIA), X. Kang (PMO) CDM problems, hence WDM
Visible Matter. References: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology - Par. 8.1 Liddle, Introduction to Modern Cosmology - Par. 9.1
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Koji Ichikawa. (In preparation) TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015
 Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015 Direct Detection Dark Matter Search
Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015 Direct Detection Dark Matter Search
Dark matter. Anne Green University of Nottingham
 Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster
 DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
DM Workshop@UT Austin May 7, 2012 Constraints on dark matter annihilation cross section with the Fornax cluster Shin ichiro Ando University of Amsterdam Ando & Nagai, arxiv:1201.0753 [astro-ph.he] Galaxy
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos
 Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
halo formation in peaks halo bias if halos are formed without regard to the underlying density, then δn h n h halo bias in simulations
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Statistics of flux ratios in strong lenses: probing of dark matter on small scales
 Statistics of flux ratios in strong lenses: probing of dark matter on small scales Daniel Gilman (UCLA) With: Simon Birrer, Tommaso Treu, Anna Nierenberg, Chuck Keeton, Andrew Benson image: ESA/Hubble,
Statistics of flux ratios in strong lenses: probing of dark matter on small scales Daniel Gilman (UCLA) With: Simon Birrer, Tommaso Treu, Anna Nierenberg, Chuck Keeton, Andrew Benson image: ESA/Hubble,
The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters
 The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters Phil Breen University of Edinburgh in collaboration with A. L. Varri, J. Peñarrubia and D. C. Heggie Current observational evidence Example:
The physical origin of stellar envelopes around globular clusters Phil Breen University of Edinburgh in collaboration with A. L. Varri, J. Peñarrubia and D. C. Heggie Current observational evidence Example:
Effects of baryons on the circular velocities of dwarf satellites
 Effects of baryons on the circular velocities of dwarf satellites Anatoly Klypin, Kenza Arraki, Surhud More NMSU, U. Chicago August 15, 2012; Santa Cruz Galaxy Workshop LCDM and dwarfs: love to hate Missing
Effects of baryons on the circular velocities of dwarf satellites Anatoly Klypin, Kenza Arraki, Surhud More NMSU, U. Chicago August 15, 2012; Santa Cruz Galaxy Workshop LCDM and dwarfs: love to hate Missing
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation
 Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
EARLY SUPERSYMMETRIC COLD DARK MATTER SUBSTRUCTURE
 ApJ in press Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 EARLY SUPERSYMMETRIC COLD DARK MATTER SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics,
ApJ in press Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 11/26/04 EARLY SUPERSYMMETRIC COLD DARK MATTER SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics,
Gamma-ray background anisotropy from Galactic dark matter substructure
 Gamma-ray background anisotropy from Galactic dark matter substructure Shin ichiro Ando (TAPIR, Caltech) Ando, arxiv:0903.4685 [astro-ph.co] 1. Introduction Dark matter annihilation and substructure Dark
Gamma-ray background anisotropy from Galactic dark matter substructure Shin ichiro Ando (TAPIR, Caltech) Ando, arxiv:0903.4685 [astro-ph.co] 1. Introduction Dark matter annihilation and substructure Dark
Koji Ichikawa. Prospects on the indirect dark matter detection and a future spectroscopic survey of dwarf spheroidal galaxies.
 Prospects on the indirect dark matter detection and a future spectroscopic survey of dwarf spheroidal galaxies Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N.
Prospects on the indirect dark matter detection and a future spectroscopic survey of dwarf spheroidal galaxies Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N.
Our Galaxy. Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust. Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye
 Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
A tool to test galaxy formation theories. Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12. The Problems with Satellite Galaxies
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 13 May 2008
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals
 Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals NGC 4636 & NGC 1399 Ylva Schuberth Tom Richtler, Michael Hilker, Boris Dirsch 1 July 2010 / Strasbourg Y. Schuberth (AIfA) Strasbourg 1 / 16 Outline 1 Globular
Dark Matter and/or MOND in Giant Ellipticals NGC 4636 & NGC 1399 Ylva Schuberth Tom Richtler, Michael Hilker, Boris Dirsch 1 July 2010 / Strasbourg Y. Schuberth (AIfA) Strasbourg 1 / 16 Outline 1 Globular
The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites. Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler
 The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler Introduction As seen earlier in this conference, the Bolshoi simulation + SHAM does
The Mass of the Milky Way from its Satellites Michael Busha KIPAC/Stanford Collaborators: Phil Marshall, Risa Wechsler Introduction As seen earlier in this conference, the Bolshoi simulation + SHAM does
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology
 The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures.
 CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals
 Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals Julien Lavalle Institute & Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Madrid Aut. Univ. & CSIC DESY Theory Astroparticle, Hamburg 16 V 2011
Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals Julien Lavalle Institute & Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Madrid Aut. Univ. & CSIC DESY Theory Astroparticle, Hamburg 16 V 2011
Theorem : Proof... Pavel Kroupa. Pavel Kroupa: AIfA, University of Bonn
 Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Theorem : dsph = TDG = LCDM Proof... Pavel Kroupa 1 Two Zwicky Conjectures of fundamental importance : 1. Zwicky (1937) galaxies are about 500 times heavier in the Coma galaxy cluster than judged from
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of. M87 as revealed by Planetary Nebulae. A.Longobardi M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard. Garching 2015, 26th Feb.
 The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching 2015, 26th Feb. Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation Formation
The kinematics of the extreme outer halo of A. M.Arnaboldi O.Gerhard Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik Garching 2015, 26th Feb. Outer regions of galaxies and structure formation Formation
Koji Ichikawa In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai.
 Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 PPP2015, Kyoto, Sep. 14-18, 2015 Koji Ichikawa (In preparation)
Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 PPP2015, Kyoto, Sep. 14-18, 2015 Koji Ichikawa (In preparation)
Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, 1237 1249 (2003) Dependence of the inner dark matter profile on the halo mass Massimo Ricotti Institute of Astronomy, Madingley Road, Cambridge CB3 0HA Accepted 2003 June
halo merger histories
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Dark matter from cosmological probes
 PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
Astro 242. The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu
 Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
Dark Matter Halos of M31. Joe Wolf
 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf Team Irvine: Louie Strigari, James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark
Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf Team Irvine: Louie Strigari, James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching
 Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics
 Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies
 The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies
 Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1
 The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
The inside-out Growth of the Stellar Mass Distribution in Galaxy Clusters since z 1 Remco van der Burg CEA Saclay, France A&A in press (ArXiv:1412.2137) Henk Hoekstra, Adam Muzzin, Cristóbal Sifón, Michael
James Bullock UC Irvine
 Can Feedback Solve Too Big to Fail Problem? James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Shea Garrison-Kimmel Mike Boylan-Kolchin Jose Oñorbe Jaspreet Lally Manoj Kaplinghat dsphs
Can Feedback Solve Too Big to Fail Problem? James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Shea Garrison-Kimmel Mike Boylan-Kolchin Jose Oñorbe Jaspreet Lally Manoj Kaplinghat dsphs
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Galaxy threshing and the origin of intracluster stellar objects arxiv:astro-ph/0310350v1 14 Oct 2003 Kenji
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
N-body Simulations. Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY
 N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
The HERMES project. Reconstructing Galaxy Formation. Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU. The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012
 The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
The HERMES project Reconstructing Galaxy Formation Ken Freeman RSAA, ANU The metallicity distribution in the Milky Way discs Bologna May 2012 HERMES is a new high-resolution fiber-fed multi-object spectrometer
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and old stellar populations
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 19 (2005) Printed 20 April 2006 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The distribution and kinematics of early high-σ peaks in present-day haloes: implications for rare objects and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
A.Klypin. Dark Matter Halos
 A.Klypin Dark Matter Halos 1 Major codes: GADET N-body Hydro Cooling/Heating/SF Metal enrichment Radiative transfer Multistepping/Multiple masses Springel, SDM White PKDGRAV - GASOLINE ART ENZO Quinn,
A.Klypin Dark Matter Halos 1 Major codes: GADET N-body Hydro Cooling/Heating/SF Metal enrichment Radiative transfer Multistepping/Multiple masses Springel, SDM White PKDGRAV - GASOLINE ART ENZO Quinn,
The Accretion History of the Milky Way
 The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
The Accretion History of the Milky Way Julio F. Navarro The Milky Way as seen by COBE Collaborators Mario Abadi Amina Helmi Matthias Steinmetz Ken Ken Freeman Andres Meza The Hierarchical Formation of
Reionization. High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function. Axion Dark Matter. Rosemary Wyse
 Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges
 Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph. Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others
 Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others Stellar kinematics in dwarfs Dwarfs most dark matter dominated
Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others Stellar kinematics in dwarfs Dwarfs most dark matter dominated
Feedback and Galaxy Formation
 Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Heating and Cooling in Galaxies and Clusters Garching August 2006 Feedback and Galaxy Formation Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Cluster assembly in ΛCDM Gao et al 2004 'Concordance'
Signal Model vs. Observed γ-ray Sky
 Signal Model vs. Observed γ-ray Sky Springel+, Nature (2008) Two main dark matter signal components: 1. galactocentric diffuse 2. small structures Observed sky modeled with bremsstrahlung π 0 decay up-scattered
Signal Model vs. Observed γ-ray Sky Springel+, Nature (2008) Two main dark matter signal components: 1. galactocentric diffuse 2. small structures Observed sky modeled with bremsstrahlung π 0 decay up-scattered
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
