Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
|
|
|
- Megan Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dark Matter Substructure and their associated Galaxies Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
2 Outline PART I: The Subhalo Mass Function (van den Bosch, Tormen & Giocoli, 2005) PART II: Statistical Properties of Satellite Galaxies PART II: Evidence for Galactic Conformity (Weinmann, van den Bosch, Yang & Mo, 2005)
3 Substructure: Why Bother? Satellite Galaxies: Dark matter subhaloes are thought to be associated with satellite galaxies Cosmology: Abundance of subhaloes is cosmology dependent, and may provide constraints on the power-spectrum on small scales Dark matter annihilation: Because of high phase-space densities, subhaloes are expected to be sites of pronounced gamma-ray emission from neutralino annihilations Gravitational Lensing: Substructure may explain flux-ratio anomalies Dynamics: Subhaloes are associated with interesting dynamical processes, such as dynamical friction, tidal stripping, and tidal heating Disk Formation: The presence of dark matter substructure may have important implications for formation and structure of disk galaxies (disk heating and onset of bar instabilities through impulsive encounters)
4 Part One: The Subhalo Mass Function
5 Part One: The Subhalo Mass Function or How & beat(s)
6 Simulations: Handy Tool or HandiCap? Because of complex, non-linear processes involved, the statistics and properties of subhaloes are typically investigated using N -body Simulations. Problems with Simulations Resolution: It took until before substructure appeared. Ghigna et al. (1998), Klypin et al. (1999), Moore et al. (1999) Identification: A plethora of subhalo finders is available, but they often yield conflicting results. See Kravtsov s talk Expensive: Many CPU cycles and students are required to produce (statistically relevant) results Advantages of Simulations All the relevant Physics is (in principle) included: Merger histories (progenitor masses & accretion times), orbital properties, dynamical friction, tidal stripping and heating, non-sphericity of haloes, subhalo-subhalo mergers Pretty Pictures: The Whoaaahh-that-looks-so-cooool-effect
7 Many CPU cycles later...self-similarity In terms of substructure, haloes of widely different masses look self-similar: subhalo mass function is universal Only cosmology dependence no mass dependence Missing Satellite Problem buf WDM CDM Problems: Ghao et al. (2004) finds weak trend for mass dependence Problems: Disagreement on subhalo mass function; 6% < f s < 100% Problems: Poor statistics because of heavy CPU requirements
8 Uncle SAM to the rescue Several studies used semi-analytical methods as alternative Zentner & Bullock 2003; Oguri & Lee 2004; Taylor & Babul 2004 Ingredients Merger trees (PS formalism) Orbit Integration (Spherical Haloes) Dynamical Friction (Chandrasekhar 1943) Tidal Stripping & Heating Many of these ingredients are poorly understood (difficult to model) Simulations provide little help because of resolution dependence Integration of individual orbits code is complicated & relatively slow Orbits do not adjust adiabatically to (violent) major mergers... Predictions for Subhalo Mass Function: Taylor & Babul do not discuss subhalo mass function Zentner & Bullock discuss cosmology- but not mass-dependence Oguri & Lee subhalo mass functions are self-similar
9 Solution: Less Physics Parent haloes have self-similar NFW potentials: c(m) is weak compared to scatter in P(c M) Orbital eccentricity distributions P(ε) independent of parent halo mass Consider the average orbit only; focus on average mass loss rate, averaged over all individual orbits, weighted by P(ε) This average mass loss rate is only a function of the mass ratio ψ = m/m 1 m dm dt = 1 τ ψζ The characteristic time τ is proportional to dynamical time t dyn 1/ ρ ( ) 1/2 ( ) 1 τ = τ(z) = τ vir (z) H(z) 0 vir (0) H 0 The two free parameters, τ 0 and ζ capture the physics of dynamical friction, tidal stripping, and tidal heating Calibrate τ 0 and ζ at a fixed parent mass using numerical simulations The only property that is dependent on parent mass is mass assembly history, which can be modelled with EPS formalism
10 Diagrammatica a c b t=t 1 2 Merging a b b a c Evolution = Merger trees from EPS formalism = ṁ = m τ ψζ t=t b a c = Subhalo Mass Function at t = t 2
11 The Pros and Cons of Simplicity Advantage Extremely fast Subhalo mass function of individual halo is a matter of seconds on modern wristwatch Parameter Space Allows detailed study of mass dependence, cosmology dependence, redshift dependence, and scatter Disadvantage No Phase-Space Info Because no individual orbits are followed, no predictions can be made regarding the spatial or kinematic distribution of subhaloes
12 A Matter of Tuning Data used for calibration: the subhalo mass function of massive clusters (M h 1 M ) from three independent N -body sources We tune τ 0 and ζ by reproducing these results. τ 0 = 0.13 Gyr and ζ = 0.36 buf dn/dψ ψ 1.9 mass budget dominated by most massive subhaloes, but only marginally so. Also, note the high mass cut-off (as expected)
13 SHMFs are NOT self-similar More massive haloes assemble later less time for mass loss to operate larger subhalo mass fraction. Our results accurately match the simulation results of Gao et al. (2004)
14 Haloes grow, Subhaloes shrink At higher redshifts, haloes have a larger subhalo mass fraction This is a reflection of the fact that the time-scale for subhalo mass loss, τ, is always smaller than the mass accretion time-scale on which new subhaloes are accreted
15 Halo-to-Halo Variance The Subhalo Mass Fraction Define: f s 1 ψ dn dψ dψ 10 4 and δ f f s f s f s buf Note that P(δ f ) is extremely skewed and broad. This scatter in f s owes entirely to scatter in the mass assembly histories. Scatter in P(ε), not modelled here, will only make true scatter larger To obtain an accurate, average subhalo mass function, one needs to average over many individual haloes Trends predicted are difficult to test with N -body simulations Constraining cosmology with flux-ratio anomalies is virtually impossible.
16 Origin of the Variance Scatter is virtually uncorrelated with the halo assembly time... but δ f is strongly correlated with the mass fraction that has been accreted in the last Gyr. buf Present-Day Subhaloes have been accreted fairly recently
17 Conclusions Part I As long as P(ε) does not significantly depend on halo mass, one expects the average mass loss rate of subhaloes to only depend on the instantaneous mass ratio ψ = m/m In this case the only mass dependence of the subhalo mass function originates from the mass dependence of the halo assembly histories The subhalo mass function is not self-similar or universal A halo of h 1 M has, on average, a suhalo mass fraction that is a factor 4 lower than a halo of h 1 M. Haloes of the same mass have a larger subhalo mass fraction at higher redshifts. Large halo-to-halo variance; correlated with mass fraction that has been accreted recently ( < 1Gyr). Present day subhaloes have been accreted recently All these results are in excellent agreement with the numerical simulations of Gao et al. (2004).
18 Part II: Galaxy Ecology Many studies have investigated the relation between various galaxy properties (morphology/sfr/colour) and environment (e.g., Oemler 1974; Dressler 1980; Postman & Geller 1984; Dominguez et al. 2002; Kauffmann et al. 2004; Balogh et al. 2004; Goto et al. 2003; Gomez et al. 2003; Hogg et al. 2004; Tanaka et al. 2004) Environment estimated using galaxy overdensity (projected) to nth nearest neighbour, Σ n or using fixed, metric aperture, Σ R. Fraction of early types increases with density There is a characteristic density ( group-scale) below which environment dependence vanishes Groups and Clusters also reveal radial dependence: late type fraction increases with radius No radial dependence in groups with M < h 1 M Danger: Physical meaning of Σ n and Σ R depends on environment. Physically more meaningful to investigate halo mass dependence of galaxy properties. This requires galaxy group catalogues. Important: Separate luminosity dependence from halo mass dependence.
19 Defining Galaxy Types Data from NYU-VAGC (Blanton et al. 2005): SSFRs from Kauffmann et al. (2003) and Brinchmann et al. (2004)
20 Halo Mass Dependence The fractions of early and late type galaxies depend strongly on halo mass. At fixed halo mass, there is virtually no luminosity dependence. The mass dependence is smooth: there is no characteristic mass scale; i.e., no indication that something special happens at the group or cluster scales. The intermediate type fraction is independent of luminosity and mass. (Weinmann, vdb, Yang & Mo, 2005)
21 Dependence on Group-centric Radius As noticed before, the late type fraction of satellites increases with radius. This trend is independent of halo mass! Inconsistent with previous studies, but these included central galaxies. Our results rule out group- and cluster-specific processes such as ram-pressure stripping and harassment: nature rather than nurture! (Weinmann, vdb, Yang & Mo, 2005)
22 Galactic Conformity Satellite galaxies adjust themselves to properties of their central galaxy: late type centrals have preferentially late type satellites, and vice versa. This has been noticed before, but only for small samples of loose groups (Wirth 1983; Ramella et al. 1987; Osmond & Ponmon 2004). Our results indicate that this Galactic Conformity is present over large ranges in luminosity and halo mass. (Weinmann, vdb, Yang & Mo, 2005)
23 Conclusions Part II Galaxy properties scale smoothly with halo mass. There is no indication for a specific transition at either group or cluster scale. Galaxy type (early vs. late) is determined by the mass of the halo in which the galaxy lives. Not by the mass (or luminosity) of the galaxy. Late type fractions increase with halo-centric radius, independent of halo mass. Satellite galaxies adjust their properties to those of their central galaxy: Galactic Conformity (Weinmann, vdb, Yang & Mo 2005)
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Aspen,
Galaxy Ecology. an Environmental Impact Assessment. Frank van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
Galaxy an Environmental Impact Assessment Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zürich) Anna Pasquali (MPIA), Daniel Aquino (MPIA) Heidelberg,
The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters
 The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters results from the SDSS Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More (MPIA), Marcello
The Galaxy Content of Groups and Clusters results from the SDSS Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Houjun Mo (UMass), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More (MPIA), Marcello
The Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection Constraining Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More
The Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection Constraining Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Frank van den Bosch (MPIA) in collaboration with Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO), Simone Weinmann (Zurich) Surhud More
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Galaxy Alignment. Misleading Myths, Miserable Mistakes & Mirky Mysteries. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA)
 Galaxy Alignment Misleading Myths, Miserable Mistakes & Mirky Mysteries Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Two Types of Alignment Alignment between orientations of neighbouring galaxies Important for weak lensing
Galaxy Alignment Misleading Myths, Miserable Mistakes & Mirky Mysteries Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Two Types of Alignment Alignment between orientations of neighbouring galaxies Important for weak lensing
Probing Dark Matter Halos with Satellite Kinematics & Weak Lensing
 Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters
 Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Satellite Galaxy Evolution in Groups & Clusters Andrew Wetzel Yale University Jeremy Tinker (NYU) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) Tinker, Wetzel & Conroy 2011, ArXiv 1107.5046 Wetzel, Tinker & Conroy 2011,
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
N-body Simulations. Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY
 N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
N-body Simulations N-body Simulations N-body Simulations Initial conditions: What kind of Dark Matter? How much Dark Matter? Initial density fluctuations P(k) GRAVITY Final distribution of dark matter.
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
halo formation in peaks halo bias if halos are formed without regard to the underlying density, then δn h n h halo bias in simulations
 Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
Physics 463, Spring 07 Bias, the Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Lecture 8 Halo Bias the matter distribution is highly clustered. halos form at the peaks of this distribution 3 2 1 0 halo formation
How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective
 How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective Anna Pasquali Astronomisches Rechen Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg NGC 4651 Why do we care? At
How environment shapes galaxy evolution: the satellite galaxies' perspective Anna Pasquali Astronomisches Rechen Institut, Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg NGC 4651 Why do we care? At
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies
 Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
Next Generation (Semi-)Empirical galaxy formation models - Matching individual galaxies Benjamin Moster (IoA/KICC)! Simon White, Thorsten Naab (MPA), Rachel Somerville (Rutgers), Frank van den Bosch (Yale),
high density low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) Springel (2010)
 GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
GAS MIXES high density Springel (2010) low density Rayleigh-Taylor Test: High density medium starts on top of low density medium and they mix (oil+vinegar) HOT HALO highest resolved density nth= 50x10
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More (MPIA) Kunming,
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
On the Assembly of Galaxies in Dark Matter Halos
 On the Assembly of Galaxies in Dark Matter Halos...new insights from halo occupation modeling... collaborators: Zhankhui Lu, Houjun Mo, Neal Katz, Martin Weinberg (UMass), Xiaohu Yang, Youcai Zhang, Jiaxin
On the Assembly of Galaxies in Dark Matter Halos...new insights from halo occupation modeling... collaborators: Zhankhui Lu, Houjun Mo, Neal Katz, Martin Weinberg (UMass), Xiaohu Yang, Youcai Zhang, Jiaxin
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation
 Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Origin of Bi-modality
 Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
Origin of Bi-modality and Downsizing Avishai Dekel HU Jerusalem Galaxies and Structures Through Cosmic Times Venice, March 2006 Summary Q: z
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology
 The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Milky Way and Near-Field Cosmology Kathryn V Johnston (Columbia University) Collaborators (theorists): James S Bullock (Irvine), Andreea Font (Durham), Brant Robertson (Chicago), Sanjib Sharma (Columbia),
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
A Self-Consistent, Dynamic Model for the Evolution of the Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection across Cosmic Time. Frank van den Bosch.
 A Self-Consistent, Dynamic Model for the Evolution of the Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection across Cosmic Time Frank van den Bosch Yale University In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (HU), Surhud More
A Self-Consistent, Dynamic Model for the Evolution of the Galaxy-Dark Matter Connection across Cosmic Time Frank van den Bosch Yale University In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (HU), Surhud More
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos
 Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
Gamma-rays from Earth-Size dark-matter halos Tomoaki Ishiyama, Jun Makino, Toshikazu Ebisuzaki, and Veniamin Berezinsky Presentation by: JM Bottom line Microhalos (mass earth mass) do survive to the present
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
Galaxy interaction and transformation
 Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
Galaxy interaction and transformation Houjun Mo April 13, 2004 A lot of mergers expected in hierarchical models. The main issues: The phenomena of galaxy interaction: tidal tails, mergers, starbursts When
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 15: Galaxy Interactions Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 Galaxy Interactions & Transformations In this lecture we discuss galaxy interactions
The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics COSMO11, Porto, August 2011 Mark Vogelsberger The fine-scale structure of dark
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: The Halo Model & Halo Occupation Statistics Frank van den Bosch Yale University, Fall 2018 The Halo Model & Occupation Statistics In this lecture we discuss
How much of their stellar mass have group galaxies lost to the ICL?
 GEPI How much of their stellar mass have group galaxies lost to the ICL? Édouard Tollet Andrea Cattaneo Gary Mamon 3 1,2 * 1 1 Observatoire de Paris - GEPI Université Paris Diderot 3 Institut d'astrophysique
GEPI How much of their stellar mass have group galaxies lost to the ICL? Édouard Tollet Andrea Cattaneo Gary Mamon 3 1,2 * 1 1 Observatoire de Paris - GEPI Université Paris Diderot 3 Institut d'astrophysique
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure of Dark Matter Haloes In this lecture we examine the detailed
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 11: Structure of Dark Matter Halos Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure of Dark Matter Haloes In this lecture we examine the detailed
the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications
 the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications R isa Wechsler with Peter Behroozi, Michael Busha, Rachel Reddick (KIPAC/Stanford) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) subhalo
the galaxy-halo connection from abundance matching: simplicity and complications R isa Wechsler with Peter Behroozi, Michael Busha, Rachel Reddick (KIPAC/Stanford) & Charlie Conroy (Harvard/CfA) subhalo
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes. Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz
 Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
Killing Dwarfs with Hot Pancakes Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) with Houjun Mo, Xiaohu Yang & Neal Katz The Paradigm... SN feedback AGN feedback The halo mass function is much steeper than luminosity function
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Dark Matter on Small Scales: Merging and Cosmogony. David W. Hogg New York University CCPP
 Dark Matter on Small Scales: Merging and Cosmogony David W. Hogg New York University CCPP summary galaxy merger rates suggest growth of ~1 percent per Gyr galaxy evolution is over can we rule out CDM now
Dark Matter on Small Scales: Merging and Cosmogony David W. Hogg New York University CCPP summary galaxy merger rates suggest growth of ~1 percent per Gyr galaxy evolution is over can we rule out CDM now
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
Black Hole Mergers at Galactic. The Final Parsec: Supermassive. Centers. Milos Milosavljevic. California Institute of Technology
 The Final Parsec: Supermassive Black Hole Mergers at Galactic Centers Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology MBH Binaries Form in Galaxy Mergers Borne et al 2000 by transferring binding
The Final Parsec: Supermassive Black Hole Mergers at Galactic Centers Milos Milosavljevic California Institute of Technology MBH Binaries Form in Galaxy Mergers Borne et al 2000 by transferring binding
Galaxy Cluster Mergers
 Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
Galaxy Cluster Mergers Alexia Schulz Institute for Advanced Study Andrew Wetzel Daniel Holz Mike Warren Talk Overview! Introduction " Why are cluster mergers of interest? " Where will mergers complicate
arxiv:astro-ph/ v3 13 May 2008
 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 0/09/06 FORMATION AND EOLUTION OF GALAXY DARK MATTER HALOS AND THEIR SUBSTRUCTURE Jürg Diemand,, Michael Kuhlen, & Piero Madau, arxiv:astro-ph/0707v May
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation
 Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
Numerical Cosmology & Galaxy Formation Lecture 13: Example simulations Isolated galaxies, mergers & zooms Benjamin Moster 1 Outline of the lecture course Lecture 1: Motivation & Historical Overview Lecture
THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
 GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
GALAXY FORMATION - Durham -18 July 2011 THE BOLSHOI COSMOLOGICAL SIMULATIONS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS JOEL PRIMACK, UCSC ΛCDM Cosmological Parameters for Bolshoi and BigBolshoi Halo Mass Function is 10x
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies
 ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
ASTR 610 Theory of Galaxy Formation Lecture 18: Disk Galaxies Frank van den Bosch Yale University, spring 2017 The Structure & Formation of Disk Galaxies In this lecture we discuss the structure and formation
Simulations and the Galaxy Halo Connection
 Simulations and the Galaxy Halo Connection Yao-Yuan Mao (Stanford/SLAC PITT PACC) @yaoyuanmao yymao.github.io SCMA6 @ CMU 6/10/16 My collaborators at Stanford/SLAC Joe DeRose Ben Lehmann ( UCSC) Vincent
Simulations and the Galaxy Halo Connection Yao-Yuan Mao (Stanford/SLAC PITT PACC) @yaoyuanmao yymao.github.io SCMA6 @ CMU 6/10/16 My collaborators at Stanford/SLAC Joe DeRose Ben Lehmann ( UCSC) Vincent
The Iguaçu Lectures. Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures
 April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
April 2006 The Iguaçu Lectures Nonlinear Structure Formation: The growth of galaxies and larger scale structures Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics z = 0 Dark Matter ROT EVOL Cluster structure
The Cosmological Angular Momentum Problem of Low-Mass. Disk Galaxies
 The Cosmological Angular Momentum Problem of Low-Mass Disk Galaxies Andreas Burkert Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany Received ; accepted 2 ABSTRACT The rotational
The Cosmological Angular Momentum Problem of Low-Mass Disk Galaxies Andreas Burkert Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany Received ; accepted 2 ABSTRACT The rotational
How can Mathematics Reveal Dark Matter?
 How can Mathematics Reveal? Chuck Keeton Rutgers University April 2, 2010 Evidence for dark matter galaxy dynamics clusters of galaxies (dynamics, X-rays) large-scale structure cosmography gravitational
How can Mathematics Reveal? Chuck Keeton Rutgers University April 2, 2010 Evidence for dark matter galaxy dynamics clusters of galaxies (dynamics, X-rays) large-scale structure cosmography gravitational
halo merger histories
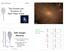 Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Physics 463, Spring 07 Lecture 5 The Growth and Structure of Dark Mater Halos z=7! z=3! z=1! expansion scalefactor z=0! ~milky way M>3e12M! /h c vir ~13 ~virgo cluster M>3e14M! /h, c vir ~6 halo merger
Dark Matter Detection Using Pulsar Timing
 Dark Matter Detection Using Pulsar Timing ABSTRACT An observation program for detecting and studying dark matter subhalos in our galaxy is propsed. The gravitational field of a massive object distorts
Dark Matter Detection Using Pulsar Timing ABSTRACT An observation program for detecting and studying dark matter subhalos in our galaxy is propsed. The gravitational field of a massive object distorts
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way
 The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way David Law James Bullock (UC Irvine) The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way Chris Purcell (Irvine U Pittsburgh) Erik Tollerud (Irvine)
The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way David Law James Bullock (UC Irvine) The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way Chris Purcell (Irvine U Pittsburgh) Erik Tollerud (Irvine)
The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data
 Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Venice, October 2003 The Formation of Galaxies: connecting theory to data Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The Emergence of the Cosmic Initial Conditions > 105 independent ~ 5 measurements
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix
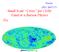 Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM
 Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
Cosmological Simulations: Successes & Tensions of ɅCDM Volker Springel Large scale predictions Small scale predictions Challenges for ɅCDM from non-linear structure formation PASCOS 2011 Conference Cambridge,
Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations-
 Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations- Sinziana Paduroiu University of Geneva / Observatoire de Geneve In memoriam Hector de Vega Chalonge Cosmology Colloquium
Structure Formation and Evolution in Warm Dark Matter Cosmologies -Numerical Simulations- Sinziana Paduroiu University of Geneva / Observatoire de Geneve In memoriam Hector de Vega Chalonge Cosmology Colloquium
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND
 Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure
 Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
Formation and evolution of CDM halos and their substructure 1) cold dark matter and structures on all scales 2) via lactea, z=0 results 3) subhalo evolution Jürg Diemand UC Santa Cruz 4) DM annihilation
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content
 Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Galaxies in dark matter halos: luminosity-velocity relation, abundance and baryon content arxiv:1005.1289 arxiv:1002.3660 S. Trujillo-Gomez (NMSU) in collaboration with: A. Klypin (NMSU), J. Primack (UCSC)
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters. Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009
 The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The theoretical view of high-z Clusters Nelson Padilla, PUC, Chile Pucón, November 2009 The Plan: 1) To see what the observations are telling us using models that agree with the cosmology, and with other
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises
 The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
The edge of darkness, and other halo surprises Benedikt Diemer ITC Fellow, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (in collaboration with Andrey Kravtsov and Surhud More) APEC Seminar IPMU 4/7/26 Strength
Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies
 Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies Anna Gallazzi INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Co#funded)by)the)) European)Union) with: Anna Pasquali (ARI-Heidelberg)
Element abundance ratios and star formation quenching: satellite versus central galaxies Anna Gallazzi INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Co#funded)by)the)) European)Union) with: Anna Pasquali (ARI-Heidelberg)
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies
 Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
Peculiar (Interacting) Galaxies Not all galaxies fall on the Hubble sequence: many are peculiar! In 1966, Arp created an Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies based on pictures from the Palomar Sky Survey. In 1982,
The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection
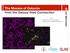 with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
with Charlie Conroy (Princeton) Peter Behroozi (KIPAC/Stanford) R isa Wechsler The Masses of Galaxies from the Galaxy-Halo Connection The Basic Idea Theory: We now have a reasonable accounting for the
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation?
 Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692, 298 * *Also described as a Research Highlight in Nature,
Morphological Composition of z~0.4 Groups: The site of S0 Formation? Dave Wilman Wilman, Oemler, Mulchaey, McGee, Balogh & Bower 2009, ApJ, 692, 298 * *Also described as a Research Highlight in Nature,
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation. Debora Sijacki
 Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
Feedback, AGN and galaxy formation Debora Sijacki Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture Planck data, 2013 (new results 2015) Formation of black hole seeds: the big picture CMB black body spectrum
Galaxy Evolution. Part 4. Jochen Liske Hamburger Sternwarte
 Galaxy Evolution Part 4 Jochen Liske Hamburger Sternwarte jochen.liske@uni-hamburg.de Astronomical picture of the week NGC 1275 Central galaxy of the Perseus cluster Active Source: APOD Astronomical picture
Galaxy Evolution Part 4 Jochen Liske Hamburger Sternwarte jochen.liske@uni-hamburg.de Astronomical picture of the week NGC 1275 Central galaxy of the Perseus cluster Active Source: APOD Astronomical picture
Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals
 Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals Julien Lavalle Institute & Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Madrid Aut. Univ. & CSIC DESY Theory Astroparticle, Hamburg 16 V 2011
Impact of substructures on predictions of dark matter annihilation signals Julien Lavalle Institute & Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Madrid Aut. Univ. & CSIC DESY Theory Astroparticle, Hamburg 16 V 2011
Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias
 Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias Angela Berti UC San Diego GalFRESCA 2018 1 Galactic Conformity Correlation between star formation rates (SFRs) of central galaxies and their satellites/neighbors
Two-halo Galactic Conformity as a Test of Assembly Bias Angela Berti UC San Diego GalFRESCA 2018 1 Galactic Conformity Correlation between star formation rates (SFRs) of central galaxies and their satellites/neighbors
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2017 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Jun 2017](/thumbs/96/129201251.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2015) Printed 30 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An observational proxy of halo assembly time and its correlation with galaxy properties arxiv:1502.01256v3 [astro-ph.ga]
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 13 (2015) Printed 30 July 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) An observational proxy of halo assembly time and its correlation with galaxy properties arxiv:1502.01256v3 [astro-ph.ga]
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations
 Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
Origin and Evolution of Disk Galaxy Scaling Relations Aaron A. Dutton (CITA National Fellow, University of Victoria) Collaborators: Frank C. van den Bosch (Utah), Avishai Dekel (HU Jerusalem), + DEEP2
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations
 The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS. Frank van den Bosch.
 Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
Cosmological Constraints from a Combined Analysis of Clustering & Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing in the SDSS In collaboration with: Marcello Cacciato (Leiden), Surhud More (IPMU), Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang
Structure of Dark Matter Halos
 Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Structure of Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos profiles: DM only: NFW vs. Einasto Halo concentration: evolution with time Dark matter halos profiles: Effects of baryons Adiabatic contraction Cusps and
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11. Tidal Debris
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 11 Tidal Debris Goals (1) We ll explore whether we can trace the accretion events that should have formed the Milky Way. (2) We ll discuss the impact of tidal debris on direct detection
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics
 Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
Clusters and groups of galaxies: internal structure and dynamics Strong constraints on cosmological theories and on the nature of dark matter can be obtained from the study of cluster masses, mass distribution,
Moore et al Kenney et al. 2004
 Moore et al. 1996 Kenney et al. 2004 (i) Interaction with other cluster members and/or with the cluster potential (ii) Interactions with the hot gas that permeates massive galaxy systems. The influence
Moore et al. 1996 Kenney et al. 2004 (i) Interaction with other cluster members and/or with the cluster potential (ii) Interactions with the hot gas that permeates massive galaxy systems. The influence
CHAPTER 20. Collisions & Encounters of Collisionless Systems
 CHAPTER 20 Collisions & Encounters of Collisionless Systems Consider an encounter between two collisionless N-body systems (i.e., dark matter halos or galaxies): a perturber P and a system S. Let q denote
CHAPTER 20 Collisions & Encounters of Collisionless Systems Consider an encounter between two collisionless N-body systems (i.e., dark matter halos or galaxies): a perturber P and a system S. Let q denote
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites. Jacqueline Chen
 The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory
 The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory Christopher J. Conselice (University of Nottingham) Kuala Lumpur 2009 How/when do galaxies form/evolve? Some questions a. Do galaxies evolve
The Merger History of Massive Galaxies: Observations and Theory Christopher J. Conselice (University of Nottingham) Kuala Lumpur 2009 How/when do galaxies form/evolve? Some questions a. Do galaxies evolve
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 3 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Shapes of halo equidensity surfaces Group Jing & Suto 2002 Galaxy δ 100 2500 6250 Shapes of halo
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 February 2008 (MN LATEX style file v1.4) The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes L. Gao, 1 S. D. M. White 1, A. Jenkins 2, F. Stoehr 3, V. Springel
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Nov 1999
 Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Where are the First Stars now? Simon D.M. White & Volker Springel Max-Planck-Institute for Astrophysics, Garching bei München, Germany arxiv:astro-ph/9911378v1 19 Nov 1999 Abstract. We use high-resolution
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12. The Problems with Satellite Galaxies
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Luminosity function and radial distribution of Milky Way satellites in a CDM Universe
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 1995 2008 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16031.x Luminosity function and radial distribution of Milky Way satellites in a CDM Universe Andrea V. Macciò, 1 Xi Kang, 1
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 1995 2008 (2010) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16031.x Luminosity function and radial distribution of Milky Way satellites in a CDM Universe Andrea V. Macciò, 1 Xi Kang, 1
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies
 The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
The galaxy population in cold and warm dark matter cosmologies Lan Wang National Astronomical Observatories, CAS Collaborators: Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Lizhi Xie, Andrew Cooper, Carlos Frenk, Liang Gao,
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
AST541 Lecture Notes: Galaxy Formation Dec, 2016
 AST541 Lecture Notes: Galaxy Formation Dec, 2016 GalaxyFormation 1 The final topic is galaxy evolution. This is where galaxy meets cosmology. I will argue that while galaxy formation have to be understood
AST541 Lecture Notes: Galaxy Formation Dec, 2016 GalaxyFormation 1 The final topic is galaxy evolution. This is where galaxy meets cosmology. I will argue that while galaxy formation have to be understood
Galaxy Formation: Overview
 Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
Galaxy Formation: Overview Houjun Mo March 30, 2004 The basic picture Formation of dark matter halos. Gas cooling in dark matter halos Star formation in cold gas Evolution of the stellar populaion Metal
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 26 Mar 2014](/thumbs/88/115103634.jpg) Accepted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECTS OF VARYING COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON HALO SUBSTRUCTURE Gregory A. Dooley 1, Brendan F. Griffen 1, Phillip Zukin 2,3,
Accepted to ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE EFFECTS OF VARYING COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETERS ON HALO SUBSTRUCTURE Gregory A. Dooley 1, Brendan F. Griffen 1, Phillip Zukin 2,3,
Dark Matter Halos. They will have a large impact on galaxies
 Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos form through gravitational instability. Density perturbations grow linearly until they reach a critical density, after which they turn around from the expansion of the
Dark Matter Halos Dark matter halos form through gravitational instability. Density perturbations grow linearly until they reach a critical density, after which they turn around from the expansion of the
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies
 Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
Simulating non-linear structure formation in dark energy cosmologies Volker Springel Distribution of WIMPS in the Galaxy Early Dark Energy Models (Margherita Grossi) Coupled Dark Energy (Marco Baldi) Fifth
