Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies
|
|
|
- Barnaby Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 Dark Matter in Disk Galaxies Rotation curves of disk galaxies rise steeply in their inner regions and then remain roughly flat out to the last point measured. To explain these observations within the framework of Newtonian gravity, a considerable amount of unseen mass is required. The idea that unseen matter is needed to account for the rotation velocities of disk galaxies was put forward by Freeman (1970): [T]here must be undetected matter beyond the optical extent of NGC 300; its mass must be at least of the same order as the mass of the detected galaxy. This idea was instantly controversial; many wondered if dark matter on galactic scales is unavoidable. Kalnajis (1983) showed that within the radii accessible to optical spectroscopy, the rotation curves of disk galaxies could be well-fit without any dark matter. Indeed, a truncated exponential disk and a de Vaucouleurs bulge can be combined to yield a rotation curve which is flat to about 10% out to four times the disk s exponential scale length h (van Albada et al. 1985). Thus neutralhydrogen (HI) observations like Freeman s, extending well beyond the optical radii of galaxies, were required to establish the presence of dark matter Rotation Curves While optical spectroscopy couldn t prove that dark halos exist, rotation curves measured using optical emission lines were important in posing the problem of dark matter in disk galaxies. Results of optical studies are reviewed by Rubin (1983). These show that most disk galaxies have rotation curves which rise at small radii and then level off. For galaxies of a given morphological type (e.g. Sc) the shape of the rotation curve shows a systematic trend with luminosity: low-luminosity galaxies show a fairly gradual rise, while in high-luminosity galaxies the rotation curve rises sharply and then levels off or even drops slightly NGC 3198 Radio-synthesis velocity maps of neutral hydrogen emission provide the most convincing evidence for dark matter (e.g. Carignan & Freeman 1985). In NGC 3198 the rotation curve has been measured to 11h, or about 31kpc (van Albada et al. 1985). Over such radii most galactic disks are slightly warped, and NGC 3198 is no exception. The warped disk is modeled as a set of concentric circular 91
2 92 CHAPTER 14. DARK MATTER IN DISK GALAXIES rings with inclinations varying fairly smoothly from 72 at the center to 76 at the edge. The fitted circular velocity of each ring, plotted against its radius, defines the rotation curve. After rising fairly slowly to a peak value of 157km/sec at about 3h, the rotation curve does not fall significantly below 150km/sec out to the last point measured. The rotation curve of NGC 3198 can be modeled by combining the gravitational forces of a thin exponential disk, and a dark halo with a core and power-law envelope. The disk has the usual surface-density profile,!(r) =! 0 exp( R/h), (14.1) where! 0 is the central surface density and h is the disk scale length. For such a mass distribution the circular speed in the plane of the disk is v 2 d (R) = 4"G! 0hy 2 (I 0 (y)k 0 (y) I 1 (y)k 1 (y)), (14.2) where y R/(2h), and I n (y) and K n (y) are modified Bessel functions of the first and second kinds (BT87, Ch (b)). The halo is assigned the space density profile # h (r) = # (r/a) $, (14.3) where r is the spherical radius, a sets the halo length scale, and $ is the asymptotic slope of the profile at large r. The core radius of the halo, defined by # h (r core ) = # 0 /2 3/2 (roughly, the 3-D equivalent of the half central surface density definition used observationally) is Since the halo is assumed to be spherical the circular speed is r core = a(2 3/2 1) (1/$). (14.4) v 2 h (r) = GM h(r) r = G 4" r drr 2 # h (r). (14.5) The rotation curve in the plane of the disk is found by adding the disk and halo contributions in quadrature: v c (R) = (v 2 d(r) + v 2 h(r)) 1/2. (14.6) Assuming that the observed disk has a constant M/L ratio, surface photometry gives a disk scale length of h = 2.68kpc. Good fits to the observed rotation curve can be obtained for a wide range of model parameters; even more so than in fitting luminosity profiles, the problem of modeling galactic rotation curves is severely underconstrained. The model with the maximum disk mass has a disk mass-to-light ratio of M/L B = 3.6, consistent with a disk-type stellar population. But even this choice does not nail down the halo model; the slope and scale parameters may be varied in a correlated fashion over the range 1.9 < $ < 2.9 and 7 < a < 12kpc. The halo core radius is somewhat better determined, with subjective 1-sigma limits of r core = (12.5±1.5)kpc. Within the last point measured at 30kpc the total disk mass is M and the total halo mass is about 4 times greater. The detected neutral hydrogen amounts to M, or about 15% of the maximum disk mass (van Albada et al. 1985).
3 14.2. HALO SHAPES DDO 154 & other dwarf disk galaxies Uncertainties in mass-to-light ratios make luminous disk galaxies problematic for detailed studies of halo structure. In dwarf disk galaxies, however, the mass in stars is relatively small, and more definitive results can be obtained. The dwarf irregular galaxy DDO 154 is a striking example of a gas-rich dwarf. While its optical morphology is somewhat irregular, HI observations reveal a regular disk extending to 15h. At an adopted distance of 4Mpc, DDO 154 has absolute magnitude M B = 13.8, typical of a dwarf galaxy. The HI flux implies a total mass in neutral hydrogen of M HI M. This completely overshadows the mass in stars, estimated at M M for a mass-to-light ratio of M/L B 1. Neither component comes close to explaining the inclination-corrected rotation curve, which rises to a gentle maximum of 45km/s at a radius of 5.5kpc; the total mass of M tot M within a radius of 7.6kpc must be almost entirely dark. The rather well-determined dark matter distribution in galaxies like DDO 154 allows a comparison with the predicted halo profiles in a Cold Dark Matter (CDM) cosmology (Blumenthal et al. 1984). High-resolution simulations of gravitational clustering by CDM predict that halos should have cuspy central density profiles; a standard fitting function has the form #(r) = # 0 (r/r s ) % (1 + r/r s ) (3 %) (14.7) where r s is a scale radius and the inner slope % = 1 (Navarro, Frenk, & White 1996; hereafter NFW); this profile completely fails to fit the rotation curve of DDO 154 (e.g. Burkert & Silk 1997). Indeed, early studies consistently indicated that rotation curves of dwarf and low-surface-brightness galaxies are better fit by halo models with constant-density cores than by models with central cusps (e.g. Moore 1994; Burkert 1995,...). More recent studies have modified but not entirely reversed this conclusion. To accuratly probe the central density profiles requires velocity observations with high spatial resolution (van den Bosch et al. 2000), since smearing due to finite beam size would obliterate the kinematic signature of a steep central cusp. Both H $ and CO observations are now being used to obtain higher spatial and spectral resolution (e.g. Simon et al. 2005). The result is that no single profile fits all dwarf galaxies; a minority do indeed fit the standard NFW profile with % 1, but other fits favor much shallower cusps or even constant-density cores Halo Shapes Rotation curves imply the presence of significant amounts of dark matter but provide little constraint on the shape of the dark matter distribution. A highly flattened and dynamically cold dark matter distribution would run afoul of the same stability problem afflicting bare disk galaxies, but few other a priori constraints are available. Gas orbits in the disk plane provide some information about halo shapes. The gas settles onto closed, non-intersecting orbits. In an axisymmetric potential such orbits will be circular, but a nonaxisymmetric halo will force the gas onto non-circular orbits. Non-axisymmetric halos may cause oval distortions in some disk galaxies (Kormendy 1982) and kinematic asymmetries in HI maps (e.g. MB87, Fig. 8-31). Asymmetries in the Milky Way s HI kinematics have been attributed to a rotating
4 94 CHAPTER 14. DARK MATTER IN DISK GALAXIES triaxial halo (Blitz & Spergel 1991). But non-axisymmetric halos will also increase the scatter in the Tully & Fisher (1977) relationship between luminosity and circular velocity; by comparing the observed and predicted scatter, Franx & de Zeeuw (1992) conclude that the potentials of typical disk galaxies can be no flatter than about 0.9 : 1 in the disk plane. Stronger limits are available in special cases; for example, the potential of the E/S0 galaxy IC 2006 is axisymmetric to better than 0.98 : 1 (Franx, van Gorkom, & de Zeeuw 1994) NGC 4650A The three-dimensional shape of a disk galaxy s potential can only be inferred from tracers which travel far from the plane of the disk. Polar-ring galaxies are therefore important for discussions of halo shapes; these are S0 galaxies with rings or disks of gas and stars in polar orbits. Such rings probably form via mergers or mass transfers (Schweizer, Whitmore, & Rubin 1983). Early studies established that the central objects resemble S0 galaxies seen roughly edge-on; in particular, these objects exhibit the rapid rotation characteristic of S0 disks. Observed rotation velocities in the disk plane and in the ring plane are comparable. Simple models in which the potential is halo-dominated and both the disk and ring rotate at the local circular velocity then imply that the dark halos of these systems are nearly spherical (Whitmore, McElroy, & Schweizer 1987). However, more sophisticated models including the gravitational potentials of the central galaxy and polar ring and the effects of random motions in the S0 disk appear to rule out a spherical halo for the polar-ring galaxy NGC 4650A. These models assign the ring a mass significantly greater than the observed HI mass (Sackett & Sparke 1990); presumably the stellar component of the ring accounts for the difference, though the blue colors of this population (Whitmore et al. 1987) imply a relatively low mass-to-light ratio. Best-fit halo models have minor axis ratios between 0.3 : 1 and 0.4 : 1 (Sackett et al. 1994). This is comparable to the axial ratio of the central S0; in this case the dark matter appears to be as strongly flattened as the luminosity! 14.3 Is There a Disk-Halo Conspiracy? Besides the apparent coincidence of shapes just mentioned, yet another coincidence demands explanation: Bahcall & Casertano (1985) argue that at least one parameter of a two-component mass model must be finely tuned in order to reproduce the observed flatness of... rotation curve[s]. At small radii, the rotation velocities of disk galaxies are set by the luminous components, while at large radii they are set by the dark matter. It appears that these two components must conspire to produce rotation curves which remain flat to many times the disk scale length, h (van Albada & Scancisi 1986). Recent studies have somewhat blunted the teeth of this conspiracy. For one thing, rotation curves are not invariably flat; low-luminosity disk galaxies exhibit gently rising rotation curves, while highluminosity disk galaxies have rotation curves which peak at about 2h and gently decline further out (Ruben et al. 1985, Casertano & van Gorkom 1991). Moreover, at least part of the proposed conspiracy may be explained by the dynamical response of a pre-existing dark halo as a disk slowly grows inside it (Blumenthal et al. 1986, Barnes 1987, Athanassoula 1988, Ryden 1991). But the shapes of halos may provide fresh evidence for conspiracy theorists. Numerical simula-
5 14.4. CONCLUSIONS 95 tions of clustering in a universe full of CDM generally yield strongly triaxial halos. Highly flattened yet axisymmetric halos might be easier to explain if dark matter is baryonic and dissipative (e.g. Pfenniger, Combes, & Martinet 1994) Conclusions The evidence indicates that dark halos are many times more massive than visible galaxies, that the dark matter is much more extended than the luminous component, that dark halos often have relatively large core radii, and that halos are somewhat flattened (e.g. Trimble 1987, Ashman 1992). The dark halo hypothesis for flat rotation curves would be in trouble if the gas was the only tracer providing evidence for massive halos. But there is ample evidence for massive halos from other observations (BT87, Ch. 10). In the Milky Way, maximum stellar velocities in the solar neighborhood imply that our galaxy has a potential well deeper than the visible matter alone can generate; velocities of globular clusters and satellite galaxies do not show the fall-off with radius expected in a Keplerian potential, and the tidal forces required to explain the truncations of these systems and the tearing-off of the Magellanic Stream likewise demand more mass than is seen in stars and gas. The present motion of the Milky Way and M31 toward each other implies a total mass at least ten times the luminous mass of these galaxies, and the orbits of binary galaxies seem to be inconsistent with Keplerian potentials. Finally, not only gas and stars but even light seems to respond to the gravitational field of the dark matter in galaxy halos; distortions of background galaxies may be attributed to weak gravitational lensing by halos extending to at least 100kpc (Brainerd, Blandford, & Smail 1996). More problematic is the relationship between the halos detected in real galaxies and those predicted in a CDM-dominated universe. A general mechanism capable of disrupting the steep central cusps produced in gravitational clustering experiments is needed. Moreover, the scant information on axial ratios of halos does not seem that consistent with the predictions of CDM simulations. Despite the successes of CDM in describing structure on larger scales, an outside possibility remains that a good part of the dark matter associated with individual galaxies is composed of baryons.
6 96 CHAPTER 14. DARK MATTER IN DISK GALAXIES
Rotation curves of spiral galaxies
 Rotation curves of spiral galaxies Rotation curves Mass discrepancy Circular velocity of spherical systems and disks Dark matter halos Inner and outer regions Tully-Fisher relation From datacubes to rotation
Rotation curves of spiral galaxies Rotation curves Mass discrepancy Circular velocity of spherical systems and disks Dark matter halos Inner and outer regions Tully-Fisher relation From datacubes to rotation
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Nov 2003
 **TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** The visible matter dark matter coupling arxiv:astro-ph/0311348v1 14 Nov 2003 Renzo Sancisi Osservatorio Astronomico,
**TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME***, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** The visible matter dark matter coupling arxiv:astro-ph/0311348v1 14 Nov 2003 Renzo Sancisi Osservatorio Astronomico,
Visible Matter. References: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology - Par. 8.1 Liddle, Introduction to Modern Cosmology - Par. 9.1
 COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
COSMOLOGY PHYS 30392 DENSITY OF THE UNIVERSE Part I Giampaolo Pisano - Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics The University of Manchester - March 2013 http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~gp/ giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk
Scaling Relations of late-type galaxies
 Scaling Relations of late-type galaxies - an observational perspective - Lecture I Lecture II Trends along the Hubble sequence Galaxy rotation curves Lecture III Tully-Fisher relations Marc Verheijen Kapteyn
Scaling Relations of late-type galaxies - an observational perspective - Lecture I Lecture II Trends along the Hubble sequence Galaxy rotation curves Lecture III Tully-Fisher relations Marc Verheijen Kapteyn
Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies
 Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies Se-Heon Oh (ICRAR/UWA) Content cusp/core controversy in ΛCDM simulations Dark matter distribution of THINGS dwarf galaxies High-resolution N-body+SPH
Central dark matter distribution in dwarf galaxies Se-Heon Oh (ICRAR/UWA) Content cusp/core controversy in ΛCDM simulations Dark matter distribution of THINGS dwarf galaxies High-resolution N-body+SPH
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 20 Nov 1996
 PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 48,?? (2018) Mass of the Galaxy Inferred from Outer Rotation Curve Mareki Honma and Yoshiaki Sofue Institute of Astronomy, University of Tokyo, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo,
PASJ: Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 48,?? (2018) Mass of the Galaxy Inferred from Outer Rotation Curve Mareki Honma and Yoshiaki Sofue Institute of Astronomy, University of Tokyo, 2-21-1 Osawa, Mitaka, Tokyo,
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Polar Ring Galaxies FINDING THE DARK HALO SHAPE BY CAROLINE VAN BORM
 Polar Ring Galaxies FINDING THE DARK HALO SHAPE BY CAROLINE VAN BORM Papers (1) Polar ring galaxies and the Tully-Fisher relation: Implications for the dark halo shape Iodice, E.; Arnaboldi, M.; Bournaud,
Polar Ring Galaxies FINDING THE DARK HALO SHAPE BY CAROLINE VAN BORM Papers (1) Polar ring galaxies and the Tully-Fisher relation: Implications for the dark halo shape Iodice, E.; Arnaboldi, M.; Bournaud,
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 5. SPIRAL GALAXIES
 Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
Whittle : EXTRAGALACTIC ASTRONOMY 1 : Preliminaries 6 : Dynamics I 11 : Star Formation 16 : Cosmology : Morphology 7 : Ellipticals 1 : Interactions 17 : Structure Growth 3 : Surveys 8 : Dynamics II 13
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology. Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology
 Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
Hubble Sequence Qualitative description of galaxy morphology Surface Photometry Quantitative description of galaxy morphology Galaxy structure contains clues about galaxy formation and evolution Point
3 The lives of galaxies
 Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 24 3 The lives of galaxies In this section, we look at how galaxies formed and evolved, and likewise how the large scale pattern of galaxies formed. But before
Discovering Astronomy : Galaxies and Cosmology 24 3 The lives of galaxies In this section, we look at how galaxies formed and evolved, and likewise how the large scale pattern of galaxies formed. But before
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution. for several Spiral Galaxies. Abstract
 Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies
 Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Surface Brightness of Spiral Galaxies M104: SA N4535: SAB LMC: dwarf irregular,barred Normal 1/4-law+exp fits An example of surface brightness profile. The top curve is the sum of exp disk+1/4-bulge. The
Upcoming class schedule
 Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
Upcoming class schedule Thursday March 15 2pm AGN evolution (Amy Barger) th Monday March 19 Project Presentation (Brad) nd Thursday March 22 postponed to make up after spring break.. Spring break March
The cosmic distance scale
 The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
The cosmic distance scale Distance information is often crucial to understand the physics of astrophysical objects. This requires knowing the basic properties of such an object, like its size, its environment,
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E )
 Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) and the Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-558) Alan G. Aversa ABSTRACT Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) is a theory that modifies Newton s force law to explain observations that
5.1 Circular Velocities and Rotation Curves
 Chapter 5 otation Curves 5.1 Circular Velocities and otation Curves The circular velocity v circ is the velocity that a star in a galaxy must have to maintain a circular orbit at a specified distance from
Chapter 5 otation Curves 5.1 Circular Velocities and otation Curves The circular velocity v circ is the velocity that a star in a galaxy must have to maintain a circular orbit at a specified distance from
Structure formation in the concordance cosmology
 Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Structure formation in the Universe, Chamonix, May 2007 Structure formation in the concordance cosmology Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team WMAP3 team In
Probing Galaxy Halos with Tidal Interactions. Kyoto University Astronomy Department June 27, 2013
 Probing Galaxy Halos with Tidal Interactions Kyoto University Astronomy Department June 27, 2013 Galaxy Formation Baryons cool & collapse in dark halo potentials. White & Rees 78 Galaxy Formation Baryons
Probing Galaxy Halos with Tidal Interactions Kyoto University Astronomy Department June 27, 2013 Galaxy Formation Baryons cool & collapse in dark halo potentials. White & Rees 78 Galaxy Formation Baryons
AST1100 Lecture Notes
 AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
AST1100 Lecture Notes 4 Stellar orbits and dark matter 1 Using Kepler s laws for stars orbiting the center of a galaxy We will now use Kepler s laws of gravitation on much larger scales. We will study
1924: Hubble classification scheme 1925: Hubble measures Cepheids (Period-Luminosity) in Andromeda case closed
 Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Galaxies 1920 - Curtis-Shapley debate on nature of spiral nebulae - distribution in the sky: zone of avoidance Curtis: extinction Shapley:? - apparent brightness of stars(?) observed in some nebulae Shapley:
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution. for several Spiral Galaxies. Abstract
 Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Estimates of the Enclosed Mass and its Distribution for several Spiral Galaxies Geoffrey M. Williams email: gmwill@charter.net Abstract Recently, high quality rotation curves for several spiral galaxies
Survey of Astrophysics A110
 Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Goals: Galaxies To determine the types and distributions of galaxies? How do we measure the mass of galaxies and what comprises this mass? How do we measure distances to galaxies and what does this tell
Major Review: A very dense article" Dawes Review 4: Spiral Structures in Disc Galaxies; C. Dobbs and J Baba arxiv "
 The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
The Los Cabos Lectures
 January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
January 2009 The Los Cabos Lectures Dark Matter Halos: 2 Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics EPS statistics for the standard ΛCDM cosmology Millennium Simulation cosmology: Ωm = 0.25, ΩΛ
Se-Heon Oh. Se-Heon Oh
 High-resolution mass models of rotation curves & LITTLE THINGS 1,2 1. International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) The University of Western Australia 2. ARC Centre for All-sky Astrophysics
High-resolution mass models of rotation curves & LITTLE THINGS 1,2 1. International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) The University of Western Australia 2. ARC Centre for All-sky Astrophysics
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies
 II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
II. Morphology and Structure of Dwarf Galaxies Ferguson & Binggeli 1994, A&ARev 6, 67 1 1. Properties low mass : 10 6 10 10 M slow rotators : 10 100 km s -1 low luminosity : 10 6 10 10 L low surface brightness
Everything in baryons?
 Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Everything in baryons? Benoit Famaey (ULB) Rencontres de Blois 2007 General Relativity -> Dark Matter R αβ - 1/2 R g αβ + Λg αβ = (8πG/c 4 ) T αβ very precisely tested on solar system scales (but Pioneer)
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Clicker Question: Galaxy Classification. What type of galaxy do we live in? The Variety of Galaxy Morphologies Another barred galaxy
 Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Galaxies Galaxies First spiral nebula found in 1845 by the Earl of Rosse. Speculated it was beyond our Galaxy. 1920 - "Great Debate" between Shapley and Curtis on whether spiral nebulae were galaxies beyond
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Does Dark Matter Exist? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 30, 2007 Questions I ll be addressing Does dark matter exist? Where do we know it does not exist? How
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Does Dark Matter Exist? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 30, 2007 Questions I ll be addressing Does dark matter exist? Where do we know it does not exist? How
The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds.
 The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds. Image taken from the European Southern Observatory in Chile
The Milky Way, Hubble Law, the expansion of the Universe and Dark Matter Chapter 14 and 15 The Milky Way Galaxy and the two Magellanic Clouds. Image taken from the European Southern Observatory in Chile
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
This week at Astro Lecture 06, Sep 13, Pick up PE#6. Please turn in HW#2. HW#3 is posted
 This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
This week at Astro 3303 Lecture 06, Sep 13, 2017 Pick up PE#6 Please turn in HW#2 HW#3 is posted Today: Introduction to galaxy photometry Quantitative morphology Elliptical galaxies Reading: Continue reading
GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER
 GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER Isaac Shlosman Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Kentucky at Lexington, USA and Theoretical Astrophysics Osaka University, Japan The goal: Explain
GALACTIC DYNAMICS AND INTERSTELLAR MATTER Isaac Shlosman Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Kentucky at Lexington, USA and Theoretical Astrophysics Osaka University, Japan The goal: Explain
There are three main ways to derive q 0 :
 Measuring q 0 Measuring the deceleration parameter, q 0, is much more difficult than measuring H 0. In order to measure the Hubble Constant, one needs to derive distances to objects at 100 Mpc; this corresponds
Measuring q 0 Measuring the deceleration parameter, q 0, is much more difficult than measuring H 0. In order to measure the Hubble Constant, one needs to derive distances to objects at 100 Mpc; this corresponds
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review. Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory
 MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
MOdified Newtonian Dynamics an introductory review By Riccardo Scarpa European Southern Observatory Everything started in 1933 with the work by Zwicky on the Coma cluster of galaxies, but were galaxy rotation
Laws of Galactic Rotation. Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University
 Laws of Galactic Rotation Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University UGC 2885 Galaxies NGC 2403 Huge dynamic range in 10 kpc Gravitationally self-bound entities composed of stars, gas, dust, [& dark
Laws of Galactic Rotation Stacy McGaugh Case Western Reserve University UGC 2885 Galaxies NGC 2403 Huge dynamic range in 10 kpc Gravitationally self-bound entities composed of stars, gas, dust, [& dark
Spheroidal (Elliptical) Galaxies MBW chap 13, S+G ch 6!
 " The project: Due May 2!! I expect ~10 pages double spaced (250 words/page) with references from material you used (I do not expect 'densely' cited but a sufficient number).! It must be in a subject related
" The project: Due May 2!! I expect ~10 pages double spaced (250 words/page) with references from material you used (I do not expect 'densely' cited but a sufficient number).! It must be in a subject related
Chapter 19 Galaxies. Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past. halo
 Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
Chapter 19 Galaxies Hubble Ultra Deep Field: Each dot is a galaxy of stars. More distant, further into the past halo disk bulge Barred Spiral Galaxy: Has a bar of stars across the bulge Spiral Galaxy 1
DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE. edited by. John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA. Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel
 DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE n d edited by John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel Steven Weinberg University of Texas, Austin, USA TECHNiSCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK
DARK MATTER IN UNIVERSE n d edited by John Bahcall Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, USA Tsvi Piran The Hebrew University, Israel Steven Weinberg University of Texas, Austin, USA TECHNiSCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
ASTR 200 : Lecture 22 Structure of our Galaxy 1 The 'Milky Way' is known to all cultures on Earth (perhaps, unfortunately, except for recent city-bound dwellers) 2 Fish Eye Lens of visible hemisphere (but
The dark and visible matter content of low surface brightness disk galaxies Blok, W. J. G. de; McGaugh, S. S.
 University of Groningen The dark and visible matter content of low surface brightness disk galaxies Blok, W. J. G. de; McGaugh, S. S. Published in: The Astrophysical Journal IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised
University of Groningen The dark and visible matter content of low surface brightness disk galaxies Blok, W. J. G. de; McGaugh, S. S. Published in: The Astrophysical Journal IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23)
 The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
The Milky Way Galaxy (ch. 23) [Exceptions: We won t discuss sec. 23.7 (Galactic Center) much in class, but read it there will probably be a question or a few on it. In following lecture outline, numbers
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Astronomy 114. Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies
 Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
Stellar Dynamics and Structure of Galaxies Gerry Gilmore H47 email: gil@ast.cam.ac.uk Lectures: Monday 12:10-13:00 Wednesday 11:15-12:05 Friday 12:10-13:00 Books: Binney & Tremaine Galactic Dynamics Princeton
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Dark Matter. ASTR 333/433 Spring 2018 T R 4:00-5:15pm Sears 552
 Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Spring 2018 T R 4:00-5:15pm Sears 552 TODAY - Laws of Galactic Rotation - Flat rotation curves - Tully-Fisher - Universal Rotation curve - central Density Relation - Renzo s Rule
Dark Matter ASTR 333/433 Spring 2018 T R 4:00-5:15pm Sears 552 TODAY - Laws of Galactic Rotation - Flat rotation curves - Tully-Fisher - Universal Rotation curve - central Density Relation - Renzo s Rule
Astro 242. The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu
 Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
Astro 242 The Physics of Galaxies and the Universe: Lecture Notes Wayne Hu Syllabus Text: An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics 2nd Ed., Carroll and Ostlie First class Wed Jan 3. Reading period Mar 8-9
Structure of the Milky Way. Structure of the Milky Way. The Milky Way
 Key Concepts: Lecture 29: Our first steps into the Galaxy Exploration of the Galaxy: first attempts to measure its structure (Herschel, Shapley). Structure of the Milky Way Initially, star counting was
Key Concepts: Lecture 29: Our first steps into the Galaxy Exploration of the Galaxy: first attempts to measure its structure (Herschel, Shapley). Structure of the Milky Way Initially, star counting was
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs
 A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
A new mechanism for the formation of PRGs Spavone Marilena (INAF-OAC) Iodice Enrica (INAF-OAC), Arnaboldi Magda (ESO-Garching), Longo Giuseppe (Università Federico II ), Gerhard Ortwin (MPE-Garching).
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8. Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 8 Angular Momentum & the Cusp/Core Problem Summary to Date We first learned how to construct the Power Spectrum with CDM+baryons. Found CDM agrees with the observed Power Spectrum
Homework 1. Astronomy 202a. Fall 2009
 Homework 1 Astronomy 0a Fall 009 Solutions Problems: 1. A galaxy has an integrated blue magnitude of 6.5, a rotation velocity (essentially flat) of 107 km s 1, and is ellptical in overall shape with major
Homework 1 Astronomy 0a Fall 009 Solutions Problems: 1. A galaxy has an integrated blue magnitude of 6.5, a rotation velocity (essentially flat) of 107 km s 1, and is ellptical in overall shape with major
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney
 ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
ASTRO 310: Galactic & Extragalactic Astronomy Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 3 January 23, 2017 The Milky Way Galaxy: Vertical Distributions of Stars & the Stellar Disk disks exist in many astrophysical systems
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Galaxies. Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations
 Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies Hubble's measurement of distance to M31 Normal versus other galaxies Classification of galaxies Ellipticals Spirals Scaling relations Cepheids in M31 Up to 1920s, the Milky Way was thought by
Galaxies. CESAR s Booklet
 What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe. Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent with
 Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Notes for Cosmology course, fall 2005 Dark Matter Prelude Cosmologists dedicate a great deal of effort to determine the density of matter in the universe Type Ia supernovae observations are consistent
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy
 Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Stellar Populations in the Galaxy Stars are fish in the sea of the galaxy, and like fish they often travel in schools. Star clusters are relatively small groupings, the true schools are stellar populations.
Our View of the Milky Way. 23. The Milky Way Galaxy
 23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
23. The Milky Way Galaxy The Sun s location in the Milky Way galaxy Nonvisible Milky Way galaxy observations The Milky Way has spiral arms Dark matter in the Milky Way galaxy Density waves produce spiral
Does Low Surface Brightness Mean Low Density? W.J.G. de Blok. Kapteyn Astronomical Institute. P.O. Box AV Groningen. The Netherlands.
 Does Low Surface Brightness Mean Low Density? W.J.G. de Blok Kapteyn Astronomical Institute P.O. Box 800 9700 AV Groningen The Netherlands and S.S. McGaugh Department of Terrestrial Magnetism Carnegie
Does Low Surface Brightness Mean Low Density? W.J.G. de Blok Kapteyn Astronomical Institute P.O. Box 800 9700 AV Groningen The Netherlands and S.S. McGaugh Department of Terrestrial Magnetism Carnegie
An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology. Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3
 An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3 2.1 Introduction external galaxies normal galaxies - majority active galaxies - 2% high luminosity (non-stellar origin) variability
An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology Jun 29, 2005 Chap.2.1~2.3 2.1 Introduction external galaxies normal galaxies - majority active galaxies - 2% high luminosity (non-stellar origin) variability
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
Observational Cosmology
 Astr 102: Introduction to Astronomy Fall Quarter 2009, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 15: Observational Cosmology 1 Outline Observational Cosmology: observations that allow us to test
Astr 102: Introduction to Astronomy Fall Quarter 2009, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 15: Observational Cosmology 1 Outline Observational Cosmology: observations that allow us to test
Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things
 Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things Fundamental Considerations Different libraries of galaxies are liable to lead to the ID of different classes Images in library must be homogeneous (filter,
Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things Fundamental Considerations Different libraries of galaxies are liable to lead to the ID of different classes Images in library must be homogeneous (filter,
Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters. Formation and Evolution Hubble s Law
 The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
The American astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1924, according to appearance of galaxies categorized them into four basic types. Classification Distribution in Space Galaxy Clusters Masses Formation and Evolution
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Nature of Dark Matter
 Nature of Dark Matter Amir Ali Tavajoh 1 1 Amir_ali3640@yahoo.com Introduction Can we apply Kepler s Laws to the motion of stars of a galaxy? Is it true that luminous matter contains the total galaxy s
Nature of Dark Matter Amir Ali Tavajoh 1 1 Amir_ali3640@yahoo.com Introduction Can we apply Kepler s Laws to the motion of stars of a galaxy? Is it true that luminous matter contains the total galaxy s
Large Scale Structure
 Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
Large Scale Structure Measuring Distance in Universe-- a ladder of steps, building from nearby Redshift distance Redshift = z = (λ observed - λ rest )/ λ rest Every part of a distant spectrum has same
Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
 ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
ASTR 3830 Astrophysics 2 - Galactic and Extragalactic Phil Armitage office: JILA tower A909 email: pja@jilau1.colorado.edu Spitzer Space telescope image of M81 Part two of a year-long introduction to astrophysics:
Galaxy Luminosity Function. Galaxy Luminosity Function. Schechter Function. Schechter Function by environment. Schechter (1976) found that
 Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
Galaxy Luminosity Function Count the number of galaxies as a function of luminosity (or absolute magnitude) Useful for: Understanding galaxy formation (distribution by luminosity implies distribution by
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology:
 Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
Lecture Two: Galaxy Morphology: Looking more deeply at the Hubble Sequence Galaxy Morphology How do you quantify the properties of galaxies? and how do you put them in groups which allow you to study physically
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-1 13-4-12see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies12 12-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group
 Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
Cosmological Puzzles: Dwarf Galaxies and the Local Group Julio F. Navarro Dark-matter-only simulations have highlighted a number of cosmological puzzles Local Group puzzles Missing satellites problem Satellite
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY. Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy)
 OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
OBSERVATIONAL EVIDENCE FOR DARK MATTER AND DARK ENERGY Marco Roncadelli INFN Pavia (Italy) ABSTRACT Assuming KNOWN physical laws, I first discuss OBSERVATIONAL evidence for dark matter in galaxies and
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy. 2. Classification
 ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
ASTRO504 Extragalactic Astronomy 2. Classification Morphological classification Elliptical (E) galaxies Lenticular (SO) galaxies Spiral (S) galaxies Irregular (Im) galaxies The realm of nebulae Hubble
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
A. Thermal radiation from a massive star cluster. B. Emission lines from hot gas C. 21 cm from hydrogen D. Synchrotron radiation from a black hole
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 26 Thur 14 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre HST Abell 2218 Reading clicker what makes the light? What
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 26 Thur 14 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre HST Abell 2218 Reading clicker what makes the light? What
12.1 Elliptical Galaxies
 12.1 Elliptical Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies Old view: ellipticals are boring, simple systems Ellipticals contain no gas & dust Ellipticals are composed of old stars Ellipticals formed in a monolithic
12.1 Elliptical Galaxies Elliptical Galaxies Old view: ellipticals are boring, simple systems Ellipticals contain no gas & dust Ellipticals are composed of old stars Ellipticals formed in a monolithic
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter
 Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group!
 Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group Discussion of detailed properties of M31, M33 comparison to MW; differences in how they formed; MW very few 'major mergers' M31 more; not all galaxies even those close
Summary of Last Lecture - Local Group Discussion of detailed properties of M31, M33 comparison to MW; differences in how they formed; MW very few 'major mergers' M31 more; not all galaxies even those close
Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies
 Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies Thorsten Naab with ATLAS 3D MPA L. Oser, M.Hilz, E. Emsellem, M. Cappellari, D. Krajnovic, R. M. McDermid, N. Scott, P. Serra, G. A.
Cosmological formation of slowly rotating massive elliptical galaxies Thorsten Naab with ATLAS 3D MPA L. Oser, M.Hilz, E. Emsellem, M. Cappellari, D. Krajnovic, R. M. McDermid, N. Scott, P. Serra, G. A.
MOND and the Galaxies
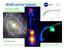 MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
MOND and the Galaxies Françoise Combes Observatoire de Paris With Olivier Tiret Angus, Famaey, Gentile, Wu, Zhao Wednesday 1st July 2009 MOND =MOdified Newtonian Dynamics Modification at weak acceleration
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching
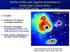 Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
Stellar Orbits and Angular Momentum in Early-Type Galaxy Halos Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de 1. Preamble Arnaboldi et al 2013 2. Predictions: ETG halos in cosmological simulations 3.
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation
 Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Angular Momentum Problems in Disk Formation MPIA Theory Group Seminar, 07/03/2006 The Standard Picture Disks galaxies are systems in centrifugal equilibrium Structure of disks is governed by angular momentum
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
The Milky Way & Galaxies
 The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
The Shape of Dark Matter Halos
 The Shape of Dark Matter Halos Penny D. Sackett Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands Abstract. Techniques for inferring the radial and geometric form of dark matter halos
The Shape of Dark Matter Halos Penny D. Sackett Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands Abstract. Techniques for inferring the radial and geometric form of dark matter halos
stellar systems Large N systems interacting with long-range forces F = G M m /r^2
 stellar systems Large N systems interacting with long-range forces F = G M m /r^2 Examples of stellar systems: globular cluster galaxy cluster of galaxy connection to celestial mechanics, statistical mechanics,
stellar systems Large N systems interacting with long-range forces F = G M m /r^2 Examples of stellar systems: globular cluster galaxy cluster of galaxy connection to celestial mechanics, statistical mechanics,
