NASA telescopes help solve ancient supernova mystery
|
|
|
- Logan Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NASA telescopes help solve ancient supernova mystery RCW 86: A Type Ia Supernova in a Wind-Blown Bubble Williams, Brian J., el. al. ApJ 741, 96 (2011) Jeng-Lun (Alan) Chiu Institute of Astronomy, NTHU 2011/10/31 HEAG NTHU [Picture]:
2 RCW 86 (G ;MSH 14-63) Location: (RA, Dec) = (14h 43m 04s, ) (in Circinus) Distance: ~ kpc away from Earth (Sollerman et al. 2003; Rosado et al. 1996) (~85 light year at ~8,000 light-years away) Angular Size: ~45 arcmin (larger than the moon [29-34 arcmin] as seen from Earth) A Galactic SNR proposed to be the remains of SN 185 A.D. (adopting a distance of 2.5 kpc in Williams work) The "guest star, SN 185, was observed by Chinese astronomers in the Book of Later Han in the year 185 AD and remained visible in the night sky for eight months. This is believed to have been the first supernova recorded by humankind since 1960s. The gaseous shell RCW 86 is suspected as being the supernova remnant of this event. The star's spherical remains are larger than expected with 2000-year expansion. Recent X-ray studies show a good match for the expected age. Differing modern interpretations of the Chinese records of the guest star have led to quite different suggestions for the astronomical mechanism behind the event, from a core-collapse supernova to a distant, slow-moving comet (Chin & Huang 1994) with correspondingly wide-ranging estimates of its apparent visual magnitude ( 8 to +4). The recent Chandra results suggest that it was most likely a Type Ia supernova (a type with consistent absolute magnitude), similar therefore to Tycho's star (which had apparent magnitude 4 at a similar distance).
3 News A mystery that began nearly 2,000 years ago, when Chinese astronomers witnessed what would turn out to be an exploding star in the sky, has been solved: New infrared observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) reveal how the first supernova ever recorded occurred and how its shattered remains ultimately spread out to great distances. Brian J. Williams, el. al. found that the stellar explosion took place in a hollowed-out cavity, allowing material expelled by the star to travel much faster and farther than it would have otherwise (i.e. two to three times bigger than expectation). Arguments: 1). Spitzer and WISE allowed temperature measurement of the dust making up the RCW 86 remnant at about -200 C calculated how much gas must be present within the remnant to heat the dust to those temperatures a low-density environment for much of the life of the remnant, essentially a cavity. The observations show for the first time that a white dwarf can create a cavity around it before blowing up in a Type Ia event: A cavity the ejected material would have traveled unimpeded by gas and dust and spread out quickly after explosion big remains of RCW 86. Was RCW 86 from a core-collapse (CC) supernova, where massive stars blow material away from them before they blow up, carving out holes around them? 2). X-ray data from Chandra and XMM-Newton indicated that the object consisted of high amounts of iron a telltale sign of a Type Ia blast. Together with the infrared observations, a picture of a Type Ia explosion into a cavity emerged.
4 [ A filament in the NW stretching 7 ] Significant correlation between IR, X-ray, and optical images a tight coupling between IR-emitting dust & X-ray-emitting gas. angular resolution 7 angular resolution 20 A few faint filaments are observed that correspond to features seen at 24μm. These filaments also appear as radiative filaments in the [S ii] image (Smith 1997), making it likely that the IRAC emission comes from lines (most likely [Ar ii] at 7μm and [Fe ii] at 5.4μm). It is possible that emission from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) heated immediately behind the shock front. Figure 1. [Top left]: MIPS 24 μm image, with NW extraction region indicated a green ellipse. [Top right]: MIPS 70 μm image. [Bottom right]: XMM-Newton EPIC image: ( kev in red, kev in green, and kev in blue). [Bottom left]: NOAO/CTIO star-subtracted optical image (Smith 97): Hα in red and [S ii] in green. Areas appearing yellow contain both non-radiative and radiative shocks. Cyan rectangle (lower left panel) marks the Spitzer/IRS spectral extraction region Figure 2. [Top left]: IRAC three-color image of the SW region: 8 μm in red, 5.8 μm in green, and 4.5 μm in blue. Yellow regions highlight structures also seen at 24 μm. [Top right]: the MIPS 24 μm image with IRAC regions overlaid. [Bottom right]: Optical Hα and [S ii] image, as in Fig 1, with the region highlighting a purely non-radiative filament, used for the IR analysis of the SW region. [Bottom left]: the EPIC-MOS2 X-ray image, with colors as in Figure 1. Generally speaking, emission from younger SNRs expanding into a low-density medium (characterized by non-radiative shocks in the optical) will be dominated by continuum (Williams et al. 2011), while older shocks or those encountering molecular clouds will become radiative and show strong mid-ir line emission (Hewitt et al. 2009).
5 The colors of this image, which reflect the temperature of the dust, separate the emission that is associated with the SNR from that of the background. This is particularly important in the east, where the thin red filaments trace the blast wave. Figure 3. Spitzer and WISE mosaic of the entire remnant, with Spitzer 24μm emission in red, WISE 12μm emission in green, and WISE 4.6μm emission in blue. The 22μm image from WISE, not shown, looks virtually identical to the Spitzer 24μm image. We display the MIPS 24μm image here because of the sharper resolution and better signal-to-noise ratio. Only the brightest sections of the NW and SW are visible at 12μm (note the slightly yellowish colors of these regions).
6 EPIC-MOS 1 and 2 spectra, in black and red, respectively, of the NW region, overlaid with a model of thermal and nonthermal emission. An additional thermal model to account for the Fe Kα line at 6.4 kev is included as well. Data are 3σ binned for plotting purposes only. Figure 4. (The shock speed of this filament is km/s (Ghavamian 1999).) Visible in the spectra is a continuum extending to high energies, featureless except for an Fe Kα line at 6.4 kev. We account for these components with an srcut model for the synchrotron emission (Reynolds & Keohane 1999) and an Fe-only vpshock model with kt = 5 kev and τi = 10 9 cm 3 s. The nonthermal continuum in the NW does not show the same morphology as the low-energy thermal emission. Thermal X-rays in that region are well contained to the thin filament seen in Figure 1, but the synchrotron emission appears much more diffuse. Similar discrepancies were observed in the SW, leading R02 to conclude that the synchrotron emission is associated with reverse shocks driven into the ejecta, and not the forward shock. Figure 5. EPIC-MOS image of the NW filament, with kev emission in red, kev emission in green, and kev nonthermal emission shown in blue. The low-energy bands highlight thermal emission, while the high-energy band shows the location of the nonthermal synchrotron radiation. Images have been smoothed with a two-pixel Gaussian to highlight extended emission.
7 The density profile from a 1D simulation (a model with n 0,I = cm 3 and R = 10.8 pc. The current shock speed in this model is 740 km/s) Figure 6. Density profile of the wind-blown bubble model, as described in the text, in one dimension. Identified in the image are the forward shock (FS), the contact discontinuity separating the shocked ISM material from the shocked bubble material (CD1), the contact discontinuity separating the shocked bubble material from the shocked ejecta (CD2), and the reverse shock (RS). The collision of the blast wave with a shell of density contrast 250 leads to density structures from transmitted and reflected shocks, which can also be seen in the figure. Pressure, normalized to 1 at CD2, is shown by a dashed line.
8 The extraction region in Figure 1 begins at a radial distance of 93%of the forward shock radius. SIM. Significant amounts of shocked ejecta at a radius of >93% of the forward shock radius. One thing the 2D (spherically-symmetric) hydro model cannot account for is the extremely high shock speed reported for the NE limb, found fromchandra proper motions to be 6000±2800 km/s. This symmetry must be broken to explain shock speeds that differ by an order of magnitude from one side of the remnant to the other. D: distance from the center of explosion to any point on the wall of the shell R: the fixed radius of the shell wall (in this case, 12 pc). θ: polar angle between the center of explosion and a point on the shell wall.
9 At a distance of 2.5 kpc, the diameter of the remnant is 25 pc, requiring an average shock speed of >7000 km/s. Measured shock speeds vary greatly within the remnant. In the regions of interest considered in this paper (where the shell is detected at both 24 and 70μm), shock speeds from optical spectroscopy are km/s, while shock speeds in the eastern limb from the proper motion of X-ray-emitting filaments have been reported as high as 6000 (±2800) km/s. Figure 9. Density structure in the off-center explosion model, as seen in the plane of the sky, shown at the current age of the remnant. The center of the explosion is marked by a black star, and the center of the bubble is marked by a yellow star. The distance between the two (R0 in the text) is 7 pc. At θ = 0, measured from the center of explosion, the forward shock has reached a radius of 13.5 pc with respect to the center of the bubble, while at θ = π/2, the shock is at 12.7 pc, again with respect to the center of the bubble. On the far side (θ = π), the forward shock is still in the low-density bubble and has not yet reached the wall. The lack of an instability at the contact discontinuity is the result of the low angular resolution used in this model.
10 This is the first time that this type of cavity has been seen around a white dwarf system prior to explosion. Scientists say the results may have significant implications for theories of whitedwarf binary systems and Type Ia supernovae. X-ray images from the XMM and Chandra are combined to form the blue and green colors in the image, showing the interstellar gas that has been heated to millions of degrees by the passage of the shock wave from the supernova. Infrared data from Spitzer and WISE are shown in yellow and red, revealing dust radiating at a temperature of several hundred degrees below zero, warm by comparison to normal dust in our Milky Way galaxy.
11 Thank You References: Brian J. Williams, William P. Blair, John M. Blondin, Kazimierz J. Borkowski, Parviz Ghavamian, Knox S. Long, John C. Raymond, Stephen P. Reynolds, Jeonghee Rho and P. Frank Winkler, ApJ 741 (2): (2011) Links:
Remnants of Type Ia Supernovae
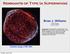 Remnants of Type Ia Supernovae Brian J. Williams NPP Fellow NASA GSFC Collaborators: Steve Reynolds, Kazik Borkowski, John Blondin (NCSU), Rob Petre, Jack Hewitt (GSFC), Frank Winkler (Middlebury), Knox
Remnants of Type Ia Supernovae Brian J. Williams NPP Fellow NASA GSFC Collaborators: Steve Reynolds, Kazik Borkowski, John Blondin (NCSU), Rob Petre, Jack Hewitt (GSFC), Frank Winkler (Middlebury), Knox
Observations of supernova remnants
 Observations of supernova remnants Anne Decourchelle Service d Astrophysique, CEA Saclay I- Ejecta dominated SNRs: Cas A, Tycho and Kepler II- Synchrotron-dominated SNRs: SN 1006, G347.3-0.5 Young supernova
Observations of supernova remnants Anne Decourchelle Service d Astrophysique, CEA Saclay I- Ejecta dominated SNRs: Cas A, Tycho and Kepler II- Synchrotron-dominated SNRs: SN 1006, G347.3-0.5 Young supernova
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Supernova remnants: X-ray observations with XMM-Newton
 Supernova remnants: X-ray observations with XMM-Newton Anne DECOURCHELLE, Service d Astrophysique, IRFU, DSM, CEA Supernova remnants: key ingredients to understand our Universe Chemical enrichment, heating
Supernova remnants: X-ray observations with XMM-Newton Anne DECOURCHELLE, Service d Astrophysique, IRFU, DSM, CEA Supernova remnants: key ingredients to understand our Universe Chemical enrichment, heating
Particle acceleration in Supernova Remnants
 Particle acceleration in Supernova Remnants Anne Decourchelle Service d Astrophysique, CEA Saclay Collaborators: J. Ballet, G. Cassam-Chenai, D. Ellison I- Efficiency of particle acceleration at the forward
Particle acceleration in Supernova Remnants Anne Decourchelle Service d Astrophysique, CEA Saclay Collaborators: J. Ballet, G. Cassam-Chenai, D. Ellison I- Efficiency of particle acceleration at the forward
The Cygnus Loop/Veil Nebula Hubble Space Telescope. William P. Blair Department of Physics and Astronomy The Johns Hopkins University September, 2015
 The Cygnus Loop/Veil Nebula Hubble Space Telescope William P. Blair Department of Physics and Astronomy The Johns Hopkins University September, 2015 Overall context: The Cygnus Loop, or Veil Nebula as
The Cygnus Loop/Veil Nebula Hubble Space Telescope William P. Blair Department of Physics and Astronomy The Johns Hopkins University September, 2015 Overall context: The Cygnus Loop, or Veil Nebula as
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants
 Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Supernova Remnant Science with AXIS. Brian Williams & Hiroya Yamaguchi
 Supernova Remnant Science with AXIS Brian Williams & Hiroya Yamaguchi Big Picture Questions - How do supernovae dictate the life cycle of elements in the ISM? - What are the progenitors of the various
Supernova Remnant Science with AXIS Brian Williams & Hiroya Yamaguchi Big Picture Questions - How do supernovae dictate the life cycle of elements in the ISM? - What are the progenitors of the various
Progenitor signatures in Supernova Remnant Morphology. Jacco Vink Utrecht University
 Progenitor signatures in Supernova Remnant Morphology Jacco Vink Utrecht University The evolution of SNRs Heating by two shocks: 1. forward shocks heating ISM/CSM 2. reverse shock heating ejecta radius
Progenitor signatures in Supernova Remnant Morphology Jacco Vink Utrecht University The evolution of SNRs Heating by two shocks: 1. forward shocks heating ISM/CSM 2. reverse shock heating ejecta radius
Shell supernova remnants as cosmic accelerators: II
 Shell supernova remnants as cosmic accelerators: II Stephen Reynolds, North Carolina State University I. Observational tools II. Radio inferences III. X ray synchrotron emission IV. MeV GeV observations
Shell supernova remnants as cosmic accelerators: II Stephen Reynolds, North Carolina State University I. Observational tools II. Radio inferences III. X ray synchrotron emission IV. MeV GeV observations
Universe Now. 9. Interstellar matter and star clusters
 Universe Now 9. Interstellar matter and star clusters About interstellar matter Interstellar space is not completely empty: gas (atoms + molecules) and small dust particles. Over 10% of the mass of the
Universe Now 9. Interstellar matter and star clusters About interstellar matter Interstellar space is not completely empty: gas (atoms + molecules) and small dust particles. Over 10% of the mass of the
Balmer-Dominated Supernova Remnants and the Physics of Collisionless Shocks
 Balmer-Dominated Supernova Remnants and the Physics of Collisionless Shocks Parviz Ghavamian SNR 0509-67.5 HST ACS Hα (F657N) Supernova Remnants Heat and Enrich the ISM and Accelerate Cosmic Rays reverse-shocked
Balmer-Dominated Supernova Remnants and the Physics of Collisionless Shocks Parviz Ghavamian SNR 0509-67.5 HST ACS Hα (F657N) Supernova Remnants Heat and Enrich the ISM and Accelerate Cosmic Rays reverse-shocked
Supernovae. Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization
 Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33
 Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Energy Sources of the Far IR Emission of M33 Hinz, Reike et al., ApJ 154: S259 265 (2004). Presented by James Ledoux 24 µm 70 µm 160 µm Slide 1 M33 Properties Distance 840kpc = 2.7 Mlyr (1'' ~ 4 pc) Also
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21)
 Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
Stellar Explosions (ch. 21) First, a review of low-mass stellar evolution by means of an illustration I showed in class. You should be able to talk your way through this diagram and it should take at least
X-Ray Spectroscopy of Supernova Remnants. Introduction and Background:
 X-Ray Spectroscopy of Supernova Remnants Introduction and Background: RCW 86 (Chandra, XMM-Newton) RCW 86 is a supernova remnant that was created by the destruction of a star approximately two thousand
X-Ray Spectroscopy of Supernova Remnants Introduction and Background: RCW 86 (Chandra, XMM-Newton) RCW 86 is a supernova remnant that was created by the destruction of a star approximately two thousand
Supernovae. Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization
 Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Supernovae Supernova basics Supernova types Light Curves SN Spectra after explosion Supernova Remnants (SNRs) Collisional Ionization 1 Supernova Basics Supernova (SN) explosions in our Galaxy and others
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
The Milky Way Galaxy. Some thoughts. How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of?
 Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Some thoughts The Milky Way Galaxy How big is it? What does it look like? How did it end up this way? What is it made up of? Does it change 2 3 4 5 This is not a constant zoom The Milky Way Almost everything
Supernovae Through the Ages
 Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Supernovae Through the Ages We ourselves are stardust. -Carl Sagan Jason Kezwer September 11, 2013 Outline - What are supernovae? Why are they important? - An observational history - How supernovae affect
Particle acceleration in SN 1006
 Particle acceleration in SN 1006 Anne DECOURCHELLE, Service d Astrophysique/AIM, IRFU CEA, France First results from an XMM-Newton LP on SN 1006 Co-Is: G. Maurin (post-doc), M. Miceli, F. Bocchino, G.
Particle acceleration in SN 1006 Anne DECOURCHELLE, Service d Astrophysique/AIM, IRFU CEA, France First results from an XMM-Newton LP on SN 1006 Co-Is: G. Maurin (post-doc), M. Miceli, F. Bocchino, G.
Astrophysical Quantities
 Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
Astr 8300 Resources Web page: http://www.astro.gsu.edu/~crenshaw/astr8300.html Electronic papers: http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abstract_service.html (ApJ, AJ, MNRAS, A&A, PASP, ARAA, etc.) General astronomy-type
The Dusty Universe. Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy
 The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
The Dusty Universe Joe Weingartner George Mason University Dept of Physics and Astronomy To astronomers, dust means: sub micron solid grains (1 micron = 1 m = 10 6 m = one millionth of a meter) Typical
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
CHAPTER 28 STARS AND GALAXIES 28.1 A CLOSER LOOK AT LIGHT Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, which is energy that travels in waves. Waves of energy travel at 300,000 km/sec (speed of light Ex:
Supernova Remnants and GLAST
 SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
Expanding molecular bubble surrounding Tycho's SNR evidence for a single-degenerate progenitor
 Expanding molecular bubble surrounding Tycho's SNR evidence for a single-degenerate progenitor Ping Zhou (Nanjing University) Collaborators: Yang Chen, Zhi-Yu Zhang, Xiang-Dong Li, Samar Safi-Harb, Xin
Expanding molecular bubble surrounding Tycho's SNR evidence for a single-degenerate progenitor Ping Zhou (Nanjing University) Collaborators: Yang Chen, Zhi-Yu Zhang, Xiang-Dong Li, Samar Safi-Harb, Xin
Midterm Results. The Milky Way in the Infrared. The Milk Way from Above (artist conception) 3/2/10
 Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
Lecture 13 : The Interstellar Medium and Cosmic Recycling Midterm Results A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath The Milky Way in the Infrared View from the Earth: Edge On Infrared light penetrates the clouds and shows
3/18/14. Today on Stellar Explosions. Second Mid-Term Exam. Things to do SECOND MID-TERM EXAM. Making a millisecond pulsars spin it up!
 3/18/14 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Binary mass transfer: accretion disk Today on Stellar Explosions Spinning up pulsars through mass transfer from (surviving!) companions White dwarf supernovae from mass
3/18/14 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Binary mass transfer: accretion disk Today on Stellar Explosions Spinning up pulsars through mass transfer from (surviving!) companions White dwarf supernovae from mass
Radio emission from Supernova Remnants. Gloria Dubner IAFE Buenos Aires, Argentina
 Radio emission from Supernova Remnants Gloria Dubner IAFE Buenos Aires, Argentina History Before radio astronomy, only 2 SNRs were known: Crab and Kepler s SNR 1948: Ryle and Smith detected an unusually
Radio emission from Supernova Remnants Gloria Dubner IAFE Buenos Aires, Argentina History Before radio astronomy, only 2 SNRs were known: Crab and Kepler s SNR 1948: Ryle and Smith detected an unusually
Wednesday, January 25, 2017
 Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Powerpoint of lectures posted as pdf after every class, on Canvas and at http://www.as.utexas.edu/astronomy/education/spring17/wheeler/ 309n.html?a=lec Wednesday Star Parties
Accretion Disks. Review: Stellar Remnats. Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath 2/25/10. Review: Creating Stellar Remnants
 Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
Lecture 12: Black Holes & the Milky Way A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: Creating Stellar Remnants Binaries may be destroyed in white dwarf supernova Binaries be converted into black holes Review: Stellar
January 2012 NGC 281. S M T W Th F Sa
 NGC 281 High-mass stars are responsible for much of the energy pumped into a galaxy over its lifetime. Unfortunately, these stars are not well understood because they are often found relatively far away
NGC 281 High-mass stars are responsible for much of the energy pumped into a galaxy over its lifetime. Unfortunately, these stars are not well understood because they are often found relatively far away
- Strong extinction due to dust
 The Galactic Centre - Strong extinction due to dust At optical wavelemgth the absorption is almost total Information from the 21 line, IR and radio 10 Region between and cm 14 10 22 1 arcsec at the distance
The Galactic Centre - Strong extinction due to dust At optical wavelemgth the absorption is almost total Information from the 21 line, IR and radio 10 Region between and cm 14 10 22 1 arcsec at the distance
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe
 Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
Beyond the Visible -- Exploring the Infrared Universe Prof. T. Jarrett (UCT) Infrared Window Telescopes ISM -- Galaxies Infrared Window Near-infrared: 1 to 5 µm Mid-infrared: 5 to 50 µm
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training
 Personal Section The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training Program at the University of Iowa. There, I interned for Professor Ugur Akgun to simulate the unfolding
Personal Section The summer before my junior year, I went to attend the Secondary Student Training Program at the University of Iowa. There, I interned for Professor Ugur Akgun to simulate the unfolding
Galaxies and the Universe
 Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Standard 7.3.1: Recognize and describe that the Sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a diskshaped galaxy of stars and that the universe contains many billions of galaxies and each galaxy
Name Date Period. 10. convection zone 11. radiation zone 12. core
 240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
240 points CHAPTER 29 STARS SECTION 29.1 The Sun (40 points this page) In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and the Sun s atmosphere. Use each of the terms below just once to complete
Subaru telescope observes echo of the exploding star first seen in 1572, and reveals its nature
 Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe IPMU Press Release 2008 12 04 Subaru telescope observes echo of the exploding star first seen in 1572, and reveals its nature Kashiwa, Japan A
Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe IPMU Press Release 2008 12 04 Subaru telescope observes echo of the exploding star first seen in 1572, and reveals its nature Kashiwa, Japan A
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
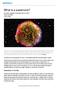 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18)
 The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
The Interstellar Medium (ch. 18) The interstellar medium (ISM) is all the gas (and about 1% dust) that fills our Galaxy and others. It is the raw material from which stars form, and into which stars eject
Mass loss from stars
 Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Today in Milky Way. Clicker on deductions about Milky Way s s stars. Why spiral arms? ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 21 Tues 3 Apr 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Superbubble NGC 3079 Today in Milky Way Look at why spiral
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nick Featherstone Lecture 21 Tues 3 Apr 07 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Superbubble NGC 3079 Today in Milky Way Look at why spiral
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Distances & the Milky Way. The Curtis View. Our Galaxy. The Shapley View 3/27/18
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Distances & the Milky Way 14-2 Historical Overview: the Curtis-Shapley Debate ³What is the size of our galaxy? ³What is the nature of spiral nebula? The Curtis
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Distances & the Milky Way 14-2 Historical Overview: the Curtis-Shapley Debate ³What is the size of our galaxy? ³What is the nature of spiral nebula? The Curtis
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D.
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Distances & the Milky Way Historical Overview: the Curtis-Shapley Debate ³What is the size of our galaxy? ³What is the nature of spiral nebula? 14-2 ³Occurred in
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. Distances & the Milky Way Historical Overview: the Curtis-Shapley Debate ³What is the size of our galaxy? ³What is the nature of spiral nebula? 14-2 ³Occurred in
Lecture 2 Supernovae and Supernova Remnants
 Lecture 2 Supernovae and Supernova Remnants! The destiny of the stars! Explosive nucleosynthesis! Facts about SNe! Supernova remnants * Morphological classification * Evolutive stages! Emission of SNRs
Lecture 2 Supernovae and Supernova Remnants! The destiny of the stars! Explosive nucleosynthesis! Facts about SNe! Supernova remnants * Morphological classification * Evolutive stages! Emission of SNRs
Supernova Explosions. Novae
 Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Supernova Explosions Novae Novae occur in close binary-star systems in which one member is a white dwarf. First, mass is transferred from the normal star to the surface of its white dwarf companion. 1
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Presented at the 2016 International Training Symposium: Hubble Space Telescope
 Hubble Space Telescope Hubble s Name NASA named the world's first spacebased optical telescope after American astronomer Edwin P. Hubble (1889 1953). Dr. Hubble confirmed an "expanding" universe, which
Hubble Space Telescope Hubble s Name NASA named the world's first spacebased optical telescope after American astronomer Edwin P. Hubble (1889 1953). Dr. Hubble confirmed an "expanding" universe, which
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9
 Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Phys 0 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 9 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. We know that giant stars are larger in diameter than the sun because * a. they are more luminous but have about the
Astronomy 422! Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III!
 Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Astronomy 422 Lecture 7: The Milky Way Galaxy III Key concepts: The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Radio and X-ray sources Announcements: Test next Tuesday, February 16 Chapters
Dust. The four letter word in astrophysics. Interstellar Emission
 Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
Dust The four letter word in astrophysics Interstellar Emission Why Dust Dust attenuates and scatters UV/optical/NIR Amount of attenuation and spectral shape depends on dust properties (grain size/type)
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name
 ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
ASTRONOMY 1 FINAL EXAM 1 Name Multiple Choice (2 pts each) 1. Sullivan Star is an F spectral class star that is part of a binary star system. It has a MS lifetime of 5 billion years. Its life will eventually
Near-infrared line imaging of supernova remnant
 Near-infrared line imaging of supernova remnant : Background study: Wide infrared IFU observations of G11.2-0.3 2013 March 15 IoA Ho-Gyu LEE Motivation Position of pulsar SN AD386? Origin of bright [Fe
Near-infrared line imaging of supernova remnant : Background study: Wide infrared IFU observations of G11.2-0.3 2013 March 15 IoA Ho-Gyu LEE Motivation Position of pulsar SN AD386? Origin of bright [Fe
Star systems like our Milky Way. Galaxies
 Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
Galaxies Star systems like our Milky Way Galaxies Contain a few thousand to tens of billions of stars,as well as varying amounts of gas and dust Large variety of shapes and sizes Gas and Dust in
On Today s s Radar. Reading and Events SECOND MID-TERM EXAM. ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies. Another useful experience (we hope)
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 20 Thur 17 Mar 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Edge-on spiral galaxy NGG 4013 On Today s s Radar Look
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 20 Thur 17 Mar 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Edge-on spiral galaxy NGG 4013 On Today s s Radar Look
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12)
 Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Stars and their properties: (Chapters 11 and 12) To classify stars we determine the following properties for stars: 1. Distance : Needed to determine how much energy stars produce and radiate away by using
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009
 Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Supernova Feedback in Low and High Mass Galaxies: Luke Hovey 10 December 2009 Galactic Winds: Mathews, W. et al. 1971 Effects of Supernovae on the Early Evolution of Galaxies: Larson, R. 1974 The origin
Galactic Supershells and GSH Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November
 Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
Galactic Supershells and GSH 006-15+7 Vanessa A. Moss Parkes 50th Symposium 3rd November 2011 1 Contents Early history of supershells Discovery Early interpretation Surveys of supershells Northern hemisphere
NuSTAR s Extreme Universe. Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University
 NuSTAR s Extreme Universe Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University The NASA Education and Public Outreach Program at SSU We are a group of scientists and educators
NuSTAR s Extreme Universe Prof. Lynn Cominsky NASA Education and Public Outreach Sonoma State University The NASA Education and Public Outreach Program at SSU We are a group of scientists and educators
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the passage below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble's discovery of a pattern in the red
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Neutron Stars. Neutron Stars and Black Holes. The Crab Pulsar. Discovery of Pulsars. The Crab Pulsar. Light curves of the Crab Pulsar.
 Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Chapter 11: Neutron Stars and Black Holes A supernova explosion of an M > 8 M sun star blows away its outer layers. Neutron Stars The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M sun.
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars
 Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Astr 5465 Feb. 5, 2018 Kinematics of Nearby Stars Properties of Nearby Stars Most in orbit with the Sun around Galactic Center Stellar Kinematics Reveal Groups of Stars with Common Space Motion (Moving
Great Observatories Galactic Center Region Image Unveiling Science Telecon. October 6, 2009
 Great Observatories Galactic Center Region Image Unveiling Science Telecon October 6, 2009 1 Multiwavelength Observations Dr. Frank Summers 2 3 4 Support Web Site http://hubblesource.stsci.edu/events/iyafinale/support/
Great Observatories Galactic Center Region Image Unveiling Science Telecon October 6, 2009 1 Multiwavelength Observations Dr. Frank Summers 2 3 4 Support Web Site http://hubblesource.stsci.edu/events/iyafinale/support/
Science with the New Hubble Instruments. Ken Sembach STScI Hubble Project Scientist
 Science with the New Hubble Instruments Ken Sembach STScI Hubble Project Scientist 1 Hubble Has Improved Over Time Servicing missions have improved Hubble s vision. Hubble sees farther and with greater
Science with the New Hubble Instruments Ken Sembach STScI Hubble Project Scientist 1 Hubble Has Improved Over Time Servicing missions have improved Hubble s vision. Hubble sees farther and with greater
ASTR Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
 ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
ASTR 1120-001 Midterm 2 Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson SECOND MID-TERM EXAM MARCH 21 st 2006: Closed books and notes, 1 hour. Please PRINT your name and student ID on the places provided on the scan sheet.
Outline. Stellar Explosions. Novae. Death of a High-Mass Star. Binding Energy per nucleon. Nova V838Mon with Hubble, May Dec 2002
 Outline Novae (detonations on the surface of a star) Supernovae (detonations of a star) The Mystery of Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) Sifting through afterglows for clues! Stellar Explosions Novae Nova V838Mon
Outline Novae (detonations on the surface of a star) Supernovae (detonations of a star) The Mystery of Gamma Ray Bursts (GRBs) Sifting through afterglows for clues! Stellar Explosions Novae Nova V838Mon
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
The Formation of Stars
 The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
The Formation of Stars A World of Dust The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful objects in the sky. We are interested
Exploring the Depths of the Universe
 Exploring the Depths of the Universe Jennifer Lotz Hubble Science Briefing Jan. 16, 2014 Hubble is now observing galaxies 97% of the way back to the Big Bang, during the first 500 million years 2 Challenge:
Exploring the Depths of the Universe Jennifer Lotz Hubble Science Briefing Jan. 16, 2014 Hubble is now observing galaxies 97% of the way back to the Big Bang, during the first 500 million years 2 Challenge:
Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Observing the Night Sky. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Constellations are groups of stars named over antiquity. A familiar constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. Chapter 29 THE UNIVERSE The monthly
Supernova events and neutron stars
 Supernova events and neutron stars So far, we have followed stellar evolution up to the formation of a C-rich core. For massive stars ( M initial > 8 M Sun ), the contracting He core proceeds smoothly
Supernova events and neutron stars So far, we have followed stellar evolution up to the formation of a C-rich core. For massive stars ( M initial > 8 M Sun ), the contracting He core proceeds smoothly
The physics of stars. A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure.
 Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
The electrons then interact with the surrounding medium, heat it up, and power the light curve. 56 Ni 56 Co + e (1.72 MeV) half life 6.
 Supernovae The spectra of supernovae fall into many categories (see below), but beginning in about 1985, astronomers recognized that there were physically, only two basic types of supernovae: Type Ia and
Supernovae The spectra of supernovae fall into many categories (see below), but beginning in about 1985, astronomers recognized that there were physically, only two basic types of supernovae: Type Ia and
Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and. Supernovae. Welcome! On the back table:
 Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and Welcome! On the back table: Supernovae Lecture notes for today s s lecture Extra copies of last week s s are on the back table Sign-up sheets please fill one out only
Compton Lecture #4: Massive Stars and Welcome! On the back table: Supernovae Lecture notes for today s s lecture Extra copies of last week s s are on the back table Sign-up sheets please fill one out only
Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330
 The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
The Evolving ISM in the Milky Way & Nearby Galaxies Ram Pressure Stripping in NGC 4330 Anne Abramson 1 & Jeffrey D. P. Kenney 1 1 Astronomy Department, Yale University, P.O. Box 208101 New Haven, CT 06520-8101
Chapter 19: Our Galaxy
 Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
Chapter 19 Lecture Chapter 19: Our Galaxy Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed Our goals for learning: What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? What does our galaxy look like?
The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science
 The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science Margaret Meixner (STScI) Xander Tielens (NASA/Ames/Leiden Univ.), Jesse Dotson (NASA/ARC), Bruce Draine (Princeton), Mark Wolfire (U. Maryland), Jackie
The Interstellar Medium in Galaxies: SOFIA Science Margaret Meixner (STScI) Xander Tielens (NASA/Ames/Leiden Univ.), Jesse Dotson (NASA/ARC), Bruce Draine (Princeton), Mark Wolfire (U. Maryland), Jackie
PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B
 Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
Astrophysics, Vol. 56, No. 2, June, 2013 PMS OBJECTS IN THE STAR FORMATION REGION Cep OB3. II. YOUNG STELLAR OBJECTS IN THE Ha NEBULA Cep B E. H. Nikoghosyan Models for the spectral energy distributions
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Cepheid Distance Measurement. Clusters of Galaxies. The Nature of Galaxies
 Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
Big Galaxies Are Rare! Potato Chip Rule: More small things than large things Big, bright spirals are easy to see, but least common Dwarf ellipticals & irregulars are most common Faint, hard to see Mostly
High Energy Astrophysics
 High Energy Astrophysics Supernovae and their Remnants 2/2 Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk March 2012 Supernovae and their
High Energy Astrophysics Supernovae and their Remnants 2/2 Giampaolo Pisano Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics - University of Manchester giampaolo.pisano@manchester.ac.uk March 2012 Supernovae and their
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
galaxies: individual: NGC 6946 galaxies: spiral galaxies:
 Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
Baltic Astronomy, vol. 25, 369 376, 2016 UNUSUAL OBJECTS IN THE SPIRAL GALAXY NGC 6946 Yu. N. Efremov Sternberg Astronomical Institute, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Universitetskij pr. 13,
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017 Team Name: Team Number: Directions: ~Answer all questions on the answer sheet provided. ~Please do NOT access the
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event Golden Gate Invitational February 11, 2017 Team Name: Team Number: Directions: ~Answer all questions on the answer sheet provided. ~Please do NOT access the
Shock Waves. = 0 (momentum conservation)
 PH27: Aug-Dec 2003 Shock Waves A shock wave is a surface of discontinuity moving through a medium at a speed larger than the speed of sound upstream. The change in the fluid properties upon passing the
PH27: Aug-Dec 2003 Shock Waves A shock wave is a surface of discontinuity moving through a medium at a speed larger than the speed of sound upstream. The change in the fluid properties upon passing the
Physics HW Set 3 Spring 2015
 1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
1) If the Sun were replaced by a one solar mass black hole 1) A) life here would be unchanged. B) we would still orbit it in a period of one year. C) all terrestrial planets would fall in immediately.
Discovery of TeV Gamma-ray Emission Towards Supernova Remnant SNR G Last Updated Tuesday, 30 July :01
 Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
Background-subtracted gamma-ray count map of SNR G78.2+2.1 showing the VERITAS detection (VER2019+407). For details, see Figure 1 below. Reference: E. Aliu et al. (The VERITAS Collaboration), Astrophysical
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Aug 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Aug 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Aug 2011](/thumbs/91/107461239.jpg) Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Overionization in X-ray spectra: a new paradigm for Mixed-Morphology SNRs arxiv:1108.5544v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Aug 2011 M. Miceli 1,2 1 Dipartimento di
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 282 c SAIt 2008 Memorie della Overionization in X-ray spectra: a new paradigm for Mixed-Morphology SNRs arxiv:1108.5544v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Aug 2011 M. Miceli 1,2 1 Dipartimento di
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)
 This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
This class: Life cycle of high mass stars Supernovae Neutron stars, pulsars, pulsar wind nebulae, magnetars Quark-nova stars Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs)!1 Cas$A$ All$Image$&$video$credits:$Chandra$X7ray$ Observatory$
Physics Homework Set 2 Sp 2015
 1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
1) A large gas cloud in the interstellar medium that contains several type O and B stars would appear to us as 1) A) a reflection nebula. B) a dark patch against a bright background. C) a dark nebula.
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Symbolically: E0.E7.. S0..Sa..Sb..Sc..Sd..Irr
 Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Normal Galaxies (Ch. 24) + Galaxies and Dark Matter (Ch. 25) Here we will cover topics in Ch. 24 up to 24.4, but then skip 24.4, 24.5 and proceed to 25.1, 25.2, 25.3. Then, if there is time remaining,
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 23. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
The Stars. Chapter 14
 The Stars Chapter 14 Great Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star s nuclear fuel is depleted, the star must burn out. Chapter Outline
The Stars Chapter 14 Great Idea: The Sun and other stars use nuclear fusion reactions to convert mass into energy. Eventually, when a star s nuclear fuel is depleted, the star must burn out. Chapter Outline
