PTOLEMY DAY 26 DETERMINATION OF STATIONS EPICYCLIC PROGRESSION PROOF:
|
|
|
- Blaze Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PTOLMY Y 26 TRMITIO O STTIOS PIYLI PRORSSIO PROO: iven: Prove: is our eye : > epicycle speed : speed and hence we can draw secant that ½ : = epicycle speed : speed is a random point on arc When the goes through arc, it is in PRORSSIO epicycle Join through to L (only for regression part later). Join,,. ow, > [closer to center] : > : [Lemma, ay 25] ½ : > : 2 i.e. epicycle speed : speed > : ut if we give ourselves an angle through which the epicycle moved in the same time that the moved through angle, then epicycle speed : speed = : hence >. (To adjust the disproportion to a proportion.) So, while the epicycle goes from to, the goes from to. So to our eye, the goes from to, which is PRORSSIO. Q
2 Incidentally, if 1 : 3 = : 60 [i.e. if the epicyclic speed is to the speed as 1 to 3, and = 60 ], then = 20, and we can t construct this without conics. nd if the epicycle speed is to the speed in me irrational ratio, then maybe we cannot construct at all. ut that s okay, because is not a math construction, but the angle swept out by point on the s epicycle in a given time, i.e. it is a physical reality. TRI PRORSSIO PROO: iven: Prove: H is our eye (and arc = arc, H joined) : > epicycle speed : speed ½ : = epicyclic speed : speed but ½ : = ½ H : H (by Lemma, ay 25) ½ H : H = epicyclic speed : speed = L : ½ H + H : H = L + : ½ : H = L + : i.e. ½ : H = eccentric speed : speed is a random point on arc. When the goes through arc, it is in PRORSSIO. L M H (eye) eccentric Join through to L, H through to M. Since H is the harmonic point for secants from (since arc = arc), thus arc L = arc M thus arc L = arc M. ow < : > : [Lemma, ay 25] 192
3 + : > + : i.e. : > L : [uc. 1.32] H : H > L : [: = H:H, Thm p.394] or H : H > M : [arcl = arcm] H : H > M : [, on same arc ] H + H : H > M + : i.e. : H > H : [uc. 1.32] ½ : H > H : 2 ½ : H > H : [angle at center is double] ut, by our givens, ½ : H = eccentric speed : speed and therefore eccentric speed : speed > H :. So if it follows eccentric speed : speed = H :, H > H. ut the eye is at H. Therefore, while the goes from to on the eccentric, in the same time the eccentric circle itself goes from to, and thus the appears to go from to, which is PRORSSIO. Q... L M H (eye) eccentric ' OT: The outer circle is drawn just to indicate the motion of the eccentric LM around point H, i.e. from to. 193
4 PIYLI & TRI RRSSIO PIYLI RRSSIO PROO: L iven: is our eye : > epicycle speed : speed and hence we can draw secant L that ½ L : = epicycle speed : speed is a random point on arc epicycle Prove: When the goes through arc, it is in RRSSIO i.e. it retrogrades through during the time it goes through arc Well, > L : < : L [Lemma, ay 25] ½ L : < : 2 L ½ L : < : thus epic.spd : spd. < : [½L : is as speeds] So if we replace with as to make the ratios equal, then and > epic.spd : spd. = : So in the same time that the epicycle progresses through angle, the will sweep out angle around the center of the epicycle, that the s net motion will be from to, i.e. angle to our eye, which is RRSSIO. Hence, too, if we replace with X to make the ratios equal (p. : Star = X : ), then X <, and in time goes from to, epicycle goes less than, hence the is regressing. Q... Q: Why give that : > ep. :? (Otherwise we can t draw the secant.) Q: What if spd. = zero? (The planet is always in progression.) Q: What if ep. spd. = zero? ( Stations are at the tangent points!) Q: What if : = ep. :? (One station at.) Q: What if : < ep. :? (o stations; all progression.) xercise: In a diagram, correlate (with letters) the planet s zig-zag (or loop) pattern in the sky with the places the is on the epicycle. 194
5 TRI RRSSIO PROO: iven: Prove: H is our eye ½ M : H = eccentric spd. : spd. (the unseparated ratio corresponding to ½ L : for the epicyclic) is a random point on arc When the goes through arc, it is in RRSSIO. Well, L : < : L [as before, for epicycle, above] L + : < + L : L L : < L : L [uc.1.32] MH : H < L : L [p.394] MH + H : H < L + L : L M : H < M + M : L i.e. M : H < H : L [uc.1.32, r HM] L ½ M : H < H : 2 L ecc.spd : spd < H : H M So if we replace with as to make the ratios equal then and > : ecc.spd : spd. = H : eccentric So in the same time that the eccentric progresses through angle H, the will sweep out angle around the center of the eccentric, that the s net motion will be from to, i.e. angle H to our eye, which is RRSSIO. Q
6 OT: If : is not greater than e : s, then either : = e : s, in which case you get one station at, or : < e : s, and we get no station at all, because, given the foregoing proofs, progression will always produce the greater angle, and therefore we get nothing but progression. L M eccentric H 196
7 OSTRUTIO O TH STTIO POIT. P an we construct the station points? iven our eye is at, and given an epicycle with center, radius, and given that : > epicycle speed : speed can we construct the line that ½ : = epicycle speed : speed? We could employ me rt of edekindian postulate, and say to ourselves the ratio of the half of the intercepted segment to the external segment decreases continuously as goes away from, there must be a place in between where the proportion holds good. ut it turns out we can actually construct it. H iven: To do: e : s is a given ratio (expressed in numbers or lines) ind a secant that ½ : = e : s irst cut at H that H : H = e : s [uc.6.10] ext, describe a circle on H as diameter, cutting circle at. escribe a circle on as diameter. ow join, cutting the circle on at P, and cutting circle at. Join P. Join H. ow, P is 90 [angle in a semicircle] and H is 90 [angle in a semicircle] P is parallel to H P : = H : H P : = e : s [we cut H : H = e : s] ut P is perpendicular to P, and is the center, hence P = P, hence P = ½ ½ : = e : s Q
8 PORISM: Since the construction is possible only if the circle on H cuts the circle, H must be inside circle, and therefore : > H : H, i.e. : > e : s, and hence this is a condition for the possibility of the construction. WIT SO WHR S TH QUT? Ptolemy appears to have ignored the equant, and even the eccentricity of the deferent, for these initial demonstrations. That is, he assumes that the center of the epicycle makes its mean movement about, our eye, when in fact it does not. This is because he is far only considering the matter abstractly and in the simplest case. It is only in h. 2 that he begins to study the particular planets, and to apply the general theorem to the model for Saturn (for example), to find out where it makes stations, how long it should spend in regression (depending on the place in the zodiac etc.). irst he takes it at its mean distance, where the mean movements in longitude and anomaly will be very nearly the same as the apparent movements. So that is like the ideal case already done, but with the particular numbers for Saturn s speeds in L and. He finds the angle about the center of the epicycle subtending the semi-arc of the regression, and from knowing the mean speed in anomaly (by the tables generated from the periodic joint returns), he knows the time it takes Saturn to move through double that angle, and figures the regression, when Saturn s epicycle is at its mean distance from arth, should take about 138 days. HOW O RTH I THY IUR THIS OUT? How did Ptolemy s predecesrs discover this rule for where station occurs? One way could be by observations. We can observe the at station () at a given time. nowing when it is at station, by our tables of planetary motion, we can al know how far the has gone from its last time at apogee, i.e. we know. y planetary theory, we know the magnitude of the epicycle, i.e. we know :. Since we know, we know its supplement,. Hence we know and the ratio :, and therefore r is lved, and all its sides and angles are known. Therefore we al know, and too its supplement,. ut =, and hence =, and we know, i.e.. Thus we know [from r ] and we know [by uc.1.32] and we know the ratio : [the magnitude of the epicycle] and therefore r is lved, and all its sides and angles are known. Therefore we know : [from r ] and we know : [from r ] that, putting in the same terms for each ratio, we know : we know : as well, i.e. : is given. P 198
9 omparing this value (for each planet) to the ratio of the epicycle s speed to the s speed, we notice in each case that ½ : = epicycle speed : speed IM LITR. ut since it is very difficult (or impossible) to observe a station accurately, i.e. to say exactly when a is at station (since it is really just an instant in time, and just seems longer because the planet is moving slowly for a while on either side of station), this is not likely to be the way the ancients discovered the rule. Perhaps they discovered it by beginning with a simple case, e.g. when there is only 1 station, namely at P, perigee, and by thinking (if this is not anachronistic to say) ewton-style. We know that if a station occurs at P, then the speed of the and of the epicycle must be such that, as we take equal arcs P, P smaller and smaller, T P arc ep. speed : speed u = : sp. speed : speed u = : P sp. speed : speed u = : P P P P sp. speed : speed u = P : arcp P (chords ult. as arcs) ( : = P :, and P = P) (ratio of inverses) ep.speed : speed = P : P since is ultimately equal to P, and since (the ratio P : P being fixed, and that of the speeds al being a fixed ratio) there is no longer any rean to say ultimately. ut P is half of PT. So this might lead to suspicion that this is an instance of a general rule, which could easily be verified by a procedure like the one above, looking to a pair of symmetrical stations, instead of just one of them at P. QUSTIO: oes the TULLY sit still in space (i.e. have an instantaneous velocity of zero)? Or does it just appear to be still, when in fact it is heading right for us or straight away from us? In the simple case of one station, where it happens at perigee, it seems to be a real standstill. ut maybe not in the more general case. 199
PTOLEMY DAY 25. Let s look to some old raw data about Saturn s retrograde motions, of the sort that Ptolemy would have had available to him.
 PTOLMY DY 25 We are now moving on to material which Ptolemy covers in ook 12 of the lmagest: stations. We want to be able to predict stations, and to say exactly where the planet is on its epicycle when
PTOLMY DY 25 We are now moving on to material which Ptolemy covers in ook 12 of the lmagest: stations. We want to be able to predict stations, and to say exactly where the planet is on its epicycle when
PTOLEMY DAY 24 FINDING VENUS S EQUANT CENTER; BASICS FOR THE OUTER PLANETS; THE MOVING ECCENTRIC EQUIVALENCE
 PTOMY Y 24 ININ VNUS S QUNT NTR; SIS OR T OUTR PNTS; T MOVIN NTRI QUIVN ININ VNUS S QUNT NTR Ptolemy opens lmagest.3 with the line Since it is not clear whether the regular movement of the epicycle is
PTOMY Y 24 ININ VNUS S QUNT NTR; SIS OR T OUTR PNTS; T MOVIN NTRI QUIVN ININ VNUS S QUNT NTR Ptolemy opens lmagest.3 with the line Since it is not clear whether the regular movement of the epicycle is
PTOLEMY DAY 22 PERIODIC JOINT RETURNS; THE EQUANT
 PTOLMY DAY 22 PRIODIC JOINT RTURNS; TH QUANT We want to get the least periodic joint returns for the 5 planets that is, we want to be able to say, for a given planet, the number of times the epicycle goes
PTOLMY DAY 22 PRIODIC JOINT RTURNS; TH QUANT We want to get the least periodic joint returns for the 5 planets that is, we want to be able to say, for a given planet, the number of times the epicycle goes
If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen?
 A more in depth explanation from last week: If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen? The equator would be much hotter due to the direct sunlight which would lead to a lower survival rate and little
A more in depth explanation from last week: If Earth had no tilt, what else would happen? The equator would be much hotter due to the direct sunlight which would lead to a lower survival rate and little
9/12/2010. The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature. 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force
 The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force The Universe is made of matter Gravity the force of attraction between matter
The Four Fundamental Forces of Nature 1. Gravity 2. Electromagnetism 3. The Strong Nuclear Force 4. The Weak Nuclear Force The Universe is made of matter Gravity the force of attraction between matter
Ancient Astronomy. Lectures 5-6. Course website:
 Ancient Astronomy Lectures 5-6 Course website: www.scs.fsu.edu/~dduke/lectures Lectures 5-6 Almagest Books 9 13 geocentric vs. heliocentric point of view the wandering stars, or planets the two anomalies
Ancient Astronomy Lectures 5-6 Course website: www.scs.fsu.edu/~dduke/lectures Lectures 5-6 Almagest Books 9 13 geocentric vs. heliocentric point of view the wandering stars, or planets the two anomalies
Honors Geometry Circle Investigation - Instructions
 Honors Geometry ircle Investigation - Instructions 1. On the first circle a. onnect points and O with a line segment. b. onnect points O and also. c. Measure O. d. Estimate the degree measure of by using
Honors Geometry ircle Investigation - Instructions 1. On the first circle a. onnect points and O with a line segment. b. onnect points O and also. c. Measure O. d. Estimate the degree measure of by using
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws
 Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Observational Astronomy - Lecture 4 Orbits, Motions, Kepler s and Newton s Laws Craig Lage New York University - Department of Physics craig.lage@nyu.edu February 24, 2014 1 / 21 Tycho Brahe s Equatorial
Circles. II. Radius - a segment with one endpoint the center of a circle and the other endpoint on the circle.
 Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
Circles Circles and Basic Terminology I. Circle - the set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point (called the center) in the plane. Circles are named by their center. II.
PTOLEMY DAY 16 THE BASICS OF SOLAR THEORY: THE SOLAR PERIOD AND ITS REGULAR AND IRREGULAR MOVEMENT
 PTOLEMY DAY 16 THE BASICS OF SOLAR THEORY: THE SOLAR PERIOD AND ITS REGULAR AND IRREGULAR MOVEMENT We are now in Book 3 of the Almagest. We ve spent a lot of time on Earth. Now it s time to begin studying
PTOLEMY DAY 16 THE BASICS OF SOLAR THEORY: THE SOLAR PERIOD AND ITS REGULAR AND IRREGULAR MOVEMENT We are now in Book 3 of the Almagest. We ve spent a lot of time on Earth. Now it s time to begin studying
RETROGRADE MOTION AND PLANETARY ORBITS Computer Simulations
 RETROGRADE MOTION AND PLANETARY ORBITS Computer Simulations OBJECTIVE: To see planetary orbits simulated on a computer and to see how this suncentered model explains retrograde motion. Initial Procedure:
RETROGRADE MOTION AND PLANETARY ORBITS Computer Simulations OBJECTIVE: To see planetary orbits simulated on a computer and to see how this suncentered model explains retrograde motion. Initial Procedure:
Chapter 2 The Science of Life in the Universe
 In ancient times phenomena in the sky were not understood! Chapter 2 The Science of Life in the Universe The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
In ancient times phenomena in the sky were not understood! Chapter 2 The Science of Life in the Universe The Ancient Greeks The Scientific Method Our ideas must always be consistent with our observations!
Math & 8.7 Circle Properties 8.6 #1 AND #2 TANGENTS AND CHORDS
 Math 9 8.6 & 8.7 Circle Properties 8.6 #1 AND #2 TANGENTS AND CHORDS Property #1 Tangent Line A line that touches a circle only once is called a line. Tangent lines always meet the radius of a circle at
Math 9 8.6 & 8.7 Circle Properties 8.6 #1 AND #2 TANGENTS AND CHORDS Property #1 Tangent Line A line that touches a circle only once is called a line. Tangent lines always meet the radius of a circle at
MODELS OF PLANETARY MOTION The first anomaly
 MODELS OF PLANETARY MOTION The first anomaly The guiding principle of ancient astronomy a principle that guided early European astronomers as well was uniform circular motion. It became the task of astronomy
MODELS OF PLANETARY MOTION The first anomaly The guiding principle of ancient astronomy a principle that guided early European astronomers as well was uniform circular motion. It became the task of astronomy
Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how many common tangents the circles have and draw them.
 Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 EQ: How can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Circle: Center: Radius: Chord: Diameter: Secant: Tangent: Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how
Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 EQ: How can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Circle: Center: Radius: Chord: Diameter: Secant: Tangent: Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how
cosmogony geocentric heliocentric How the Greeks modeled the heavens
 Cosmogony A cosmogony is theory about ones place in the universe. A geocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes Earth to be at the center of the universe. A heliocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes
Cosmogony A cosmogony is theory about ones place in the universe. A geocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes Earth to be at the center of the universe. A heliocentric cosmogony is a theory that proposes
Hipparchus of Rhodes.
 Hipparchus of Rhodes Hipparchus worked from about 160 to 130 B.C. He was a mathematician who used geometry to try to solve the problem of retrograde motion. http://universe-review.ca/i08-18-hipparchus.jpg
Hipparchus of Rhodes Hipparchus worked from about 160 to 130 B.C. He was a mathematician who used geometry to try to solve the problem of retrograde motion. http://universe-review.ca/i08-18-hipparchus.jpg
Comment on the Origin of the Equant papers by Evans, Swerdlow, and Jones
 Comment on the Origin of the Equant papers by Evans, Swerdlow, and Jones Dennis W Duke, Florida State University A 1984 paper by Evans 1, a 1979 paper by Swerdlow (published recently in revised form) 2,
Comment on the Origin of the Equant papers by Evans, Swerdlow, and Jones Dennis W Duke, Florida State University A 1984 paper by Evans 1, a 1979 paper by Swerdlow (published recently in revised form) 2,
Satellite Communications
 Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
Satellite Communications Lecture (3) Chapter 2.1 1 Gravitational Force Newton s 2nd Law: r r F = m a Newton s Law Of Universal Gravitation (assuming point masses or spheres): Putting these together: r
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS.
 ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
ARCS An ARC is any unbroken part of the circumference of a circle. It is named using its ENDPOINTS. A B X Z Y A MINOR arc is LESS than 1/2 way around the circle. A MAJOR arc is MORE than 1/2 way around
Circles and Volume. Circle Theorems. Essential Questions. Module Minute. Key Words. What To Expect. Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume
 Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume Circles and Volume There is something so special about a circle. It is a very efficient shape. There is no beginning, no end. Every point on the edge is the same
Analytical Geometry Circles and Volume Circles and Volume There is something so special about a circle. It is a very efficient shape. There is no beginning, no end. Every point on the edge is the same
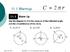
C=2πr C=πd. Chapter 10 Circles Circles and Circumference. Circumference: the distance around the circle
 10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
10.1 Circles and Circumference Chapter 10 Circles Circle the locus or set of all points in a plane that are A equidistant from a given point, called the center When naming a circle you always name it by
Chapter 10. Properties of Circles
 Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect Circles
 Name ate lass STION 11 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect ircles ind these vocabulary words in Lesson 11-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary interior of a circle exterior
Name ate lass STION 11 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 11-1 Lines That Intersect ircles ind these vocabulary words in Lesson 11-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary interior of a circle exterior
Lecture #5: Plan. The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo
 Lecture #5: Plan The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo Geocentric ( Ptolemaic ) Model Retrograde Motion: Apparent backward (= East-to-West) motion of a planet with respect to stars Ptolemy
Lecture #5: Plan The Beginnings of Modern Astronomy Kepler s Laws Galileo Geocentric ( Ptolemaic ) Model Retrograde Motion: Apparent backward (= East-to-West) motion of a planet with respect to stars Ptolemy
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1
 Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
Astronomy 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 1 Chapter 1 1. A scientific hypothesis is a) a wild, baseless guess about how something works. b) a collection of ideas that seems to explain
How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos?
 Remember to check the links for videos! How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos? Universe ~ 13.7 bya First Stars ~ 13.3 bya First Galaxies ~ 12.7
Remember to check the links for videos! How does the solar system, the galaxy, and the universe fit into our understanding of the cosmos? Universe ~ 13.7 bya First Stars ~ 13.3 bya First Galaxies ~ 12.7
Most of the time during full and new phases, the Moon lies above or below the Sun in the sky.
 6/16 Eclipses: We don t have eclipses every month because the plane of the Moon s orbit about the Earth is different from the plane the ecliptic, the Earth s orbital plane about the Sun. The planes of
6/16 Eclipses: We don t have eclipses every month because the plane of the Moon s orbit about the Earth is different from the plane the ecliptic, the Earth s orbital plane about the Sun. The planes of
What is the longest chord?.
 Section: 7-6 Topic: ircles and rcs Standard: 7 & 21 ircle Naming a ircle Name: lass: Geometry 1 Period: Date: In a plane, a circle is equidistant from a given point called the. circle is named by its.
Section: 7-6 Topic: ircles and rcs Standard: 7 & 21 ircle Naming a ircle Name: lass: Geometry 1 Period: Date: In a plane, a circle is equidistant from a given point called the. circle is named by its.
April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
 11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
11.1 Warmup April 28, 2017 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length 1 Geometry 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length mbhaub@mpsaz.org 11.1 Essential Question How can you find the length of a circular arc?
Chapter-wise questions
 hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
hapter-wise questions ircles 1. In the given figure, is circumscribing a circle. ind the length of. 3 15cm 5 2. In the given figure, is the center and. ind the radius of the circle if = 18 cm and = 3cm
1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle.
 Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
Master 8.17 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1 Properties of Tangents to a Circle 1. Draw and label a diagram to illustrate the property of a tangent to a circle. 2. Point O is the centre of the circle. Points
What is a Satellite? A satellite is an object that orbits another object. Ex. Radio satellite, moons, planets
 Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
Planetary Orbit Planetary Orbits What shape do planets APPEAR to orbit the sun? Planets APPEAR to orbit in a circle. What shape do the planets orbit the sun??? Each planet Orbits the Sun in an ellipse
The Heliocentric Model of Copernicus
 Celestial Mechanics The Heliocentric Model of Copernicus Sun at the center and planets (including Earth) orbiting along circles. inferior planets - planets closer to Sun than Earth - Mercury, Venus superior
Celestial Mechanics The Heliocentric Model of Copernicus Sun at the center and planets (including Earth) orbiting along circles. inferior planets - planets closer to Sun than Earth - Mercury, Venus superior
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet
 Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Circle geometry investigation: Student worksheet http://topdrawer.aamt.edu.au/geometric-reasoning/good-teaching/exploringcircles/explore-predict-confirm/circle-geometry-investigations About these activities
Days of the week: - named after 7 Power (moving) objects in the sky (Sun, Moon, 5 planets) Models of the Universe:
 Motions of the Planets ( Wanderers ) Planets move on celestial sphere - change RA, Dec each night - five are visible to naked eye Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn Days of the week: - named after 7
Motions of the Planets ( Wanderers ) Planets move on celestial sphere - change RA, Dec each night - five are visible to naked eye Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn Days of the week: - named after 7
Planets & The Origin of Science
 Planets & The Origin of Science Reading: Chapter 2 Required: Guided Discovery (p.44-47) Required: Astro. Toolbox 2-1 Optional: Astro. Toolbox 2-2, 2-3 Next Homework Due. Sept. 26 Office Hours: Monday,
Planets & The Origin of Science Reading: Chapter 2 Required: Guided Discovery (p.44-47) Required: Astro. Toolbox 2-1 Optional: Astro. Toolbox 2-2, 2-3 Next Homework Due. Sept. 26 Office Hours: Monday,
A Year Length Hidden in Ancient Planetary Mean Motions Dennis Duke, Florida State University
 A Year Length Hidden in Ancient Planetary Mean Motions Dennis Duke, Florida State University The mean motions in anomaly for the five planets as determined in the Almagest are all too small. The differences
A Year Length Hidden in Ancient Planetary Mean Motions Dennis Duke, Florida State University The mean motions in anomaly for the five planets as determined in the Almagest are all too small. The differences
MT EDUCARE LTD. MATHEMATICS SUBJECT : Q L M ICSE X. Geometry STEP UP ANSWERSHEET
 IS X MT UR LT. SUJT : MTHMTIS Geometry ST U NSWRSHT 003 1. In QL and RM, LQ MR [Given] LQ RM [Given] QL ~ RM [y axiom of similarity] (i) Since, QL ~ RM QL M L RM QL RM L M (ii) In QL and RQ, we have Q
IS X MT UR LT. SUJT : MTHMTIS Geometry ST U NSWRSHT 003 1. In QL and RM, LQ MR [Given] LQ RM [Given] QL ~ RM [y axiom of similarity] (i) Since, QL ~ RM QL M L RM QL RM L M (ii) In QL and RQ, we have Q
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday October Problem Set 3
 The CETRE for EDUCTI in MTHEMTICS and CMPUTIG Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday ctober 24 2012 Problem Set 3.. Unless otherwise stated, any point labelled is assumed to represent the centre of the circle.
The CETRE for EDUCTI in MTHEMTICS and CMPUTIG Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday ctober 24 2012 Problem Set 3.. Unless otherwise stated, any point labelled is assumed to represent the centre of the circle.
Circles in Neutral Geometry
 Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS
 Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
Exercise 4.0 PLANETARY ORBITS AND CONFIGURATIONS I. Introduction The planets revolve around the Sun in orbits that lie nearly in the same plane. Therefore, the planets, with the exception of Pluto, are
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy
 PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
PHYS 155 Introductory Astronomy - observing sessions: Sunday Thursday, 9pm, weather permitting http://www.phys.uconn.edu/observatory - Exam - Tuesday March 20, - Review Monday 6:30-9pm, PB 38 Marek Krasnansky
PTOLEMY DAY 10 PREPARING TO FIND OTHER ARCS BETWEEN THE ECLIPTIC AND EQUATOR. You might have noticed that in Day 9, when we found the arc
 PTOLEMY DAY 10 PREPARING TO FIND OTHER ARS BETWEEN THE ELIPTI AND EQUATOR You might have noticed that in Day 9, when we found the arc D between the tropics, we made no use of our table of chords. We simply
PTOLEMY DAY 10 PREPARING TO FIND OTHER ARS BETWEEN THE ELIPTI AND EQUATOR You might have noticed that in Day 9, when we found the arc D between the tropics, we made no use of our table of chords. We simply
Astronomy Notes Chapter 02.notebook April 11, 2014 Pythagoras Aristotle geocentric retrograde motion epicycles deferents Aristarchus, heliocentric
 Around 2500 years ago, Pythagoras began to use math to describe the world around him. Around 200 years later, Aristotle stated that the Universe is understandable and is governed by regular laws. Most
Around 2500 years ago, Pythagoras began to use math to describe the world around him. Around 200 years later, Aristotle stated that the Universe is understandable and is governed by regular laws. Most
What was once so mysterious about planetary motion in our sky? We see apparent retrograde motion when we pass by a planet
 What was once so mysterious about planetary motion in our sky? Planets usually move slightly eastward from night to night relative to the stars. You cannot see this motion on a single night. But sometimes
What was once so mysterious about planetary motion in our sky? Planets usually move slightly eastward from night to night relative to the stars. You cannot see this motion on a single night. But sometimes
Introduction To Modern Astronomy II
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy II Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
18. Kepler as a young man became the assistant to A) Nicolaus Copernicus. B) Ptolemy. C) Tycho Brahe. D) Sir Isaac Newton.
 Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
Name: Date: 1. The word planet is derived from a Greek term meaning A) bright nighttime object. B) astrological sign. C) wanderer. D) nontwinkling star. 2. The planets that were known before the telescope
The first term involves the cross product of two parallel vectors and so it vanishes. We then get
 Physics 3550 Angular Momentum. Relevant Sections in Text: 3.4, 3.5 Angular Momentum You have certainly encountered angular momentum in a previous class. The importance of angular momentum lies principally
Physics 3550 Angular Momentum. Relevant Sections in Text: 3.4, 3.5 Angular Momentum You have certainly encountered angular momentum in a previous class. The importance of angular momentum lies principally
Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles
 Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles Inscribed angles have: Vertex on the circle Sides are chords (Chords AB and BC) Angle ABC is inscribed in the circle AC is the intercepted arc because it is created
Arcs and Inscribed Angles of Circles Inscribed angles have: Vertex on the circle Sides are chords (Chords AB and BC) Angle ABC is inscribed in the circle AC is the intercepted arc because it is created
Solve problems involving tangents to a circle. Solve problems involving chords of a circle
 8UNIT ircle Geometry What You ll Learn How to Solve problems involving tangents to a circle Solve problems involving chords of a circle Solve problems involving the measures of angles in a circle Why Is
8UNIT ircle Geometry What You ll Learn How to Solve problems involving tangents to a circle Solve problems involving chords of a circle Solve problems involving the measures of angles in a circle Why Is
Unit 10 Geometry Circles. NAME Period
 Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
Unit 10 Geometry Circles NAME Period 1 Geometry Chapter 10 Circles ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (10-1) Circles and Circumference
Alien Skies. Todd Timberlake
 Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
Alien Skies Todd Timberlake Have you ever wanted to send your students to another planet? What would they see while looking up at the skies from their new home? Would they be able to interpret what they
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry
 Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com Core Mathematics 2 Coordinate Geometry 1 Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane Coordinate geometry of the circle
The Science of Astronomy - Copernicus, Tycho, and Kepler. Reminder to take out your clicker and turn it on!
 The Science of Astronomy - Copernicus, Tycho, and Kepler Reminder to take out your clicker and turn it on! Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) here? hear? hear, hear! Clicker Registration
The Science of Astronomy - Copernicus, Tycho, and Kepler Reminder to take out your clicker and turn it on! Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) here? hear? hear, hear! Clicker Registration
ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS
 ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS A1.1. Kepler s laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered the laws of orbital motion, now called Kepler's laws.
ANNEX 1. DEFINITION OF ORBITAL PARAMETERS AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS OF CELESTIAL MECHANICS A1.1. Kepler s laws Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) discovered the laws of orbital motion, now called Kepler's laws.
+ 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 if S
 CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
CIRCLE DEFINITIONS A circle is the locus of a point which moves in such a way that its distance from a fixed point, called the centre, is always a constant. The distance r from the centre is called the
Today. Review. Momentum and Force Consider the rate of change of momentum. What is Momentum?
 Today Announcements: HW# is due Wednesday 8:00 am. HW#3 will be due Wednesday Feb.4 at 8:00am Review and Newton s 3rd Law Gravity, Planetary Orbits - Important lesson in how science works and how ultimately
Today Announcements: HW# is due Wednesday 8:00 am. HW#3 will be due Wednesday Feb.4 at 8:00am Review and Newton s 3rd Law Gravity, Planetary Orbits - Important lesson in how science works and how ultimately
PHYS 106 Fall 2151 Homework 3 Due: Thursday, 8 Oct 2015
 PHYS 106 Fall 2151 Homework 3 Due: Thursday, 8 Oct 2015 When you do a calculation, show all your steps. Do not just give an answer. You may work with others, but the work you submit should be your own.
PHYS 106 Fall 2151 Homework 3 Due: Thursday, 8 Oct 2015 When you do a calculation, show all your steps. Do not just give an answer. You may work with others, but the work you submit should be your own.
Introduction To Modern Astronomy I
 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
ASTR 111 003 Fall 2006 Lecture 03 Sep. 18, 2006 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-17) Ch1: Astronomy and the Universe Ch2: Knowing the Heavens
11. Concentric Circles: Circles that lie in the same plane and have the same center.
 Circles Definitions KNOW THESE TERMS 1. Circle: The set of all coplanar points equidistant from a given point. 2. Sphere: The set of all points equidistant from a given point. 3. Radius of a circle: The
Circles Definitions KNOW THESE TERMS 1. Circle: The set of all coplanar points equidistant from a given point. 2. Sphere: The set of all points equidistant from a given point. 3. Radius of a circle: The
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle.
 Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
Edexcel New GCE A Level Maths workbook Circle. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Finding the Midpoint of a Line To work out the midpoint of line we need to find the halfway point Midpoint
6 The Orbit of Mercury
 6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION p. 1
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION p. 1 Motion involves a change in position. Position can be indicated by an x-coordinate on a number line. ex/ A bumblebee flies along a number line... x = 2 when t = 1 sec 2
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION p. 1 Motion involves a change in position. Position can be indicated by an x-coordinate on a number line. ex/ A bumblebee flies along a number line... x = 2 when t = 1 sec 2
Circles. Exercise 9.1
 9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
9 uestion. Exercise 9. How many tangents can a circle have? Solution For every point of a circle, we can draw a tangent. Therefore, infinite tangents can be drawn. uestion. Fill in the blanks. (i) tangent
Circular Motion.
 1 Circular Motion www.njctl.org 2 Topics of Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Kinematics of UCM Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency, and Rotational Velocity Dynamics of UCM Vertical
1 Circular Motion www.njctl.org 2 Topics of Uniform Circular Motion (UCM) Kinematics of UCM Click on the topic to go to that section Period, Frequency, and Rotational Velocity Dynamics of UCM Vertical
Physics 107 Ideas of Modern Physics (uw.physics.wisc.edu/~rzchowski/phy107) Goals of the course. What will we cover? How do we do this?
 Physics 107 Ideas of Modern Physics (uw.physics.wisc.edu/~rzchowski/phy107) Main emphasis is Modern Physics: essentially post-1900 Why 1900? Two radical developments: Relativity & Quantum Mechanics Both
Physics 107 Ideas of Modern Physics (uw.physics.wisc.edu/~rzchowski/phy107) Main emphasis is Modern Physics: essentially post-1900 Why 1900? Two radical developments: Relativity & Quantum Mechanics Both
Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion. Lecture 5 January 30, 2014
 Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Lecture 5 January 30, 2014 Parallax If distance is measured in parsecs then d = 1 PA Where PA is the parallax angle, in arcsec NOTE: The distance from the Sun to the Earth
Kepler s Laws of Orbital Motion Lecture 5 January 30, 2014 Parallax If distance is measured in parsecs then d = 1 PA Where PA is the parallax angle, in arcsec NOTE: The distance from the Sun to the Earth
Circles-Tangent Properties
 15 ircles-tangent roperties onstruction of tangent at a point on the circle. onstruction of tangents when the angle between radii is given. Tangents from an external point - construction and proof Touching
15 ircles-tangent roperties onstruction of tangent at a point on the circle. onstruction of tangents when the angle between radii is given. Tangents from an external point - construction and proof Touching
F = ma. G mm r 2. S center
 In the early 17 th century, Kepler discovered the following three laws of planetary motion: 1. The planets orbit around the sun in an ellipse with the sun at one focus. 2. As the planets orbit around the
In the early 17 th century, Kepler discovered the following three laws of planetary motion: 1. The planets orbit around the sun in an ellipse with the sun at one focus. 2. As the planets orbit around the
Assignment. Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to Circles. 1. For each term, name all of the components of circle Y that are examples of the term.
 ssignment ssignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to Circles 1. For each term, name all of the components of circle Y that are examples of the term. G R Y O T M a. Chord b.
ssignment ssignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to Circles 1. For each term, name all of the components of circle Y that are examples of the term. G R Y O T M a. Chord b.
DÉTERMINER L ORBITE DES COMÈTES
 NOUVELLE MÉTHODE POUR DÉTERMINER L ORBITE DES COMÈTES D APRES LES OBSERVATIONS Lagrange Connaissance des Temps... pour l an 181. (1818) Œuvres de Lagrange Tome 7 (1877) pp. 469 483 1. The methods that
NOUVELLE MÉTHODE POUR DÉTERMINER L ORBITE DES COMÈTES D APRES LES OBSERVATIONS Lagrange Connaissance des Temps... pour l an 181. (1818) Œuvres de Lagrange Tome 7 (1877) pp. 469 483 1. The methods that
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B
 PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
PHYS 160 Astronomy Test #1 Fall 2017 Version B 1 I. True/False (1 point each) Circle the T if the statement is true, or F if the statement is false on your answer sheet. 1. An object has the same weight,
Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus
 Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus On 3 June 1769 Captain Cook observed the Transit of Venus in Tahiti. The intention was to use the observations to obtain an accurate estimate of the distance
Scaling the Universe via a Transit of Venus On 3 June 1769 Captain Cook observed the Transit of Venus in Tahiti. The intention was to use the observations to obtain an accurate estimate of the distance
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016
 Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Mathematical spheres and solid globes
 ancient reek : Mathematical spheres and solid globes Nathan Sidoli (joint work with Ken Saito) I Paris, February 2010 Instrumental practices of reek geometry xamples of constructions in Practice s I I
ancient reek : Mathematical spheres and solid globes Nathan Sidoli (joint work with Ken Saito) I Paris, February 2010 Instrumental practices of reek geometry xamples of constructions in Practice s I I
Circles. Riding a Ferris Wheel. Take the Wheel. Manhole Covers. Color Theory. Solar Eclipses Introduction to Circles...
 Circles That s no moon. It s a picture of a solar eclipse in the making. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun. Scientists can predict when solar eclipses will happen
Circles That s no moon. It s a picture of a solar eclipse in the making. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun. Scientists can predict when solar eclipses will happen
14.1 Earth Satellites. The path of an Earth satellite follows the curvature of the Earth.
 The path of an Earth satellite follows the curvature of the Earth. A stone thrown fast enough to go a horizontal distance of 8 kilometers during the time (1 second) it takes to fall 5 meters, will orbit
The path of an Earth satellite follows the curvature of the Earth. A stone thrown fast enough to go a horizontal distance of 8 kilometers during the time (1 second) it takes to fall 5 meters, will orbit
10.1 Tangents to Circles. Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005
 10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
Introduction Circle Some terms related with a circle
 141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
Prentice Hall Geometry (c) 2007 correlated to American Diploma Project, High School Math Benchmarks
 I1.1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide integers, fractions and decimals. I1.2. Calculate and apply ratios, proportions, rates and percentages to solve problems. I1.3. Use the correct order of operations
I1.1. Add, subtract, multiply and divide integers, fractions and decimals. I1.2. Calculate and apply ratios, proportions, rates and percentages to solve problems. I1.3. Use the correct order of operations
Answers. Chapter10 A Start Thinking. and 4 2. Sample answer: no; It does not pass through the center.
 hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
hapter10 10.1 Start Thinking 6. no; is not a right triangle because the side lengths do not satisf the Pthagorean Theorem (Thm. 9.1). 1. (3, ) 7. es; is a right triangle because the side lengths satisf
Keplerian Elements Tutorial
 Keplerian Elements Tutorial This tutorial is based on the documentation provided with InstantTrack, written by Franklin Antonio, N6NKF. Satellite Orbital Elements are numbers that tell us the orbit of
Keplerian Elements Tutorial This tutorial is based on the documentation provided with InstantTrack, written by Franklin Antonio, N6NKF. Satellite Orbital Elements are numbers that tell us the orbit of
Learning Objectives. one night? Over the course of several nights? How do true motion and retrograde motion differ?
 Kepler s Laws Learning Objectives! Do the planets move east or west over the course of one night? Over the course of several nights? How do true motion and retrograde motion differ?! What are geocentric
Kepler s Laws Learning Objectives! Do the planets move east or west over the course of one night? Over the course of several nights? How do true motion and retrograde motion differ?! What are geocentric
WEEK 7 NOTES AND EXERCISES
 WEEK 7 NOTES AND EXERCISES RATES OF CHANGE (STRAIGHT LINES) Rates of change are very important in mathematics. Take for example the speed of a car. It is a measure of how far the car travels over a certain
WEEK 7 NOTES AND EXERCISES RATES OF CHANGE (STRAIGHT LINES) Rates of change are very important in mathematics. Take for example the speed of a car. It is a measure of how far the car travels over a certain
Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets
 Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets 1 Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets go around
Gravitation and the Motion of the Planets 1 Guiding Questions 1. How did ancient astronomers explain the motions of the planets? 2. Why did Copernicus think that the Earth and the other planets go around
ASTRO 6570 Lecture 1
 ASTRO 6570 Lecture 1 Historical Survey EARLY GREEK ASTRONOMY: Earth-centered universe - Some radical suggestions for a sun-centered model Shape of the Earth - Aristotle (4 th century BCE) made the first
ASTRO 6570 Lecture 1 Historical Survey EARLY GREEK ASTRONOMY: Earth-centered universe - Some radical suggestions for a sun-centered model Shape of the Earth - Aristotle (4 th century BCE) made the first
How big is the Universe and where are we in it?
 Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
Announcements Results of clicker questions from Monday are on ICON. First homework is graded on ICON. Next homework due one minute before midnight on Tuesday, September 6. Labs start this week. All lab
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION
 KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler culminated his analysis of the extensive data taken by Tycho Brahe and published his three laws of planetary motion, which we know
KEPLER S LAWS OF PLANETARY MOTION In the early 1600s, Johannes Kepler culminated his analysis of the extensive data taken by Tycho Brahe and published his three laws of planetary motion, which we know
Planetary motion around the Sun
 Planetary motion around the Sun Luciano Ancora Draft date February 25, 2016 Author s note This article is an example of essential synthesis (in only 7 pages) of the contents of an entire book of about
Planetary motion around the Sun Luciano Ancora Draft date February 25, 2016 Author s note This article is an example of essential synthesis (in only 7 pages) of the contents of an entire book of about
Riding a Ferris Wheel. Students should be able to answer these questions after Lesson 10.1:
 .1 Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Students should be able to answer these questions after Lesson.1: What are the parts of a circle? How are the parts of a circle drawn? Read Question 1 and
.1 Riding a Ferris Wheel Introduction to ircles Students should be able to answer these questions after Lesson.1: What are the parts of a circle? How are the parts of a circle drawn? Read Question 1 and
Chapter 4. The Origin Of Modern Astronomy. Is okay to change your phone? From ios to Android From Android to ios
 Chapter 4 The Origin Of Modern Astronomy Slide 14 Slide 15 14 15 Is Change Good or Bad? Do you like Homer to look like Homer or with hair? Does it bother you when your schedule is changed? Is it okay to
Chapter 4 The Origin Of Modern Astronomy Slide 14 Slide 15 14 15 Is Change Good or Bad? Do you like Homer to look like Homer or with hair? Does it bother you when your schedule is changed? Is it okay to
2) The number one million can be expressed in scientific notation as: (c) a) b) 10 3 c) 10 6 d)
 Astronomy Phys 181 Midterm Examination Choose the best answer from the choices provided. 1) What is the range of values that the coordinate Declination can have? (a) a) -90 to +90 degrees b) 0 to 360 degrees
Astronomy Phys 181 Midterm Examination Choose the best answer from the choices provided. 1) What is the range of values that the coordinate Declination can have? (a) a) -90 to +90 degrees b) 0 to 360 degrees
Physics Test 7: Circular Motion page 1
 Name Physics Test 7: Circular Motion page 1 hmultiple Choice Read each question and choose the best answer by putting the corresponding letter in the blank to the left. 1. The SI unit of angular speed
Name Physics Test 7: Circular Motion page 1 hmultiple Choice Read each question and choose the best answer by putting the corresponding letter in the blank to the left. 1. The SI unit of angular speed
Chapter 02 The Rise of Astronomy
 Chapter 02 The Rise of Astronomy Multiple Choice Questions 1. The moon appears larger when it rises than when it is high in the sky because A. You are closer to it when it rises (angular-size relation).
Chapter 02 The Rise of Astronomy Multiple Choice Questions 1. The moon appears larger when it rises than when it is high in the sky because A. You are closer to it when it rises (angular-size relation).
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall Prof. Peter Hirschfeld, Physics
 PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Prof. Peter Hirschfeld, Physics Announcements HW 1 due today; HW 2 posted, due Sept. 13 Lab 1 today 2
PHY1033C/HIS3931/IDH 3931 : Discovering Physics: The Universe and Humanity s Place in It Fall 2016 Prof. Peter Hirschfeld, Physics Announcements HW 1 due today; HW 2 posted, due Sept. 13 Lab 1 today 2
The Copernican Revolution
 The Copernican Revolution The Earth moves and Science is no longer common sense SC/NATS 1730, XII 1 Nicholas Copernicus 1473-1543 Studied medicine at University of Crakow Discovered math and astronomy.
The Copernican Revolution The Earth moves and Science is no longer common sense SC/NATS 1730, XII 1 Nicholas Copernicus 1473-1543 Studied medicine at University of Crakow Discovered math and astronomy.
Fundamentals of Satellite technology
 Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Fundamentals of Satellite technology Prepared by A.Kaviyarasu Assistant Professor Department of Aerospace Engineering Madras Institute Of Technology Chromepet, Chennai Orbital Plane All of the planets,
Wednesday, January 28
 Ptolemy to Copernicus Wednesday, January 28 Astronomy of the ancients Many ancient cultures took note of celestial objects and celestial lphenomena. They noted tdcertain ti patterns in the heavens and
Ptolemy to Copernicus Wednesday, January 28 Astronomy of the ancients Many ancient cultures took note of celestial objects and celestial lphenomena. They noted tdcertain ti patterns in the heavens and
