The Current Solar Minimum and Its Consequences for Climate
|
|
|
- Vanessa Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 11 The Current Solar and Its Consequences for Climate David Archibald Summa Development Limited Chapter Outline 1. Introduction The Current Summary INTRODUCTION A number of cycles in solar activity have been recognized, including the Schwabe (11 years), Hale (22 years), Gleissberg (88 years), de Vries (21 years), and Bond (1,47 years) cycles. There is nothing to suggest that cyclic behavior in solar activity has ceased for any reason. Therefore, predicting when the next minimum should occur should be as simple as counting forward from the last one. The last major minimum, the Dalton from 1798 to 1822, was two solar cycles long e Solar Cycles 5 and 6. Recent Gleissberg minima appear to be the decade 169e17, Solar Cycle 13 from 1889 to 191, and Solar Cycle 2 from 1964 to A de Vries cycle event, herein termed the Eddy, has started exactly 21 years after the start of the Dalton. Friis-Christensen and Lassen theory, using methodology pioneered by Butler and Johhnson at Armagh, can be used to predict the temperature response to the Eddy for individual climate stations with a high degree of confidence. The latitude of the US-Canadian border is expected to lose a month from its growing season with the potential for un-seasonal frosts to further reduce agricultural productivity. Evidence-Based Climate Science. DOI: 1.116/B Copyright Ó 211 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. 277
2 278 PART j IV Solar Activity 2. THE CURRENT MINIMUM As recently as 28, there was a wide range in estimated amplitudes for Solar Cycle 24, from Dikpati at 19 and Hathaway at 17 respectively to Clilverd (25) at 42 and Badalyan et al. (21) at 5. This enormous divergence in projections of solar activity generated very little interest from the climate science community, despite the large impact it would have on climate (Archibald, 26, 27). The basis of Clilverd s prediction was a model for sunspot number using low-frequency solar oscillations, with periods of 22, 53, 88, 16, 213, and 42 years modulating the 11-year Schwabe cycle. The model predicts a period of quiet solar activity lasting until approximately 23 followed by a recovery during the middle of the century to more typical solar activity cycles with peak sunspot numbers around 12. The graphs in Figs. 1e15 show data related to solar activity. Additional data may be found in Archibald (21). The Eddy (Fig. 1) has started 21 years after the start of the Dalton, consistent with it being a de Vries Cycle event. The graph in Fig. 2 shows that Solar Cycles 3 and 4, leading up to the Dalton, are very similar in amplitude and morphology to Solar Cycles 22 and 23, leading up to the current minimum. The two data sets are aligned on the month of transition between Solar Cycles 4 and 5 and between Solar Cycles 23 and 24. In the absence of a significant change in Total Solar Irradiance over the solar cycle, modulation of the Earth s climate by the changing flux in galactic cosmic Dalton Projected Eddy FIGURE 1 Solar cycle amplitude 171e245.
3 Chapter j 11 The Current Solar Solar Cycle 3 Solar Cycle 22 Solar Cycle 4 Solar Cycle 23 compared to Solar Cycle 4 Aligned on month of minimum Solar Cycle Amplitude Solar Cycle 23 May 21 Dalton Solar Cycle 5 Solar Cycle FIGURE 2 Similarity between precursor cycles Sporer Maunder Dalton Decreasing Galactic Cosmic Rays Little Ice Age Modern Warm Period FIGURE 3 Be 1 from the Dye 3 ice core, Greenland Plateau. rays was proposed by Svensmark and Friis-Christensen (1997). The Dye 3 Be 1 record (Fig.3) shows a correlation between spikes in Be 1 and cold periods for the last 6 years. It also shows a steep decline in Be 1 in the Modern Warm Period, suggesting a solar origin for this warming. Usokin et al. (25) found
4 28 PART j IV Solar Activity s cooling period Interplanetary Magnetic Field smoothed 27 day average 8 nanoteslas Solar Cycle 2 Solar Cycle 21 Solar Cycle 22 Solar Cycle FIGURE 4 Interplanetary Magnetic Field 1966e Solar Cycle 23 Solar Flux Units s Cooling Period Projection 5 F1.7 Flux FIGURE 5 F1.7 flux 1948e22. that the level of solar activity during the past 7 years is exceptional, and the previous period of equally high activity occurred more than 8, years ago. The strength of the Interplanetary Magnetic Field (Fig. 4) has fallen to levels below that of previous solar cycle transitions. What is also interesting in
5 Chapter j 11 The Current Solar aa Index s Cooling Period Increasing Solar Activity 5 Little Ice Age Modern Warm Period FIGURE 6 The aa Index 1868e21. Monthly Average Counts per Minute Oulu Neutron Count s Cooling Period 21/22 Solar 22/23 Solar 23/24 Solar Data: Sodankyla Geophysical Observatory FIGURE 7 Oulu, Finland neutron monitor count 196e21. this data is the flatness of this solar magnetic indicator during the 197s cooling period. The F1.7 index (Fig. 5) is a measure of the solar radio flux near the peak of the observed solar radio emission. Emission from the Sun at radio wavelengths
6 282 PART j IV Solar Activity FIGURE 8 The correlation between solar cycle length and mean annual temperature at Armagh, Northern Ireland. 1.6 Degrees Celsius Archangel, Russia rsq =.38 Correlation =.6 degrees/annum FIGURE 9 Solar Cycle Length Years Archangel, Russia e solar cycle length relative to average annual temperature.
7 Chapter j 11 The Current Solar Providence, Rhode Island rsq =.38 Degrees Celsius Correlation =.62 degrees/annum Solar Cycle Length Years FIGURE 1 Providence, Rhode Island e solar cycle length relative to average annual temperature Hanover, New Hampshire rsq =.53 Degrees Celsius Correlation =.73 degrees/annum Solar Cycle Length Years FIGURE 11 Hanover, New Hampshire e solar cycle length relative to average annual temperature.
8 284 PART j IV Solar Activity West Chester, Pennsylvania rsq =.29 Degree Celsius Correlation =.5 degrees/annum Solar Cycle Length Years FIGURE 12 West Chester, Pennsylvania e solar cycle length relative to average annual temperature Portland, Maine rsq = Degree Celsius Correlation =.7 degrees/annum Solar Cycle Length Years FIGURE 13 Portland, Maine e solar cycle length relative to average annual temperature. is due primarily to diffuse, non-radiative heating of coronal plasma trapped in the magnetic fields overlying active regions. It is the best indicator of overall solar activity levels and is not subject to observer bias in the way that the counting of sunspots is. The graph above shows the F1.7 flux from 1948 with
9 Chapter j 11 The Current Solar Solar Cycle Amplitude S.C. 24 S.C. 25 Eddy FIGURE 14 The ability to look forward using a model of solar activity. 4 3 Parana River Streamflow 2 1 Sunspot Number FIGURE 15 The correlation between the de-trended time series for the Parana River stream flow and sunspot number. a projection to 22. Note the lower activity of the 197s cooling period. Activity over the next 1 years is projected to be much lower again. The aa Index (Fig. 6) is a geomagnetic activity index which is driven by the solar coronal magnetic field strength. The strength of the solar coronal magnetic field doubled over the 2 th century. At the same time, the Earth came
10 286 PART j IV Solar Activity out of the Little Ice Age. There was a dip in the aa Index associated with the 197s cooling period. The aa Index has now fallen back to levels last seen in the Little Ice Age in the late 19 th century. A weaker Interplanetary Magnetic Field results in more galactic cosmic rays reaching the inner planets of the solar system, seen in Fig. 7 of the neutron count of the Oulu station in Finland. The peak neutron count can be more than a year later than the month of solar minimum. This is due to the time the solar wind takes to reach the heliopause, which is the boundary of the solar atmosphere with interstellar space. Note the much higher average neutron count during the 197s cooling period associated with Solar Cycle 2. The increased galactic cosmic ray flux expected over Solar Cycle 24 will cause increased cloudiness, which will in turn increase the Earth s albedo, and the world will then cool in search of a new equilibrium temperature. Friis-Christensen and Lassen (1991) demonstrated that global temperature over a solar cycle is better correlated with the length of the previous solar cycle than with solar cycle amplitude. In 1996, Butler and Johnson at the Armagh Observatory applied that theory to the temperature record of the observatory and produced the graph shown in Fig. 8. This graph can be considered as the Rosetta Stone of solareclimate studies; in that it has significant predictive power. Simply, Solar Cycle 22 was 9.6 years long, equating to a temperature of about 9.6 C at Armagh. Solar Cycle 23 was 12.5 years long, equating to a temperature of 8.2 C at Armagh. The difference is 1.4 C which is the temperature fall, on average, predicted over Solar Cycle 24. There is not much scatter on this graph and therefore this result is almost certain. A number of European temperature records show a correlation between solar cycle length and temperature, including the Central England Temperature record and de Bilt in the Netherlands. Generally, the more northerly the location, the better the correlation. The graph in Fig. 9 shows the correlation for Archangel in Russia. Providence, Rhode Island will be 1.8 C colder over Solar Cycle 24 relative to its average temperature over Solar Cycle 23 (Fig. 1). Hanover, New Hampshire will be 2.2 C colder over Solar Cycle 24 relative to its average temperature over Solar Cycle 23 (Fig. 11). West Chester, Pennsylvania will be 1.5 C colder over Solar Cycle 24 relative to its average temperature over Solar Cycle 23 (Fig. 12). Portland, Maine will be 2.1 C colder over Solar Cycle 24 relative to its average temperature over Solar Cycle 23 (Fig. 13). The graph in Fig. 14 is from a model provided by Ed Fix (this volume). The notion that the orbits of the planets, particularly Jupiter, are responsible for generating the sunspot cycle has been with us since the discovery of the sunspot cycle by Samuel Schwabe in The model is based on changes in the Sun s orbit about the barycenter of the solar system as the driver of the sunspot cycle. It is a simple oscillatory model driven by the acceleration of the radial component of the barycenter s position relative to the Sun. The model has
11 Chapter j 11 The Current Solar 287 a very good hindcast match. At face value, it is predicting two very short and weak cycles. What is more likely is that there will be phase destruction over Solar Cycle 24, including the possibility that the solar magnetic poles will not reverse at solar maximum, predicted by other methods to be in 215. The Parana River, in central South America, runs through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for nearly 4, km and is the second largest river in South America after the Amazon. Its outlet is the River Plata a few kilometers north of Buenos Aires. In 21, three Argentinean researchers, Pablo Mauas, Andrea Buccino, and Eduardo Flamenco, published a paper showing the very strong correlation between sunspot activity and stream flow of the Parana River (Fig. 15). The relationship demonstrated has predictive power, and points to future drought conditions in the Amazon region as a consequence of the weak activity of Solar Cycle SUMMARY The world has entered a de Vries cycle event in solar activity which will produce a decline in temperature in the range of 1.2e2.2 C in the mid-latitude regions, with a consequent impact on agricultural productivity. REFERENCES Archibald, D., 26. Solar cycles 24 and 25 and predicted climate response: Energy and Environment 17, 29e38. Archibald, D., 27. Climate outlook to 23: Energy and Environment 18, 615e619. Archibald, D., 21. The Past and Future of Climate. Rhaetian Management Pty Ltd, p Badalyan, O.G., Obridko, V.N., Sykora, J., 21. Brightness of the coronal green line and prediction for activity cycles 23 and 24: Solar Physics 199, 421e435. Butler, C.J., Johnston, D.J., A provisional long mean air temperature series for Armagh Observatory. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics 58, 1657e1672. Clilverd, M., 25. Prediction of solar activity the next 1 years. Solar Activity: Exploration, Understanding and Prediction, Workshop in Lund, Sweden. Friis-Christensen, E., Lassen, K., Length of the solar cycle: an indicator of solar activity closely associated with climate: Science 254, 698e7. Solheim, E., 21. Solen varsler et kaldere tiar: Astronomi 4/1, 4e6. Svensmark, H., Friis-Christensen, E., Variation in cosmic ray flux and global cloud coverageda missing link in solar-climate relationships: Journal of Atmospheric and Solar Terrestrial Physics 59, Usokin, I.G., Schuessler, M., Solanki, S.K., Mursula, K., 25. Solar activity, cosmic rays, and the Earth s temperature: a millennium-scale comparison. Journal of Geophysical Research 11, A112.
Saltbush Solar Activity Watch. December 2018
 Saltbush Solar Activity Watch December 2018 The first connection between solar activity and climate was made by the Greek astronomer Meton in the 5 th century BC. Meton had noticed a correlation between
Saltbush Solar Activity Watch December 2018 The first connection between solar activity and climate was made by the Greek astronomer Meton in the 5 th century BC. Meton had noticed a correlation between
A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity
 10 A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity S. R. Lahauriya and A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, Govt. P. G. Autonomous College, Datia (M.P.) Abstract:- The Sun is ultimate source of
10 A Correlative Study of Climate Changes and Solar Activity S. R. Lahauriya and A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, Govt. P. G. Autonomous College, Datia (M.P.) Abstract:- The Sun is ultimate source of
CLIMATE CHANGE: THE SUN S ROLE HUGH S 80 TH!
 CLIMATE CHANGE: THE SUN S ROLE Gerald E. Marsh FOR HUGH S 80 TH! 1 BACKGROUND MATERIALS IPCC: Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis: http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/index.htm
CLIMATE CHANGE: THE SUN S ROLE Gerald E. Marsh FOR HUGH S 80 TH! 1 BACKGROUND MATERIALS IPCC: Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis: http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/index.htm
FORECASTING SOLAR CYCLES By Joseph D Aleo
 FORECASTING SOLAR CYCLES By Joseph D Aleo In the ICECAP section on solar cycles, we explain why the sun is a driver for climate changes over time. Historically, the sun undergoes changes on periods of
FORECASTING SOLAR CYCLES By Joseph D Aleo In the ICECAP section on solar cycles, we explain why the sun is a driver for climate changes over time. Historically, the sun undergoes changes on periods of
Solar Activity and Climate Change Hazards. Department of Astronomy & Space and Meteorology, Faculty of Sciences, Cairo University, Giza 12613, Egypt
 Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 3 (2014) 151-157 doi: 10.17265/2328-2193/2014.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Ahmed A. Hady Department of Astronomy & Space and Meteorology, Faculty of Sciences,
Journal of Geological Resource and Engineering 3 (2014) 151-157 doi: 10.17265/2328-2193/2014.03.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Ahmed A. Hady Department of Astronomy & Space and Meteorology, Faculty of Sciences,
Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24
 Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24 David H. Hathaway and Robert M. Wilson NASA/National Space Science and Technology Center Huntsville, AL USA Abstract. The level of geomagnetic
Geomagnetic activity indicates large amplitude for sunspot cycle 24 David H. Hathaway and Robert M. Wilson NASA/National Space Science and Technology Center Huntsville, AL USA Abstract. The level of geomagnetic
Long term solar/heliospherc variability
 1 Long term solar/heliospherc variability Ilya Usoskin Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, University of Oulu, Finland Cosmic Ray variability at Earth 2 Cosmic Rays 1E+5 Geomagnetic field Local Interstellar
1 Long term solar/heliospherc variability Ilya Usoskin Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory, University of Oulu, Finland Cosmic Ray variability at Earth 2 Cosmic Rays 1E+5 Geomagnetic field Local Interstellar
Cyclic variations of the heliospheric tilt angle and cosmic ray modulation
 Advances in Space Research 4 (27) 164 169 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Cyclic variations of the heliospheric tilt angle and cosmic ray modulation K. Alanko-Huotari a, I.G. Usoskin b, *, K. Mursula a, G.A.
Advances in Space Research 4 (27) 164 169 www.elsevier.com/locate/asr Cyclic variations of the heliospheric tilt angle and cosmic ray modulation K. Alanko-Huotari a, I.G. Usoskin b, *, K. Mursula a, G.A.
PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD. 1. Introduction
 PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD K. MURSULA 1, I. G. USOSKIN 2, and G. A. KOVALTSOV 3 1 Department of Physical Sciences, FIN-90014 University of Oulu,
PERSISTENT 22-YEAR CYCLE IN SUNSPOT ACTIVITY: EVIDENCE FOR A RELIC SOLAR MAGNETIC FIELD K. MURSULA 1, I. G. USOSKIN 2, and G. A. KOVALTSOV 3 1 Department of Physical Sciences, FIN-90014 University of Oulu,
ARE SOME CLOUDS OBSCURED IN SATELLITE VIEW? *
 ARE SOME CLOUDS OBSCURED IN SATELLITE VIEW? * MIRELA VOICULESCU 1, ILYA USOSKIN 2, LUCIAN PUIU GEORGESCU 1 1 Faculty of Sciences, Dunarea de Jos University, Galati, ROMANIA, 2 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory
ARE SOME CLOUDS OBSCURED IN SATELLITE VIEW? * MIRELA VOICULESCU 1, ILYA USOSKIN 2, LUCIAN PUIU GEORGESCU 1 1 Faculty of Sciences, Dunarea de Jos University, Galati, ROMANIA, 2 Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory
TR0612-8: Cooler Temps -- Dalton Minimum Returns?
 TR0612-8: Cooler Temps -- Dalton Minimum Returns? 8 December 2006 Russell Steele SESF, Director of Information Sierra Environmental Studies Foundation Nevada City, California, 95959 sesfoundation.org 2006
TR0612-8: Cooler Temps -- Dalton Minimum Returns? 8 December 2006 Russell Steele SESF, Director of Information Sierra Environmental Studies Foundation Nevada City, California, 95959 sesfoundation.org 2006
SOME ASPECTS of COSMIC RAY MODULATION
 SOME ASPECTS of COSMIC RAY MODULATION Yuri Stozhkov P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky Prospect 53, 119991 Moscow, Russia stozhkov@fian.fiandns.mipt.ru FORGES,
SOME ASPECTS of COSMIC RAY MODULATION Yuri Stozhkov P.N. Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Leninsky Prospect 53, 119991 Moscow, Russia stozhkov@fian.fiandns.mipt.ru FORGES,
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle. Observations of the Solar Cycle. Babcock-Leighton Model. Outline
 Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
Lecture 14: Solar Cycle Outline 1 Observations of the Solar Cycle 2 Babcock-Leighton Model Observations of the Solar Cycle Sunspot Number 11-year (average) cycle period as short as 8 years as long as 15
There are two more types of solar wind! The ballerina Sun right before activity minimum. The ballerina dancing through the solar cycle
 There are two more types of solar wind! 3. Low speed wind of "maximum" type Similar characteristics as (2), except for Lectures at the International Max-Planck-Research School Oktober 2002 by Rainer Schwenn,
There are two more types of solar wind! 3. Low speed wind of "maximum" type Similar characteristics as (2), except for Lectures at the International Max-Planck-Research School Oktober 2002 by Rainer Schwenn,
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
THE SUN EARTH CONNECTION IN TIME SCALES FROM YEARS TO DECADES AND CENTURIES. 1. Introduction
 THE SUN EARTH CONNECTION IN TIME SCALES FROM YEARS TO DECADES AND CENTURIES T. I. PULKKINEN 1,H.NEVANLINNA 1, P. J. PULKKINEN 2 and M. LOCKWOOD 3 1 Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 2
THE SUN EARTH CONNECTION IN TIME SCALES FROM YEARS TO DECADES AND CENTURIES T. I. PULKKINEN 1,H.NEVANLINNA 1, P. J. PULKKINEN 2 and M. LOCKWOOD 3 1 Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 2
The influence of cosmic rays on terrestrial clouds and global warming
 Page 1 of 8 The influence of cosmic rays on terrestrial clouds and global warming E. Palle Bago and C. J. Butler Paper appeared in Astronomy & Geophysics, August 2000. Vol 41, Issue 4, pp 18-22. Original
Page 1 of 8 The influence of cosmic rays on terrestrial clouds and global warming E. Palle Bago and C. J. Butler Paper appeared in Astronomy & Geophysics, August 2000. Vol 41, Issue 4, pp 18-22. Original
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Nov 2004
 Did Open Solar Magnetic Field Increase during the Last 1 Years: A Reanalysis of Geomagnetic Activity arxiv:astro-ph/1167v1 16 Nov K. Mursula Department of Physical Sciences, University of Oulu, Finland;
Did Open Solar Magnetic Field Increase during the Last 1 Years: A Reanalysis of Geomagnetic Activity arxiv:astro-ph/1167v1 16 Nov K. Mursula Department of Physical Sciences, University of Oulu, Finland;
Study of High Energy Cosmic Ray Anisotropies with Solar and Geomagnetic Disturbance Index
 International Journal of Astronomy 2012, 1(5): 73-80 DOI: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120105.01 Study of High Energy Cosmic Ray Anisotropies with Solar and Geomagnetic Disturbance Index C. M. Tiwari *, D. P.
International Journal of Astronomy 2012, 1(5): 73-80 DOI: 10.5923/j.astronomy.20120105.01 Study of High Energy Cosmic Ray Anisotropies with Solar and Geomagnetic Disturbance Index C. M. Tiwari *, D. P.
If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing?
 If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing? Sarah Gibson Talk outline Overview of differences between current and past solar minima (with extreme bias towards comparison to space age cycles!)
If the Sun is so quiet, why is the Earth still ringing? Sarah Gibson Talk outline Overview of differences between current and past solar minima (with extreme bias towards comparison to space age cycles!)
Short-Term Climate Variability (Ch.15) Volcanos and Climate Other Causes of Holocene Climate Change
 Short-Term Climate Variability (Ch.15) Volcanos and Climate Other Causes of Holocene Climate Change Volcanos and Climate We learned in Chapter 12 that the volanos play an important role in Earth s climate
Short-Term Climate Variability (Ch.15) Volcanos and Climate Other Causes of Holocene Climate Change Volcanos and Climate We learned in Chapter 12 that the volanos play an important role in Earth s climate
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING
 TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING (Start on p 67 in Class Notes) p 67 ENERGY BALANCE (review) Global climate variability and change are caused by changes in the ENERGY BALANCE that are FORCED review FORCING
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING (Start on p 67 in Class Notes) p 67 ENERGY BALANCE (review) Global climate variability and change are caused by changes in the ENERGY BALANCE that are FORCED review FORCING
XV. Understanding recent climate variability
 XV. Understanding recent climate variability review temperature from thermometers, satellites, glacier lengths and boreholes all show significant warming in the 2th C+ reconstruction of past temperatures
XV. Understanding recent climate variability review temperature from thermometers, satellites, glacier lengths and boreholes all show significant warming in the 2th C+ reconstruction of past temperatures
Solar Cycle 24. Overview of predictions on the start and amplitude of a new solar cycle. Jan Janssens Belgian Solar Section
 Solar Cycle 24 Overview of predictions on the start and amplitude of a new solar cycle Jan Janssens Belgian Solar Section Summary The coming solar cycle minimum The coming solar cycle maximum Current Conclusions
Solar Cycle 24 Overview of predictions on the start and amplitude of a new solar cycle Jan Janssens Belgian Solar Section Summary The coming solar cycle minimum The coming solar cycle maximum Current Conclusions
Predicting Solar Cycle 24 and beyond
 Click Here for Full Article SPACE WEATHER, VOL. 4,, doi:10.1029/2005sw000207, 2006 Predicting Solar Cycle 24 and beyond Mark A. Clilverd, 1 Ellen Clarke, 2 Thomas Ulich, 3 Henry Rishbeth, 4 and Martin
Click Here for Full Article SPACE WEATHER, VOL. 4,, doi:10.1029/2005sw000207, 2006 Predicting Solar Cycle 24 and beyond Mark A. Clilverd, 1 Ellen Clarke, 2 Thomas Ulich, 3 Henry Rishbeth, 4 and Martin
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction. Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center
 Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
Solar Cycle Prediction and Reconstruction Dr. David H. Hathaway NASA/Ames Research Center Outline Solar cycle characteristics Producing the solar cycle the solar dynamo Polar magnetic fields producing
SC24 Where are the sunspots?
 SC24 Where are the sunspots? VSW URANIA 22 October 2009 Jan Janssens Measuring Solar Activity! Dalton Min. Modern Maximum 2 The average solar cycle Sunspotnumber R max : 117 +/- 42 T max : 51 +/- 13 D:
SC24 Where are the sunspots? VSW URANIA 22 October 2009 Jan Janssens Measuring Solar Activity! Dalton Min. Modern Maximum 2 The average solar cycle Sunspotnumber R max : 117 +/- 42 T max : 51 +/- 13 D:
The Earth is NOT Warming in the 21st Century!
 The Earth is NOT Warming in the 21st Century! Yoshiaki FUJII Hokkaido Univ., JAPAN *First presented as Fujii, Y. (2012), The Earth is not Warming in the 21st Century! Proc. MMIJ Spring Meeting, pp. 83-84,
The Earth is NOT Warming in the 21st Century! Yoshiaki FUJII Hokkaido Univ., JAPAN *First presented as Fujii, Y. (2012), The Earth is not Warming in the 21st Century! Proc. MMIJ Spring Meeting, pp. 83-84,
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review
 Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
Astronomy Chapter 12 Review Approximately how massive is the Sun as compared to the Earth? A. 100 times B. 300 times C. 3000 times D. 300,000 times E. One million times Approximately how massive is the
The Marshall Institute - The Sun Also Warms
 Page 1 of 12 The Sun Also Warms by Dr. Sallie Baliunas and Dr. Willie Soon March 24, 2000 Recent discoveries that shed light on the possible influence of the Sun on the climate of the Earth owe to experiments
Page 1 of 12 The Sun Also Warms by Dr. Sallie Baliunas and Dr. Willie Soon March 24, 2000 Recent discoveries that shed light on the possible influence of the Sun on the climate of the Earth owe to experiments
How Low is Low? Tom Woods. Latest News on this Current Solar Cycle Minimum. LASP / University of Colorado.
 How Low is Low? Latest News on this Current Solar Cycle Minimum Tom Woods LASP / University of Colorado Many Contributions: Phil Chamberlin, Giulianna detoma, Leonid tom.woods@lasp.colorado.edu Didkovsky,
How Low is Low? Latest News on this Current Solar Cycle Minimum Tom Woods LASP / University of Colorado Many Contributions: Phil Chamberlin, Giulianna detoma, Leonid tom.woods@lasp.colorado.edu Didkovsky,
Solar Activity The Solar Wind
 Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
Solar Activity The Solar Wind The solar wind is a flow of particles away from the Sun. They pass Earth at speeds from 400 to 500 km/s. This wind sometimes gusts up to 1000 km/s. Leaves Sun at highest speeds
Sunspot Cycles source: NOAA
 Sunspots and Global Warming Charlie Nelson November 23 There is a statistically significant correlation between the amplitude of the sunspot cycle and the temperature of the atmosphere. This relationship
Sunspots and Global Warming Charlie Nelson November 23 There is a statistically significant correlation between the amplitude of the sunspot cycle and the temperature of the atmosphere. This relationship
Long-term Modulation of Cosmic Ray Intensity in relation to Sunspot Numbers and Tilt Angle
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2006) 27, 455 464 Long-term Modulation of Cosmic Ray Intensity in relation to Sunspot Numbers and Tilt Angle Meera Gupta, V. K. Mishra & A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, A. P. S.
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2006) 27, 455 464 Long-term Modulation of Cosmic Ray Intensity in relation to Sunspot Numbers and Tilt Angle Meera Gupta, V. K. Mishra & A. P. Mishra Department of Physics, A. P. S.
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Correlative Study of Solar Activity and Cosmic Ray Intensity Variations during Present Solar Cycle 24 in Comparison to Previous Solar Cycles
 Correlative Study of Solar Activity and Cosmic Ray Intensity Variations during Present Solar Cycle 24 in Comparison to Previous Solar Cycles ABSTRACT Meera Gupta 1, S.R. Narang 1, V. K. Mishra* 2 & A.
Correlative Study of Solar Activity and Cosmic Ray Intensity Variations during Present Solar Cycle 24 in Comparison to Previous Solar Cycles ABSTRACT Meera Gupta 1, S.R. Narang 1, V. K. Mishra* 2 & A.
The Solar Cycle or El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) as a Criterion for the Definition of Public Policies
 The Solar Cycle or El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) as a Criterion for the Definition of Public Policies Juan Manuel Rodríguez Torres* Gerardo Zavala Guzmán** * e-mail: rodrito@ugto.mx; Departamento
The Solar Cycle or El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) as a Criterion for the Definition of Public Policies Juan Manuel Rodríguez Torres* Gerardo Zavala Guzmán** * e-mail: rodrito@ugto.mx; Departamento
Title: AMPLITUDE OF SOLAR CYCLE 24 BASED ON POLAR MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE SUN
 Solar Physics Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: SOLA Title: AMPLITUDE OF SOLAR CYCLE BASED ON POLAR MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE SUN Article Type: Original Research Keywords: "Solar activity"; "solar cycle"
Solar Physics Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: SOLA Title: AMPLITUDE OF SOLAR CYCLE BASED ON POLAR MAGNETIC FIELD OF THE SUN Article Type: Original Research Keywords: "Solar activity"; "solar cycle"
THE CAUSE OF GLOBAL WARMING STAGNATION IN THE 21ST CENTURY
 THE CAUSE OF GLOBAL WARMING STAGNATION IN THE 21ST CENTURY Yoshiaki Fujii 1 1 Rock Mechanics Laboratory, Division of Sustainable Resources Engineering, Hokkaido University, N13W8, Sapporo, 060-8628, JAPAN,
THE CAUSE OF GLOBAL WARMING STAGNATION IN THE 21ST CENTURY Yoshiaki Fujii 1 1 Rock Mechanics Laboratory, Division of Sustainable Resources Engineering, Hokkaido University, N13W8, Sapporo, 060-8628, JAPAN,
DIN EN : (E)
 DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
ATS150 Global Climate Change Spring 2019 Candidate Questions for Exam #1
 1. How old is the Earth? About how long ago did it form? 2. What are the two most common gases in the atmosphere? What percentage of the atmosphere s molecules are made of each gas? 3. About what fraction
1. How old is the Earth? About how long ago did it form? 2. What are the two most common gases in the atmosphere? What percentage of the atmosphere s molecules are made of each gas? 3. About what fraction
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric
MAGNETIC POLES AND CLIMATE
 MAGNETIC POLES AND CLIMATE Reno, NV June 25, 2009 1 The strength of the Earth s magnetic field varies tremendously around the world. The following figure shows the magnetic field intensity around the world,
MAGNETIC POLES AND CLIMATE Reno, NV June 25, 2009 1 The strength of the Earth s magnetic field varies tremendously around the world. The following figure shows the magnetic field intensity around the world,
EFFECT OF EAST-WEST AND RADIAL ANISOTROPY ON HALE CYCLE IN THE HARMONICS OF DAILY VARIATION IN C R INTENSITY
 28th International Cosmic Ray Conference 4005 EFFECT OF EAST-WEST AND RADIAL ANISOTROPY ON HALE CYCLE IN THE HARMONICS OF DAILY VARIATION IN C R INTENSITY Rekha Agarwal Mishra 1 and Rajesh K. Mishra 2
28th International Cosmic Ray Conference 4005 EFFECT OF EAST-WEST AND RADIAL ANISOTROPY ON HALE CYCLE IN THE HARMONICS OF DAILY VARIATION IN C R INTENSITY Rekha Agarwal Mishra 1 and Rajesh K. Mishra 2
A) usually less B) dark colored and rough D) light colored with a smooth surface A) transparency of the atmosphere D) rough, black surface
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo
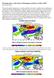 Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo The pop in global temperatures, even the satellite, the last few months seems surprising to some in the Northern Hemisphere
Warming after a cold winter will disappear quickly as it did in 2007 By Joseph D Aleo The pop in global temperatures, even the satellite, the last few months seems surprising to some in the Northern Hemisphere
Ice Age Canada. Understanding our climate future. By Rolf A. F. Witzsche 2013 Published by Cygni Communications Ltd. Canada
 Ice Age Canada Understanding our climate future By Rolf A. F. Witzsche 2013 Published by Cygni Communications Ltd. Canada In love with our humanity The incredible intelligence that we have as human beings
Ice Age Canada Understanding our climate future By Rolf A. F. Witzsche 2013 Published by Cygni Communications Ltd. Canada In love with our humanity The incredible intelligence that we have as human beings
The Waldmeier Effect and the Calibration of Sunspot Numbers
 The Waldmeier Effect and the Calibration of Sunspot Numbers Leif Svalgaard Stanford University, California, USA http://www.leif.org/research David H. Hathaway NASA Ames Research Center, California, USA
The Waldmeier Effect and the Calibration of Sunspot Numbers Leif Svalgaard Stanford University, California, USA http://www.leif.org/research David H. Hathaway NASA Ames Research Center, California, USA
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology.
 What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
Chapter 2 Solar and Infrared Radiation
 Chapter 2 Solar and Infrared Radiation Chapter overview: Fluxes Energy transfer Seasonal and daily changes in radiation Surface radiation budget Fluxes Flux (F): The transfer of a quantity per unit area
Chapter 2 Solar and Infrared Radiation Chapter overview: Fluxes Energy transfer Seasonal and daily changes in radiation Surface radiation budget Fluxes Flux (F): The transfer of a quantity per unit area
SOME WEATHER EXTREMES ARE REAL, BUT CAUSES ARE NATURAL. by Joseph D Aleo
 SOME WEATHER EXTREMES ARE REAL, BUT CAUSES ARE NATURAL by Joseph D Aleo SPPI REPRINT SERIES October 1, 2010 SOME WEATHER EXTREMES ARE REAL, BUT CAUSES ARE NATURAL by Joseph D Aleo October 1, 2010 We have
SOME WEATHER EXTREMES ARE REAL, BUT CAUSES ARE NATURAL by Joseph D Aleo SPPI REPRINT SERIES October 1, 2010 SOME WEATHER EXTREMES ARE REAL, BUT CAUSES ARE NATURAL by Joseph D Aleo October 1, 2010 We have
The vertical cut-off rigidity means that charged particle with rigidity below this value cannot reach the top of atmosphere because of the earth's
 EXPACS: Excel-based Program for calculating Atmospheric Cosmic-ray Spectrum User s Manual (Last update Dec. 21, 2018) Tatsuhiko Sato, Japan Atomic Energy Agency nsed-expacs@jaea.go.jp I. INTRODUCTION EXPACS
EXPACS: Excel-based Program for calculating Atmospheric Cosmic-ray Spectrum User s Manual (Last update Dec. 21, 2018) Tatsuhiko Sato, Japan Atomic Energy Agency nsed-expacs@jaea.go.jp I. INTRODUCTION EXPACS
The Shining Sun: Understanding the Solar Irradiance Variability
 The Shining Sun: Understanding the Solar Irradiance Variability Prof. Dr. Werner K. Schmutz Director PMOD/WRC Davos Switzerland Summer School Alpbach 23.7. 1.8.2002 Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium
The Shining Sun: Understanding the Solar Irradiance Variability Prof. Dr. Werner K. Schmutz Director PMOD/WRC Davos Switzerland Summer School Alpbach 23.7. 1.8.2002 Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium
Cosmogenic isotopes as proxies for the solar activity
 Cosmogenic isotopes as proxies for the solar activity Edouard BARD & Mélanie BARONI CEREGE, Aix-en-Provence VolSol project Max Planck Institute, Jena 14 C production and decay Geo- and helio-magnetic fields
Cosmogenic isotopes as proxies for the solar activity Edouard BARD & Mélanie BARONI CEREGE, Aix-en-Provence VolSol project Max Planck Institute, Jena 14 C production and decay Geo- and helio-magnetic fields
Solar variability and global climate change
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(5), May 2014, pp. 871-875 Solar variability and global climate change S.C. Dubey Department of Physics, S.G.S. Govt. P.G. College, Sidhi (M.P.) Pin-486 661,
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(5), May 2014, pp. 871-875 Solar variability and global climate change S.C. Dubey Department of Physics, S.G.S. Govt. P.G. College, Sidhi (M.P.) Pin-486 661,
An Introduction to Space Weather. J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR
 An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
An Introduction to Space Weather J. Burkepile High Altitude Observatory / NCAR What is Space Weather? Space Weather refers to conditions in interplanetary space, produced by the Sun, that can disrupt
A possible role of the solar inertial motion in climatic changes
 A possible role of the solar inertial motion in climatic changes Ivanka Charvátová and Pavel Hejda Institute of Geophysics of the ASCR, Prague, Czech Republic Solar inertial motion - SIM Solar inertial
A possible role of the solar inertial motion in climatic changes Ivanka Charvátová and Pavel Hejda Institute of Geophysics of the ASCR, Prague, Czech Republic Solar inertial motion - SIM Solar inertial
How The Sun Could Control Earth s Temperature
 How The Sun Could Control Earth s Temperature Introduction: by Stephen Wilde. The Holy Grail of climatology has always been to ascertain whether, and if so how, the sun might affect the Earth s energy
How The Sun Could Control Earth s Temperature Introduction: by Stephen Wilde. The Holy Grail of climatology has always been to ascertain whether, and if so how, the sun might affect the Earth s energy
TOPIC #12. Wrap Up on GLOBAL CLIMATE PATTERNS
 TOPIC #12 Wrap Up on GLOBAL CLIMATE PATTERNS POLE EQUATOR POLE Now lets look at a Pole to Pole Transect review ENERGY BALANCE & CLIMATE REGIONS (wrap up) Tropics Subtropics Subtropics Polar Extratropics
TOPIC #12 Wrap Up on GLOBAL CLIMATE PATTERNS POLE EQUATOR POLE Now lets look at a Pole to Pole Transect review ENERGY BALANCE & CLIMATE REGIONS (wrap up) Tropics Subtropics Subtropics Polar Extratropics
Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties
Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and the Other Terrestrial Worlds 10.1 Atmospheric Basics Our goals for learning: What is an atmosphere? How does the greenhouse effect warm a planet? Why do atmospheric properties
Polar Portal Season Report 2013
 Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
Polar Portal Season Report 2013 All in all, 2013 has been a year with large melting from both the Greenland Ice Sheet and the Arctic sea ice but not nearly as large as the record-setting year of 2012.
Long-term Variations in Solar Activity and their Apparent Effect on the Earth's Climate
 Long-term Variations in Solar Activity and their Apparent Effect on the Earth's Climate K.Lassen Danish Meteorological Institute, Solar-Terrestrial Physics Division, Lyngbyvej,100, DK-2100 Copenhagen (2),
Long-term Variations in Solar Activity and their Apparent Effect on the Earth's Climate K.Lassen Danish Meteorological Institute, Solar-Terrestrial Physics Division, Lyngbyvej,100, DK-2100 Copenhagen (2),
Comparative study of solar and geomagnetic indices for the solar cycle 22 and 23 C. M Tiwari Dept. of Physics, APS University, Rewa (M. P.
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
THE SUN S EFFECT ON CLIMATE
 Biblical Astronomer, number 128 37 THE SUN S EFFECT ON CLIMATE Gerardus D. Bouw, Ph.D. For some ten years now we have pointed out the blatant errors and outright fraud of the global warming alarmists.
Biblical Astronomer, number 128 37 THE SUN S EFFECT ON CLIMATE Gerardus D. Bouw, Ph.D. For some ten years now we have pointed out the blatant errors and outright fraud of the global warming alarmists.
Tri-diurnal anisotropy of cosmic ray daily variation for the solar cycle 23
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 39, December 2010, pp. 341-345 Tri-diurnal anisotropy of cosmic ray daily variation for the solar cycle 23 Kamlesh Singh & Pankaj K Shrivastava $,* Department
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 39, December 2010, pp. 341-345 Tri-diurnal anisotropy of cosmic ray daily variation for the solar cycle 23 Kamlesh Singh & Pankaj K Shrivastava $,* Department
Our Cooling Climate. David Archibald University of Oslo, 1 st November 2013
 Our Cooling Climate David Archibald University of Oslo, 1 st November 2013 1. Has the world warmed?! 2. Has warming happened in the past?! 3. Is warming linked to CO2?! 4. Is there a more logical reason
Our Cooling Climate David Archibald University of Oslo, 1 st November 2013 1. Has the world warmed?! 2. Has warming happened in the past?! 3. Is warming linked to CO2?! 4. Is there a more logical reason
The Interior Structure of the Sun
 The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
The Interior Structure of the Sun Data for one of many model calculations of the Sun center Temperature 1.57 10 7 K Pressure 2.34 10 16 N m -2 Density 1.53 10 5 kg m -3 Hydrogen 0.3397 Helium 0.6405 The
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Event type: Various geomagnetic disturbances including coronal hole high-speed stream, coronal mass ejection, sudden impulse and reverse shock effects Background: This background section defines the various
Extra-terrestrial Influences on Nature s Risks
 Extra-terrestrial Influences on Nature s Risks Brent Walker Session Number: WBR9 Gravitational Influences Phase Locks & Harmonic Resonances After billions of years of evolution the solar system is still
Extra-terrestrial Influences on Nature s Risks Brent Walker Session Number: WBR9 Gravitational Influences Phase Locks & Harmonic Resonances After billions of years of evolution the solar system is still
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1
 Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather. Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia
 Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
Solar-terrestrial relation and space weather Mateja Dumbović Hvar Observatory, University of Zagreb Croatia Planets Comets Solar wind Interplanetary magnetic field Cosmic rays Satellites Astronauts HELIOSPHERE
A climatological study of the relations among solar activity, galactic cosmic ray and precipitation on various regions over the globe
 A climatological study of the relations among solar activity, galactic cosmic ray and precipitation on various regions over the globe Sourabh Bal and MBose Department of Physics, Jadavpur University, Kolkata
A climatological study of the relations among solar activity, galactic cosmic ray and precipitation on various regions over the globe Sourabh Bal and MBose Department of Physics, Jadavpur University, Kolkata
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp
 The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
The Solar Wind Space physics 7,5hp Teknisk fysik '07 1 Contents History... 3 Introduction... 3 Two types of solar winds... 4 Effects of the solar wind... 5 Magnetospheres... 5 Atmospheres... 6 Solar storms...
4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explore this Phenomena. The same sun shines on the entire Earth. Explain why these two areas have such different climates.
 Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate. Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop
 The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop - 2016 3 Bsp 10 G Maunder (1904) Besides the 11 yr cycle ~80 yr
The solar dynamo and its influence on the earth climate Gustavo A. Guerrero Departamento de Física (UFMG) IAG-USP Palio-climate Workshop - 2016 3 Bsp 10 G Maunder (1904) Besides the 11 yr cycle ~80 yr
Solar dynamo theory recent progress, questions and answers
 Solar dynamo theory recent progress, questions and answers Katya Georgieva, Boian Kirov Crisan Demetrescu, Georgeta Maris, Venera Dobrica Space and Solar-Terrestrial Research Institute, Bulgarian Academy
Solar dynamo theory recent progress, questions and answers Katya Georgieva, Boian Kirov Crisan Demetrescu, Georgeta Maris, Venera Dobrica Space and Solar-Terrestrial Research Institute, Bulgarian Academy
Documentation of the solar activity variations and it's influence on climate
 Documentation of the solar activity variations and it's influence on climate Poulos Dimitris Civil Engineer NTUA, MSc Water Resources Management NTUA web: http://dimispoulos.wix.com/dimis Abstract: The
Documentation of the solar activity variations and it's influence on climate Poulos Dimitris Civil Engineer NTUA, MSc Water Resources Management NTUA web: http://dimispoulos.wix.com/dimis Abstract: The
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle
 Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L)
Lecture 3: Global Energy Cycle Planetary energy balance Greenhouse Effect Vertical energy balance Latitudinal energy balance Seasonal and diurnal cycles Solar Flux and Flux Density Solar Luminosity (L)
A new mechanism to account for acceleration of the solar wind
 A new mechanism to account for acceleration of the solar wind Henry D. May Email: hankmay@earthlink.net Abstract An enormous amount of effort has been expended over the past sixty years in attempts to
A new mechanism to account for acceleration of the solar wind Henry D. May Email: hankmay@earthlink.net Abstract An enormous amount of effort has been expended over the past sixty years in attempts to
Solar Activity and Global Warming Revisited
 12 Solar Activity and Global Warming Revisited K. Georgieva, B. Kirov Solar-Terrestrial Influences Laboratory, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria kgeorg@bas.bg, bkirov@space.bas.bg While in
12 Solar Activity and Global Warming Revisited K. Georgieva, B. Kirov Solar-Terrestrial Influences Laboratory, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria kgeorg@bas.bg, bkirov@space.bas.bg While in
The point in an orbit around the Sun at which an object is at its greatest distance from the Sun (Opposite of perihelion).
 ASTRONOMY TERMS Albedo Aphelion Apogee A measure of the reflectivity of an object and is expressed as the ratio of the amount of light reflected by an object to that of the amount of light incident upon
ASTRONOMY TERMS Albedo Aphelion Apogee A measure of the reflectivity of an object and is expressed as the ratio of the amount of light reflected by an object to that of the amount of light incident upon
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant
 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement number 721624. Space weather and the variable
This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie-Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement number 721624. Space weather and the variable
CLIMATE. SECTION 14.1 Defining Climate
 Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge. Chi Wang. National Space Science Center, CAS
 Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Solar Activity during the Rising Phase of Solar Cycle 24
 International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
International Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 213, 3, 212-216 http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijaa.213.3325 Published Online September 213 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijaa) Solar Activity during the
Interstellar and Interplanetary Material. HST Astrobiology Workshop: May 5-9, 2002 P.C. Frisch University of Chicago
 Interstellar and Interplanetary Material HST Astrobiology Workshop: May 5-9, 2002 P.C. Frisch University of Chicago Outline: The solar system is our template for understanding interplanetary material Heliosphere,
Interstellar and Interplanetary Material HST Astrobiology Workshop: May 5-9, 2002 P.C. Frisch University of Chicago Outline: The solar system is our template for understanding interplanetary material Heliosphere,
Climate. What is climate? STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Name Class Date
 Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure
 Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Atmospheric Responses to Solar Wind Dynamic Pressure Hua Lu British Antarctic Survey Outline Background: Sun-Earth Climate Connection Solar wind/geomagnetic activity signals with 3 examples stratospheric
Sami K. Solanki and Manfred Schüssler
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol.??, 1 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della "!# %$ &' ( ) *!+, & Sami K. Solanki and Manfred Schüssler Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Max-Planck-Str. 2, 37191, Katlenburg- Lindau,
Mem. S.A.It. Vol.??, 1 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della "!# %$ &' ( ) *!+, & Sami K. Solanki and Manfred Schüssler Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung, Max-Planck-Str. 2, 37191, Katlenburg- Lindau,
The Atmosphere. Importance of our. 4 Layers of the Atmosphere. Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate. What makes up the atmosphere?
 The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
The Atmosphere Introduction to atmosphere, weather, and climate Where is the atmosphere? Everywhere! Completely surrounds Earth February 20, 2010 What makes up the atmosphere? Argon Inert gas 1% Variable
1. Weather and climate.
 Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Climate Changes due to Natural Processes
 Climate Changes due to Natural Processes 2.6.2a Summarize natural processes that can and have affected global climate (particularly El Niño/La Niña, volcanic eruptions, sunspots, shifts in Earth's orbit,
Climate Changes due to Natural Processes 2.6.2a Summarize natural processes that can and have affected global climate (particularly El Niño/La Niña, volcanic eruptions, sunspots, shifts in Earth's orbit,
Hale cycle in solar-rotation related recurrence of galactic cosmic rays
 Hale cycle in solar-rotation related recurrence of galactic cosmic rays Institute of Mathematics and Physics, Siedlce University, 3 Maja 54, 08-0 Siedlce, Poland E-mail: gila@uph.edu.pl Kalevi Mursula
Hale cycle in solar-rotation related recurrence of galactic cosmic rays Institute of Mathematics and Physics, Siedlce University, 3 Maja 54, 08-0 Siedlce, Poland E-mail: gila@uph.edu.pl Kalevi Mursula
Solar activity and climate in Central America
 Geofísica Internacional (), ol., 39, Num. 1, pp. 97-11 Solar activity and climate in Central America Esteban Araya, Javier Bonatti and Walter Fernández Laboratory for Atmospheric and Planetary Research,
Geofísica Internacional (), ol., 39, Num. 1, pp. 97-11 Solar activity and climate in Central America Esteban Araya, Javier Bonatti and Walter Fernández Laboratory for Atmospheric and Planetary Research,
Insolation and Temperature variation. The Sun & Insolation. The Sun (cont.) The Sun
 Insolation and Temperature variation Atmosphere: blanket of air surrounding earth Without our atmosphere: cold, quiet, cratered place Dynamic: currents and circulation cells June 23, 2008 Atmosphere important
Insolation and Temperature variation Atmosphere: blanket of air surrounding earth Without our atmosphere: cold, quiet, cratered place Dynamic: currents and circulation cells June 23, 2008 Atmosphere important
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
THE G INDEX OF INTERPLANETARY SCINTILLATION DATA AND ITS RELATION TO FORBUSH DECREASES DURING and
 Solar Physics (06) 236: 389 397 DOI:.7/s117-006-0074-9 C Springer 06 THE G INDEX OF INTERPLANETARY SCINTILLATION DATA AND ITS RELATION TO FORBUSH DECREASES DURING 1991 1994 R. PÉREZ-ENRÍQUEZ Centro de
Solar Physics (06) 236: 389 397 DOI:.7/s117-006-0074-9 C Springer 06 THE G INDEX OF INTERPLANETARY SCINTILLATION DATA AND ITS RELATION TO FORBUSH DECREASES DURING 1991 1994 R. PÉREZ-ENRÍQUEZ Centro de
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOLAR MAXIMUM AMPLITUDE AND MAX MAX CYCLE LENGTH
 The Astronomical Journal, 132:1485 1489, 2006 October # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOLAR MAXIMUM AMPLITUDE AND MAX MAX CYCLE LENGTH
The Astronomical Journal, 132:1485 1489, 2006 October # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOLAR MAXIMUM AMPLITUDE AND MAX MAX CYCLE LENGTH
