FuncICA for time series pattern discovery
|
|
|
- Leona Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FuncICA for time series pattern discovery Nishant Mehta and Alexander Gray Georgia Institute of Technology
2 The problem Given a set of inherently continuous time series (e.g. EEG) Find a set of patterns that vary independently over the data Existing solutions: 1 Standard independent component analysis (ICA) 2 Functional principal component analysis 2 / 29
3 High level Data Basis functions Principal curves Independent curves 3 / 29
4 High level FuncICA - Functional independent component analysis ICA for time series data 1 Express the data using a set of basis functions. 2 Functional PCA - Find the k curves of maximum variation across the data, subject to smoothness constraint 3 Rotate functional principal components to maximize independence and yield independent components Y 4 Optimize an independence objective Q(Y ) with respect to a smoothness regularization term 4 / 29
5 Towards automating science ICA used in pattern discovery in natural domains like neuroscience, genetics, and astrophysics, but patterns are often smooth Many domains created by humans, including financial markets and chemical processes, involve smooth variation FuncICA offers a way to find optimally smoothed patterns in these domains. Automatic identification of event-related potentials in EEG Automatic discovery of gene signaling mechanisms from microarray gene expression data Identifying spatiotemporal activation patterns in fmri 5 / 29
6 Independent component analysis Observe multiple signals X (t) over time Univariate signal X (t) i is mixture of independent sources S (t) Linear instantaneous mixing model: X (t) = AS (t) Find unmixing transformation that maximizes statistical independence of recovered sources 1 Sources 0.6 Mixtures / 29
7 Independent component analysis Find unmixing matrix W such that Y = WX = WAS Y S up to a scaling and permutation of sources Maximizing independence Minimizing difference between joint and product of marginals P[Y ] P[Yi ] Use the Kullback-Leibler Divergence: H(Y ) = D KL (P[Y ] n i=1 P[Y i]) = n i=1 H(Y i) H(Y ) 7 / 29
8 ICA duality Primal Dual sample 1 IC 1 varies in loading over samples of x x 1 IC 1 loading varies over samples sample 2 x 2 sample 1, IC 1 IC 1 sample 1 8 / 29
9 Why functional data? Higher sampling rate Higher dimensional data No principled way of dimensionality reduction Subsampling? No principled way to handle asynchronous observations Missing data from occasionally offline sensors Each observation lives in different space Alternative? Generative (parametric) models - HMM, dynamic Bayesian network OR Functional representation 9 / 29
10 Functional data Set of n curves X = {X 1 (t),..., X n (t)}, X i X Set of m basis functions β = {β 1,..., β m } Decompose data as X i (t) = m j=1 ψ i,jβ j (t) X L 2 (Hilbert space), with inner product f, g = f (t)g(t)dt / 29
11 Functional PCA Functional PCA to get principal curves E i (t) = m ρ i,j β j (t) j=1 Principal components (curve loadings) over the data σ (E) i,j = E i, X j = σ (E) = ρbψ T m k=1 l=1 m ρ i,k β k, β l ψ j,l 11 / 29
12 Functional ICA Independent curves are rotation W of principal curves Independent components Y i (t) = σ (Y ) i,j = Y i, X j = σ (Y ) = W σ (E) m [W ρ] i,j β j (t) j=1 m k=1 l=1 m [W ρ] i,k β k, β l ψ j,l Now, just solve for W to find IC basis weights φ = W ρ 12 / 29
13 Independence objective KL-divergence objective After FPCA, we have H(Y ) = n H(Y i ) H(Y ) i=1 n H(E) = H(E i ) H(E) i=1 Y = WE and W orthogonal yield minimum marginal entropy objective H (Y ) = n H(Y i ) i=1 13 / 29
14 Entropy estimator to evaluate H(Y i ) Vasicek entropy estimator nonparametric entropy estimator that considers order statistics 1 Order samples in non-decreasing order Z (1) Z (2)... Z (N) 2 m-spacing is Z (i+m) Z (i) 3 Ĥ N (Z 1, Z 2,..., Z N ) = N m 1 N ( ) N log (Z (i+mn) Z (i) N m N i=1 14 / 29
15 Optimizer Plug-in ICA estimator: RADICAL ICA [Learned-Miller and Fisher 2003] RADICAL uses Vasicek entropy estimator For ICA in D dimensions (D eigenfunctions), do pairwise separation. 2-D rotation matrix is parameterized by one angle parameter θ: ( ) cos θ sin θ sin θ cos θ Since θ [ π 2, π 2 ], use brute-force to optimize Ĥ N (θ) 15 / 29
16 Smoothing FPCA chooses smoothing level α p minimizing leave-one-out cross-validation error α p not optimal for source recovery FuncICA balances reconstruction error while avoiding Gaussian components 16 / 29
17 L 2 Smoothing (FPCA) [Ramsay and Silverman 2002] Penalize the second derivative so that functions are not too wiggly ξ(t) 2 dt + α (D 2 ξ(t)) 2 dt = 1, for α 0 Smooths the principal curves directly Hence also smooths independent curves Select optimal reconstruction error αp via leave-one-out cross-validation 17 / 29
18 Inverse negentropy smoothing (FuncICA) Motivation - Penalize Gaussian components Why? ICA fails if there is more than 1 Gaussian component Oversmoothing components become noisy non-gaussian components may become Gaussian How? Inverse negentropy objective function: Q(Y ) = p i=1 1 J(Y i ) where J(Y i ) = H(N (0, 1)) H(Y i ) is the negentropy of unit-variance Y i 18 / 29
19 Optimal FuncICA inverse negentropy smoothing Algorithm 1 α = αp, τ = 0, Q (0) = 2 repeat 3 τ = τ (Y, Q (τ) ) = FuncICA(X, α (τ) ) 5 α (τ+1) = γα (τ) 6 until Q (τ) > Q (τ 1) 7 return α (τ 1) Intuition: αp optimally smooths for reconstruction error Can further smoothing be beneficial for source recovery? Yes! Can effectively dampen Gaussian noise components 19 / 29
20 Synthetic data results Perfect source recovery for mixture of Laplace-distributed harmonics f(t) t Successful isolation of single high-frequency Gaussian source FuncICA performs well for α 0 FPCA blends high-frequency source into all recovered curves Dampening of two high-frequency Gaussian sources Q statistic performs well in recovering Laplacian sources 20 / 29
21 Synthetic data results 130 Effect of smoothing on Q 125 Source curves S 1 (t) = 1 2 sin(10πt) S 2 (t) = 1 2 cos(10πt) S 3 (t) = sin(40πt) S 4 (t) = cos(40πt) Distributions Laplace Laplace Gaussian Gaussian Q α Effect of smoothing on accuracy accuracy α 21 / 29
22 Event-related potential discovery results FuncICA ICA FPCA Empirical P Accuracy column row letter 22 / 29
23 Microarray gene expression results 6178 genes observed at 18 times in 7 minute increments Goal: identify co-regulated genes related to specific phases of the cell cycle G 1 phase regulated vs non-g 1 phase regulated IC PC Top % 9.2% Filtered 6.2% 8.2% 23 / 29
24 Conclusion Functional ICA offers a way to find smooth, independent modes of variation in time series and other continuous-natured data Alternative to FPCA when components of interest may not be Gaussian Applicable for EEG, gene expression, finance, and other domains 24 / 29
25 Questions? 25 / 29
26 Perhaps not functional PCA Let s see what FPCA does for our ERP data 2 f(t) Looks like a Fourier basis Makes sense α rhythm β rhythm µ rhythm t 26 / 29
27 Let s see what Functional ICA (FuncICA) extracts 3 IC closest to P300 ERP for α = 5E 8 IC 6 (t) Closest IC to P300 for α = t 3.5 Empirical P300 waveform 3 P300(t) Empirical P300 waveform calculated from 2550 trials t 2 IC closest to P300 ERP for α = 1E IC 3 (t) Closest IC to P300 for α = t 27 / 29
28 Event-related potential discovery results 1250 Effect of smoothing on Q Q α 0.6 Effect of smoothing on accuracy accuracy α 28 / 29
29 Smoothing Choices to make Spline functional form? cubic b-spline - computationally efficient, common in statistics Number of knots? As many as we can use tractably Number of principal curves to retain? Use reconstruction error threshold OR Largest number that is tractable for FuncICA 29 / 29
Multidimensional scaling (MDS)
 Multidimensional scaling (MDS) Just like SOM and principal curves or surfaces, MDS aims to map data points in R p to a lower-dimensional coordinate system. However, MSD approaches the problem somewhat
Multidimensional scaling (MDS) Just like SOM and principal curves or surfaces, MDS aims to map data points in R p to a lower-dimensional coordinate system. However, MSD approaches the problem somewhat
Principal Component Analysis
 Principal Component Analysis Introduction Consider a zero mean random vector R n with autocorrelation matri R = E( T ). R has eigenvectors q(1),,q(n) and associated eigenvalues λ(1) λ(n). Let Q = [ q(1)
Principal Component Analysis Introduction Consider a zero mean random vector R n with autocorrelation matri R = E( T ). R has eigenvectors q(1),,q(n) and associated eigenvalues λ(1) λ(n). Let Q = [ q(1)
Independent Component Analysis
 1 Independent Component Analysis Background paper: http://www-stat.stanford.edu/ hastie/papers/ica.pdf 2 ICA Problem X = AS where X is a random p-vector representing multivariate input measurements. S
1 Independent Component Analysis Background paper: http://www-stat.stanford.edu/ hastie/papers/ica.pdf 2 ICA Problem X = AS where X is a random p-vector representing multivariate input measurements. S
Unsupervised learning: beyond simple clustering and PCA
 Unsupervised learning: beyond simple clustering and PCA Liza Rebrova Self organizing maps (SOM) Goal: approximate data points in R p by a low-dimensional manifold Unlike PCA, the manifold does not have
Unsupervised learning: beyond simple clustering and PCA Liza Rebrova Self organizing maps (SOM) Goal: approximate data points in R p by a low-dimensional manifold Unlike PCA, the manifold does not have
Independent Component Analysis. Contents
 Contents Preface xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Linear representation of multivariate data 1 1.1.1 The general statistical setting 1 1.1.2 Dimension reduction methods 2 1.1.3 Independence as a guiding principle
Contents Preface xvii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Linear representation of multivariate data 1 1.1.1 The general statistical setting 1 1.1.2 Dimension reduction methods 2 1.1.3 Independence as a guiding principle
Variational Principal Components
 Variational Principal Components Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research 7 J. J. Thomson Avenue, Cambridge, CB3 0FB, U.K. cmbishop@microsoft.com http://research.microsoft.com/ cmbishop In Proceedings
Variational Principal Components Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research 7 J. J. Thomson Avenue, Cambridge, CB3 0FB, U.K. cmbishop@microsoft.com http://research.microsoft.com/ cmbishop In Proceedings
ICA and ISA Using Schweizer-Wolff Measure of Dependence
 Keywords: independent component analysis, independent subspace analysis, copula, non-parametric estimation of dependence Abstract We propose a new algorithm for independent component and independent subspace
Keywords: independent component analysis, independent subspace analysis, copula, non-parametric estimation of dependence Abstract We propose a new algorithm for independent component and independent subspace
Information geometry for bivariate distribution control
 Information geometry for bivariate distribution control C.T.J.Dodson + Hong Wang Mathematics + Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Optimal control of stochastic
Information geometry for bivariate distribution control C.T.J.Dodson + Hong Wang Mathematics + Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Optimal control of stochastic
HST.582J/6.555J/16.456J
 Blind Source Separation: PCA & ICA HST.582J/6.555J/16.456J Gari D. Clifford gari [at] mit. edu http://www.mit.edu/~gari G. D. Clifford 2005-2009 What is BSS? Assume an observation (signal) is a linear
Blind Source Separation: PCA & ICA HST.582J/6.555J/16.456J Gari D. Clifford gari [at] mit. edu http://www.mit.edu/~gari G. D. Clifford 2005-2009 What is BSS? Assume an observation (signal) is a linear
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning. Jen-Tzung Chien
 Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent voices Nonparametric likelihood
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent voices Nonparametric likelihood
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning
 Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien National Cheng Kung University TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien National Cheng Kung University TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent
LECTURE :ICA. Rita Osadchy. Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng
 LECURE :ICA Rita Osadchy Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng Cocktail Party Person 1 2 s 1 Mike 2 s 3 Person 3 1 Mike 1 s 2 Person 2 3 Mike 3 microphone signals are mied speech signals 1 2 3 ( t) ( t) ( t)
LECURE :ICA Rita Osadchy Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng Cocktail Party Person 1 2 s 1 Mike 2 s 3 Person 3 1 Mike 1 s 2 Person 2 3 Mike 3 microphone signals are mied speech signals 1 2 3 ( t) ( t) ( t)
CIFAR Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images
 CIFAR Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Dept of Computer Science University of Helsinki, Finland Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference to PCA Importance of non-gaussianity
CIFAR Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Dept of Computer Science University of Helsinki, Finland Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference to PCA Importance of non-gaussianity
Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu
 Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu 02-01-2018 Biomedical data are usually high-dimensional Number of samples (n) is relatively small whereas number of features (p) can be large Sometimes p>>n Problems
Machine Learning (BSMC-GA 4439) Wenke Liu 02-01-2018 Biomedical data are usually high-dimensional Number of samples (n) is relatively small whereas number of features (p) can be large Sometimes p>>n Problems
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018 Last Time: PCA with Orthogonal/Sequential Basis When k = 1, PCA has a scaling problem. When k > 1, have scaling, rotation,
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018 Last Time: PCA with Orthogonal/Sequential Basis When k = 1, PCA has a scaling problem. When k > 1, have scaling, rotation,
HST.582J / 6.555J / J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego
 Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsdedu References 1 Hyvarinen, A, Karhunen, J, & Oja, E (2004) Independent component analysis (Vol 46)
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Bhaskar D Rao University of California, San Diego Email: brao@ucsdedu References 1 Hyvarinen, A, Karhunen, J, & Oja, E (2004) Independent component analysis (Vol 46)
Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II
 Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II Gatsby Unit University College London 27 Feb 2017 Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference
Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II Gatsby Unit University College London 27 Feb 2017 Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference
Independent Component Analysis and Its Applications. By Qing Xue, 10/15/2004
 Independent Component Analysis and Its Applications By Qing Xue, 10/15/2004 Outline Motivation of ICA Applications of ICA Principles of ICA estimation Algorithms for ICA Extensions of basic ICA framework
Independent Component Analysis and Its Applications By Qing Xue, 10/15/2004 Outline Motivation of ICA Applications of ICA Principles of ICA estimation Algorithms for ICA Extensions of basic ICA framework
CS281 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA
 CS81 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA Scott Linderman At this point we have seen a variety of machine learning models, with a particular emphasis on models for supervised learning. In particular, we
CS81 Section 4: Factor Analysis and PCA Scott Linderman At this point we have seen a variety of machine learning models, with a particular emphasis on models for supervised learning. In particular, we
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
Density Estimation. Seungjin Choi
 Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA
 Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA Yoshua Bengio Pascal Vincent Jean-François Paiement University of Montreal April 2, Snowbird Learning 2003 Learning Modal Structures
Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA Yoshua Bengio Pascal Vincent Jean-François Paiement University of Montreal April 2, Snowbird Learning 2003 Learning Modal Structures
Artificial Intelligence Module 2. Feature Selection. Andrea Torsello
 Artificial Intelligence Module 2 Feature Selection Andrea Torsello We have seen that high dimensional data is hard to classify (curse of dimensionality) Often however, the data does not fill all the space
Artificial Intelligence Module 2 Feature Selection Andrea Torsello We have seen that high dimensional data is hard to classify (curse of dimensionality) Often however, the data does not fill all the space
Variational Message Passing. By John Winn, Christopher M. Bishop Presented by Andy Miller
 Variational Message Passing By John Winn, Christopher M. Bishop Presented by Andy Miller Overview Background Variational Inference Conjugate-Exponential Models Variational Message Passing Messages Univariate
Variational Message Passing By John Winn, Christopher M. Bishop Presented by Andy Miller Overview Background Variational Inference Conjugate-Exponential Models Variational Message Passing Messages Univariate
DEEP LEARNING CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY & INFORMATION THEORY
 DEEP LEARNING CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY & INFORMATION THEORY OUTLINE 3.1 Why Probability? 3.2 Random Variables 3.3 Probability Distributions 3.4 Marginal Probability 3.5 Conditional Probability 3.6 The Chain
DEEP LEARNING CHAPTER 3 PROBABILITY & INFORMATION THEORY OUTLINE 3.1 Why Probability? 3.2 Random Variables 3.3 Probability Distributions 3.4 Marginal Probability 3.5 Conditional Probability 3.6 The Chain
Neural coding Ecological approach to sensory coding: efficient adaptation to the natural environment
 Neural coding Ecological approach to sensory coding: efficient adaptation to the natural environment Jean-Pierre Nadal CNRS & EHESS Laboratoire de Physique Statistique (LPS, UMR 8550 CNRS - ENS UPMC Univ.
Neural coding Ecological approach to sensory coding: efficient adaptation to the natural environment Jean-Pierre Nadal CNRS & EHESS Laboratoire de Physique Statistique (LPS, UMR 8550 CNRS - ENS UPMC Univ.
Dimensionality Reduction. CS57300 Data Mining Fall Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro
 Dimensionality Reduction CS57300 Data Mining Fall 2016 Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro Goal } Visualize high dimensional data (and understand its Geometry) } Project the data into lower dimensional spaces }
Dimensionality Reduction CS57300 Data Mining Fall 2016 Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro Goal } Visualize high dimensional data (and understand its Geometry) } Project the data into lower dimensional spaces }
Introduction to Independent Component Analysis. Jingmei Lu and Xixi Lu. Abstract
 Final Project 2//25 Introduction to Independent Component Analysis Abstract Independent Component Analysis (ICA) can be used to solve blind signal separation problem. In this article, we introduce definition
Final Project 2//25 Introduction to Independent Component Analysis Abstract Independent Component Analysis (ICA) can be used to solve blind signal separation problem. In this article, we introduce definition
Independent Component Analysis. PhD Seminar Jörgen Ungh
 Independent Component Analysis PhD Seminar Jörgen Ungh Agenda Background a motivater Independence ICA vs. PCA Gaussian data ICA theory Examples Background & motivation The cocktail party problem Bla bla
Independent Component Analysis PhD Seminar Jörgen Ungh Agenda Background a motivater Independence ICA vs. PCA Gaussian data ICA theory Examples Background & motivation The cocktail party problem Bla bla
Slide11 Haykin Chapter 10: Information-Theoretic Models
 Slide11 Haykin Chapter 10: Information-Theoretic Models CPSC 636-600 Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Spring 2015 ICA section is heavily derived from Aapo Hyvärinen s ICA tutorial: http://www.cis.hut.fi/aapo/papers/ijcnn99_tutorialweb/.
Slide11 Haykin Chapter 10: Information-Theoretic Models CPSC 636-600 Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Spring 2015 ICA section is heavily derived from Aapo Hyvärinen s ICA tutorial: http://www.cis.hut.fi/aapo/papers/ijcnn99_tutorialweb/.
An Improved Cumulant Based Method for Independent Component Analysis
 An Improved Cumulant Based Method for Independent Component Analysis Tobias Blaschke and Laurenz Wiskott Institute for Theoretical Biology Humboldt University Berlin Invalidenstraße 43 D - 0 5 Berlin Germany
An Improved Cumulant Based Method for Independent Component Analysis Tobias Blaschke and Laurenz Wiskott Institute for Theoretical Biology Humboldt University Berlin Invalidenstraße 43 D - 0 5 Berlin Germany
The Behaviour of the Akaike Information Criterion when Applied to Non-nested Sequences of Models
 The Behaviour of the Akaike Information Criterion when Applied to Non-nested Sequences of Models Centre for Molecular, Environmental, Genetic & Analytic (MEGA) Epidemiology School of Population Health
The Behaviour of the Akaike Information Criterion when Applied to Non-nested Sequences of Models Centre for Molecular, Environmental, Genetic & Analytic (MEGA) Epidemiology School of Population Health
ICA Using Spacings Estimates of Entropy
 Journal of Machine Learning Research 4 (2003) 1271-1295 Submitted 10/02; Published 12/03 ICA Using Spacings Estimates of Entropy Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Journal of Machine Learning Research 4 (2003) 1271-1295 Submitted 10/02; Published 12/03 ICA Using Spacings Estimates of Entropy Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Decision-making, inference, and learning theory. ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016
 Decision-making, inference, and learning theory ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 22 What do we have here? Given measurements or observations of some physical process, we ask the simple question what do
Decision-making, inference, and learning theory ECE 830 & CS 761, Spring 2016 1 / 22 What do we have here? Given measurements or observations of some physical process, we ask the simple question what do
Learning with Noisy Labels. Kate Niehaus Reading group 11-Feb-2014
 Learning with Noisy Labels Kate Niehaus Reading group 11-Feb-2014 Outline Motivations Generative model approach: Lawrence, N. & Scho lkopf, B. Estimating a Kernel Fisher Discriminant in the Presence of
Learning with Noisy Labels Kate Niehaus Reading group 11-Feb-2014 Outline Motivations Generative model approach: Lawrence, N. & Scho lkopf, B. Estimating a Kernel Fisher Discriminant in the Presence of
Missing Data Issues in the Studies of Neurodegenerative Disorders: the Methodology
 Missing Data Issues in the Studies of Neurodegenerative Disorders: the Methodology Sheng Luo, PhD Associate Professor Department of Biostatistics & Bioinformatics Duke University Medical Center sheng.luo@duke.edu
Missing Data Issues in the Studies of Neurodegenerative Disorders: the Methodology Sheng Luo, PhD Associate Professor Department of Biostatistics & Bioinformatics Duke University Medical Center sheng.luo@duke.edu
Rigid Structure from Motion from a Blind Source Separation Perspective
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Rigid Structure from Motion from a Blind Source Separation Perspective Jeff Fortuna Aleix M. Martinez Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Rigid Structure from Motion from a Blind Source Separation Perspective Jeff Fortuna Aleix M. Martinez Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We
Natural Gradient Learning for Over- and Under-Complete Bases in ICA
 NOTE Communicated by Jean-François Cardoso Natural Gradient Learning for Over- and Under-Complete Bases in ICA Shun-ichi Amari RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Wako-shi, Hirosawa, Saitama 351-01, Japan Independent
NOTE Communicated by Jean-François Cardoso Natural Gradient Learning for Over- and Under-Complete Bases in ICA Shun-ichi Amari RIKEN Brain Science Institute, Wako-shi, Hirosawa, Saitama 351-01, Japan Independent
An Introduction to Independent Components Analysis (ICA)
 An Introduction to Independent Components Analysis (ICA) Anish R. Shah, CFA Northfield Information Services Anish@northinfo.com Newport Jun 6, 2008 1 Overview of Talk Review principal components Introduce
An Introduction to Independent Components Analysis (ICA) Anish R. Shah, CFA Northfield Information Services Anish@northinfo.com Newport Jun 6, 2008 1 Overview of Talk Review principal components Introduce
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. More PCA Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More PCA Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. No class Monday due to holiday. There will be tutorials next week on MAP/PCA (except Monday).
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More PCA Fall 2017 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. No class Monday due to holiday. There will be tutorials next week on MAP/PCA (except Monday).
Threshold models with fixed and random effects for ordered categorical data
 Threshold models with fixed and random effects for ordered categorical data Hans-Peter Piepho Universität Hohenheim, Germany Edith Kalka Universität Kassel, Germany Contents 1. Introduction. Case studies
Threshold models with fixed and random effects for ordered categorical data Hans-Peter Piepho Universität Hohenheim, Germany Edith Kalka Universität Kassel, Germany Contents 1. Introduction. Case studies
Lecture 10: Dimension Reduction Techniques
 Lecture 10: Dimension Reduction Techniques Radu Balan Department of Mathematics, AMSC, CSCAMM and NWC University of Maryland, College Park, MD April 17, 2018 Input Data It is assumed that there is a set
Lecture 10: Dimension Reduction Techniques Radu Balan Department of Mathematics, AMSC, CSCAMM and NWC University of Maryland, College Park, MD April 17, 2018 Input Data It is assumed that there is a set
Dimension Reduction (PCA, ICA, CCA, FLD,
 Dimension Reduction (PCA, ICA, CCA, FLD, Topic Models) Yi Zhang 10-701, Machine Learning, Spring 2011 April 6 th, 2011 Parts of the PCA slides are from previous 10-701 lectures 1 Outline Dimension reduction
Dimension Reduction (PCA, ICA, CCA, FLD, Topic Models) Yi Zhang 10-701, Machine Learning, Spring 2011 April 6 th, 2011 Parts of the PCA slides are from previous 10-701 lectures 1 Outline Dimension reduction
Fractal functional regression for classification of gene expression data by wavelets
 Fractal functional regression for classification of gene expression data by wavelets Margarita María Rincón 1 and María Dolores Ruiz-Medina 2 1 University of Granada Campus Fuente Nueva 18071 Granada,
Fractal functional regression for classification of gene expression data by wavelets Margarita María Rincón 1 and María Dolores Ruiz-Medina 2 1 University of Granada Campus Fuente Nueva 18071 Granada,
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715
 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715 Independent Component Analysis Barnabás Póczos Independent Component Analysis 2 Independent Component Analysis Model original signals Observations (Mixtures)
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715 Independent Component Analysis Barnabás Póczos Independent Component Analysis 2 Independent Component Analysis Model original signals Observations (Mixtures)
Fundamentals of Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Independent Component Analysis (ICA), and Independent Vector Analysis (IVA)
 Fundamentals of Principal Component Analysis (PCA),, and Independent Vector Analysis (IVA) Dr Mohsen Naqvi Lecturer in Signal and Information Processing, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
Fundamentals of Principal Component Analysis (PCA),, and Independent Vector Analysis (IVA) Dr Mohsen Naqvi Lecturer in Signal and Information Processing, School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution
 PHYSTAT, SLAC, Stanford, California, September 8-, Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution K. Zarb Adami Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK This paper gives an introduction to the
PHYSTAT, SLAC, Stanford, California, September 8-, Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution K. Zarb Adami Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK This paper gives an introduction to the
Statistical Analysis of fmrl Data
 Statistical Analysis of fmrl Data F. Gregory Ashby The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface xi Acronyms xv 1 Introduction 1 What Is fmri? 2 The Scanning Session 4 Experimental Design
Statistical Analysis of fmrl Data F. Gregory Ashby The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Preface xi Acronyms xv 1 Introduction 1 What Is fmri? 2 The Scanning Session 4 Experimental Design
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen PCA. Tobias Scheffer
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen PCA Tobias Scheffer Overview Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Kernel-PCA Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis t-sne 2 PCA: Motivation
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen PCA Tobias Scheffer Overview Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Kernel-PCA Fisher Linear Discriminant Analysis t-sne 2 PCA: Motivation
Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides
 Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic Inference Lecture
Lecture 16: Small Sample Size Problems (Covariance Estimation) Many thanks to Carlos Thomaz who authored the original version of these slides Intelligent Data Analysis and Probabilistic Inference Lecture
FA Homework 5 Recitation 1. Easwaran Ramamurthy Guoquan (GQ) Zhao Logan Brooks
 FA17 10-701 Homework 5 Recitation 1 Easwaran Ramamurthy Guoquan (GQ) Zhao Logan Brooks Note Remember that there is no problem set covering some of the lecture material; you may need to study these topics
FA17 10-701 Homework 5 Recitation 1 Easwaran Ramamurthy Guoquan (GQ) Zhao Logan Brooks Note Remember that there is no problem set covering some of the lecture material; you may need to study these topics
Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm
 Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic 3.1 Clustering and Mixture Modelling K-means and hierarchical clustering are non-probabilistic
Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic 3.1 Clustering and Mixture Modelling K-means and hierarchical clustering are non-probabilistic
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 4 Problem: Density Estimation We have observed data, y 1,..., y n, drawn independently from some unknown
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 4 Problem: Density Estimation We have observed data, y 1,..., y n, drawn independently from some unknown
Empirical Wavelet Transform
 Jérôme Gilles Department of Mathematics, UCLA jegilles@math.ucla.edu Adaptive Data Analysis and Sparsity Workshop January 31th, 013 Outline Introduction - EMD 1D Empirical Wavelets Definition Experiments
Jérôme Gilles Department of Mathematics, UCLA jegilles@math.ucla.edu Adaptive Data Analysis and Sparsity Workshop January 31th, 013 Outline Introduction - EMD 1D Empirical Wavelets Definition Experiments
Independent Component Analysis (ICA)
 Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
PROPERTIES OF THE EMPIRICAL CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO TESTING FOR INDEPENDENCE. Noboru Murata
 ' / PROPERTIES OF THE EMPIRICAL CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO TESTING FOR INDEPENDENCE Noboru Murata Waseda University Department of Electrical Electronics and Computer Engineering 3--
' / PROPERTIES OF THE EMPIRICAL CHARACTERISTIC FUNCTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO TESTING FOR INDEPENDENCE Noboru Murata Waseda University Department of Electrical Electronics and Computer Engineering 3--
Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting area with many potential applications. Methods developed for solving sparse signal recovery proble
 Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
Spatial smoothing using Gaussian processes
 Spatial smoothing using Gaussian processes Chris Paciorek paciorek@hsph.harvard.edu August 5, 2004 1 OUTLINE Spatial smoothing and Gaussian processes Covariance modelling Nonstationary covariance modelling
Spatial smoothing using Gaussian processes Chris Paciorek paciorek@hsph.harvard.edu August 5, 2004 1 OUTLINE Spatial smoothing and Gaussian processes Covariance modelling Nonstationary covariance modelling
From independent component analysis to score matching
 From independent component analysis to score matching Aapo Hyvärinen Dept of Computer Science & HIIT Dept of Mathematics and Statistics University of Helsinki Finland 1 Abstract First, short introduction
From independent component analysis to score matching Aapo Hyvärinen Dept of Computer Science & HIIT Dept of Mathematics and Statistics University of Helsinki Finland 1 Abstract First, short introduction
13: Variational inference II
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
Independent Component Analysis
 Independent Component Analysis Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr March 4, 2009 1 / 78 Outline Theory and Preliminaries
Independent Component Analysis Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr March 4, 2009 1 / 78 Outline Theory and Preliminaries
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Bishop Chapter 6: Kernel Methods
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 6: Kernel Methods Vasil Khalidov Alex Kläser December 13, 2007 Training Data: Keep or Discard? Parametric methods (linear/nonlinear) so far: learn parameter
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 6: Kernel Methods Vasil Khalidov Alex Kläser December 13, 2007 Training Data: Keep or Discard? Parametric methods (linear/nonlinear) so far: learn parameter
Bayesian ensemble learning of generative models
 Chapter Bayesian ensemble learning of generative models Harri Valpola, Antti Honkela, Juha Karhunen, Tapani Raiko, Xavier Giannakopoulos, Alexander Ilin, Erkki Oja 65 66 Bayesian ensemble learning of generative
Chapter Bayesian ensemble learning of generative models Harri Valpola, Antti Honkela, Juha Karhunen, Tapani Raiko, Xavier Giannakopoulos, Alexander Ilin, Erkki Oja 65 66 Bayesian ensemble learning of generative
Machine learning - HT Maximum Likelihood
 Machine learning - HT 2016 3. Maximum Likelihood Varun Kanade University of Oxford January 27, 2016 Outline Probabilistic Framework Formulate linear regression in the language of probability Introduce
Machine learning - HT 2016 3. Maximum Likelihood Varun Kanade University of Oxford January 27, 2016 Outline Probabilistic Framework Formulate linear regression in the language of probability Introduce
13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
Factor Analysis (10/2/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Factor Analysis (10/2/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Li Zhu, Fan Li, Ni Guan Factor Analysis Factor analysis is related to the mixture models we have studied.
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Factor Analysis (10/2/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Li Zhu, Fan Li, Ni Guan Factor Analysis Factor analysis is related to the mixture models we have studied.
Robust Statistics, Revisited
 Robust Statistics, Revisited Ankur Moitra (MIT) joint work with Ilias Diakonikolas, Jerry Li, Gautam Kamath, Daniel Kane and Alistair Stewart CLASSIC PARAMETER ESTIMATION Given samples from an unknown
Robust Statistics, Revisited Ankur Moitra (MIT) joint work with Ilias Diakonikolas, Jerry Li, Gautam Kamath, Daniel Kane and Alistair Stewart CLASSIC PARAMETER ESTIMATION Given samples from an unknown
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques
 Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA CIS 520: Machine Learning Final, Fall 2013
 UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA CIS 520: Machine Learning Final, Fall 2013 Exam policy: This exam allows two one-page, two-sided cheat sheets; No other materials. Time: 2 hours. Be sure to write your name and
UNIVERSITY of PENNSYLVANIA CIS 520: Machine Learning Final, Fall 2013 Exam policy: This exam allows two one-page, two-sided cheat sheets; No other materials. Time: 2 hours. Be sure to write your name and
2234 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 52, NO. 8, AUGUST Nonparametric Hypothesis Tests for Statistical Dependency
 2234 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 52, NO. 8, AUGUST 2004 Nonparametric Hypothesis Tests for Statistical Dependency Alexander T. Ihler, Student Member, IEEE, John W. Fisher, Member, IEEE,
2234 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 52, NO. 8, AUGUST 2004 Nonparametric Hypothesis Tests for Statistical Dependency Alexander T. Ihler, Student Member, IEEE, John W. Fisher, Member, IEEE,
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision
 Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
Linear Dynamical Systems
 Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
Nonparametric Regression With Gaussian Processes
 Nonparametric Regression With Gaussian Processes From Chap. 45, Information Theory, Inference and Learning Algorithms, D. J. C. McKay Presented by Micha Elsner Nonparametric Regression With Gaussian Processes
Nonparametric Regression With Gaussian Processes From Chap. 45, Information Theory, Inference and Learning Algorithms, D. J. C. McKay Presented by Micha Elsner Nonparametric Regression With Gaussian Processes
Variational Inference (11/04/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
STATS 306B: Unsupervised Learning Spring Lecture 12 May 7
 STATS 306B: Unsupervised Learning Spring 2014 Lecture 12 May 7 Lecturer: Lester Mackey Scribe: Lan Huong, Snigdha Panigrahi 12.1 Beyond Linear State Space Modeling Last lecture we completed our discussion
STATS 306B: Unsupervised Learning Spring 2014 Lecture 12 May 7 Lecturer: Lester Mackey Scribe: Lan Huong, Snigdha Panigrahi 12.1 Beyond Linear State Space Modeling Last lecture we completed our discussion
Week 3: The EM algorithm
 Week 3: The EM algorithm Maneesh Sahani maneesh@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London Term 1, Autumn 2005 Mixtures of Gaussians Data: Y = {y 1... y N } Latent
Week 3: The EM algorithm Maneesh Sahani maneesh@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London Term 1, Autumn 2005 Mixtures of Gaussians Data: Y = {y 1... y N } Latent
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
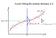 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Sparse linear models
 Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
Dimension Reduction. David M. Blei. April 23, 2012
 Dimension Reduction David M. Blei April 23, 2012 1 Basic idea Goal: Compute a reduced representation of data from p -dimensional to q-dimensional, where q < p. x 1,...,x p z 1,...,z q (1) We want to do
Dimension Reduction David M. Blei April 23, 2012 1 Basic idea Goal: Compute a reduced representation of data from p -dimensional to q-dimensional, where q < p. x 1,...,x p z 1,...,z q (1) We want to do
MACHINE LEARNING. Methods for feature extraction and reduction of dimensionality: Probabilistic PCA and kernel PCA
 1 MACHINE LEARNING Methods for feature extraction and reduction of dimensionality: Probabilistic PCA and kernel PCA 2 Practicals Next Week Next Week, Practical Session on Computer Takes Place in Room GR
1 MACHINE LEARNING Methods for feature extraction and reduction of dimensionality: Probabilistic PCA and kernel PCA 2 Practicals Next Week Next Week, Practical Session on Computer Takes Place in Room GR
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework 3 Due Nov 12, 10.30 am Rules 1. Homework is due on the due date at 10.30 am. Please hand over your homework at the beginning of class. Please see
10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning Homework 3 Due Nov 12, 10.30 am Rules 1. Homework is due on the due date at 10.30 am. Please hand over your homework at the beginning of class. Please see
Random Sampling of Bandlimited Signals on Graphs
 Random Sampling of Bandlimited Signals on Graphs Pierre Vandergheynst École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) School of Engineering & School of Computer and Communication Sciences Joint work with
Random Sampling of Bandlimited Signals on Graphs Pierre Vandergheynst École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) School of Engineering & School of Computer and Communication Sciences Joint work with
2.3. Clustering or vector quantization 57
 Multivariate Statistics non-negative matrix factorisation and sparse dictionary learning The PCA decomposition is by construction optimal solution to argmin A R n q,h R q p X AH 2 2 under constraint :
Multivariate Statistics non-negative matrix factorisation and sparse dictionary learning The PCA decomposition is by construction optimal solution to argmin A R n q,h R q p X AH 2 2 under constraint :
Switching-state Dynamical Modeling of Daily Behavioral Data
 Switching-state Dynamical Modeling of Daily Behavioral Data Randy Ardywibowo Shuai Huang Cao Xiao Shupeng Gui Yu Cheng Ji Liu Xiaoning Qian Texas A&M University University of Washington IBM T.J. Watson
Switching-state Dynamical Modeling of Daily Behavioral Data Randy Ardywibowo Shuai Huang Cao Xiao Shupeng Gui Yu Cheng Ji Liu Xiaoning Qian Texas A&M University University of Washington IBM T.J. Watson
On the Behavior of Marginal and Conditional Akaike Information Criteria in Linear Mixed Models
 On the Behavior of Marginal and Conditional Akaike Information Criteria in Linear Mixed Models Thomas Kneib Department of Mathematics Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg Sonja Greven Department of
On the Behavior of Marginal and Conditional Akaike Information Criteria in Linear Mixed Models Thomas Kneib Department of Mathematics Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg Sonja Greven Department of
Functional Preprocessing for Multilayer Perceptrons
 Functional Preprocessing for Multilayer Perceptrons Fabrice Rossi and Brieuc Conan-Guez Projet AxIS, INRIA, Domaine de Voluceau, Rocquencourt, B.P. 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France CEREMADE, UMR CNRS
Functional Preprocessing for Multilayer Perceptrons Fabrice Rossi and Brieuc Conan-Guez Projet AxIS, INRIA, Domaine de Voluceau, Rocquencourt, B.P. 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France CEREMADE, UMR CNRS
Independent Component Analysis
 A Short Introduction to Independent Component Analysis Aapo Hyvärinen Helsinki Institute for Information Technology and Depts of Computer Science and Psychology University of Helsinki Problem of blind
A Short Introduction to Independent Component Analysis Aapo Hyvärinen Helsinki Institute for Information Technology and Depts of Computer Science and Psychology University of Helsinki Problem of blind
CS Lecture 19. Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation
 CS 6347 Lecture 19 Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation Discrete State Spaces We have been focusing on the case of MRFs over discrete state spaces Probability distributions over discrete spaces
CS 6347 Lecture 19 Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation Discrete State Spaces We have been focusing on the case of MRFs over discrete state spaces Probability distributions over discrete spaces
Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference
 Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference Prof. Nathan L. Gibson Department of Mathematics Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar March 4, 2011 Prof. Gibson (OSU) Spectral Approaches to
Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference Prof. Nathan L. Gibson Department of Mathematics Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar March 4, 2011 Prof. Gibson (OSU) Spectral Approaches to
PCA & ICA. CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 PCA & ICA CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2015 Soleymani Dimensionality Reduction: Feature Selection vs. Feature Extraction Feature selection Select a subset of a given
PCA & ICA CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2015 Soleymani Dimensionality Reduction: Feature Selection vs. Feature Extraction Feature selection Select a subset of a given
ICA [6] ICA) [7, 8] ICA ICA ICA [9, 10] J-F. Cardoso. [13] Matlab ICA. Comon[3], Amari & Cardoso[4] ICA ICA
![ICA [6] ICA) [7, 8] ICA ICA ICA [9, 10] J-F. Cardoso. [13] Matlab ICA. Comon[3], Amari & Cardoso[4] ICA ICA ICA [6] ICA) [7, 8] ICA ICA ICA [9, 10] J-F. Cardoso. [13] Matlab ICA. Comon[3], Amari & Cardoso[4] ICA ICA](/thumbs/94/118075880.jpg) 16 1 (Independent Component Analysis: ICA) 198 9 ICA ICA ICA 1 ICA 198 Jutten Herault Comon[3], Amari & Cardoso[4] ICA Comon (PCA) projection persuit projection persuit ICA ICA ICA 1 [1] [] ICA ICA EEG
16 1 (Independent Component Analysis: ICA) 198 9 ICA ICA ICA 1 ICA 198 Jutten Herault Comon[3], Amari & Cardoso[4] ICA Comon (PCA) projection persuit projection persuit ICA ICA ICA 1 [1] [] ICA ICA EEG
Massoud BABAIE-ZADEH. Blind Source Separation (BSS) and Independent Componen Analysis (ICA) p.1/39
 Blind Source Separation (BSS) and Independent Componen Analysis (ICA) Massoud BABAIE-ZADEH Blind Source Separation (BSS) and Independent Componen Analysis (ICA) p.1/39 Outline Part I Part II Introduction
Blind Source Separation (BSS) and Independent Componen Analysis (ICA) Massoud BABAIE-ZADEH Blind Source Separation (BSS) and Independent Componen Analysis (ICA) p.1/39 Outline Part I Part II Introduction
HMM and IOHMM Modeling of EEG Rhythms for Asynchronous BCI Systems
 HMM and IOHMM Modeling of EEG Rhythms for Asynchronous BCI Systems Silvia Chiappa and Samy Bengio {chiappa,bengio}@idiap.ch IDIAP, P.O. Box 592, CH-1920 Martigny, Switzerland Abstract. We compare the use
HMM and IOHMM Modeling of EEG Rhythms for Asynchronous BCI Systems Silvia Chiappa and Samy Bengio {chiappa,bengio}@idiap.ch IDIAP, P.O. Box 592, CH-1920 Martigny, Switzerland Abstract. We compare the use
Copula Based Independent Component Analysis
 Copula Based Independent Component Analysis CUNY October 2008 Kobi Abayomi + + Asst. Professor Industrial Engineering - Statistics Group Georgia Institute of Technology October 2008 Introduction Outline
Copula Based Independent Component Analysis CUNY October 2008 Kobi Abayomi + + Asst. Professor Industrial Engineering - Statistics Group Georgia Institute of Technology October 2008 Introduction Outline
ICES REPORT Model Misspecification and Plausibility
 ICES REPORT 14-21 August 2014 Model Misspecification and Plausibility by Kathryn Farrell and J. Tinsley Odena The Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences The University of Texas at Austin
ICES REPORT 14-21 August 2014 Model Misspecification and Plausibility by Kathryn Farrell and J. Tinsley Odena The Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences The University of Texas at Austin
Kernel methods, kernel SVM and ridge regression
 Kernel methods, kernel SVM and ridge regression Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Collaborative Filtering 2 Collaborative Filtering R: rating matrix; U: user factor;
Kernel methods, kernel SVM and ridge regression Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Collaborative Filtering 2 Collaborative Filtering R: rating matrix; U: user factor;
GWAS V: Gaussian processes
 GWAS V: Gaussian processes Dr. Oliver Stegle Christoh Lippert Prof. Dr. Karsten Borgwardt Max-Planck-Institutes Tübingen, Germany Tübingen Summer 2011 Oliver Stegle GWAS V: Gaussian processes Summer 2011
GWAS V: Gaussian processes Dr. Oliver Stegle Christoh Lippert Prof. Dr. Karsten Borgwardt Max-Planck-Institutes Tübingen, Germany Tübingen Summer 2011 Oliver Stegle GWAS V: Gaussian processes Summer 2011
Independent Component Analysis of Incomplete Data
 Independent Component Analysis of Incomplete Data Max Welling Markus Weber California Institute of Technology 136-93 Pasadena, CA 91125 fwelling,rmwg@vision.caltech.edu Keywords: EM, Missing Data, ICA
Independent Component Analysis of Incomplete Data Max Welling Markus Weber California Institute of Technology 136-93 Pasadena, CA 91125 fwelling,rmwg@vision.caltech.edu Keywords: EM, Missing Data, ICA
