Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates. A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System
|
|
|
- Posy Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theory of Force Transmission and Rigidity in Granular Aggregates A Different kind of NonEquilibrium System
2 Dapeng Bi Sumantra Sarkar Kabir Ramola Jetin Thomas Bob Behringer, Jie Ren Dong Wang Jeff Morris Romain Mari Ryohei Seto
3 GRANULAR WORLD Collection of macroscopic objects Purely repulsive, contact interactions. No thermal fluctuations to restore broken contacts Friction: Forces are independent degrees of freedom States controlled by driving at the boundaries or body forces: shear, gravity Non-ergodic in the extreme sense: stays in one configuration unless driven
4 LOOKING INSIDE SAND
5 Stress Metric
6 Statics of Granular Media: Constraints of mechanical equilibrium determine collective behavior Local force & torque balance satisfied for every grain Friction law on each contact!!!!!! Positivity of all forces!! 0! Imposed stresses determine sum of stresses over all grains
7 Imposing force balance (2D) Forces on every grain sum to zero: Newton s third law dictates:
8 Height Representation Ball & Blumenfeld, 2003 ~ hg,v1 ~ hg,v2 The conditions of mechanical equilibrium ensure the uniqueness of the height representation r ˆ =0! Vector potential The heights live on a random network
9 Force Tilings For systems where all normal forces are repulsive, we have a single sheet
10 TWO REPRESENTATIONS
11 Two problems: Stress Transmission in Static Granular Aggregates Procaccia group: Numerical Simulations (2016) Discontinuous Shear Thickening in Dense Suspensions
12 How do granular materials respond to applied forces? Forces are carried primarily by a tenuous network that is a fraction of the total number of grains Geng et al, PRL (2001) Ensemble averaged patterns are sensitive to nature of underlying spatial disorder
13 Theoretical Models q-model (Coppersmith et al (1996)): Scalar force balance on an ordered network. Disorder incorporated at contacts: how forces get transmitted at contacts. In continuum, reduces to the diffusion equation. Broad distribution of forces. In response to a localized force at the top of a pile, the pressure profile at the bottom has a peak with width proportional to the square root of the height.
14 Theoretical Models Missing stress-geometry equation: no well defined strain field/compatibility relations Continuum models with prescribed constitutive law relating stress components. determined by history of preparation. For example, zz = c 2 0 xx More elaborate closure relations: (Review: J.-P. Bouchaud Les Houches Lectures) Stresses propagate/ get transmitted along lines
15 Force Response of a network to a perturbation Geometry of contact network represented by the network Laplacian Random matrix: diagonal elements contain the number of contacts, otherwise the adjacency matrix
16 Framework 2 ~ i = ~ f body i Equation defining the auxiliary fields Given a contact network and a set of body forces, solution is unique If the solution violates torque balance/static friction condition, network will rearrange Disorder of contact network represented by network Laplacian Diffusion on a random network: Localization? Eigenfunction expansion 2 = P N i=1 i iih i One zero mode 1 =0, 1i =( ) Localized? ~ i = P N i=1 1 i h i ~ f body i ii Different from q model: On a given contact network, how the force perturbation gets distributed among contacts is completely determined by the constraints of force balance Constitutive Law determined by statistical properties of the ensemble of Laplacians
17 Response of a frictionless granular solid
18 Highest eigenvalue: strongly localized Lowest eigenvalue: delocalized
19 Ensemble average: Spectral properties E G =10 5 E G =10 10 E G =10 15 IPR(λ) Density of States 0.8 E G = E G = Inverse Participation Ratio λ ρ(λ) E G = λ
20 Stress Localization Maps granular response problem to the localization problem Absence of Diffusion in Certain Random Lattices P. W. Anderson (1958) Theory relates response to the disorder in the underlying network Random Matrix Ensembles: Characterizing Jammed Networks Many Body Localization: Strongly Interacting System
21 Discontinuous Shear Thickening 21
22 A Thickening Scenario 22
23 Phase Diagram from Rheology: Abhi Singh & Jeff Morris Is this a cri*cal point? 23
24 Clustering of points Clustering/Clumping of points
25 # of clusters
26 Equibrium Model Repulsive interaction between heights with a single stress scale Simplest: If height points are closer than this scale, they repel 6= 0 V(h) =0 6= 0 Clumping Transition: Many points clustered close together. 6= 0 These clumps/clusters form a crystalline or amorphous arrangement Mapping to Shear Thickening Role of inverse temperature is played by the packing fraction =0 Density is controlled by imposed stress =0 =0 6= 0 / 1/T A tricri*cal point?
27 Statistical Mechanics of Granular Media Dual Networks: Contacts and Force Tilings History Dependence: Including forces in defining microstates takes away that indeterminacy Contact Networks are random but can characterize ensembles Pattern formation in height fields: Distinguish phases
28
29 Cluster Analysis s = s = s = 0.1 s = 1 s = 0.5 s =
30 Response in a frictionless jammed packing
Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening
 Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening The essential idea underlying the jamming-based rheology model [3, 6] for DST is that it requires
Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening The essential idea underlying the jamming-based rheology model [3, 6] for DST is that it requires
Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening
 Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Shear-induced organization of forces in dense suspensions: signatures of discontinuous shear thickening The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 15 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 15 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 15 May 2013](/thumbs/87/96930086.jpg) Origin of Rigidity in Dry Granular Solids Sumantra Sarkar, Dapeng Bi 2, Jie Zhang 3, R. P. Behringer 4, and Bulbul Chakraborty Martin Fisher School of Physics, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA 2454, USA
Origin of Rigidity in Dry Granular Solids Sumantra Sarkar, Dapeng Bi 2, Jie Zhang 3, R. P. Behringer 4, and Bulbul Chakraborty Martin Fisher School of Physics, Brandeis University, Waltham, MA 2454, USA
Discontinuous Shear Thickening
 Discontinuous Shear Thickening dynamic jamming transition Ryohei Seto, Romain Mari, Jeffrey F. Morris, Morton M. Denn Levich Institute, City College of New York First experimental data Williamson and Hecker
Discontinuous Shear Thickening dynamic jamming transition Ryohei Seto, Romain Mari, Jeffrey F. Morris, Morton M. Denn Levich Institute, City College of New York First experimental data Williamson and Hecker
A model for the transmission of contact forces in granular piles
 Author: Javier Cristín. Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain Advisor: Carmen Miguel. Abstract:Granular matter is fundamentally different from other, more conventional,
Author: Javier Cristín. Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 645, 08028 Barcelona, Spain Advisor: Carmen Miguel. Abstract:Granular matter is fundamentally different from other, more conventional,
collisions inelastic, energy is dissipated and not conserved
 LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
LECTURE 1 - Introduction to Granular Materials Jamming, Random Close Packing, The Isostatic State Granular materials particles only interact when they touch hard cores: rigid, incompressible, particles
A simulation study on shear thickening in wide-gap Couette geometry. Ryohei Seto, Romain Mari Jeffery Morris, Morton Denn, Eliot Fried
 A simulation study on shear thickening in wide-gap Couette geometry Ryohei Seto, Romain Mari Jeffery Morris, Morton Denn, Eliot Fried Stokes flow: Zero-Reynolds number fluid mechanics Repulsive Attractive
A simulation study on shear thickening in wide-gap Couette geometry Ryohei Seto, Romain Mari Jeffery Morris, Morton Denn, Eliot Fried Stokes flow: Zero-Reynolds number fluid mechanics Repulsive Attractive
The Statistical Physics of Athermal Particles (The Edwards Ensemble at 25)
 The Statistical Physics of Athermal Particles (The Edwards Ensemble at 25) Karen Daniels Dept. of Physics NC State University http://nile.physics.ncsu.edu 1 Sir Sam Edwards Why Consider Ensembles? for
The Statistical Physics of Athermal Particles (The Edwards Ensemble at 25) Karen Daniels Dept. of Physics NC State University http://nile.physics.ncsu.edu 1 Sir Sam Edwards Why Consider Ensembles? for
Statistical Mechanics of Granular Systems
 Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Martí i Franquès 1, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: Antoni Planes Vila Abstract: This work is a review that deals with the possibility of application
Author: Facultat de Física, Universitat de Barcelona, Martí i Franquès 1, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. Advisor: Antoni Planes Vila Abstract: This work is a review that deals with the possibility of application
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007](/thumbs/93/111468426.jpg) Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Universal Anisotropy in Force Networks under Shear Srdjan Ostojic, 1, Thijs J. H. Vlugt, 2 and Bernard Nienhuis 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0610483v2 [cond-mat.soft] 28 Mar 2007 1 Institute for Theoretical Physics,
Indiana University, January T. Witten, University of Chicago
 Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Indiana University, January 2007 T. Witten, University of Chicago Force propagation in a simple solid: two pictures Add circular beads to a container one by one How does an added force reach the ground?
Granular Matter and the Marginal Rigidity State.
 1 Granular Matter and the Marginal Rigidity State. R Blumenfeld*, SF Edwards and RC Ball*, *Department of Physics, University of Warwick, CV4 7AL Coventry, UK. Polymers and Colloids, Cavendish Laboratory,
1 Granular Matter and the Marginal Rigidity State. R Blumenfeld*, SF Edwards and RC Ball*, *Department of Physics, University of Warwick, CV4 7AL Coventry, UK. Polymers and Colloids, Cavendish Laboratory,
Discontinuous shear thickening on dense non-brownian suspensions via lattice Boltzmann method
 Discontinuous shear thickening on dense non-brownian suspensions via lattice Boltzmann method Pradipto and Hisao Hayakawa Yukawa Insitute for Theoretical Physics Kyoto University Rheology of disordered
Discontinuous shear thickening on dense non-brownian suspensions via lattice Boltzmann method Pradipto and Hisao Hayakawa Yukawa Insitute for Theoretical Physics Kyoto University Rheology of disordered
Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach
 May 2013 EPL, 2 (2013) 34002 doi:.1209/029-07/2/34002 www.epljournal.org Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach Dapeng Bi 1, Jie Zhang 2,R.P.Behringer 3 and Bulbul Chakraborty
May 2013 EPL, 2 (2013) 34002 doi:.1209/029-07/2/34002 www.epljournal.org Fluctuations in shear-jammed states: A statistical ensemble approach Dapeng Bi 1, Jie Zhang 2,R.P.Behringer 3 and Bulbul Chakraborty
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
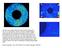 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors
 Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Granular Micro-Structure and Avalanche Precursors L. Staron, F. Radjai & J.-P. Vilotte Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, Cambridge CB3 0WA, UK. Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie
Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model. David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712
 Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model by David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 Abstract We introduce a model of granular matter and use a stress
Dilatancy Transition in a Granular Model by David Aristoff and Charles Radin * Mathematics Department, University of Texas, Austin, TX 78712 Abstract We introduce a model of granular matter and use a stress
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids
 Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Inhomogeneous elastic response of amorphous solids Jean-Louis Barrat Université de Lyon Institut Universitaire de France Acknowledgements: Anne Tanguy, Fabien Chay Goldenberg, Léonforte, Michel Tsamados
Micro-Macro transition (from particles to continuum theory) Granular Materials. Approach philosophy. Model Granular Materials
 Micro-Macro transition (from particles to continuum theory) Stefan Luding MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Stefan Luding, s.luding@utwente.nl MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Granular Materials Real: sand, soil, rock,
Micro-Macro transition (from particles to continuum theory) Stefan Luding MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Stefan Luding, s.luding@utwente.nl MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Granular Materials Real: sand, soil, rock,
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming
 Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Statistical Mechanics of Jamming Lecture 1: Timescales and Lengthscales, jamming vs thermal critical points Lecture 2: Statistical ensembles: inherent structures and blocked states Lecture 3: Example of
Table of Contents. Preface... xiii
 Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media
 Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Continuum Model of Avalanches in Granular Media David Chen May 13, 2010 Abstract A continuum description of avalanches in granular systems is presented. The model is based on hydrodynamic equations coupled
Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Diego Berzi Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We apply the Extended
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Diego Berzi Extended kinetic theory applied to dense, granular, simple shear flows Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We apply the Extended
Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media
 Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
Copyright 011 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.71, no., pp.149-155, 011 Turbulentlike Quantitative Analysis on Energy Dissipation in Vibrated Granular Media Zhi Yuan Cui 1, Jiu Hui Wu 1 and Di Chen Li 1 Abstract:
On Phase Transition and Self-Organized Critical State in Granular Packings
 arxiv:cond-mat/9812204v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 11 Dec 1998 On Phase Transition and Self-Organized Critical State in Granular Packings Einat Aharonov 1, David Sparks 2, 1 Lamont-Doherty Earth-Observatory, Columbia
arxiv:cond-mat/9812204v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 11 Dec 1998 On Phase Transition and Self-Organized Critical State in Granular Packings Einat Aharonov 1, David Sparks 2, 1 Lamont-Doherty Earth-Observatory, Columbia
Introduction to Theory of Mesoscopic Systems
 Introduction to Theory of Mesoscopic Systems Boris Altshuler Princeton University, Columbia University & NEC Laboratories America Lecture 3 Beforehand Weak Localization and Mesoscopic Fluctuations Today
Introduction to Theory of Mesoscopic Systems Boris Altshuler Princeton University, Columbia University & NEC Laboratories America Lecture 3 Beforehand Weak Localization and Mesoscopic Fluctuations Today
Prestress stability. Lecture VI. Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré. R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics
 Prestress stability Lecture VI Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics 1 Potential functions How is the stability of a structure determined
Prestress stability Lecture VI Session on Granular Matter Institut Henri Poincaré R. Connelly Cornell University Department of Mathematics 1 Potential functions How is the stability of a structure determined
Flow of Glasses. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Flow of Glasses Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Liquid or Solid? Liquid or Solid? Example: Pitch Solid! 1 day 1 year Menkind 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 4 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 sec Time scale Liquid!
Anderson Localization Looking Forward
 Anderson Localization Looking Forward Boris Altshuler Physics Department, Columbia University Collaborations: Also Igor Aleiner Denis Basko, Gora Shlyapnikov, Vincent Michal, Vladimir Kravtsov, Lecture2
Anderson Localization Looking Forward Boris Altshuler Physics Department, Columbia University Collaborations: Also Igor Aleiner Denis Basko, Gora Shlyapnikov, Vincent Michal, Vladimir Kravtsov, Lecture2
Force Network Statistics
 Force Network Statistics Brian Tighe with Rianne van Eerd and Thijs Vlugt nonequilibrium ensemble of static states here: force network ensemble many force networks one contact network statistics of local
Force Network Statistics Brian Tighe with Rianne van Eerd and Thijs Vlugt nonequilibrium ensemble of static states here: force network ensemble many force networks one contact network statistics of local
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials
 JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
JMBC Workshop Statics and dynamics of soft and granular materials Drienerburght, University of Twente, February 25 - March 1, 2013 Speakers: Dirk van der Ende - Nico Gray - Detlef Lohse - Stefan Luding
Response of a hexagonal granular packing under a localized external force
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 July 5 Europhys. Lett., 71 (1), pp. 7 76 (5) DOI: 1.19/epl/i-153-9 Response of a hexagonal granular packing under a localized external force S. Ostojic and D. Panja Institute for
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 July 5 Europhys. Lett., 71 (1), pp. 7 76 (5) DOI: 1.19/epl/i-153-9 Response of a hexagonal granular packing under a localized external force S. Ostojic and D. Panja Institute for
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 2005](/thumbs/83/88963522.jpg) Driven lattice gas with nearest-neighbor exclusion: shear-like drive arxiv:cond-mat/57114v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 25 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
Driven lattice gas with nearest-neighbor exclusion: shear-like drive arxiv:cond-mat/57114v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Jul 25 Fabricio Q. Potiguar and Ronald Dickman Departamento de Física, ICEx, Universidade
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II. Peter Schall University of Amsterdam
 Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Nonequilibrium transitions in glassy flows II Peter Schall University of Amsterdam Flow of glasses 1st Lecture Glass Phenomenology Basic concepts: Free volume, Dynamic correlations Apply Shear Glass? Soft
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming
 Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Effective Temperatures in Driven Systems near Jamming Andrea J. Liu Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Pennsylvania Tom Haxton Yair Shokef Tal Danino Ian Ono Corey S. O Hern Douglas Durian
Mechanics of Granular Matter
 Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
Mechanics of Granular Matter Mechanics of Granular Matter Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Qicheng Sun & Guangqian Wang Tsinghua University, Beijing, China Published by
Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions
 294 DOI 10.1007/s12182-009-0047-3 Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions Dong Zhaoxia, Li Yahua, Lin Meiqin and Li Mingyuan Enhanced Oil Recovery Research Center, China University of Petroleum,
294 DOI 10.1007/s12182-009-0047-3 Rheological properties of polymer micro-gel dispersions Dong Zhaoxia, Li Yahua, Lin Meiqin and Li Mingyuan Enhanced Oil Recovery Research Center, China University of Petroleum,
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 2, 24 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 2, 24 March 2006 1 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Università degli Studi di Bari. mechanics 1. Load system determination. Joint load. Stress-strain distribution. Biological response 2/45 3/45
 Università degli Studi di Bari mechanics 1 Load system determination Joint load Stress-strain distribution Biological response 2/45 3/45 ? 4/45 The human body machine Energy transformation Work development
Università degli Studi di Bari mechanics 1 Load system determination Joint load Stress-strain distribution Biological response 2/45 3/45 ? 4/45 The human body machine Energy transformation Work development
Particle flow simulation of sand under biaxial test
 5th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Transportation (ICCET 2015) Particle flow simulation of sand under biaxial test Xiao-li Dong1,2, a *,Wei-hua Zhang1,a 1 Beijing City University, China
5th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Transportation (ICCET 2015) Particle flow simulation of sand under biaxial test Xiao-li Dong1,2, a *,Wei-hua Zhang1,a 1 Beijing City University, China
Introduction to Granular Physics and Modeling Methods
 Introduction to Granular Physics and Modeling Methods Stefan Luding MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Stefan Luding, s.luding@utwente.nl MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Granular Materials Real: sand, soil, rock, grain,
Introduction to Granular Physics and Modeling Methods Stefan Luding MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Stefan Luding, s.luding@utwente.nl MSM, TS, CTW, UTwente, NL Granular Materials Real: sand, soil, rock, grain,
Viscoelasticity. Basic Notions & Examples. Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity. Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies. Non-linear behavior
 Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Viscoelasticity Basic Notions & Examples Formalism for Linear Viscoelasticity Simple Models & Mechanical Analogies Non-linear behavior Viscoelastic Behavior Generic Viscoelasticity: exhibition of both
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Background
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Despite being common in everyday experience, granular materials are poorly understood from a theoretical standpoint, and even in the simplest of situations, they can
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Background Despite being common in everyday experience, granular materials are poorly understood from a theoretical standpoint, and even in the simplest of situations, they can
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008
 MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING EPS SEMINAR SERIES MARCH 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON THE ROADMAP MOTIVATION
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda
 ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation )
 Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
Granular materials (Assemblies of particles with dissipation ) Saturn ring Sand mustard seed Ginkaku-ji temple Sheared granular materials packing fraction : Φ Inhomogeneous flow Gas (Φ = 012) Homogeneous
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY. Conditions for static equilibrium Center of gravity (weight) Examples of static equilibrium
 CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
Forces on bins: The effect of random friction
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1998 Forces on bins: The effect of random friction E. Bruce Pitman* Department of Mathematics, State University of New York, Buffalo, New York 14214 Received
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 57, NUMBER 3 MARCH 1998 Forces on bins: The effect of random friction E. Bruce Pitman* Department of Mathematics, State University of New York, Buffalo, New York 14214 Received
Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology
 CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
CEA-Saclay/SPEC; Group Instabilities and Turbulence Clusters in granular flows : elements of a non-local rheology Olivier Dauchot together with many contributors: D. Bonamy, E. Bertin, S. Deboeuf, B. Andreotti,
Continuum Mechanics. Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations
 Continuum Mechanics Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations Continuum mechanics pertains to the description of mechanical behavior of materials under the assumption that the material is a uniform
Continuum Mechanics Continuum Mechanics and Constitutive Equations Continuum mechanics pertains to the description of mechanical behavior of materials under the assumption that the material is a uniform
Bifurcation Analysis in Geomechanics
 Bifurcation Analysis in Geomechanics I. VARDOULAKIS Department of Engineering Science National Technical University of Athens Greece and J. SULEM Centre d'enseignement et de Recherche en Mecanique des
Bifurcation Analysis in Geomechanics I. VARDOULAKIS Department of Engineering Science National Technical University of Athens Greece and J. SULEM Centre d'enseignement et de Recherche en Mecanique des
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems
 Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
Measurements of the yield stress in frictionless granular systems Ning Xu 1 and Corey S. O Hern 1,2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520-8284, USA 2 Department
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES
 MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AFOSR WORKSHOP ON PARTICULATE MECHANICS JANUARY 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON
MODELING GEOMATERIALS ACROSS SCALES JOSÉ E. ANDRADE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING AFOSR WORKSHOP ON PARTICULATE MECHANICS JANUARY 2008 COLLABORATORS: DR XUXIN TU AND MR KIRK ELLISON
Rheology of Soft Materials. Rheology
 Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Τ Thomas G. Mason Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Department of Physics and Astronomy California NanoSystems Institute Τ γ 26 by Thomas G. Mason All rights reserved. γ (t) τ (t) γ τ Δt 2π t γ
Sand Ripple Dynamics on the Inner Shelf
 Sand Ripple Dynamics on the Inner Shelf Donald N. Slinn Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering, University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6590, Phone: (352) 392-9537 x 1431 Fax: (352) 392-3466 E-mail:
Sand Ripple Dynamics on the Inner Shelf Donald N. Slinn Department of Civil and Coastal Engineering, University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-6590, Phone: (352) 392-9537 x 1431 Fax: (352) 392-3466 E-mail:
Micro-macro modelling for fluids and powders
 Micro-macro modelling for fluids and powders Stefan Luding 1,2 1 Particle Technology, DelftChemTech, TU Delft, Julianalaan 136, 2628 BL Delft, The Netherlands 2 e-mail: s.luding@tnw.tudelft.nl ABSTRACT
Micro-macro modelling for fluids and powders Stefan Luding 1,2 1 Particle Technology, DelftChemTech, TU Delft, Julianalaan 136, 2628 BL Delft, The Netherlands 2 e-mail: s.luding@tnw.tudelft.nl ABSTRACT
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis
 6-1 Introduction 6-2Newton s Law and Conservation of Momentum 6-3 Choosing a Control Volume 6-4 Forces Acting on a Control Volume 6-5Linear Momentum Equation 6-6 Angular Momentum 6-7 The Second Law of
6-1 Introduction 6-2Newton s Law and Conservation of Momentum 6-3 Choosing a Control Volume 6-4 Forces Acting on a Control Volume 6-5Linear Momentum Equation 6-6 Angular Momentum 6-7 The Second Law of
Lecture 20: Spinodals and Binodals; Continuous Phase Transitions; Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Lecture 20: 11.28.05 Spinodals and Binodals; Continuous Phase Transitions; Introduction to Statistical Mechanics Today: LAST TIME: DEFINING METASTABLE AND UNSTABLE REGIONS ON PHASE DIAGRAMS...2 Conditions
Lecture 20: 11.28.05 Spinodals and Binodals; Continuous Phase Transitions; Introduction to Statistical Mechanics Today: LAST TIME: DEFINING METASTABLE AND UNSTABLE REGIONS ON PHASE DIAGRAMS...2 Conditions
Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory
 Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory S. Torquato, 1,2 A. Donev 2,3, and F. H. Stillinger 1 Department of Chemistry, 1 Princeton Materials
Breakdown of Elasticity Theory for Jammed Hard-Particle Packings: Conical Nonlinear Constitutive Theory S. Torquato, 1,2 A. Donev 2,3, and F. H. Stillinger 1 Department of Chemistry, 1 Princeton Materials
Packing grains by thermally cycling
 Packing grains by thermally cycling One of the oldest and most intriguing problems in the handling of materials is how a collection of solid grains packs together. 1 While granular packing is normally
Packing grains by thermally cycling One of the oldest and most intriguing problems in the handling of materials is how a collection of solid grains packs together. 1 While granular packing is normally
ORIGINS. E.P. Wigner, Conference on Neutron Physics by Time of Flight, November 1956
 ORIGINS E.P. Wigner, Conference on Neutron Physics by Time of Flight, November 1956 P.W. Anderson, Absence of Diffusion in Certain Random Lattices ; Phys.Rev., 1958, v.109, p.1492 L.D. Landau, Fermi-Liquid
ORIGINS E.P. Wigner, Conference on Neutron Physics by Time of Flight, November 1956 P.W. Anderson, Absence of Diffusion in Certain Random Lattices ; Phys.Rev., 1958, v.109, p.1492 L.D. Landau, Fermi-Liquid
Universiteit Leiden
 Universiteit Leiden 1 481 565 3. BiBLIOTHEEK 2 4 SEP 2003 Statistics of Force Networks in Granular Media J. H. Snoeijer Statistics of Force Networks in Granular Media PROEFSCHRIFT TER VERKRIJGING VAN
Universiteit Leiden 1 481 565 3. BiBLIOTHEEK 2 4 SEP 2003 Statistics of Force Networks in Granular Media J. H. Snoeijer Statistics of Force Networks in Granular Media PROEFSCHRIFT TER VERKRIJGING VAN
Chapter 2 Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential
 Chapter Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential Abstract In this chapter, we discuss the basic formalism of statistical physics Also, we consider in detail the concept of the free
Chapter Ensemble Theory in Statistical Physics: Free Energy Potential Abstract In this chapter, we discuss the basic formalism of statistical physics Also, we consider in detail the concept of the free
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems
 Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems Introduction Fluid flow problems can be analyzed using one of three basic approaches: differential, experimental, and integral (or control volume). In Chap.
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems Introduction Fluid flow problems can be analyzed using one of three basic approaches: differential, experimental, and integral (or control volume). In Chap.
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings. Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney
 Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Local Anisotropy In Globally Isotropic Granular Packings Kamran Karimi Craig E Maloney Granular Materials 2 A Granular Material Is A Conglomeration Of Discrete Solid, Natural Macroscopic Particles Characterized
Variable Definition Notes & comments
 Extended base dimension system Pi-theorem (also definition of physical quantities, ) Physical similarity Physical similarity means that all Pi-parameters are equal Galileo-number (solid mechanics) Reynolds
Extended base dimension system Pi-theorem (also definition of physical quantities, ) Physical similarity Physical similarity means that all Pi-parameters are equal Galileo-number (solid mechanics) Reynolds
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies
 Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies Bachelor Program in AUTOMATION ENGINEERING Prof. Rong-yong Zhao (zhaorongyong@tongji.edu.cn) First Semester,2014-2015 Content of chapter 4 4.1 Static equilibrium
Chapter 4 Statics and dynamics of rigid bodies Bachelor Program in AUTOMATION ENGINEERING Prof. Rong-yong Zhao (zhaorongyong@tongji.edu.cn) First Semester,2014-2015 Content of chapter 4 4.1 Static equilibrium
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22836 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Woldhuis, Erik Title: Foam rheology near the jamming transition Issue Date: 2013-12-11
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22836 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Woldhuis, Erik Title: Foam rheology near the jamming transition Issue Date: 2013-12-11
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis
 Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Xiaoming Mao Physics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor IGERT Summer Institute 2017 Brandeis Elastic Networks A family of discrete model networks involving masses connected by springs 1 2 kk( ll)2 Disordered
Critical scaling near the yielding transition in granular media
 Critical scaling near the yielding transition in granular media Abram H. Clark, 1 Mark D. Shattuck, 2 Nicholas T. Ouellette, 3 1, 4, 5 and Corey S. O Hern 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering and Materials
Critical scaling near the yielding transition in granular media Abram H. Clark, 1 Mark D. Shattuck, 2 Nicholas T. Ouellette, 3 1, 4, 5 and Corey S. O Hern 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering and Materials
27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation
 27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 27. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 27. Impact Chapter 1 Manipulation 1
27. Impact Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 27. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 27. Impact Chapter 1 Manipulation 1
A unified flow theory for viscous fluids
 Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Paris 27/10/2015 A unified flow theory for viscous fluids ILYA PESHKOV CHLOE, University of Pau, France joint work with EVGENIY ROMENSKI Sobolev Institute of Mathematics,
Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions, Paris 27/10/2015 A unified flow theory for viscous fluids ILYA PESHKOV CHLOE, University of Pau, France joint work with EVGENIY ROMENSKI Sobolev Institute of Mathematics,
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Lecture 21 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics
 Lecture 1 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics Program: 1. Maxwell s Equations.. Magnetic induction and electric displacement. 3. Origins of the electric permittivity and magnetic permeability. 4. Wave
Lecture 1 Reminder/Introduction to Wave Optics Program: 1. Maxwell s Equations.. Magnetic induction and electric displacement. 3. Origins of the electric permittivity and magnetic permeability. 4. Wave
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow
 Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Steady Flow and its Instability of Gravitational Granular Flow Namiko Mitarai Department of Chemistry and Physics of Condensed Matter, Graduate School of Science, Kyushu University, Japan. A thesis submitted
Microstructural studies for rheology. Chapter 7: Microstructural studies for rheology. Separation of length scales. Micro & macro views
 Chapter 7: Microstructural studies for rheology Microstructural studies for rheology To calculate the flow of complex fluids, need governing equations, in particular, the constitutive equation relating
Chapter 7: Microstructural studies for rheology Microstructural studies for rheology To calculate the flow of complex fluids, need governing equations, in particular, the constitutive equation relating
Jamming and Flow of Rod-Like Granular Materials
 Scott Franklin svfsps@rit.edu http://piggy.rit.edu/franklin Undergraduate Researchers Kevin Stokely Ari Diacou Ken Desmond Jess Gallagher Scott Barker Jamming and Flow of Rod-Like Granular Materials PRE
Scott Franklin svfsps@rit.edu http://piggy.rit.edu/franklin Undergraduate Researchers Kevin Stokely Ari Diacou Ken Desmond Jess Gallagher Scott Barker Jamming and Flow of Rod-Like Granular Materials PRE
SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED
 1 SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED WITH LATERAL FRICTIONAL EFFECTS High slope results and comparison with experimental data Nathan Martin1, Ioan Ionescu2, Anne Mangeney1,3 François
1 SIMULATION OF A 2D GRANULAR COLUMN COLLAPSE ON A RIGID BED WITH LATERAL FRICTIONAL EFFECTS High slope results and comparison with experimental data Nathan Martin1, Ioan Ionescu2, Anne Mangeney1,3 François
(2.1) Is often expressed using a dimensionless drag coefficient:
 1. Introduction Multiphase materials occur in many fields of natural and engineering science, industry, and daily life. Biological materials such as blood or cell suspensions, pharmaceutical or food products,
1. Introduction Multiphase materials occur in many fields of natural and engineering science, industry, and daily life. Biological materials such as blood or cell suspensions, pharmaceutical or food products,
Review. Network analysis of particles and grains. Edited by: Ernesto Estrada
 Journal of Complex Networks (2018) 6, 485 565 doi: 10.1093/comnet/cny005 Advance Access Publication on 3 April 2018 Review Network analysis of particles and grains Lia Papadopoulos Department of Physics
Journal of Complex Networks (2018) 6, 485 565 doi: 10.1093/comnet/cny005 Advance Access Publication on 3 April 2018 Review Network analysis of particles and grains Lia Papadopoulos Department of Physics
Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics
 Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Phases Solid increasing increasing spacing and intermolecular liquid latitude of cohesive Fluid gas (vapor) molecular force plasma motion 1.1.2 Fluidity
Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Phases Solid increasing increasing spacing and intermolecular liquid latitude of cohesive Fluid gas (vapor) molecular force plasma motion 1.1.2 Fluidity
Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION
 17 Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION 3.1 Fundamental Poisson Equation The simplest version of the frictionless laminated model was originally introduced in 1961 by Salamon, and more recently explored
17 Chapter 3 LAMINATED MODEL DERIVATION 3.1 Fundamental Poisson Equation The simplest version of the frictionless laminated model was originally introduced in 1961 by Salamon, and more recently explored
Lattice element method
 Lattice element method Vincent Topin, Jean-Yves Delenne and Farhang Radjai Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie Civil, CNRS - Université Montpellier 2, Place Eugène Bataillon, 34095 Montpellier cedex 05 1
Lattice element method Vincent Topin, Jean-Yves Delenne and Farhang Radjai Laboratoire de Mécanique et Génie Civil, CNRS - Université Montpellier 2, Place Eugène Bataillon, 34095 Montpellier cedex 05 1
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II
 CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 The Schrödinger Wave Equation Expectation Values Infinite Square-Well Potential Finite Square-Well Potential Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential
CHAPTER 6 Quantum Mechanics II 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 The Schrödinger Wave Equation Expectation Values Infinite Square-Well Potential Finite Square-Well Potential Three-Dimensional Infinite-Potential
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
Three-Dimensional Discrete Element Simulations of Direct Shear Tests
 Three-Dimensional Discrete Element Simulations of Direct Shear Tests Catherine O Sullivan Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Imperial College London, UK Liang Cui Department of Civil Engineering,
Three-Dimensional Discrete Element Simulations of Direct Shear Tests Catherine O Sullivan Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Imperial College London, UK Liang Cui Department of Civil Engineering,
Physics Important Terms and their Definitions
 Physics Important Terms and their S.No Word Meaning 1 Acceleration The rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time 2 Angular Momentum A measure of the momentum of a body in rotational
Physics Important Terms and their S.No Word Meaning 1 Acceleration The rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time 2 Angular Momentum A measure of the momentum of a body in rotational
Feshbach-Schur RG for the Anderson Model
 Feshbach-Schur RG for the Anderson Model John Z. Imbrie University of Virginia Isaac Newton Institute October 26, 2018 Overview Consider the localization problem for the Anderson model of a quantum particle
Feshbach-Schur RG for the Anderson Model John Z. Imbrie University of Virginia Isaac Newton Institute October 26, 2018 Overview Consider the localization problem for the Anderson model of a quantum particle
CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION
 CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION 7.1 THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
CHAPTER 7 SEVERAL FORMS OF THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION 7.1 THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS Under the assumption of a Newtonian stress-rate-of-strain constitutive equation and a linear, thermally conductive medium,
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
LAMMPS Simulation of a Microgravity Shear Cell 299r Progress Report 2 Taiyo Wilson. Introduction:
 Introduction: After our initial simulations outlined in the first progress report, we determined that a shear cell with a bidisperse composition of particles would be a promising system to explore. However,
Introduction: After our initial simulations outlined in the first progress report, we determined that a shear cell with a bidisperse composition of particles would be a promising system to explore. However,
Newton s Method and Localization
 Newton s Method and Localization Workshop on Analytical Aspects of Mathematical Physics John Imbrie May 30, 2013 Overview Diagonalizing the Hamiltonian is a goal in quantum theory. I would like to discuss
Newton s Method and Localization Workshop on Analytical Aspects of Mathematical Physics John Imbrie May 30, 2013 Overview Diagonalizing the Hamiltonian is a goal in quantum theory. I would like to discuss
Fundamental Principles
 Fundamental Principles Newton s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line. First Law: A. body will remain at rest
Fundamental Principles Newton s First Law: If the resultant force on a particle is zero, the particle will remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line. First Law: A. body will remain at rest
Dry and wet granular flows. Diego Berzi
 Dry and wet granular flows Diego Berzi Outline 2 What? Why? How? When? Who? Where? Then? What? Granular flows many solid moving particles 3 particle mass is large (at least 10 20 molecular masses). Hence,
Dry and wet granular flows Diego Berzi Outline 2 What? Why? How? When? Who? Where? Then? What? Granular flows many solid moving particles 3 particle mass is large (at least 10 20 molecular masses). Hence,
Xiaoming Mao. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pennsylvania. Collaborators: Tom Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu
 Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Xiaoing Mao Departent of Physics and Astronoy, University of Pennsylvania Collaborators: To Lubensky, Ning Xu, Anton Souslov, Andrea Liu Feb., 009 What is isostaticity? Isostatic systes are at the onset
Analytical and Numerical Study of Coupled Atomistic-Continuum Methods for Fluids
 Analytical and Numerical Study of Coupled Atomistic-Continuum Methods for Fluids Weiqing Ren Courant Institute, NYU Joint work with Weinan E Multiscale modeling for two types of problems: Complex fluids
Analytical and Numerical Study of Coupled Atomistic-Continuum Methods for Fluids Weiqing Ren Courant Institute, NYU Joint work with Weinan E Multiscale modeling for two types of problems: Complex fluids
CHAPTER V. Brownian motion. V.1 Langevin dynamics
 CHAPTER V Brownian motion In this chapter, we study the very general paradigm provided by Brownian motion. Originally, this motion is that a heavy particle, called Brownian particle, immersed in a fluid
CHAPTER V Brownian motion In this chapter, we study the very general paradigm provided by Brownian motion. Originally, this motion is that a heavy particle, called Brownian particle, immersed in a fluid
