Poisson Data. Handout #4
|
|
|
- Russell Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Poisson Data The other response variable of interest records the number of blue spots observed after incubation. This type of data, i.e. count data, is often skewed showing numerous small values with occasional large ones. Note that these counts differ from the binomial case above. There, the count of successes was bounded by the number of experimental units: 3 reps x 8 explants = 24. In this example, the number of spots observed is unbounded or open ended. The maximum number possible is not known. A probability distribution which can describe this type of data is the Poisson. The SAS code to analyze Poisson data is similar to that of the Binomial: proc genmod; class treat; model spots = treat/dist=poisson link = log type3; lsmeans treat/diff; contrast 'Osmotic Effect' treat ; by cultivar; with the obvious exceptions of the DIST and LINK options. In the 1/6
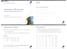
2 case of the Poisson distribution, the log LINK is most appropriate (log here designates natural log, ln). However, as was seen with the binomial, a count of 0 can cause errors. Therefore, a data step can be used prior to the analysis to adjust these values before PROC GENMOD is called: data osmotic; set osmotic; if spots = 0 then spots =.5; Again, a small value is added to those observations having a count of 0 spots. The output for cultivar MUM follows cult=mum Class Level Information Class Levels Values treat Source DF Square Pr > ChiSq treat < /6
3 Least Squares Means Standard Effect treat Estimate Error DF Square Pr > ChiSq treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat <.0001 Differences of Least Squares Means Standard Effect treat _treat Estimate Error DF Square Pr > ChiSq treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat treat <.0001 treat treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat <.0001 treat < /6
4 Contrast Results Contrast DF Square Pr > ChiSq Type Osmotic Effect <.0001 LR The treatment level information is given followed by the overall test of model effects. Here, TREAT is highly significant with a p-value less than The means are given in the next table. As was the case above, these reflect the transformed (log) values. All the treatment means are significantly different from zero indicating that all treatments had more than one spot. Pair-wise comparison of the means is given next. In this example, all the pair-wise comparisons are significant, i.e. all treatments are apparently different from one another. Finally, the contrast for any osmotic effect is also highly significant with a chi-square value of Given this significance, it might be of interest to actually estimate the mean number of spots for each component of the contrast, i.e. a mean for no osmotic pressure (equilibrium) and a mean where osmotic pressure was applied. This can be accomplished with the ESTIMATE statement. However, because SAS implicitly includes an overall intercept in the model, the actual ESTIMATE statement can be 4/6
5 rather tricky to formulate. One method of avoiding this is to rerun the model without the intercept term: proc genmod; class treat; model spots = treat/dist=poisson link = log type3 noint; lsmeans treat/diff; contrast 'Osmotic Effect' treat ; estimate 'Equilibrium' treat ; estimate 'Osmotic Applied' treat ; by cult; The intercept is omitted with the NOINT option in the MODEL statement. Two ESTIMATE statements have been added; one for the osmotic treatment of 0 and another for the average of the remaining treatments. Note that, like CONTRAST, each statement has a unique label given in quotes. The resulting output is: Contrast Estimate Results Standard Label Estimate Error Alpha Confidence Limits Square Pr > ChiSq Equilibrium < /6
6 Osmotic Applied <.0001 Each ESTIMATE statement produces the value of its estimate, the associated standard error, and confidence limits. Also given are test results for the hypothesis that the estimate is equal to 0. (Notice that the Equilibrium estimate is the same as that for TREAT = 0 above). The results show that the application of osmotic pressure increased the number of spots over the equilibrium condition. Since these are still the log transformed values, the actual count estimates can be determined by utilizing the exponential (anti-log) function: and Equilibrium number of spots = e = 3.92 Avg. number of spots with treatment = e = This shows the osmotic treatments on average gave more than a 3 fold increase in the number of spots. The associated standard errors and confidence limits may also be back-transformed in a similar manner. 6/6
Q30b Moyale Observed counts. The FREQ Procedure. Table 1 of type by response. Controlling for site=moyale. Improved (1+2) Same (3) Group only
 Moyale Observed counts 12:28 Thursday, December 01, 2011 1 The FREQ Procedure Table 1 of by Controlling for site=moyale Row Pct Improved (1+2) Same () Worsened (4+5) Group only 16 51.61 1.2 14 45.16 1
Moyale Observed counts 12:28 Thursday, December 01, 2011 1 The FREQ Procedure Table 1 of by Controlling for site=moyale Row Pct Improved (1+2) Same () Worsened (4+5) Group only 16 51.61 1.2 14 45.16 1
You can specify the response in the form of a single variable or in the form of a ratio of two variables denoted events/trials.
 The GENMOD Procedure MODEL Statement MODEL response = < effects > < /options > ; MODEL events/trials = < effects > < /options > ; You can specify the response in the form of a single variable or in the
The GENMOD Procedure MODEL Statement MODEL response = < effects > < /options > ; MODEL events/trials = < effects > < /options > ; You can specify the response in the form of a single variable or in the
Cohen s s Kappa and Log-linear Models
 Cohen s s Kappa and Log-linear Models HRP 261 03/03/03 10-11 11 am 1. Cohen s Kappa Actual agreement = sum of the proportions found on the diagonals. π ii Cohen: Compare the actual agreement with the chance
Cohen s s Kappa and Log-linear Models HRP 261 03/03/03 10-11 11 am 1. Cohen s Kappa Actual agreement = sum of the proportions found on the diagonals. π ii Cohen: Compare the actual agreement with the chance
Logistic Regression. Interpretation of linear regression. Other types of outcomes. 0-1 response variable: Wound infection. Usual linear regression
 Logistic Regression Usual linear regression (repetition) y i = b 0 + b 1 x 1i + b 2 x 2i + e i, e i N(0,σ 2 ) or: y i N(b 0 + b 1 x 1i + b 2 x 2i,σ 2 ) Example (DGA, p. 336): E(PEmax) = 47.355 + 1.024
Logistic Regression Usual linear regression (repetition) y i = b 0 + b 1 x 1i + b 2 x 2i + e i, e i N(0,σ 2 ) or: y i N(b 0 + b 1 x 1i + b 2 x 2i,σ 2 ) Example (DGA, p. 336): E(PEmax) = 47.355 + 1.024
Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Chapter 18.1 Logistic Regression (Dose - Response)
 Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Logistic Regression ( - Response) ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10, 11), Part IV
Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Logistic Regression ( - Response) ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10, 11), Part IV
Homework 5: Answer Key. Plausible Model: E(y) = µt. The expected number of arrests arrests equals a constant times the number who attend the game.
 EdPsych/Psych/Soc 589 C.J. Anderson Homework 5: Answer Key 1. Probelm 3.18 (page 96 of Agresti). (a) Y assume Poisson random variable. Plausible Model: E(y) = µt. The expected number of arrests arrests
EdPsych/Psych/Soc 589 C.J. Anderson Homework 5: Answer Key 1. Probelm 3.18 (page 96 of Agresti). (a) Y assume Poisson random variable. Plausible Model: E(y) = µt. The expected number of arrests arrests
Overdispersion Workshop in generalized linear models Uppsala, June 11-12, Outline. Overdispersion
 Biostokastikum Overdispersion is not uncommon in practice. In fact, some would maintain that overdispersion is the norm in practice and nominal dispersion the exception McCullagh and Nelder (1989) Overdispersion
Biostokastikum Overdispersion is not uncommon in practice. In fact, some would maintain that overdispersion is the norm in practice and nominal dispersion the exception McCullagh and Nelder (1989) Overdispersion
The GENMOD Procedure. Overview. Getting Started. Syntax. Details. Examples. References. SAS/STAT User's Guide. Book Contents Previous Next
 Book Contents Previous Next SAS/STAT User's Guide Overview Getting Started Syntax Details Examples References Book Contents Previous Next Top http://v8doc.sas.com/sashtml/stat/chap29/index.htm29/10/2004
Book Contents Previous Next SAS/STAT User's Guide Overview Getting Started Syntax Details Examples References Book Contents Previous Next Top http://v8doc.sas.com/sashtml/stat/chap29/index.htm29/10/2004
ESTIMATE PROP. IMPAIRED PRE- AND POST-INTERVENTION FOR THIN LIQUID SWALLOW TASKS. The SURVEYFREQ Procedure
 ESTIMATE PROP. IMPAIRED PRE- AND POST-INTERVENTION FOR THIN LIQUID SWALLOW TASKS 18:58 Sunday, July 26, 2015 1 The SURVEYFREQ Procedure Data Summary Number of Clusters 30 Number of Observations 360 time_cat
ESTIMATE PROP. IMPAIRED PRE- AND POST-INTERVENTION FOR THIN LIQUID SWALLOW TASKS 18:58 Sunday, July 26, 2015 1 The SURVEYFREQ Procedure Data Summary Number of Clusters 30 Number of Observations 360 time_cat
Analysis of Count Data A Business Perspective. George J. Hurley Sr. Research Manager The Hershey Company Milwaukee June 2013
 Analysis of Count Data A Business Perspective George J. Hurley Sr. Research Manager The Hershey Company Milwaukee June 2013 Overview Count data Methods Conclusions 2 Count data Count data Anything with
Analysis of Count Data A Business Perspective George J. Hurley Sr. Research Manager The Hershey Company Milwaukee June 2013 Overview Count data Methods Conclusions 2 Count data Count data Anything with
Contrasting Marginal and Mixed Effects Models Recall: two approaches to handling dependence in Generalized Linear Models:
 Contrasting Marginal and Mixed Effects Models Recall: two approaches to handling dependence in Generalized Linear Models: Marginal models: based on the consequences of dependence on estimating model parameters.
Contrasting Marginal and Mixed Effects Models Recall: two approaches to handling dependence in Generalized Linear Models: Marginal models: based on the consequences of dependence on estimating model parameters.
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Mathematics and Statistics Applied Statistics Friday, January 15, 2016
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Mathematics and Statistics Applied Statistics Friday, January 15, 2016 Work all problems. 60 points are needed to pass at the Masters Level and 75 to pass at the
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Department of Mathematics and Statistics Applied Statistics Friday, January 15, 2016 Work all problems. 60 points are needed to pass at the Masters Level and 75 to pass at the
Wrap-up. The General Linear Model is a special case of the Generalized Linear Model. Consequently, we can carry out any GLM as a GzLM.
 Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Analysis of Continuous Data ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10, 11), Part IV (Ch13,
Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Analysis of Continuous Data ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9, 10, 11), Part IV (Ch13,
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO. Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2010 EXAMINATIONS STA 303 H1S / STA 1002 HS. Duration - 3 hours. Aids Allowed: Calculator
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2010 EXAMINATIONS STA 303 H1S / STA 1002 HS Duration - 3 hours Aids Allowed: Calculator LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: There are 27 pages
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2010 EXAMINATIONS STA 303 H1S / STA 1002 HS Duration - 3 hours Aids Allowed: Calculator LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: There are 27 pages
The GENMOD Procedure (Book Excerpt)
 SAS/STAT 9.22 User s Guide The GENMOD Procedure (Book Excerpt) SAS Documentation This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 9.22 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation for the complete
SAS/STAT 9.22 User s Guide The GENMOD Procedure (Book Excerpt) SAS Documentation This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 9.22 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation for the complete
Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis. Irmgard Hollweck / Meike Best 13.OCT.2013
 Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis Irmgard Hollweck / Meike Best 13.OCT.2013 Agenda 2 Introduction to Dactylitis Background Definitions: Trial Definitions:Terms Statistics:
Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis Irmgard Hollweck / Meike Best 13.OCT.2013 Agenda 2 Introduction to Dactylitis Background Definitions: Trial Definitions:Terms Statistics:
Regression Models for Risks(Proportions) and Rates. Proportions. E.g. [Changes in] Sex Ratio: Canadian Births in last 60 years
![Regression Models for Risks(Proportions) and Rates. Proportions. E.g. [Changes in] Sex Ratio: Canadian Births in last 60 years Regression Models for Risks(Proportions) and Rates. Proportions. E.g. [Changes in] Sex Ratio: Canadian Births in last 60 years](/thumbs/83/87443434.jpg) Regression Models for Risks(Proportions) and Rates Proportions E.g. [Changes in] Sex Ratio: Canadian Births in last 60 years Parameter of Interest: (male)... just above 0.5 or (male)/ (female)... "ODDS"...
Regression Models for Risks(Proportions) and Rates Proportions E.g. [Changes in] Sex Ratio: Canadian Births in last 60 years Parameter of Interest: (male)... just above 0.5 or (male)/ (female)... "ODDS"...
Logistic regression analysis. Birthe Lykke Thomsen H. Lundbeck A/S
 Logistic regression analysis Birthe Lykke Thomsen H. Lundbeck A/S 1 Response with only two categories Example Odds ratio and risk ratio Quantitative explanatory variable More than one variable Logistic
Logistic regression analysis Birthe Lykke Thomsen H. Lundbeck A/S 1 Response with only two categories Example Odds ratio and risk ratio Quantitative explanatory variable More than one variable Logistic
Normal distribution We have a random sample from N(m, υ). The sample mean is Ȳ and the corrected sum of squares is S yy. After some simplification,
 Likelihood Let P (D H) be the probability an experiment produces data D, given hypothesis H. Usually H is regarded as fixed and D variable. Before the experiment, the data D are unknown, and the probability
Likelihood Let P (D H) be the probability an experiment produces data D, given hypothesis H. Usually H is regarded as fixed and D variable. Before the experiment, the data D are unknown, and the probability
Generalized Linear Models for Count, Skewed, and If and How Much Outcomes
 Generalized Linear Models for Count, Skewed, and If and How Much Outcomes Today s Class: Review of 3 parts of a generalized model Models for discrete count or continuous skewed outcomes Models for two-part
Generalized Linear Models for Count, Skewed, and If and How Much Outcomes Today s Class: Review of 3 parts of a generalized model Models for discrete count or continuous skewed outcomes Models for two-part
Introduction to SAS proc mixed
 Faculty of Health Sciences Introduction to SAS proc mixed Analysis of repeated measurements, 2017 Julie Forman Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen 2 / 28 Preparing data for analysis The
Faculty of Health Sciences Introduction to SAS proc mixed Analysis of repeated measurements, 2017 Julie Forman Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen 2 / 28 Preparing data for analysis The
SAS/STAT 14.2 User s Guide. The GENMOD Procedure
 SAS/STAT 14.2 User s Guide The GENMOD Procedure This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 14.2 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc.
SAS/STAT 14.2 User s Guide The GENMOD Procedure This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 14.2 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc.
Where have all the puffins gone 1. An Analysis of Atlantic Puffin (Fratercula arctica) Banding Returns in Newfoundland
 Where have all the puffins gone 1 An Analysis of Atlantic Puffin (Fratercula arctica) Banding Returns in Newfoundland Dave Fifield 1 With apologies to Pete Seeger. Introduction Seabirds are the most visible
Where have all the puffins gone 1 An Analysis of Atlantic Puffin (Fratercula arctica) Banding Returns in Newfoundland Dave Fifield 1 With apologies to Pete Seeger. Introduction Seabirds are the most visible
Introduction to SAS proc mixed
 Faculty of Health Sciences Introduction to SAS proc mixed Analysis of repeated measurements, 2017 Julie Forman Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen Outline Data in wide and long format
Faculty of Health Sciences Introduction to SAS proc mixed Analysis of repeated measurements, 2017 Julie Forman Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen Outline Data in wide and long format
unadjusted model for baseline cholesterol 22:31 Monday, April 19,
 unadjusted model for baseline cholesterol 22:31 Monday, April 19, 2004 1 Class Level Information Class Levels Values TRETGRP 3 3 4 5 SEX 2 0 1 Number of observations 916 unadjusted model for baseline cholesterol
unadjusted model for baseline cholesterol 22:31 Monday, April 19, 2004 1 Class Level Information Class Levels Values TRETGRP 3 3 4 5 SEX 2 0 1 Number of observations 916 unadjusted model for baseline cholesterol
Simple logistic regression
 Simple logistic regression Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Simple logistic regression p. 1/47 Model assumptions 1. The observed data are independent realizations of a binary response variable Y that follows a
Simple logistic regression Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Simple logistic regression p. 1/47 Model assumptions 1. The observed data are independent realizations of a binary response variable Y that follows a
STAT 5200 Handout #23. Repeated Measures Example (Ch. 16)
 Motivating Example: Glucose STAT 500 Handout #3 Repeated Measures Example (Ch. 16) An experiment is conducted to evaluate the effects of three diets on the serum glucose levels of human subjects. Twelve
Motivating Example: Glucose STAT 500 Handout #3 Repeated Measures Example (Ch. 16) An experiment is conducted to evaluate the effects of three diets on the serum glucose levels of human subjects. Twelve
Appendix: Computer Programs for Logistic Regression
 Appendix: Computer Programs for Logistic Regression In this appendix, we provide examples of computer programs to carry out unconditional logistic regression, conditional logistic regression, polytomous
Appendix: Computer Programs for Logistic Regression In this appendix, we provide examples of computer programs to carry out unconditional logistic regression, conditional logistic regression, polytomous
Testing Indirect Effects for Lower Level Mediation Models in SAS PROC MIXED
 Testing Indirect Effects for Lower Level Mediation Models in SAS PROC MIXED Here we provide syntax for fitting the lower-level mediation model using the MIXED procedure in SAS as well as a sas macro, IndTest.sas
Testing Indirect Effects for Lower Level Mediation Models in SAS PROC MIXED Here we provide syntax for fitting the lower-level mediation model using the MIXED procedure in SAS as well as a sas macro, IndTest.sas
SAS Commands. General Plan. Output. Construct scatterplot / interaction plot. Run full model
 Topic 23 - Unequal Replication Data Model Outline - Fall 2013 Parameter Estimates Inference Topic 23 2 Example Page 954 Data for Two Factor ANOVA Y is the response variable Factor A has levels i = 1, 2,...,
Topic 23 - Unequal Replication Data Model Outline - Fall 2013 Parameter Estimates Inference Topic 23 2 Example Page 954 Data for Two Factor ANOVA Y is the response variable Factor A has levels i = 1, 2,...,
Generalized linear models
 Generalized linear models Douglas Bates November 01, 2010 Contents 1 Definition 1 2 Links 2 3 Estimating parameters 5 4 Example 6 5 Model building 8 6 Conclusions 8 7 Summary 9 1 Generalized Linear Models
Generalized linear models Douglas Bates November 01, 2010 Contents 1 Definition 1 2 Links 2 3 Estimating parameters 5 4 Example 6 5 Model building 8 6 Conclusions 8 7 Summary 9 1 Generalized Linear Models
Product Held at Accelerated Stability Conditions. José G. Ramírez, PhD Amgen Global Quality Engineering 6/6/2013
 Modeling Sub-Visible Particle Data Product Held at Accelerated Stability Conditions José G. Ramírez, PhD Amgen Global Quality Engineering 6/6/2013 Outline Sub-Visible Particle (SbVP) Poisson Negative Binomial
Modeling Sub-Visible Particle Data Product Held at Accelerated Stability Conditions José G. Ramírez, PhD Amgen Global Quality Engineering 6/6/2013 Outline Sub-Visible Particle (SbVP) Poisson Negative Binomial
Inference for Binomial Parameters
 Inference for Binomial Parameters Dipankar Bandyopadhyay, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University D. Bandyopadhyay (VCU) BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1 / 58 Inference for
Inference for Binomial Parameters Dipankar Bandyopadhyay, Ph.D. Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University D. Bandyopadhyay (VCU) BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1 / 58 Inference for
Chapter 5: Logistic Regression-I
 : Logistic Regression-I Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
: Logistic Regression-I Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
Section Poisson Regression
 Section 14.13 Poisson Regression Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 705: Data Analysis II 1 / 26 Poisson regression Regular regression data {(x i, Y i )} n i=1,
Section 14.13 Poisson Regression Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 705: Data Analysis II 1 / 26 Poisson regression Regular regression data {(x i, Y i )} n i=1,
1) Answer the following questions with one or two short sentences.
 1) Answer the following questions with one or two short sentences. a) What is power and how can you increase it? (2 marks) Power is the probability of rejecting a false null hypothesis. It may be increased
1) Answer the following questions with one or two short sentences. a) What is power and how can you increase it? (2 marks) Power is the probability of rejecting a false null hypothesis. It may be increased
T-test: means of Spock's judge versus all other judges 1 12:10 Wednesday, January 5, judge1 N Mean Std Dev Std Err Minimum Maximum
 T-test: means of Spock's judge versus all other judges 1 The TTEST Procedure Variable: pcwomen judge1 N Mean Std Dev Std Err Minimum Maximum OTHER 37 29.4919 7.4308 1.2216 16.5000 48.9000 SPOCKS 9 14.6222
T-test: means of Spock's judge versus all other judges 1 The TTEST Procedure Variable: pcwomen judge1 N Mean Std Dev Std Err Minimum Maximum OTHER 37 29.4919 7.4308 1.2216 16.5000 48.9000 SPOCKS 9 14.6222
A CASE STUDY IN HANDLING OVER-DISPERSION IN NEMATODE COUNT DATA SCOTT EDWIN DOUGLAS KREIDER. B.S., The College of William & Mary, 2008 A THESIS
 A CASE STUDY IN HANDLING OVER-DISPERSION IN NEMATODE COUNT DATA by SCOTT EDWIN DOUGLAS KREIDER B.S., The College of William & Mary, 2008 A THESIS submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
A CASE STUDY IN HANDLING OVER-DISPERSION IN NEMATODE COUNT DATA by SCOTT EDWIN DOUGLAS KREIDER B.S., The College of William & Mary, 2008 A THESIS submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
ZERO INFLATED POISSON REGRESSION
 STAT 6500 ZERO INFLATED POISSON REGRESSION FINAL PROJECT DEC 6 th, 2013 SUN JEON DEPARTMENT OF SOCIOLOGY UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY POISSON REGRESSION REVIEW INTRODUCING - ZERO-INFLATED POISSON REGRESSION SAS
STAT 6500 ZERO INFLATED POISSON REGRESSION FINAL PROJECT DEC 6 th, 2013 SUN JEON DEPARTMENT OF SOCIOLOGY UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY POISSON REGRESSION REVIEW INTRODUCING - ZERO-INFLATED POISSON REGRESSION SAS
Mixed Models Lecture Notes By Dr. Hanford page 199 More Statistics& SAS Tutorial at
 Mixed Models Lecture Notes By Dr. Hanford page 199 Variance Balance Cross-Over Designs Variance balance cross-over designs are designs where all treatment contrasts have the same precision and all carry-over
Mixed Models Lecture Notes By Dr. Hanford page 199 Variance Balance Cross-Over Designs Variance balance cross-over designs are designs where all treatment contrasts have the same precision and all carry-over
ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Two-way Contingency Tables. 2 2 Tables, Relative Risks and Odds Ratios
 ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Two-way Contingency Tables 2 2 Tables, Relative Risks and Odds Ratios 1 What Is A Contingency Table (p.16) Suppose X and Y are two categorical variables X has I categories
ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Two-way Contingency Tables 2 2 Tables, Relative Risks and Odds Ratios 1 What Is A Contingency Table (p.16) Suppose X and Y are two categorical variables X has I categories
SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model
 SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model Gordon Johnston, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC Abstract In recent years, the class of generalized linear models has gained popularity as a statistical modeling
SAS Software to Fit the Generalized Linear Model Gordon Johnston, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC Abstract In recent years, the class of generalized linear models has gained popularity as a statistical modeling
Answer to exercise: Blood pressure lowering drugs
 Answer to exercise: Blood pressure lowering drugs The data set bloodpressure.txt contains data from a cross-over trial, involving three different formulations of a drug for lowering of blood pressure:
Answer to exercise: Blood pressure lowering drugs The data set bloodpressure.txt contains data from a cross-over trial, involving three different formulations of a drug for lowering of blood pressure:
4.8 Alternate Analysis as a Oneway ANOVA
 4.8 Alternate Analysis as a Oneway ANOVA Suppose we have data from a two-factor factorial design. The following method can be used to perform a multiple comparison test to compare treatment means as well
4.8 Alternate Analysis as a Oneway ANOVA Suppose we have data from a two-factor factorial design. The following method can be used to perform a multiple comparison test to compare treatment means as well
Testing Independence
 Testing Independence Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1/50 Testing Independence Previously, we looked at RR = OR = 1
Testing Independence Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1/50 Testing Independence Previously, we looked at RR = OR = 1
Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis
 Paper SP03 Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis Irmgard Hollweck, UCB Biosciences GmbH, Monheim, Germany Meike Best, UCB Biosciences GmbH, Monheim, Germany ABSTRACT A common
Paper SP03 Using PROC GENMOD to Analyse Ratio to Placebo in Change of Dactylitis Irmgard Hollweck, UCB Biosciences GmbH, Monheim, Germany Meike Best, UCB Biosciences GmbH, Monheim, Germany ABSTRACT A common
ANOVA Longitudinal Models for the Practice Effects Data: via GLM
 Psyc 943 Lecture 25 page 1 ANOVA Longitudinal Models for the Practice Effects Data: via GLM Model 1. Saturated Means Model for Session, E-only Variances Model (BP) Variances Model: NO correlation, EQUAL
Psyc 943 Lecture 25 page 1 ANOVA Longitudinal Models for the Practice Effects Data: via GLM Model 1. Saturated Means Model for Session, E-only Variances Model (BP) Variances Model: NO correlation, EQUAL
Two Hours. Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 26 May :00 16:00
 Two Hours MATH38052 Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER GENERALISED LINEAR MODELS 26 May 2016 14:00 16:00 Answer ALL TWO questions in Section
Two Hours MATH38052 Mathematical formula books and statistical tables are to be provided THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER GENERALISED LINEAR MODELS 26 May 2016 14:00 16:00 Answer ALL TWO questions in Section
Count data page 1. Count data. 1. Estimating, testing proportions
 Count data page 1 Count data 1. Estimating, testing proportions 100 seeds, 45 germinate. We estimate probability p that a plant will germinate to be 0.45 for this population. Is a 50% germination rate
Count data page 1 Count data 1. Estimating, testing proportions 100 seeds, 45 germinate. We estimate probability p that a plant will germinate to be 0.45 for this population. Is a 50% germination rate
BIOSTATS Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2017 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Practice Problems SOLUTIONS
 BIOSTATS 640 - Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2017 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Practice Problems SOLUTIONS Practice Question 1 Both the Binomial and Poisson distributions have been used to model the quantal
BIOSTATS 640 - Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2017 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Practice Problems SOLUTIONS Practice Question 1 Both the Binomial and Poisson distributions have been used to model the quantal
Generalized Linear Models
 Generalized Linear Models Lecture 7. Models with binary response II GLM (Spring, 2018) Lecture 7 1 / 13 Existence of estimates Lemma (Claudia Czado, München, 2004) The log-likelihood ln L(β) in logistic
Generalized Linear Models Lecture 7. Models with binary response II GLM (Spring, 2018) Lecture 7 1 / 13 Existence of estimates Lemma (Claudia Czado, München, 2004) The log-likelihood ln L(β) in logistic
Topic 12. The Split-plot Design and its Relatives (continued) Repeated Measures
 12.1 Topic 12. The Split-plot Design and its Relatives (continued) Repeated Measures 12.9 Repeated measures analysis Sometimes researchers make multiple measurements on the same experimental unit. We have
12.1 Topic 12. The Split-plot Design and its Relatives (continued) Repeated Measures 12.9 Repeated measures analysis Sometimes researchers make multiple measurements on the same experimental unit. We have
Week 7.1--IES 612-STA STA doc
 Week 7.1--IES 612-STA 4-573-STA 4-576.doc IES 612/STA 4-576 Winter 2009 ANOVA MODELS model adequacy aka RESIDUAL ANALYSIS Numeric data samples from t populations obtained Assume Y ij ~ independent N(μ
Week 7.1--IES 612-STA 4-573-STA 4-576.doc IES 612/STA 4-576 Winter 2009 ANOVA MODELS model adequacy aka RESIDUAL ANALYSIS Numeric data samples from t populations obtained Assume Y ij ~ independent N(μ
Outline. Topic 20 - Diagnostics and Remedies. Residuals. Overview. Diagnostics Plots Residual checks Formal Tests. STAT Fall 2013
 Topic 20 - Diagnostics and Remedies - Fall 2013 Diagnostics Plots Residual checks Formal Tests Remedial Measures Outline Topic 20 2 General assumptions Overview Normally distributed error terms Independent
Topic 20 - Diagnostics and Remedies - Fall 2013 Diagnostics Plots Residual checks Formal Tests Remedial Measures Outline Topic 20 2 General assumptions Overview Normally distributed error terms Independent
STA6938-Logistic Regression Model
 Dr. Ying Zhang STA6938-Logistic Regression Model Topic 2-Multiple Logistic Regression Model Outlines:. Model Fitting 2. Statistical Inference for Multiple Logistic Regression Model 3. Interpretation of
Dr. Ying Zhang STA6938-Logistic Regression Model Topic 2-Multiple Logistic Regression Model Outlines:. Model Fitting 2. Statistical Inference for Multiple Logistic Regression Model 3. Interpretation of
Correlation and the Analysis of Variance Approach to Simple Linear Regression
 Correlation and the Analysis of Variance Approach to Simple Linear Regression Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Correlation and the Analysis of Variance Approach to Simple Linear Regression p. 1/35 Correlation
Correlation and the Analysis of Variance Approach to Simple Linear Regression Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Correlation and the Analysis of Variance Approach to Simple Linear Regression p. 1/35 Correlation
STAT 7030: Categorical Data Analysis
 STAT 7030: Categorical Data Analysis 5. Logistic Regression Peng Zeng Department of Mathematics and Statistics Auburn University Fall 2012 Peng Zeng (Auburn University) STAT 7030 Lecture Notes Fall 2012
STAT 7030: Categorical Data Analysis 5. Logistic Regression Peng Zeng Department of Mathematics and Statistics Auburn University Fall 2012 Peng Zeng (Auburn University) STAT 7030 Lecture Notes Fall 2012
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 7: Generalized linear mixed models
 Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 7: Generalized linear mixed models Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team University of
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 7: Generalized linear mixed models Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team University of
dm'log;clear;output;clear'; options ps=512 ls=99 nocenter nodate nonumber nolabel FORMCHAR=" = -/\<>*"; ODS LISTING;
 dm'log;clear;output;clear'; options ps=512 ls=99 nocenter nodate nonumber nolabel FORMCHAR=" ---- + ---+= -/\*"; ODS LISTING; *** Table 23.2 ********************************************; *** Moore, David
dm'log;clear;output;clear'; options ps=512 ls=99 nocenter nodate nonumber nolabel FORMCHAR=" ---- + ---+= -/\*"; ODS LISTING; *** Table 23.2 ********************************************; *** Moore, David
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200 Spring 2018 University of California, Berkeley
 "PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200 Spring 2018 University of California, Berkeley D.D. Ackerly Feb. 26, 2018 Maximum Likelihood Principles, and Applications to
"PRINCIPLES OF PHYLOGENETICS: ECOLOGY AND EVOLUTION" Integrative Biology 200 Spring 2018 University of California, Berkeley D.D. Ackerly Feb. 26, 2018 Maximum Likelihood Principles, and Applications to
A course in statistical modelling. session 06b: Modelling count data
 A Course in Statistical Modelling University of Glasgow 29 and 30 January, 2015 session 06b: Modelling count data Graeme Hutcheson 1 Luiz Moutinho 2 1 Manchester Institute of Education Manchester university
A Course in Statistical Modelling University of Glasgow 29 and 30 January, 2015 session 06b: Modelling count data Graeme Hutcheson 1 Luiz Moutinho 2 1 Manchester Institute of Education Manchester university
Laboratory Topics 4 & 5
 PLS205 Lab 3 January 23, 2014 Orthogonal contrasts Class comparisons in SAS Trend analysis in SAS Multiple mean comparisons Laboratory Topics 4 & 5 Orthogonal contrasts Planned, single degree-of-freedom
PLS205 Lab 3 January 23, 2014 Orthogonal contrasts Class comparisons in SAS Trend analysis in SAS Multiple mean comparisons Laboratory Topics 4 & 5 Orthogonal contrasts Planned, single degree-of-freedom
COMPLEMENTARY LOG-LOG MODEL
 COMPLEMENTARY LOG-LOG MODEL Under the assumption of binary response, there are two alternatives to logit model: probit model and complementary-log-log model. They all follow the same form π ( x) =Φ ( α
COMPLEMENTARY LOG-LOG MODEL Under the assumption of binary response, there are two alternatives to logit model: probit model and complementary-log-log model. They all follow the same form π ( x) =Φ ( α
GROUPED DATA E.G. FOR SAMPLE OF RAW DATA (E.G. 4, 12, 7, 5, MEAN G x / n STANDARD DEVIATION MEDIAN AND QUARTILES STANDARD DEVIATION
 FOR SAMPLE OF RAW DATA (E.G. 4, 1, 7, 5, 11, 6, 9, 7, 11, 5, 4, 7) BE ABLE TO COMPUTE MEAN G / STANDARD DEVIATION MEDIAN AND QUARTILES Σ ( Σ) / 1 GROUPED DATA E.G. AGE FREQ. 0-9 53 10-19 4...... 80-89
FOR SAMPLE OF RAW DATA (E.G. 4, 1, 7, 5, 11, 6, 9, 7, 11, 5, 4, 7) BE ABLE TO COMPUTE MEAN G / STANDARD DEVIATION MEDIAN AND QUARTILES Σ ( Σ) / 1 GROUPED DATA E.G. AGE FREQ. 0-9 53 10-19 4...... 80-89
Chapter 11: Robust & Quantile regression
 Chapter 11: Robust & Adapted from Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 704: Data Analysis I 1 / 13 11.3: Robust regression Leverages h ii and deleted residuals t i
Chapter 11: Robust & Adapted from Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 704: Data Analysis I 1 / 13 11.3: Robust regression Leverages h ii and deleted residuals t i
Multinomial Logistic Regression Models
 Stat 544, Lecture 19 1 Multinomial Logistic Regression Models Polytomous responses. Logistic regression can be extended to handle responses that are polytomous, i.e. taking r>2 categories. (Note: The word
Stat 544, Lecture 19 1 Multinomial Logistic Regression Models Polytomous responses. Logistic regression can be extended to handle responses that are polytomous, i.e. taking r>2 categories. (Note: The word
ssh tap sas913, sas https://www.statlab.umd.edu/sasdoc/sashtml/onldoc.htm
 Kedem, STAT 430 SAS Examples: Logistic Regression ==================================== ssh abc@glue.umd.edu, tap sas913, sas https://www.statlab.umd.edu/sasdoc/sashtml/onldoc.htm a. Logistic regression.
Kedem, STAT 430 SAS Examples: Logistic Regression ==================================== ssh abc@glue.umd.edu, tap sas913, sas https://www.statlab.umd.edu/sasdoc/sashtml/onldoc.htm a. Logistic regression.
Case-control studies C&H 16
 Case-control studies C&H 6 Bendix Carstensen Steno Diabetes Center & Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen bxc@steno.dk http://bendixcarstensen.com PhD-course in Epidemiology, Department
Case-control studies C&H 6 Bendix Carstensen Steno Diabetes Center & Department of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen bxc@steno.dk http://bendixcarstensen.com PhD-course in Epidemiology, Department
Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3
 Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 770: Categorical Data Analysis 1/ 32 Chapter 4: Introduction to Generalized Linear Models Generalized linear
Sections 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 Timothy Hanson Department of Statistics, University of South Carolina Stat 770: Categorical Data Analysis 1/ 32 Chapter 4: Introduction to Generalized Linear Models Generalized linear
Confirmatory and Exploratory Data Analyses Using PROC GENMOD: Factors Associated with Red Light Running Crashes
 Confirmatory and Exploratory Data Analyses Using PROC GENMOD: Factors Associated with Red Light Running Crashes Li wan Chen, LENDIS Corporation, McLean, VA Forrest Council, Highway Safety Research Center,
Confirmatory and Exploratory Data Analyses Using PROC GENMOD: Factors Associated with Red Light Running Crashes Li wan Chen, LENDIS Corporation, McLean, VA Forrest Council, Highway Safety Research Center,
Some comments on Partitioning
 Some comments on Partitioning Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1/30 Partitioning Chi-Squares We have developed tests
Some comments on Partitioning Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM 1/30 Partitioning Chi-Squares We have developed tests
Topic 23: Diagnostics and Remedies
 Topic 23: Diagnostics and Remedies Outline Diagnostics residual checks ANOVA remedial measures Diagnostics Overview We will take the diagnostics and remedial measures that we learned for regression and
Topic 23: Diagnostics and Remedies Outline Diagnostics residual checks ANOVA remedial measures Diagnostics Overview We will take the diagnostics and remedial measures that we learned for regression and
STA 4504/5503 Sample Exam 1 Spring 2011 Categorical Data Analysis. 1. Indicate whether each of the following is true (T) or false (F).
 STA 4504/5503 Sample Exam 1 Spring 2011 Categorical Data Analysis 1. Indicate whether each of the following is true (T) or false (F). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) In 2 2 tables, statistical independence is equivalent
STA 4504/5503 Sample Exam 1 Spring 2011 Categorical Data Analysis 1. Indicate whether each of the following is true (T) or false (F). (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) In 2 2 tables, statistical independence is equivalent
Faculty of Health Sciences. Correlated data. Count variables. Lene Theil Skovgaard & Julie Lyng Forman. December 6, 2016
 Faculty of Health Sciences Correlated data Count variables Lene Theil Skovgaard & Julie Lyng Forman December 6, 2016 1 / 76 Modeling count outcomes Outline The Poisson distribution for counts Poisson models,
Faculty of Health Sciences Correlated data Count variables Lene Theil Skovgaard & Julie Lyng Forman December 6, 2016 1 / 76 Modeling count outcomes Outline The Poisson distribution for counts Poisson models,
PubHlth Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2015 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Study Guide
 PubHlth 640 - Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2015 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Study Guide Unit 3 (Discrete Distributions) Take care to know how to do the following! Learning Objective See: 1. Write down
PubHlth 640 - Intermediate Biostatistics Spring 2015 Exam 2 (Units 3, 4 & 5) Study Guide Unit 3 (Discrete Distributions) Take care to know how to do the following! Learning Objective See: 1. Write down
Topic 28: Unequal Replication in Two-Way ANOVA
 Topic 28: Unequal Replication in Two-Way ANOVA Outline Two-way ANOVA with unequal numbers of observations in the cells Data and model Regression approach Parameter estimates Previous analyses with constant
Topic 28: Unequal Replication in Two-Way ANOVA Outline Two-way ANOVA with unequal numbers of observations in the cells Data and model Regression approach Parameter estimates Previous analyses with constant
Survival Regression Models
 Survival Regression Models David M. Rocke May 18, 2017 David M. Rocke Survival Regression Models May 18, 2017 1 / 32 Background on the Proportional Hazards Model The exponential distribution has constant
Survival Regression Models David M. Rocke May 18, 2017 David M. Rocke Survival Regression Models May 18, 2017 1 / 32 Background on the Proportional Hazards Model The exponential distribution has constant
Preface Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis Overview: Statistical Inference, Samples, Populations, and Experimental Design The Role of
 Preface Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis Overview: Statistical Inference, Samples, Populations, and Experimental Design The Role of Probability Sampling Procedures Collection of Data Measures
Preface Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis Overview: Statistical Inference, Samples, Populations, and Experimental Design The Role of Probability Sampling Procedures Collection of Data Measures
Analysis of binary repeated measures data with R
 Analysis of binary repeated measures data with R Right-handed basketball players take right and left-handed shots from 3 locations in a different random order for each player. Hit or miss is recorded.
Analysis of binary repeated measures data with R Right-handed basketball players take right and left-handed shots from 3 locations in a different random order for each player. Hit or miss is recorded.
STAT 501 EXAM I NAME Spring 1999
 STAT 501 EXAM I NAME Spring 1999 Instructions: You may use only your calculator and the attached tables and formula sheet. You can detach the tables and formula sheet from the rest of this exam. Show your
STAT 501 EXAM I NAME Spring 1999 Instructions: You may use only your calculator and the attached tables and formula sheet. You can detach the tables and formula sheet from the rest of this exam. Show your
General Linear Model (Chapter 4)
 General Linear Model (Chapter 4) Outcome variable is considered continuous Simple linear regression Scatterplots OLS is BLUE under basic assumptions MSE estimates residual variance testing regression coefficients
General Linear Model (Chapter 4) Outcome variable is considered continuous Simple linear regression Scatterplots OLS is BLUE under basic assumptions MSE estimates residual variance testing regression coefficients
Chapter 4: Generalized Linear Models-I
 : Generalized Linear Models-I Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
: Generalized Linear Models-I Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
STAT 5200 Handout #26. Generalized Linear Mixed Models
 STAT 5200 Handout #26 Generalized Linear Mixed Models Up until now, we have assumed our error terms are normally distributed. What if normality is not realistic due to the nature of the data? (For example,
STAT 5200 Handout #26 Generalized Linear Mixed Models Up until now, we have assumed our error terms are normally distributed. What if normality is not realistic due to the nature of the data? (For example,
BIOS 625 Fall 2015 Homework Set 3 Solutions
 BIOS 65 Fall 015 Homework Set 3 Solutions 1. Agresti.0 Table.1 is from an early study on the death penalty in Florida. Analyze these data and show that Simpson s Paradox occurs. Death Penalty Victim's
BIOS 65 Fall 015 Homework Set 3 Solutions 1. Agresti.0 Table.1 is from an early study on the death penalty in Florida. Analyze these data and show that Simpson s Paradox occurs. Death Penalty Victim's
BMI 541/699 Lecture 22
 BMI 541/699 Lecture 22 Where we are: 1. Introduction and Experimental Design 2. Exploratory Data Analysis 3. Probability 4. T-based methods for continous variables 5. Power and sample size for t-based
BMI 541/699 Lecture 22 Where we are: 1. Introduction and Experimental Design 2. Exploratory Data Analysis 3. Probability 4. T-based methods for continous variables 5. Power and sample size for t-based
Model selection and comparison
 Model selection and comparison an example with package Countr Tarak Kharrat 1 and Georgi N. Boshnakov 2 1 Salford Business School, University of Salford, UK. 2 School of Mathematics, University of Manchester,
Model selection and comparison an example with package Countr Tarak Kharrat 1 and Georgi N. Boshnakov 2 1 Salford Business School, University of Salford, UK. 2 School of Mathematics, University of Manchester,
a = 4 levels of treatment A = Poison b = 3 levels of treatment B = Pretreatment n = 4 replicates for each treatment combination
 In Box, Hunter, and Hunter Statistics for Experimenters is a two factor example of dying times for animals, let's say cockroaches, using 4 poisons and pretreatments with n=4 values for each combination
In Box, Hunter, and Hunter Statistics for Experimenters is a two factor example of dying times for animals, let's say cockroaches, using 4 poisons and pretreatments with n=4 values for each combination
Epidemiology Wonders of Biostatistics Chapter 13 - Effect Measures. John Koval
 Epidemiology 9509 Wonders of Biostatistics Chapter 13 - Effect Measures John Koval Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario What is being covered 1. risk factors 2. risk
Epidemiology 9509 Wonders of Biostatistics Chapter 13 - Effect Measures John Koval Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics University of Western Ontario What is being covered 1. risk factors 2. risk
ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Multicategory Logit Models. Logit Models For Nominal Responses
 ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Multicategory Logit Models Logit Models For Nominal Responses 1 Models For Nominal Responses Y is nominal with J categories. Let {π 1,, π J } denote the response probabilities
ST3241 Categorical Data Analysis I Multicategory Logit Models Logit Models For Nominal Responses 1 Models For Nominal Responses Y is nominal with J categories. Let {π 1,, π J } denote the response probabilities
PARTICLE COUNTS MISLEAD SCIENTISTS: A JMP AND SAS INTEGRATION CASE STUDY INVESTIGATING MODELING
 PARTICLE COUNTS MISLEAD SCIENTISTS: A JMP AND SAS INTEGRATION CASE STUDY INVESTIGATING MODELING Kathleen Kiernan, Diane Michelson, PhD, Annie Zangi, SAS Many researchers and statisticians deal with data
PARTICLE COUNTS MISLEAD SCIENTISTS: A JMP AND SAS INTEGRATION CASE STUDY INVESTIGATING MODELING Kathleen Kiernan, Diane Michelson, PhD, Annie Zangi, SAS Many researchers and statisticians deal with data
Chapter 4: Generalized Linear Models-II
 : Generalized Linear Models-II Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
: Generalized Linear Models-II Dipankar Bandyopadhyay Department of Biostatistics, Virginia Commonwealth University BIOS 625: Categorical Data & GLM [Acknowledgements to Tim Hanson and Haitao Chu] D. Bandyopadhyay
11 November 2011 Department of Biostatistics, University of Copengen. 9:15 10:00 Recap of case-control studies. Frequency-matched studies.
 Matched and nested case-control studies Bendix Carstensen Steno Diabetes Center, Gentofte, Denmark http://staff.pubhealth.ku.dk/~bxc/ Department of Biostatistics, University of Copengen 11 November 2011
Matched and nested case-control studies Bendix Carstensen Steno Diabetes Center, Gentofte, Denmark http://staff.pubhealth.ku.dk/~bxc/ Department of Biostatistics, University of Copengen 11 November 2011
EVALUATION OF WILDLIFE REFLECTORS IN REDUCING VEHICLE-DEER COLLISIONS ON INDIANA INTERSTATE 80/90
 Final Report FHWA/IN/JTRP-2006/18 EVALUATION OF WILDLIFE REFLECTORS IN REDUCING VEHICLE-DEER COLLISIONS ON INDIANA INTERSTATE 80/90 By Sedat Gulen Statistical Pavement Research Engineer Division of Research
Final Report FHWA/IN/JTRP-2006/18 EVALUATION OF WILDLIFE REFLECTORS IN REDUCING VEHICLE-DEER COLLISIONS ON INDIANA INTERSTATE 80/90 By Sedat Gulen Statistical Pavement Research Engineer Division of Research
Generalized linear models
 Generalized linear models Outline for today What is a generalized linear model Linear predictors and link functions Example: estimate a proportion Analysis of deviance Example: fit dose- response data
Generalized linear models Outline for today What is a generalized linear model Linear predictors and link functions Example: estimate a proportion Analysis of deviance Example: fit dose- response data
A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using R. Brian S. Everitt and Torsten Hothorn
 A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using R Brian S. Everitt and Torsten Hothorn CHAPTER 6 Logistic Regression and Generalised Linear Models: Blood Screening, Women s Role in Society, and Colonic Polyps
A Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using R Brian S. Everitt and Torsten Hothorn CHAPTER 6 Logistic Regression and Generalised Linear Models: Blood Screening, Women s Role in Society, and Colonic Polyps
Stat 529 (Winter 2011) Experimental Design for the Two-Sample Problem. Motivation: Designing a new silver coins experiment
 Stat 529 (Winter 2011) Experimental Design for the Two-Sample Problem Reading: 2.4 2.6. Motivation: Designing a new silver coins experiment Sample size calculations Margin of error for the pooled two sample
Stat 529 (Winter 2011) Experimental Design for the Two-Sample Problem Reading: 2.4 2.6. Motivation: Designing a new silver coins experiment Sample size calculations Margin of error for the pooled two sample
Repeated Measures Part 2: Cartoon data
 Repeated Measures Part 2: Cartoon data /*********************** cartoonglm.sas ******************/ options linesize=79 noovp formdlim='_'; title 'Cartoon Data: STA442/1008 F 2005'; proc format; /* value
Repeated Measures Part 2: Cartoon data /*********************** cartoonglm.sas ******************/ options linesize=79 noovp formdlim='_'; title 'Cartoon Data: STA442/1008 F 2005'; proc format; /* value
Outline. Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 5: Generalized linear mixed models. Parts of LMMs carried over to GLMMs
 Outline Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 5: Generalized linear mixed models Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team UseR!2009,
Outline Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 5: Generalized linear mixed models Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team UseR!2009,
STAT 525 Fall Final exam. Tuesday December 14, 2010
 STAT 525 Fall 2010 Final exam Tuesday December 14, 2010 Time: 2 hours Name (please print): Show all your work and calculations. Partial credit will be given for work that is partially correct. Points will
STAT 525 Fall 2010 Final exam Tuesday December 14, 2010 Time: 2 hours Name (please print): Show all your work and calculations. Partial credit will be given for work that is partially correct. Points will
STA 303 H1S / 1002 HS Winter 2011 Test March 7, ab 1cde 2abcde 2fghij 3
 STA 303 H1S / 1002 HS Winter 2011 Test March 7, 2011 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: ENROLLED IN: (circle one) STA 303 STA 1002 INSTRUCTIONS: Time: 90 minutes Aids allowed: calculator. Some formulae
STA 303 H1S / 1002 HS Winter 2011 Test March 7, 2011 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: ENROLLED IN: (circle one) STA 303 STA 1002 INSTRUCTIONS: Time: 90 minutes Aids allowed: calculator. Some formulae
