Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
|
|
|
- Bonnie Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Aptitude (GA) Set-4 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 When she fell down the, she received many but little help. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) stairs, stares (C) stares, stairs (B) stairs, stairs (D) stares, stares Q.2 In spite of being warned repeatedly, he failed to correct his behaviour. The word that best fills the blank in the above sentence is (A) rational (B) reasonable (C) errant (D) good Q.3 For 0 x 2π, sin x and cos x are both decreasing functions in the interval. (A) (0, π 2 ) (B) (π 2, π) (C) (π, 3π 2 ) (D) (3π 2, 2π) Q.4 The area of an equilateral triangle is 3. What is the perimeter of the triangle? (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8 Q.5 Arrange the following three-dimensional objects in the descending order of their volumes: (i) A cuboid with dimensions 10 cm, 8 cm and 6 cm (ii) A cube of side 8 cm (iii) A cylinder with base radius 7 cm and height 7 cm (iv) A sphere of radius 7 cm (A) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) (B) (ii), (i), (iv), (iii) (C) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv) (D) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i) Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. Q.6 An automobile travels from city A to city B and returns to city A by the same route. The speed of the vehicle during the onward and return journeys were constant at 60 km/h and 90 km/h, respectively. What is the average speed in km/h for the entire journey? (A) 72 (B) 73 (C) 74 (D) 75 GA 1/2
2 General Aptitude (GA) Set-4 Q.7 A set of 4 parallel lines intersect with another set of 5 parallel lines. How many parallelograms are formed? (A) 20 (B) 48 (C) 60 (D) 72 Q.8 To pass a test, a candidate needs to answer at least 2 out of 3 questions correctly. A total of 6,30,000 candidates appeared for the test. Question A was correctly answered by 3,30,000 candidates. Question B was answered correctly by 2,50,000 candidates. Question C was answered correctly by 2,60,000 candidates. Both questions A and B were answered correctly by 1,00,000 candidates. Both questions B and C were answered correctly by 90,000 candidates. Both questions A and C were answered correctly by 80,000 candidates. If the number of students answering all questions correctly is the same as the number answering none, how many candidates failed to clear the test? (A) 30,000 (B) 2,70,000 (C) 3,90,000 (D) 4,20,000 Q.9 If x 2 + x 1 = 0 what is the value of x x 4? (A) 1 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9 Q.10 In a detailed study of annual crow births in India, it was found that there was relatively no growth during the period 2002 to 2004 and a sudden spike from 2004 to In another unrelated study, it was found that the revenue from cracker sales in India which remained fairly flat from 2002 to 2004, saw a sudden spike in 2005 before declining again in The solid line in the graph below refers to annual sale of crackers and the dashed line refers to the annual crow births in India. Choose the most appropriate inference from the above data. (A) There is a strong correlation between crow birth and cracker sales. (B) Cracker usage increases crow birth rate. (C) If cracker sale declines, crow birth will decline. (D) Increased birth rate of crows will cause an increase in the sale of crackers. END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA 2/2
3 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Let A = [ a b 2 b ] and X = ( 1 1 ). If AX = ( 3 ), then A is equal to 1 (A) 2 (B) 2 (C) 6 (D) 6 Q.2 If A and B are two independent events such that P(A) = 1 4 and P(B) = 2 3, then P(A B) is equal to (A) (B) 1 12 (C) 3 4 (D) 5 6 Q.3 Which one of the following is a leaf fibre? (A) Coir (B) Sisal (C) Jute (D) Hemp Q.4 The pair of fibres most prone to accumulation of static charge is (A) Cotton and Polyester (B) Silk and Polyester (C) Polyester and Polypropylene (D) Silk and Polypropylene Q.5 Heat-setting of melt-spun and drawn Nylon 6 filament yarn under slack condition leads to increase in its (A) Tenacity (C) Molecular weight (B) Molecular orientation (D) Dimensional stability Q.6 Which one of the fibres, having stress-strain curves as shown in the figure, is the most suitable for making mountaineering ropes? Stress P Q R Strain (A) P (B) Q (C) R (D) S S Q.7 The technology that produces yarn with the maximum fibre migration is (A) Rotor spinning (B) Friction spinning (C) Air-jet spinning (D) Ring spinning TF 1/10
4 Q.8 The cleaning machine, located in the fine cleaning zone of blowroom, uses the following as the opening element (A) Roller with saw tooth wire points (B) Drum with large spikes (C) Roller with discs having double edged teeth (D) Drum with large bladed discs Q.9 The purpose of having grooves or notches in modern flyer tops in speed frames is to (A) Increase real twist in roving (B) Insert false twist in roving (C) Reduce neps in roving (D) Increase fineness of roving Q.10 With time, wind per double traverse in a drum-driven winder (A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Remains constant (D) First increases and then decreases Q.11 In a loom, seven-wheel take-up motion is (A) Negative and intermittent (B) Negative and continuous (C) Positive and intermittent (D) Positive and continuous Q.12 The relative humidity (in %) and temperature (in C) of standard testing atmosphere are respectively (A) 65 and 25 (B) 65 and 20 (C) 60 and 25 (D) 60 and 20 Q.13 In Stelometer, if F is the force acting on a fibre bundle and is the angle through which the pendulum is moved, then F is directly proportional to (A) sin (B) cos (C) tan (D) cot Q.14 Yarn diameter varies (A) Directly with yarn packing density (B) Inversely with yarn packing density (C) Directly with square root of yarn packing density (D) Inversely with square root of yarn packing density TF 2/10
5 Q.15 The constant-rate-of-extension type tensile tester is NOT used for (A) Tongue tear test (B) Wing rip tear test (C) Elmendorf tear test (D) Trapezoid tear test Q.16 During bleaching of cotton with hydrogen peroxide, addition of sodium silicate (A) Reduces the viscosity of bath (B) Controls the rate of decomposition of perhydroxyl ions (HO 2 ) (C) Reduces the surface tension of bath (D) Enhances swelling of cotton Q.17 In dyeing of wool with levelling acid dyes, with time, the ph of dye bath (A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Remains constant (D) First increases and then decreases Q.18 The discharging agent used in discharge printing of cotton with reactive dyes is (A) Citric acid (B) Sodium dithionite (C) Thio-urea dioxide (D) Sodium formaldehyde sulphoxylate Q.19 Application of a fluorochemical based finish on a textile fabric imparts P. Water repellency Q. Oil repellency R. Soil repellency S. Soil release property (A) P, Q & R only (C) P, R & S only (B) Q, R & S only (D) P, Q & S only Q.20 If a = i + 2 j, b = j + 2 k and c = 2i k are three vectors such that a + λ b is perpendicular to c, then the value of λ is Q.21 If y(x) is the solution of the differential equation y y = 8 x, y(0) = 2, then the absolute value of y(2) is Q.22 4 x, x 2 If f(x) = { kx 4, x > 2 is equal to is a continuous function for all real values of x, then f(8) Q.23 A twistless polyester yarn has 90 filaments, each of 2 denier. The metric count of the yarn is TF 3/10
6 Q.24 Bottom shaft of a shuttle loom, weaving 2 up 1 down twill weave, is rotating at 90 rpm. The speed of cam shaft (in rpm) is Q.25 If wale constant and course constant for knitted fabrics are 4.2 and 5.46, respectively, then the value of the loop shape factor, accurate to one decimal place, is TF 4/10
7 Q. 26 Q. 55 carry two marks each. Q.26 The cross-sectional shape of a fibre affects the following properties of yarn P. Lustre Q. Torsional rigidity R. Flexural rigidity S. Packing density (A) P & Q only (C) P, Q & R only (B) P & R only (D) P, Q, R & S Q.27 Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [a]: The reaction temperature and rate of agitation during polymerization of polyethylene terephthalate have an important effect on molecular weight of the polymer produced. [r]: Polymerization of polyester by melt polycondensation is a predominantly diffusion controlled process. (A) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] (B) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] (C) Both [a] and [r] are false (D) [a] is true but [r] is false Q.28 Group I gives a list of fibres and Group II contains their applications. Match the fibre with its application. Group I Group II P. Polypropylene 1. Fire proof jacket Q. Carbon 2. Bullet proof jacket R. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene 3. Carpet S. Meta-aramid 4. Windmill blade (A) P-4, Q-2, R-3, S-1 (B) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1 (C) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2 (D) P-4, Q-1, R-2, S-3 Q.29 Techniques used to determine the glass transition temperature of textile fibres are P. X-ray diffraction (XRD) Q. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) R. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) S. Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) (A) P & Q only (C) Q & S only (B) Q & R only (D) R & S only TF 5/10
8 Q.30 Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [a]: In a carding machine, carding type of wire point configuration is used between cylinder and doffer. [r]: Carding type of wire point configuration gives the best fibre transfer without disturbing the fibre alignment. (A) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] (B) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] (C) Both [a] and [r] are false (D) [a] is true but [r] is false Q.31 Match the spinning technology listed in Group I with the machine component / function listed in Group II. Group I Group II P. Wrap spinning 1. False twisting Q. Rotor spinning 2. Perforated drums R. Air-jet spinning 3. Back doubling S. DREF II friction spinning 4. Hollow spindle (A) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1 (B) P-4, Q-1, R-3, S-2 (C) P-4, Q-3, R-1, S-2 (D) P-3, Q-1, R-2, S-4 Q.32 Compared to filaments in spunbonded nonwovens, those in meltblown nonwovens have P. Lower orientation of molecular chains Q. Higher orientation of molecular chains R. Lower variability in diameter S. Higher variability in diameter (A) P & R only (C) Q & R only (B) P & S only (D) Q & S only Q.33 Match the weave in Group I with fabric attribute in Group II. Group I Group II P. Plain 1. Holes in fabric Q. 2 up 1 down twill 2. High tear resistance R. 7 end satin 3. High shear resistance S. Mock leno 4. Continuous diagonal line (A) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-1 (B) P-1, Q-4, R-2, S-3 (C) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2 (D) P-3, Q-1, R-2, S-4 TF 6/10
9 Q.34 Match the test in Group I with fabric property in Group II. Group I Group II P. Cup test 1. Flexural rigidity Q. Heart loop test 2. Water vapour permeability R. Spray rating test 3. Resistance to water penetration S. Hydrostatic head test 4. Resistance to surface wettability (A) P-1, Q-2, R-3, S-4 (B) P-1, Q-2, R-4, S-3 (C) P-2, Q-1, R-3, S-4 (D) P-2, Q-1, R-4, S-3 Q.35 Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [a]: The work factor of silk fibre is greater than 0.5. [r]: The work factor is calculated by assuming the following as the stress-strain curve of silk fibre. Stress Strain (A) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] (B) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] (C) Both [a] and [r] are false (D) [a] is true but [r] is false Q.36 Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [a]: As the concentration of a surfactant in water increases, the surface tension of water initially decreases and then becomes constant. [r]: After reaching the Critical Micelle Concentration, additional surfactant molecules do not further reduce the surface tension. (A) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] (B) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] (C) Both [a] and [r] are false (D) [a] is true but [r] is false TF 7/10
10 Q.37 A dye is applied on a fibre using Na2S2O4 as an auxiliary. Washing fastness of the dye on fibre is good. The correct combination of the dye and the fibre is (A) Cationic dye, acrylic fibre (C) Acid dye, wool fibre (B) Vat dye, cotton fibre (D) Reactive dye, cotton fibre Q.38 Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [a]: Emulsion thickener is used in pigment printing of textiles. [r]: Emulsion thickener has high solid content. (A) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] (B) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] (C) Both [a] and [r] are false (D) [a] is true but [r] is false Q.39 Match the dye-fibre in Group I with the interactions in Group II. Group I Group II P. Reactive dye on cotton 1. Van der Waals forces Q. Disperse dye on polyester 2. Covalent bonds R. Vat dye on cotton 3. Electrostatic bonds S. Basic dye on acrylic 4. Mechanical entrapment (A) P-1, Q-2, R-4, S-3 (B) P-1, Q-2, R-3, S-4 (C) P-2, Q-1, R-4, S-3 (D) P-2, Q-1, R-3, S-4 Q.40 Let X be a random variable following the binomial distribution. If E(X) = 2 and Var(X) = 1.2, then P(X = 2), accurate to three decimal places, is equal to Q.41 The value of the integral is 4 16 x 2 y x 2 + y dy dx Q.42 Starting from the initial point x 0 = 10, if the sequence {x n } is generated using Newton Raphson method to compute the root of the equation x = 0, then x 2, accurate to two decimal places, is equal to TF 8/10
11 Q.43 If A = [ ], then the sum of all eigenvalues of the matrix M = A2 4 A 1 is equal to Q.44 If the density of 100% crystalline polyethylene is 1000 kg m -3 and that of 100% amorphous polyethylene is 865 kg m -3, then the mass fractional crystallinity of a polyethylene fibre with density 970 kg m -3, accurate to two decimal places, is Q.45 In winding zone of ring spinning, the permissible minimum angle of lead is 30. For a ring of 40 mm diameter, the minimum diameter (in mm) of bobbin required is Q.46 A sliver of 4.2 kilotex is fed in a rotor spinning machine with opening zone draft of The draft in the transport duct is 5 and the sliding draft on the rotor wall till the rotor groove is 2. If the total back doubling within the rotor is 120, then the linear density (in tex) of the output yarn is Q.47 An eight head comber is running at 400 nips/min. The lap fed is 60 kilotex and noil extracted is 20%. If the feed/nip is 7 mm, then with machine utilization of 80%, the production rate (in kg/h), accurate to one decimal place, is Q.48 A shuttle loom having 1.75 m reed width is running at 180 rpm. The shuttle enters and leaves the shed at 120 and 240 angular positions of crankshaft, respectively. If length of the shuttle is 0.25 m, then the mean velocity (in m/s) of the shuttle within the shed is Q.49 The diameter and length of torsion rod used in a projectile loom are increased by 5% and 20%, respectively. If the torque required to twist the rod increases by X%, then the value of X, accurate to two decimal places, is Q.50 Cloth cover factor of a square plain jammed cotton fabric, accurate to one decimal place, is Q.51 In a vibroscope, a cotton fibre of 25 mm length is clamped at one end, led over a knifeedge support, tensioned by a weight of 350 mg, and is inclined to vibrate at a fundamental resonant frequency of 2.6 khz. The linear density of the fibre (in tex), accurate to two decimal places, is TF 9/10
12 Q.52 The theoretical limit coefficient of variation (Vr in %) of the weight per unit length of cotton sliver is V r = 106/ N, where N is the average number of fibres present in the crosssection of the sliver. To derive this expression, the coefficient of variation (in %) of the fibre weight per unit length, accurate to two decimal places, is considered as Q.53 The bending length of a nonwoven fabric in machine direction is two times the bending length in cross-machine direction. The ratio of flexural rigidities of this fabric in machine direction to cross-machine direction is Q.54 The standard deviation of population P is two times the standard deviation of population Q. The size of a random sample from population P is four times the size of a random sample from population Q. If e P and e Q denote the standard error of means of the samples from P and Q, respectively, then the ratio of e P to e Q is Q.55 A crease resist (CR) agent is applied by padding on a fabric of 1 m width and 200 g/m 2 areal density. The concentration of CR agent in the pad bath is 100 gpl and the fabric speed is 50 m/min. The expression is 110% and the specific gravity of the pad liquor is 1.1. In order to maintain the bath concentration, the rate (in kg/min) at which the CR agent needs to be added to the bath, accurate to one decimal place, is END OF THE QUESTION PAPER TF 10/10
MATERIALS SCIENCE POLYMERS
 POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
POLYMERS 1) Types of Polymer (a) Plastic Possibly the largest number of different polymeric materials come under the plastic classification. Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene,
Fibre Friction WHAT IS FIBRE
 Fibre Friction WHAT IS FIBRE Fibre is a class of materials that are continuous filaments. Any thing having high length to width ratio. Diameter or width of fibre is negligible which cant be measured. Fibres
Fibre Friction WHAT IS FIBRE Fibre is a class of materials that are continuous filaments. Any thing having high length to width ratio. Diameter or width of fibre is negligible which cant be measured. Fibres
Department of Textile Engineering. COURSE DESCRIPTIONS for the Degree of Master of Science in Textile Engineering: Textile Chemistry and Fiber Science
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS for the Degree of Master of Science in Textile Engineering: Textile Chemistry and Fiber Science 19-12-503 Statistics & Research Methodology 3 Cr. Probability distributions, tests of
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS for the Degree of Master of Science in Textile Engineering: Textile Chemistry and Fiber Science 19-12-503 Statistics & Research Methodology 3 Cr. Probability distributions, tests of
2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state
 2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state or concentrated from the solution, molecules are often
2. Amorphous or Crystalline Structurally, polymers in the solid state may be amorphous or crystalline. When polymers are cooled from the molten state or concentrated from the solution, molecules are often
(Refer Slide Time: 00:58)
 Nature and Properties of Materials Professor Bishak Bhattacharya Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 18 Effect and Glass Transition Temperature In the last
Nature and Properties of Materials Professor Bishak Bhattacharya Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Lecture 18 Effect and Glass Transition Temperature In the last
High strength high modulus Fibres
 High strength high modulus Fibres Module 2: FAQ Q1. Define aramids. A manufactured fibre in which the fibre-forming substance is a long-chain synthetic polyamide in which at least 85% of the amide (-CO-NH-)
High strength high modulus Fibres Module 2: FAQ Q1. Define aramids. A manufactured fibre in which the fibre-forming substance is a long-chain synthetic polyamide in which at least 85% of the amide (-CO-NH-)
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours
 PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials There are two Sections
PHYSICS ADMISSIONS TEST SAMPLE PAPER (2015 style, issued September 2015) Time allowed: 2 hours For candidates applying to Physics, Physics and Philosophy, Engineering, or Materials There are two Sections
Static and kinetic frictional characteristics of staple fibres and woven fabrics
 Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 32, March 2007, pp. 80-87 Static and kinetic frictional characteristics of staple fibres and woven fabrics A Das a & S M Ishtiaque Department of Textile
Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 32, March 2007, pp. 80-87 Static and kinetic frictional characteristics of staple fibres and woven fabrics A Das a & S M Ishtiaque Department of Textile
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Figure 1.1 Torsional Pendulum
 Torsional Pendulum Torsional Pendulum Torsional Pendulum (without masses) (with masses at d1 (with masses at d close to the axis) away from the axis) Figure 1.1 Torsional Pendulum Department of Physical
Torsional Pendulum Torsional Pendulum Torsional Pendulum (without masses) (with masses at d1 (with masses at d close to the axis) away from the axis) Figure 1.1 Torsional Pendulum Department of Physical
Contents. Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker
 Table of Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker Preface page xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 How big is a nanometer? 1 1.2 What is nanotechnology? 1 1.3 Historical development of nanotechnology 2 1.4 Classification
Table of Foreword by Darrell H. Reneker Preface page xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 How big is a nanometer? 1 1.2 What is nanotechnology? 1 1.3 Historical development of nanotechnology 2 1.4 Classification
1. The number of moles of solute present in 1 kg of a solvent is called its A. molality B. molarity C. normality D. formality
 1. The number of moles of solute present in 1 kg of a solvent is called its A. molality B. molarity C. normality D. formality 2. The most electronegative element among the following is A. sodium B. bromine
1. The number of moles of solute present in 1 kg of a solvent is called its A. molality B. molarity C. normality D. formality 2. The most electronegative element among the following is A. sodium B. bromine
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr.
 Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
Reading Assignments Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 305 Fluid Mechanics I Fall 2018 Section 4 (Dr. Sert) Study Set 1 You can find the answers of some of the following
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
Syllabus of UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE COURSE. Textile Chemistry. Rajasthan Technical University, Kota
 Syllabus of UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE COURSE Textile Chemistry Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Effective from session: 201 2019 [Common with 3TT2-01, 3TE2-01] 3TC2-01: ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-
Syllabus of UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE COURSE Textile Chemistry Rajasthan Technical University, Kota Effective from session: 201 2019 [Common with 3TT2-01, 3TE2-01] 3TC2-01: ADVANCED ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
POLYFLUOR Fabric Protector (PFOS & PFOA free)
 POLYFLUOR Fabric Protector (PFOS & PFOA free) imagine! Resins Grade BS BS 3901 SR NI 3918 3936 Description emulsion emulsion solution Solids 30% 30% 20% 20% 15% 20% Ionicity Cationic Cationic - Non ionic
POLYFLUOR Fabric Protector (PFOS & PFOA free) imagine! Resins Grade BS BS 3901 SR NI 3918 3936 Description emulsion emulsion solution Solids 30% 30% 20% 20% 15% 20% Ionicity Cationic Cationic - Non ionic
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity
 2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
DYNAMICS ME HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS
 DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
1 2 Models, Theories, and Laws 1.5 Distinguish between models, theories, and laws 2.1 State the origin of significant figures in measurement
 Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 2018
 TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
The syllabus is approved for use in England, Wales and Northern Ireland as a Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate.
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certificate *013456789* FURTHER MATHEMATICS (PRINCIPAL) 9795/0 Paper Further Applications of Mathematics For Examination from 016
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certificate *013456789* FURTHER MATHEMATICS (PRINCIPAL) 9795/0 Paper Further Applications of Mathematics For Examination from 016
Downloaded from
 Question 1.1: What is the force between two small charged spheres having charges of 2 10 7 C and 3 10 7 C placed 30 cm apart in air? Repulsive force of magnitude 6 10 3 N Charge on the first sphere, q
Question 1.1: What is the force between two small charged spheres having charges of 2 10 7 C and 3 10 7 C placed 30 cm apart in air? Repulsive force of magnitude 6 10 3 N Charge on the first sphere, q
2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Aug. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Set No - 1 I B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Aug. 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to CE, ME, CSE, PCE, IT, Chem E, Aero E, AME, Min E, PE, Metal E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided. Table 10- from your text is assumed, and will be provided on the final exam. 1. A rock is thrown downward from
Physics 10 Spring 009 George Williams FINAL EXAM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A data sheet is provided. Table 10- from your text is assumed, and will be provided on the final exam. 1. A rock is thrown downward from
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
(3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 3 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) AND 3/4 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Two hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 000 MATHEMATICS UNIT (ADDITIONAL) AND /4 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Two hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 000 MATHEMATICS UNIT (ADDITIONAL) AND /4 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Two hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions. ALL questions
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Mechanics HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
A Novel Approach for Measurement of Fiber-on-fiber Friction
 F98S-09 Page 1 A Novel Approach for Measurement of Fiber-on-fiber Friction Number: F98S-09 Competency: Fabrication Team Leader and members: Y. Qiu, NCSU; Y. Wang, Georgia Tech; J.Z. Mi, Cotton Inc. Graduate
F98S-09 Page 1 A Novel Approach for Measurement of Fiber-on-fiber Friction Number: F98S-09 Competency: Fabrication Team Leader and members: Y. Qiu, NCSU; Y. Wang, Georgia Tech; J.Z. Mi, Cotton Inc. Graduate
( ) Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key. The next three problems refer to the following situation:
 Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key The next three problems refer to the following situation: Two masses, m 1 and m 2, m 1 > m 2, are suspended by a massless rope over a
Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key The next three problems refer to the following situation: Two masses, m 1 and m 2, m 1 > m 2, are suspended by a massless rope over a
CHAPTER 17 FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HAFTIRMAN
 CHAPTER 17 LEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HATIRMAN lexible Mechanical Elements Belts Roller chains Wire rope lexible shafts lexible Mechanical Elements Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar
CHAPTER 17 LEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS LECTURE NOTES DR. HATIRMAN lexible Mechanical Elements Belts Roller chains Wire rope lexible shafts lexible Mechanical Elements Belts, ropes, chains, and other similar
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Modelling Tension and Torque Properties of Fibre Ropes and splices
 Proceedings of the Third (1993) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Singapore, 6-11 June 1993 Modelling Tension and Torque Properties of Fibre Ropes and splices C M Leech, Reader in
Proceedings of the Third (1993) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Singapore, 6-11 June 1993 Modelling Tension and Torque Properties of Fibre Ropes and splices C M Leech, Reader in
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. EXAM #2 October 18, :00 9:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz EXAM #2 October 18, 2001 7:00 9:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last name
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz EXAM #2 October 18, 2001 7:00 9:00 PM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last name
Solution Only gravity is doing work. Since gravity is a conservative force mechanical energy is conserved:
 8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
8) roller coaster starts with a speed of 8.0 m/s at a point 45 m above the bottom of a dip (see figure). Neglecting friction, what will be the speed of the roller coaster at the top of the next slope,
Conceptual Questions. Fig.8.51 EXERCISES. 8. Why can t electric field lines cross? 9. In which direction do charges always move in an electric field?
 EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
EXERCISES Conceptual Questions 1. Explain why a neutral object can be attracted to a charged object. Why can this neutral object not be repelled by a charged object? 2. What is the function of an electroscope?
Test 7 wersja angielska
 Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture. Mike Wheatland
 Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 4 MOMENT OF INERTIA. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to
 ENGINEEING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTOIAL 4 MOMENT OF INETIA On completion of this tutorial you should be able to evise angular motion. Define and derive the moment of inertia of a body.
ENGINEEING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTOIAL 4 MOMENT OF INETIA On completion of this tutorial you should be able to evise angular motion. Define and derive the moment of inertia of a body.
Qualitative analysis of aramide polymers by FT-IR spectroscopy
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 2 ǁ February 2014 ǁ PP.01-07 Qualitative analysis of aramide polymers by FT-IR spectroscopy
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 3 Issue 2 ǁ February 2014 ǁ PP.01-07 Qualitative analysis of aramide polymers by FT-IR spectroscopy
PHYSICS LAB Experiment 9 Fall 2004 THE TORSION PENDULUM
 PHYSICS 83 - LAB Experiment 9 Fall 004 THE TORSION PENDULUM In this experiment we will study the torsion constants of three different rods, a brass rod, a thin steel rod and a thick steel rod. We will
PHYSICS 83 - LAB Experiment 9 Fall 004 THE TORSION PENDULUM In this experiment we will study the torsion constants of three different rods, a brass rod, a thin steel rod and a thick steel rod. We will
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Rotational Motion Examples:
 Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
1. An object is dropped from rest. Which of the five following graphs correctly represents its motion? The positive direction is taken to be downward.
 Unless otherwise instructed, use g = 9.8 m/s 2 Rotational Inertia about an axis through com: Hoop about axis(radius=r, mass=m) : MR 2 Hoop about diameter (radius=r, mass=m): 1/2MR 2 Disk/solid cyllinder
Unless otherwise instructed, use g = 9.8 m/s 2 Rotational Inertia about an axis through com: Hoop about axis(radius=r, mass=m) : MR 2 Hoop about diameter (radius=r, mass=m): 1/2MR 2 Disk/solid cyllinder
Physics. Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT)
 Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT) 1. Define physical quantity and write steps for measurement. 2. What are fundamental units and derived units? 3. List the seven basic and two supplementary physical
Assignment-1(UNITS AND MEASUREMENT) 1. Define physical quantity and write steps for measurement. 2. What are fundamental units and derived units? 3. List the seven basic and two supplementary physical
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 24, 2014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm
 Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 4, 014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm 1. No notes or textbooks allowed.. Formula sheets are included (may
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 4, 014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm 1. No notes or textbooks allowed.. Formula sheets are included (may
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Periodic table with the elements associated with commercial polymers in color.
 Polymers 1. What are polymers 2. Polymerization 3. Structure features of polymers 4. Thermoplastic polymers and thermosetting polymers 5. Additives 6. Polymer crystals 7. Mechanical properties of polymers
Polymers 1. What are polymers 2. Polymerization 3. Structure features of polymers 4. Thermoplastic polymers and thermosetting polymers 5. Additives 6. Polymer crystals 7. Mechanical properties of polymers
Sensor Accessories. Rotary Motion Accessory Pack. Pendulum Rod with two masses, Angular Momentum disc set and Linear Rack with mini c-clamp
 Sensor Accessories Rotary Motion Accessory Pack (Product No 3288) Pendulum Rod with two masses, Angular Momentum disc set and Linear Rack with mini c-clamp DATA HARVEST Data Harvest Group Ltd 1 Eden Court,
Sensor Accessories Rotary Motion Accessory Pack (Product No 3288) Pendulum Rod with two masses, Angular Momentum disc set and Linear Rack with mini c-clamp DATA HARVEST Data Harvest Group Ltd 1 Eden Court,
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
Chapter Rotational Motion
 26 Chapter Rotational Motion 1. Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω 1. Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc.
26 Chapter Rotational Motion 1. Initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω 1. Then two small spheres of mass m are attached gently to diametrically opposite points on the edge of the disc.
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
EXERCISE - 01 NEETIIT.COM. d x dt. = 2 x 2 (4)
 1. The acceleration of a particle executing S.H.M. is (1) Always directed towards the equillibrium position () Always towards the one end (3) Continuously changing in direction () Maximum at the mean position.
1. The acceleration of a particle executing S.H.M. is (1) Always directed towards the equillibrium position () Always towards the one end (3) Continuously changing in direction () Maximum at the mean position.
Vectors. Scalars & vectors Adding displacement vectors. What about adding other vectors - Vector equality Order does not matter: i resultant A B
 Vectors Scalars & vectors Adding displacement vectors i resultant f What about adding other vectors - Vector equality Order does not matter: B C i A A f C B A B Vector addition I Graphical vector addition
Vectors Scalars & vectors Adding displacement vectors i resultant f What about adding other vectors - Vector equality Order does not matter: B C i A A f C B A B Vector addition I Graphical vector addition
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Annual Exam 2012 Subject: PHYSICS Level: ADVANCED 1 ST Year Time: 3 hrs Name: Year: Answer all questions. This paper carries 200 marks.
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO CENTRE FOR FURTHER STUDIES VICTORIA GOZO Annual Exam 2012 Subject: PHYSICS Level: ADVANCED 1 ST Year Time: 3 hrs Name: Year: Answer all questions. This paper carries 200 marks.
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Wrench Demo Torque Torque, τ, is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis τ = Fd F is the force d is the lever arm (or moment
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Wrench Demo Torque Torque, τ, is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about some axis τ = Fd F is the force d is the lever arm (or moment
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
Name: School Name: PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION
 PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
Circular motion minutes. 62 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor Page 1 of 22. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks:
 Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design
 Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
Foundations of Ultraprecision Mechanism Design S.T. Smith University of North Carolina at Charlotte, USA and D.G. Chetwynd University of Warwick, UK GORDON AND BREACH SCIENCE PUBLISHERS Switzerland Australia
A study on measures to reduce infrequent yarn faults - Development of an attachment
 Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 20, December 1995, pp. 176-180 A study on measures to reduce infrequent yarn faults - Development of an attachment A Kanthimathinathan; M Kathirvel, K Gnanasekar,
Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 20, December 1995, pp. 176-180 A study on measures to reduce infrequent yarn faults - Development of an attachment A Kanthimathinathan; M Kathirvel, K Gnanasekar,
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Physics 53 Exam 3 November 3, 2010 Dr. Alward
 1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is. 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i (C) (D) 3 (C)
 1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
1. If z is a complex number and if 8 z 2, then the greatest value of z is z (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 4 2. The principal argument/amplitude of the complex number 1 2 i 1 3i is (A) 2 (B) 4 (C) (D) 3 4 3.
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
USHA RAMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
 Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
Set No - 1 I B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Feb. - 2015 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, Bio-Tech, E Com.E, Agri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists
FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH. Automatic Single-Fibre Testers
 FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH Automatic Single-Fibre Testers Single-Fibre Testers FAVIMAT and FAVIGRAPH The FAVIMAT testing methods Testing and evaluation of a wide range of fibre properties are essential
FAVIMAT (AI)ROBOT2 FAVIGRAPH Automatic Single-Fibre Testers Single-Fibre Testers FAVIMAT and FAVIGRAPH The FAVIMAT testing methods Testing and evaluation of a wide range of fibre properties are essential
Investigation of Performance Properties of Graphene Coated Fabrics
 Investigation of Performance Properties of Graphene Coated Fabrics Rumeysa Celen, Gizem Manasoglu, Mehmet Kanik, Yusuf Ulcay (Department of Textile Engineering, Bursa Uludag University, TURKEY) ABSTRACT:
Investigation of Performance Properties of Graphene Coated Fabrics Rumeysa Celen, Gizem Manasoglu, Mehmet Kanik, Yusuf Ulcay (Department of Textile Engineering, Bursa Uludag University, TURKEY) ABSTRACT:
Q1. A) 46 m/s B) 21 m/s C) 17 m/s D) 52 m/s E) 82 m/s. Ans: v = ( ( 9 8) ( 98)
 Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 2
 Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
Pleeeeeeeeeeeeeease mark your UFID, exam number, and name correctly. 20 problems 3 problems from exam 1 3 problems from exam 2 6 problems 13.1 14.6 (including 14.5) 8 problems 1.1---9.6 Go through the
STATICS. Friction VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
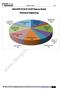 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
SCH4U Synthesis and Polymers. Synthesis Reactions and Addition and Condensation Polymers
 SCH4U Synthesis and Polymers Synthesis Reactions and Addition and Condensation Polymers ADDITION POLYMERS ADDITION POLYMERS A + A + A + A A A A A monomers polymer + + + ethylene (ethene) polyethylene
SCH4U Synthesis and Polymers Synthesis Reactions and Addition and Condensation Polymers ADDITION POLYMERS ADDITION POLYMERS A + A + A + A A A A A monomers polymer + + + ethylene (ethene) polyethylene
Physics 207 Lecture 9. Lecture 9
 Lecture 9 Today: Review session Assignment: For Thursday, Read through Chapter 8 (first four sections) Exam Wed., Feb. 17 th from 7:15-8:45 PM Chapters 1-6 One 8½ X 11 hand written note sheet and a calculator
Lecture 9 Today: Review session Assignment: For Thursday, Read through Chapter 8 (first four sections) Exam Wed., Feb. 17 th from 7:15-8:45 PM Chapters 1-6 One 8½ X 11 hand written note sheet and a calculator
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 July 2012 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: July 3, 2012 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 July 2012 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: July 3, 2012 TIME: DURATION:
How materials work. Compression Tension Bending Torsion
 Materials How materials work Compression Tension Bending Torsion Elemental material atoms: A. Composition a) Nucleus: protons (+), neutrons (0) b) Electrons (-) B. Neutral charge, i.e., # electrons = #
Materials How materials work Compression Tension Bending Torsion Elemental material atoms: A. Composition a) Nucleus: protons (+), neutrons (0) b) Electrons (-) B. Neutral charge, i.e., # electrons = #
Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures. D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E.
 Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E. Title of meeting IOM Bla blah Topics Materials: Environmental acids, water, oil, radiation etc. Bonding. Cost.
Features and design of elastomer / textile engineered structures D Boast, C Eng. F Mech E. Title of meeting IOM Bla blah Topics Materials: Environmental acids, water, oil, radiation etc. Bonding. Cost.
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two men, Joel and Jerry, push against a wall. Jerry stops after 10 min, while Joel is
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two men, Joel and Jerry, push against a wall. Jerry stops after 10 min, while Joel is
PART A. 4cm 1 =1.4 1 =1.5. 5cm
 PART A Straight Objective Type This section contains 30 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1), (), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. 1. The apparent depth
PART A Straight Objective Type This section contains 30 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1), (), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is correct. 1. The apparent depth
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW
 Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Name St. Mary's HS AP Physics Circular Motion HW Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the following situation. An object weighing 10 N swings at the end of a rope that is 0.72 m long as a simple pendulum.
Where, m = slope of line = constant c = Intercept on y axis = effort required to start the machine
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING
 CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
CHAPTER 6 FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS FOR BUSHING 6.1 TEST RIG SETUP FOR THE FRICTION AND WEAR ANALYSIS Knowing the frictional coefficient is important for the determination of wear loss and power loss
