What Is This? Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 1 / 18
|
|
|
- Owen Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What Is This? Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 1 / 18
2 What Is This? The Louvre in Paris Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 1 / 18
3 How Much Would You Pay For This Painting? La Bohemienne (1630) The Painter - Frans Hals Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 2 / 18
4 How Much Would You Pay For This Painting? La Bohemienne (1630) How do you know it s not a fake? The Painter - Frans Hals Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 2 / 18
5 How Much Would You Pay For This Painting? La Bohemienne (1630) How do you know it s not a fake? The Painter - Frans Hals SCIENCE! Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 2 / 18
6 How Much Would You Pay For This Painting? La Bohemienne (1630) How do you know it s not a fake? LIBERAL ARTS! The Painter - Frans Hals SCIENCE! Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 2 / 18
7 Nuclear Physics at the Louvre Ion Beam Analysis (IBA) is used at the Louvre to study the structure of paintings and test their authenticity. 2 The Louvre has it s own accelerator! 3 The figure shows the accelerator and Elastic Backscattering (EBS) setup. 4 The spectrum shows the elastic backscattering of 4 He from a target consisting of a thin gold layer and a thick silicon layer. Source Accelerator 1 Detector Scattered protons Target Incident protons Thick Target Ein θ E0 θ Eout Energy Detector Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 3 / 18
8 Nuclear Physics at the Louvre Ion Beam Analysis (IBA) is used at the Louvre to study the structure of paintings and test their authenticity. 2 The Louvre has it s own accelerator! 3 The figure shows the accelerator and Elastic Backscattering (EBS) setup. 4 The spectrum shows the elastic backscattering of 4 He from a target consisting of a thin gold layer and a thick silicon layer. Source Accelerator 1 Detector Scattered protons Target Incident protons Thick Target Ein θ E0 θ Eout Energy Detector Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 3 / 18
9 What is in La Bohemienne? A beam of protons of energy E proj = MeV strikes a fragment of the painting La Bohemienne. The scattered protons are detected at an angle θ = 150 and their energies measured producing the spectrum below. The peak labeled He is from protons elastically scattered off 4 He nuclei and has energy E He = MeV. The shoulders labeled A, B, and C are from protons elastically scattering off other, unknown nuclei. 1 What is the ratio of the elastically scattered proton kinetic energy K 1 to its incident energy K 0 in terms of the masses and scattering angles? 2 The shoulder at A corresponds to a scattered proton energy E A = MeV. What is the mass of the nucleus that creates this shoulder? L.Beck et al., NIM B266, 1871 (2008). Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 4 / 18 A B C
10 Newton s Laws 1 Consider a body with no net force acting on it. If it is at rest, it will remain at rest. If it is moving with a constant velocity, it will continue to move at that velocity. 2 For all the different forces acting on a body Fi = m a = d p dt. 3 For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. F AB = F BA Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 5 / 18
11 Newton s Third Law Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 6 / 18
12 How the Lagrangian Fits In Newton s 2nd Law L Newton s 3rd Law Assume V(x 2 x 1) Σ p i = const Σ p i = const Assume V(x 2 x 1) Do Homework Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 7 / 18
13 What is in La Bohemienne? A beam of protons of energy E proj = MeV strikes a fragment of the painting La Bohemienne. The scattered protons are detected at an angle θ = 150 and their energies measured producing the spectrum below. The peak labeled He is from protons elastically scattered off 4 He nuclei and has energy E He = MeV. The shoulders labeled A, B, and C are from protons elastically scattering off other, unknown nuclei. 1 What is the ratio of the elastically scattered proton kinetic energy K 1 to its incident energy K 0 in terms of the masses and scattering angles? 2 The shoulder at A corresponds to a scattered proton energy E A = MeV. What is the mass of the nucleus that creates this shoulder? L.Beck et al., NIM B266, 1871 (2008). Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 8 / 18 A B C
14 What is in La Bohemienne? 10 f 1 (α) = lhs(m 2 /m 1 ) f 2 (α) = rhs(m 2 /m 1 ) f1(α)-f2(α) 5 0 Proton beam, unknown target E proj =2.964 MeV E scatt =2.214 MeV θ=150 deg α=m 2 /m 1 Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 9 / 18
15 What is in La Bohemienne? f1(α) = lhs(m2/m1) f2(α) = rhs(m2/m1) f1(α)-f2(α) 5 Proton beam, unknown target Eproj=2.964 MeV 0 Escatt=2.377 MeV θ=150 deg α=m2/m1 150 f1(α)-f2(α) Proton beam, unknown target Eproj=2.964 MeV Escatt=2.911 MeV f1(α) = lhs(m2/m1) θ=150 deg f2(α) = rhs(m2/m1) α=m2/m1 Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 10 / 18
16 What happened to them? Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 11 / 18
17 The Iridium Anomaly in the K-T Boundary Alvarez, et al data (1980). Vajda and McLoughlin data (2004). Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 12 / 18
18 The End of the Dinosaurs It is now believed the dinosaurs and many other species were driven to extinction 65 million years ago by an ecological disaster brought on by the collision of an asteroid with the Earth. Consider the following scenario. The asteroid collides with the Earth as the Earth orbits the Sun and sticks to the surface as shown in the figure (a perfectly inelastic collision). How much does the velocity of the Earth change? How much energy is released in the collision? How does this compare with the energy released by the Hiroshima atomic bomb ( J)? Asteroid mass: Asteroid speed: Earth mass: Earth speed: Angle: m A = kg v A = m/s m E = kg v A = m/s θ = 30 Direction of Asteroid Earth θ Asteroid Direction of Earth Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 13 / 18
19 Effects of the Chicxulub Asteroid Strike 1 Megatsunamis as high as 5 kilometers (3.1 mi); enough to completely inundate even large islands such as Madagascar. 2 Excavated material along with pieces of the impactor, ejected out of the atmosphere by the blast, would have been heated to incandescence upon re-entry, broiling the Earth s surface and possibly igniting wildfires. 3 Colossal shock waves would have triggered global earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. 4 The emission of dust and particles could have covered the entire surface of the Earth for years, possibly a decade. Photosynthesis by plants would be interrupted, affecting the entire food chain. 5 Sunlight would have been blocked from reaching the surface of the earth by the dust particles in the atmosphere, cooling the surface dramatically. 6 It is estimated that 75% or more of all species on Earth vanished. Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 14 / 18
20 More Evidence (and What to Worry About) 1 An impact crater the right size and age is on the Yucatan Peninsula containing shocked crystals and melted rock. 2 There is abundant evidence of other cataclysmic collisions with Solar System debris. 3 Frequency of impacts: Pea-size meteoroids 10 per hour Walnut-size 1 per hour Grapefruit-size 1 every 10 hours Basketball-size 1 per month 50-m rock 1 per 100 years 1-km asteroid 1 per 100,000 years 2-km asteroid 1 per 500,000 years Gravity Anomaly Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 15 / 18
21 Big Explosions Event Energy Released (J) Fatalities Hiroshima (1945) ,000 prompt, 250,000 delayed Soviet Test (1961) None we know of. Krakatoa (1883) ,000 Tambora (1815) Unknown 92,000 Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 16 / 18
22 What would happen now? Effect of 5-km-wide asteroid striking the mid-atlantic. Watch Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 17 / 18
23 CO 2 Normal Modes HW Instructions 1 Your homework solution should be written out by hand on paper and the Mathematica notebook stapled to it. The written solution should include the items below. The Mathematica notebook should clearly show how you obtained those items. 2 Clearly and legibly write out the matrix for the CO 2 molecule, the eigenvalues of the matrix, and the eigenvectors. 3 Show that each eigenvector behaves properly with its associated eigenvalue. 4 Clearly write out the general solution to the CO 2 problem and its first derivative with respect to time. 5 State your initial conditions. See list here. 6 Clearly write out the equations the coefficients in the general solution must satisfy. 7 Obtain the coefficients for the particular solution in terms of parameters in the initial conditions. Jerry Gilfoyle Collisions 18 / 18
Where s the heat? You are here! Jerry Gilfoyle Where s the heat? 1 / 98
 Where s the heat? The Earth s troposphere - where we live - is getting warmer. The science of this phenomenon is complex, but we can start by building simple models with physics ideas like conservation
Where s the heat? The Earth s troposphere - where we live - is getting warmer. The science of this phenomenon is complex, but we can start by building simple models with physics ideas like conservation
What Happened to the Dinosaurs?
 What Happened To The Dinosaurs? p. 1/3 What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Dinosaurs were the dominant vertebrate animals of terrestrial ecosystems for over 160 million years from about 230 million years ago
What Happened To The Dinosaurs? p. 1/3 What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Dinosaurs were the dominant vertebrate animals of terrestrial ecosystems for over 160 million years from about 230 million years ago
Big Impacts and Bio-Extinctions ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Big Impacts and Bio-Extinctions ASTR 2120 Sarazin Final Exam Saturday, May 5, 9:00 am - noon ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Big Impacts and Bio-Extinctions ASTR 2120 Sarazin Final Exam Saturday, May 5, 9:00 am - noon ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Questions. 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion!
 Questions 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion! 2. What is the dose the average South Bend citizen would receive from
Questions 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion! 2. What is the dose the average South Bend citizen would receive from
What is Nuclear Winter?
 Nuclear Winter What is Nuclear Winter? Prediction by some scientists that smoke and debris rising from massive fires of a nuclear war could block sunlight for weeks or months, cooling the earth's surface
Nuclear Winter What is Nuclear Winter? Prediction by some scientists that smoke and debris rising from massive fires of a nuclear war could block sunlight for weeks or months, cooling the earth's surface
5/3/17. Extinction of the Dinosaurs. Extinction of Dinosaurs - Causes. #40 Meteorite Impacts III - Dinosaur Extinction, Future Risk, Mitigation
 Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 12: The Mesozoic Dies
 Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE
 INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs. (Answers) Solar System Impacts. Author: Sarah Roberts
 Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Nuclear Physics 2. D. atomic energy levels. (1) D. scattered back along the original direction. (1)
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy
 Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Homework Issues Two significant figures are enough! You can round your calculations to 2 significant figures. Hopefully this will prevent some of the sloppy mistakes. The speed of light is 299,792,458
Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions elastic collision inelastic collision. completely inelastic collision
 Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions In our initial discussion of collisions, we looked at one object at a time, however we'll now look at the system of objects, with the assumption that
Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions In our initial discussion of collisions, we looked at one object at a time, however we'll now look at the system of objects, with the assumption that
Vagabonds of the Solar System. Chapter 15
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
The Sun sends the Earth:
 The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
The Sun sends the Earth: Solar Radiation - peak wavelength.visible light - Travels at the speed of light..takes 8 minutes to reach Earth Solar Wind, Solar flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections of Plasma (ionized
The Moon: Earth s Closest Neighbor. 238,866 miles away
 The Moon: Earth s Closest Neighbor 238,866 miles away The same age as Earth. It is believed that the moon is 4.5 billion years old. Moon s Formation One theory The Capture Theory The moon formed elsewhere
The Moon: Earth s Closest Neighbor 238,866 miles away The same age as Earth. It is believed that the moon is 4.5 billion years old. Moon s Formation One theory The Capture Theory The moon formed elsewhere
Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium
 Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Terrestrial Planetary Atmospheres
 Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler
 When Worlds Collide GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. Introduction This talk is about impacts between objects
When Worlds Collide GET-WISE Presentation on Collisions in the Solar System Dr. Jeffrey Morgenthaler Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. Introduction This talk is about impacts between objects
Grade 1.) 2.) 3.) 3.7 (EVOLUTION & EXTINCTION) HISTORY OF THE EARTH CATALYST
 SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
SCIENCE Grade / Name: Date: Cohort: CATALYST 1.) 2.) 3.) OBJECTIVE SWBAT define extinction and describe how meteorite impacts can cause mass extinction events and have altered the evolutionary history
Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects
![Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects](/thumbs/89/98264569.jpg) ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements Near-Earth Objects
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements Near-Earth Objects
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS
 Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
Chapter 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass Systems with Changing
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32. Paleoclimate
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 32 Paleoclimate Natural changes in the Earth s climate also occur at much longer timescales The study of prehistoric climates and their variability is called paleoclimate.
Vagabonds of the Solar System
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
12/3/14. Guiding Questions. Vagabonds of the Solar System. A search for a planet between Mars and Jupiter led to the discovery of asteroids
 Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Physics 1A Fall 2013: Quiz 4 Version A 1. Department of Physics Physics 1A Fall Quarter 2013 Dr. Paddock. Version A
 Physics 1A Fall 2013: Quiz 4 Version A 1 Department of Physics Physics 1A Fall Quarter 2013 Dr. Paddock Version A DO NOT TURN OVER THIS PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PUT AWAY ALL BOOKS, NOTES, PHONES,
Physics 1A Fall 2013: Quiz 4 Version A 1 Department of Physics Physics 1A Fall Quarter 2013 Dr. Paddock Version A DO NOT TURN OVER THIS PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PUT AWAY ALL BOOKS, NOTES, PHONES,
Terrestrial World Surfaces
 1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
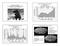 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth
 The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 4
 Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 4 1. Under what conditions can all the initial kinetic energy of an isolated system consisting of two colliding objects be lost in a collision? Explain how this result
Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 4 1. Under what conditions can all the initial kinetic energy of an isolated system consisting of two colliding objects be lost in a collision? Explain how this result
Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum and Collisions Vocabulary linear momemtum second law of motion isolated system elastic collision inelastic collision completly inelastic center of mass center of gravity 9-1 Momentum and Its Relation
Momentum and Collisions Vocabulary linear momemtum second law of motion isolated system elastic collision inelastic collision completly inelastic center of mass center of gravity 9-1 Momentum and Its Relation
Contents. Contents. Contents
 Physics 121 for Majors Schedule HW #5 is due Friday Quiz #2 is due 9/29 Lab #2 is due Monday Midterm 1 is 10/2 in the classroom. Class 6 and Collisions Relative Velocity Last Class Natural motion is straight-line
Physics 121 for Majors Schedule HW #5 is due Friday Quiz #2 is due 9/29 Lab #2 is due Monday Midterm 1 is 10/2 in the classroom. Class 6 and Collisions Relative Velocity Last Class Natural motion is straight-line
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice. Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto
 Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
Chapter 9 Remnants of Rock and Ice Asteroids, Comets, and Pluto 9.1 Asteroids and Meteorites Our Goals for Learning Why is there an asteroid belt? How are meteorites related to asteroids? Asteroid Facts
The Sun. the main show in the solar system. 99.8% of the mass % of the energy. Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6
 The Sun the main show in the solar system 99.8% of the mass 99.9999...% of the energy 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6 The
The Sun the main show in the solar system 99.8% of the mass 99.9999...% of the energy 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Homework due next time - will count best 5 of 6 The
Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
 Chapter 9 Part 2 Dwarf Planets and Impacts Pluto s Orbit Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
Chapter 9 Part 2 Dwarf Planets and Impacts Pluto s Orbit Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids
 Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids Bode s Law In 1772 Johann Bode, a German astronomer, created a mathematical formula now called Bode s Law. This formula determines the pattern that describes the distances
Asteroids, Comets, and Meteoroids Bode s Law In 1772 Johann Bode, a German astronomer, created a mathematical formula now called Bode s Law. This formula determines the pattern that describes the distances
Physics 10 Lecture 6A. "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates
 Physics 10 Lecture 6A "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates Momentum Which is harder to stop a small ball moving at 1 m/s or a car moving at 1 m/s? Obviously
Physics 10 Lecture 6A "And in knowing that you know nothing, that makes you the smartest of all. --Socrates Momentum Which is harder to stop a small ball moving at 1 m/s or a car moving at 1 m/s? Obviously
Boardworks Ltd Asteroids and Comets
 1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids and Comets 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What are asteroids? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids are large rocks which normally orbit the Sun. Scientists believe that
1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids and Comets 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 What are asteroids? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Asteroids are large rocks which normally orbit the Sun. Scientists believe that
Solar System Formation/The Sun
 Solar System Formation/The Sun Objective 4 Examine the orbital paths of planets and other astronomical bodies (comets and asteroids). Examine the theories of geocentric and heliocentric models and Kepler
Solar System Formation/The Sun Objective 4 Examine the orbital paths of planets and other astronomical bodies (comets and asteroids). Examine the theories of geocentric and heliocentric models and Kepler
The End of the World...
 The End of the World... as we know it. Impacts in the Inner Solar System Collisions have played a key role in the past formation of planets by accretion fragmentation (formation of the Moon) sustained
The End of the World... as we know it. Impacts in the Inner Solar System Collisions have played a key role in the past formation of planets by accretion fragmentation (formation of the Moon) sustained
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions.
 History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
History of life on Earth Mass Extinctions. Agenda or Summary Layout A summary of the topics discussed 1 2 3 4 Explanation of Mass extinctions The five major mass extinctions Two particular extinctions
6. (11.2) What shape are typical asteroids and how do we know? Why does Ceres not have this shape?
 SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
Asteroids: Introduction
 Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Planet Earth. Our Home APOD
 Planet Earth Our Home APOD 1 Earth a highly evolved planet = altered dramatically since formation, due to flow of energy from interior to surface 2 Planet Earth Facts diameter (equator) 12,756 km radius
Planet Earth Our Home APOD 1 Earth a highly evolved planet = altered dramatically since formation, due to flow of energy from interior to surface 2 Planet Earth Facts diameter (equator) 12,756 km radius
This Week. 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring
 This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
This Week Gravity: Dropping and throwing objects From Baseballs to satellites What causes motion. All changes involve motion Extinction of the dinosaurs 1/15/2015 Physics 214 Spring 2015 1 One dimensional
Welcome to Physics 107
 Welcome to Physics 107 Ideas of Modern Physics Physics for Future Presidents 1 What scares us? Radioactivity in the basement Being hit by lightning Terrorist dirty bomb Return of the Ice Age Global warming
Welcome to Physics 107 Ideas of Modern Physics Physics for Future Presidents 1 What scares us? Radioactivity in the basement Being hit by lightning Terrorist dirty bomb Return of the Ice Age Global warming
Physics 100 PIXE F06
 Introduction: Ion Target Interaction Elastic Atomic Collisions Very low energies, typically below a few kev Surface composition and structure Ion Scattering spectrometry (ISS) Inelastic Atomic Collisions
Introduction: Ion Target Interaction Elastic Atomic Collisions Very low energies, typically below a few kev Surface composition and structure Ion Scattering spectrometry (ISS) Inelastic Atomic Collisions
Nuclear Physics 3 8 O+ B. always take place and the proton will be emitted with kinetic energy.
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 3. A student suggests that the following transformation may take place. Measurement of rest masses shows that 7 7 N+ He 8 O+ total rest mass( N 7 + He ) < total rest mass( O
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 3. A student suggests that the following transformation may take place. Measurement of rest masses shows that 7 7 N+ He 8 O+ total rest mass( N 7 + He ) < total rest mass( O
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More
 12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
The Moon. Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon
 The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
C12 Power, Collisions, and Impacts. General Physics 1
 C12 Power, Collisions, and Impacts General Physics 1 Power The magnitude of the rate at which energy flows into or out of a given form P! dk dt or dv dt or du dt We select the formula based on the which
C12 Power, Collisions, and Impacts General Physics 1 Power The magnitude of the rate at which energy flows into or out of a given form P! dk dt or dv dt or du dt We select the formula based on the which
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy.
 PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
Momentum Conceptual Questions. 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity?
 AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 07 Oct. 15, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B.
 Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion 1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B. Draw a line to link each description in List A to its correct name
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion 1. Four different processes are described in List A. The names of these processes are given in List B. Draw a line to link each description in List A to its correct name
The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition Test Bank Chapter 03 - Near-Earth Objects
 Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis
 Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Solutions to Homework #2, AST 203, Spring 2009
 Solutions to Homework #2, AST 203, Spring 2009 Due on February 24, 2009 General grading rules: One point off per question (e.g., a or 2c) for egregiously ignoring the admonition to set the context of your
Solutions to Homework #2, AST 203, Spring 2009 Due on February 24, 2009 General grading rules: One point off per question (e.g., a or 2c) for egregiously ignoring the admonition to set the context of your
ET Life #10. Neat Scale of the Universe flash animation Today: Finish up Impacts Earth Geologic Activity & Life
 ET Life #10 Neat Scale of the Universe flash animation http://htwins.net/scale2 Today: Finish up Impacts Earth Geologic Activity & Life Apophis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zazuzko9nnk Energy At 390
ET Life #10 Neat Scale of the Universe flash animation http://htwins.net/scale2 Today: Finish up Impacts Earth Geologic Activity & Life Apophis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zazuzko9nnk Energy At 390
Causes of Extinction
 Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Causes of Extinction Extinction the process through which a species disappears from Earth, when the birth rate is less than the death rate. When a species becomes extinct, it no longer exists, which can
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19, we began our study of planetary astronomy by asking how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed, we surveyed the
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19, we began our study of planetary astronomy by asking how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed, we surveyed the
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 8. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 8 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 8 The Moon and Mercury Units of Chapter 8 8.1 Orbital Properties 8.2 Physical Properties 8.3 Surface Features on the Moon
Lecture Outlines Chapter 8 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 8 The Moon and Mercury Units of Chapter 8 8.1 Orbital Properties 8.2 Physical Properties 8.3 Surface Features on the Moon
Asteroid/Comet/Meteor Reading Homework Instructions: Read pages and answer the following questions.
 Name Date Block: Due Date: Asteroid/Comet/Meteor Reading Homework Instructions: Read pages 333-358 and answer the following questions. Page 333 1. What are 4 examples of minor bodies in our solar system?
Name Date Block: Due Date: Asteroid/Comet/Meteor Reading Homework Instructions: Read pages 333-358 and answer the following questions. Page 333 1. What are 4 examples of minor bodies in our solar system?
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System. Chapter Eight
 Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Comparative Planetology II: The Origin of Our Solar System Chapter Eight ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 06 Oct. 09, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6)
Chapter 25. Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19 you began your study of planetary astronomy by considering evidence about how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed
Chapter 25 Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Guidepost In Chapter 19 you began your study of planetary astronomy by considering evidence about how our solar system formed. In the five chapters that followed
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcements: 1. Midterm exam on Thursday (in this room) 2. Oct 21 st - 26 th : Sections replaced by evening observing) Lecture 8: October 18, 2016 Previously on Astro 1 Solar System
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcements: 1. Midterm exam on Thursday (in this room) 2. Oct 21 st - 26 th : Sections replaced by evening observing) Lecture 8: October 18, 2016 Previously on Astro 1 Solar System
August 20, EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines th Street Golden, CO Dear EPICS 1 Teams,
 Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
Joel G. Duncan, Ph.D. Teaching Professor Design EPICS Program GOLDEN, CO 80401-1887 USA August 20, 2013 EPICS Design 1 Teams Design EPICS Program Colorado School of Mines 815 15 th Street Golden, CO 80401
HOW GEOGRAPHY AND GEOLOGY AFFECT BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY
 HOW GEOGRAPHY AND GEOLOGY AFFECT BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY Factors Affecting Extinction Rates Natural Factors Climate change Cataclysmic event (volcano, earthquake) Human Activities Habitat Loss/Fragmentation
HOW GEOGRAPHY AND GEOLOGY AFFECT BIOLOGICAL DIVERSITY Factors Affecting Extinction Rates Natural Factors Climate change Cataclysmic event (volcano, earthquake) Human Activities Habitat Loss/Fragmentation
Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System
 Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System José Antonio Caballero Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA) CAB-ESAC μseminars Atmospheric mass ratio
Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System José Antonio Caballero Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA) CAB-ESAC μseminars Atmospheric mass ratio
 http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ Nucleosynthesis neutron electron + proton = é + H + t 1/2 = 12 minutes H + + neutron Deuterium (D) 2 H + + neutrons Helium (He) 3 H + + neutrons Lithium (Li) From: W.S.
http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ Nucleosynthesis neutron electron + proton = é + H + t 1/2 = 12 minutes H + + neutron Deuterium (D) 2 H + + neutrons Helium (He) 3 H + + neutrons Lithium (Li) From: W.S.
Momentum and Impulse Practice Multiple Choice
 Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
What Happened to the Dinosaurs?
 A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
A great extinction event occurred 65 million years ago, and creatures like these disappeared. What Happened to the Dinosaurs? Great Extinction Event @ 65 MA Walt Disney s view. On land, the big dinosaurs
Our Sun. The centre of our solar system
 Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
Lecture 2 The Earth. I. The Interior. Earth vital statistics. Planet size & mass determination. Orbital semi-major axis x 10 8 km (1.
 Lecture 2 The Earth. I. The Interior Vital statistics Size & mass of a planet Gravity & magnetic mapping Seismology Structure of Earth s interior Plate tectonics Reminder: lectures at http://www.star.le.ac.uk/~pto/planets.html
Lecture 2 The Earth. I. The Interior Vital statistics Size & mass of a planet Gravity & magnetic mapping Seismology Structure of Earth s interior Plate tectonics Reminder: lectures at http://www.star.le.ac.uk/~pto/planets.html
GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes
 3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
3.3.1 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH GEOS 2900 Sample Instructor Notes Things to do before class begins: 1. Place the following daily agenda on the board: a. Announcements b. Go over Activity 3.2.2 (Absolute
Chapter 14 Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Our Star Basic Types of Energy Kinetic (motion) Radiative (light) Potential (stored) Energy can change type, but cannot be created or destroyed. Thermal Energy: the collective kinetic energy
Chapter 14 Our Star Basic Types of Energy Kinetic (motion) Radiative (light) Potential (stored) Energy can change type, but cannot be created or destroyed. Thermal Energy: the collective kinetic energy
ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF Astronomy Building. Outline. The Early Universe? HW1 due today!
 This Class (Lecture 5): From Atoms to Molecules to Clouds Next Class: Star Formation ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 134 Astronomy Building HW1 due today! Outline What is life made of? We are
This Class (Lecture 5): From Atoms to Molecules to Clouds Next Class: Star Formation ET: Astronomy 230 Section 1 MWF 1400-1450 134 Astronomy Building HW1 due today! Outline What is life made of? We are
UNIT 2 MECHANICS CHAPTER 6 ENERGY
 UNIT 2 MECHANICS CHAPTER 6 ENERGY Chapter 6A The Nature of Energy Objectives: Discuss the importance of energy State what energy can do and the units in which energy is measured Define mechanical work
UNIT 2 MECHANICS CHAPTER 6 ENERGY Chapter 6A The Nature of Energy Objectives: Discuss the importance of energy State what energy can do and the units in which energy is measured Define mechanical work
Physics 2514 Lecture 26
 Physics 2514 Lecture 26 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/12 Review We have defined the following using Newton s second law of motion ( F net = d p
Physics 2514 Lecture 26 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/12 Review We have defined the following using Newton s second law of motion ( F net = d p
Where did all the dinosaurs go?
 Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
2010 Pearson Education, Inc. MAVEN launch yesterday
 MAVEN launch yesterday Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) How is Mars losing its atmosphere now? How did Mars lose its atmosphere in the past? 1. Determine the role that loss of volatiles to
MAVEN launch yesterday Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) How is Mars losing its atmosphere now? How did Mars lose its atmosphere in the past? 1. Determine the role that loss of volatiles to
PTYS 214 Fall Announcements. Materials from last week moved to web page. Midterm #4 next Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
Measuring the Age of things (Astro 202 2/12/08) Nomenclature. Different Elements. Three Types of Nuclear Decay. Carbon 14 Decay.
 Measuring the Age of things (Astro 202 2/12/08) Nomenclature + Proton Different Elements Neutron Electron Element: Number of Protons Carbon 12 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons Nitrogen 14 7 protons 7 neutrons
Measuring the Age of things (Astro 202 2/12/08) Nomenclature + Proton Different Elements Neutron Electron Element: Number of Protons Carbon 12 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons Nitrogen 14 7 protons 7 neutrons
Collisions. Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions. Serway For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75
 Collisions Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions Serway 9.3-9.4 For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75 Momentum: p = mv Impulse (a vector) is defined as F t (for a constant
Collisions Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions Serway 9.3-9.4 For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75 Momentum: p = mv Impulse (a vector) is defined as F t (for a constant
Death From the Skies
 Death From the Skies Learning Objectives! Use the Titius-Bode Rule to list the planet s distances. What connects the Titius-Bode Rule to the asteroids?! How big is Ceres? How big are typical asteroids?
Death From the Skies Learning Objectives! Use the Titius-Bode Rule to list the planet s distances. What connects the Titius-Bode Rule to the asteroids?! How big is Ceres? How big are typical asteroids?
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday.
 Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Outline. Atoms in the Solar System. Atoms in the Earth. Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am!
 Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Ch. 17 Review. Life in the Cretaceous
 Ch. 17 Review Life in the Cretaceous Diversification of diatoms, planktonic forams, calcareous nannoplankton Diversification of mobile predators (especially mollusks and teleost fishes) Origin of the angiosperms
Ch. 17 Review Life in the Cretaceous Diversification of diatoms, planktonic forams, calcareous nannoplankton Diversification of mobile predators (especially mollusks and teleost fishes) Origin of the angiosperms
Chapter 14 Lecture. Chapter 14: Our Star Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE?
Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE?
Plate Tectonics. These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page.
 Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far. Interiors of Terrestrial Planets. The Terrestrial Planets
 Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15
 Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15 Hour Exam 1 next time, Feb 17, in class more later today Planetarium: report due Feb 24 extra show added tomorrow, Thursday Feb 16 or can
Assignments: Astronomy 150: Killer Skies Lecture 13, February 15 Hour Exam 1 next time, Feb 17, in class more later today Planetarium: report due Feb 24 extra show added tomorrow, Thursday Feb 16 or can
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
1) Which area has experienced the highest number of fatalities caused by natural disasters? a) North America b) Africa c) Europe d) Asia e) Australia
 SIO15 Midterm 1, Monday Oct. 29, 2018 TEST VARIATION: A 1) Which area has experienced the highest number of fatalities caused by natural disasters? a) North America b) Africa c) Europe d) Asia e) Australia
SIO15 Midterm 1, Monday Oct. 29, 2018 TEST VARIATION: A 1) Which area has experienced the highest number of fatalities caused by natural disasters? a) North America b) Africa c) Europe d) Asia e) Australia
10/17/ A Closer Look at the Sun. Chapter 11: Our Star. Why does the Sun shine? Lecture Outline
 Lecture Outline 11.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Chapter 11: Our Star Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE? Chemical
Lecture Outline 11.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Chapter 11: Our Star Our goals for learning: Why does the Sun shine? What is the Sun's structure? Why does the Sun shine? Is it on FIRE? Is it on FIRE? Chemical
