Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 4
|
|
|
- Blaze Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 4 1. Under what conditions can all the initial kinetic energy of an isolated system consisting of two colliding objects be lost in a collision? Explain how this result can be, and yet the momentum of the system can be conserved? 1
2 2. Bored, a boy shoots his pellet gun at a piece of cheese that sits on a massive block of ice. On one particular shot, his 1.2 g pellet gets stuck in the cheese, causing it to slide 25 cm before coming to a stop. If the muzzle velocity of the gun is known to be 65 m/s and the cheese has a mass of 120 g, what is the coefficient of friction between the cheese and the ice? 2
3 3. Most geologists believe that the dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago when a large comet or asteroid struck the earth, throwing up so much dust that the sun was blocked out for a period of many months. Suppose an asteroid with a diameter of 2.0 km and a mass of kg hits the earth with an impact speed of m/s. (a) What is the earth s recoil speed after such a collision? (Use a reference frame in which the earth was initially at rest.) (b) What percentage is this of the earth s speed around the sun? 3
4 4. A proton of mass m is moving with initial speed v 0 directly toward the center of an α particle of mass 4m, which is initially at rest. Both particles carry positive charge, so they repel each other. (The repulsive forces are sufficient to prevent the two particles from coming into direct contact.) Find the speed v α of the α particle (a) when the distance between the two particles is a minimum, and (b) later when the two particles are far apart. 4
5 5. Show that in a one-dimensional elastic collision, if the mass and velocity of object 1 are m 1 and v 1i, and if the mass and velocity of object 2 are m 2 and v 2i, then their final velocities v 1f and v 2f are given by v 1f = m 1 m 2 m 1 + m 2 v 1i + 2m 2 m 1 + m 2 v 2i and v 2f = 2m 1 m 1 + m 2 v 1i + m 2 m 1 m 1 + m 2 v 2i. 5
6 6. A bullet of mass m 1 is fired horizontally with a speed v 0 into the bob of a ballistic pendulum of mass m 2. The pendulum consists of a bob attached to one end of a very light rod of length L. The rod is free to rotate about a horizontal axis through its other end. The bullet is stopped in the bob. Find the minimum v 0 such that the bob will swing through a complete circle. 6
7 7. The light isotope, 5 Li, of lithium is unstable and breaks up spontaneously into a proton and an α particle. In this process, J of energy are released, appearing as the kinetic energy of the two decay products. Determine the velocities of the proton and the α particle that arise from the decay of a 5 Li nucleus at rest. (Note: The masses of the proton and the alpha particle are m p = kg and m α = 4m p = kg.) 7
8 8. In a pool game, the cue ball, which has an initial speed of 5.0 m/s, makes an elastic collision with the eight ball, which is initially at rest. After the collision, the eight ball moves at an angle of 30 to the right of the original direction of the cue ball. Assume that the balls have equal mass. (a) Find the direction of motion of the cue ball immediately after the collision. (b) Find the speed of each ball immediately after the collision. 8
9 9. In the slingshot effect, the transfer of energy in an elastic collision is used to boost the energy of a space probe so that it can escape from the solar system. All speeds are relative to an inertial frame in which the center of the Sun remains at rest. The figure shows a space probe moving at 10.4 km/s toward Saturn, which is moving at 9.6 km/s toward the probe. Because of the gravitational attraction between Saturn and the probe, the probe swings around Saturn and heads back in the opposite direction with speed v f. (a) Assuming this collision to be a one-dimensional elastic collision with the mass of Saturn much much greater than that of the probe, find v f. (b) By what factor is the kinetic energy of the probe increased? Where does this energy come from? 9
10 10. A neutron of mass m makes an elastic head-on collision with a stationary nucleus of mass M. (a) Show that the kinetic energy of the nucleus after the collision is given by K nucleus = [ 4mM/ (m + M) 2 ] K n, where K n is the initial kinetic energy of the neutron. (b) Show that the fractional change in the kinetic energy of the neutron is given by K n K n = 4 (m/m) (1 + [m/m]) 2. (c) Show that this expression gives plausible results both if m M and if m = M. What is the best stationary nucleus for the neutron to collide head-on with if the objective is to produce a maximum loss in kinetic energy of the neutron? 10
card timer glider B glider A light gates (a) *(i) Describe how you would use the apparatus shown to verify the law of conservation of momentum.
 1 The law of conservation of momentum can be investigated using a low-friction track with two gliders. Glider B is stationary. Glider A is given a gentle push towards glider B. The gliders collide, stick
1 The law of conservation of momentum can be investigated using a low-friction track with two gliders. Glider B is stationary. Glider A is given a gentle push towards glider B. The gliders collide, stick
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
AP Homework 6.1. (4) A kg golf ball initially at rest is given a speed of 25.0 m/s when a club strikes. If the club and ball are
 AP Homework 6.1 Momentum & Impulse Name: Date: Class Period: (1) (a) What is the magnitude of the momentum of a 10,000 kg truck whose speed is 12.0 m/s? (b) What speed would a 2000 kg SUV have to attain
AP Homework 6.1 Momentum & Impulse Name: Date: Class Period: (1) (a) What is the magnitude of the momentum of a 10,000 kg truck whose speed is 12.0 m/s? (b) What speed would a 2000 kg SUV have to attain
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum 7 12/7 16/7 Units of Chapter 9 Momentum, Impulse and Collisions Momentum and Impulse Define momentum Force and rate of change of momentum; resultant force as rate of change of
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum 7 12/7 16/7 Units of Chapter 9 Momentum, Impulse and Collisions Momentum and Impulse Define momentum Force and rate of change of momentum; resultant force as rate of change of
Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters
 Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters A 186 MeV/u beam of radioactive 8 He (doublycharged) collides with normal 4 He Experiments
Tetraneutron? Can a four-neutron, no-proton particle exist? Published Feb. 3, 2016 in Physical Review Letters A 186 MeV/u beam of radioactive 8 He (doublycharged) collides with normal 4 He Experiments
Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions
 Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions Key points: Momentum and impulse Condition for conservation of momentum and why How to solve collision problems Centre of mass Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions Key points: Momentum and impulse Condition for conservation of momentum and why How to solve collision problems Centre of mass Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Energy Conservation AP
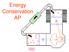 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
St. Vincent College PH : General Physics 1. Exam 5 11/17/2014
 St. Vincent College PH 111-01: General Physics 1 Exam 5 11/17/2014 The exam consists of 4 questions. The questions may not be worth the same number of points, so read the entire exam before beginning work.
St. Vincent College PH 111-01: General Physics 1 Exam 5 11/17/2014 The exam consists of 4 questions. The questions may not be worth the same number of points, so read the entire exam before beginning work.
horizontal motion? Assume that the positive direction is the direction the ball is traveling before it is hit by the opponent's racket.
 Ch 8 Supplemental [ Edit ] Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Ch 8 Supplemental Due: 6:59pm on Wednesday, November 16, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading
Ch 8 Supplemental [ Edit ] Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Ch 8 Supplemental Due: 6:59pm on Wednesday, November 16, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 7; Linear Momentum and Collisions 7.4, 9, , 33, 34, 36, 43, 48, 53, 56, 63
 PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 7; Linear Momentum and Collisions 7.4, 9, 23. 30, 33, 34, 36, 43, 48, 53, 56, 63 7.4 What is the momentum of a 1200 kg sedan traveling at 90 km/hr? At what speed must a 3600
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 7; Linear Momentum and Collisions 7.4, 9, 23. 30, 33, 34, 36, 43, 48, 53, 56, 63 7.4 What is the momentum of a 1200 kg sedan traveling at 90 km/hr? At what speed must a 3600
A ballistic pendulum
 A ballistic pendulum A ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a bullet. A bullet of mass m is fired at a block of wood (mass M) hanging from a string. The bullet embeds itself in the
A ballistic pendulum A ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a bullet. A bullet of mass m is fired at a block of wood (mass M) hanging from a string. The bullet embeds itself in the
This Week. 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
General Physics I Momentum
 General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
Momentum in 1-Dimension
 Momentum in 1-Dimension Level : Physics I Date : Warm-up Questions If you were in a car that was out of control and had to choose between hitting a concrete wall or a haystack to stop, which would you
Momentum in 1-Dimension Level : Physics I Date : Warm-up Questions If you were in a car that was out of control and had to choose between hitting a concrete wall or a haystack to stop, which would you
Impulse and Momentum continued
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a
 Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
Dynamics Examples. Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung. 28 th June, 2010
 Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the
 23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
Collision Theory Challenge Problems
 Collision Theory Challenge Problems Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds. Problem 2 You just
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds. Problem 2 You just
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum? Newton defined momentum as the quantity of motion
 AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
Which force causes the path of the stream of water to change due to the plastic rod? A) nuclear B) magnetic C) electrostatic D) gravitational
 1. A positively charged rod is held near the knob of a neutral electroscope. Which diagram best represents the distribution of charge on the electroscope? A) B) C) D) 2. A charged electroscope can detect
1. A positively charged rod is held near the knob of a neutral electroscope. Which diagram best represents the distribution of charge on the electroscope? A) B) C) D) 2. A charged electroscope can detect
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
AP Physics B Summer Assignment
 BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions
 Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
Energy in Collisions Problems AP Physics C
 1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
Notes Momentum. Momentum and Impulse. - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum.
 Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
Name Period Date. (m 1 + m 2. m 1. v 2i. v 1i
 Example Problems 8.2 Conservation of Momentum Brake Apart: p i p f ( )v 1,2i v 1f v 2 f Stick Together: p i p f v 1i v 2i ( )v 1,2 f Bouncing/Pass Through: p i p f v 1i v 2i v 1f v 2 f Example 1: - A monkey
Example Problems 8.2 Conservation of Momentum Brake Apart: p i p f ( )v 1,2i v 1f v 2 f Stick Together: p i p f v 1i v 2i ( )v 1,2 f Bouncing/Pass Through: p i p f v 1i v 2i v 1f v 2 f Example 1: - A monkey
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
Classical Mechanics Lecture 11
 Classical Mechanics Lecture 11 Today s Examples Center of Mass Today s Concept: Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions Mechanics Lecture 11, Slide 1 Unit 10 Homework Problems Mechanics Lecture 10,
Classical Mechanics Lecture 11 Today s Examples Center of Mass Today s Concept: Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions Mechanics Lecture 11, Slide 1 Unit 10 Homework Problems Mechanics Lecture 10,
(D) Based on Ft = m v, doubling the mass would require twice the time for same momentum change
 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
This Week. 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
Momentum ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Momentum ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Momentum ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the assignment
Conservation of Momentum
 Conservation of Momentum Newton: Quantity of Motion Forces applied for a period of time change an object s quantity of motion. F = ma F = m Δ v t F t = mδv = mv f mv i p mv Ft = Δp F = dp dt Conservation?
Conservation of Momentum Newton: Quantity of Motion Forces applied for a period of time change an object s quantity of motion. F = ma F = m Δ v t F t = mδv = mv f mv i p mv Ft = Δp F = dp dt Conservation?
Lecture 13. Impulse and Linear Momentum. Center of Mass for a system of particles. Momentum Conservation And Collisions. Physics 105 Summer 2006
 Lecture 13 Center of Mass for a system of particles 2 bodies, 1 dimension Momentum Conservation And Collisions (HR&W, Chapters 9) http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ 0 COM Physics 105 Summer 2006 Lecture 13
Lecture 13 Center of Mass for a system of particles 2 bodies, 1 dimension Momentum Conservation And Collisions (HR&W, Chapters 9) http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ 0 COM Physics 105 Summer 2006 Lecture 13
Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions Level : AP Physics Date : 9.1 Linear Momentum The linear momentum of a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as p mv [kg m/s] 9.3 Nonisolated System:
Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions Level : AP Physics Date : 9.1 Linear Momentum The linear momentum of a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as p mv [kg m/s] 9.3 Nonisolated System:
PHYSICS. Chapter 11 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
Physics! Review Problems Unit A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s.
 Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
Energy and Momentum Review Problems
 Energy and Momentum Review Problems NAME 1. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? A) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. B) A physics student stretches a spring. C) A projectile
Energy and Momentum Review Problems NAME 1. In which one of the following situations is zero net work done? A) A ball rolls down an inclined plane. B) A physics student stretches a spring. C) A projectile
Chapter 10 Collision and Impulse
 Chapter 10 Collision and Impulse Momentum provides a new analysis technique. With fce analysis and wk-energy analysis, application of the appropriate analysis technique to the problems at the end of the
Chapter 10 Collision and Impulse Momentum provides a new analysis technique. With fce analysis and wk-energy analysis, application of the appropriate analysis technique to the problems at the end of the
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that.
 Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday
 Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday Friday, May3, 2013 Chapter 6 Questions - none Multiple-Choice 66 C 67 D 68 B 69 C Problems 612 It s velocity as the ball hits the ground is found from
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday Friday, May3, 2013 Chapter 6 Questions - none Multiple-Choice 66 C 67 D 68 B 69 C Problems 612 It s velocity as the ball hits the ground is found from
weight (Total 1 mark)
 Q1.Which one of the following has the same unit as the rate of change of momentum? B work energy acceleration weight Q2.The nucleus of a radioactive isotope X is at rest and decays by emitting an α particle
Q1.Which one of the following has the same unit as the rate of change of momentum? B work energy acceleration weight Q2.The nucleus of a radioactive isotope X is at rest and decays by emitting an α particle
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
You are given two carts, A and B. They look identical, and you are told they are made of the same material. You put A at rest on a low-friction
 You are given two carts, A and B. They look identical, and you are told they are made of the same material. You put A at rest on a low-friction track, then send B towards it to the right. After the collision,
You are given two carts, A and B. They look identical, and you are told they are made of the same material. You put A at rest on a low-friction track, then send B towards it to the right. After the collision,
Conserv. of Momentum (Applications)
 Conserv. of Momentum (Applications) Announcements: Next midterm a week from Thursday (3/15). Chapters 6 9 will be covered LA information session at 6pm today, UMC 235. Will do some longer examples today.
Conserv. of Momentum (Applications) Announcements: Next midterm a week from Thursday (3/15). Chapters 6 9 will be covered LA information session at 6pm today, UMC 235. Will do some longer examples today.
10. Ballistic Pendulum*
 10. Ballistic Pendulum* Use is made of a ballistic pendulum to determine projectile velocity. Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the ideas of energy and momentum conservation, particularly the conditions
10. Ballistic Pendulum* Use is made of a ballistic pendulum to determine projectile velocity. Learning Objectives: 1. Explore the ideas of energy and momentum conservation, particularly the conditions
MOMENTUM. The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard.
 MOMENTUM The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard Honors Physics CONSERVATION OF Energy Linear Momentum Angular Momentum Electric
MOMENTUM The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard Honors Physics CONSERVATION OF Energy Linear Momentum Angular Momentum Electric
3. How long must a 100 N net force act to produce a change in momentum of 200 kg m/s? (A) 0.25 s (B) 0.50 s (C) 1.0 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 4.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
Physics 211: Lecture 14. Today s Agenda
 Physics 211: Lecture 14 Today s Agenda Systems of Particles Center of mass Linear Momentum Example problems Momentum Conservation Inelastic collisions in one dimension Ballistic pendulum Physics 211: Lecture
Physics 211: Lecture 14 Today s Agenda Systems of Particles Center of mass Linear Momentum Example problems Momentum Conservation Inelastic collisions in one dimension Ballistic pendulum Physics 211: Lecture
a) Calculate the height that m 2 moves up the bowl after the collision (measured vertically from the bottom of the bowl).
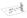 2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Lab 10: Ballistic Pendulum Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Collisions. Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions. Serway For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75
 Collisions Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions Serway 9.3-9.4 For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75 Momentum: p = mv Impulse (a vector) is defined as F t (for a constant
Collisions Conservation of Momentum Elastic and inelastic collisions Serway 9.3-9.4 For practice: Chapter 9, problems 10, 11, 23, 70, 75 Momentum: p = mv Impulse (a vector) is defined as F t (for a constant
Phy211: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 PCC-Cascade
 Phy11: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 Experiment: The Ballistic Pendulum Objectives: Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to an inelastic collision Apply the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
Phy11: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 Experiment: The Ballistic Pendulum Objectives: Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to an inelastic collision Apply the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
Solution Figure 2(a) shows the situation. Since there is no net force acting on the system, momentum is conserved. Thus,
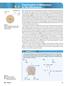 large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
Physics 231. Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions. Alex Brown October MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions Alex Brown October 7 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 Momentum F = m a Newton s 2nd law F = m v/ t a= v/ t F = m (v final - v inital )/ t Define p = mv p: momentum
Physics 231 Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions Alex Brown October 7 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 Momentum F = m a Newton s 2nd law F = m v/ t a= v/ t F = m (v final - v inital )/ t Define p = mv p: momentum
I pt mass = mr 2 I sphere = (2/5) mr 2 I hoop = mr 2 I disk = (1/2) mr 2 I rod (center) = (1/12) ml 2 I rod (end) = (1/3) ml 2
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 3 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Physics 1501 Lecture 17
 Physics 50: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda Homework #6: due Friday Midterm I: Friday only Topics Chapter 9» Momentum» Introduce Collisions Physics 50: Lecture 7, Pg Newton s nd Law: Chapter 9 Linear Momentum
Physics 50: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda Homework #6: due Friday Midterm I: Friday only Topics Chapter 9» Momentum» Introduce Collisions Physics 50: Lecture 7, Pg Newton s nd Law: Chapter 9 Linear Momentum
Impulse (J) J = FΔ t Momentum Δp = mδv Impulse and Momentum j = (F)( p = ( )(v) F)(Δ ) = ( )(Δv)
 Impulse (J) We create an unbalancing force to overcome the inertia of the object. the integral of force over time The unbalancing force is made up of the force we need to unbalance the object and the time
Impulse (J) We create an unbalancing force to overcome the inertia of the object. the integral of force over time The unbalancing force is made up of the force we need to unbalance the object and the time
Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2
 Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2 1) A rock of mass m is whirled in a horizontal circle on a string of length L. The period of its motion is T seconds. If the length of the string is increased to 4L
Physics 103, Practice Midterm Exam 2 1) A rock of mass m is whirled in a horizontal circle on a string of length L. The period of its motion is T seconds. If the length of the string is increased to 4L
Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum
 Physics 221 Name: Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum Part 1: The projectile launcher s spring constant Objective: Through the use of the principle of conservation of energy (first law
Physics 221 Name: Exercise 6: The conservation of energy and momentum Part 1: The projectile launcher s spring constant Objective: Through the use of the principle of conservation of energy (first law
Momentum Conceptual Questions. 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity?
 AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test. Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b)2.25e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b)2 (c)1.5 (d) (e).
 AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS
 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Chapter 9 Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass
LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Chapter 9 Units of Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Momentum and Newton s Second Law Impulse Conservation of Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Center of Mass
Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions
 Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Nov 9, 2017 Last time collisions elastic collisions Overview inelastic collisions the ballistic pendulum Linear Momentum and Collisions
Linear Momentum Inelastic Collisions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Nov 9, 2017 Last time collisions elastic collisions Overview inelastic collisions the ballistic pendulum Linear Momentum and Collisions
REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions
 REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions Question 1 (Adapted from DBE November 2014, Question 2) Two blocks of masses 20 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected by a light inextensible string,
REVISING MECHANICS (LIVE) 30 JUNE 2015 Exam Questions Question 1 (Adapted from DBE November 2014, Question 2) Two blocks of masses 20 kg and 5 kg respectively are connected by a light inextensible string,
Midterm Exam 3 November 29, 2012
 Midterm Exam 3 November 29, 2012 Name: Instructions 1. This examination is closed book and closed notes. All your belongings except a pen or pencil and a calculator should be put away and your bookbag
Midterm Exam 3 November 29, 2012 Name: Instructions 1. This examination is closed book and closed notes. All your belongings except a pen or pencil and a calculator should be put away and your bookbag
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions
 Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Collision Theory Challenge Problems Solutions Problem 1 Estimate the energy loss in a completely inelastic collision between two identical cars that collide head-on traveling at highway speeds! Solution:
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B
 Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located
Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B Name Multiple Choice 1. A block with a mass M is attached to a spring with a spring constant k. The block undergoes SHM. Where is the block located
u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1]
![u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1] u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig [1]](/thumbs/79/80122691.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 6.1 shows the quark composition of some particles. proton neutron A B u u d u d d u d u u u u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig. 6.1. (ii) State
1 (a) Fig. 6.1 shows the quark composition of some particles. proton neutron A B u u d u d d u d u u u u d Fig. 6.1 (i) Identify the anti-proton from the table of particles shown in Fig. 6.1. (ii) State
Physics 30 - Ballistic Pendulum Lab 2010, Science Kit All Rights Reserved
 BACKGROUND Energy The maximum height achieved by the pendulum on the Ballistic Pendulum apparatus can be determined by using the angle it achieved. Figure S1 shows the pendulum in two different positions,
BACKGROUND Energy The maximum height achieved by the pendulum on the Ballistic Pendulum apparatus can be determined by using the angle it achieved. Figure S1 shows the pendulum in two different positions,
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN
 2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
2017 PHYSICS FINAL REVIEW PACKET EXAM BREAKDOWN Topics: Forces Motion Momentum Gravity Electrostatics DATE: TIME: ROOM: PROCTOR: YOU ARE REQUIRED TO BRING: 1. CALCULATOR (YOUR OWN NO SHARING) 2. PENCIL
Nuclear Physics 2. D. atomic energy levels. (1) D. scattered back along the original direction. (1)
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Problem Set 8
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Spring-Loop-the-Loop Problem Set 8 A small block of mass m is pushed against a spring with spring constant k and held in place
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1. Spring-Loop-the-Loop Problem Set 8 A small block of mass m is pushed against a spring with spring constant k and held in place
PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 9 : Linear Momentum. Key Concepts Methods in this chapter give us tools for analyzing:
 PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 9 : Linear Momentum Key Concepts Methods in this chapter give us tools for analyzing: collisions (pool balls, car wrecks, football tackle, etc) explosions (recoil) time-varying
PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 9 : Linear Momentum Key Concepts Methods in this chapter give us tools for analyzing: collisions (pool balls, car wrecks, football tackle, etc) explosions (recoil) time-varying
Exam 3--PHYS 101--F15
 Name: Exam 3--PHYS 0--F5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. It takes 00 m to stop a car initially moving at 25.0 m/s. The distance required
Name: Exam 3--PHYS 0--F5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. It takes 00 m to stop a car initially moving at 25.0 m/s. The distance required
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum, Work and Energy Review
 Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
The Ballistic Pendulum
 The Ballistic Pendulum Physics 110 Laboratory Angle indicator Vertical upright θ R cm R b Trigger String cm Projectile Launcher Ballistic Pendulum Base m v cm after h Ramrod Steel ball before In this experiment
The Ballistic Pendulum Physics 110 Laboratory Angle indicator Vertical upright θ R cm R b Trigger String cm Projectile Launcher Ballistic Pendulum Base m v cm after h Ramrod Steel ball before In this experiment
Your Thoughts. What is the difference between elastic collision and inelastic collision?
 Your Thoughts This seemed pretty easy...before we got the checkpoint questions What is the difference between elastic collision and inelastic collision? The most confusing part of the pre lecture was the
Your Thoughts This seemed pretty easy...before we got the checkpoint questions What is the difference between elastic collision and inelastic collision? The most confusing part of the pre lecture was the
Laws of Conservation 2.1 INTRODUCTION. 2.2 CONSERVATIVE AND NON CONSERVATIVE FORCES Conservative Force. Properties of Conservative Force
 CHAPTER 2 Laws of Conservation 2.1 INTRODUCTION Laws of conservation are generally the consequences of some underlying symmetry in the universe. In Physics, we come across a number of conservation laws
CHAPTER 2 Laws of Conservation 2.1 INTRODUCTION Laws of conservation are generally the consequences of some underlying symmetry in the universe. In Physics, we come across a number of conservation laws
October 24. Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components
 October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory : Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory : Solutions Problem : Impulse and Momentum The compressive force per
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.0T Fall Term 2004 Problem Set 9: Momentum and Collision Theory : Solutions Problem : Impulse and Momentum The compressive force per
9.2 Conservation of Momentum
 Worksheet 9. Conservation of Momentum 1. Mya and Kengo are both at rest and facing each other on roller skates. Mya has a mass of 65 kg and Kengo has a mass of 40 kg. When they push against each other
Worksheet 9. Conservation of Momentum 1. Mya and Kengo are both at rest and facing each other on roller skates. Mya has a mass of 65 kg and Kengo has a mass of 40 kg. When they push against each other
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem There are many situations when the force on an object is not constant. 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem DEFINITION OF IMPULSE The impulse
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem There are many situations when the force on an object is not constant. 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem DEFINITION OF IMPULSE The impulse
Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions elastic collision inelastic collision. completely inelastic collision
 Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions In our initial discussion of collisions, we looked at one object at a time, however we'll now look at the system of objects, with the assumption that
Nov. 27, 2017 Momentum & Kinetic Energy in Collisions In our initial discussion of collisions, we looked at one object at a time, however we'll now look at the system of objects, with the assumption that
An Introduction. Work
 Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015
 PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015 Some of these practice problems are easy and some are not. Most of them should require between 5 and 15 minutes for you to solve. The more of them that you attempt on
PHY2020 Practice Problems Fall 2015 Some of these practice problems are easy and some are not. Most of them should require between 5 and 15 minutes for you to solve. The more of them that you attempt on
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
Fundamental Forces of the Universe
 Fundamental Forces of the Universe There are four fundamental forces, or interactions in nature. Strong nuclear Electromagnetic Weak nuclear Gravitational Strongest Weakest Strong nuclear force Holds the
Fundamental Forces of the Universe There are four fundamental forces, or interactions in nature. Strong nuclear Electromagnetic Weak nuclear Gravitational Strongest Weakest Strong nuclear force Holds the
Phys 2210 S18 Practice Exam 3: Ch 8 10
 1. As a 1.0-kg object moves from point A to point B, it is acted upon by a single conservative force which does 40 J of work during this motion. At point A the speed of the particle is 6.0 m/s and the
1. As a 1.0-kg object moves from point A to point B, it is acted upon by a single conservative force which does 40 J of work during this motion. At point A the speed of the particle is 6.0 m/s and the
