Conservation of Momentum
|
|
|
- Lucas Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Conservation of Momentum
2 Newton: Quantity of Motion Forces applied for a period of time change an object s quantity of motion. F = ma F = m Δ v t F t = mδv = mv f mv i p mv Ft = Δp F = dp dt
3 Conservation? Two particles that are interacting with each other via some force apply equal and opposite forces to each other (Newton s 3rd Law), for some amount of time t. m 6 v 6i m 3 v 3i m 3 v 3f m 6 v 6f F 36 = F 63 dp 3 = dp 6 dt dt d( p 3 + p 6 ) = 0 dt p 3 + p 6 = constant p 3 + p 6 = p 3 # + p 6 #
4 Law of Conservation of Momentum (isolated sys) Whenever two or more particles in an isolated system interact, their total momentum remains constant. p 1 + p 2 = p 1 " + p2 " m 1 v 1 v 2 = m 1 v 1 " + m2 v 2 "
5 Example 1 Alex (m=75 kg) sits on a 5kg cart with no-friction wheels, and gets hit by a 7.0 kg bowling ball with a velocity of 5.0 m/s. a) What is Alex s velocity after catching the ball? m 1 v 1 v 2 = (m 1 )v final (7.0kg)(5.0m / s)+ (80kg)(0) = (7+80)v final v final = 35kg m / s 87kg = 0.40m / s b) What is Alex s velocity after the collision if the bowling ball bounces off with a velocity of m/s? m 1 v 1 v 2 = m 1 v 1 final v 2 final (7.0kg)(5.0m / s)+ (80kg)(0) = (7)( 0.5)+ (80)v final v final = = 0.48m / s
6 Impulse (non-isolated sys) = Change in momentum F = dp dt dp = F dt t f dp = F dt t i J = t f F dt = Δp t i Note: for some reason, our textbook uses the symbol I to indicate impulse.
7 Impulse Area under the curve of a force-time curve
8 Example 2 Alex (still 75 kg) sits on the 5 kg cart and slams into the wall with an initial velocity of 90 km/h. The collision lasts seconds. a) What was the impulse in this collision? b) What average force is exerted on Alex during the collision?
9 Example A 4.00 kg gun with a 80 cm long barrel fires a 50-gram bullet with at a velocity of 400 m/s. Find: a) recoil velocity of gun b) impulse on bullet c) time the bullet accelerated d) average acceleration of the bullet e) force applied to the gun by the bullet
10 Example A 4.00 kg gun with a 80 cm long barrel fires a 50-gram bullet with at a velocity of 400 m/s. Find: a) recoil velocity of gun b) impulse on bullet c) time the bullet accelerated d) average acceleration of the bullet e) force applied to the gun by the bullet a) m 1 v 1 v 2 = m 1 v 1 final v 2 final 0 = (4kg)v 1 final + (0.050kg)(400m / s) v 1 final = 5.0m / s b) Impulse = Ft = m v = (0.050kg)(400 0) = 20kg m / s c) t = distance speed = 0.80m 200m / s = 0.004s d) a = v f v i t = 400m / s s =1.0e5m / s 2 e) F = ma = (0.050kg)(1.0e5m / s 2 ) F = 5000N
11 Collisions Elastic Inelastic Perfectly inelastic
12 Collisions Momentum (in isolated system) is always conserved p=0, or p 1 +p 2 =p 1 +p 2 Energy (in isolated system) is always conserved E=0, or E i = E f In some collisions, there is very little energy lost to heat (sound, deformation). In these elastic collisions, kinetic energy is conserved: K 1 +K 2 =K 1 +K 2
13 Collisions Elastic Inelastic Perfectly inelastic
14 ! Collisions Elastic collisions:k 1 +K 2 =K 1 +K 2 & p 1 +p 2 =p 1 +p m 1 v 2 1 v 2 2 = m 1 v v 2 2 & m 1 v 1 +m 2 v 2 =m 1 v 1 +m 2 v 2 Inelastic collisions: p 1 +p 2 =p 1 +p 2 or m 1 v 1 +m 2 v 2 =m 1 v 1 +m 2 v 2 Perfectly inelastic collisions: p 1 +p 2 =p 1 +p 2 or m 1 v 1 +m 2 v 2 =(m 1 +m 2 )v 2
15 Example 4 A ballistic pendulum is used to measure the speed of a projectile: a 5- gram bullet is fired into a 1-kg block of wood, which swings up to a height of 5-cm. bullet block θ h Find the initial speed of the projectile, and the energy lost in the collision. For pendulum swinging up, use Cons. of Energy: K i = U f 1 2 mv 2 bottom = mgh v bottom = 2gh = 2(9.8m /s 2 )(0.05m) v bottom = 0.99m /s For collision, use Cons. of Momentum: ( ) v " m bullet v bullet + m block v block = m bullet + m block (0.005kg)v bullet + 0 = (1.005kg)(0.99m /s) v bullet =199m /s
16 Example 5 Tarzan (69kg) is on the ground, about to be eaten by a tiger. Jane (62 kg) climbs 14 meters up a nearby tree and swings down towards the ground on a vine. She swings past Tarzan, grabbing him as she passes by, and they swing together up into another tree. What is the maximum height that Jane and Tarzan can reach on their upswing?
17 Example 6 A 100 gram rubber bullet is fired horizontally at an 800 gram block of wood which is sitting on top of a flat surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block of wood and the surface is 0.70., and the block slides 50 cm before coming to rest. If the bullet collided elastically with the block, what were its initial and final velocities? bullet block
18 Example 6 1 m 2 1v 2 1i + 1 m 2 2v 2 2i = 1 m 2 1v 2 1 f + 1 m 2 2 2v 2 f m 1 v 1i v 2i = m 1 v 1 f v 2 f m 1 (v 1i 2 v 1 f 2 ) = m 2 (v 2 f 2 v 2i 2 ) m 1 (v 1i v 1 f )(v 1i + v 1 f ) = m 2 (v 2 f v 2i )(v 2 f + v 2i ) m 1 (v 1i v 1 f ) = m 2 (v 2 f v 2i ) Divide eqns to get : (v 1i + v 1 f ) = (v 2 f + v 2i ) F net = ma, F f = ma, µmg = ma, a = (0.7)(9.80) = 6.86m /s 2 (a of block) Useful relationship for 1-d elastic collision problems bullet block v 2 f = v 2 i + 2aΔx, v i = 2aΔx = 2(6.86)(.50) = 2.62m /s (v i of block) m 1 v 1i v 2i = m 1 v 1 f v 2 f 0.1v 1i + 0 = 0.1v 1 f + (0.8)(2.62) v 1i = v 1f (v 1i + v 1 f ) = (v 2 f + v 2i ) v 1i + v 1 f = ( ) Combine eqns to get v 1 f = 9.17m /s, v 1i =11.79m /s
19 2-D Collisions m 3 v 3i m 3 v 3f p 1i + p 2i = p 1 f + p 2 f m 6 v 6i m 6 v 6f x : m 1 v 1ix v 2ix = m 1 v 1 fx v 2 fx y : m 1 v 1iy v 2iy = m 1 v 1 fy v 2 fy 1 2 m 1 v 1i m 2 v 2i2 = 1 2 m 1 v 1f m 2 v 2 f 2
20 Example 7 A 1000 kg car traveling north at 4 m/s collides with a 800 kg car traveling east at 3 m/s. After the masses of the two cars have locked together, what is the final velocity of the wreckage just after the collision?
21 2-D Collisions- Glancing v cue v cue θ Φ x : m 1 v 1ix + 0 = m 1 v 1 f cosθ v 2 f cosφ y : = m 1 v 1f sinθ m 2 v 2 f sinφ K : 1 m 2 1v 2 1i + 0 = 1 m 2 1v 2 1 f + 1 m 2 2 2v 2 f v 5
22 Example 8 In a billiard game, a player needs to sink the eight-ball into a corner pocket as shown. If the cue ball approaches at 1.00 m/s x : m cue v cue x + m 8 v 8 x = m cue v cue x " + m 8 v 8 x " (1)+ (0) = v cue " cos55+ v 8 " cos35 y : m cue v cue y + m 8 v 8 y = m cue v cue y " + m 8 v 8 y " (0)+ (0) = v cue "sin55+ v 8 "sin35 v cue! sin55 = v 8!sin35 v cue! = 0.700v 8!...what angle is the cue ball deflected? What are the final velocities of each ball? (Assume same mass, elastic collision.)
23 Center of Mass
24 Center of Mass A force applied at the center of mass will cause the system of total mass m to accelerate in the direction of F, without rotation. The center-of-mass is located at the weighted average position of the system s mass. cm x
25 Center of Mass = m 1x 1 x 2 m 1 m 1 m 2 x 1 x 2
26 Example 9 Where is the center of mass in this system? 3m m = m 1x 1 x 2 m 1 3m(0) + m(1) = 3m + m 1.00m = 1 4
27 Comple? = m 1x 1 x m n x n m m n = m i x i m i y cm = z cm = m i y i m i m i z i m i r cm = i + y cm j + z cm k m i x i i + m i y i j + m i z i k r cm = r cm = m i r i M M
28 Example 10 A 2 kg mass is located at position (2,3), and a 4 kg mass is located at position (-2,-1). Sketch this two-mass system, and calculate the position of its center of mass. -4/6, 1/3
29 Example 11 Calculate the center-ofmass for this 3-particle system. 2m 4m h d b m
30 cm Continuous Locating the center of mass for a large, extended object can be a little trickier, but the same basic principles apply: large objects have lots of particles, all located various distances from the cm. = lim Δm i 0 r dm x i Δm i M = 1 M x dm y cm = 1 M y dm r cm = 1 M r dm z cm = 1 M z dm
31 Densities For these analyses, we re going to need some way of relating dm to the location of that mass. We can do this by considering the linear density λ, surface area density σ, or volume density ρ of the object. r cm = 1 M λ = m L = dm dl σ = m A = dm da ρ = m V = dm dv r dm dm = λ dx dm = σ da dm = ρ dv
32 Example 12 Assuming that a long, thin, rod has a uniform linear density λ=m/l, show that the center of mass for the rod, with mass M and length L, is in the middle. = 1 M x dm dm = λ dx = 1 M = λ M = λ M L L2 x λ dx x dx λ = M L = L 2
33 Example 13 Assuming that a long, thin, rod has a changing linear density λ= α x, calculate the location of the center of mass. = 1 M x dm dm = λ dx = 1 M = 1 M = α M M = = L 0 x λ dx αx 2 dx 1 3 L3 L dm = λ dx = αx dx α ( 1 2 αl2 ) L3 = 2 3 L L 0 = 1 2 αl2
34 Example 14 Find the center of mass of the 2-d right triangle shown here, of constant density. = 1 M x dm dm = σ da = 1 M x σ da y = b x is the height of a column a c a b da = b a x dx = 1 M = σb Ma a 0 x σ b a x dx $ 1 ' & % 3 a3 ) ( σ = M A = M 1 2 ab $ = M ' & 1 ) b % 2 ab( Ma $ 1 ' & % 3 a3 ) = 2 ( 3 a
35 System in Motion What happens if we take the time-derivative of r cm?! r cm = m i! ri M What happens if we take the time-derivative of v cm? d dt r cm = d dt v cm = M v cm = m i v i M v cm = p total d v cm = d dt dt a cm = F total M m i r i M M m i v i = p total M p i
36 Example 15 An exploding hockey puck of mass m is moving at 10 m/s in the +x direction when it explodes into two pieces, one of them with mass m/3 traveling in the +x direction at 15m/s. a. What is the final velocity of the second piece? (m 1 )v = m 1 v 1 " v 2 " m(+10) = m 3 (+15) mv 2 " v 2 " = +7.5m /s b. Where is the center of mass of the system 3 seconds after the explosion? v cm =10m /s x = vt = (10m /s)(3s) = 30m or Find location of two particles and calculate cm manually.
37 AP Problem
38 AP Problem
6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum? Newton defined momentum as the quantity of motion
 AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
AP Physics Mechanics Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Text chapter 6 - Reading pp. 141-161 - textbook HW -- #1,3,4,6,9,15,16,20,21,23,26,27,25,34,63,70,71 1 6.1 Momentum and Impulse A. What is momentum?
Momentum and Its Relation to Force
 Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force Momentum is a vector symbolized by the symbol p, and is defined as: It is a vector and has units of: (kg m/s) or (Ns) The rate of change of momentum is
Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force Momentum is a vector symbolized by the symbol p, and is defined as: It is a vector and has units of: (kg m/s) or (Ns) The rate of change of momentum is
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions
 Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
Ch 7 Impulse-Momentum Theorem, Conservation of Momentum, and Collisions Momentum and its relation to force Momentum describes an object s motion. Linear momentum is the product of an object s mass and
Impulse and Momentum continued
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum External forces Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity
Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions
 Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions Key points: Momentum and impulse Condition for conservation of momentum and why How to solve collision problems Centre of mass Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Phys101 Lectures 14, 15, 16 Momentum and Collisions Key points: Momentum and impulse Condition for conservation of momentum and why How to solve collision problems Centre of mass Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
Impulse (J) J = FΔ t Momentum Δp = mδv Impulse and Momentum j = (F)( p = ( )(v) F)(Δ ) = ( )(Δv)
 Impulse (J) We create an unbalancing force to overcome the inertia of the object. the integral of force over time The unbalancing force is made up of the force we need to unbalance the object and the time
Impulse (J) We create an unbalancing force to overcome the inertia of the object. the integral of force over time The unbalancing force is made up of the force we need to unbalance the object and the time
Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions Level : AP Physics Date : 9.1 Linear Momentum The linear momentum of a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as p mv [kg m/s] 9.3 Nonisolated System:
Chapter 9. Momentum and Collisions Level : AP Physics Date : 9.1 Linear Momentum The linear momentum of a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined as p mv [kg m/s] 9.3 Nonisolated System:
Momentum Practice Problems
 Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Momentum Practice Problems PSI AP Physics C Name Multiple Choice 1. A steel ball and a piece of clay have equal mass. They are dropped from the same height on a horizontal steel platform. The ball bounces
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum 7 12/7 16/7 Units of Chapter 9 Momentum, Impulse and Collisions Momentum and Impulse Define momentum Force and rate of change of momentum; resultant force as rate of change of
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum 7 12/7 16/7 Units of Chapter 9 Momentum, Impulse and Collisions Momentum and Impulse Define momentum Force and rate of change of momentum; resultant force as rate of change of
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 1) Linear momentum p = mv (units: kg m / s) 2) Impulse (produces a finite change in momentum) (a) Constant force: J = FΔt From the 2nd law, F = Δ(m v) Δt = Δ p Δt, so J =
An astronaut of mass 80 kg pushes away from a space Both!p x
 Chapter 6 Momentum Collisions Definition: Momentum Important because it is CONSERVED proof: p = m v F = m v t = p t Ft = p Since F 12 =-F 21, p 1 + p 2 = 0 p i for isolated particles never changes Vector
Chapter 6 Momentum Collisions Definition: Momentum Important because it is CONSERVED proof: p = m v F = m v t = p t Ft = p Since F 12 =-F 21, p 1 + p 2 = 0 p i for isolated particles never changes Vector
Chapter 9. Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Momentum Analysis Models Force and acceleration are related by Newton s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated.
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions Momentum Analysis Models Force and acceleration are related by Newton s second law. When force and acceleration vary by time, the situation can be very complicated.
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday
 Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday Friday, May3, 2013 Chapter 6 Questions - none Multiple-Choice 66 C 67 D 68 B 69 C Problems 612 It s velocity as the ball hits the ground is found from
Physics 110 Homework Solutions Week #6 - Wednesday Friday, May3, 2013 Chapter 6 Questions - none Multiple-Choice 66 C 67 D 68 B 69 C Problems 612 It s velocity as the ball hits the ground is found from
February 06, Momentum Impulse.notebook. Momentum
 Momentum In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum (plural momenta; SI unit kg m/s, or, equivalently, N s) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. For example, a heavy
Momentum In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum (plural momenta; SI unit kg m/s, or, equivalently, N s) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. For example, a heavy
General Physics I Momentum
 General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
General Physics I Momentum Linear Momentum: Definition: For a single particle, the momentum p is defined as: p = mv (p is a vector since v is a vector). So p x = mv x etc. Units of linear momentum are
Momentum and Its Relation to Force
 Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force The linear momentum, or momentum, of an object is defined as the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, p, is a vector and its direction is the
Linear Momentum Momentum and Its Relation to Force The linear momentum, or momentum, of an object is defined as the product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum, p, is a vector and its direction is the
An Introduction. Work
 Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
Work and Energy An Introduction Work Work tells us how much a force or combination of forces changes the energy of a system. Work is the bridge between force (a vector) and energy (a scalar). W = F Dr
Momentum Conceptual Questions. 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity?
 AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
AP Physics I Momentum Conceptual Questions 1. Which variable has more impact on an object s motion? Its mass or its velocity? 2. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? Explain. 3. How does changing the duration
This Week. 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 9/5/2018 Physics 214 Fall 2018 1 Momentum What
Name ID Section. 1. One mile is equal to 1609 m; 1 hour is equal to 3600 s. The highway speed limit of 65 mph is equivalent to the speed of:
 The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
This Week. 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall
 This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
This Week Momentum Is momentum in basketball physics? Rockets and guns How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 7/29/2010 Physics 214 Fall 2010 1 Momentum What
(k = force constant of the spring)
 Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
Lecture 10: Potential Energy, Momentum and Collisions 1 Chapter 7: Conservation of Mechanical Energy in Spring Problems The principle of conservation of Mechanical Energy can also be applied to systems
Momentum and Impulse
 Momentum and Impulse Momentum All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables:
Momentum and Impulse Momentum All objects have mass; so if an object is moving, then it has momentum - it has its mass in motion. The amount of momentum which an object has is dependent upon two variables:
LINEAR MOMENTUM. Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Momentum In 2 Dimensions Center of Mass
 LINEAR MOMENTUM Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Momentum In 2 Dimensions Center of Mass MOMENTUM Quantity of Motion Product of Mass and Velocity p = mv
LINEAR MOMENTUM Momentum Impulse Conservation of Momentum Inelastic Collisions Elastic Collisions Momentum In 2 Dimensions Center of Mass MOMENTUM Quantity of Motion Product of Mass and Velocity p = mv
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the
 23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
Think-Pair-Share. Linear Momentum (Ch 9) Linear Momentum, cont. Newton and Momentum
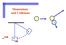
 Linear Momentum (Ch 9) The linear momentum of a particle or an object that can be modeled as a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: p = m v
Linear Momentum (Ch 9) The linear momentum of a particle or an object that can be modeled as a particle of mass m moving with a velocity v is defined to be the product of the mass and velocity: p = m v
Linear Momentum Collisions and Energy Collisions in 2 Dimensions
 Linear Momentum Collisions and Energy Collisions in 2 Dimensions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 1, 2019 Last time collisions elastic collision example inelastic collisions Overview the ballistic pendulum
Linear Momentum Collisions and Energy Collisions in 2 Dimensions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Mar 1, 2019 Last time collisions elastic collision example inelastic collisions Overview the ballistic pendulum
What is momentum? Inertia in Motion.
 What is momentum? Inertia in Motion. p = mv From Newton s 2 nd Law: F = ma = dv d( mv) m = dt dt F = dp dt The time rate of change of the linear momentum of a particle is equal to the net force acting
What is momentum? Inertia in Motion. p = mv From Newton s 2 nd Law: F = ma = dv d( mv) m = dt dt F = dp dt The time rate of change of the linear momentum of a particle is equal to the net force acting
particle p = m v F ext = d P = M d v cm dt
 Lecture 11: Momentum and Collisions; Introduction to Rotation 1 REVIEW: (Chapter 8) LINEAR MOMENTUM and COLLISIONS The first new physical quantity introduced in Chapter 8 is Linear Momentum Linear Momentum
Lecture 11: Momentum and Collisions; Introduction to Rotation 1 REVIEW: (Chapter 8) LINEAR MOMENTUM and COLLISIONS The first new physical quantity introduced in Chapter 8 is Linear Momentum Linear Momentum
Momentum Mass in Motion
 Momentum Mass in Motion What do you think that means? Based on this description, what two things do you think affect momentum? 1 Momentum Inertia in motion Why are supertanker engines shut off 25 km from
Momentum Mass in Motion What do you think that means? Based on this description, what two things do you think affect momentum? 1 Momentum Inertia in motion Why are supertanker engines shut off 25 km from
A. Incorrect! Remember that momentum depends on both mass and velocity. B. Incorrect! Remember that momentum depends on both mass and velocity.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 08: Momentum and Collisions No. 1 of 10 1. A car and motor bike are travelling down the road? Which of these is a correct statement? (A) The car will have a higher momentum.
AP Physics - Problem Drill 08: Momentum and Collisions No. 1 of 10 1. A car and motor bike are travelling down the road? Which of these is a correct statement? (A) The car will have a higher momentum.
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
p p I p p p I p I p p
 Net momentum conservation for collision on frictionless horizontal surface v1i v2i Before collision m1 F on m1 from m2 During collision for t v1f m2 F on m2 from m1 v2f +x direction After collision F F
Net momentum conservation for collision on frictionless horizontal surface v1i v2i Before collision m1 F on m1 from m2 During collision for t v1f m2 F on m2 from m1 v2f +x direction After collision F F
1 kg. 10,000 kg. 1 Page. Momentum is a vector so it has a magnitude and a velocity. Its magnitude is the product of its mass and velocity, p = mv.
 Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
Momentum The momentum of a single object is simply equal to the product of its mass and its velocity. The symbol for momentum is p. Since mass is a scalar and velocity is a vector, momentum is also a vector.
1. A tennis ball of mass m moving horizontally with speed u strikes a vertical tennis racket. The ball bounces back with a horizontal speed v.
 1. A tennis ball of mass m moving horizontally with speed u strikes a vertical tennis racket. The ball bounces back with a horizontal speed v. The magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball is A.
1. A tennis ball of mass m moving horizontally with speed u strikes a vertical tennis racket. The ball bounces back with a horizontal speed v. The magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball is A.
(1) Center of mass of a symmetric object always lies on an axis of symmetry. (2) Center of mass of an object does NOT need to be on the object.
 x com = 1 M N i=1 m ix i x com = 1 M xdm x com = 1 V xdv y com = 1 M N i=1 m iy i y com = 1 M ydm z com = 1 M N i=1 m iz i z com = 1 M zdm M = N i=1 m i ρ = dm dv = M V Here mass density replaces mass
x com = 1 M N i=1 m ix i x com = 1 M xdm x com = 1 V xdv y com = 1 M N i=1 m iy i y com = 1 M ydm z com = 1 M N i=1 m iz i z com = 1 M zdm M = N i=1 m i ρ = dm dv = M V Here mass density replaces mass
Momentum and Collisions
 Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Momentum and Collisions Objectives: You Should Be Able To: Define and give examples of impulse and momentum along with appropriate units. Write and apply a relationship between impulse and momentum in
Linear Momentum and Collisions
 P U Z Z L E R Airbags have saved countless lives by reducing the forces exerted on vehicle occupants during collisions. How can airbags change the force needed to bring a person from a high speed to a
P U Z Z L E R Airbags have saved countless lives by reducing the forces exerted on vehicle occupants during collisions. How can airbags change the force needed to bring a person from a high speed to a
Impulse simply refers to a change in momentum, and is usually caused by a change in velocity, as described by p = m v.
 1 Impulse and Momentum Recall from Newton s 1 st Law: inertia is the tendency of an object to keep on doing what its already doing, that is: either remaining stationary, or: travelling at a constant velocity.
1 Impulse and Momentum Recall from Newton s 1 st Law: inertia is the tendency of an object to keep on doing what its already doing, that is: either remaining stationary, or: travelling at a constant velocity.
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
AP Physics 1 Momentum and Impulse Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal
6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb
 Momentum Rockets and guns 6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb. 16. 2018. How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 2/11/2018 Physics 214 Spring 2018 1 Announcements
Momentum Rockets and guns 6 th week Lectures Feb. 12. Feb. 16. 2018. How do spaceships work? Collisions of objects They get impulses! Practical Propulsion 2/11/2018 Physics 214 Spring 2018 1 Announcements
Physics! Review Problems Unit A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s.
 Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
Name Physics! Review Problems Unit 8 1. A force acting on a 7.0 kg body increases its speed uniformly from 1.0 m/s to 9.0 m/s in 3 s. a) What is the initial momentum of the body? b) What is the final momentum
7-6 Inelastic Collisions
 7-6 Inelastic Collisions With inelastic collisions, some of the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical
7-6 Inelastic Collisions With inelastic collisions, some of the initial kinetic energy is lost to thermal or potential energy. It may also be gained during explosions, as there is the addition of chemical
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 17: Ch.15, Sec.2 4
 1 / 38 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 17: Ch.15, Sec.2 4 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, October 16, 2012 2 / 38 PRINCIPLE
1 / 38 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 17: Ch.15, Sec.2 4 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, October 16, 2012 2 / 38 PRINCIPLE
Physics 231 Lecture 14
 Physics 231 Lecture 14 Impulses: forces that last a short time Momentum: p = mv Impulse-Momentum theorem: FΔt = Δp = mδv = m( v f v i ) Momentum conservation: p tot,f p 1,f + p 2,f = p 1,i + p 2,i p tot,i
Physics 231 Lecture 14 Impulses: forces that last a short time Momentum: p = mv Impulse-Momentum theorem: FΔt = Δp = mδv = m( v f v i ) Momentum conservation: p tot,f p 1,f + p 2,f = p 1,i + p 2,i p tot,i
AAST/AEDT. Center of mass
 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS C: Center of mass Let us run an experiment: We take an object of a random shape and pull it by applying a force as shown on a diagram. The object experiences translational and rotational
AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS C: Center of mass Let us run an experiment: We take an object of a random shape and pull it by applying a force as shown on a diagram. The object experiences translational and rotational
Linear Momentum, Center of Mass, Conservation of Momentum, and Collision.
 PHYS1110H, 2011 Fall. Shijie Zhong Linear Momentum, Center of Mass, Conservation of Momentum, and Collision. Linear momentum. For a particle of mass m moving at a velocity v, the linear momentum for the
PHYS1110H, 2011 Fall. Shijie Zhong Linear Momentum, Center of Mass, Conservation of Momentum, and Collision. Linear momentum. For a particle of mass m moving at a velocity v, the linear momentum for the
3. How long must a 100 N net force act to produce a change in momentum of 200 kg m/s? (A) 0.25 s (B) 0.50 s (C) 1.0 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 4.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Circular motion Impulse and momentum 08-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 9 in textbook Prelecture due next Thursday HW#8 due NEXT Friday (extension!)
Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Circular motion Impulse and momentum 08-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 9 in textbook Prelecture due next Thursday HW#8 due NEXT Friday (extension!)
Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation
 Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation Which is easier to stop? Truck, car, bowling ball, or baseball all moving at 30 mph. Baseball -it is the least massive. Baseball at 30 mph or a baseball at 90 mph.
Impulse/Momentum And Its Conservation Which is easier to stop? Truck, car, bowling ball, or baseball all moving at 30 mph. Baseball -it is the least massive. Baseball at 30 mph or a baseball at 90 mph.
PHYSICS 30 MOMENTUM AND IMPULSE ASSIGNMENT 4 VERSION:0 55 MARKS
 Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
(t)dt I. p i. (impulse) F ext. Δ p = p f. Review: Linear Momentum and Momentum Conservation q Linear Momentum. Physics 201, Lecture 15
 Physics 0, Lecture 5 Today s Topics q ore on Linear omentum nd Collisions Elastic and Perfect Inelastic Collision (D) Two Dimensional Elastic Collisions Exercise: illiards oard Explosion q ulti-particle
Physics 0, Lecture 5 Today s Topics q ore on Linear omentum nd Collisions Elastic and Perfect Inelastic Collision (D) Two Dimensional Elastic Collisions Exercise: illiards oard Explosion q ulti-particle
Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as. K = 1 2 mv2 (1) m 1 v 2 1 = 1 2 m 2v 2 2 (2)
 PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 7. Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as K = 1 mv (1) Therefore, two bodies of respective masses m 1 and m and speeds
PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 7. Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as K = 1 mv (1) Therefore, two bodies of respective masses m 1 and m and speeds
Chapter 9. 9 Momentum. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 1 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Conservation of Momentum
 Conservation of Momentum Law of Conservation of Momentum The sum of the momenta before a collision equal the sum of the momenta after the collision in an isolated system (=no external forces acting).
Conservation of Momentum Law of Conservation of Momentum The sum of the momenta before a collision equal the sum of the momenta after the collision in an isolated system (=no external forces acting).
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum Chaper 6 Review: Work and Energy Forces and Displacements Effect of forces acting over a displacement Work W = (F cos)s Work changes the Kinetic Energy of a mass Kinetic
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum Chaper 6 Review: Work and Energy Forces and Displacements Effect of forces acting over a displacement Work W = (F cos)s Work changes the Kinetic Energy of a mass Kinetic
Unit 5: Momentum. Vocabulary: momentum, impulse, center of mass, conservation of momentum, elastic collision, inelastic collision.
 Text: Chapter 9 Unit 5: Momentum NAME: Problems (p. 229-240) #1: 18, 20, 27, 31, 37 (momentum & impulse) #2: 40, 42, 45, 46, 100 (conservation of momentum) #3: 49, 103, 123, 129 (collisions) Vocabulary:
Text: Chapter 9 Unit 5: Momentum NAME: Problems (p. 229-240) #1: 18, 20, 27, 31, 37 (momentum & impulse) #2: 40, 42, 45, 46, 100 (conservation of momentum) #3: 49, 103, 123, 129 (collisions) Vocabulary:
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8
 Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Chapter 8 Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions q q q q q q 8.1 Momentum and Impulse 8.2 Conservation of Momentum 8.3 Momentum Conservation
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 8 Bin Chen NJIT Physics Department Chapter 8 Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions q q q q q q 8.1 Momentum and Impulse 8.2 Conservation of Momentum 8.3 Momentum Conservation
October 24. Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components
 October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
October 24 Linear Momentum: - It is a vector which may require breaking it into components Newton s First Law: A body continues with Constant Linear Momentum unless it is acted upon by a Net External Force.
Chap. 8: Collisions and Momentum Conservation
 Chap. 8: Collisions and Momentum Conservation 1. System in Collision and Explosion C.M. 2. Analysis of Motion of System (C.M.) Kinematics and Dynamics Conservation between Before and After a) b) Energy
Chap. 8: Collisions and Momentum Conservation 1. System in Collision and Explosion C.M. 2. Analysis of Motion of System (C.M.) Kinematics and Dynamics Conservation between Before and After a) b) Energy
Sometimes (like on AP test) you will see the equation like this:
 Work, Energy & Momentum Notes Chapter 5 & 6 The two types of energy we will be working with in this unit are: (K in book KE): Energy associated with of an object. (U in book PE): Energy associated with
Work, Energy & Momentum Notes Chapter 5 & 6 The two types of energy we will be working with in this unit are: (K in book KE): Energy associated with of an object. (U in book PE): Energy associated with
Physics 131: Lecture 15. Today s Agenda
 Physics 131: Lecture 15 Today s Agenda Impulse and Momentum (or the chapter where physicists run out of letters) Non-constant t forces Impulse-momentum thm Conservation of Linear momentum External/Internal
Physics 131: Lecture 15 Today s Agenda Impulse and Momentum (or the chapter where physicists run out of letters) Non-constant t forces Impulse-momentum thm Conservation of Linear momentum External/Internal
MOMENTUM. The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard.
 MOMENTUM The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard Honors Physics CONSERVATION OF Energy Linear Momentum Angular Momentum Electric
MOMENTUM The world is wide, and I will not waste my life in friction when it could be turned into momentum. Frances E. Willard Honors Physics CONSERVATION OF Energy Linear Momentum Angular Momentum Electric
Chapter 9. Linear Momentum
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Linear Momentum Conservation of Linear Momentum Kinetic Energy of a System Collisions Collisions in Center of Mass Reference Frame MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap09Ha-Momentum-Revised-10//01
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Linear Momentum Conservation of Linear Momentum Kinetic Energy of a System Collisions Collisions in Center of Mass Reference Frame MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap09Ha-Momentum-Revised-10//01
Notes Momentum. Momentum and Impulse. - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum.
 Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
Notes Momentum Momentum and Impulse - The product (multiplication) of an objects mass and velocity is called momentum. Momentum is the energy of motion of an object. Momentum is represented by the letter.
Momentum. A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball, is... straight up straight down to the right to the left
 Momentum A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball,, is... A: B: C: D: straight up straight down to the right to the left This is also the direction of Momentum A
Momentum A ball bounces off the floor as shown. The direction of the impulse on the ball,, is... A: B: C: D: straight up straight down to the right to the left This is also the direction of Momentum A
Chapter 9. Momentum. PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
Chapter 9 Momentum PowerPoint Lectures for College Physics: A Strategic Approach, Second Edition 9 Momentum Slide 9-2 Slide 9-3 Slide 9-4 Reading Quiz 1. Impulse is A. a force that is applied at a random
HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum
 HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will be able to... understand that forces can act over time (impulse) resulting in changes in momentum identify characteristics of motion with
HONORS PHYSICS Linear Momentum LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will be able to... understand that forces can act over time (impulse) resulting in changes in momentum identify characteristics of motion with
UNIT 2G. Momentum & It s Conservation
 Name: Date:_ UNIT 2G Momentum & It s Conservation Momentum & Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Newton s 2 nd Law states When an unbalanced force acts upon a body, it accelerates that body in the direction of
Name: Date:_ UNIT 2G Momentum & It s Conservation Momentum & Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Newton s 2 nd Law states When an unbalanced force acts upon a body, it accelerates that body in the direction of
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum. So far we considered only constant force/s BUT There are many situations when the force on an object is not constant
 Chapter 7 Ipulse and Moentu So far we considered only constant force/s BUT There are any situations when the force on an object is not constant Force varies with tie 7. The Ipulse-Moentu Theore DEFINITION
Chapter 7 Ipulse and Moentu So far we considered only constant force/s BUT There are any situations when the force on an object is not constant Force varies with tie 7. The Ipulse-Moentu Theore DEFINITION
PHYSICS. Chapter 11 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 11 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 11 Impulse and Momentum IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn to use the concepts of impulse and momentum.
Physics 231. Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions. Alex Brown October MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions Alex Brown October 7 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 Momentum F = m a Newton s 2nd law F = m v/ t a= v/ t F = m (v final - v inital )/ t Define p = mv p: momentum
Physics 231 Topic 6: Momentum and Collisions Alex Brown October 7 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 Momentum F = m a Newton s 2nd law F = m v/ t a= v/ t F = m (v final - v inital )/ t Define p = mv p: momentum
Conservation of Momentum
 Conservation of Momentum Momentum is a vector quantity that is always conserved. If J = 0, p i = p f The total momentum of an isolated system is constant. Conservation of Energy Energy is a scalar quantity
Conservation of Momentum Momentum is a vector quantity that is always conserved. If J = 0, p i = p f The total momentum of an isolated system is constant. Conservation of Energy Energy is a scalar quantity
Practice Problems for Exam 2 Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 008 Practice Problems for Exam Solutions Part I Concept Questions: Circle your answer. 1) A spring-loaded toy dart gun
Table of Contents. Pg. # Momentum & Impulse (Bozemanscience Videos) 1 1/11/16
 Table of Contents g. # 1 1/11/16 Momentum & Impulse (Bozemanscience Videos) 2 1/13/16 Conservation of Momentum 3 1/19/16 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions 4 1/19/16 Lab 1 Momentum Chapter 6 Work & Energy
Table of Contents g. # 1 1/11/16 Momentum & Impulse (Bozemanscience Videos) 2 1/13/16 Conservation of Momentum 3 1/19/16 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions 4 1/19/16 Lab 1 Momentum Chapter 6 Work & Energy
Mechanics. Time (s) Distance (m) Velocity (m/s) Acceleration (m/s 2 ) = + displacement/time.
 Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
Mechanics Symbols: Equations: Kinematics The Study of Motion s = distance or displacement v = final speed or velocity u = initial speed or velocity a = average acceleration s u+ v v v u v= also v= a =
PSI AP Physics I Momentum
 PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
PSI AP Physics I Momentum Multiple-Choice questions 1. A truck moves along a frictionless level road at a constant speed. The truck is open on top. A large load of gravel is suddenly dumped into the truck.
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
 CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
CHAPTER 9 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION Couse Outline : Linear momentum and its conservation Impulse and Momentum Collisions in one dimension Collisions in two dimension The center of mass (CM) 9.1 Linear
Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions
 Name Date Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the SI unit of momentum? A) N/s B)
Name Date Chapter 6 - Linear Momemtum and Collisions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the SI unit of momentum? A) N/s B)
Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the new concepts of impulse and momentum. Slide 9-2 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-3 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-4 Chapter 9 Preview Slide
Chapter 9 Impulse and Momentum Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the new concepts of impulse and momentum. Slide 9-2 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-3 Chapter 9 Preview Slide 9-4 Chapter 9 Preview Slide
Momentum in 2 Dimensions. Unit 1B
 Momentum in 2 Dimensions Unit 1B You were introduced to momentum and momentum calculations, including 1D collisions, in Physics 2204. In this part of unit 1 we will study: 2D collisions Explosions where
Momentum in 2 Dimensions Unit 1B You were introduced to momentum and momentum calculations, including 1D collisions, in Physics 2204. In this part of unit 1 we will study: 2D collisions Explosions where
Chapter 7. Impulse and Momentum
 Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem There are many situations when the force on an object is not constant. 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem DEFINITION OF IMPULSE The impulse
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem There are many situations when the force on an object is not constant. 7.1 The Impulse-Momentum Theorem DEFINITION OF IMPULSE The impulse
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME:
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
Physics 11 Honours. x-dir px : m1 v1 = (m1 + m2 ) V cos y-dir py : m2 v2 = (m1 + m2 ) V sin A Collision at an Intersection Example 1:
 Name: Physics 11 Honours Date: Unit 7 Momentum and Its Conservation 7.4 A perfectly inelastic collision in 2-D Consider a collision in 2-D (cars crashing at a slippery intersection...no friction). Because
Name: Physics 11 Honours Date: Unit 7 Momentum and Its Conservation 7.4 A perfectly inelastic collision in 2-D Consider a collision in 2-D (cars crashing at a slippery intersection...no friction). Because
AP Homework 6.1. (4) A kg golf ball initially at rest is given a speed of 25.0 m/s when a club strikes. If the club and ball are
 AP Homework 6.1 Momentum & Impulse Name: Date: Class Period: (1) (a) What is the magnitude of the momentum of a 10,000 kg truck whose speed is 12.0 m/s? (b) What speed would a 2000 kg SUV have to attain
AP Homework 6.1 Momentum & Impulse Name: Date: Class Period: (1) (a) What is the magnitude of the momentum of a 10,000 kg truck whose speed is 12.0 m/s? (b) What speed would a 2000 kg SUV have to attain
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Impulse and momentum 09-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 10 in textbook Prelecture due next Tuesday HW#8 due this Friday at 5 pm. 09-2 2 9-2.1 A crash
Welcome back to Physics 211 Today s agenda: Impulse and momentum 09-2 1 Current assignments Reading: Chapter 10 in textbook Prelecture due next Tuesday HW#8 due this Friday at 5 pm. 09-2 2 9-2.1 A crash
Physics 5A Final Review Solutions
 Physics A Final Review Solutions Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz November 6, 0. A stone is dropped into the water from a tower 44.m above the ground. Another stone
Physics A Final Review Solutions Eric Reichwein Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz November 6, 0. A stone is dropped into the water from a tower 44.m above the ground. Another stone
PHYSICS FORMULAS. A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B)
 PHYSICS FORMULAS A = A x i + A y j Φ = tan 1 A y A x A + B = (A x +B x )i + (A y +B y )j A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B) linear motion v = v 0 + at x - x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 2a(x - x
PHYSICS FORMULAS A = A x i + A y j Φ = tan 1 A y A x A + B = (A x +B x )i + (A y +B y )j A. B = A x B x + A y B y + A z B z = A B cos (A,B) linear motion v = v 0 + at x - x 0 = v 0 t + ½ at 2 2a(x - x
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7
 Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
Physics 130: Questions to study for midterm #1 from Chapter 7 1. Kinetic energy is defined to be one-half the a. mass times the speed. b. mass times the speed squared. c. mass times the acceleration. d.
IMPACT Today s Objectives: In-Class Activities:
 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. 2. Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique cases of impact. IMPACT
Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. 2. Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique cases of impact. IMPACT
IMPACT (Section 15.4)
 IMPACT (Section 15.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. b) Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique
IMPACT (Section 15.4) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Understand and analyze the mechanics of impact. b) Analyze the motion of bodies undergoing a collision, in both central and oblique
1 A freight car of mass 20,000 kg moves along a frictionless level railroad track with a constant speed of 15 m/s. What is the momentum of the car?
 Slide 1 / 26 1 freight car of mass 20,000 kg moves along a frictionless level railroad track with a constant speed of 15 m/s. What is the momentum of the car? 30,000 kg m/s 3,000 kg m/s 300,000 kg m/s
Slide 1 / 26 1 freight car of mass 20,000 kg moves along a frictionless level railroad track with a constant speed of 15 m/s. What is the momentum of the car? 30,000 kg m/s 3,000 kg m/s 300,000 kg m/s
2015 AQA A Level Physics. Momentum and collisions
 2015 AQA A Level Physics Momentum and collisions 9/22/2018 Momentum An object having mass and velocity has MOMENTUM. Momentum (symbol p ) is simply given by the formula: Momentum = Mass x Velocity (in
2015 AQA A Level Physics Momentum and collisions 9/22/2018 Momentum An object having mass and velocity has MOMENTUM. Momentum (symbol p ) is simply given by the formula: Momentum = Mass x Velocity (in
Σp before ± I = Σp after
 Transfer of Momentum The Law of Conservation of Momentum Momentum can be transferred when objects collide. The objects exert equal and opposite forces on each other, causing both objects to change velocity.
Transfer of Momentum The Law of Conservation of Momentum Momentum can be transferred when objects collide. The objects exert equal and opposite forces on each other, causing both objects to change velocity.
Activity 8. Conservation of Momentum. What Do You Think? For You To Do GOALS. The outcome of a collision between two objects is predictable.
 Activity 8 Conservation of Momentum Activity 8 Conservation of Momentum GOALS In this activity you will: Understand and apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum. Measure the momentum before and after
Activity 8 Conservation of Momentum Activity 8 Conservation of Momentum GOALS In this activity you will: Understand and apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum. Measure the momentum before and after
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name:
 Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse)
 Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse) Intro: - earlier in the year, we introduced Galileo's Principle of Inertia and we talked how Newton used this idea to formulate his first law of motion - Newton discussed
Lecture Notes (Momentum & Impulse) Intro: - earlier in the year, we introduced Galileo's Principle of Inertia and we talked how Newton used this idea to formulate his first law of motion - Newton discussed
