Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Physics 131
|
|
|
- Loren Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 - Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists i I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Quiz 7 Random Motion Diffusion 2
2 So far we have studied about 1-5 objects. to study cells, fluids,etc LOTS of objects MANY interactions 3
3 Predictions for membrane proteins Even a complex system such as a membrane and protein follow Newton s laws. However, its impossible to predict motion of atoms/molecules accurately after multiple interactions (and interactions are very frequent!) What could we potentially predict for the motion of the membrane protein? Whiteboard, TA & LA 10/24/13 4
4 Emergent Properties The question: Can the properties of a system can be explained in terms of the properties of its component parts (so, biology can be explained by chemistry, chemistry by physics)? Emergence some phenomena are undetectable when looked at in the small. They emerge only when looking at the system as a whole rather than its parts. 5
5 Example of emergence 6
6 Biological Example of Emergence Spores Brain 7
7 Biological Example of Emergence slime mold aggregate by chemotaxis 8
8 Biological Example of Emergence Evolution If a single species of birds on an isolated island have a range of bill thicknesses, they may all survive and interbreed well under normal circumstances. If the climate shifts so that the birds at the two extremes are more likely l to survive than those in the middle by only a little bit! after a few decades the population may consist only of birds with only the smallest and largest bills. If the climate now stays shifted, after a few millennia, genetic drift can take the two populations apart so that they can no longer interbreed and would be identified as different species. The shifts are in fact visible over only a few generations. Jonathan Weiner, Physics The 131 Beak of the Finch 9
9 Foothold principles: Randomness Matter is made of of molecules in constant motion and interaction. This motion moves stuff around. If the distribution of a chemical is non-uniform, the randomness of molecular motion will tend to result in molecules moving from more dense regions to less. This is not directed but is an emergent phenomenon arising from the combination of random motion and non-uniform concentration. 10
10 Random Motion 5 m m sized beads (analogs for mammalian cells) 1 m m sized beads (bacteria analogs) (3.2 m m in this video) 11
11 Does random motion have emergent properties? (properties p that emerge only when looking at the system as a whole rather than its parts) 1. Yes 2. No 3. The answer has not yet emerged Whiteboard, TA & LA H ld d t i h th th b d How could we determine whether the observed motion is consistent with random motion?
12
13 Reading questions How is it that every single object has a net momentum of zero? If molecules move randomly, how does each one have another molecule canceling out its movement? I'm a little confused about how random motion isn t the same thing as coherent motion, because even with random motion aren't all parts of object moving together which is definition of coherent motion? When the object (example water balloon) is thrown, is the internal momentum still equal to zero? Or does the internal momentum of the random motion equal to the new total momentum after the object is thrown (some non-zero momentum value?) 10/24/13 14
14 Making a mathematical model 15
15 A new start Our mathematical model based on identifying position, velocity, and all the forces on an object and then calculating the motion using Newton s second law is too hard for a small particle being hit by many molecules. An alternative starting point is to describe the result of all the forces acting on a small object as random motion. Average phenomena that emerge from the randomness can still be reliable even though the motion at any given instant can t be predicted. 16
16 A mathematical model without equations* Describe the position of our object as being on a grid. Run the clock in small time steps, letting the object move to each neighboring point (or stay where it is) with equal probability. *Although the model is defined without equations, lots of equations can be derived about averages and distributions. See, e.g., H.C. Berg, Random Physics walks 131 in biology. 17
17 If the probability is equal that in the next time step the object moves to any one of the sites in the red box, what is the probability for going to any one particular site? Whiteboard, TA & LA 10/29/13 18
18 If the probability is equal that, in the next time step, the object moves to any one of the sites in the red box, what is the probability for the x-coordinate to change by: +1, 0, or -1? The y? 10/29/13 19
19 If the probability is equal that, in the next time step, the object moves to any one of the sites in the red box, what is the probability for the x-coordinate to change by: +1, 0, or -1? (or the y, for that matter!) A. 1/2 B. 1/3 C. 1/4 D. 1/9 E. Can tpredict
20 If we use a 3D lattice model, what is the probability to step to each of the neighboring sites? 21
21 If the probability is equal that, in the next time step, the object moves to any one of the sites in the cube. What is the probability for the x-coordinate to change by: +1, 0, or -1? The y? The z? 22
22 In this simulation, a walker starts at 0 and steps left and right with equal probability. We will let it take N steps. If we release a lot of walkers from the origin i at once, on the average, what will our distribution of particles look like? 1. There will be equal numbers near +N/2 and N/2 2. They will be mostly near 0 no matter how many steps you take. 3. It will peak at 0 and getting farther will decrease in probability. bili 4. There will be peaks at + and values but not at +N/2 and N/2; 0 will be less likely. Whiteboard, TA & LA Stp_RandomWalk 1D.jar 23
23 Foothold ideas: Randomwalkin1D As a result of random motion, an initially iti localized li distribution ib ti will spread out, getting wider and wider. This phenomenon is called diffusion The width of the distribution will grow like x 2 2Dt D is called the diffusion constant and has dimensionality [D] = L 2 /T
24 If the average rate at which a 1D particle moves is given by what will be the rate at which it moves in 2D? 3D? x 2 2Dt A. B. C. r 2 2Dt r 2 4Dt r 2 6Dt D. Something else 25
25 Sodium ions are at different densities on the inside and outside of a cell. Assume each ion moves randomly as a result of collisions with other atoms and molecules. A small patch of membrane (area A) is shown in yellow. There are more ions are on the left than on the right. What do you expect is true about the ions on the left side of the membrane? A. More go to the right B. More go to the left C. Equal amount goes left and right D. There is not enough information Physics to tell
October 21, 2015 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish. Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits
 October 21, 2015 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits 1 Outline Quiz 6 Emergent phenomenon Randomness Diffusion 2 So far we have studied
October 21, 2015 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits 1 Outline Quiz 6 Emergent phenomenon Randomness Diffusion 2 So far we have studied
Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits
 October 24, 2016 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits 1 So far we have studied about 1-5 objects. n To study cells, fluids,etc n we have
October 24, 2016 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Elvis Presley All Shook Up Cartoon: Scott & Borgman Zits 1 So far we have studied about 1-5 objects. n To study cells, fluids,etc n we have
Theme Music: Robert Alda Luck be a lady Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot. Foothold ideas: Inter-atomic interactions
 February 1, 2013 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Robert Alda Luck be a lady Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot From Guys & Dolls original cast recording 1 Inter-atomic interactions The interaction between atoms
February 1, 2013 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Robert Alda Luck be a lady Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot From Guys & Dolls original cast recording 1 Inter-atomic interactions The interaction between atoms
Outline. Physics 131- Fundamentals of. Physics for Biologists I. Quiz 3. Newton s Laws. What s a force? The conceptual ideas behind Newton s Laws
 Quiz 3 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Newton s Laws Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Outline What s a force? The conceptual ideas behind Newton s Laws Physics 131 1 Quiz 2 Physics 131
Quiz 3 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Newton s Laws Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Outline What s a force? The conceptual ideas behind Newton s Laws Physics 131 1 Quiz 2 Physics 131
Phys /7/13. November 7, 2013 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish. Theme Music: Duke Ellington Take the A Train. Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot
 November 7, 2013 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Duke Ellington Take the A Train Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot 1 Tension: The Spring A spring changes its length in response to pulls (or pushes)
November 7, 2013 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Duke Ellington Take the A Train Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot 1 Tension: The Spring A spring changes its length in response to pulls (or pushes)
Outline. Physics 131- Fundamentals of. Physics for Biologists I. Quiz 4. Newton s Laws. Newton s Laws Kinds of Forces
 Quiz 4 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Newton s Laws What s a force? Newton s Laws Kinds of Forces Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Outline Quiz 3: Average 8.2/10 Physics 131 1 Quiz 3
Quiz 4 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Newton s Laws What s a force? Newton s Laws Kinds of Forces Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Outline Quiz 3: Average 8.2/10 Physics 131 1 Quiz 3
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I
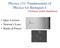 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Quiz 4 review Newton s Laws Kinds of Forces Physics 131 1 Quiz 4 review Physics 131 2 35 QUESTION 1.2 30 25 20 15 10 5
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Quiz 4 review Newton s Laws Kinds of Forces Physics 131 1 Quiz 4 review Physics 131 2 35 QUESTION 1.2 30 25 20 15 10 5
Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Physics 131
 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Before the Quiz. Make sure you have SIX pennies
 Before the Quiz Make sure you have SIX pennies If you have more than 6, please share with your neighbors There are some additional pennies in the baskets up front please be sure to return them after class!!!
Before the Quiz Make sure you have SIX pennies If you have more than 6, please share with your neighbors There are some additional pennies in the baskets up front please be sure to return them after class!!!
Theme Music: Take the A Train Duke Ellington Cartoon: FoxTrot Bill Amend
 November 11, 2016 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Take the A Train Duke Ellington Cartoon: FoxTrot Bill Amend 1 Basic Principles of Motion Prof. Redish Description of motion v = Δ r vector displacement
November 11, 2016 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Take the A Train Duke Ellington Cartoon: FoxTrot Bill Amend 1 Basic Principles of Motion Prof. Redish Description of motion v = Δ r vector displacement
( ) ( ) + ( K D. Energy Conservation with Chemical Reactions. Theme Music: Blondie Atomic. Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot. If A + B C + D + E A ) + K B
 January 30, 2017 Physics 132 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Blondie Atomic Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot 1 Energy Conservation with Chemical Reactions If A + B C + D ( K A + E A ) + K B + E B ( ) ( ) +
January 30, 2017 Physics 132 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Blondie Atomic Cartoon: Bill Amend FoxTrot 1 Energy Conservation with Chemical Reactions If A + B C + D ( K A + E A ) + K B + E B ( ) ( ) +
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I
 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Wolfgang Losert wlosert@umd.edu Technotronic - Pump Up The Jam Zebrafish Lateral Line Migration Deborah Hemingway, Losert Lab QUIZ 1 Outline
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Wolfgang Losert wlosert@umd.edu Technotronic - Pump Up The Jam Zebrafish Lateral Line Migration Deborah Hemingway, Losert Lab QUIZ 1 Outline
Charged objects in Conducting Fluids
 Charged objects in Conducting Fluids Net charge in a sphere of radius λ D is approximately zero. λ D 2 = ε 0κ k B T c 0 e 2 Z 2 k B T k c = 1 / 4πε 0 c 0 Z e κ Thermal energy (Joules) Coulomb constant
Charged objects in Conducting Fluids Net charge in a sphere of radius λ D is approximately zero. λ D 2 = ε 0κ k B T c 0 e 2 Z 2 k B T k c = 1 / 4πε 0 c 0 Z e κ Thermal energy (Joules) Coulomb constant
Got Me Under Pressure
 October 31, 2013 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish In part, in honor of the Theme Music: ZZ Top Boston Red Sox World Series victory! Got Me Under Pressure Cartoon: Bill Watterson Calvin & Hobbes 1 National
October 31, 2013 Physics 131 Prof. E. F. Redish In part, in honor of the Theme Music: ZZ Top Boston Red Sox World Series victory! Got Me Under Pressure Cartoon: Bill Watterson Calvin & Hobbes 1 National
Outline. March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples. 2/17/17 Physics 132 1
 Outline March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples 2/17/17 Physics 132 1 The Electric Field!!!! Fq ( r ) E (r ) = q 2/17/17 2 Physics 132 Foothold idea:
Outline March 2 is the day of the first midterm Heads up! Recap of electric forces Fields Examples 2/17/17 Physics 132 1 The Electric Field!!!! Fq ( r ) E (r ) = q 2/17/17 2 Physics 132 Foothold idea:
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
Quiz 2 Info. Average 5.06 St. Dev Frequency. 2/20/2014 Physics 132
 Quiz 2 Info Average 5.06 St. Dev 1.85 30 25 20 Frequency 15 10 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2/20/2014 Physics 132 1 1. (3 pts) The internal energy of an object at atmospheric pressure is observed to increase.
Quiz 2 Info Average 5.06 St. Dev 1.85 30 25 20 Frequency 15 10 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2/20/2014 Physics 132 1 1. (3 pts) The internal energy of an object at atmospheric pressure is observed to increase.
Doing Physics with Random Numbers
 Doing Physics with Random Numbers Andrew J. Schultz Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering University at Buffalo The State University of New York Concepts Random numbers can be used to measure
Doing Physics with Random Numbers Andrew J. Schultz Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering University at Buffalo The State University of New York Concepts Random numbers can be used to measure
Atomic Motion and Interactions
 Atomic Motion and Interactions 1. Handout: Unit Notes 2. Have You Seen an Atom Lately? 1. Lab: Oil Spreading on Water 2. Demo: Computer animation of spreading oil 3. Lab: Mixing Alcohol and Water 4. Demo:
Atomic Motion and Interactions 1. Handout: Unit Notes 2. Have You Seen an Atom Lately? 1. Lab: Oil Spreading on Water 2. Demo: Computer animation of spreading oil 3. Lab: Mixing Alcohol and Water 4. Demo:
Unit 1: Statistical Analysis. IB Biology SL
 Unit 1: Statistical Analysis IB Biology SL Statistics Why do we use statistics in Biology? o Biologists use the scientific method when performing experiments. o Scientists gather measurable data when performing
Unit 1: Statistical Analysis IB Biology SL Statistics Why do we use statistics in Biology? o Biologists use the scientific method when performing experiments. o Scientists gather measurable data when performing
Diffusion and cellular-level simulation. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 7 and 9, 2017 Ron Dror
 Diffusion and cellular-level simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 7 and 9, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline How do molecules move around in a cell? Diffusion as a random walk (particle-based perspective)
Diffusion and cellular-level simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 7 and 9, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline How do molecules move around in a cell? Diffusion as a random walk (particle-based perspective)
Plasma Physics Prof. Vijayshri School of Sciences, IGNOU. Lecture No. # 38 Diffusion in Plasmas
 Plasma Physics Prof. Vijayshri School of Sciences, IGNOU Lecture No. # 38 Diffusion in Plasmas In today s lecture, we will be taking up the topic diffusion in plasmas. Diffusion, why do you need to study
Plasma Physics Prof. Vijayshri School of Sciences, IGNOU Lecture No. # 38 Diffusion in Plasmas In today s lecture, we will be taking up the topic diffusion in plasmas. Diffusion, why do you need to study
Week 4. Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential
 Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
What is Quantum Mechanics?
 Quantum Worlds, session 1 1 What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum mechanics is the theory, or picture of the world, that physicists use to describe and predict the behavior of the smallest elements of matter.
Quantum Worlds, session 1 1 What is Quantum Mechanics? Quantum mechanics is the theory, or picture of the world, that physicists use to describe and predict the behavior of the smallest elements of matter.
Contents. Contents. Contents
 Physics 121 for Majors Schedule HW #5 is due Friday Quiz #2 is due 9/29 Lab #2 is due Monday Midterm 1 is 10/2 in the classroom. Class 6 and Collisions Relative Velocity Last Class Natural motion is straight-line
Physics 121 for Majors Schedule HW #5 is due Friday Quiz #2 is due 9/29 Lab #2 is due Monday Midterm 1 is 10/2 in the classroom. Class 6 and Collisions Relative Velocity Last Class Natural motion is straight-line
Learning Objective. Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology. Class Exercise: What does it mean to be living? Properties of Life
 1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE
 What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE Learning Goals I can determine if something is alive based on the criteria for life. I can describe the history of life on Earth. I can describe how organisms
What makes things alive? CRITERIA FOR LIFE Learning Goals I can determine if something is alive based on the criteria for life. I can describe the history of life on Earth. I can describe how organisms
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 21: Diffusion
 Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 21: Diffusion Junping Shi College of William and Mary November 12, 2018 Functions of several variables z = f (x, y): two variables, one function value Domain: a subset
Math 345 Intro to Math Biology Lecture 21: Diffusion Junping Shi College of William and Mary November 12, 2018 Functions of several variables z = f (x, y): two variables, one function value Domain: a subset
Physics 107: Ideas of Modern Physics
 1 Physics 107: Ideas of Modern Physics Exam 1 Sep. 27, 2006 Name ID # Section # On the Scantron sheet, 1) Fill in your name 2) Fill in your student ID # (not your social security #) 3) Fill in your section
1 Physics 107: Ideas of Modern Physics Exam 1 Sep. 27, 2006 Name ID # Section # On the Scantron sheet, 1) Fill in your name 2) Fill in your student ID # (not your social security #) 3) Fill in your section
ATP Synthase. Proteins as nanomachines. ATP Synthase. Protein physics, Lecture 11. Create proton gradient across. Thermal motion and small objects
 Proteins as nanomachines Protein physics, Lecture 11 ATP Synthase ATP synthase, a molecular motor Thermal motion and small objects Brownian motors and ratchets Actin and Myosin using random motion to go
Proteins as nanomachines Protein physics, Lecture 11 ATP Synthase ATP synthase, a molecular motor Thermal motion and small objects Brownian motors and ratchets Actin and Myosin using random motion to go
Learning objectives. Chemical Bond. Intro to Chemical Bonding. Molecular Orbitals on the Web. Shape of Molecular Orbitals
 Learning objectives Why do atoms form chemical bonds? Why are some reactions fast, and others slow? How do energy and entropy play a role What is equilibrium The Elements Tom Lehrer Rates of cooking, or
Learning objectives Why do atoms form chemical bonds? Why are some reactions fast, and others slow? How do energy and entropy play a role What is equilibrium The Elements Tom Lehrer Rates of cooking, or
Announcements 9 Sep 2014
 Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Name. University of Maryland Department of Physics
 Name University of Maryland Department of Physics 17. April. 2009 Instructions: Do not open this examination until the proctor tells you to begin. 1. When the proctor tells you to begin, write your full
Name University of Maryland Department of Physics 17. April. 2009 Instructions: Do not open this examination until the proctor tells you to begin. 1. When the proctor tells you to begin, write your full
Random walks. Marc R. Roussel Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge. March 18, 2009
 Random walks Marc R. Roussel Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge March 18, 009 1 Why study random walks? Random walks have a huge number of applications in statistical mechanics.
Random walks Marc R. Roussel Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge March 18, 009 1 Why study random walks? Random walks have a huge number of applications in statistical mechanics.
Name 2 The Chemical Basis of Life Test Date Study Guide You must know: The three subatomic particles and their significance. The types of bonds, how
 Name 2 The Chemical Basis of Life Test Date Study Guide You must know: The three subatomic particles and their significance. The types of bonds, how they form, and their relative strengths. The importance
Name 2 The Chemical Basis of Life Test Date Study Guide You must know: The three subatomic particles and their significance. The types of bonds, how they form, and their relative strengths. The importance
DEMONSTRATION 4.1 MOLECULES HITTING EACH OTHER
 DEMONSTRATION 4.1 MOLECULES HITTING EACH OTHER Directions for doing the demonstration are in the Science Book Teacher's Guide. 1. Students should include these ideas: The air moving out of the hair dryer
DEMONSTRATION 4.1 MOLECULES HITTING EACH OTHER Directions for doing the demonstration are in the Science Book Teacher's Guide. 1. Students should include these ideas: The air moving out of the hair dryer
MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, hi. This is the second in my videos about the main ideas, the big picture of calculus. And this is an important one, because I want to introduce
MITOCW big_picture_derivatives_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, hi. This is the second in my videos about the main ideas, the big picture of calculus. And this is an important one, because I want to introduce
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes
 Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Topic 6: Transferring Energy
 Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up
 AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up So what do you need to know about this motion in two-dimension stuff to get a good score on the old AP Physics Test? First off, here are the equations that you ll have to work
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up So what do you need to know about this motion in two-dimension stuff to get a good score on the old AP Physics Test? First off, here are the equations that you ll have to work
12:40-2:40 3:00-4:00 PM
 Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Evolution of Populations
 Evolution of Populations Gene Pools 1. All of the genes in a population - Contains 2 or more alleles (forms of a gene) for each trait 2. Relative frequencies - # of times an allele occurs in a gene pool
Evolution of Populations Gene Pools 1. All of the genes in a population - Contains 2 or more alleles (forms of a gene) for each trait 2. Relative frequencies - # of times an allele occurs in a gene pool
MOTION OF BODIES IN FLUIDS
 41 FE4 MOTION OF BODIES IN FLUIDS Aims OBJECTIVES By studying this chapter you will extend your knowledge and understanding of forces - in particular the nature of forces exerted on solid bodies and small
41 FE4 MOTION OF BODIES IN FLUIDS Aims OBJECTIVES By studying this chapter you will extend your knowledge and understanding of forces - in particular the nature of forces exerted on solid bodies and small
Today we begin the first technical topic related directly to the course that is: Equilibrium Carrier Concentration.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 3 Equilibrium and Carrier Concentration Today we begin the
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 3 Equilibrium and Carrier Concentration Today we begin the
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS. Skills Worksheet. Multiple Choice
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. adaptation evolution species natural selection generation time
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. adaptation evolution species natural selection generation time
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Condensed Matter Physics Prof. G. Rangarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 10 The Free Electron Theory of Metals - Electrical Conductivity (Refer Slide Time: 00:20)
Building your toolbelt
 March 3, 2017 Physics 132 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Take the A Train Duke Ellington Cartoon: Fox Trot Bill Amend 3/3/17 Physics 132 1 Building your toolbelt Using math to make meaning in the physical
March 3, 2017 Physics 132 Prof. E. F. Redish Theme Music: Take the A Train Duke Ellington Cartoon: Fox Trot Bill Amend 3/3/17 Physics 132 1 Building your toolbelt Using math to make meaning in the physical
Understanding Natural Selection
 Understanding Natural Selection Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously
Understanding Natural Selection Charles Darwin (1809-1882) Sailed around the world 1831-1836 What did Darwin s Travels reveal The diversity of living species was far greater than anyone had previously
Part I Electrostatics. 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008
 Part I Electrostatics 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008 1.1 What is Electric Charge? 1.1.1 History Before 1600CE, very little was known about electric properties of materials, or anything to do
Part I Electrostatics 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008 1.1 What is Electric Charge? 1.1.1 History Before 1600CE, very little was known about electric properties of materials, or anything to do
Momentum. Physics 1425 Lecture 15. Michael Fowler, UVa
 Momentum Physics 1425 Lecture 15 Michael Fowler, UVa Physics Definition of Momentum Momentum is another word (like work, energy, etc.) from everyday life that has a precise meaning when used in physics.
Momentum Physics 1425 Lecture 15 Michael Fowler, UVa Physics Definition of Momentum Momentum is another word (like work, energy, etc.) from everyday life that has a precise meaning when used in physics.
UNIT 1: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY. Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century
 UNIT 1: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century UNIT 1: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century I. The Study of Life (1.1) A. Earth is home to an incredible diversity
UNIT 1: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century UNIT 1: INTRODUCING BIOLOGY Chapter 1: Biology in the 21st Century I. The Study of Life (1.1) A. Earth is home to an incredible diversity
What is a change of state? What happens during a change of state? What can happen when a substance loses or gains energy?
 CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
CHAPTER 3 3 Changes of State SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a change of state? What happens during a change
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
Mechanisms of Evolution Darwinian Evolution Descent with modification by means of natural selection All life has descended from a common ancestor The mechanism of modification is natural selection Concept
I. Aim # 40: Classification 1. Why do we classify organisms? II. 2. Define taxonomy: 3. Who is Carlous Linnaeus? What is he known for?
 Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 8 Evolution Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 8 Important Topics: Aim # 40: Classification Aim # 41: Dichotomous Keys Aim # 42: Cladograms Aim # 43: Evolutionary
Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 8 Evolution Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 8 Important Topics: Aim # 40: Classification Aim # 41: Dichotomous Keys Aim # 42: Cladograms Aim # 43: Evolutionary
Molecular dynamics simulation. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror
 Molecular dynamics simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Molecular dynamics (MD): The basic idea Equations of motion Key properties of MD simulations Sample applications
Molecular dynamics simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Molecular dynamics (MD): The basic idea Equations of motion Key properties of MD simulations Sample applications
Talk Science Professional Development
 Talk Science Professional Development Transcript for Grade 5 Scientist Case: The Water to Ice Investigations 1. The Water to Ice Investigations Through the Eyes of a Scientist We met Dr. Hugh Gallagher
Talk Science Professional Development Transcript for Grade 5 Scientist Case: The Water to Ice Investigations 1. The Water to Ice Investigations Through the Eyes of a Scientist We met Dr. Hugh Gallagher
(Refer Slide Time: 0:16)
 Engineering Mechanics Professor Manoj K Harbola Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 1 Lecture No 01 Introduction to vectors (Refer Slide Time: 0:16) This is a course on engineering
Engineering Mechanics Professor Manoj K Harbola Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 1 Lecture No 01 Introduction to vectors (Refer Slide Time: 0:16) This is a course on engineering
Physics 8 Friday, October 7, 2011 Please turn in HW as you come in.
 Physics 8 Friday, October 7, 2011 Please turn in HW 3 1 2 as you come in. If you ve never done so, I highly recommend googling Steve Jobs Stanford for his 2005 commencement speech at Stanford. HW 3 1 2
Physics 8 Friday, October 7, 2011 Please turn in HW 3 1 2 as you come in. If you ve never done so, I highly recommend googling Steve Jobs Stanford for his 2005 commencement speech at Stanford. HW 3 1 2
Liquids & Solids. For the condensed states the ave KE is less than the attraction between molecules so they are held together.
 Liquids & Solids Intermolecular Forces Matter exists in 3 states. The state of matter is influenced by the physical properties of a substance. For liquids & solids, the condensed states, many of the physical
Liquids & Solids Intermolecular Forces Matter exists in 3 states. The state of matter is influenced by the physical properties of a substance. For liquids & solids, the condensed states, many of the physical
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES LAB STATION 1 SURFACE TENSION
 INTERMOLECULAR FORCES LAB STATION 1 SURFACE TENSION LEARNING TARGET: You should be able to identify the comparative strength of intermolecular forces through observations of the surface tension in droplets.
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES LAB STATION 1 SURFACE TENSION LEARNING TARGET: You should be able to identify the comparative strength of intermolecular forces through observations of the surface tension in droplets.
Physics 207 Lecture 11. Lecture 11. Chapter 8: Employ rotational motion models with friction or in free fall
 Goals: Lecture 11 Chapter 8: Employ rotational motion models with friction or in free fall Chapter 9: Momentum & Impulse Understand what momentum is and how it relates to forces Employ momentum conservation
Goals: Lecture 11 Chapter 8: Employ rotational motion models with friction or in free fall Chapter 9: Momentum & Impulse Understand what momentum is and how it relates to forces Employ momentum conservation
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I
 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Wolfgang Losert 11/6/01 wlosert@umd.edu Metabolism A biological example of energy transfer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1kgdxdlznji&feature=related
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Wolfgang Losert 11/6/01 wlosert@umd.edu Metabolism A biological example of energy transfer http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1kgdxdlznji&feature=related
The Characteristics of Life. AP Biology Notes: #1
 The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
Did you read chapter 7? Housekeeping. Special Relativity Postulates. Famous quotes from Einstein. Symmetry. (Special Principle of Relativity) 5/9/2007
 Housekeeping Vocab quiz: Do Due Exam versus Vocab Quiz Did you read chapter 7? a) Yes b) No c) We have a book? 1 2 Famous quotes from Einstein "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not
Housekeeping Vocab quiz: Do Due Exam versus Vocab Quiz Did you read chapter 7? a) Yes b) No c) We have a book? 1 2 Famous quotes from Einstein "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not
A. 0.7 ev B. 1.1 ev C. 1.4 ev D. 1.8 ev E. 2.1 ev F. 3.2 ev G. Something else
 A molecule has the energy levels shown in the diagram at the right. We begin with a large number of these molecules in their ground states. We want to raise a lot of these molecules to the state labeled
A molecule has the energy levels shown in the diagram at the right. We begin with a large number of these molecules in their ground states. We want to raise a lot of these molecules to the state labeled
MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8
 MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ko0vmalkgj8 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
BASICS OF HMT-1. This subject is always fun to teach/study in winters
 BASICS OF HMT-1 This subject is always fun to teach/study in winters #1 What is heat? Heat is a form of thermal energy which is defined ONLY when it moves from one place to other. Otherwise, the thermal
BASICS OF HMT-1 This subject is always fun to teach/study in winters #1 What is heat? Heat is a form of thermal energy which is defined ONLY when it moves from one place to other. Otherwise, the thermal
Cell day 1.notebook September 01, Study the picture of a prokaryotic cell on page 162 in a textbook and the two eukaryotic cells on page 163.
 BellRinger: Log into a clicker! Study the picture of a prokaryotic cell on page 162 in a textbook and the two eukaryotic cells on page 163. Compare them and list similarities and differences. Sep 11 11:00
BellRinger: Log into a clicker! Study the picture of a prokaryotic cell on page 162 in a textbook and the two eukaryotic cells on page 163. Compare them and list similarities and differences. Sep 11 11:00
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live The Molecule that Supports all Life CONCEPTS: 3.1 Polar covalent bonds in water molecules result in hydrogen bonding 3.2 Four
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 3: Water and Life: The Molecule that supports all Live The Molecule that Supports all Life CONCEPTS: 3.1 Polar covalent bonds in water molecules result in hydrogen bonding 3.2 Four
Chaos, Quantum Mechanics, and Computers
 What do Climate Modeling and Quantum Mechanics have in common? Chaos, Quantum Mechanics, and Computers Computer simulation: now one of the most important ingredients for progress... Dark Matter Technology
What do Climate Modeling and Quantum Mechanics have in common? Chaos, Quantum Mechanics, and Computers Computer simulation: now one of the most important ingredients for progress... Dark Matter Technology
Diffusion. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 15 and 20, 2016 Ron Dror
 Diffusion CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 15 and 20, 2016 Ron Dror 1 Outline How do molecules move around in a cell? Diffusion as a random walk (particle-based perspective) Continuum view of diffusion
Diffusion CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Nov. 15 and 20, 2016 Ron Dror 1 Outline How do molecules move around in a cell? Diffusion as a random walk (particle-based perspective) Continuum view of diffusion
Review Chapters 1-9. Did you read the article on helmets before coming to class? A. Yes B. No
 Review Chapters 1-9 Did you read the article on helmets before coming to class? A. Yes B. No Review Sessions Th 4-6 in W112 BNSN Th 6-8 in 377 CB F 3-5 in 445 MARB Forces on an object Block inside monument
Review Chapters 1-9 Did you read the article on helmets before coming to class? A. Yes B. No Review Sessions Th 4-6 in W112 BNSN Th 6-8 in 377 CB F 3-5 in 445 MARB Forces on an object Block inside monument
Characteristics of Life (pp )
 Characteristics of Life (pp. 390-401) In order for something to be considered alive, it must have all of the following characteristics: All living things grow All living things move All living things respond
Characteristics of Life (pp. 390-401) In order for something to be considered alive, it must have all of the following characteristics: All living things grow All living things move All living things respond
Simple math for a complex world: Random walks in biology and finance. Jake Hofman Physics Department Columbia University
 Simple math for a complex world: Random walks in biology and finance Jake Hofman Physics Department Columbia University 2007.10.31 1 Outline Complex systems The atomic hypothesis and Brownian motion Mathematics
Simple math for a complex world: Random walks in biology and finance Jake Hofman Physics Department Columbia University 2007.10.31 1 Outline Complex systems The atomic hypothesis and Brownian motion Mathematics
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k
 MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-5_60-s08-lec17_300k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Physics 131: Lecture 15. Today s Agenda
 Physics 131: Lecture 15 Today s Agenda Impulse and Momentum (or the chapter where physicists run out of letters) Non-constant t forces Impulse-momentum thm Conservation of Linear momentum External/Internal
Physics 131: Lecture 15 Today s Agenda Impulse and Momentum (or the chapter where physicists run out of letters) Non-constant t forces Impulse-momentum thm Conservation of Linear momentum External/Internal
Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver
 Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver Hello. My name is Dr. Kathy Vandiver. And we're here at the Edgerton Center at MIT, a university in the United States. And the Edgerton Center is
Recognizing Chemical_Reactions By Dr. Kathleen Vandiver Hello. My name is Dr. Kathy Vandiver. And we're here at the Edgerton Center at MIT, a university in the United States. And the Edgerton Center is
Physics 142 Energy in Mechanics Page 1. Energy in Mechanics
 Physics 4 Energy in Mechanics Page Energy in Mechanics This set of notes contains a brief review of the laws and theorems of Newtonian mechanics, and a longer section on energy, because of its central
Physics 4 Energy in Mechanics Page Energy in Mechanics This set of notes contains a brief review of the laws and theorems of Newtonian mechanics, and a longer section on energy, because of its central
PHYSICS 107. Lecture 8 Conservation Laws. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
 PHYSICS 107 Lecture 8 Conservation Laws Newton s Third Law This is usually stated as: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. However in this form it's a little vague. I prefer the form:
PHYSICS 107 Lecture 8 Conservation Laws Newton s Third Law This is usually stated as: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. However in this form it's a little vague. I prefer the form:
1.20 Formulas, Equations, Expressions and Identities
 1.0 Formulas, Equations, Expressions and Identities Collecting terms is equivalent to noting that 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 can be written as 6 4; i.e., that multiplication is repeated addition. It s wise
1.0 Formulas, Equations, Expressions and Identities Collecting terms is equivalent to noting that 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 can be written as 6 4; i.e., that multiplication is repeated addition. It s wise
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION FORCE WHAT IS FORCE? Force is anything that can change the state of motion of a body. In simpler terms, force is a push or a pull. For example, wind pushing on a flag is
Announcements - 9 Oct 2014
 Announcements - 9 Oct 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 2 results a. Median Score: b. Curve: c. Exams will be returned soon, our office assistant should put them in the boxes near N357 ESC sometime today. d. I'll
Announcements - 9 Oct 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 2 results a. Median Score: b. Curve: c. Exams will be returned soon, our office assistant should put them in the boxes near N357 ESC sometime today. d. I'll
The Extraordinary Properties of Water
 The Extraordinary Properties of Water Chemical Elements and Water Elements Substances that cannot be broken down into different components by chemical means Atoms The smallest particle of an element, Protons
The Extraordinary Properties of Water Chemical Elements and Water Elements Substances that cannot be broken down into different components by chemical means Atoms The smallest particle of an element, Protons
Evidence of Evolution
 16.4 Evidence for Evolution Biogeography Biogeography - study of where organisms live, where they and ancestors lived. Two significant patterns: - closely related species separate in different climates.
16.4 Evidence for Evolution Biogeography Biogeography - study of where organisms live, where they and ancestors lived. Two significant patterns: - closely related species separate in different climates.
Heat Transfer. Conduction, Convection, and Radiation. Review: Temperature
 Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Review: Temperature! Temperature is:! The quantity that tells how hot or cold something is compared with a standard! A measure of the average kinetic
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Review: Temperature! Temperature is:! The quantity that tells how hot or cold something is compared with a standard! A measure of the average kinetic
MITOCW watch?v=ybcsmyk5xmg
 MITOCW watch?v=ybcsmyk5xmg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=ybcsmyk5xmg The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture, this day, is differential equations day. I just feel even though these are not on the BC exams, that we've got everything
MITOCW MITRES18_005S10_DiffEqnsMotion_300k_512kb-mp4 PROFESSOR: OK, this lecture, this day, is differential equations day. I just feel even though these are not on the BC exams, that we've got everything
Chapter 2 Motion Speed Speed. Definitions: Speed The rate at which something moves a given distance. Faster speeds = greater distances
 Chapter 2 Motion 2-1. Speed 2-2. Vectors 2-3. Acceleration 2-4. Distance, Time, and Acceleration 2-5. Free Fall System 2-6. Air Resistance 2-7. First Law of Motion 2-8. Mass 2-9. Second Law of Motion 2-10.
Chapter 2 Motion 2-1. Speed 2-2. Vectors 2-3. Acceleration 2-4. Distance, Time, and Acceleration 2-5. Free Fall System 2-6. Air Resistance 2-7. First Law of Motion 2-8. Mass 2-9. Second Law of Motion 2-10.
What makes something alive? Prokaryotic Cells. Two Main Classes of Cells. Eukaryotic Cell Structure. What features define living systems?
 What makes something alive? What features define living systems? 1. Composed of a common organization of atoms, molecules, cells... with emergent properties. 2. Share a similar chemical composition. 3.
What makes something alive? What features define living systems? 1. Composed of a common organization of atoms, molecules, cells... with emergent properties. 2. Share a similar chemical composition. 3.
Matter, Atoms & Molecules
 Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
Matter, Atoms & Molecules Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are too small to see with the naked eye. Matter Matter is anything
37-6 Watching the electrons (matter waves)
 37-6 Watching the electrons (matter waves) 1 testing our proposition: the electrons go either through hole 1 or hole 2 add a very strong light source behind walls between two holes, electrons will scatter
37-6 Watching the electrons (matter waves) 1 testing our proposition: the electrons go either through hole 1 or hole 2 add a very strong light source behind walls between two holes, electrons will scatter
Cell Processes: Diffusion Part 1: Fick s First Law
 MathBench- Australia Diffusion Part 1 December 2015 page 1 Cell Processes: Diffusion Part 1: Fick s First Law URL: http://mathbench.org.au/cellular-processes/introduction-to-diffusion/ Measuring Movement
MathBench- Australia Diffusion Part 1 December 2015 page 1 Cell Processes: Diffusion Part 1: Fick s First Law URL: http://mathbench.org.au/cellular-processes/introduction-to-diffusion/ Measuring Movement
The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner
 The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner Joseph Nicolls Stanford University Professor W.E Moerner earned two B.S. degrees, in Physics and Electrical Engineering,
The Intersection of Chemistry and Biology: An Interview with Professor W. E. Moerner Joseph Nicolls Stanford University Professor W.E Moerner earned two B.S. degrees, in Physics and Electrical Engineering,
Evolution Evidence of Change
 6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 3 Evolution and Plate Tectonics Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.f. Students know how movements of Earth's continental and oceanic plates through time, with
6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 3 Evolution and Plate Tectonics Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.f. Students know how movements of Earth's continental and oceanic plates through time, with
STATIC ELECTRICITY. II. Directions:Answer the following questions with short answers. Use the back of this sheet to write your answers.
 1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
1 Pre-Test I. Directions: Circle the word that completes the sentence. 1. The "building blocks of matter" are called neutrons atoms electrons. 2. When charged objects jump apart we say they each other.
Unit 3 Force and Motion Student understandings for 8.6A
 Motion and Forces Unit 3 Force and Motion Student understandings for 8.6A Learning Goals (TEKS): Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy.
Motion and Forces Unit 3 Force and Motion Student understandings for 8.6A Learning Goals (TEKS): Force, motion, and energy. The student knows that there is a relationship between force, motion, and energy.
Guided Notes: Evolution. is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms
 Guided Notes: Evolution The Theory of Evolution is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms How Have Organisms Changed? At the time life emerged, the Earth was
Guided Notes: Evolution The Theory of Evolution is the change in traits through generations over! Occurs in, NOT individual organisms How Have Organisms Changed? At the time life emerged, the Earth was
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD
 Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the questions are in your Guided Notes, be sure to record your answers in your DFAD. You have 5 mins. Haveouts Guided
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card DFAD Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the questions are in your Guided Notes, be sure to record your answers in your DFAD. You have 5 mins. Haveouts Guided

 Circular Orbits for m
Circular Orbits for m