A generalized Fucik type eigenvalue problem for p-laplacian
|
|
|
- Betty Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations 009, No. 18, 1-9; htt:// A generalized Fucik tye eigenvalue roblem for -Lalacian Yuanji Cheng School of Technology Malmö University, SE Malmö, Sweden yuanji.cheng@mah.se Abstract In this aer we study the generalized Fucik tye eigenvalue for the boundary value roblem of one dimensional Lalace tye differential equations (ϕ(u )) = ψ(u), T < x < T; ( ) u( T) = 0, u(t) = 0 where ϕ(s) = αs 1 + βs 1,ψ(s) = s 1 + s 1, > 1. We obtain a exlicit characterization of Fucik sectrum (α,β,,), i.e., for which the (*) has a nontrivial solution. (1991) AMS Subject Classification: 35J65, 34B15, 49K0. 1 Introduction In the study of nonhomogeneous semilinear boundary roblem u = f(u) + g(x), in Ω u = 0, on Ω it has been discovered in [3, 7] that the solvability of another boundary value roblem u = u+ u, in Ω u = 0, on Ω where u + = maxu, 0}, u = max u, 0} lays an imortant role. Since then there are many works devoted to this subject [5, 13, 14, references therein], and the study has also been extended to the -Lalacian u = u 1 + u 1, in Ω u = 0, on Ω EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 1
2 where =: div u u}, > 1 [, 4, 6, 10, 1] and even associated trigonometrical sine and cosine functions have been studied [9]. In this aer, we are interested in generalization of such Fucik sectrum and will consider one dimensional boundary value roblem (α(u ) 1 + β(u ) 1 )) = u 1 + u 1, T < x < T (1.1) u( T) = 0, u(t) = 0 where α, β,, > 0 are arameters, and call (α, β,, ) the generalized Fucik sectrum, if (1.1) has a non-trivial solution. The roblem is motivated by the study of two-oint boundary value roblem (ϕ(u ))) = ψ(x, u), T < x < T (1.) u( T) = 0, u(t) = 0 and to our knowledge it is always assumed in the literature that ϕ is an odd function. Thus a natural question arises: what would haen, if the function ϕ is merely a homeomorhism, not necessarily odd function on R? Here we shall first investigate the autonomous eigenvalue tye roblem and in the forthcoming treat non-resonance roblem. By a solution of (1.) we mean that u(x) is of C 1 such that ϕ(u (x)) is differentiable and the equation (1.) is satisfied ointwise almost everywhere. The main results of this aer are comlete characterization of Fucik tye eigenvalues, their associated eigenfunctions and observations of changes of frequency, amlitude of solutions, when they ass the mini- and maximum oints resective change their signs (see the figures below and (3.8) in details). Let π = π sin(π/), then we have Theorem 1 (α, β,, ) belongs to the generalized Fucik sectrum of (1.1), if and only if for some integer k 0 1) ( α + β)((k + 1) 1 + k 1 )π = T and corresonding eigenfunction u is initially ositive and has recisely k nodes. ) ( α + β)(k 1 + (k + 1) 1 )π = T and the corresonding eigenfunction u is initially negative and has also k nodes 3) (k+1)( α+ β)( )π = T and the corresonding eigenfunction u 1, u has exact k + 1 nodes and u 1 is initially ositive and u is negative. Moreover, the eigenfunctions are iecewise sine functions (see art for definitions) Fucik ositive eigenfunction, α = 1, β = 4, = 9 Fucik eigenfunction Classical eigenfunction Nodal eigenfunction α = 1, β = 4, = 81, = 81/4 Switch of frequency /amlitude Classical eigenfunction 1.5 Fucik eigenfunction EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,.
3 Review on 1D Lalacian We shall review some basic results about eigenvalues and associated eigenfunctions for one dimensional Lalacian. Eigenfunctions are also called sine and -cosine functions, sin (x), cos (x), which have been discussed in details in [9, 11], but for our urose we adot the version in [1]. Let π = sin (x), cos (x) are defined via x = sin(x) 0 π sin π, the sine, cosine functions dt 1 t, 0 x π / (.1) and extended to [π /, π ] by sin (π /+x) = sin (π / x) and to [ π, 0] by sin (x) = sin ( x) then finally extended to a π eriodic function on the whole real line; Then cosine function is defined as cos x = d dx (sin x) and they have the roerties: sin 0 = 0, sin π / = 1; cos 0 = 1, cos π / = 0. They share several remarkable relations as ordinary trigonometric functions, for instance sin x + cos x = 1. But d dx (cos x) = tan x sin x sin x, where tan x = sin x/ cos x. The eigenvalues of one dimensional -Lalace oerator ( u (x) u (x)) = u(x) u(x), 0 x π u(0) = 0, u(π ) = 0 are 1,, 3, and the corresonding eigenfunctions are recisely sin (x), sin (x), sin (3x), and therefore we have another relation between cosine and sine functions ( cos (kx) cos (kx)) = k sin (kx) sin (kx), k = 1,, (.) EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 3
4 Here we note that function sin (x) is a solution to the following roblem ( u (x) u (x)) = u(x) u(x), 0 < x < π / u(0) = 0, u (π /) = 0 (.3) and any solution is of form C sin (x) for some constant C. If the Lalacian is associated to another interval [a, b], different from [0, π ], then by change of variables we see that eigenvalues and the associated eigenfunctions are ( kπ b a ), sin (k x a b a π ), k = 1,, 3,. (.4) 3 Proof of Theorem 1 To understand the generalized Fucik sectrum of (1.1), we need to examine the following Dirichlet-Neumann boundary value roblem (α(u ) 1 + β(u ) 1 )) = u 1 + u 1, a < x < b u(a) = 0, u (b) = 0 (3.1) We shall focus only on the constant sign solutions of (3.1) and note that there exist essentially only two solutions, one ositive and another negative, due to the ositive homogeneity of (3.1). If u(x) is a ositive solution of (3.1), then u must be increasing on [a, b), because the equation (3.1) says that the function g(x) =: ϕ(u (x)) is decreasing on (a, b] and satisfies g(b) = 0, thus g(x) is ositive for all x [a, b) and thus u (x) has to be ositive, due to strict monotonicity of function ϕ(s) and ϕ(0) = 0. It follows that u satisfies ( u (x) u (x)) = α u(x) u(x), a < x < b u(a) = 0, u (3.) (b) = 0 It follows from (.3) that C sin ( x a ) and α, satisfy π α α/ = b a. Likely if u is negative solution to (3.1), then ( u (x) u (x)) = β u(x) u(x), a < x < b u(a) = 0, u (b) = 0 C sin ( x a ) and β, satisfy π β β/ = b a. In analogy we see that for the following boundary value roblem (3.3) (α(u ) 1 + β(u ) 1 )) = u 1 + u 1, a < x < b u (a) = 0, u(b) = 0 (3.4) the ositive and negative solutions are D sin ( b x D sin ( b x b a b a π ) resectively π ) and α, β,, satisfy π β/ = b a or π α/ = b a. EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 4
5 It follows from the above analysis that if u is a ositive solution to (1.1) and u(x 0 ) = maxu(x) := C, then x 0 is determined by α/π = x 0 + T and α, β,, satisfy Furthermore the solution u(x) is given by C sin ( x+t α ), C sin ( T x ), β L + := ( α/ + β/)π = T. and for the negative solution u of (1.1), then it holds L := ( α/ + β/)π = T D sin ( x+t D sin ( T x T x T + π α T π β x T (3.5) ), T x T + π β β ), T π α α x T (3.5 ) It is clear from (3.5) that u(x) changes its frequency, when it asses its maximum oint and is not symmetric anymore, which is in contrast to the symmetry rincile of Gidas, Ni and Nirenberg [8]. For an initially ositive nodal solution u to (1.1) with only one node at T 1, we get that T 1, α, β,, ν satisfy ( α/ + β/)π = T 1 + T. ( α + β)( )π = T (3.6) If C = max x [ T,T1 ] u(x), D = max x [T,T] u(x), then in view of identity α (u (x)) + + β (u (x)) + + (u(x)) + + (u (x)) = constant, x [ T, T] (3.7) we deduce C = D, C = t, D = t, for some t > 0. Using the ositive homogeneity of (1.1) we derive that the solution u(x) is given in by t sin ( x+t ), T x T + π α α t sin ( T 1 x ), T β β 1 π x T 1 t sin ( x T 1 ), T (3.8) β β 1 x T 1 + π t sin ( T x ), T π α α x T EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 5
6 It follows from (3.8) that the differences between α and β are reflected by change of amlitudes between ositive and negative waves at the switch between lus and minus. For the switch from negative wave to ositive wave, it holds sin ( x+t ), β sin ( T 1 x ), α sin ( x T 1 ), α sin ( T 1 x ), β T x T + π β T 1 π α x T 1 T 1 x T 1 + π α T π β x T (3.8 ) where T 1 = T +( α/+ β/)π. In view of (3.8) and (3.8 ) we see that u ( T) = u (T) and therefore can extend u(x) to a T-eriodic function on the whole real line R. For any given integer k 1. If u is a solution of (1.1) with (k + 1) nodes, then it must have equal number of ositive and negative (k+1) waves. Let T 1 < T < < T k+1 be the nodal oints of u, it follows from (3.7) that all ositive waves of u have same height and so are the same for negative waves. Moreover similarly as deriving (3.6) we get ( α + β)( )π = T i+ T i, i = 1,, k 1. Thereby α, β,, satisfy (k + 1)( α + β)( )π = T (3.6 ) and the nodes are T 1+i = T+(1+i)L + +il, T i = T+i(L + +L ), i = 0, 1,,, k. Furthermore let T 0 = T, T k+ = T then the initially ositive solution u(x) on [T i, T i+ ], i = 0, 1,, k, is given by t sin ( x T i t sin ( T i+1 x t sin ( x T 1 t sin ( T i+ x ), α ), β ), β ), α T i x T i + π α T β i+1 π x T i+1 T i+1 x T i+1 + π T i+ π α β x T i+ (3.9) and the initially negative solution u by t sin ( x T i ), β t sin ( T i+1 x ), α t sin ( x T i+1 ), α t sin ( T i+ x ), β T i x T i + π T i+1 π α β x T i+1 T i+1 x T i+1 + π α T β i+ π x T i+ (3.9 ) where T 1+i = T + (1 + i)l + il +, T i = T + i(l + + L ), i = 0, 1,,, k. EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 6
7 If u has k nodes, then there are two ossibilities 1) (k + 1) ositive waves and k negative waves, ) k ositive waves and (k + 1) negative waves. In 1) the solution should be initially ositive and be initially negative in ). It follows then 1) ( α + β)((k + 1) 1 + k 1 )π = T (3.10) and the solution u on [ T, T L ] is (T L )/k-eriodic and is given by (3.9) on [T i, T i+ ], i = 0, 1,, k, and on [T k, T], u(x) is given by t sin ( x T k ), T α k x T k + π α t sin ( T x ), T π β β x T (3.11) ) For an initially negative solution with k nodes, then ( α + β)(k 1 + (k + 1) 1 )π = T (3.1) and on [T i, T i+ ] the solution u is given by (3.9 ) for i = 0, 1,, k, and on [T k, T], u(x) is given by t sin ( x T k β ), T β k x T k + π t sin ( T x ), T π α α x T. (3.11 ) So the roof is comlete. 4 A final remark In the study of nontrivial solutions to one dimensional nonlinear differential equation (ϕ(x, u )) = f(x, u) (4.1) one usually adot the notation of solution by (4.1) being satisfied ointwise, which in turn ensures er definition only C 1 smoothness of solution. Of course, one exects higher order smoothness of the solutions. Here we shall examine this question for a very secial case, namely ϕ(x, s) = α(x)s 1 + β(x)s q 1,, q > 1 e.g., (α(x)(u ) 1 + β(x)(u ) q 1 ) = f(x, u) (4.) If we assume that the equation (4.) is satisfied ointwise and moreover α, β > 0 are also C 1, then any solution u is obviously C for any oint x where u (x) 0. So in order to get differentiability of u we need a closer examination at those oints where u (x) = 0. Let x 0 be a critical oint of u(x), u 0 = u(x 0 ), if = q =, then we easily deduce from the equation (4.) that for small δ > 0 u (x 0 δ) = f(x 0, u 0 )/α(x 0 )(δ + o(δ)); u (x 0 + δ) = f(x 0, u 0 )/β(x 0 )(δ + o(δ)) EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 7
8 thereafter u (x) has a jum at x 0 since α β and thus u C 1,1, but not C. In general, for any critical oint x = x 0 of u(x), we have the following asymtotic as δ 0 u (x 0 δ) = C 1 δ 1/( 1) (1 + o(1)) u (x 0 + δ) = C δ 1/(q 1) (1 + o(1)) where C 1 = 1 f(x 0, u 0 )/α(x 0 ), C = q 1 f(x 0, u 0 )/β(x 0 ). In view of the above estimates, we deduce that 1. If 1 <, q < then u C. If max, q} = then u C 1,1 3. If <, q then u C 1,ε, ε = min q 1 Acknowledgement This work is artially suorted by the roject Nr 0-06/10 for romotion of research at Malmö University and also the G S Magnusons fond, the Swedish Royal Academy of Science. The author thanks the referee for careful reading and suggestions which lead to imrovement of the resentation. References [1] Bennewitz C. and Saito Y. An embedding norm and the Lindqvist trigonometric functions. Electronic J. Diff. Equa. (00) No. 86, 1-6. [] Cuesta M., de Figueriredo D., Gossez, J.-P., The beginning of the Fucik sektrum for the Lalacian. J. Diff. Equa., 159: (1999) [3] Dancer N., On the Dirichlet roblem for weakly nonlinear ellitic differential equations. Proc. Royal Soci. Edinburgh, 76 (1977) [4] Dancer, E. N., Remarks on juming nonlinearities. Toics in nonlinear analysis, Birkhäuser, Basel, 1999, [5] de Figueiredo D., Gossez J.-P., On the first curve of the Fucik sectrum of an ellitic oerator. Diff. and Integral Equa. 7:5 (1994), [6] Drábek P., Solvability and bifurcations of nonlinear equations. Pitman Research Notes in Math. vol 64 Longman, New York, 199. [7] Fucik S., Boundary value roblems with juming nonlinearities, Casois Pest. Mat. 101 (1976) [8] Gidas B., Ni N. and Nirenberg L., Symmetry and related roerties via the maximum rincile. Comm. Math. Phys. 68 (1979) [9] Lindqvist, P. Some remarkable sine and cosine functions, Ricerche di Matematica, XLIV (1995) EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 8
9 [10] Manasévich, R. and Mawhin J., The sectrum of -Lalacian systems under Dirichlet, Neumann and eriodic boundary conditions. Morse theory, minimax theory and their alications to nonlinear differential equations, 01 16, New Stud. Adv. Math., 1, Int. Press, Somerville, MA, 003. [11] Otani M., A remark on certain nonlinear ellitic equations, Proc. of the Faculty of Science, Tokai Univ., 19(1984) 3-8. [1] Perera K., On the Fucik Sectrum of the -Lalacian NoDEA 11: (004) [13] Sadyrbaev F. and Gritsans A. Nolinear sectra for arameter deendent ordinary differential equations, Nonlinear analysis: modelling and control, 1:(007) [14] Schechter M. The Fucik sectrum. Indiana Univ. Math. J., 43(1994) (Received January 15, 008) EJQTDE, 009 No. 18,. 9
Existence of solutions to a superlinear p-laplacian equation
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 66,. 1 6. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.swt.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ft) Existence of solutions
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2001(2001), No. 66,. 1 6. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.swt.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.swt.edu (login: ft) Existence of solutions
On the minimax inequality and its application to existence of three solutions for elliptic equations with Dirichlet boundary condition
 ISSN 1 746-7233 England UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 2. 83-89 On the minimax inequality and its alication to existence of three solutions for ellitic equations with Dirichlet
ISSN 1 746-7233 England UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 2. 83-89 On the minimax inequality and its alication to existence of three solutions for ellitic equations with Dirichlet
Location of solutions for quasi-linear elliptic equations with general gradient dependence
 Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations 217, No. 87, 1 1; htts://doi.org/1.14232/ejqtde.217.1.87 www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/ Location of solutions for quasi-linear ellitic equations
Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations 217, No. 87, 1 1; htts://doi.org/1.14232/ejqtde.217.1.87 www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/ Location of solutions for quasi-linear ellitic equations
Inequalities for the generalized trigonometric and hyperbolic functions with two parameters
 Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Al. 8 5, 35 33 Research Article Inequalities for the generalized trigonometric and hyerbolic functions with two arameters Li Yin a,, Li-Guo Huang a a
Available online at www.tjnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Al. 8 5, 35 33 Research Article Inequalities for the generalized trigonometric and hyerbolic functions with two arameters Li Yin a,, Li-Guo Huang a a
KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS INVOLVING P -BIHARMONIC OPERATORS AND CRITICAL EXPONENTS
 Journal of Alied Analysis and Comutation Volume 7, Number 2, May 2017, 659 669 Website:htt://jaac-online.com/ DOI:10.11948/2017041 KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS INVOLVING P -BIHARMONIC OPERATORS AND CRITICAL
Journal of Alied Analysis and Comutation Volume 7, Number 2, May 2017, 659 669 Website:htt://jaac-online.com/ DOI:10.11948/2017041 KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS INVOLVING P -BIHARMONIC OPERATORS AND CRITICAL
Multiplicity results for some quasilinear elliptic problems
 Multilicity results for some uasilinear ellitic roblems Francisco Odair de Paiva, Deartamento de Matemática, IMECC, Caixa Postal 6065 Universidade Estadual de Caminas - UNICAMP 13083-970, Caminas - SP,
Multilicity results for some uasilinear ellitic roblems Francisco Odair de Paiva, Deartamento de Matemática, IMECC, Caixa Postal 6065 Universidade Estadual de Caminas - UNICAMP 13083-970, Caminas - SP,
Boundary problems for fractional Laplacians and other mu-transmission operators
 Boundary roblems for fractional Lalacians and other mu-transmission oerators Gerd Grubb Coenhagen University Geometry and Analysis Seminar June 20, 2014 Introduction Consider P a equal to ( ) a or to A
Boundary roblems for fractional Lalacians and other mu-transmission oerators Gerd Grubb Coenhagen University Geometry and Analysis Seminar June 20, 2014 Introduction Consider P a equal to ( ) a or to A
MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS INVOLVING CONCAVE AND CONVEX NONLINEARITIES IN R 3
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 301,. 1 16. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 301,. 1 16. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu MULTIPLE POSITIVE SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE
Periodic and antiperiodic eigenvalues for half-linear version of Hill s equation
 INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF MAHEMAICAL MODELS AND MEHODS IN APPLIED SCIENCES INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF MAHEMAICAL MODELS AND MEHODS IN APPLIED SCIENCES Periodic antieriodic eigenvalues for half-linear version
INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF MAHEMAICAL MODELS AND MEHODS IN APPLIED SCIENCES INERNAIONAL JOURNAL OF MAHEMAICAL MODELS AND MEHODS IN APPLIED SCIENCES Periodic antieriodic eigenvalues for half-linear version
A PRIORI ESTIMATES AND APPLICATION TO THE SYMMETRY OF SOLUTIONS FOR CRITICAL
 A PRIORI ESTIMATES AND APPLICATION TO THE SYMMETRY OF SOLUTIONS FOR CRITICAL LAPLACE EQUATIONS Abstract. We establish ointwise a riori estimates for solutions in D 1, of equations of tye u = f x, u, where
A PRIORI ESTIMATES AND APPLICATION TO THE SYMMETRY OF SOLUTIONS FOR CRITICAL LAPLACE EQUATIONS Abstract. We establish ointwise a riori estimates for solutions in D 1, of equations of tye u = f x, u, where
On the minimax inequality for a special class of functionals
 ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3,. 220-224 On the minimax inequality for a secial class of functionals G. A. Afrouzi, S. Heidarkhani, S. H. Rasouli Deartment
ISSN 1 746-7233, Engl, UK World Journal of Modelling Simulation Vol. 3 (2007) No. 3,. 220-224 On the minimax inequality for a secial class of functionals G. A. Afrouzi, S. Heidarkhani, S. H. Rasouli Deartment
arxiv: v2 [math.ap] 19 Jan 2010
![arxiv: v2 [math.ap] 19 Jan 2010 arxiv: v2 [math.ap] 19 Jan 2010](/thumbs/94/121031210.jpg) GENERALIZED ELLIPTIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO A NONLINEAR EIGENVALUE PROBLEM WITH -LAPLACIAN arxiv:11.377v2 [math.ap] 19 Jan 21 SHINGO TAKEUCHI Dedicated to Professor Yoshio Yamada on occasion
GENERALIZED ELLIPTIC FUNCTIONS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO A NONLINEAR EIGENVALUE PROBLEM WITH -LAPLACIAN arxiv:11.377v2 [math.ap] 19 Jan 21 SHINGO TAKEUCHI Dedicated to Professor Yoshio Yamada on occasion
INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS WITH NONLINEAR NEUMANN BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 2016, No. 188,. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 2016, No. 188,. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS
Multiplicity of weak solutions for a class of nonuniformly elliptic equations of p-laplacian type
 Nonlinear Analysis 7 29 536 546 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Multilicity of weak solutions for a class of nonuniformly ellitic equations of -Lalacian tye Hoang Quoc Toan, Quô c-anh Ngô Deartment of Mathematics,
Nonlinear Analysis 7 29 536 546 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Multilicity of weak solutions for a class of nonuniformly ellitic equations of -Lalacian tye Hoang Quoc Toan, Quô c-anh Ngô Deartment of Mathematics,
A TWO PARAMETERS AMBROSETTI PRODI PROBLEM*
 PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol. 53 Fasc. 3 1996 A TWO PARAMETERS AMBROSETTI PRODI PROBLEM* C. De Coster** and P. Habets 1 Introduction The study of the Ambrosetti Prodi problem has started with the paper
PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol. 53 Fasc. 3 1996 A TWO PARAMETERS AMBROSETTI PRODI PROBLEM* C. De Coster** and P. Habets 1 Introduction The study of the Ambrosetti Prodi problem has started with the paper
Received: / Revised: / Accepted:
 Transactions of NAS of Azerbaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36 4, -36 6. Series of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. Solvability of a boundary value roblem for second order differential-oerator equations
Transactions of NAS of Azerbaijan, Issue Mathematics, 36 4, -36 6. Series of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. Solvability of a boundary value roblem for second order differential-oerator equations
THE EIGENVALUE PROBLEM FOR A SINGULAR QUASILINEAR ELLIPTIC EQUATION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2004(2004), o. 16,. 1 11. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ft) THE EIGEVALUE
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2004(2004), o. 16,. 1 11. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ft) THE EIGEVALUE
Spectrum of one dimensional p-laplacian Operator with indefinite weight
 Spectrum of one dimensional p-laplacian Operator with indefinite weight A. Anane, O. Chakrone and M. Moussa 2 Département de mathématiques, Faculté des Sciences, Université Mohamed I er, Oujda. Maroc.
Spectrum of one dimensional p-laplacian Operator with indefinite weight A. Anane, O. Chakrone and M. Moussa 2 Département de mathématiques, Faculté des Sciences, Université Mohamed I er, Oujda. Maroc.
An extension to the theory of trigonometric functions as exact periodic solutions to quadratic Liénard type equations
 An extension to the theory of trigonometric functions as exact eriodic solutions to quadratic Liénard tye equations D. K. K. Adjaï a, L. H. Koudahoun a, J. Akande a, Y. J. F. Komahou b and M. D. Monsia
An extension to the theory of trigonometric functions as exact eriodic solutions to quadratic Liénard tye equations D. K. K. Adjaï a, L. H. Koudahoun a, J. Akande a, Y. J. F. Komahou b and M. D. Monsia
IMPROVED BOUNDS IN THE SCALED ENFLO TYPE INEQUALITY FOR BANACH SPACES
 IMPROVED BOUNDS IN THE SCALED ENFLO TYPE INEQUALITY FOR BANACH SPACES OHAD GILADI AND ASSAF NAOR Abstract. It is shown that if (, ) is a Banach sace with Rademacher tye 1 then for every n N there exists
IMPROVED BOUNDS IN THE SCALED ENFLO TYPE INEQUALITY FOR BANACH SPACES OHAD GILADI AND ASSAF NAOR Abstract. It is shown that if (, ) is a Banach sace with Rademacher tye 1 then for every n N there exists
GROUND STATES OF LINEARLY COUPLED SCHRÖDINGER SYSTEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), o. 05,. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu GROUD STATES OF LIEARLY COUPLED SCHRÖDIGER SYSTEMS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), o. 05,. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu GROUD STATES OF LIEARLY COUPLED SCHRÖDIGER SYSTEMS
1. Introduction. ( u p 2 u ) (p 1) u p 2 u = 0, u(0) = 0, u (0) = 1,
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 208 (208), No. 35,.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu MACLAURIN SERIES FOR sin WITH AN INTEGER GREATER THAN
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 208 (208), No. 35,.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu MACLAURIN SERIES FOR sin WITH AN INTEGER GREATER THAN
Spectral Properties of Schrödinger-type Operators and Large-time Behavior of the Solutions to the Corresponding Wave Equation
 Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. Vol. 8, No., 23,. 27 24 DOI:.5/mmn/2386 Sectral Proerties of Schrödinger-tye Oerators and Large-time Behavior of the Solutions to the Corresonding Wave Equation A.G. Ramm Deartment
Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. Vol. 8, No., 23,. 27 24 DOI:.5/mmn/2386 Sectral Proerties of Schrödinger-tye Oerators and Large-time Behavior of the Solutions to the Corresonding Wave Equation A.G. Ramm Deartment
EIGENVALUES HOMOGENIZATION FOR THE FRACTIONAL p-laplacian
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 312,. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu EIGENVALUES HOMOGENIZATION FOR THE FRACTIONAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 312,. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu EIGENVALUES HOMOGENIZATION FOR THE FRACTIONAL
FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS
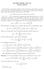 FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS We extend the construction of Fourier series to functions with arbitrary eriods, then we associate to functions defined on an interval [, L] Fourier sine and Fourier
FOURIER SERIES PART III: APPLICATIONS We extend the construction of Fourier series to functions with arbitrary eriods, then we associate to functions defined on an interval [, L] Fourier sine and Fourier
Generic Singularities of Solutions to some Nonlinear Wave Equations
 Generic Singularities of Solutions to some Nonlinear Wave Equations Alberto Bressan Deartment of Mathematics, Penn State University (Oberwolfach, June 2016) Alberto Bressan (Penn State) generic singularities
Generic Singularities of Solutions to some Nonlinear Wave Equations Alberto Bressan Deartment of Mathematics, Penn State University (Oberwolfach, June 2016) Alberto Bressan (Penn State) generic singularities
NONLOCAL p-laplace EQUATIONS DEPENDING ON THE L p NORM OF THE GRADIENT MICHEL CHIPOT AND TETIANA SAVITSKA
 NONLOCAL -LAPLACE EQUATIONS DEPENDING ON THE L NORM OF THE GRADIENT MICHEL CHIPOT AND TETIANA SAVITSKA Abstract. We are studying a class of nonlinear nonlocal diffusion roblems associated with a -Lalace-tye
NONLOCAL -LAPLACE EQUATIONS DEPENDING ON THE L NORM OF THE GRADIENT MICHEL CHIPOT AND TETIANA SAVITSKA Abstract. We are studying a class of nonlinear nonlocal diffusion roblems associated with a -Lalace-tye
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics
 Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics THE METHOD OF LOWER AND UPPER SOLUTIONS FOR SOME FOURTH-ORDER EQUATIONS ZHANBING BAI, WEIGAO GE AND YIFU WANG Department of Applied Mathematics,
Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics THE METHOD OF LOWER AND UPPER SOLUTIONS FOR SOME FOURTH-ORDER EQUATIONS ZHANBING BAI, WEIGAO GE AND YIFU WANG Department of Applied Mathematics,
A NOTE ON THE EXISTENCE OF TWO NONTRIVIAL SOLUTIONS OF A RESONANCE PROBLEM
 PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol. 51 Fasc. 4 1994 A NOTE ON THE EXISTENCE OF TWO NONTRIVIAL SOLUTIONS OF A RESONANCE PROBLEM To Fu Ma* Abstract: We study the existence of two nontrivial solutions for an elliptic
PORTUGALIAE MATHEMATICA Vol. 51 Fasc. 4 1994 A NOTE ON THE EXISTENCE OF TWO NONTRIVIAL SOLUTIONS OF A RESONANCE PROBLEM To Fu Ma* Abstract: We study the existence of two nontrivial solutions for an elliptic
On Maximum Principle and Existence of Solutions for Nonlinear Cooperative Systems on R N
 ISS: 2350-0328 On Maximum Princile and Existence of Solutions for onlinear Cooerative Systems on R M.Kasturi Associate Professor, Deartment of Mathematics, P.K.R. Arts College for Women, Gobi, Tamilnadu.
ISS: 2350-0328 On Maximum Princile and Existence of Solutions for onlinear Cooerative Systems on R M.Kasturi Associate Professor, Deartment of Mathematics, P.K.R. Arts College for Women, Gobi, Tamilnadu.
Sharp gradient estimate and spectral rigidity for p-laplacian
 Shar gradient estimate and sectral rigidity for -Lalacian Chiung-Jue Anna Sung and Jiaing Wang To aear in ath. Research Letters. Abstract We derive a shar gradient estimate for ositive eigenfunctions of
Shar gradient estimate and sectral rigidity for -Lalacian Chiung-Jue Anna Sung and Jiaing Wang To aear in ath. Research Letters. Abstract We derive a shar gradient estimate for ositive eigenfunctions of
A note on Hardy s inequalities with boundary singularities
 A note on Hardy s inequalities with boundary singularities Mouhamed Moustaha Fall Abstract. Let be a smooth bounded domain in R N with N 1. In this aer we study the Hardy-Poincaré inequalities with weight
A note on Hardy s inequalities with boundary singularities Mouhamed Moustaha Fall Abstract. Let be a smooth bounded domain in R N with N 1. In this aer we study the Hardy-Poincaré inequalities with weight
An Estimate For Heilbronn s Exponential Sum
 An Estimate For Heilbronn s Exonential Sum D.R. Heath-Brown Magdalen College, Oxford For Heini Halberstam, on his retirement Let be a rime, and set e(x) = ex(2πix). Heilbronn s exonential sum is defined
An Estimate For Heilbronn s Exonential Sum D.R. Heath-Brown Magdalen College, Oxford For Heini Halberstam, on his retirement Let be a rime, and set e(x) = ex(2πix). Heilbronn s exonential sum is defined
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.sp] 31 Oct 2004
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.sp] 31 Oct 2004 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.sp] 31 Oct 2004](/thumbs/74/69640321.jpg) On the fundamental eigenvalue ratio of the Lalacian Jacqueline Fleckinger, Evans M. Harrell II, François de Thélin arxiv:math/0403v [math.sp] 3 Oct 2004 Abstract It is shown that the fundamental eigenvalue
On the fundamental eigenvalue ratio of the Lalacian Jacqueline Fleckinger, Evans M. Harrell II, François de Thélin arxiv:math/0403v [math.sp] 3 Oct 2004 Abstract It is shown that the fundamental eigenvalue
Existence and number of solutions for a class of semilinear Schrödinger equations
 Existence numer of solutions for a class of semilinear Schrödinger equations Yanheng Ding Institute of Mathematics, AMSS, Chinese Academy of Sciences 100080 Beijing, China Andrzej Szulkin Deartment of
Existence numer of solutions for a class of semilinear Schrödinger equations Yanheng Ding Institute of Mathematics, AMSS, Chinese Academy of Sciences 100080 Beijing, China Andrzej Szulkin Deartment of
A SINGULAR PERTURBATION PROBLEM FOR THE p-laplace OPERATOR
 A SINGULAR PERTURBATION PROBLEM FOR THE -LAPLACE OPERATOR D. DANIELLI, A. PETROSYAN, AND H. SHAHGHOLIAN Abstract. In this aer we initiate the study of the nonlinear one hase singular erturbation roblem
A SINGULAR PERTURBATION PROBLEM FOR THE -LAPLACE OPERATOR D. DANIELLI, A. PETROSYAN, AND H. SHAHGHOLIAN Abstract. In this aer we initiate the study of the nonlinear one hase singular erturbation roblem
EXISTENCE OF THREE WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A QUASILINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEM. Saeid Shokooh and Ghasem A. Afrouzi. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69 4 (217 271 28 December 217 research paper originalni nauqni rad EXISTENCE OF THREE WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A QUASILINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEM Saeid Shokooh and Ghasem A.
MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69 4 (217 271 28 December 217 research paper originalni nauqni rad EXISTENCE OF THREE WEAK SOLUTIONS FOR A QUASILINEAR DIRICHLET PROBLEM Saeid Shokooh and Ghasem A.
NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian UNDER NONHOMOGENEOUS NEUMANN BOUNDARY CONDITION
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 210, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu NONLINEAR FREDHOLM ALTERNATIVE FOR THE p-laplacian
Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various Families of R n Norms and Some Open Problems
 Int. J. Oen Problems Comt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Coyright c ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various
Int. J. Oen Problems Comt. Math., Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2010 ISSN 1998-6262; Coyright c ICSRS Publication, 2010 www.i-csrs.org Various Proofs for the Decrease Monotonicity of the Schatten s Power Norm, Various
The Nemytskii operator on bounded p-variation in the mean spaces
 Vol. XIX, N o 1, Junio (211) Matemáticas: 31 41 Matemáticas: Enseñanza Universitaria c Escuela Regional de Matemáticas Universidad del Valle - Colombia The Nemytskii oerator on bounded -variation in the
Vol. XIX, N o 1, Junio (211) Matemáticas: 31 41 Matemáticas: Enseñanza Universitaria c Escuela Regional de Matemáticas Universidad del Valle - Colombia The Nemytskii oerator on bounded -variation in the
Existence Results for Quasilinear Degenerated Equations Via Strong Convergence of Truncations
 Existence Results for Quasilinear Degenerated Equations Via Strong Convergence of Truncations Youssef AKDIM, Elhoussine AZROUL, and Abdelmoujib BENKIRANE Déartement de Mathématiques et Informatique, Faculté
Existence Results for Quasilinear Degenerated Equations Via Strong Convergence of Truncations Youssef AKDIM, Elhoussine AZROUL, and Abdelmoujib BENKIRANE Déartement de Mathématiques et Informatique, Faculté
REGULARITY OF SOLUTIONS TO DOUBLY NONLINEAR DIFFUSION EQUATIONS
 Seventh Mississii State - UAB Conference on Differential Equations and Comutational Simulations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conf. 17 2009,. 185 195. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu
Seventh Mississii State - UAB Conference on Differential Equations and Comutational Simulations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conf. 17 2009,. 185 195. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu
ON THE EXISTENCE OF THREE SOLUTIONS FOR QUASILINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEM. Paweł Goncerz
 Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 32 No. 3 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/opmath.2012.32.3.473 ON THE EXISTENCE OF THREE SOLUTIONS FOR QUASILINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEM Paweł Goncerz Abstract. We consider a quasilinear
Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 32 No. 3 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/opmath.2012.32.3.473 ON THE EXISTENCE OF THREE SOLUTIONS FOR QUASILINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEM Paweł Goncerz Abstract. We consider a quasilinear
MATH 819 FALL We considered solutions of this equation on the domain Ū, where
 MATH 89 FALL. The D linear wave equation weak solutions We have considered the initial value problem for the wave equation in one space dimension: (a) (b) (c) u tt u xx = f(x, t) u(x, ) = g(x), u t (x,
MATH 89 FALL. The D linear wave equation weak solutions We have considered the initial value problem for the wave equation in one space dimension: (a) (b) (c) u tt u xx = f(x, t) u(x, ) = g(x), u t (x,
Deng Songhai (Dept. of Math of Xiangya Med. Inst. in Mid-east Univ., Changsha , China)
 J. Partial Diff. Eqs. 5(2002), 7 2 c International Academic Publishers Vol.5 No. ON THE W,q ESTIMATE FOR WEAK SOLUTIONS TO A CLASS OF DIVERGENCE ELLIPTIC EUATIONS Zhou Shuqing (Wuhan Inst. of Physics and
J. Partial Diff. Eqs. 5(2002), 7 2 c International Academic Publishers Vol.5 No. ON THE W,q ESTIMATE FOR WEAK SOLUTIONS TO A CLASS OF DIVERGENCE ELLIPTIC EUATIONS Zhou Shuqing (Wuhan Inst. of Physics and
Existence and nonexistence of positive solutions for quasilinear elliptic systems
 ISSN 1746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 1,. 44-48 Existence and nonexistence of ositive solutions for uasilinear ellitic systems G. A. Afrouzi, H. Ghorbani
ISSN 1746-7233, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 4 (2008) No. 1,. 44-48 Existence and nonexistence of ositive solutions for uasilinear ellitic systems G. A. Afrouzi, H. Ghorbani
Research Article Positive Solutions of Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value Problems in Presence of Upper and Lower Solutions
 International Differential Equations Volume 11, Article ID 38394, 11 ages doi:1.1155/11/38394 Research Article Positive Solutions of Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value Problems in Presence of Uer and Lower
International Differential Equations Volume 11, Article ID 38394, 11 ages doi:1.1155/11/38394 Research Article Positive Solutions of Sturm-Liouville Boundary Value Problems in Presence of Uer and Lower
A Note on the Positive Nonoscillatory Solutions of the Difference Equation
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 4, 1, no. 36, 1787-1798 A Note on the Positive Nonoscillatory Solutions of the Difference Equation x n+1 = α c ix n i + x n k c ix n i ) Vu Van Khuong 1 and Mai Nam
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 4, 1, no. 36, 1787-1798 A Note on the Positive Nonoscillatory Solutions of the Difference Equation x n+1 = α c ix n i + x n k c ix n i ) Vu Van Khuong 1 and Mai Nam
Infinitely Many Insolvable Diophantine Equations
 ACKNOWLEDGMENT. After this aer was submitted, the author received messages from G. D. Anderson and M. Vuorinen that concerned [10] and informed him about references [1] [7]. He is leased to thank them
ACKNOWLEDGMENT. After this aer was submitted, the author received messages from G. D. Anderson and M. Vuorinen that concerned [10] and informed him about references [1] [7]. He is leased to thank them
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR NONLOCAL p-laplacian PROBLEMS
 Electronic Journal of ifferential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 274,. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE AN UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR NONLOCAL
Electronic Journal of ifferential Equations, Vol. 2016 (2016), No. 274,. 1 9. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE AN UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR NONLOCAL
On a class of Rellich inequalities
 On a class of Rellich inequalities G. Barbatis A. Tertikas Dedicated to Professor E.B. Davies on the occasion of his 60th birthday Abstract We rove Rellich and imroved Rellich inequalities that involve
On a class of Rellich inequalities G. Barbatis A. Tertikas Dedicated to Professor E.B. Davies on the occasion of his 60th birthday Abstract We rove Rellich and imroved Rellich inequalities that involve
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 25 Sep 2002
 Energy fluctuations at the multicritical oint in two-dimensional sin glasses arxiv:cond-mat/0207694 v2 25 Se 2002 1. Introduction Hidetoshi Nishimori, Cyril Falvo and Yukiyasu Ozeki Deartment of Physics,
Energy fluctuations at the multicritical oint in two-dimensional sin glasses arxiv:cond-mat/0207694 v2 25 Se 2002 1. Introduction Hidetoshi Nishimori, Cyril Falvo and Yukiyasu Ozeki Deartment of Physics,
Quasilinear degenerated equations with L 1 datum and without coercivity in perturbation terms
 Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations 2006, No. 19, 1-18; htt://www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/ Quasilinear degenerated equations with L 1 datum and without coercivity in erturbation
Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations 2006, No. 19, 1-18; htt://www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/ Quasilinear degenerated equations with L 1 datum and without coercivity in erturbation
MATH 251 Final Examination December 19, 2012 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Final Examination December 19, 2012 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 17 questions for a total of 150 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all
MATH 251 Final Examination December 19, 2012 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 17 questions for a total of 150 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all
Schwarz rearrangement does not decrease the energy for the pseudo p-laplacian operator. Key Words:Schwarz symmetrization, pseudo p-laplacian operator.
 Bol. Soc. Paran. Mat. (3s. v. 9 1 (11: 49 53. c SPM ISSN-175-1188 on line ISSN-37871 in ress SPM: www.sm.uem.br/sm doi:1.569/bsm.v9i1.148 Schwarz rearrangement does not decrease the energy for the seudo
Bol. Soc. Paran. Mat. (3s. v. 9 1 (11: 49 53. c SPM ISSN-175-1188 on line ISSN-37871 in ress SPM: www.sm.uem.br/sm doi:1.569/bsm.v9i1.148 Schwarz rearrangement does not decrease the energy for the seudo
Removable singularities for some degenerate non-linear elliptic equations
 Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 5, 2015, no. 1, 21-27 Removable singularities for some degenerate non-linear ellitic equations Tahir S. Gadjiev Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of NAS of Azerbaijan, 9,
Mathematica Aeterna, Vol. 5, 2015, no. 1, 21-27 Removable singularities for some degenerate non-linear ellitic equations Tahir S. Gadjiev Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of NAS of Azerbaijan, 9,
Variations on the p Laplacian
 www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl Toics -harmonic functions u = 1 overdetermined roblems oen roblems Lalace oerator u = u x1 x 1 +... + u xnx n = u νν + u ν div(ν) where ν(x) = u(x) u(x) is direction of steeest
www.mi.uni-koeln.de/ kawohl Toics -harmonic functions u = 1 overdetermined roblems oen roblems Lalace oerator u = u x1 x 1 +... + u xnx n = u νν + u ν div(ν) where ν(x) = u(x) u(x) is direction of steeest
An Existence Theorem for a Class of Nonuniformly Nonlinear Systems
 Australian Journal of Basic and Alied Sciences, 5(7): 1313-1317, 11 ISSN 1991-8178 An Existence Theorem for a Class of Nonuniformly Nonlinear Systems G.A. Afrouzi and Z. Naghizadeh Deartment of Mathematics,
Australian Journal of Basic and Alied Sciences, 5(7): 1313-1317, 11 ISSN 1991-8178 An Existence Theorem for a Class of Nonuniformly Nonlinear Systems G.A. Afrouzi and Z. Naghizadeh Deartment of Mathematics,
Multiplicative group law on the folium of Descartes
 Multilicative grou law on the folium of Descartes Steluţa Pricoie and Constantin Udrişte Abstract. The folium of Descartes is still studied and understood today. Not only did it rovide for the roof of
Multilicative grou law on the folium of Descartes Steluţa Pricoie and Constantin Udrişte Abstract. The folium of Descartes is still studied and understood today. Not only did it rovide for the roof of
BASIS PROPERTIES OF EIGENFUNCTIONS OF THE p-laplacian
 BASIS PROPERTIES OF EIGENFUNCTIONS OF THE p-laplacian Paul Binding 1, Lyonell Boulton 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Calgary Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4 Jan Čepička3, Pavel
BASIS PROPERTIES OF EIGENFUNCTIONS OF THE p-laplacian Paul Binding 1, Lyonell Boulton 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Calgary Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4 Jan Čepička3, Pavel
Positivity, local smoothing and Harnack inequalities for very fast diffusion equations
 Positivity, local smoothing and Harnack inequalities for very fast diffusion equations Dedicated to Luis Caffarelli for his ucoming 60 th birthday Matteo Bonforte a, b and Juan Luis Vázquez a, c Abstract
Positivity, local smoothing and Harnack inequalities for very fast diffusion equations Dedicated to Luis Caffarelli for his ucoming 60 th birthday Matteo Bonforte a, b and Juan Luis Vázquez a, c Abstract
MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE AND EXISTENCE RESULTS FOR ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS ON R N. 1. Introduction This work is mainly concerned with the elliptic system
 Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 2010(2010), No. 60,. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.txstate.edu MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE AND
Electronic Journal of Differential Euations, Vol. 2010(2010), No. 60,. 1 13. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu ft ejde.math.txstate.edu MAXIMUM PRINCIPLE AND
Global solution of reaction diffusion system with full matrix
 Global Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 3 (3) (2015) 109-120 www.scienceubco.com/index.h/gjma c Science Publishing Cororation doi: 10.14419/gjma.v3i3.4683 Research Paer Global solution of reaction diffusion
Global Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 3 (3) (2015) 109-120 www.scienceubco.com/index.h/gjma c Science Publishing Cororation doi: 10.14419/gjma.v3i3.4683 Research Paer Global solution of reaction diffusion
ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR FOR THE BEST LOWER BOUND OF JENSEN S FUNCTIONAL
 75 Kragujevac J. Math. 25 23) 75 79. ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR FOR THE BEST LOWER BOUND OF JENSEN S FUNCTIONAL Stojan Radenović and Mirjana Pavlović 2 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
75 Kragujevac J. Math. 25 23) 75 79. ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOR FOR THE BEST LOWER BOUND OF JENSEN S FUNCTIONAL Stojan Radenović and Mirjana Pavlović 2 University of Belgrade, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS. Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S. L. Yadava. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Statics and dynamics: some elementary concepts
 1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
1 Statics and dynamics: some elementary concets Dynamics is the study of the movement through time of variables such as heartbeat, temerature, secies oulation, voltage, roduction, emloyment, rices and
Applications to stochastic PDE
 15 Alications to stochastic PE In this final lecture we resent some alications of the theory develoed in this course to stochastic artial differential equations. We concentrate on two secific examles:
15 Alications to stochastic PE In this final lecture we resent some alications of the theory develoed in this course to stochastic artial differential equations. We concentrate on two secific examles:
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR CROSS CRITICAL EXPONENTIAL N-LAPLACIAN SYSTEMS
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), o. 28, pp. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTECE OF SOLUTIOS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2014 (2014), o. 28, pp. 1 10. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu EXISTECE OF SOLUTIOS
FRACTIONAL ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS WITH NONLINEARITIES OF ARBITRARY GROWTH
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017, No. 206,. 1 20. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu FRACTIONAL ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS WITH NONLINEARITIES
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017, No. 206,. 1 20. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: htt://ejde.math.txstate.edu or htt://ejde.math.unt.edu FRACTIONAL ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS WITH NONLINEARITIES
On some nonlinear elliptic systems with coercive perturbations in R N
 On some nonlinear ellitic systems with coercive erturbations in R Said EL MAOUI and Abdelfattah TOUZAI Déartement de Mathématiues et Informatiue Faculté des Sciences Dhar-Mahraz B.P. 1796 Atlas-Fès Fès
On some nonlinear ellitic systems with coercive erturbations in R Said EL MAOUI and Abdelfattah TOUZAI Déartement de Mathématiues et Informatiue Faculté des Sciences Dhar-Mahraz B.P. 1796 Atlas-Fès Fès
PROPERTIES OF L P (K)-SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR NONHOMOGENEOUS IMPULSIVE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNBOUNDED LINEAR OPERATOR
 PROPERTIES OF L P (K)-SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR NONHOMOGENEOUS IMPULSIVE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNBOUNDED LINEAR OPERATOR Atanaska Georgieva Abstract. Sufficient conditions for the existence of L (k)-solutions
PROPERTIES OF L P (K)-SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR NONHOMOGENEOUS IMPULSIVE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH UNBOUNDED LINEAR OPERATOR Atanaska Georgieva Abstract. Sufficient conditions for the existence of L (k)-solutions
An Inverse Problem for Two Spectra of Complex Finite Jacobi Matrices
 Coyright 202 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.86, no.4,.30-39, 202 An Inverse Problem for Two Sectra of Comlex Finite Jacobi Matrices Gusein Sh. Guseinov Abstract: This aer deals with the inverse sectral roblem
Coyright 202 Tech Science Press CMES, vol.86, no.4,.30-39, 202 An Inverse Problem for Two Sectra of Comlex Finite Jacobi Matrices Gusein Sh. Guseinov Abstract: This aer deals with the inverse sectral roblem
{ sin(t), t [0, sketch the graph of this f(t) = L 1 {F(p)}.
 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform c Habala 3 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform Find the Lalace transform of the following functions: ft t sint; ft e 3t cos3t; 3 ft e 3s ds; { sint,
EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform c Habala 3 EM Solved roblems Lalace & Fourier transform Find the Lalace transform of the following functions: ft t sint; ft e 3t cos3t; 3 ft e 3s ds; { sint,
PERIODIC PROBLEMS WITH φ-laplacian INVOLVING NON-ORDERED LOWER AND UPPER FUNCTIONS
 Fixed Point Theory, Volume 6, No. 1, 25, 99-112 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm PERIODIC PROBLEMS WITH φ-laplacian INVOLVING NON-ORDERED LOWER AND UPPER FUNCTIONS IRENA RACHŮNKOVÁ1 AND MILAN
Fixed Point Theory, Volume 6, No. 1, 25, 99-112 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.htm PERIODIC PROBLEMS WITH φ-laplacian INVOLVING NON-ORDERED LOWER AND UPPER FUNCTIONS IRENA RACHŮNKOVÁ1 AND MILAN
Global Behavior of a Higher Order Rational Difference Equation
 International Journal of Difference Euations ISSN 0973-6069, Volume 10, Number 1,. 1 11 (2015) htt://camus.mst.edu/ijde Global Behavior of a Higher Order Rational Difference Euation Raafat Abo-Zeid The
International Journal of Difference Euations ISSN 0973-6069, Volume 10, Number 1,. 1 11 (2015) htt://camus.mst.edu/ijde Global Behavior of a Higher Order Rational Difference Euation Raafat Abo-Zeid The
TRIGONOMETRIC WAVELET INTERPOLATION IN BESOV SPACES. Woula Themistoclakis. 1. Introduction
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS NIŠ) Ser. Math. Inform. 4 999), 49 7 TRIGONOMETRIC WAVELET INTERPOLATION IN BESOV SPACES Woula Themistoclakis Dedicated to Prof. M.R. Occorsio for his 65th birthday Abstract. In the
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS NIŠ) Ser. Math. Inform. 4 999), 49 7 TRIGONOMETRIC WAVELET INTERPOLATION IN BESOV SPACES Woula Themistoclakis Dedicated to Prof. M.R. Occorsio for his 65th birthday Abstract. In the
Existence and Multiplicity of Solutions for a Class of Semilinear Elliptic Equations 1
 Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 257, 321 331 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2000.7347, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Existence and Multiplicity of Solutions for a Class of
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 257, 321 331 (2001) doi:10.1006/jmaa.2000.7347, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Existence and Multiplicity of Solutions for a Class of
Pseudodifferential operators with homogeneous symbols
 Pseudodifferential oerators with homogeneous symbols Loukas Grafakos Deartment of Mathematics University of Missouri Columbia, MO 65211 Rodolfo H. Torres Deartment of Mathematics University of Kansas Lawrence,
Pseudodifferential oerators with homogeneous symbols Loukas Grafakos Deartment of Mathematics University of Missouri Columbia, MO 65211 Rodolfo H. Torres Deartment of Mathematics University of Kansas Lawrence,
Blow up points of solution curves for a semilinear problem
 Blow up points of solution curves for a semilinear problem Junping Shi Department of Mathematics, Tulane University New Orleans, LA 70118 Email: shij@math.tulane.edu 1 Introduction Consider a semilinear
Blow up points of solution curves for a semilinear problem Junping Shi Department of Mathematics, Tulane University New Orleans, LA 70118 Email: shij@math.tulane.edu 1 Introduction Consider a semilinear
ON FREIMAN S 2.4-THEOREM
 ON FREIMAN S 2.4-THEOREM ØYSTEIN J. RØDSETH Abstract. Gregory Freiman s celebrated 2.4-Theorem says that if A is a set of residue classes modulo a rime satisfying 2A 2.4 A 3 and A < /35, then A is contained
ON FREIMAN S 2.4-THEOREM ØYSTEIN J. RØDSETH Abstract. Gregory Freiman s celebrated 2.4-Theorem says that if A is a set of residue classes modulo a rime satisfying 2A 2.4 A 3 and A < /35, then A is contained
A note on the Dancer Fučík spectra of the fractional p-laplacian and Laplacian operators
 DOI 10.1515/anona-2014-0038 Adv. Nonlinear Anal. 2015; 4 (1):13 23 Research Article Kanishka Perera, Marco Squassina and Yang Yang A note on the Dancer Fučík spectra of the fractional p-laplacian and Laplacian
DOI 10.1515/anona-2014-0038 Adv. Nonlinear Anal. 2015; 4 (1):13 23 Research Article Kanishka Perera, Marco Squassina and Yang Yang A note on the Dancer Fučík spectra of the fractional p-laplacian and Laplacian
Solutions of the Duffing and Painlevé-Gambier Equations by Generalized Sundman Transformation
 Solutions of the Duffing and Painlevé-Gambier Equations by Generalized Sundman Transformation D.K.K. Adjaï a, L. H. Koudahoun a, J. Akande a, Y.J.F. Komahou b and M. D. Monsia a 1 a Deartment of Physics,
Solutions of the Duffing and Painlevé-Gambier Equations by Generalized Sundman Transformation D.K.K. Adjaï a, L. H. Koudahoun a, J. Akande a, Y.J.F. Komahou b and M. D. Monsia a 1 a Deartment of Physics,
#A47 INTEGERS 15 (2015) QUADRATIC DIOPHANTINE EQUATIONS WITH INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS IN POSITIVE INTEGERS
 #A47 INTEGERS 15 (015) QUADRATIC DIOPHANTINE EQUATIONS WITH INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS IN POSITIVE INTEGERS Mihai Ciu Simion Stoilow Institute of Mathematics of the Romanian Academy, Research Unit No. 5,
#A47 INTEGERS 15 (015) QUADRATIC DIOPHANTINE EQUATIONS WITH INFINITELY MANY SOLUTIONS IN POSITIVE INTEGERS Mihai Ciu Simion Stoilow Institute of Mathematics of the Romanian Academy, Research Unit No. 5,
HASSE INVARIANTS FOR THE CLAUSEN ELLIPTIC CURVES
 HASSE INVARIANTS FOR THE CLAUSEN ELLIPTIC CURVES AHMAD EL-GUINDY AND KEN ONO Astract. Gauss s F x hyergeometric function gives eriods of ellitic curves in Legendre normal form. Certain truncations of this
HASSE INVARIANTS FOR THE CLAUSEN ELLIPTIC CURVES AHMAD EL-GUINDY AND KEN ONO Astract. Gauss s F x hyergeometric function gives eriods of ellitic curves in Legendre normal form. Certain truncations of this
GENERALIZED NORMS INEQUALITIES FOR ABSOLUTE VALUE OPERATORS
 International Journal of Analysis Alications ISSN 9-8639 Volume 5, Number (04), -9 htt://www.etamaths.com GENERALIZED NORMS INEQUALITIES FOR ABSOLUTE VALUE OPERATORS ILYAS ALI, HU YANG, ABDUL SHAKOOR Abstract.
International Journal of Analysis Alications ISSN 9-8639 Volume 5, Number (04), -9 htt://www.etamaths.com GENERALIZED NORMS INEQUALITIES FOR ABSOLUTE VALUE OPERATORS ILYAS ALI, HU YANG, ABDUL SHAKOOR Abstract.
Solutions of two-point boundary value problems via phase-plane analysis
 Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations Proc. 1th Coll. Qualitative Theory of Diff. Equ. (July 1 4, 215, Szeged, Hungary) 216, No. 4, 1 1; doi: 1.14232/ejqtde.216.8.4 http://www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/
Electronic Journal of Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations Proc. 1th Coll. Qualitative Theory of Diff. Equ. (July 1 4, 215, Szeged, Hungary) 216, No. 4, 1 1; doi: 1.14232/ejqtde.216.8.4 http://www.math.u-szeged.hu/ejqtde/
Anna Andruch-Sobi lo, Ma lgorzata Migda. FURTHER PROPERTIES OF THE RATIONAL RECURSIVE SEQUENCE x n+1 =
 Ouscula Mathematica Vol. 26 No. 3 2006 Anna Andruch-Sobi lo, Ma lgorzata Migda FURTHER PROPERTIES OF THE RATIONAL RECURSIVE SEQUENCE x n+1 = Abstract. In this aer we consider the difference equation x
Ouscula Mathematica Vol. 26 No. 3 2006 Anna Andruch-Sobi lo, Ma lgorzata Migda FURTHER PROPERTIES OF THE RATIONAL RECURSIVE SEQUENCE x n+1 = Abstract. In this aer we consider the difference equation x
FROM A CAPILLARY PHENOMENA 1. INTRODUCTION
 J. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. 08 08, Article ID htts://doi.org/0.395/jnfa.08. x-laplacian-like PROBLEMS WITH NEUMANN CONDITION ORIGINATED FROM A CAPILLARY PHENOMENA SHAPOUR HEIDARKHANI, AMJAD SALARI Deartment
J. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. 08 08, Article ID htts://doi.org/0.395/jnfa.08. x-laplacian-like PROBLEMS WITH NEUMANN CONDITION ORIGINATED FROM A CAPILLARY PHENOMENA SHAPOUR HEIDARKHANI, AMJAD SALARI Deartment
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 19 Mar 2011
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 19 Mar 2011 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 19 Mar 2011](/thumbs/82/86406819.jpg) Life-San of Solutions to Critical Semilinear Wave Equations Yi Zhou Wei Han. Abstract arxiv:113.3758v1 [math.ap] 19 Mar 11 The final oen art of the famous Strauss conjecture on semilinear wave equations
Life-San of Solutions to Critical Semilinear Wave Equations Yi Zhou Wei Han. Abstract arxiv:113.3758v1 [math.ap] 19 Mar 11 The final oen art of the famous Strauss conjecture on semilinear wave equations
Commutators on l. D. Dosev and W. B. Johnson
 Submitted exclusively to the London Mathematical Society doi:10.1112/0000/000000 Commutators on l D. Dosev and W. B. Johnson Abstract The oerators on l which are commutators are those not of the form λi
Submitted exclusively to the London Mathematical Society doi:10.1112/0000/000000 Commutators on l D. Dosev and W. B. Johnson Abstract The oerators on l which are commutators are those not of the form λi
On Character Sums of Binary Quadratic Forms 1 2. Mei-Chu Chang 3. Abstract. We establish character sum bounds of the form.
 On Character Sums of Binary Quadratic Forms 2 Mei-Chu Chang 3 Abstract. We establish character sum bounds of the form χ(x 2 + ky 2 ) < τ H 2, a x a+h b y b+h where χ is a nontrivial character (mod ), 4
On Character Sums of Binary Quadratic Forms 2 Mei-Chu Chang 3 Abstract. We establish character sum bounds of the form χ(x 2 + ky 2 ) < τ H 2, a x a+h b y b+h where χ is a nontrivial character (mod ), 4
Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent
 Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent Yūki Naito a and Tokushi Sato b a Department of Mathematics, Ehime University, Matsuyama 790-8577, Japan b Mathematical
Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent Yūki Naito a and Tokushi Sato b a Department of Mathematics, Ehime University, Matsuyama 790-8577, Japan b Mathematical
POTENTIAL LANDESMAN-LAZER TYPE CONDITIONS AND. 1. Introduction We investigate the existence of solutions for the nonlinear boundary-value problem
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 25(25), No. 94, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) POTENTIAL
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 25(25), No. 94, pp. 1 12. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu (login: ftp) POTENTIAL
Sobolev Spaces with Weights in Domains and Boundary Value Problems for Degenerate Elliptic Equations
 Sobolev Saces with Weights in Domains and Boundary Value Problems for Degenerate Ellitic Equations S. V. Lototsky Deartment of Mathematics, M.I.T., Room 2-267, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA 02139-4307,
Sobolev Saces with Weights in Domains and Boundary Value Problems for Degenerate Ellitic Equations S. V. Lototsky Deartment of Mathematics, M.I.T., Room 2-267, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA 02139-4307,
A Note on Massless Quantum Free Scalar Fields. with Negative Energy Density
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 7, 13, no. 1, 549 554 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com A Note on Massless Quantum Free Scalar Fields with Negative Energy Density M. A. Grado-Caffaro and M. Grado-Caffaro Scientific
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 7, 13, no. 1, 549 554 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com A Note on Massless Quantum Free Scalar Fields with Negative Energy Density M. A. Grado-Caffaro and M. Grado-Caffaro Scientific
MATH 251 Final Examination December 16, 2015 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 5 Final Examination December 6, 5 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 7 questions for a total of 5 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
MATH 5 Final Examination December 6, 5 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 7 questions for a total of 5 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
Extension of Karamata inequality for generalized inverse trigonometric functions
 Stud. Univ. Baeş-Bolyai Math. 60205, No., 79 8 Extension of Karamata ineuality for generalized inverse trigonometric functions Árád Baricz and Tior K. Pogány Astract. Discussing Ramanujan s Question 29,
Stud. Univ. Baeş-Bolyai Math. 60205, No., 79 8 Extension of Karamata ineuality for generalized inverse trigonometric functions Árád Baricz and Tior K. Pogány Astract. Discussing Ramanujan s Question 29,
Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-step monotone missing data
 Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-ste monotone missing data Masashi Hyodo, Nobumichi Shutoh 2, Takashi Seo, and Tatjana Pavlenko 3 Deartment of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo
Estimation of the large covariance matrix with two-ste monotone missing data Masashi Hyodo, Nobumichi Shutoh 2, Takashi Seo, and Tatjana Pavlenko 3 Deartment of Mathematical Information Science, Tokyo
Intrinsic Approximation on Cantor-like Sets, a Problem of Mahler
 Intrinsic Aroximation on Cantor-like Sets, a Problem of Mahler Ryan Broderick, Lior Fishman, Asaf Reich and Barak Weiss July 200 Abstract In 984, Kurt Mahler osed the following fundamental question: How
Intrinsic Aroximation on Cantor-like Sets, a Problem of Mahler Ryan Broderick, Lior Fishman, Asaf Reich and Barak Weiss July 200 Abstract In 984, Kurt Mahler osed the following fundamental question: How
Heteroclinic Bifurcation of a Predator-Prey System with Hassell-Varley Functional Response and Allee Effect
 International Journal of ngineering Research And Management (IJRM) ISSN: 49-058 Volume-05 Issue-0 October 08 Heteroclinic Bifurcation of a Predator-Prey System with Hassell-Varley Functional Resonse and
International Journal of ngineering Research And Management (IJRM) ISSN: 49-058 Volume-05 Issue-0 October 08 Heteroclinic Bifurcation of a Predator-Prey System with Hassell-Varley Functional Resonse and
