Answers to Odd Problems in Intermediate Dynamics
|
|
|
- Moses Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answes to Odd Pobems in Intemediate Dynamics Patick Hami San Jose State Univesity San Jose, Caifonia Januay, 9 Capte cm/sec at.8 above te oizonta. (a) 44ft= sec (b) mp..5 v = k b e bt (bt + ) x = x + k b e bt t + b + t.7 t =. sec m m.5..9 (a) ( 4a 4b ) (b) x cm = y cm = 4. R cm = ( 8 R 8 R 8 R) b a b a (c) (677 8). p 6 a mg.9 (a) 7 mp (b) 4 mp.. 5 watt.. 4 m/s..5 v i =v f = 89 te steetcas wi un about pecent faste. Capte. 6 m/s.. (a) v = v +kv x = x t + k [n( + kv t)] (b) As t!, v!..5 v = vx + v y = [(g x =yg) + (yg)] = = tan (v y =v x ) = tan (y=x) km..9 (a) = p a (b) a = 98 m/s, v = 79 m/s, = 844 min.. = = (=).9 v = 4 sin ^ + (4 4 cos ) ^ a = ( cos 6)^+ sin ^ b
2 . ^( _ ) + ^( + _ + ) m/s..7 + z cos + p z.9 x = a cos!(t ) cos (t ) y = a cos!(t ) sin (t ) z = a sin!(t ).. = + z = tan z = = sin = z = cos. (a) An inwad spia. (b) p b + (akt bkt ) Capte.!A sin!t! A cos!t. 8 4 N..5 M M M M.7 (a)a = m m g m +m T = mm m +m g (b) g(m m )=(m + m I=R ). T=T = (7 6 ) = = 79 Peiods di e by about.8% coud be detetected easiy.. (a) ()Book/Eat (gavitationa) Book/Tabe (eectostatic) Tabe/Suface (eectostatic) Tabe/Eat(gavitationa) ()Rocket/Eat (gavitationa) Rocket/Pume (moecua coisions - fundamentay eectostatic), Pume/Atmospee (moecua coisions) () Donkey/Road (fiction) Donkey/Cat (mecanica). (b) Unbaanced foce on inne wa opposite to nozze. (c) Road on donkey s ooves..5 5L=6 5L=6 i.7 (a)v = F t m (t=m x = F m ) m t n( m t) (b) F m t +.9 T bot = 56 NT mid = 7 NT top = 59 N Euation T (x) = g( + 7x). 58 m/s m/s, 77 m..7 v(t) = b n e bv + A bm t.9 v(t) = p mg=b tan p gb=mt. x(t) = m b og cos p p gb=mt = m b og e gb=mt +e (a) v T = p mg=d (b) = (m=d) n v + vt =v T (c) v g = v T v = p v + v T. (a) 8 m (b) 5 s..5 (a) 5587 m/s. p (b) v = v T exp( gx=v T ) (c) 8 m/s..7 y = mg b t + m b e bt=m.9 (a) 9 m/s, (b) 47 s p m/s..4 x =8GM p gb=mt
3 .45 (a)x(t) = D ep t + k (b)v = m x.47 6X s ' 4 min. Capte 4 C D e p t 4. L = ma _ + ma _ sin mga cos 4. L = m _z kz C 4.5 Euations of motion (M + m)x + M cos M _ sin = M + Mx cos + mg sin =. Constant of te motion (M + m) _x + M _ cos g sin 4.7 s = [m=(m+m)] cos and X m = m+m 4.9 L = M + m _s + (M + 4m)gs sin g sin [m=(m+m)] cos cos 4. (a) L = (M + m) X _ + m X s cos + m _s + mgs sin ks (b) p X = (m + M) X _ + m _s cos p s = m X _ cos + m _s. (c) (m + M) X + ms cos = mx cos + ms mg sin + ks = 4. (a) L = m _x + mg( x) k(d x) (b) mx + kx = kd mg o m k x = x C (c) p k=m 4.5 a p + sin 4.7 y = c p x c + d 4.9 = y p + y 4. i 4. H = p m mg cos _p = mg sin _ = p m. Capte J. 5. kr 5.5 (a) = = (b) ds = ^d+^d da = dd = = a(sin u cos v + cos u sin v) = a(cos u sin v + sin u cos v) = ds = a(sin u cos v + cos u sin v) = du^e u +a(cos u sin v + sin u cos v) = dv^e v + dz^k. 5.9 = ^e =a cos sin + sin +^e =a sin cos + cos +^e =a sin R A
4 5. (b) f = ^ 5.5 (a) T = (î+ˆ±+ˆk) ) 46 K/m. (b) 45 K. (c) Te ate of tempeatue decease is getting age te fute we move fom te oigin. 5.7 v max = m n (Q+Q ) 4 a N kg. 5. = G Mem jej R e 5.7 (a) F = A ^{x+^ y+^kz (x +y +z ) = (b) W = A= p x + y + z A oi p b +a at y = (c) F = Q 5.9 Q Q Q 4" 4" Gm 5. m 5. (b) 44 m/s, (c) +577 and x = 77 m. p 5.5 x(t) = v m x a sin p a m t y(t) = v p m y b sin Capte 6 6. (a) 5 m/s (b) 45 m/s. 6. v = m+m p m g 6.7 (a) v = v m = m 4= (b) F = + 4kvm k(vm) K = = 6.9 cos mm m M +m W () b m t =4 ti K wee k = d and K = m= = i m 4= + 4kvm t K = 6. kmv. 6.5 v(t) = gt + mg m k n m kt kg/s, 6 kg/s. 6.9 t =66 s = m p times te eigt fom wic it was dopped. 6. m/s., km/s. Capte 7 7. (b) Tota toue is zeo so angua momentum is constant. (c) Patices ave te same inea momentum, so angua momentum is independent of te coice of oigin. 7.5 = (=)v x F e t ^{ 7.7 d = DR ad/s. 7. M(R + R) 4
5 MR 7.7 Numbe of tuns =! I p + =4amg t = + p p! I + amg 7.9 (a)w = d mg (b)! f = p! i + gd=a (c) F = mg 7. (a)! = 9v= (b)! = Capte 8 8. Enegy. 8. Yes. Capte m/s. 9. G 9.5 GM R L v L p Z + R p (Z L) + R i Gm 9.7 d 9.9 G^ 9. Outside = GM g = GM ^ Inside g = GM R ^ = GM 9. (a) = R Gad GM R s = GM GM s = p z +a a + sin i i R (b) = min. 9.7 (a) Fo spee outside and inside, g = GM g = GM (b)fo se outside and inside, g = GM R 9.9 g = G (towads pane). 5k 9. 4G Fo te second ed, te mass density is a deta function, zeo eveywee except at te oigin. Capte. n (Å) E(eV) = (GM) = T 5= V V.7 (a) = m m +m = + m m +m m m (b)l = (m + m ) R _ + m +m _ + G mm (c) _ + G mm = d dt _ = (d) = G (m+m) 5
6 (e) 4 = G(m +m ) a.9 (a) = (a=)( + cos ) (b) =8 p ma 5 =K. km.. e = (v max v min ) = (v min + v max ) Capte. b =4m = k.. k = 4 4 N/m, b = kg/s..5 t p k b 6= m m.7 x + v =. x(t) = x + A!! d + c A!! d +A!! d cos!d t + (! d b=m) sin! d t.. x(t) = Ae t cos (! t + ) + F 4a m ( e at ).5! = k m+m m m.9 Noma mode feuencies! = m+m k m m,! = Capte. Wok = I _ f = T i sin4 m.5 (a) L = m _ ma f _ sin sin ft + m A f sin ft (b) = mg( Af cos + A cos i ft) sin cos ft + g Af cos ft + g (c)! =.7 (a) 85 s, (b) m T = p m=k 4k. pg F sin max.5 48 ad/sec..7 T = E mg cos cos.9 H = Capte p m + E mg p m sin + mg cos _p = _ = A! d b=m t e c t p m sin. m+m. a = a + ( +!) v +! +! (! E ).5 a cent = a co = V R ^x.7 d = g sin cos + = 79 cm..9.5 km Sout and.5 km East of te expected taget. It is in igt. seconds onge tan expected. m k m 6
7 . 767 km/.. m..5 ad..7 (a) v^ (b) v^ (c) (d) d = m (Not).. (a)! = Capte 4 k m (b) (t) = a + cos(! o t) v g e 4. tan = (tan tan ) T = [mg= (sin + cos tan )] T = [mg= (sin + cos tan )] cos cos o Mg at a point 86 aong te od. = (a) CW otation and inea acceeation aong te x axis. (b) newtons acting at a distance y = 866 m fom x axis. 4.5 cg = (a=) + y =4 =y = m K/m. Capte Te otation as a magnitude of 57 Te axis of otation is in te euatoia pane and diected at an ange of west of Geenwic. = p 5 5= p = p 4 5 = p = p 4 5 = p A (a) A e ection toug te x-axis. (b) A otation of 8 about te z-axis. 5. = p and = = 5 = p 5 Capte 6 = p 5 = p 5 p p = 5 = 5 = p 5 = p Ma 5Ma =p = p =p = p A i 6.9 T = I _ + _ sin + I _ + _ cos L = I _ sin sin ^e + I _ sin cos ^e + I _ + _ cos ^e 6. (a) p = I cos! p = I! (cos cos ) V () = I! I + mgd cos + sin I! E = mgd cos + I! 7
8 (b) cos = 4 cos + 4 i = 6. _ = 8 ad/s. Capte 7 7. y(x t) = A sin x L cos p F= L t 7.5 y(x t) ' L 4R + P L n n R ( )n cos nx L cos! nt wee! n = nc=l i @y = (b) m + b _ m + F m =L m = (c) m = e bt= (A m sin! mt+b m cos! mt) wee! m = 7.9 (a) Q n + F n Q n = ( b) Q n = A n cos F nt+b n sin Capte 8 m L F F nt 8. Assume x and x ae measued in opposite diections fom te euiibium points. Mass matix is m and te potentia matix is k 6 8.! = k m 8 () = p 84m 6 () = p 6m 6 k 8.5 m k m k m 8.7 (a) L = m( _ + _ ) k + k k + k m k m = + k m k m = 8.9 (t) = C cos(! t + ) + C cos(! t + ) + K sin!t (t) = C cos(! t + ) C cos(! t + ) + K sin!t m + M M 8. M = M m + M k V = k! k = m k m m m+m 8. (a) L = m P N i= _ mg P N i i= i k P N i= (b) m i + mg i + k i k i+ + i = Capte 9 (c)! = g + 4 k ka m sin b 4 i i + i+ i i 9. (a) x = 75 m, t = 5 ns. (b) x = 74 m, t = 7 9 s. 9.5 (a) x = 7 8 m, t = 87 sec. 8
9 (b) x = m, t = 44 s. p c c cm. 9.5 (a) 8c (b) 55s 9.7 (b)f = 5 (c) 964 (d) Te same amount of igt is concentated into a smae cone. 9.9 v = p c = 77c T = 44m c 9. T = 5 9 J, p = 499 kg m/s. 9. (a) p f = m c (b)v f = 55c (c) cassicay, v f = 4c 9.5 g. 9.7 Factiona cange in aea = 6 9
 Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
Hoizontal Cicula Motion 1. A paticle of mass m is tied to a light sting and otated with a speed v along a cicula path of adius. If T is tension in the sting and mg is gavitational foce on the paticle then,
c) (6) Assuming the tires do not skid, what coefficient of static friction between tires and pavement is needed?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 10, 2012 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs
 Capte Functions and Gaps Section.... 6 7. 6 8 8 6. 6 6 8 8.... 6.. 6. n n n n n n n 6 n 6 n n 7. 8 7 7..8..8 8.. 8. a b ± ± 6 c ± 6 ± 8 8 o 8 6. 8y 8y 7 8y y 8y y 8 o y y. 7 7 o 7 7 Capte : Functions and
Capte Functions and Gaps Section.... 6 7. 6 8 8 6. 6 6 8 8.... 6.. 6. n n n n n n n 6 n 6 n n 7. 8 7 7..8..8 8.. 8. a b ± ± 6 c ± 6 ± 8 8 o 8 6. 8y 8y 7 8y y 8y y 8 o y y. 7 7 o 7 7 Capte : Functions and
Quiz 6--Work, Gravitation, Circular Motion, Torque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible)
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Quiz 6--Wok, Gavitation, Cicula Motion, Toque. (60 pts available, 50 points possible) Multiple Choice, 2 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement o answes
b) (5) What is the magnitude of the force on the 6.0-kg block due to the contact with the 12.0-kg block?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
Geneal Physics I Exam 2 - Chs. 4,5,6 - Foces, Cicula Motion, Enegy Oct. 13, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults with
PHYS 1114, Lecture 21, March 6 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
PHYS 1114, Lectue 21, Mach 6 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, being eplaced by the common exam Tuesday, Mach 7, 5:30 PM. A eview and Q&A session is scheduled instead duing class time. 2 Exam
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 5 Lectue 5 Centa Foce Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamiton s Pincipe Action intega is stationay fo the actua path Deived Lagange s Equations Used cacuus of vaiation
Mechanics Physics 5 Lectue 5 Centa Foce Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamiton s Pincipe Action intega is stationay fo the actua path Deived Lagange s Equations Used cacuus of vaiation
Exam 3: Equation Summary
 MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8. TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t = Exam 3: Equation ummay = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ =,P dp F P τ =,P
MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8. TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t = Exam 3: Equation ummay = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ =,P dp F P τ =,P
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 5 Lectue 5 Centa Foce Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamiton s Pincipe Action intega is stationay fo the actua path Deived Lagange s Equations Used cacuus of vaiation
Mechanics Physics 5 Lectue 5 Centa Foce Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Intoduced Hamiton s Pincipe Action intega is stationay fo the actua path Deived Lagange s Equations Used cacuus of vaiation
Circular Motion. Mr. Velazquez AP/Honors Physics
 Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Cicula Motion M. Velazquez AP/Honos Physics Objects in Cicula Motion Accoding to Newton s Laws, if no foce acts on an object, it will move with constant speed in a constant diection. Theefoe, if an object
Physics 1C Fall 2011: Quiz 1 Version A 1
 Physics 1C Fall 2011: Quiz 1 Vesion A 1 Depatment of Physics Physics 1C Fall Quate - 2011 D. Mak Paddock INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Pint you full name below LAST NAME FIRST NAME MIDDLE INITIAL 2. You code numbe
Physics 1C Fall 2011: Quiz 1 Vesion A 1 Depatment of Physics Physics 1C Fall Quate - 2011 D. Mak Paddock INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Pint you full name below LAST NAME FIRST NAME MIDDLE INITIAL 2. You code numbe
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 6 Kepe Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Discussed enegy consevation Defined enegy function h Conseved if Conditions fo h = E Stated discussing Centa Foce Pobems Reduced
Mechanics Physics 151 Lectue 6 Kepe Pobem (Chapte 3) What We Did Last Time Discussed enegy consevation Defined enegy function h Conseved if Conditions fo h = E Stated discussing Centa Foce Pobems Reduced
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homework (Answers)
 Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Physics 1114: Unit 5 Hand-out Homewok (Answes) Poblem set 1 1. The flywheel on an expeimental bus is otating at 420 RPM (evolutions pe minute). To find (a) the angula velocity in ad/s (adians/second),
Physics 181. Assignment 4
 Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Physics 181 Assignment 4 Solutions 1. A sphee has within it a gavitational field given by g = g, whee g is constant and is the position vecto of the field point elative to the cente of the sphee. This
Exam 3: Equation Summary
 MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8. TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t = Exam 3: Equation ummay = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ =,P dp F P τ =,P
MAACHUETT INTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Depatment of Physics Physics 8. TEAL Fall Tem 4 Momentum: p = mv, F t = p, Fext ave t= t f t = Exam 3: Equation ummay = Impulse: I F( t ) = p Toque: τ =,P dp F P τ =,P
Central Force Motion
 Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
Cental Foce Motion Cental Foce Poblem Find the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): m1m F 1, ( ) =! G ˆ Linea estoing foce: F 1, ( ) =! k ˆ Two
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 08. Textbook Sections Lecture 8 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
PHYSICS 0 Lectue 08 Cicula Motion Textbook Sections 5.3 5.5 Lectue 8 Pudue Univesity, Physics 0 1 Oveview Last Lectue Cicula Motion θ angula position adians ω angula velocity adians/second α angula acceleation
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam)
 (Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
Extra notes for circular motion: Circular motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and
 Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
Exta notes fo cicula motion: Cicula motion : v keeps changing, maybe both speed and diection ae changing. At least v diection is changing. Hence a 0. Acceleation NEEDED to stay on cicula obit: a cp v /,
 Rotatoy Motion Hoizontal Cicula Motion In tanslatoy motion, evey point in te body follows te pat of its pecedin one wit same velocity includin te cente of mass In otatoy motion, evey point move wit diffeent
Rotatoy Motion Hoizontal Cicula Motion In tanslatoy motion, evey point in te body follows te pat of its pecedin one wit same velocity includin te cente of mass In otatoy motion, evey point move wit diffeent
b) (5) What average force magnitude was applied by the students working together?
 Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Geneal Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibium Nov. 3, 2010 Name Rec. Inst. Rec. Time Fo full cedit, make you wok clea to the gade. Show fomulas used, essential steps, and esults
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION
 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion Chapte 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFOM CICULA MOTION PEVIEW An object which is moing in a cicula path with a constant speed is said to be in unifom cicula motion. Fo an object
Physics Courseware Electromagnetism
 Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
Pysics Cousewae lectomagnetism lectic field Poblem.- a) Find te electic field at point P poduced by te wie sown in te figue. Conside tat te wie as a unifom linea cage distibution of λ.5µ C / m b) Find
Newton s Laws, Kepler s Laws, and Planetary Orbits
 Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
Newton s Laws, Keple s Laws, and Planetay Obits PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TUESDAY AT START OF LECTURE 28 Septembe 2017 ASTRONOMY 111 FALL 2017 1 Newton s & Keple s laws and planetay obits Unifom cicula motion
When a mass moves because of a force, we can define several types of problem.
 Mechanics Lectue 4 3D Foces, gadient opeato, momentum 3D Foces When a mass moves because of a foce, we can define seveal types of poblem. ) When we know the foce F as a function of time t, F=F(t). ) When
Mechanics Lectue 4 3D Foces, gadient opeato, momentum 3D Foces When a mass moves because of a foce, we can define seveal types of poblem. ) When we know the foce F as a function of time t, F=F(t). ) When
Experiment 09: Angular momentum
 Expeiment 09: Angula momentum Goals Investigate consevation of angula momentum and kinetic enegy in otational collisions. Measue and calculate moments of inetia. Measue and calculate non-consevative wok
Expeiment 09: Angula momentum Goals Investigate consevation of angula momentum and kinetic enegy in otational collisions. Measue and calculate moments of inetia. Measue and calculate non-consevative wok
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Central Force Problems I
 1 PHYS 705: Cassica Mechanics Centa Foce Pobems I Two-Body Centa Foce Pobem Histoica Backgound: Kepe s Laws on ceestia bodies (~1605) - Based his 3 aws on obsevationa data fom Tycho Bahe - Fomuate his
1 PHYS 705: Cassica Mechanics Centa Foce Pobems I Two-Body Centa Foce Pobem Histoica Backgound: Kepe s Laws on ceestia bodies (~1605) - Based his 3 aws on obsevationa data fom Tycho Bahe - Fomuate his
Physics C Rotational Motion Name: ANSWER KEY_ AP Review Packet
 Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Linea and angula analogs Linea Rotation x position x displacement v velocity a T tangential acceleation Vectos in otational motion Use the ight hand ule to detemine diection of the vecto! Don t foget centipetal
Rotational Motion. Lecture 6. Chapter 4. Physics I. Course website:
 Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Lectue 6 Chapte 4 Physics I Rotational Motion Couse website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andiy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Today we ae going to discuss: Chapte 4: Unifom Cicula Motion: Section 4.4 Nonunifom Cicula
Coordinate Geometry. = k2 e 2. 1 e + x. 1 e. ke ) 2. We now write = a, and shift the origin to the point (a, 0). Referred to
 Coodinate Geomet Conic sections These ae pane cuves which can be descibed as the intesection of a cone with panes oiented in vaious diections. It can be demonstated that the ocus of a point which moves
Coodinate Geomet Conic sections These ae pane cuves which can be descibed as the intesection of a cone with panes oiented in vaious diections. It can be demonstated that the ocus of a point which moves
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS NAME & LOGO XII-JEE (MAINS)-YEAR Topic Names: Cicula motion Test Numbe Test Booklet No. 000001 110001 Wite/Check this Code on you Answe Sheet : IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS : Wite
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS NAME & LOGO XII-JEE (MAINS)-YEAR Topic Names: Cicula motion Test Numbe Test Booklet No. 000001 110001 Wite/Check this Code on you Answe Sheet : IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS : Wite
Chap 5. Circular Motion: Gravitation
 Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
Chap 5. Cicula Motion: Gavitation Sec. 5.1 - Unifom Cicula Motion A body moves in unifom cicula motion, if the magnitude of the velocity vecto is constant and the diection changes at evey point and is
KEPLER S LAWS AND PLANETARY ORBITS
 KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
KEPE S AWS AND PANETAY OBITS 1. Selected popeties of pola coodinates and ellipses Pola coodinates: I take a some what extended view of pola coodinates in that I allow fo a z diection (cylindical coodinates
Recall from last week:
 Recall fom last week: Length of a cuve '( t) dt b Ac length s( t) a a Ac length paametization ( s) with '( s) 1 '( t) Unit tangent vecto T '(s) '( t) dt Cuvatue: s ds T t t t t t 3 t ds u du '( t) dt Pincipal
Recall fom last week: Length of a cuve '( t) dt b Ac length s( t) a a Ac length paametization ( s) with '( s) 1 '( t) Unit tangent vecto T '(s) '( t) dt Cuvatue: s ds T t t t t t 3 t ds u du '( t) dt Pincipal
Problem Set 5: Universal Law of Gravitation; Circular Planetary Orbits
 Poblem Set 5: Univesal Law of Gavitation; Cicula Planetay Obits Design Engineeing Callenge: Te Big Dig.007 Contest Evaluation of Scoing Concepts: Spinne vs. Plowe PROMBLEM 1: Daw a fee-body-diagam of a
Poblem Set 5: Univesal Law of Gavitation; Cicula Planetay Obits Design Engineeing Callenge: Te Big Dig.007 Contest Evaluation of Scoing Concepts: Spinne vs. Plowe PROMBLEM 1: Daw a fee-body-diagam of a
Physics 111 Lecture 5 Circular Motion
 Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Physics 111 Lectue 5 Cicula Motion D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Multiple Objects q A block of mass m1 on a ough, hoizontal suface is connected to a ball of mass m by a lightweight
Answers to test yourself questions
 Answes to test youself questions opic. Cicula motion π π a he angula speed is just ω 5. 7 ad s. he linea speed is ω 5. 7 3. 5 7. 7 m s.. 4 b he fequency is f. 8 s.. 4 3 a f. 45 ( 3. 5). m s. 3 a he aeage
Answes to test youself questions opic. Cicula motion π π a he angula speed is just ω 5. 7 ad s. he linea speed is ω 5. 7 3. 5 7. 7 m s.. 4 b he fequency is f. 8 s.. 4 3 a f. 45 ( 3. 5). m s. 3 a he aeage
Objects usually are charged up through the transfer of electrons from one object to the other.
 1 Pat 1: Electic Foce 1.1: Review of Vectos Review you vectos! You should know how to convet fom pola fom to component fom and vice vesa add and subtact vectos multiply vectos by scalas Find the esultant
1 Pat 1: Electic Foce 1.1: Review of Vectos Review you vectos! You should know how to convet fom pola fom to component fom and vice vesa add and subtact vectos multiply vectos by scalas Find the esultant
cos kd kd 2 cosθ = π 2 ± nπ d λ cosθ = 1 2 ± n N db
 . (Balanis 6.43) You can confim tat AF = e j kd cosθ + e j kd cosθ N = cos kd cosθ gives te same esult as (6-59) and (6-6), fo a binomial aay wit te coefficients cosen as in section 6.8.. Tis single expession
. (Balanis 6.43) You can confim tat AF = e j kd cosθ + e j kd cosθ N = cos kd cosθ gives te same esult as (6-59) and (6-6), fo a binomial aay wit te coefficients cosen as in section 6.8.. Tis single expession
PROGRESS TEST-4 GR, GRK & GRS JEE MAIN PATTERN
 PROGRESS TEST- GR, GRK & GRS JEE MIN PTTERN Test Date: -7-7 [ ] PT-IV (Main) GR, GRK & GRS_.7.7 PHYSIS. () mg mg m m. () If acceleation of block is a upwad along the incline, then acceleation of block
PROGRESS TEST- GR, GRK & GRS JEE MIN PTTERN Test Date: -7-7 [ ] PT-IV (Main) GR, GRK & GRS_.7.7 PHYSIS. () mg mg m m. () If acceleation of block is a upwad along the incline, then acceleation of block
AP Physics 1 - Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test (Multiple Choice Section) Answer Section
 AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
AP Physics 1 - Cicula Motion and Gaitation Pactice est (Multiple Choice Section) Answe Section MULIPLE CHOICE 1. B he centipetal foce must be fiction since, lacking any fiction, the coin would slip off.
Exam 3, vers Physics Spring, 2003
 1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
Chapter 4. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Chapte 4 Newton s Laws of Motion 4.1 Foces and Inteactions A foce is a push o a pull. It is that which causes an object to acceleate. The unit of foce in the metic system is the Newton. Foce is a vecto
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Problem Solutions
 Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
Magnetic Dipoles Challenge Poblem Solutions Poblem 1: Cicle the coect answe. Conside a tiangula loop of wie with sides a and b. The loop caies a cuent I in the diection shown, and is placed in a unifom
GCSE: Volumes and Surface Area
 GCSE: Volumes and Suface Aea D J Fost (jfost@tiffin.kingston.sc.uk) www.dfostmats.com GCSE Revision Pack Refeence:, 1, 1, 1, 1i, 1ii, 18 Last modified: 1 st August 01 GCSE Specification. Know and use fomulae
GCSE: Volumes and Suface Aea D J Fost (jfost@tiffin.kingston.sc.uk) www.dfostmats.com GCSE Revision Pack Refeence:, 1, 1, 1, 1i, 1ii, 18 Last modified: 1 st August 01 GCSE Specification. Know and use fomulae
Gravitation. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapte 12 Gavitation PowePoint Lectues fo Univesity Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roge A. Feedman Lectues by James Pazun Modified by P. Lam 5_31_2012 Goals fo Chapte 12 To study Newton s Law
Chapter 13 Gravitation
 Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Chapte 13 Gavitation In this chapte we will exploe the following topics: -Newton s law of gavitation, which descibes the attactive foce between two point masses and its application to extended objects
Physics Spring 2012 Announcements: Mar 07, 2012
 Physics 00 - Sping 01 Announcements: Ma 07, 01 HW#6 due date has been extended to the moning of Wed. Ma 1. Test # (i. Ma ) will cove only chaptes 0 and 1 All of chapte will be coveed in Test #4!!! Test
Physics 00 - Sping 01 Announcements: Ma 07, 01 HW#6 due date has been extended to the moning of Wed. Ma 1. Test # (i. Ma ) will cove only chaptes 0 and 1 All of chapte will be coveed in Test #4!!! Test
OSCILLATIONS AND GRAVITATION
 1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
1. SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple hamonic motion is any motion that is equivalent to a single component of unifom cicula motion. In this situation the velocity is always geatest in the middle of the motion,
Lecture 52. Dynamics - Variable Acceleration
 Dynamics - Vaiable Acceleation Lectue 5 Example. The acceleation due to avity at a point outside the eath is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance x fom the cente, i.e., ẍ = k x. Nelectin ai
Dynamics - Vaiable Acceleation Lectue 5 Example. The acceleation due to avity at a point outside the eath is invesely popotional to the squae of the distance x fom the cente, i.e., ẍ = k x. Nelectin ai
CIRCULAR MOTION. Particle moving in an arbitrary path. Particle moving in straight line
 1 CIRCULAR MOTION 1. ANGULAR DISPLACEMENT Intoduction: Angle subtended by position vecto of a paticle moving along any abitay path w..t. some fixed point is called angula displacement. (a) Paticle moving
1 CIRCULAR MOTION 1. ANGULAR DISPLACEMENT Intoduction: Angle subtended by position vecto of a paticle moving along any abitay path w..t. some fixed point is called angula displacement. (a) Paticle moving
Motions and Coordinates
 Chapte Kinematics of Paticles Motions and Coodinates Motion Constained motion Unconstained motion Coodinates Used to descibe the motion of paticles 1 ectilinea motion (1-D) Motion Plane cuvilinea motion
Chapte Kinematics of Paticles Motions and Coodinates Motion Constained motion Unconstained motion Coodinates Used to descibe the motion of paticles 1 ectilinea motion (1-D) Motion Plane cuvilinea motion
PHYS Summer Professor Caillault Homework Solutions. Chapter 9
 PHYS - Summe 007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 9 3. Pictue the Poblem The owne walks slowly towad the notheast while the cat uns eastwad and the dog uns nothwad. Stategy Sum the momenta
PHYS - Summe 007 - Pofesso Caillault Homewok Solutions Chapte 9 3. Pictue the Poblem The owne walks slowly towad the notheast while the cat uns eastwad and the dog uns nothwad. Stategy Sum the momenta
Unit 4 Circular Motion and Centripetal Force
 Name: Unit 4 Cicula Motion and Centipetal Foce H: Gading: Show all wok, keeping it neat and oganized. Show equations used and include all units. Vocabulay Peiod: the time it takes fo one complete evolution
Name: Unit 4 Cicula Motion and Centipetal Foce H: Gading: Show all wok, keeping it neat and oganized. Show equations used and include all units. Vocabulay Peiod: the time it takes fo one complete evolution
ω = θ θ o = θ θ = s r v = rω
 Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
Unifom Cicula Motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant(unifom) speed in a cicula path. Fist we must define the angula displacement and angula velocity The angula displacement
A moving charged particle creates a magnetic field vector at every point in space except at its position.
 1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
1 Pat 3: Magnetic Foce 3.1: Magnetic Foce & Field A. Chaged Paticles A moving chaged paticle ceates a magnetic field vecto at evey point in space ecept at its position. Symbol fo Magnetic Field mks units
Ch04: Motion in two and three dimensions (2D and 3D)
 Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
Ch4: Motion in two and thee dimensions (D and 3D) Displacement, elocity and acceleation ectos Pojectile motion Cicula motion Relatie motion 4.: Position and displacement Position of an object in D o 3D
RAO IIT ACADEMY / NSEP Physics / Code : P 152 / Solutions NATIONAL STANDARD EXAMINATION IN PHYSICS SOLUTIONS
 RAO ACADEMY / NSEP Physics / Code : P 5 / Solutions NAONAL SANDARD EXAMNAON N PHYSCS - 5 SOLUONS RAO ACADEMY / NSEP Physics / Code : P 5 / Solutions NSEP SOLUONS (PHYSCS) CODE - P 5 ANSWER KEY & SOLUONS.
RAO ACADEMY / NSEP Physics / Code : P 5 / Solutions NAONAL SANDARD EXAMNAON N PHYSCS - 5 SOLUONS RAO ACADEMY / NSEP Physics / Code : P 5 / Solutions NSEP SOLUONS (PHYSCS) CODE - P 5 ANSWER KEY & SOLUONS.
Chapter 13 Solutions
 Chapter 3 Solutions 3. x = (4.00 m) cos (3.00πt + π) Compare this with x = A cos (ωt + φ) to find (a) ω = πf = 3.00π or f =.50 Hz T = f = 0.667 s A = 4.00 m (c) φ = π rad (d) x(t = 0.50 s) = (4.00 m) cos
Chapter 3 Solutions 3. x = (4.00 m) cos (3.00πt + π) Compare this with x = A cos (ωt + φ) to find (a) ω = πf = 3.00π or f =.50 Hz T = f = 0.667 s A = 4.00 m (c) φ = π rad (d) x(t = 0.50 s) = (4.00 m) cos
Between any two masses, there exists a mutual attractive force.
 YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
YEAR 12 PHYSICS: GRAVITATION PAST EXAM QUESTIONS Name: QUESTION 1 (1995 EXAM) (a) State Newton s Univesal Law of Gavitation in wods Between any two masses, thee exists a mutual attactive foce. This foce
Physics 101 Lecture 6 Circular Motion
 Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
Physics 101 Lectue 6 Cicula Motion Assist. Pof. D. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Depatment www.aovgun.com Equilibium, Example 1 q What is the smallest value of the foce F such that the.0-kg block will not slide
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 University of Wyoming 14 March ( Day!) points
 PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 2 Univesity of Wyoming 14 Mach ( Day!) 2013 150 points This test is open-note and closed-book. Calculatos ae pemitted but computes ae not. No collaboation, consultation, o communication
PS113 Chapter 5 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
 PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
PS113 Chapte 5 Dynamics of Unifom Cicula Motion 1 Unifom cicula motion Unifom cicula motion is the motion of an object taveling at a constant (unifom) speed on a cicula path. The peiod T is the time equied
1 2 U CV. K dq I dt J nqv d J V IR P VI
 o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
1 Solution to Homework 4
 Solution to Homework Section. 5. The characteristic equation is r r + = (r )(r ) = 0 r = or r =. y(t) = c e t + c e t y = c e t + c e t. y(0) =, y (0) = c + c =, c + c = c =, c =. To find the maximum value
Solution to Homework Section. 5. The characteristic equation is r r + = (r )(r ) = 0 r = or r =. y(t) = c e t + c e t y = c e t + c e t. y(0) =, y (0) = c + c =, c + c = c =, c =. To find the maximum value
Recap. Centripetal acceleration: v r. a = m/s 2 (towards center of curvature)
 a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
a = c v 2 Recap Centipetal acceleation: m/s 2 (towads cente of cuvatue) A centipetal foce F c is equied to keep a body in cicula motion: This foce poduces centipetal acceleation that continuously changes
Electric Potential and Energy
 Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
Electic Potential and Enegy Te polem: A solid spee of te adius R is omogeneously caged wit te cage Q and put inside an infinite ollow cylinde. Te cylinde inne and oute adii ae a and, R < a
7.2. Coulomb s Law. The Electric Force
 Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Coulomb s aw Recall that chaged objects attact some objects and epel othes at a distance, without making any contact with those objects Electic foce,, o the foce acting between two chaged objects, is somewhat
Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room.
![Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room. Multiple choice questions [100 points] As shown in the figure, a mass M is hanging by three massless strings from the ceiling of a room.](/thumbs/94/119386670.jpg) Multiple choice questions [00 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefully. Fill the coect ule on you scanton sheet. Each coect answe is woth 4 points. Each question has exactly
Multiple choice questions [00 points] Answe all of the following questions. Read each question caefully. Fill the coect ule on you scanton sheet. Each coect answe is woth 4 points. Each question has exactly
Cartesian Coordinate System and Vectors
 Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
Catesian Coodinate System and Vectos Coodinate System Coodinate system: used to descibe the position of a point in space and consists of 1. An oigin as the efeence point 2. A set of coodinate axes with
Physics 235 Chapter 5. Chapter 5 Gravitation
 Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Chapte 5 Gavitation In this Chapte we will eview the popeties of the gavitational foce. The gavitational foce has been discussed in geat detail in you intoductoy physics couses, and we will pimaily focus
Uniform Circular Motion
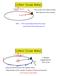 Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
Unifom Cicula Motion constant speed Pick a point in the objects motion... What diection is the velocity? HINT Think about what diection the object would tavel if the sting wee cut Unifom Cicula Motion
m1 m2 M 2 = M -1 L 3 T -2
 GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
GAVITATION Newton s Univesal law of gavitation. Evey paticle of matte in this univese attacts evey othe paticle with a foce which vaies diectly as the poduct of thei masses and invesely as the squae of
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION
 MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
MAGNETIC FIELD INTRODUCTION It was found when a magnet suspended fom its cente, it tends to line itself up in a noth-south diection (the compass needle). The noth end is called the Noth Pole (N-pole),
21 MAGNETIC FORCES AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
CHAPTER 1 MAGNETIC ORCES AND MAGNETIC IELDS ANSWERS TO OCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS 1. (d) Right-Hand Rule No. 1 gives the diection of the magnetic foce as x fo both dawings A and. In dawing C, the velocity
7 Circular Motion. 7-1 Centripetal Acceleration and Force. Period, Frequency, and Speed. Vocabulary
 7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
7 Cicula Motion 7-1 Centipetal Acceleation and Foce Peiod, Fequency, and Speed Vocabulay Vocabulay Peiod: he time it takes fo one full otation o evolution of an object. Fequency: he numbe of otations o
Translation and Rotation Kinematics
 Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
Tanslation and Rotation Kinematics Oveview: Rotation and Tanslation of Rigid Body Thown Rigid Rod Tanslational Motion: the gavitational extenal foce acts on cente-of-mass F ext = dp sy s dt dv total cm
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014
 Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Page 1 of 12 Please go to the next page... Sample Midterm 1 ODE Math 3331 (Summer 2014) June 16, 2014 50 points 1. Find the solution of the following initial-value problem 1. Solution (S.O.V) dt = ty2,
Chapter 13: Gravitation
 v m m F G Chapte 13: Gavitation The foce that makes an apple fall is the same foce that holds moon in obit. Newton s law of gavitation: Evey paticle attacts any othe paticle with a gavitation foce given
v m m F G Chapte 13: Gavitation The foce that makes an apple fall is the same foce that holds moon in obit. Newton s law of gavitation: Evey paticle attacts any othe paticle with a gavitation foce given
Honors Classical Physics I
 Hono Claical Phyic I PHY141 Lectue 9 Newton Law of Gavity Pleae et you Clicke Channel to 1 9/15/014 Lectue 9 1 Newton Law of Gavity Gavitational attaction i the foce that act between object that have a
Hono Claical Phyic I PHY141 Lectue 9 Newton Law of Gavity Pleae et you Clicke Channel to 1 9/15/014 Lectue 9 1 Newton Law of Gavity Gavitational attaction i the foce that act between object that have a
Chapter 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements
 Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Chapte 2: Basic Physics and Math Supplements Decembe 1, 215 1 Supplement 2.1: Centipetal Acceleation This supplement expands on a topic addessed on page 19 of the textbook. Ou task hee is to calculate
Easy. r p 2 f : r p 2i. r p 1i. r p 1 f. m blood g kg. P8.2 (a) The momentum is p = mv, so v = p/m and the kinetic energy is
 Chapte 8 Homewok Solutions Easy P8. Assume the velocity of the blood is constant ove the 0.60 s. Then the patient s body and pallet will have a constant velocity of 6 0 5 m 3.75 0 4 m/ s 0.60 s in the
Chapte 8 Homewok Solutions Easy P8. Assume the velocity of the blood is constant ove the 0.60 s. Then the patient s body and pallet will have a constant velocity of 6 0 5 m 3.75 0 4 m/ s 0.60 s in the
Escape Velocity. GMm ] B
![Escape Velocity. GMm ] B Escape Velocity. GMm ] B](/thumbs/84/90630003.jpg) 1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
1 PHY2048 Mach 31, 2006 Escape Velocity Newton s law of gavity: F G = Gm 1m 2 2, whee G = 667 10 11 N m 2 /kg 2 2 3 10 10 N m 2 /kg 2 is Newton s Gavitational Constant Useful facts: R E = 6 10 6 m M E
Central Force Problem. Central Force Motion. Two Body Problem: Center of Mass Coordinates. Reduction of Two Body Problem 8.01 W14D1. + m 2. m 2.
 Cental oce Poblem ind the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Cental oce Motion 8.01 W14D1 Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): 1 1, ( ) G mm Linea estoing foce: ( ) k 1, Two Body
Cental oce Poblem ind the motion of two bodies inteacting via a cental foce. Cental oce Motion 8.01 W14D1 Examples: Gavitational foce (Keple poblem): 1 1, ( ) G mm Linea estoing foce: ( ) k 1, Two Body
Name. Date. Period. Engage Examine the pictures on the left. 1. What is going on in these pictures?
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 9.a Unifom Cicula Motion Outcomes 1. Define unifom cicula motion. 2. Detemine the tangential velocity of an object moving with unifom cicula motion. 3. Detemine the centipetal acceleation
AP Physics 1 Lesson 9.a Unifom Cicula Motion Outcomes 1. Define unifom cicula motion. 2. Detemine the tangential velocity of an object moving with unifom cicula motion. 3. Detemine the centipetal acceleation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physical insight in the sound geneation mechanism can be gained by consideing simple analytical solutions to the wave equation. One example is to conside acoustic
ELECTROSTATICS::BHSEC MCQ 1. A. B. C. D.
 ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
ELETROSTATIS::BHSE 9-4 MQ. A moving electic chage poduces A. electic field only. B. magnetic field only.. both electic field and magnetic field. D. neithe of these two fields.. both electic field and magnetic
Spring 2001 Physics 2048 Test 3 solutions
 Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
Sping 001 Physics 048 Test 3 solutions Poblem 1. (Shot Answe: 15 points) a. 1 b. 3 c. 4* d. 9 e. 8 f. 9 *emembe that since KE = ½ mv, KE must be positive Poblem (Estimation Poblem: 15 points) Use momentum-impulse
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 10-1 DESCRIBING FIELDS Essential Idea: Electic chages and masses each influence the space aound them and that influence can be epesented
10. Force is inversely proportional to distance between the centers squared. R 4 = F 16 E 11.
 NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
NSWRS - P Physics Multiple hoice Pactice Gavitation Solution nswe 1. m mv Obital speed is found fom setting which gives v whee M is the object being obited. Notice that satellite mass does not affect obital
Physics 4A Chapter 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane
 Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
Physics 4A Chapte 8: Dynamics II Motion in a Plane Conceptual Questions and Example Poblems fom Chapte 8 Conceptual Question 8.5 The figue below shows two balls of equal mass moving in vetical cicles.
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Central Force Problems II
 PHYS 75: Cassica Mechanics Centa Foce Pobems II Obits in Centa Foce Pobem Sppose we e inteested moe in the shape of the obit, (not necessay the time evotion) Then, a sotion fo = () o = () wod be moe sef!
PHYS 75: Cassica Mechanics Centa Foce Pobems II Obits in Centa Foce Pobem Sppose we e inteested moe in the shape of the obit, (not necessay the time evotion) Then, a sotion fo = () o = () wod be moe sef!
EELE 3331 Electromagnetic I Chapter 4. Electrostatic fields. Islamic University of Gaza Electrical Engineering Department Dr.
 EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
EELE 3331 Electomagnetic I Chapte 4 Electostatic fields Islamic Univesity of Gaza Electical Engineeing Depatment D. Talal Skaik 212 1 Electic Potential The Gavitational Analogy Moving an object upwad against
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Circular-Rotational Motion Mock Exam. Instructions: (92 points) Answer the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK.
 AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
AP Physics C Sping, 2017 Cicula-Rotational Motion Mock Exam Name: Answe Key M. Leonad Instuctions: (92 points) Answe the following questions. SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK. ( ) 1. A stuntman dives a motocycle
6.4 Period and Frequency for Uniform Circular Motion
 6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
6.4 Peiod and Fequency fo Unifom Cicula Motion If the object is constained to move in a cicle and the total tangential foce acting on the total object is zeo, F θ = 0, then (Newton s Second Law), the tangential
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) ,
 R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
R Pena Towe, Road No, Contactos Aea, Bistupu, Jamshedpu 8, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com IIT JEE Mathematics Pape II PART III MATHEMATICS SECTION I Single Coect Answe Type This section contains 8 multiple
Momentum is conserved if no external force
 Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
Goals: Lectue 13 Chapte 9 v Employ consevation of momentum in 1 D & 2D v Examine foces ove time (aka Impulse) Chapte 10 v Undestand the elationship between motion and enegy Assignments: l HW5, due tomoow
