Effect of Structural Design Parameters of a Six-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Using Full Factorial Design
|
|
|
- Emily O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the 3rd RI International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics October 7-9, 2015, Tehran, Iran Effect of tructural Design Parameters of a ix-axis Force/Torque ensor Using Full Factorial Design Amin Valizadeh, Alireza Akbarzadeh, Mohammad Hosein Tashakori Heravi Center of Excellence on oft Computing and Intelligent Information Processing (CIIP) Mechanical Engineering Department Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Mashhad, Iran amin.valizadeh.66@gmail.com, ali_akbarzadeh_t@yahoo.com, mohamad.tashakori@gmail.com Abstract Force and torque sensors various applicabilities have raised great interest among scientists for decades. The optimal combination of design variables is a difficult task as it is affected by several input parameters. This paper presents an investigation on the effect of thickness, width and length of elastic cross-beams of the six-axis force sensor on the cross coupling interference. The finite element analysis is carried out for full factorial design experiments and the signal to noise ratio as well as analysis of variance is calculated and discussed. Keywords force and torque sensor; cross beams, full factorial design; signal to noise ratio; analysis of variance I. INTRODUCTION. The cross-beams force and torque sensors interests have been increased due to their benefits over the years. Various types of cross-beams force sensors were considered and developed in the 1980s [1, 2]. In the 1990s the field of studies mostly aims the industrial applications to perform a variety of tasks [3, ]. Due to the expensive rate price of the six-axis F/T sensor, its application has been mainly conned to the robotics eld, since precise force control is specifically essential for industrial manipulators. However, the development of economical cross-beams F/T sensors has strongly encouraged in various fields such as humanoid robots, biomechanics and medical applications [5, 6, 7]. Parallel and radial plates are extensively carried out as the main sensing elements of multi- component F/T sensors [8, 9]. Kim developed several multi- axis F/T sensors with an interference error of less than 3%, but they cannot be implemented on some applications for lack of proper size design [10, 11]. The United tates and Japan have already advanced multiple multi-axis F/T sensors and they also lack affordable price [12, 13]. Cross-beams six-axis F/T sensors commonly categorized into two types according to the relationship between the applied force and the output signal: mechanically coupled sensors which the output signal must be calibrated with a relatively complicated calibration matrix, and mechanically decoupled sensors which the output signal of a bridge selectively responds to a specic force or moment component [1, 15]. In this paper, the cross coupling is conceptually defined as the ratio of unfavorable signal to the intended signal at a given bridge circuit according to pure force components. The cross coupling term yields the objective optimization equation which is carried out for different design parameters using full factorial design. II. IX-AXI CRO-BEAM FORCE/TORQUE ENOR A. Mechanical tructure A typical cross-beams six-axis force/torque sensor is illustrated in Fig. 1. As it is shown, the model consists of six cross elastic beams which are symmetric horizontal beams (i.e., the section number 2), four compliant vertical beams (i.e., the section number 3) and a qubic center support (i.e., the section number 1). Where the vertical compliant beams connect the corresponding horizontal beams to the base (i.e., the section number ), respectively. The whole model is manufactured monolithic and symmetric and hence all the parts have same material properties. In the Fig. 1, b, t, l are width, thickness and length of the horizontal elastic beams, and d and h are thickness and height of the vertical compliant beams, respectively. Typically we set the bt, d1/3 b [16]. When the unknown load is applied to the force/torque sensor, the force and moment vectors can be considered a: F Fiˆ ˆ ˆ x + Fy j+ Fk (1) z M M iˆ+ M jˆ+ M kˆ (2) x y z Where, Fx and Mx, Fy and My, Fz and Mz are the force and moment applied along the x, y and z direction to the qubic center support, respectively /15/$ IEEE 789
2 TABLE I. WHEATONE BRIDGE TRAIN GAUGE DITRIBUTION Load Componetnt Bridge Circuit No. Fx 1 Fy 2 Fz 3 6-axis Force/Torque ensor train Gauges Axis of Distribution measurment,,, y-axis 1 2 3,,, x-axis ,,, x-axis ,,, y-axis Mx My 5 17, 18, 19, 20 x-axis Mz 6 21, 22, 23, 2 y-axis Fig. 1. Mechanical structure of a cross-beams six-axis force/torque sensor B. train Gauges In the six-axis force/torque sensor, 2 linear strain gauges required to measure the applied forces and torques in all three directions since with the smaller number of strain gauges, the sensor lacks the force measuring ability in some directions. The distribution of the 2 strain gauges is shown in Fig. 2. According to the Fig. 2, all the sensors measure axial strain where positive ones are tensile strains and the negative ones are compressive strains. Using the theory of Mechanics of Material six Wheatsone bridge circuits composed of four strain gauges are used in this study. Table 1 specifies the strain gauges distribution for each bridge as well as the load components. The output strain of each load component is calculated using (3). Consider a certain load applied to the six-axis sensor with the F [Fx Fy Fz Mx My Mz] T components. The relationship between the load vector and the strain output vector in a 6 Wheatsone bridge circuits configuration, can be expressed by (). Where [C] is a 6 6 strain compliance whose element C ij represents the strain contribution at bridge circuit i due to a unit pure load j Fx Fy Fz + Mx + My + Mz [ C] F Under the 6 imum pure load components as F F F F M M M T [ x y z x y z ], the strain matrix,, can be defined by combining six C j column vectors by (5). The matrix in (5) is the leading factor for the denitions of cross coupling and principal coupling in the sensor. (3) () Fig. 2. train gauges disrtirbution of the six-axis force/torque sensor [ ] ij Herein the cross coupling error (CC) ij is defined as: (5) 790
3 ( CC) ij ij (6) ii where i 1,..., 6 and i j. Physically (CC) ij indicates the ratio of two output strains at bridge circuit i when imum loads i and j are applied independently. In the design of a mechanically decoupled F/T sensor, the relative strain ratio (CC) ii should be minimized rather than unwanted strain ij, as the larger cross coupling error causes a decrease of resolution [17]. The cross-beams type sensors usually show larger (CC) 15 and (CC) 2 compared to other negligible (CC) ij values [11, 18]. Hence, we dened them as principal couplings which are as follows: M C ( CC),( ) (7) 15 y 15 2 Mx C2 15 CC 2 11 Fx C11 22 Fy C22 The attaching locations for each sensor in 6-axis force/moment was determined in consideration of the results of FEM analysis where the attachment location is 3mm and 6 mm from the center support. These locations are optimally gained by the FEM analysis results. In (7), The coupling term (CC) 15 expresses the ratio of two strains under pure imum moment My and pure imum force Fx at the first bridge circuit, while (CC) 2 indicates the ratio of two strains under pure imum moment Mx and pure imum force Fy at the second bridge circuit. In this study, (CC) 15 and (CC) 2 are considered as principal coupling terms and the design optimization problem is formulated to minimize them. According to all the mechanical structure variables, the structural design optimization problem is considered as find [b, t, l] to minimize: Fig. 3. The FEM model of the six-axis force/torque sensor J( x) ( CC) + ( CC) 15 2 (6) 2 The imum von Mises stress to examine the exceeding of the material yield stress, the upper and lower bounds of strain outputs and the bandwidth applied load components should be noticed before taking (8) into action. III. FINITE ELEMENT MODELING In order to evaluate the above properties, a finite element model in a commercial FEM software, ABAQU, is designed. As Fig. 3 depicts, the FEA model is designed by meshing all the regions into finite number of nodal elements with the size of 0.5 mm for each node. The model is constrained to be fixed at the ring shape base which are its static boundary conditions, and the load component is applied at the center of the qubic support center along the neutral axis of the elastic horizontal cross-beams. The Material used in this study is Aluminium (AL7075-T6) 9 with the Young s modulus of (Pa) and the Poissom ratio The variables to design the FEA model of F/T sensor are determined as follows: The rated capacity of the forces Fx, Fy and Fz is 20 N. The rated capacity of the moments Mx, My and Mz is 0.09 N.m. Fig.. Deformation of the FEM model under each single force/torque: I) Fx20N II) Fz20N III) Mz0.09 N.m 791
4 train (m/m) TABLE II. THE TRAIN OUTPUT UNDER EACH PURE MAX LOAD Max Pure Load: F x F y F z 20 N M x M y M z 0.09 N.m Design Parameters: b t 3 mm, l 21 mm F x F y F z M x M y M z The deformations of the F/T sensor under each single load calculated by the FEM software are shown in Fig., and the strain outputs are seen in the Table II. ubstituting the strain outputs in Table II into (3) and () yields the strain output matrix by (9) which is significant for next steps ij (9) IV. REULT AND DICUION Full factorial design at 2-levels and 3-levels are the most frequently methods used in manufacturing experimental designs. Full factorial designed experiment consists of all possible combinations of levels for all factors. The total number of experiments for studying k factors at 2-levels is 2 k. The 2 k full factorial design is particularly appropriate in our study since this method is significantly useful when the number of design parameters is less than or equal to. According to the structural design optimization problem discussed, 8 tests were performed based on Table III. TABLE III. REULT OF EXPERIMENT FOR THE OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION FUNCTION REGARD TO FULL FACTORIAL DEIGN Test No. Full Factorial Design Parameters b (mm) t (mm) l (mm) Optimization Function J(x) 0.30% 0.3% 0.29% 0.33% 0.1% 0.16% 0.15% 0.17% A. ignal to Noise Ratio & Analysis of Variance The /N ratio is the ratio of signal to noise which signal and noise represent the desirable (i.e., the mean for the output characteristics) and undesirable value (i.e., the squared deviations for output characteristics), respectively. /N ratio is used to evaluate the quality characteristics of the experimentally observed values which the three general categories are the larger of better, the smaller the better and nominal is better [19]. The characteristic considered is the optimization function hence the lower value represents the lower cross coupling error, that is to say smaller is better. The /N ratio can be expressed as a logarithmic transformation of the loss function using (10) and is shown in Table IV. 1 / N 10log y n 2 n (10) i 1 TABLE IV. /N RATIO FOR OPTIMIZATION FUNCTION Level b t l Delta Rank
5 of the cross-beams has the most remarkable effect on minimizing the cross coupling error. REFERENCE Fig. 5. Plot of /N ratio fot the optimization function of six-axis F/T sensor From the /N ration as shown in Table IV, it is observed that the optimal parameter combination for minimizing the cross coupling error, is at beam thickness (t) level 2 and beam length (l) level 1. In other words, increasing the thickness of the beam likewise decreasing the length of it causes the beam to bend and hence the better strain output results. Also, the negligible effect of beam width (b) on cross coupling error is clear from the results. Finally, a statistical analysis of variance (ANOVA) is performed to see which design parameters are statistically significant. The level of importance of the variable parameters on the cross coupling error has been determined by using analysis of variance as illustrated in Table V. TABLE V. PERCENTAGE OF IMPORTANCE OF THE DEIGN PARAMETER UING ANOVA Factors b t l % Table V expresses the importance of elastic cross-beams thickness is far more than two other parameters, while the width of the cross-beams has inconsiderable effect on cross coupling error. As a result, the model in test number 5 from Table II has the best design parameter combination due to minimize the cross coupling error. V. CONCLUION The effect of the structural design parameters on decreasingthe cross coupling interference for a six-axis force/torque sensor was investigated. Thickness, width and length of the elastic cross-beams are the design parameters which are considered in this study. A 2-level full factorial approach was carried out and 8 tests were experimented in a commercial finite element software, ABAQU. The statistical analysis of results shows that the thickness [1] G. Piller, A compact six degree fo freedom force sensor for assembly robot, 12 th International ymposium on Industrial Robots, Paris, France, pp , June [2] Zy. Nakamuro, T. Yoshikawa, Futamata, Design and singal processing of six-axis force sensor, th International ymposium of Robotics Research, Cambridge, MA, UA, pp , [3] M. Perry, Multi-axis force and torque sensing, ensor Rev., vol. 17, 1997, pp [] Y.F. Li, X.B. Chen, On the dynamic behavior of a force/ torque sensor for robots, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Means., vol. 7, pp , February [5] T. Liu, Y. Inoue, K. hibata, Wearable force sensor with parallel structure for measurement of ground-reaction force, Measurement, vol. 0, 2007, pp [6] J.H. Kim, J.H. Oh, Realization of dynamic walking for the humanoid robot platform KHR-1, Adv. Robot., vol. 18, 200, pp [7] J.H. Kim, J.W. Han, D.Y. Kim, Y.. Baek, Design of a walking assistance lower limb exoskeleton for paraplegic patients and hardware validation using CoP," Adv. Robot. yst., vol. 10, 2013, pp [8] Y. Hatamura, K. Matsumoto, H. A. Morishita, A miniature 6-axis force sensor of multi-layer parallel plate structure, IMEKO, 1989, pp [9] K. Ono, Y. Hatamura, A new design for 6-component force/torque sensors, Mecahnical Problems in Measuring Force and Mass, H. Wieringa, Ed., Martinus Nijhoff, Dordecht, 1986, pp [10] G.. Kim, D. I. Kang,. H. Rhee, K. W. Um, Design and fabrication of a 3-component force/moment sensor using the plate-beams, Meas. ci. Technol., vol. 10, 1999, pp [11] G.. Kim, Design of a six-axis wrist force/moment sensor using FEM and its fabrication for an intelligent robot, ensor Actuat. A-Phys., vol. 133, 2007, pp [12] ATI Industrial Automation, Multi-Axis Forcr/Torque ensor, ATI Industrial Automation, 2005, pp. -5. [13] Nisso Electric Works Co., Ltd, Multi Component Loadcell, Nisso Electric Works Co., Ltd, 1999, pp [1] L.P. Chao, K.T. Chen, hape optimal design and force sensitivity evaluation of six-axis force sensors, ensor Actuat. A-Phys., vol. 63, 1997, pp [15]. A. Liu, H.L., Tzo, A novel six-component force sensor of good measurement isotropy and sensitivities, ensor Actuat. A-Phys., vol. 100, 2002, pp [16] ong A., Wu J., Qin G., Huang W., A novel self-decoupled four degree-of-freedom wrist force/torque sensor, Measurement, vol. 0, 2007, pp [17] M.K. Kang,. Lee and J. H. Kim, hape Optimization of a Mechanically Decoupled ix-axis Force/Torque ensor, ensors Actuat. A-Phys., vol. 209, 201, pp [18] L.P. Chao, K.T. Chen, hape optimal design and force sensitivity evaluation of six-axis force sensors, ensor Actuat. A-Phys., vol. 63, 1997, pp [19] Yan-Cherng Lin, Han-Ming Chow, Biing-Hwa Yan, Hsinn-Jyh Tzeng, Effects of finishing in abrasive fluid machining on microholes fabricated by EDM Adv. Manuf. Technology, vol. 33, 2007, pp
FABRICATION, TESTING AND CALIBRATION OF TWO DIRECTIONAL FORCE SENSOR
 FABRICATION, TESTING AND CALIBRATION OF TWO DIRECTIONAL FORCE SENSOR Kuruva Veerakantha 1, G.Kirankumar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, NNRG, Telangana, India 2 Assistant Professor, Mechanical
FABRICATION, TESTING AND CALIBRATION OF TWO DIRECTIONAL FORCE SENSOR Kuruva Veerakantha 1, G.Kirankumar 2 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, NNRG, Telangana, India 2 Assistant Professor, Mechanical
reports in applied measurement
 reports in applied measurement ram reports in applied measurement A new transducer for directly measuring the forces and moments which a skier transfers to the skis F Z M Z A. Freddi, G. Olmi, D. Croccolo
reports in applied measurement ram reports in applied measurement A new transducer for directly measuring the forces and moments which a skier transfers to the skis F Z M Z A. Freddi, G. Olmi, D. Croccolo
Design of a compact six-component force and moment sensor for aerodynamic testing
 Design of a compact six-component force and moment sensor for aerodynamic testing Marin SANDU*, Adriana SANDU*, Georgeta IONAŞCU* *Corresponding author POLITEHNICA University of Bucharest, Splaiul Independenţei
Design of a compact six-component force and moment sensor for aerodynamic testing Marin SANDU*, Adriana SANDU*, Georgeta IONAŞCU* *Corresponding author POLITEHNICA University of Bucharest, Splaiul Independenţei
1 Force Sensing. Lecture Notes. 1.1 Load Cell. 1.2 Stress and Strain
 Lecture Notes 1 Force Sensing 1.1 Load Cell A Load Cell is a structure which supports the load and deflects a known amount in response to applied forces and torques. The deflections are measured to characterize
Lecture Notes 1 Force Sensing 1.1 Load Cell A Load Cell is a structure which supports the load and deflects a known amount in response to applied forces and torques. The deflections are measured to characterize
Design and nonlinear modeling of a large-displacement XYZ flexure parallel mechanism with decoupled kinematic structure
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 115101 2006 Design and nonlinear modeling of a large-displacement XYZ flexure parallel mechanism with decoupled kinematic structure Xueyan Tang, a I-Ming Chen, and
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 115101 2006 Design and nonlinear modeling of a large-displacement XYZ flexure parallel mechanism with decoupled kinematic structure Xueyan Tang, a I-Ming Chen, and
BIAXIAL STRENGTH INVESTIGATION OF CFRP COMPOSITE LAMINATES BY USING CRUCIFORM SPECIMENS
 BIAXIAL STRENGTH INVESTIGATION OF CFRP COMPOSITE LAMINATES BY USING CRUCIFORM SPECIMENS H. Kumazawa and T. Takatoya Airframes and Structures Group, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency 6-13-1, Ohsawa, Mitaka,
BIAXIAL STRENGTH INVESTIGATION OF CFRP COMPOSITE LAMINATES BY USING CRUCIFORM SPECIMENS H. Kumazawa and T. Takatoya Airframes and Structures Group, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency 6-13-1, Ohsawa, Mitaka,
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
This procedure covers the determination of the moment of inertia about the neutral axis.
 327 Sample Problems Problem 16.1 The moment of inertia about the neutral axis for the T-beam shown is most nearly (A) 36 in 4 (C) 236 in 4 (B) 136 in 4 (D) 736 in 4 This procedure covers the determination
327 Sample Problems Problem 16.1 The moment of inertia about the neutral axis for the T-beam shown is most nearly (A) 36 in 4 (C) 236 in 4 (B) 136 in 4 (D) 736 in 4 This procedure covers the determination
Design and Simulation of a Novel MEMS Bidirectional Anemometer
 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Design and Simulation of a Novel MEMS Bidirectional Anemometer Ali Pazoki Nezhad 1 and Mohamad
2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Design and Simulation of a Novel MEMS Bidirectional Anemometer Ali Pazoki Nezhad 1 and Mohamad
Application example. Measuring Force Sensors Rigid. Six series Nano, Mini, Gamma, Delta, Theta, Omega. Range of measurement, force ± 36 N..
 FT Six series Nano, Mini, Gamma, Delta, Theta, Omega Range of measurement, force ± 36 N.. ± 40000 N Range of measurement, moment ± 0.5 Nm.. ± 6000 Nm Application example Robot-supported chamfering of round
FT Six series Nano, Mini, Gamma, Delta, Theta, Omega Range of measurement, force ± 36 N.. ± 40000 N Range of measurement, moment ± 0.5 Nm.. ± 6000 Nm Application example Robot-supported chamfering of round
University of Sheffield The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire
 The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY
 THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
THE NEW 1.1 MN m TORQUE STANDARD MACHINE OF THE PTB BRAUNSCHWEIG/GERMANY D. Peschel 1, D. Mauersberger 1, D. Schwind 2, U. Kolwinski 2 1 Solid mechanics department, PTB, Germany 2 Gassmann Theiss Messtechnik
Procedure for Performing Stress Analysis by Means of Finite Element Method (FEM)
 Procedure for Performing Stress Analysis by Means of Finite Element Method (FEM) Colaboração dos engºs Patrício e Ediberto da Petrobras 1. Objective This Technical Specification sets forth the minimum
Procedure for Performing Stress Analysis by Means of Finite Element Method (FEM) Colaboração dos engºs Patrício e Ediberto da Petrobras 1. Objective This Technical Specification sets forth the minimum
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Module - 01 Lecture - 13
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
ENGN 2340 Final Project Report. Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material
 ENGN 2340 Final Project Report Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material Enrui Zhang 12/15/2017 1. Introduction of the Problem This project deals with the stress-strain response of a
ENGN 2340 Final Project Report Optimization of Mechanical Isotropy of Soft Network Material Enrui Zhang 12/15/2017 1. Introduction of the Problem This project deals with the stress-strain response of a
Multi-Capacity Load Cell Concept
 Sensors & Transducers 4 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Multi-Capacity Load Cell Concept Seif. M. OSMAN, Ebtisam H. HASAN, H. M. EL-HAKEEM, R. M. RASHAD, F. KOUTA National Institute
Sensors & Transducers 4 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Multi-Capacity Load Cell Concept Seif. M. OSMAN, Ebtisam H. HASAN, H. M. EL-HAKEEM, R. M. RASHAD, F. KOUTA National Institute
Development of Distributed Optical Torque Sensors for Realization of Local Impedance Control of the Robot Arm
 Development of Distributed Optical Torque Sensors for Realization of Local Impedance Control of the Robot Arm Dzmitry Tsetserukou, Riichiro Tadakuma, Hiroyuki Kajimoto and Susumu Tachi Graduate School
Development of Distributed Optical Torque Sensors for Realization of Local Impedance Control of the Robot Arm Dzmitry Tsetserukou, Riichiro Tadakuma, Hiroyuki Kajimoto and Susumu Tachi Graduate School
Stress Analysis of V Notches on the Components Using Photo elasticity and FEM
 Stress Analysis of V Notches on the Components Using Photo elasticity and FEM Prof. Alim Appalal Shaikh 1, Prof. Kiraneshwar. C. Goli 2 1 Department of mechanical engineering, N B Navale Sinhgad College
Stress Analysis of V Notches on the Components Using Photo elasticity and FEM Prof. Alim Appalal Shaikh 1, Prof. Kiraneshwar. C. Goli 2 1 Department of mechanical engineering, N B Navale Sinhgad College
INVESTIGATION OF STRESSES IN MASTER LEAF OF LEAF SPRING BY FEM AND ITS EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION
 INVESTIGATION OF STRESSES IN MASTER LEAF OF LEAF SPRING BY FEM AND ITS EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION * R. B. Charde, **Dr. D.V. Bhope, * P.G. Student, Department Of Mech. Engg., Rajiv Gandhi College Of Engineering
INVESTIGATION OF STRESSES IN MASTER LEAF OF LEAF SPRING BY FEM AND ITS EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION * R. B. Charde, **Dr. D.V. Bhope, * P.G. Student, Department Of Mech. Engg., Rajiv Gandhi College Of Engineering
EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 7, No. EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Robert Czabanowski Wroclaw University
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 7, No. EXPERIMENTAL IDENTIFICATION OF HYPERELASTIC MATERIAL PARAMETERS FOR CALCULATIONS BY THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Robert Czabanowski Wroclaw University
Solution: T, A1, A2, A3, L1, L2, L3, E1, E2, E3, P are known Five equations in five unknowns, F1, F2, F3, ua and va
 ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT
 2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
2004 AIMETA International Tribology Conference, September 14-17, 2004, Rome, Italy UNLOADING OF AN ELASTIC-PLASTIC LOADED SPHERICAL CONTACT Yuri KLIGERMAN( ), Yuri Kadin( ), Izhak ETSION( ) Faculty of
Performance Improvement of a 6-Axis Force-torque Sensor via Novel Electronics and Cross-shaped Double-hole Structure
 International Journal Performance of Control, Improvement Automation, of a and 6-Axis Systems, Force-torque vol. 3, no. Sensor 3, pp. via 469-476, Novel Electronics September and 2005 469 Performance Improvement
International Journal Performance of Control, Improvement Automation, of a and 6-Axis Systems, Force-torque vol. 3, no. Sensor 3, pp. via 469-476, Novel Electronics September and 2005 469 Performance Improvement
Design and Integration of a Multi-Axis Force/Moment Sensor for the Roombots
 Semester project report Design and Integration of a Multi-Axis Force/Moment Sensor for the Roombots Joël Rey Supervisors: Alexander Sproewitz Ricko Moeckel January 7, 2011 Abstract Roombots are modular
Semester project report Design and Integration of a Multi-Axis Force/Moment Sensor for the Roombots Joël Rey Supervisors: Alexander Sproewitz Ricko Moeckel January 7, 2011 Abstract Roombots are modular
Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression
 15 th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms NaCoMM011-157 Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression Sachindra Mahto Abstract In this work,
15 th National Conference on Machines and Mechanisms NaCoMM011-157 Shape Optimization of Revolute Single Link Flexible Robotic Manipulator for Vibration Suppression Sachindra Mahto Abstract In this work,
Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 29 Milan Thickness Optimization of a Piezoelectric Converter for Energy Harvesting M. Guizzetti* 1, V. Ferrari 1, D. Marioli 1 and T. Zawada 2 1 Dept.
THE EFFECT OF GEOMETRY ON FATIGUE LIFE FOR BELLOWS
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of. tubular columns and arches. Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes
 October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
Stress and Displacement Analysis of a Rectangular Plate with Central Elliptical Hole
 Stress and Displacement Analysis of a Rectangular Plate with Central Elliptical Hole Dheeraj Gunwant, J. P. Singh mailto.dheerajgunwant@gmail.com, jitenderpal2007@gmail.com, AIT, Rampur Abstract- A static
Stress and Displacement Analysis of a Rectangular Plate with Central Elliptical Hole Dheeraj Gunwant, J. P. Singh mailto.dheerajgunwant@gmail.com, jitenderpal2007@gmail.com, AIT, Rampur Abstract- A static
Module 2 Mechanics of Machining. Version 2 ME IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 2 Mechanics of Machining Lesson 10 Dynamometers for measuring cutting forces Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students would be able to (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) show the general
Module 2 Mechanics of Machining Lesson 10 Dynamometers for measuring cutting forces Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students would be able to (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) show the general
Finite Element Analysis on a Square Canister Piezoelectric Energy Harvester in Asphalt Pavement
 World Journal of Engineering and echnology, 06, 4, 6-7 Published Online May 06 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/0.46/wjet.06.405 Finite Element Analysis on a Square Canister
World Journal of Engineering and echnology, 06, 4, 6-7 Published Online May 06 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjet http://dx.doi.org/0.46/wjet.06.405 Finite Element Analysis on a Square Canister
Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys. Na Wang 1, Lei Wang 2
 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 215) Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys Na Wang 1, Lei Wang
5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 215) Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys Na Wang 1, Lei Wang
Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching. piezo-ceramic plates
 Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching piezo-ceramic plates Yuting Ma 1,2, Minkyu Choi 2 and Kenji Uchino 2 1 CAS Key Lab of Bio-Medical Diagnostics, Suzhou
Single-phase driven ultrasonic motor using two orthogonal bending modes of sandwiching piezo-ceramic plates Yuting Ma 1,2, Minkyu Choi 2 and Kenji Uchino 2 1 CAS Key Lab of Bio-Medical Diagnostics, Suzhou
The Effects of Convolution Geometry and Boundary Condition on the Failure of Bellows
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(S1), 462 466, January 2015 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8iS1/59417 The Effects of Convolution Geometry and
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(S1), 462 466, January 2015 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8iS1/59417 The Effects of Convolution Geometry and
Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration
 Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration JongHun Kang 1, Junwoo Bae 2, Seungkeun Jeong 3, SooKeun Park 4 and Hyoung Woo Lee 1 # 1 Department of Mechatronics
Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration JongHun Kang 1, Junwoo Bae 2, Seungkeun Jeong 3, SooKeun Park 4 and Hyoung Woo Lee 1 # 1 Department of Mechatronics
CHAPTER 6 A STUDY ON DISC BRAKE SQUEAL USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS
 134 CHAPTER 6 A STUDY ON DISC BRAKE SQUEAL USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS 6.1 INTRODUCTION In spite of the large amount of research work that has been carried out to solve the squeal problem during the last
134 CHAPTER 6 A STUDY ON DISC BRAKE SQUEAL USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS 6.1 INTRODUCTION In spite of the large amount of research work that has been carried out to solve the squeal problem during the last
Wearable force sensor with parallel structure for measurement of ground-reaction force
 Measurement 40 (2007) 644 653 www.elsevier.com/locate/measurement Wearable force sensor with parallel structure for measurement of ground-reaction force Tao Liu *, Yoshio Inoue, Kyoko Shibata Department
Measurement 40 (2007) 644 653 www.elsevier.com/locate/measurement Wearable force sensor with parallel structure for measurement of ground-reaction force Tao Liu *, Yoshio Inoue, Kyoko Shibata Department
Computer Aided Design of Tine of Tuning Fork Densitometer Shuang LIU, Xin-sheng CHE *, Yi-shun ZHANG and Xin-yu-han JI
 017 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Engineering (AIIE 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-50-9 Computer Aided Design of Tine of Tuning Fork Densitometer Shuang LIU, Xin-sheng
017 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Engineering (AIIE 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-50-9 Computer Aided Design of Tine of Tuning Fork Densitometer Shuang LIU, Xin-sheng
MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems
 MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 7: Actuators and Sensors Topic 7d: Piezoelectric Actuators. Reference: Various articles. Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
MCE603: Interfacing and Control of Mechatronic Systems Chapter 7: Actuators and Sensors Topic 7d: Piezoelectric Actuators. Reference: Various articles. Cleveland State University Mechanical Engineering
Stresses in Curved Beam
 Stresses in Curved Beam Consider a curved beam subjected to bending moment M b as shown in the figure. The distribution of stress in curved flexural member is determined by using the following assumptions:
Stresses in Curved Beam Consider a curved beam subjected to bending moment M b as shown in the figure. The distribution of stress in curved flexural member is determined by using the following assumptions:
A Beam Finite Element Model for Efficient Analysis of Wire Strands
 Available online at www.ijpe-online.com vol. 13, no. 3, May 17, pp. 315-3 DOI: 1.1555/1.394/ijpe.17.3.p7.3153 A Beam Finite Element Model for Efficient Analysis of Wire Strs Chunlei Yu 1, Wenguang Jiang
Available online at www.ijpe-online.com vol. 13, no. 3, May 17, pp. 315-3 DOI: 1.1555/1.394/ijpe.17.3.p7.3153 A Beam Finite Element Model for Efficient Analysis of Wire Strs Chunlei Yu 1, Wenguang Jiang
Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of Tight Joint Assembled by Press Fitting
 Modern Mechanical Engineering, 04, 4, 98-06 Published Online November 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.46/mme.04.4409 Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of
Modern Mechanical Engineering, 04, 4, 98-06 Published Online November 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/mme http://dx.doi.org/0.46/mme.04.4409 Finite-Element Analysis of Parts Stress State of
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: 2-4 July, 2015
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Experimental and FEA Approach for Optimization of Spiral Flexure Bearing N.
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 2-4 July, 2015 Experimental and FEA Approach for Optimization of Spiral Flexure Bearing N.
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
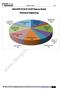 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Investigation of Circular Flexural Hinge Used in Compliant Mechanism Using FEA Tool.
 Investigation of Circular Flexural Hinge Used in Compliant Mechanism Using FEA Tool. 1 M.M.Sawant and 2 P.R.Anerao 1, 2 Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology, Kondhawa (Bk),Pune Maharashtra,
Investigation of Circular Flexural Hinge Used in Compliant Mechanism Using FEA Tool. 1 M.M.Sawant and 2 P.R.Anerao 1, 2 Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology, Kondhawa (Bk),Pune Maharashtra,
Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A WESTFALL 2800 MIXER, BETA = 0.8 GFS R1. By Kimbal A. Hall, PE. Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY
 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A WESTFALL 2800 MIXER, BETA = 0.8 GFS-411519-1R1 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY OCTOBER 2011 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC. 30 Shrewsbury Street
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A WESTFALL 2800 MIXER, BETA = 0.8 GFS-411519-1R1 By Kimbal A. Hall, PE Submitted to: WESTFALL MANUFACTURING COMPANY OCTOBER 2011 ALDEN RESEARCH LABORATORY, INC. 30 Shrewsbury Street
Chapter 1 General Introduction Instructor: Dr. Mürüde Çelikağ Office : CE Building Room CE230 and GE241
 CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 1 General Introduction Instructor: Dr. Mürüde Çelikağ Office : CE Building Room CE230 and GE241 E-mail : murude.celikag@emu.edu.tr 1. INTRODUCTION There are three
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 1 General Introduction Instructor: Dr. Mürüde Çelikağ Office : CE Building Room CE230 and GE241 E-mail : murude.celikag@emu.edu.tr 1. INTRODUCTION There are three
Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages
 Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages Pre-lab assignment: Yes No Goals: 1. To evaluate tension and bending stress models and Hooke s Law. a. σ = Mc/I and σ = P/A 2. To determine material
Lab Exercise #5: Tension and Bending with Strain Gages Pre-lab assignment: Yes No Goals: 1. To evaluate tension and bending stress models and Hooke s Law. a. σ = Mc/I and σ = P/A 2. To determine material
Strength Study of Spiral Flexure Spring of Stirling Cryocooler
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
Free-form Optimization Method for Designing Spatial Frame Structure
 0 th World Congress on tructural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-4, 03, Orlando, Florida, UA Free-form Optimization Method for Designing patial Frame tructure M. himoda, Y. Liu and F. Hayashi
0 th World Congress on tructural and Multidisciplinary Optimization May 9-4, 03, Orlando, Florida, UA Free-form Optimization Method for Designing patial Frame tructure M. himoda, Y. Liu and F. Hayashi
A new computational method for threaded connection stiffness
 Research Article A new computational method for threaded connection stiffness Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2016, Vol. 8(12) 1 9 Ó The Author(s) 2016 DOI: 10.1177/1687814016682653 aime.sagepub.com
Research Article A new computational method for threaded connection stiffness Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2016, Vol. 8(12) 1 9 Ó The Author(s) 2016 DOI: 10.1177/1687814016682653 aime.sagepub.com
Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPERIMENT #1: FORCE AND TORQUE SENSORS DC Motor Characteristics Dynamometer, Part I
 Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPEIMENT #1: FOCE AND TOQUE SENSOS DC Motor Characteristics Dynamometer, Part I Force Sensors Force and torque are not measured directly. Typically, the deformation or strain
Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPEIMENT #1: FOCE AND TOQUE SENSOS DC Motor Characteristics Dynamometer, Part I Force Sensors Force and torque are not measured directly. Typically, the deformation or strain
436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae
![436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae 436 A. Barani and G.H. Rahimi assessment models have been employed to investigate the LBB of cracked pipes that are not for combined load [8]. Yun-Jae](/thumbs/86/94473226.jpg) Scientia Iranica, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp 435{44 c Sharif University of Technology, October 27 Approximate Method for Evaluation of the J-Integral for Circumferentially Semi-Elliptical-Cracked Pipes Subjected
Scientia Iranica, Vol. 4, No. 5, pp 435{44 c Sharif University of Technology, October 27 Approximate Method for Evaluation of the J-Integral for Circumferentially Semi-Elliptical-Cracked Pipes Subjected
Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process
 Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 9/ No. 4/ December 2016 75 Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process A. R. Norouzi Department of New Sciences and Technologies,
Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 9/ No. 4/ December 2016 75 Effect of AFM Cantilever Geometry on the DPL Nanomachining process A. R. Norouzi Department of New Sciences and Technologies,
Optimal Design of a Permanent Magnetic Actuator for Vacuum Circuit Breaker using FEM
 92 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 92~97, 26 Optimal Design of a Permanent Magnetic Actuator for Vacuum Circuit Breaker using FEM Yong-Min Yoo*, Dae-Kyung Kim** and Byung-Il
92 Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 92~97, 26 Optimal Design of a Permanent Magnetic Actuator for Vacuum Circuit Breaker using FEM Yong-Min Yoo*, Dae-Kyung Kim** and Byung-Il
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
THE OPTIMIZATION OF SEVERAL TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS OF ULTRASONIC VIBRATION AIDED FLOW-FORMING
 THE OPTIMIZATION OF SEVERAL TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS OF ULTRASONIC VIBRATION AIDED FLOW-FORMING Chengcheng Zhu, Shengdun Zhao, Chao Zhang and De an Meng Xi'an Jiaotong Universityg, Xi an, China email:
THE OPTIMIZATION OF SEVERAL TECHNOLOGICAL PARAMETERS OF ULTRASONIC VIBRATION AIDED FLOW-FORMING Chengcheng Zhu, Shengdun Zhao, Chao Zhang and De an Meng Xi'an Jiaotong Universityg, Xi an, China email:
Lecture 20. Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature MECH 373. Instrumentation and Measurements
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
Reduction of the effect of floor vibrations in a checkweigher using an electromagnetic force balance system
 ACTA IMEKO ISSN: 1 870X July 017, Volume 6 Number, 65 69 Reduction of the effect of floor vibrations in a checkweigher using an electromagnetic force balance system Yuji Yamakawa 1, Takanori Yamazaki 1
ACTA IMEKO ISSN: 1 870X July 017, Volume 6 Number, 65 69 Reduction of the effect of floor vibrations in a checkweigher using an electromagnetic force balance system Yuji Yamakawa 1, Takanori Yamazaki 1
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor
 Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Numerical simulation of inertia friction welding process of GH4169 alloy
 J. Phys. IV France 120 (2004) 681-687 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2004120078 Numerical simulation of inertia friction welding process of GH4169 alloy Zhang Liwen, Liu Chengdong, Qi Shaoan,
J. Phys. IV France 120 (2004) 681-687 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis DOI: 10.1051/jp4:2004120078 Numerical simulation of inertia friction welding process of GH4169 alloy Zhang Liwen, Liu Chengdong, Qi Shaoan,
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination Analysis
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2014 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... Ph.D.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2014 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... Ph.D.
Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation on Steel Plate Girders With Deep Section
 6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 2015, University of
6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 2015, University of
Mechanics of Biomaterials
 Mechanics of Biomaterials Lecture 7 Presented by Andrian Sue AMME498/998 Semester, 206 The University of Sydney Slide Mechanics Models The University of Sydney Slide 2 Last Week Using motion to find forces
Mechanics of Biomaterials Lecture 7 Presented by Andrian Sue AMME498/998 Semester, 206 The University of Sydney Slide Mechanics Models The University of Sydney Slide 2 Last Week Using motion to find forces
Methods of Analysis. Force or Flexibility Method
 INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
ScienceDirect. Finite element analysis and optimization of flexure bearing for linear motor compressor
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 379 385 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia 67 (2015 ) 379 385 25th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference and the International Cryogenic Materials Conference in 2014,
Compact energy absorbing cellular structure
 Structures Under Shock and Impact IX 413 Compact energy absorbing cellular structure M. Ali 1, A. Qamhiyah 2, D. Flugrad 1 & M. Shakoor 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iowa State University,
Structures Under Shock and Impact IX 413 Compact energy absorbing cellular structure M. Ali 1, A. Qamhiyah 2, D. Flugrad 1 & M. Shakoor 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Iowa State University,
Lecture 8: Assembly of beam elements.
 ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
A STUDY ON MULTI-AXIS FORCE MEASUREMENT OF POLYMER SKINS USING FBG SENSOR
 A STUDY ON MULTI-AXIS FORCE MEASUREMENT OF POLYMER SKINS USING FBG SENSOR Oh Min Kwon*, Sang kyun Hwang*, Sung Su Kim** and Hui Yun Hwang* * Department of Mechanical Design Engineering, Andong National
A STUDY ON MULTI-AXIS FORCE MEASUREMENT OF POLYMER SKINS USING FBG SENSOR Oh Min Kwon*, Sang kyun Hwang*, Sung Su Kim** and Hui Yun Hwang* * Department of Mechanical Design Engineering, Andong National
Lecture 4: PRELIMINARY CONCEPTS OF STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS. Introduction
 Introduction In this class we will focus on the structural analysis of framed structures. We will learn about the flexibility method first, and then learn how to use the primary analytical tools associated
Introduction In this class we will focus on the structural analysis of framed structures. We will learn about the flexibility method first, and then learn how to use the primary analytical tools associated
Week 10 - Lecture Nonlinear Structural Analysis. ME Introduction to CAD/CAE Tools
 Week 10 - Lecture Nonlinear Structural Analysis Product Lifecycle Week 10 Requirements Portfolio Management Conceptual Design Product Engineering Manufacturing Engineering Simulation & Validation Build
Week 10 - Lecture Nonlinear Structural Analysis Product Lifecycle Week 10 Requirements Portfolio Management Conceptual Design Product Engineering Manufacturing Engineering Simulation & Validation Build
Modeling and Design Optimization of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor with Halbach Array
 Modeling and Design Optimization of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor with Halbach Array N. Roshandel Tavana, and A. Shoulaie nroshandel@ee.iust.ir, and shoulaie@ee.iust.ac.ir Department of Electrical
Modeling and Design Optimization of Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor with Halbach Array N. Roshandel Tavana, and A. Shoulaie nroshandel@ee.iust.ir, and shoulaie@ee.iust.ac.ir Department of Electrical
46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference April 2005 Austin, Texas
 th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference - April, Austin, Texas AIAA - AIAA - Bi-stable Cylindrical Space Frames H Ye and S Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference - April, Austin, Texas AIAA - AIAA - Bi-stable Cylindrical Space Frames H Ye and S Pellegrino University of Cambridge, Cambridge,
DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1
 PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. CIV. ENG. VOL. 46, NO. 1, PP. 125 148 (2002) DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1 Nándor LIEGNER Department of Highway and Railway Engineering
PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. CIV. ENG. VOL. 46, NO. 1, PP. 125 148 (2002) DETERMINING THE STRESS PATTERN IN THE HH RAILROAD TIES DUE TO DYNAMIC LOADS 1 Nándor LIEGNER Department of Highway and Railway Engineering
CEEN 3320 Behavior & Properties of Engineering Materials Laboratory Experiment No. 1 Measurement Techniques
 Laboratory Experiment No. 1 Measurement Techniques Engineers rely on data from a wide variety of sources to design the things that make up our physical world and to ensure compliance with established specifications.
Laboratory Experiment No. 1 Measurement Techniques Engineers rely on data from a wide variety of sources to design the things that make up our physical world and to ensure compliance with established specifications.
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump
 An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS
 77 CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fixed guided clamped and cantilever beams have been designed and analyzed using ANSYS and their performance were calculated. Maximum deflection
77 CHAPTER 5 FIXED GUIDED BEAM ANALYSIS 5.1 INTRODUCTION Fixed guided clamped and cantilever beams have been designed and analyzed using ANSYS and their performance were calculated. Maximum deflection
Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION
 A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
A RESEARCH ON NONLINEAR STABILITY AND FAILURE OF THIN- WALLED COMPOSITE COLUMNS WITH OPEN CROSS-SECTION H. Debski a*, J. Bienias b, P. Jakubczak b a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Department of Machine
7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces
 7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces 7.3.1 General In the previous chapters of Draft IS: 800 LSM version, we have stipulated the codal provisions for determining the stress distribution in
7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces 7.3.1 General In the previous chapters of Draft IS: 800 LSM version, we have stipulated the codal provisions for determining the stress distribution in
TORSION INCLUDING WARPING OF OPEN SECTIONS (I, C, Z, T AND L SHAPES)
 Page1 TORSION INCLUDING WARPING OF OPEN SECTIONS (I, C, Z, T AND L SHAPES) Restrained warping for the torsion of thin-wall open sections is not included in most commonly used frame analysis programs. Almost
Page1 TORSION INCLUDING WARPING OF OPEN SECTIONS (I, C, Z, T AND L SHAPES) Restrained warping for the torsion of thin-wall open sections is not included in most commonly used frame analysis programs. Almost
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF UNDER WATER ACOUSTIC MEMS SENSOR
 DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF UNDER WATER ACOUSTIC MEMS SENSOR Smitha G Prabhu 1, Nagabhushana S *2 1 Dept. Of Electronics and communication, Center for Nano Materials and MEMS, 2 Dept. of Electronics and Communication,
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF UNDER WATER ACOUSTIC MEMS SENSOR Smitha G Prabhu 1, Nagabhushana S *2 1 Dept. Of Electronics and communication, Center for Nano Materials and MEMS, 2 Dept. of Electronics and Communication,
Steel Post Load Analysis
 Steel Post Load Analysis Scope The steel posts in 73019022, 73019024, and 73019025, are considered to be traditional building products. According to the 2015 International Building Code, this type of product
Steel Post Load Analysis Scope The steel posts in 73019022, 73019024, and 73019025, are considered to be traditional building products. According to the 2015 International Building Code, this type of product
Discontinuous Distributions in Mechanics of Materials
 Discontinuous Distributions in Mechanics of Materials J.E. Akin, Rice University 1. Introduction The study of the mechanics of materials continues to change slowly. The student needs to learn about software
Discontinuous Distributions in Mechanics of Materials J.E. Akin, Rice University 1. Introduction The study of the mechanics of materials continues to change slowly. The student needs to learn about software
UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABLE CFRP LAMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF LAY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIAL CURVATURE
 THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
THE 9 TH INTERNATIONA CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIAS UNEXPECTED TWISTING CURVATURE GENERATION OF BISTABE CFRP AMINATE DUE TO THE UNCERTAINTY OF AY-UP SEQUENCE AND NEGATIVE INITIA CURVATURE J. Ryu, J-G.
Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment. P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson
 UCRL-JC-30440 PREPRINT Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Materials Research Society Spring
UCRL-JC-30440 PREPRINT Curvature of a Cantilever Beam Subjected to an Equi-Biaxial Bending Moment P. Krulevitch G. C. Johnson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Materials Research Society Spring
Finite-Element Analysis of Stress Concentration in ASTM D 638 Tension Specimens
 Monika G. Garrell, 1 Albert J. Shih, 2 Edgar Lara-Curzio, 3 and Ronald O. Scattergood 4 Journal of Testing and Evaluation, Vol. 31, No. 1 Paper ID JTE11402_311 Available online at: www.astm.org Finite-Element
Monika G. Garrell, 1 Albert J. Shih, 2 Edgar Lara-Curzio, 3 and Ronald O. Scattergood 4 Journal of Testing and Evaluation, Vol. 31, No. 1 Paper ID JTE11402_311 Available online at: www.astm.org Finite-Element
AERO 214. Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars
 AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
AERO 214 Lab II. Measurement of elastic moduli using bending of beams and torsion of bars BENDING EXPERIMENT Introduction Flexural properties of materials are of interest to engineers in many different
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever
 Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Finite Element Analysis of Piezoelectric Cantilever Nitin N More Department of Mechanical Engineering K.L.E S College of Engineering and Technology, Belgaum, Karnataka, India. Abstract- Energy (or power)
Fracture Test & Fracture Parameters of Self Compacting Concrete using ANSYS. Zeel Vashi 1,Megha Thomas 2 I. INTRODUCTION
 International Journal of Technical Innovation in Modern Engineering & Science (IJTIMES) Impact Factor: 3.45 (SJIF-2015), e-issn: 2455-2584 Volume 3, Issue 05, May-2017 Fracture Test & Fracture Parameters
International Journal of Technical Innovation in Modern Engineering & Science (IJTIMES) Impact Factor: 3.45 (SJIF-2015), e-issn: 2455-2584 Volume 3, Issue 05, May-2017 Fracture Test & Fracture Parameters
Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPERIMENT #1 MOTOR CHARACTERISTICS FORCE/TORQUE SENSORS AND DYNAMOMETER PART 1
 Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPEIMENT #1 MOTO CHAACTEISTICS FOCE/TOQUE SENSOS AND DYNAMOMETE PAT 1 Force Sensors Force and torque are not measured directly. Typically, the deformation or strain of some
Mechatronics II Laboratory EXPEIMENT #1 MOTO CHAACTEISTICS FOCE/TOQUE SENSOS AND DYNAMOMETE PAT 1 Force Sensors Force and torque are not measured directly. Typically, the deformation or strain of some
Validation of Stresses with Numerical Method and Analytical Method
 ISSN 303-451 PERIODICALS OF ENGINEERING AND NATURAL SCIENCES Vol. 4 No. 1 (016) Available online at: http://pen.ius.edu.ba Validation of Stresses with Numerical Method and Analytical Method Enes Akca International
ISSN 303-451 PERIODICALS OF ENGINEERING AND NATURAL SCIENCES Vol. 4 No. 1 (016) Available online at: http://pen.ius.edu.ba Validation of Stresses with Numerical Method and Analytical Method Enes Akca International
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES
 CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
CHAPTER 14 BUCKLING ANALYSIS OF 1D AND 2D STRUCTURES 14.1 GENERAL REMARKS In structures where dominant loading is usually static, the most common cause of the collapse is a buckling failure. Buckling may
PLAT DAN CANGKANG (TKS 4219)
 PLAT DAN CANGKANG (TKS 4219) SESI I: PLATES Dr.Eng. Achfas Zacoeb Dept. of Civil Engineering Brawijaya University INTRODUCTION Plates are straight, plane, two-dimensional structural components of which
PLAT DAN CANGKANG (TKS 4219) SESI I: PLATES Dr.Eng. Achfas Zacoeb Dept. of Civil Engineering Brawijaya University INTRODUCTION Plates are straight, plane, two-dimensional structural components of which
An Increase in Elastic Buckling Strength of Plate Girder by the Influence of Transverse Stiffeners
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 6 May 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 An Increase in Elastic Buckling Strength of Plate Girder by the Influence of Transverse Stiffeners
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 2 Issue 6 May 2017 ISSN: 2455-5703 An Increase in Elastic Buckling Strength of Plate Girder by the Influence of Transverse Stiffeners
Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures
 Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures Oldřich Šuba 1,*, Oldřich Šuba jr. 1, and Soňa Rusnáková 1 1 Tomas Bata University in
Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures Oldřich Šuba 1,*, Oldřich Šuba jr. 1, and Soňa Rusnáková 1 1 Tomas Bata University in
ScienceDirect. Experimental Validation on Lift Increment of a Flapping Rotary Wing with Boring-hole Design
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (2015 ) 1543 1547 APISAT2014, 2014 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology, APISAT2014 Experimental
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (2015 ) 1543 1547 APISAT2014, 2014 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology, APISAT2014 Experimental
Stress Analysis and Validation of Superstructure of 15-meter Long Bus under Normal Operation
 AIJSTPME (2013) 6(3): 69-74 Stress Analysis and Validation of Superstructure of 15-meter Long Bus under Normal Operation Lapapong S., Pitaksapsin N., Sucharitpwatkul S.*, Tantanawat T., Naewngerndee R.
AIJSTPME (2013) 6(3): 69-74 Stress Analysis and Validation of Superstructure of 15-meter Long Bus under Normal Operation Lapapong S., Pitaksapsin N., Sucharitpwatkul S.*, Tantanawat T., Naewngerndee R.
