WAVES. 1.) A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium. (You can t have water waves without water!)
|
|
|
- Octavia Gallagher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WAVES 1.) A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium. (You can t have water waves without water!) 2.) A wave produced by a force that is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave disturbance is called a transverse wave. a.) An example of a transverse wave is: i.) the wave produced when a taught string it jiggled. i.) the wave produced when a rock is thrown into a pond. 3.) A wave produced by a force that is in the same direction as the propagating wave disturbance is called a longitudinal wave. a.) An example of a longitudinal wave is sound wave. 1.)
2 RESONANCE 1.) A spring has one frequency at which it will vibrate. That frequency is called the natural frequency of the spring system. 2.) Apply a force to the spring. If the frequency of the force matches the natural frequency of the spring system, the amplitude of the spring s oscillation will become bigger and bigger. 3.) This is called resonance. 4.) In fact, if you apply a periodic force to system and the frequency of that force matches one of the natural frequencies of the system, the amplitude of the system s oscillation will get bigger and bigger and you will have a resonance between the force and the system. 2.)
3 SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES 1.) If waves from two sources moving in the same medium superimpose on one another, the waves will overlay one another. a.) If the overlay produces an additive effect, the superposition is said to be constructive superposition. b.) If the overlay produces a subtractive effect, the superposition is said to be destructive superposition. 3.)
4 STANDING WAVES A standing wave is generated when waves generated by two different sources in a system superimpose creating a single, orderly wave. The classic example of the production of standing waves uses a rope tied rigidly to a fixed structure at both ends. If one end is jiggled so as to generate a wave, that wave will proceed down the rope (let s say it moves to the left) until it strikes the fixed end on the left whereupon it will bounce and move back toward the right. If the jiggle is periodic producing wave after wave, the new waves moving to the left will superimpose with the bounced waves moving to the right. Normally, this superposition will appear chaotic with the rope jumping around somewhat chaotically. But under the right condition, the resulting motion will be very orderly. 4.)
5 STANDING WAVES on a ROPE The right condition is essentially that of resonance: If the frequency of the force producing the vibration just happens to match one of the natural frequencies of the oscillating system, the resulting superposition will produce standing waves. There is a trick tp determining what frequency (or frequencies) will do this. That trick starts by looking at the geometry of the system. To see how this works, we ll look at our rope example more closely. But before we do, there are a few observation we need to make. 5.)
6 1.) As you know, a wave is traditionally characterized by its frequency ν, its wavelength λ and its wave velocity v. λ (meters/cycle) v (meters/second) ν (cycles passing by per second) 2.) The relationship between these three parameters is: v = λ ν. 6.)
7 3.) That means that if we know the wave velocity, and if we can determine the appropriate wavelength for a given situation, we can determine the frequency of the wave and, hence, the frequency our force must vibrate at to generate a standing wave. 4.) So how to get the appropriate wavelength for a given system? Let s look at our rope situation. What constraint must our appropriate wavelength satisfy? Well, it better have a node (a fixed point) at each end, as each end is tied to a rigid structure and can t move. What kind of wave will do that? Three are shown below. NOTICE: In all three cases, the end-point constraints are met (that is, they ALL have nodes at both ends of their respective wavelengths). 7.)
8 5.) This is all fine and dandy, but how does it help with our problem? It helps because we know that the span between the ends is a fixed distance L. All we have to do it link L to the wavelengths viewed, and we have the wavelengths in terms of a know quantity. Specifically: a.) For the first situation: We know L, so the question is, How many wavelengths are in L? L Looking at the wave, we can see that there are two quarter-wavelengths ( ) in L (sounds obscure you ll get used to it). That is, we can write: λ 4 L = 2 λ 4 ( ) λ = 2L. 8.)
9 6.) Assuming we know the wave velocity (this would normally be given), we can write: v = λ ν = ( 2L)ν ν = v 2L 7.) So let s say the wave velocity is 3 m/s and the length of the rope is 2 meters. That means: ν = v 2L ( ) ( ) = 3 m/s 2 2 m ν =.75 sec 1 (this unit is the same as a Hertz, Hz) 9.)
10 8.) Apparently, if we jiggle the rope at.75 Hz, we will get a standing wave on the rope that, over time, looks like: 9.) We could do a similar bit of analysis for the other two waveforms. 10.) ONE OTHER THING: If there had been any internal constraints if, for instance, we had pinched the rope at L/2 making that point a node, then our waveform wouldn t have worked (look at it there is an antinode an extreme at L/2) and we would have had to have done a bit more thinking (you ll see examples of this in class). 10.)
11 So in general, what is the procedure to be followed in these kinds of problems? They are: a.) Identify the end-point constraints. (In our example, it was that there had to be nodes fixed points at each end.) b.) On a sine wave, identify what the waveform is going to look like. (You ll see examples of this in class.) c.) Once you know what the waveform should look like, be sure that any internal constraints imposed on the system are met by the waveform. (Again, you ll see examples of this in class.) d.) When satisfied, ask the question, How many quarter-wavelength are there in L? Put a little differently, fill in the? in the expression: λ (?)( λ ) 4 = L v = λ ν e.) Solve for in terms of L, then use to get the required frequency. 11.)
12 Pipe Closed at One End Another outstanding example of a standing wave is the waveform that is generated when air is piped through a tube. 1.) Consider a pipe of length L closed at one end. What frequency of sound will stand in the pipe? 2.) In a problem like this, the first thing you have to do is identity what standing waves will fit in the pipe. To do that, you have to begin by identifying the end-point constraints. a.) For a pipe closed at one end, the endpoint constraints dictate an anti-node at the open end and a node at the closed end. 12.)
13 3.) The waveforms that fit the bill are shown below, then reproduced in the vertical: node anti-node anti-node anti-node 2 nd waveform 1 st waveform 3 rd waveform 13.)
14 4.) Each section of wave has a numerical length equal to the length of the tube, or L. 5.) If we ask the question, How many wavelengths are there in L? (That is, we need to complete the?λ = L By examination, there is a quarter wavelength in L, so we can write: 1 4 λ 1 = L λ 1 = 4L Minor Note: In real life, the effective length of the tube has to be altered due to perturbation effects at the ends. In the case of a singly open tube, the effective length of the tube isn t L but rather L+.4d, where d is the tube s diameter. For doubly open tube, it s L+. 8d. 14.)
15 6.) We know the speed of sound in air is approximately 330 m/s and we know the relationship between a wave s velocity and its wavelength and frequency is v = λ 1 ν 1. Assuming the tube s length is 2 meters (and ignoring the radius correction mentioned at the bottom of the previous page), we can write: v = λ 1 ν 1 ν 1 = v λ 1 ν 1 = v 4L (330 m/s) ν 1 = 4(2 m) ν 1 = Hz 7.) Put a Hz tuning fork at the mouth of our tube and it will howl quite loudly. 15.)
16 8.) Doing the same calculation for the second situation where there is three-quarter of a wave in L, we can write: v = λ 2 ν 2 ν 2 = v λ 2 v ν 2 = ( 4 3 )L (3)(330 m/s) ν 2 = 4(2 m) ν 2 = Hz 9.) Put a Hz tuning fork at the mouth of our tube and it will howl quite loudly. 16.)
17 10.) Doing the same calculation for the third situation where there is five-quarters of a wave in L, we can write: v = λ 3 ν 3 ν 3 = v λ 3 v ν 3 = ( 4 5 )L (5)(330 m/s) ν 3 = 4(2 m) ν 3 = Hz 11.) Put a Hz tuning fork at the mouth of our tube and it will howl quite loudly. 17.)
18 Pipe Open at Both Ends 12.) Consider a pipe of length L open at both ends. What frequency of sound will stand in the pipe? 13.) In a problem like this, the first thing you have to do is identity what standing waves will fit in the pipe. To do that, you have to begin by identifying the end-point constraints. a.) For a pipe open at both ends, the endpoint constraints dictate anti-nodes at the both ends. 18.)
19 14.) On the sine wave presented below, you can see the waveforms that satisfy the endpoint constraints. Once determined, they can be put on the sketch to the right (though on a test you probably won t redraw the sketch to fit the actual pipe). anti-node anti-node anti-node anti-node 2 nd waveform 1 st waveform 3 rd waveform 19.)
20 15.) The lowest frequency--the longest wavelength--is shown as the first sketch 1 to the right. Noting that, we can 2 λ 1 = L write: v = λ 1 ν 1 ν 1 = v λ 1 ν 1 = v 2L ν 1 = (1 2 )(330 m/s) (2 m) ν 1 = 82.5 Hz 16.) Send a 330 Hz sound wave down the tube, and it will howl at that frequency. 20.)
21 16.) The second lowest frequency--the second longest wavelength--is shown as the middle sketch to the right. Noting that λ 2 = L, we can write: v = λ 2 ν 2 ν 2 = v λ 2 ν 2 = v L (330 m/s) ν 2 = (2 m) ν 2 = 165 Hz 16.) Send a 165 Hz sound wave down the tube, and it will howl at that frequency. 21.)
22 16.) The second lowest frequency--the second longest wavelength--is shown as the middle sketch to the right. Noting 6 that, we can write: 4 λ = λ = L 3 v = λ 3 ν 3 ν 3 = v λ 3 v ν 3 = 2 3 L ν 3 = (3)(330 m/s) (2)(2 m) ν 3 = Hz 16.) Send a 110 Hz sound wave down the tube and it will howl at that frequency. 15.)
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance
 Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Physics 248 Spring 2009
 Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Transverse standing waves on a string and speed of sound in air Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of the lab. You must use complete
Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Transverse standing waves on a string and speed of sound in air Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of the lab. You must use complete
Waves Review Checklist Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one
 5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
A. Incorrect! Frequency and wavelength are not directly proportional to each other.
 MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 1: Waves and Periodic Motion Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Two waves on identical strings have frequencies in a ratio of 3 to. If their wave speeds are the same, then
MCAT Physics Problem Solving Drill 1: Waves and Periodic Motion Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Two waves on identical strings have frequencies in a ratio of 3 to. If their wave speeds are the same, then
STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE
 Name: PHYSICS 119 SPRING 2008 S.N.: SECTION: Experiment 2 PARTNER: DATE: STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE Objectives Observe standing waves in a stretched string Examine how an external oscillator can cause
Name: PHYSICS 119 SPRING 2008 S.N.: SECTION: Experiment 2 PARTNER: DATE: STANDING WAVES AND RESONANCE Objectives Observe standing waves in a stretched string Examine how an external oscillator can cause
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties
 Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
Let s Review What is Sound?
 Mathematics of Sound Objectives: Understand the concept of sound quality and what it represents. Describe the conditions which produce standing waves in a stretched string. Be able to describe the formation
Mathematics of Sound Objectives: Understand the concept of sound quality and what it represents. Describe the conditions which produce standing waves in a stretched string. Be able to describe the formation
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
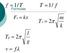 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
1 f. result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by
 result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Physics 111. Lecture 31 (Walker: ) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Standing Waves Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature
 Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Periodic Functions and Waves
 Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 06 20167ul06A Page 1 of 14 Chapter 06 Waves Periodic Functions and Waves Consider a function f of one variable x. That is, we consider a rule by which a number f(x)
Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 06 20167ul06A Page 1 of 14 Chapter 06 Waves Periodic Functions and Waves Consider a function f of one variable x. That is, we consider a rule by which a number f(x)
To prepare for this lab, you should read the following sections of the text: Sections 3.4, 11.3, and 12.1 OVERVIEW
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /35 PHYSICS 107 LAB #4: WIND INSTRUMENTS: WAVES IN AIR Equipment: Thermometer, function generator, two banana plug wires, resonance tube with
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /35 PHYSICS 107 LAB #4: WIND INSTRUMENTS: WAVES IN AIR Equipment: Thermometer, function generator, two banana plug wires, resonance tube with
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
Physics 25 Section 2 Exam #1 February 1, 2012 Dr. Alward
 1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Standing Waves If the same type of waves move through a common region and their frequencies, f, are the same then so are their wavelengths, λ.
 Standing Waves I the same type o waves move through a common region and their requencies,, are the same then so are their wavelengths,. This ollows rom: v=. Since the waves move through a common region,
Standing Waves I the same type o waves move through a common region and their requencies,, are the same then so are their wavelengths,. This ollows rom: v=. Since the waves move through a common region,
PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics. Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester
 PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Sounds of the Universe NASA/JPL, September 2016 2 Properties of Waves Wavelength: λ, length
PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Sounds of the Universe NASA/JPL, September 2016 2 Properties of Waves Wavelength: λ, length
VELOCITY OF SOUND. Apparatus Required: 1. Resonance tube apparatus
 VELOCITY OF SOUND Aim : To determine the velocity of sound in air, with the help of a resonance column and find the velocity of sound in air at 0 C, as well. Apparatus Required: 1. Resonance tube apparatus
VELOCITY OF SOUND Aim : To determine the velocity of sound in air, with the help of a resonance column and find the velocity of sound in air at 0 C, as well. Apparatus Required: 1. Resonance tube apparatus
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Sound. Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube.
 Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
13.3 Interference and Superposition. Interference and Superposition Constructive Interference Destructive Interference Standing Waves
 13.3 Interference and Superposition Interference and Superposition Constructive Interference Destructive Interference Standing Waves Interference and Superposition When raindrops fall into still water,
13.3 Interference and Superposition Interference and Superposition Constructive Interference Destructive Interference Standing Waves Interference and Superposition When raindrops fall into still water,
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Physics 1C. Lecture 13B
 Physics 1C Lecture 13B Speed of Sound! Example values (m/s): Description of a Sound Wave! A sound wave may be considered either a displacement wave or a pressure wave! The displacement of a small element
Physics 1C Lecture 13B Speed of Sound! Example values (m/s): Description of a Sound Wave! A sound wave may be considered either a displacement wave or a pressure wave! The displacement of a small element
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Physics 101 Lecture 18 Vibrations, SHM, Waves (II)
 Physics 101 Lecture 18 Vibrations, SHM, Waves (II) Reminder: simple harmonic motion is the result if we have a restoring force that is linear with the displacement: F = -k x What would happen if you could
Physics 101 Lecture 18 Vibrations, SHM, Waves (II) Reminder: simple harmonic motion is the result if we have a restoring force that is linear with the displacement: F = -k x What would happen if you could
A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion
 1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Fineman CP Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves
 Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Chapter 16 Traveling Waves GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms as it is used in physics,
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right.
 1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb Please fill in your Student ID number (UIN): IMPORTANT
 Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb. 2005 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your name neatly: Last name: First name: Sign your name:
Physics 221: Optical and Thermal Physics Exam 1, Sec. 500, 14 Feb. 2005 Instructor: Dr. George R. Welch, 415 Engineering-Physics, 845-7737 Print your name neatly: Last name: First name: Sign your name:
Fineman Honors Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Transverse Wave - Only in solids (having rigidity), in liquids possible only on the surface. Longitudinal Wave
 Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Downloaded from
 Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
 Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
VII. Vibrations, Waves and Sound. Concept Review. Conflicting Contentions. 1. Vibrating Strings 2. The Speed of Sound in Metal 3.
 VII. Vibrations, Waves and Sound Concept Review Conflicting Contentions 1. Vibrating Strings 2. The Speed of Sound in Metal 3. Wave Collisions Qualitative Reasoning 1. Piano Wires 2. Organ Pipes 3. Out
VII. Vibrations, Waves and Sound Concept Review Conflicting Contentions 1. Vibrating Strings 2. The Speed of Sound in Metal 3. Wave Collisions Qualitative Reasoning 1. Piano Wires 2. Organ Pipes 3. Out
jfpr% ekuo /kez iz.ksrk ln~xq# Jh j.knksm+nklth egkjkt
 Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Physics 231 Lecture 28
 Physics 231 Lecture 28 Main points of today s lecture: Reflection of waes. rigid end inerted wae free end non-inerted wae Standing waes on string: n 2L f n λn n 1, 2, 3,,, 2L n Standing wae in air columns:
Physics 231 Lecture 28 Main points of today s lecture: Reflection of waes. rigid end inerted wae free end non-inerted wae Standing waes on string: n 2L f n λn n 1, 2, 3,,, 2L n Standing wae in air columns:
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
Course Name: AP Physics. Team Names: Jon Collins. Velocity Acceleration Displacement
 Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Chapter 18 Solutions
 Chapter 18 Solutions 18.1 he resultant wave function has the form y A 0 cos φ sin kx ω t + φ (a) A A 0 cos φ (5.00) cos (π /4) 9.4 m f ω π 100π π 600 Hz *18. We write the second wave function as hen y
Chapter 18 Solutions 18.1 he resultant wave function has the form y A 0 cos φ sin kx ω t + φ (a) A A 0 cos φ (5.00) cos (π /4) 9.4 m f ω π 100π π 600 Hz *18. We write the second wave function as hen y
Lecture 30. Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t)
 To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Experiment IV. To find the velocity of waves on a string by measuring the wavelength and frequency of standing waves.
 Experiment IV The Vibrating String I. Purpose: To find the velocity of waves on a string by measuring the wavelength and frequency of standing waves. II. References: Serway and Jewett, 6th Ed., Vol., Chap.
Experiment IV The Vibrating String I. Purpose: To find the velocity of waves on a string by measuring the wavelength and frequency of standing waves. II. References: Serway and Jewett, 6th Ed., Vol., Chap.
3 THE P HYSICS PHYSICS OF SOUND
 Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation: Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, t =
 Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 9
 1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
Lecture 28 March
 Lecture 28 March 30. 2016. Standing waves Musical instruments, guitars, pianos, organs Doppler Effect Resonance 3/30/2016 Physics 214 Spring 2016 1 Waves on a string If we shake the end of a rope we can
Lecture 28 March 30. 2016. Standing waves Musical instruments, guitars, pianos, organs Doppler Effect Resonance 3/30/2016 Physics 214 Spring 2016 1 Waves on a string If we shake the end of a rope we can
No Lecture on Wed. But, there is a lecture on Thursday, at your normal recitation time, so please be sure to come!
 Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect
 Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect Will Stoll, Norcross High School Problem: To understand the basic principles of Quantum Mechanics through an
Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect Will Stoll, Norcross High School Problem: To understand the basic principles of Quantum Mechanics through an
