VELOCITY OF SOUND. Apparatus Required: 1. Resonance tube apparatus
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VELOCITY OF SOUND Aim : To determine the velocity of sound in air, with the help of a resonance column and find the velocity of sound in air at 0 C, as well. Apparatus Required: 1. Resonance tube apparatus It is an air column formed by a tube with an arrangement to adjust the level of water filled in it. The surface of water in the tube and open end serve the purpose of rigid and yielding reflecting surfaces respectively. The surface of water will act as the closed end. Generally, resonance apparatus (Figure 1) consists of a metal pipe of length and diameter 1 meter and 2.4 cm respectively, is clamped on a vertical wooden plank. The wooden plank is fixed on heavy metallic base with levelling screws. The lower end of the resonance column pipe is connected to water reservoir with a rubber tube. A transparent tube and scale is also connected parallel to the resonance pipe. The reservoir can be raised or lowered for adjusting the length of the air column. Figure 1. The resonance tube apparatus 2. Tunning forks of different frequencies 3. Rubber pad 4. Thermometer
2 General information related to the experiment 01. Sound is caused by the vibration motion of the particles of a medium. Sound can travel in solids, liquids and gases but not in vacuum. 02. Sound travels in the form of waves. There are two types of waves, longitudinal and transverse. 03. Longitudinal waves consist of compressions and rarefactions and particles of the medium vibrate in the same direction as that of the motion. One compression and one rarefaction form one complete wave. In gases, sound travels in the form of longitudinal wave. 04. Transverse wave consist of crests and troughs and the particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of propagation of the wave motion Time period is the time taken by the vibrating body to complete one vibration. 06. Frequency is the number of vibrations executed by a vibrating body in one second. If T be the time period of vibration, then the frequency f is given by the relation f = 07. Wavelength is the distance travelled by a wave during that time in which a particle completes one vibration, it is denoted by the letter λ. 08. Tuning fork is a U shaped bar made of steel with a handle attached at the bend. When it is struck with a hard substance, the prongs begin to vibrate. 09. Velocity of sound. The distance travelled by the sound waves in one second is called the velocity of sound. If λ is the wavelength of sound waves and f is their frequency, then the velocity v of the wave is given by the relation, v = f λ Further, the velocity of sound is proportional to Pressure and density refer to the medium in which the sound is travelling. Since at a constant temperature the ratio (pressure/density) is constant for gas, hence the velocity of sound in gas is independent of pressure. The effects of other atmospheric conditions on the velocity of sound are under. a. Temperature effect. The velocity of sound increases with the rise in temperature as v α T, T being the absolute temperature. b. Humidity Effect. Velocity of sound in humid air is relatively more compared to dry air as v α (1/ρ), ρ of humid air is less than ρ (density) of dry air.
3 c. Effect of the medium. The velocity of sound in water is about four times that in air at the same temperature. Also sound travels much faster in solids than in gases. Sound, however, does not really pass from one medium to another when the media differ. Theory : When the tuning fork is vibrated and held above the open end, longitudinal waves are sent down the air column. These waves are reflected at the water surface and thus produce standing waves. Nodes are produced at the water surface and antinodes are produced at the open end. Figure 2. Representation of nodes and antinodes A loud sound is produced in the air column, when the frequency of waves in the air column becomes equal to the natural frequency of tuning fork,. It is the condition for resonance. It occurs only when the length of air column is proportional to one-fourth of the wavelength of sound waves having frequency equal to frequency of tuning fork. Let l 1 and l 2 be the first and second resonating lengths respectively for a tuning fork of frequency f, and λ is the wavelength of the sound produced by the tuning fork. Then, for first resonance, and for the second resonance, Thus, from the above two equations, λ = 2 (l 2 l 1 ) We know that for all forms of wave motion v = f λ, where v is velocity, f is frequency and λ is wavelength. Therefore, the velocity of sound v t at the room temperature t ºC is given by the following formula V t = 2f (l 2 l 1 )...(1) Making use of the Laplace s formula the velocity of sound (v o ) at 0ºC can be given as under V 0 = ( V t -0.6t) m/sec...(2)
4 Where, v 0 - velocity of sound in air at 0 0 C. v - velocity of sound in air at temperature t. t - Room temperature. According to equation 1, when V t is constant, the graph between f and ( l 2 l 1 ) should be a rectangular hyperbola. The air inside the tube will resonate in much the same fashion as air inside an organ pipe that is when standing waves can be set up so that a pressure antinode occurs at the closed end of the tube while a pressure node occurs at the open end of the tube. Procedure : 1. Partly fill the tube and water supply container with water and stand the tube upright in it. 2. Strike a tuning fork of known frequency with the supplied rubber pad. The tuning fork now produces longitudinal waves with a frequency equal to the natural frequency of the tuning fork. 3. Hold the vibrating tuning fork horizontally above the mouth of the tube. Caution: do not touch the tube with the tuning fork. Sound waves are passes down to the tube and reflect back at the water surface. 4. Move the water surface, up and down several times by using the movable water reservoir until a maximum sound is heard. Tighten the clamp at this position. 5. Measure the length of air column at that position. This is taken as the first resonant length, l Then raise the tube approximately about three times the first resonant length. 7. Excite the tuning fork again and place it on the mouth of the tube. 8. Change the height of the tube until the maximum sound intensity is heard. 9. Measure the length of air column at that position. This is taken as the second resonant length, l Find the difference in the two resonating lengths for each tuning fork. 11. We can now calculate the velocity of sound in air at room temperature by using the relation, V t = 2f (l 2 l 1 ) 12. Repeat the above procedures for the other tuning forks supplied and in each time, calculate the value of V t. 13. The mean of the calculated values will give the velocity of sound in air at room temperature. 14. Measure the temperature of air inside the pipe with the help of a thermometer. 15. By using the value of V t, we can calculate the velocity of sound in air at 0 0 C as,
5 V 0 = ( V t -0.6t) m/sec Observation : Temperature of air column inside the pipe =...ºC Table for the first and second resonating length for air column S.N Frequency f (Hz) First resonating length, l 1 (cm) Second resonating length, l 2 (cm) Diff. Meter (l 2 -l 1 ) Velocity V t = 2f (l 2 l 1 ) I II Mean l 1 I II Mean I 2 (m/s) Calculation : 01. Substitute the values of f and (l 2 l 1 ) for each set of observation in the formula V t = 2f (l 2 l 1 ) and calculate for V t i.e. the velocity of sound at tºc.
6 02. Substitute the value of V t in Equation 2 and determine V 0, i.e. the velocity of sound in air at 0 ºC. 03. Draw a graph between f and (l 2 l 1 ) entered in observation table with f and (l 2 l 1 ) along X and Y axes respectively. Result : 01. The graph between f and (l 2 l 1 ) comes out to be a rectangular hyperbola. 02. Velocity of sound in air is obtained as...m/sec. 02. Value of the velocity of sound in air at 0ºC...m/sec. Precautions : 01. Align the resonance column perfectly vertical at the starting of the experiment. 02. Strike the tuning fork against the rubber pad carefully. 03. Near resonance, the length of air column should be changed in smaller steps. 04. The vibrating tuning fork should be held near the open end of the pipe in such a manner that its vibrations are in a vertical plane. 05. The tuning fork should not touch the pipe. 06. The surrounding should be free from any noise. QUESTIONS (a) (b) Explain what is meant by the term "resonance". Explain in qualitative terms why a pressure antinode occurs at the closed end of the tube and a pressure node occurs close to the open end of the tube. What approximate relationship holds between the length of the tube and the wavelength of the standing wave for this fundamental mode of vibration? (c) Write down the relationship that exists between V, f, and l. (d) What shape of graph should be obtained if wavelength, λ, is plotted versus frequency, f?...
7
Physics 248 Spring 2009
 Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Transverse standing waves on a string and speed of sound in air Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of the lab. You must use complete
Physics 248 Spring 2009 Lab 1: Transverse standing waves on a string and speed of sound in air Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of the lab. You must use complete
Downloaded from
 Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Sound. Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube.
 Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Sound Purpose Problem 1 Problem 2 Measure the speed of sound in air by means of resonance in a tube; Measure the speed of sound in a metal rod using Kundt s tube. Introduction and Theory When a vibrating
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance
 Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
Laboratory 4: Wave Motion and Resonance Part Introduction The sound from a vibrating tuning fork is much louder if it is held over an air column whose length allows it to vibrate in sympathy with the tuning
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right.
 1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation: Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, t =
 Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Physics 25 Section 2 Exam #1 February 1, 2012 Dr. Alward
 1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet.
 17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion
 1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
PHYSICS A 2823/01. Wave Properties. OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary GCE
 OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary GCE PHYSICS A 2823/01 Wave Properties Friday 10 JUNE 2005 Morning 45 minutes Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional materials: Electronic
OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary GCE PHYSICS A 2823/01 Wave Properties Friday 10 JUNE 2005 Morning 45 minutes Candidates answer on the question paper. Additional materials: Electronic
WAVES( SUB) 2. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity and inertia
 WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Marketed and Distributed By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
Energy - the ability to do work or cause change. 1 point
 Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Assignment - 3 Board Papers & Numericals 1. Sound 2. Calorimetry 3. Radioactivity. Submission Date : / /
 Assignment - 3 Board Papers & Numericals 1. Sound 2. Calorimetry 3. Radioactivity Submission Date : / / Sound, Calorimetry, Radioactivity (Board papers) Assignment Sheet 1. A tuning fork held over an air
Assignment - 3 Board Papers & Numericals 1. Sound 2. Calorimetry 3. Radioactivity Submission Date : / / Sound, Calorimetry, Radioactivity (Board papers) Assignment Sheet 1. A tuning fork held over an air
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Sound Waves SOUND VIBRATIONS THAT TRAVEL THROUGH THE AIR OR OTHER MEDIA WHEN THESE VIBRATIONS REACH THE AIR NEAR YOUR EARS YOU HEAR THE SOUND.
 SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
 Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
jfpr% ekuo /kez iz.ksrk ln~xq# Jh j.knksm+nklth egkjkt
 Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Phone : 93 93 7779, 9893 58881 Sount & Waves Page: 9 fo/u fopkjr Hkh# tu] ugha vkjehks dke] foifr ns[k NksM+s rqjar e/;e eu dj ';kea iq#"k flag ladyi dj] lgrs foifr vusd] ^cuk^ u NksM+s /;s; dks] j?kqcj
Resonance on Air Column
 Resonance on Air Column Objectives a. To measure the speed of sound with the help of sound wave resonance in air column inside the tube with one end closed. b. To do error analysis of speed of sound measurement.
Resonance on Air Column Objectives a. To measure the speed of sound with the help of sound wave resonance in air column inside the tube with one end closed. b. To do error analysis of speed of sound measurement.
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Lecture 28 March
 Lecture 28 March 30. 2016. Standing waves Musical instruments, guitars, pianos, organs Doppler Effect Resonance 3/30/2016 Physics 214 Spring 2016 1 Waves on a string If we shake the end of a rope we can
Lecture 28 March 30. 2016. Standing waves Musical instruments, guitars, pianos, organs Doppler Effect Resonance 3/30/2016 Physics 214 Spring 2016 1 Waves on a string If we shake the end of a rope we can
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
GENERAL PHYSICS (3) LABORATORY PHYS 203 LAB STUDENT MANUAL
 Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj By Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj GENERAL PHYSICS (3) LABORATORY PHYS 203 LAB STUDENT MANUAL Name:-. ID# KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARMENT 1st semester 1430H Contents
Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj By Haifaa altoumah& Rabab Alfaraj GENERAL PHYSICS (3) LABORATORY PHYS 203 LAB STUDENT MANUAL Name:-. ID# KING ABDULAZIZ UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARMENT 1st semester 1430H Contents
1. Data analysis question.
 1. Data analysis question. The photograph below shows a magnified image of a dark central disc surrounded by concentric dark rings. These rings were produced as a result of interference of monochromatic
1. Data analysis question. The photograph below shows a magnified image of a dark central disc surrounded by concentric dark rings. These rings were produced as a result of interference of monochromatic
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
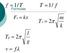 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
CHAPTERS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS
 CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
B.Sc. SEMESTER I PHYSICS COURSE : US01CPHY01 UNIT 3 : SOUND
 B.Sc. SEMESTER I PHYSICS COURSE : US01CPHY01 UNIT 3 : SOUND INTRODUCTION TO TRANSVERSE AND LONGITUDINAL WAVES Longitudinal Waves : The longitudinal waves are such that when they pass through any medium,
B.Sc. SEMESTER I PHYSICS COURSE : US01CPHY01 UNIT 3 : SOUND INTRODUCTION TO TRANSVERSE AND LONGITUDINAL WAVES Longitudinal Waves : The longitudinal waves are such that when they pass through any medium,
GAS LAWS. Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant)
 1 GAS LAWS Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant) The diagram below shows the apparatus which gives a direct reading for both the volume and pressure
1 GAS LAWS Boyle s Law: Investigating the dependence of Volume on Pressure (Temperature kept constant) The diagram below shows the apparatus which gives a direct reading for both the volume and pressure
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves. What is a wave?
 Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
Unit 4 Parent Guide: Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance or vibration that carries energy from one location to another. Some waves require a medium to transmit the energy whereas others can travel
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
 Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
Physics Worksheet Sound and Light Section: Name:
 Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Exercises The Origin of Sound (page 515) 26.2 Sound in Air (pages ) 26.3 Media That Transmit Sound (page 517)
 Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
Exercises 26.1 The Origin of (page 515) Match each sound source with the part that vibrates. Source Vibrating Part 1. violin a. strings 2. your voice b. reed 3. saxophone c. column of air at the mouthpiece
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
St Olave s Grammar School. AS Physics Mock Revision Checklist
 St Olave s Grammar School Mock Practical skills.. a Can you design experiments, including ones to solve problems set in a practical context?.. b Can you identify the variables that must be controlled in
St Olave s Grammar School Mock Practical skills.. a Can you design experiments, including ones to solve problems set in a practical context?.. b Can you identify the variables that must be controlled in
WAVES. 1.) A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium. (You can t have water waves without water!)
 WAVES 1.) A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium. (You can t have water waves without water!) 2.) A wave produced by a force that is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave
WAVES 1.) A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium. (You can t have water waves without water!) 2.) A wave produced by a force that is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Physics 111. Lecture 31 (Walker: ) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Standing Waves Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature
 Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is:
 1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
UIC PHYSICS 105 Fall 2014 Practice Final Exam. UIC Physics 105. Practice Final Exam. Fall 2014 Best if used by December 7 PROBLEM POINTS SCORE
 UIC Physics 105 Practice Final Exam Fall 2014 Best if used by December 7 PROBLEM POINTS SCORE Multiple Choice Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 50 11 8 7 11 13 Total 100 Page 1 of 7 MULTIPLE
UIC Physics 105 Practice Final Exam Fall 2014 Best if used by December 7 PROBLEM POINTS SCORE Multiple Choice Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Problem 5 50 11 8 7 11 13 Total 100 Page 1 of 7 MULTIPLE
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Contents. Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy. Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3
 Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Lehman College Department of Physics and Astronomy Lab manual for PHY 141 Sound, speech and music Contents 1 PENDULUM EXPERIMENT 3 2 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION 9 3 STANDING WAVES ON STRINGS 15 4 STANDING WAVES
Transverse Wave - Only in solids (having rigidity), in liquids possible only on the surface. Longitudinal Wave
 Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Test 3 Preparation Questions
 Test 3 Preparation Questions A1. Which statement is true concerning an object executing simple harmonic motion? (A) Its velocity is never zero. (B) Its acceleration is never zero. (C) Its velocity and
Test 3 Preparation Questions A1. Which statement is true concerning an object executing simple harmonic motion? (A) Its velocity is never zero. (B) Its acceleration is never zero. (C) Its velocity and
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test
 Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Name: Section: Forms of Energy Practice Test Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer on the line. 1. What
Activity Template. Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY
 Activity Template Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: Density and Pitch, is there a relationship? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity
Activity Template Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Subject Area(s): Sound Associated Unit: None Associated Lesson: None Activity Title: Density and Pitch, is there a relationship? Grade Level: 8 (7-9) Activity
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Periodic Functions and Waves
 Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 06 20167ul06A Page 1 of 14 Chapter 06 Waves Periodic Functions and Waves Consider a function f of one variable x. That is, we consider a rule by which a number f(x)
Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 06 20167ul06A Page 1 of 14 Chapter 06 Waves Periodic Functions and Waves Consider a function f of one variable x. That is, we consider a rule by which a number f(x)
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
Physics 2210 Fall 2005 Paolo Gondolor FIFTH MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format (no solutions for 27-29). 7 1. Assume that the planet Uranus has
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
JEE NEET FOUNDATION. Particle of the medium vibrates in the direction of wave motion.
 JEE NEET FOUNDATION WAVE MOTION It is a periodic disturbance through which energy and momentum is transferred from one point to another without the transfer of material medium. CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE
JEE NEET FOUNDATION WAVE MOTION It is a periodic disturbance through which energy and momentum is transferred from one point to another without the transfer of material medium. CHARACTERISTICS OF WAVE
Question 01. A. Incorrect! The speed of sound is not the same in all medium; it is dependent on the properties of the material.
 High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
High School Physics - Problem Drill 15: Sound 1. Which of these is not a true statement about sound waves? Question 01 (A) Sound waves are travel at different speeds in different mediums. (B) Sound waves
Write your class, index number and name in the spaces at the top of this page. For Examiner s Use
 1 DUNMAN HIGH SCHOOL Preliminary Examinations Year 6 Higher 1 CANDIDATE NAME CLASS INDEX NUMBER PHYSICS Paper 2 Structured Questions Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are
1 DUNMAN HIGH SCHOOL Preliminary Examinations Year 6 Higher 1 CANDIDATE NAME CLASS INDEX NUMBER PHYSICS Paper 2 Structured Questions Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
 1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Demo Newton's Cradle Tuning Forks. Section 8.
 Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Section 8.1 Vibrations Learning Goal: By the end of today, I will be familiar with the following concepts: Vibrations and Mechanical waves The cyclical motion about an equilibrium point is called a vibration.
Level 3 Physics, 2018
 91523 915230 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2018 91523 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 20 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
91523 915230 3SUPERVISOR S Level 3 Physics, 2018 91523 Demonstrate understanding of wave systems 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 20 November 2018 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
To prepare for this lab, you should read the following sections of the text: Sections 3.4, 11.3, and 12.1 OVERVIEW
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /35 PHYSICS 107 LAB #4: WIND INSTRUMENTS: WAVES IN AIR Equipment: Thermometer, function generator, two banana plug wires, resonance tube with
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: Total: /35 PHYSICS 107 LAB #4: WIND INSTRUMENTS: WAVES IN AIR Equipment: Thermometer, function generator, two banana plug wires, resonance tube with
Fineman CP Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The CP Physics
MEASUREMENTS ACCELERATION OF GRAVITY
 MEASUREMENTS ACCELERATION OF GRAVITY Purpose: A. To illustrate the uncertainty of a measurement in the laboratory. The measurement is that of time. The data obtained from these measurements will be used
MEASUREMENTS ACCELERATION OF GRAVITY Purpose: A. To illustrate the uncertainty of a measurement in the laboratory. The measurement is that of time. The data obtained from these measurements will be used
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Waves Final Review. Name: Date: 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented?
 Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
