Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
|
|
|
- Loraine Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things: Sample Problems 16 2, 16 3, and 16 4 You should be able to follow a deriva;on to equa;on Checkpoint 5 in Ch16 Sample problem 16 8 (you would be given eqn 16 67) Ch. 16 Ques;ons (not Problems) 1 and 11 Sample Problems 17 3 and 17 6 Chapter 17, Checkpoint 4
2 4/12/10 9:17 AM Print this page Review & Summary Frequency The frequency f of periodic, or oscillatory, motion is the number of oscillations per second. In the SI system, it is measured in hertz: (15-1) Period The period T is the time required for one complete oscillation, or cycle. It is related to the frequency by (15-2) Simple Harmonic Motion In simple harmonic motion (SHM), the displacement x(t) of a particle from its equilibrium position is described by the equation (15-3) in which x m is the amplitude of the displacement, the quantity is the phase of the motion, and φ is the phase constant. The angular frequency ω is related to the period and frequency of the motion by (15-5) Differentiating Eq leads to equations for the particle s SHM velocity and acceleration as functions of time: (15-6) and (15-7) In Eq. 15-6, the positive quantity ωx m is the velocity amplitude v m of the motion. In Eq. 15-7, the positive quantity ω 2 x m is the acceleration amplitude a m of the motion. The Linear Oscillator A particle with mass m that moves under the influence of a Hooke s law restoring force given by exhibits simple harmonic motion with (15-12) and (15-13) Such a system is called a linear simple harmonic oscillator. Energy A particle in simple harmonic motion has, at any time, kinetic energy and potential energy. If no friction is present, the mechanical energy remains constant even though K and U change. Page 1 of 2
3 4/12/10 9:17 AM Pendulums Examples of devices that undergo simple harmonic motion are the torsion pendulum of Fig. 15-7, the simple pendulum of Fig. 15-9, and the physical pendulum of Fig Their periods of oscillation for small oscillations are, respectively, (15-23) (15-28) (15-29) Simple Harmonic Motion and Uniform Circular Motion Simple harmonic motion is the projection of uniform circular motion onto the diameter of the circle in which the circular motion occurs. Figure shows that all parameters of circular motion (position, velocity, and acceleration) project to the corresponding values for simple harmonic motion. Damped Harmonic Motion The mechanical energy E in a real oscillating system decreases during the oscillations because external forces, such as a drag force, inhibit the oscillations and transfer mechanical energy to thermal energy. The real oscillator and its motion are then said to be damped. If the damping force is given by, where is the velocity of the oscillator and b is a damping constant, then the displacement of the oscillator is given by (15-42) where ω, the angular frequency of the damped oscillator, is given by (15-43) If the damping constant is small, then, where ω is the angular frequency of the undamped oscillator. For small b, the mechanical energy E of the oscillator is given by (15-44) Forced Oscillations and Resonance If an external driving force with angular frequency ω d acts on an oscillating system with natural angular frequency ω, the system oscillates with angular frequency ω d. The velocity amplitude v m of the system is greatest when (15-46) a condition called resonance. The amplitude x m of the system is (approximately) greatest under the same condition. Copyright 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 2
4 4/12/10 9:18 AM Print this page Review & Summary Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Mechanical waves can exist only in material media and are governed by Newton s laws. Transverse mechanical waves, like those on a stretched string, are waves in which the particles of the medium oscillate perpendicular to the wave s direction of travel. Waves in which the particles of the medium oscillate parallel to the wave s direction of travel are longitudinal waves. Sinusoidal Waves A sinusoidal wave moving in the positive direction of an x axis has the mathematical form (16-2) where y m is the amplitude of the wave, k is the angular wave number, is the phase. The wavelength is related to k by is the angular frequency, and (16-5) The period T and frequency f of the wave are related to by (16-9) Finally, the wave speed v is related to these other parameters by (16-13) Equation of a Traveling Wave Any function of the form (16-17) can represent a traveling wave with a wave speed given by Eq and a wave shape given by the mathematical form of h. The plus sign denotes a wave traveling in the negative direction of the x axis, and the minus sign a wave traveling in the positive direction. Wave Speed on Stretched String The speed of a wave on a stretched string is set by properties of the string. The speed on a string with tension and linear density is (16-26) Power The average power of, or average rate at which energy is transmitted by, a sinusoidal wave on a stretched string is given by (16-33) Superposition of Waves When two or more waves traverse the same medium, the displacement of any particle of the medium is the sum of the displacements that the individual waves would give it. Interference of Waves Two sinusoidal waves on the same string exhibit interference, adding or canceling according to the principle of superposition. If the two are traveling in the same direction and have the same amplitude y m and frequency (hence the same wavelength) but differ in phase by a phase constant, the result Page 1 of 2
5 4/12/10 9:18 AM is a single wave with this same frequency: (16-51) If, the waves are exactly in phase and their interference is fully constructive; if, they are exactly out of phase and their interference is fully destructive. Phasors A wave y(x, t) can be represented with a phasor. This is a vector that has a magnitude equal to the amplitude y m of the wave and that rotates about an origin with an angular speed equal to the angular frequency of the wave. The projection of the rotating phasor on a vertical axis gives the displacement y of a point along the wave s travel. Standing Waves The interference of two identical sinusoidal waves moving in opposite directions produces standing waves. For a string with fixed ends, the standing wave is given by (16-60) Standing waves are characterized by fixed locations of zero displacement called nodes and fixed locations of maximum displacement called antinodes. Resonance Standing waves on a string can be set up by reflection of traveling waves from the ends of the string. If an end is fixed, it must be the position of a node. This limits the frequencies at which standing waves will occur on a given string. Each possible frequency is a resonant frequency, and the corresponding standing wave pattern is an oscillation mode. For a stretched string of length L with fixed ends, the resonant frequencies are (16-66) The oscillation mode corresponding to is called the fundamental mode or the first harmonic; the mode corresponding to is the second harmonic; and so on. Copyright 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Page 2 of 2
6 4/12/10 9:19 AM Review & Summary Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal mechanical waves that can travel through solids, liquids, or gases. The speed v of a sound wave in a medium having bulk modulus B and density is (17-3) In air at 20 C, the speed of sound is 343 m/s. A sound wave causes a longitudinal displacement s of a mass element in a medium as given by (17-13) where s m is the displacement amplitude (maximum displacement) from equilibrium,, and,, and f being the wavelength and frequency, respectively, of the sound wave. The sound wave also causes a pressure change of the medium from the equilibrium pressure: (17.14) where the pressure amplitude is (17-15) Interference The interference of two sound waves with identical wavelengths passing through a common point depends on their phase difference there. If the sound waves were emitted in phase and are traveling in approximately the same direction, is given by where is their path length difference (the difference in the distances traveled by the waves to reach the common point). Fully constructive interference occurs when is an integer multiple of, (17-21) (17-22) and, equivalently, when is related to wavelength by (17-23) Fully destructive interference occurs when is an odd multiple of, (17-24) and, equivalently, when is related to by (17-25) Page 1 of 3
7 4/12/10 9:19 AM Sound Intensity The intensity I of a sound wave at a surface is the average rate per unit area at which energy is transferred by the wave through or onto the surface: (17-26) where P is the time rate of energy transfer (power) of the sound wave and A is the area of the surface intercepting the sound. The intensity I is related to the displacement amplitude s m of the sound wave by (17-27) The intensity at a distance r from a point source that emits sound waves of power P s is (17-28) Sound Level in Decibels The sound level in decibels (db) is defined as (17-29) where is a reference intensity level to which all intensities are compared. For every factorof-10 increase in intensity, 10 db is added to the sound level. Standing Wave Patterns in Pipes Standing sound wave patterns can be set up in pipes. A pipe open at both ends will resonate at frequencies (17-39) where v is the speed of sound in the air in the pipe. For a pipe closed at one end and open at the other, the resonant frequencies are (17-41) Beats Beats arise when two waves having slightly different frequencies, f 1 and f 2, are detected together. The beat frequency is (17-46) The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect is a change in the observed frequency of a wave when the source or the detector moves relative to the transmitting medium (such as air). For sound the observed frequency is given in terms of the source frequency f by (17-47) where v D is the speed of the detector relative to the medium, v S is that of the source, and v is the speed of sound in the medium. The signs are chosen such that tends to be greater for motion toward and less for motion away. Shock Wave If the speed of a source relative to the medium exceeds the speed of sound in the medium, the Page 2 of 3
8 4/12/10 9:19 AM Doppler equation no longer applies. In such a case, shock waves result. The half-angle given by of the Mach cone is (17-57) Copyright 2008 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Page 3 of 3
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th
 Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th Wave superposition Spatial interference Temporal interference (beating) Standing waves and resonance Sources of musical sound Doppler effect Sonic boom Examples,
Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th Wave superposition Spatial interference Temporal interference (beating) Standing waves and resonance Sources of musical sound Doppler effect Sonic boom Examples,
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p.
 Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p. 7 Review & Summary p. 8 Problems p. 8 Motion Along
Measurement p. 1 What Is Physics? p. 2 Measuring Things p. 2 The International System of Units p. 2 Changing Units p. 3 Length p. 4 Time p. 5 Mass p. 7 Review & Summary p. 8 Problems p. 8 Motion Along
Fundamentals Physics. Chapter 15 Oscillations
 Fundamentals Physics Tenth Edition Halliday Chapter 15 Oscillations 15-1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1 of 20) Learning Objectives 15.01 Distinguish simple harmonic motion from other types of periodic motion.
Fundamentals Physics Tenth Edition Halliday Chapter 15 Oscillations 15-1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1 of 20) Learning Objectives 15.01 Distinguish simple harmonic motion from other types of periodic motion.
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion
 Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Path Length Difference
 17-3 Interference Path Length Difference The interference of two sound waves with iden3cal wavelengths passing through a common point depends on their phase difference there ϕ. If the sound waves were
17-3 Interference Path Length Difference The interference of two sound waves with iden3cal wavelengths passing through a common point depends on their phase difference there ϕ. If the sound waves were
No Lecture on Wed. But, there is a lecture on Thursday, at your normal recitation time, so please be sure to come!
 Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves
 Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) periodic motion that occurs whenever the restoring force is proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction. Give some example
Simple Harmonic Motion and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) periodic motion that occurs whenever the restoring force is proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction. Give some example
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Final Exam Concept Map
 Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
Final Exam Concept Map Rule of thumb to study for any comprehensive final exam - start with what you know - look at the quiz problems. If you did not do well on the quizzes, you should certainly learn
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Physics General Physics. Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Summary PHY101 ( 2 ) T / Hanadi Al Harbi
 الكمية Physical Quantity القانون Low التعريف Definition الوحدة SI Unit Linear Momentum P = mθ be equal to the mass of an object times its velocity. Kg. m/s vector quantity Stress F \ A the external force
الكمية Physical Quantity القانون Low التعريف Definition الوحدة SI Unit Linear Momentum P = mθ be equal to the mass of an object times its velocity. Kg. m/s vector quantity Stress F \ A the external force
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Standing waves. The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave.
 Standing waves The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave. y 1 (x, t) = y m sin(kx ωt), y 2 (x, t) = y m sin(kx
Standing waves The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave. y 1 (x, t) = y m sin(kx ωt), y 2 (x, t) = y m sin(kx
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
Fineman Honors Physics Final Study Guide
 All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
All Science Tests are on Wednesday, June 17 th. Students who take more than one Science class will take their second science final on Thursday, June 18 from 8:00-10:00 AM in the Library. The Honors Physics
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Chapter 14: Periodic motion
 Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Chapter 14: Periodic motion Describing oscillations Simple harmonic motion Energy of simple harmonic motion Applications of simple harmonic motion Simple pendulum & physical pendulum Damped oscillations
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
KEY SOLUTION. 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME M 1 M 1. Fig. 1a Fig. 1b Fig. 1c
 KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I
 Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I PHY 2053 3 credits Course Description PHY 2053, College physics I, is the first semester of a two semester physics-without-calculus sequence. This
Miami-Dade Community College PHY 2053 College Physics I PHY 2053 3 credits Course Description PHY 2053, College physics I, is the first semester of a two semester physics-without-calculus sequence. This
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Chapter 13 Lecture. Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson 2 nd Edition. Oscillatory Motion Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson nd Edition Oscillatory Motion Slide 13-1 In this lecture you ll learn To describe the conditions under which oscillatory motion occurs To
Chapter 13 Lecture Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson nd Edition Oscillatory Motion Slide 13-1 In this lecture you ll learn To describe the conditions under which oscillatory motion occurs To
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum
 Content Area: Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Science Course Title/ Grade Level: Honors Physics / Gr. 11 & 12 Unit 1: Unit 2: Unit 3: Unit 4: Unit 4: Introduction, Measurement, Estimating Duration:
Content Area: Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Science Course Title/ Grade Level: Honors Physics / Gr. 11 & 12 Unit 1: Unit 2: Unit 3: Unit 4: Unit 4: Introduction, Measurement, Estimating Duration:
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Chapter 17. Waves-II Sound Waves
 Chapter 17 Waves-II 17.2 Sound Waves Wavefronts are surfaces over which the oscillations due to the sound wave have the same value; such surfaces are represented by whole or partial circles in a twodimensional
Chapter 17 Waves-II 17.2 Sound Waves Wavefronts are surfaces over which the oscillations due to the sound wave have the same value; such surfaces are represented by whole or partial circles in a twodimensional
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 13 Sound Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
General Physics I. Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM
 KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY-10012 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM Candidates should attempt ALL of PARTS A and B, and TWO questions from PART C. PARTS A and B should be answered
KEELE UNIVERSITY PHYSICS/ASTROPHYSICS MODULE PHY-10012 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES PRACTICE EXAM Candidates should attempt ALL of PARTS A and B, and TWO questions from PART C. PARTS A and B should be answered
11/17/10. Chapter 14. Oscillations. Chapter 14. Oscillations Topics: Simple Harmonic Motion. Simple Harmonic Motion
 11/17/10 Chapter 14. Oscillations This striking computergenerated image demonstrates an important type of motion: oscillatory motion. Examples of oscillatory motion include a car bouncing up and down,
11/17/10 Chapter 14. Oscillations This striking computergenerated image demonstrates an important type of motion: oscillatory motion. Examples of oscillatory motion include a car bouncing up and down,
Physics 141, Lecture 7. Outline. Course Information. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1. Quiz. Continuation of the discussion of Chapter 4.
 Physics 141, Lecture 7. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 07, Page 1 Outline. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1 Quiz. Continuation of the
Physics 141, Lecture 7. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 07, Page 1 Outline. Course information: Homework set # 3 Exam # 1 Quiz. Continuation of the
CH 17. Waves II (Sound)
 CH 17 Waves II (Sound) [SHIVOK SP211] November 1, 2015 I. Sound Waves A. Wavefronts are surfaces over which the oscillations due to the sound wave have the same value; such surfaces are represented by
CH 17 Waves II (Sound) [SHIVOK SP211] November 1, 2015 I. Sound Waves A. Wavefronts are surfaces over which the oscillations due to the sound wave have the same value; such surfaces are represented by
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
Tentative Physics 1 Standards
 Tentative Physics 1 Standards Mathematics MC1. Arithmetic: I can add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers, take their natural and common logarithms, and raise them to real powers and take real
Tentative Physics 1 Standards Mathematics MC1. Arithmetic: I can add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers, take their natural and common logarithms, and raise them to real powers and take real
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide)
 Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide) 17 November diagnostic test! Week 1 : 14 November Week 2 : 21 November Introduction, units (Ch1), Circuits (Ch25,26) Heat (Ch17), Kinematics (Ch2 3) Week 3:
Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide) 17 November diagnostic test! Week 1 : 14 November Week 2 : 21 November Introduction, units (Ch1), Circuits (Ch25,26) Heat (Ch17), Kinematics (Ch2 3) Week 3:
PREMED COURSE, 14/08/2015 OSCILLATIONS
 PREMED COURSE, 14/08/2015 OSCILLATIONS PERIODIC MOTIONS Mechanical Metronom Laser Optical Bunjee jumping Electrical Astronomical Pulsar Biological ECG AC 50 Hz Another biological exampe PERIODIC MOTIONS
PREMED COURSE, 14/08/2015 OSCILLATIONS PERIODIC MOTIONS Mechanical Metronom Laser Optical Bunjee jumping Electrical Astronomical Pulsar Biological ECG AC 50 Hz Another biological exampe PERIODIC MOTIONS
Oscillatory Motion SHM
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM
 OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 13 Units of Chapter 13 Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring
OSCILLATIONS ABOUT EQUILIBRIUM Chapter 13 Units of Chapter 13 Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring
WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
Periodic Motion. Periodic motion is motion of an object that. regularly repeats
 Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16
 Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1. Mechanical Waves
 Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
1 f. result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by
 result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
Chapter 15. Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. FINAL EXAM December 10, :00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
ANSWERS 403 INDEX. Bulk modulus 238 Buoyant force 251
 ANSWERS 403 INDEX A Absolute scale temperature 276 Absolute zero 276 Acceleration (linear) 45 Acceleration due to gravity 49,189 Accuracy 22 Action-reaction 97 Addition of vectors 67 Adiabatic process
ANSWERS 403 INDEX A Absolute scale temperature 276 Absolute zero 276 Acceleration (linear) 45 Acceleration due to gravity 49,189 Accuracy 22 Action-reaction 97 Addition of vectors 67 Adiabatic process
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL QUANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT
 CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL UANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT 11 Physical uantities and Units a) State basic quantities and their respective SI units: length (m), time (s), mass (kg), electrical current (A), temperature
CHAPTER 1: PHYSICAL UANTITIES AMD MEASUREMENT 11 Physical uantities and Units a) State basic quantities and their respective SI units: length (m), time (s), mass (kg), electrical current (A), temperature
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
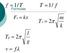 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
PHYSICS. Chapter 15 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
Chapter 15. Oscillations
 Chapter 15 Oscillations 15.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory Motion: Motion which is periodic in time; motion that repeats itself in time. Examples: SHM: Power line oscillates when the wind blows past.
Chapter 15 Oscillations 15.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory Motion: Motion which is periodic in time; motion that repeats itself in time. Examples: SHM: Power line oscillates when the wind blows past.
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
Physics 123 Unit #3 Review
 Physics 123 Unit #3 Review I. Definitions and Facts longitudinal wave transverse wave traveling wave standing wave wave front wavelength wave number frequency angular frequency period crest trough node
Physics 123 Unit #3 Review I. Definitions and Facts longitudinal wave transverse wave traveling wave standing wave wave front wavelength wave number frequency angular frequency period crest trough node
Physics 1C. Lecture 12C
 Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Chapter 16 Lectures. Oscillatory Motion and Waves
 Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
1 2 Models, Theories, and Laws 1.5 Distinguish between models, theories, and laws 2.1 State the origin of significant figures in measurement
 Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Waves Encountering Barriers
 Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described by Mr. Martin?
 Ch.1 Study Guide Outline Study the Review that is posted on the website. Make a note card to use for the test. 1. What is science and physics? 2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described
Ch.1 Study Guide Outline Study the Review that is posted on the website. Make a note card to use for the test. 1. What is science and physics? 2. What are the 4 steps of the Scientific Method as described
