Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide)
|
|
|
- Caren Gibson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Content of the course 3NAB0 (see study guide) 17 November diagnostic test! Week 1 : 14 November Week 2 : 21 November Introduction, units (Ch1), Circuits (Ch25,26) Heat (Ch17), Kinematics (Ch2 3) Week 3: 28 November Newton, Energy (Ch4 6) Week 4: 5 December Energy, Momentum (Ch7 8) 8 December Intermediate assessment Week 5: 12 December Week 6: 19 December Week 7: 9 January (2016) Rotation, Elasticity, Fluid mechanics (Ch9 12) Harmonic oscillator and Waves (Ch14 15) Sound (Ch16) Light (Ch33) 25 January Final assessment
2 Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen Applied Natural Sciences Leo Pel e mail: phys3nab@tue.nl
3 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Copyright 2012 Pearson Education Inc.
4 LEARNING GOALS What is meant by a mechanical wave, and the different varieties of mechanical waves How to use the relationship among speed, frequency, and wavelength for a periodic wave. How to interpret and use the mathematical expression for a sinusoidal periodic wave. How to calculate the speed of waves on a rope or string. How to calculate the rate at which a mechanical wave transports energy. What happens when mechanical waves overlap and interfere. The properties of standing waves on a string, and how to analyze these waves. How stringed instruments produce sounds of specific frequencies. 4
5 Simple Harmonic oscillator 5 5
6 Harmonic oscillator and waves 6
7 Types of waves Depending on the direction of the displacement relative to the direction of propagation, we can define wave motion as: Transverse if the direction of displacement is perpendicular to the direction of propagation Earth quake waves Animation courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Grad. Prog. Acoustics, Penn State 7
8 Types of waves Depending on the direction of the displacement relative to the direction of propagation, we can define wave motion as: Longitudinal if the direction of displacement is parallel to the direction of propagation Sound Animation courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Grad. Prog. Acoustics, Penn State 8
9 Types of waves But also a combination of Transverse and Longitudinal Water waves Animation courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Grad. Prog. Acoustics, Penn State 9
10 Transverse and longitudinal waves Mechanical (part I) materials Sound (part II) air 10
11 Waves have in common: 1. In each case the disturbance travels or propagates with a definite speed through the medium: the wave speed. 2. The medium itself does not travel through space. 3. To set any of these systems into motion, we have to put in energy by doing mechanical work on the system. Waves transport energy, but not matter, from one region to another. 11
12 MATHEMATICAL 12
13 Harmonic oscillator and waves 13
14 Have a description One position: SHM x( t) Acos( t ) One time shot: position in space NEED ONE 14
15 Wavelength (lambda), 16
16 Harmonic wave Shake end of string up & down with SHM period = T wavelength = Wave speed =v Wave speed = v = distance time wavelength period = = T = f V=for f=v/ but 1/T=f this is the Golden Rule for waves 17
17 Example: wave on a string 2 cm 2 cm 2 cm A wave moves on a string at a speed of 4 cm/s A snapshot of the motion shows that the wavelength, is 2 cm, what is the frequency,? v =, so = v / = (4 cm/s ) / (2 cm) = 2 Hz T = 1 / f = 1 / (2 Hz) = 0.5 s 18
18 Movement of wave Look at: 2 y( x) Acos ( x 0) x=5 x=10 2 y( x) Acos ( x 5) 2 y( x) Acos ( x 10) x( t) Acos( t) x( t) shm position = 5 t= vt Waves 2 Acos t f 2 y( x, t) Acos ( x vt) move right 2 y( x, t) Acos ( x vt) move left 19
19 ) ( 2 cos ), ( vt x A t x y vt x A t x y 2 2 cos ), ( f v t f x A t x y 2 2 cos ), ( t kx A t x y cos ), ( 2 k Wave number Alternate notation + if wave travels toward x - if wave travels toward +x 20
20 Definitions Amplitude (A, y m ) Maximum value of the displacement of a particle in a medium (radius of circular motion). Wavelength () The spatial distance between any two points that behave identically, i.e. have the same amplitude, move in the same direction (spatial period) Wave Number (k) Amount the phase changes per unit length of wave travel. (spatial frequency, angular wavenumber) Period (T) Time for a particle/system to complete one cycle. Frequency (f) The number of cycles or oscillations completed in a period of time Angular Frequency Time rate of change of the phase. Phase kx t Time varying argument of the trigonometric function. Phase Velocity (v) The velocity at which the disturbance is moving through the medium 21
21 The Wave Equation If we see an equation that looks like:... we can write down the amplitude, frequency, velocity, and wavelength of the wave it describes. y m cos s t m x y A cos( ) cos( ) Acos2ft 0.15 m 2x 2f s m m v f 343 m/s, in the x direction. -1 f 250 Hz 22
22 General description SHM The force described by Hooke s Law is the net force in Newton s Second Law. m d 2 x( t) dt 2 kx( t) x( t) where = Acos( t) k m 1. The acceleration is proportional to the displacement of the block 2. The force is conservative. In the absence of friction, the motion will continue forever. 23
23 General description waves Wave Equation: 2 y(x,t) x 2 position 1 v 2 2 y(x,t) t 2 time Partial Differential Equation (PDE) A solution is: y( x, t) Acos kx t We will not try to solve this equation 24
24 General description waves Wave Equation: y t 2 y 2 t y 2 y(x,t) x 2 ( x, t) 1 2 y(x,t) v 2 t 2 Acos kx t Asinkx t y kasinkx t x 2 A coskx t 2 y 2 k A coskx t 2 x 2 2 k A coskx t A coskx t 2 v And k 2 v f v k 25
25 Sinusoidal Wave on a String, final The maximum magnitudes of the transverse speed and transverse acceleration are v y, max = A a y, max = 2 A T v y v golf getal k The speed v is constant for a uniform medium, whereas v y varies sinusoidally. 26
26 27
27 28
28 Rope: mass + springs x ( t) Acos( t) where = k m How fast will it be transmitted 1) Mass rope: m larger > slower 2) More tension > k larger > faster 29
29 Speed of a Wave on a String The speed of the wave depends on the physical characteristics of the string and the tension to which the string is subjected. tension force v tension mass / length F (string mass / string length) This assumes that the tension is not affected by the pulse. This does not assume any particular shape for the pulse. 30
30 31
31 Energy in a Wave The average power: P ave 1 2 F 2 A 2 Duck swimming When a duck swims, it necessarily produces waves on the surface of the water. The faster the duck swims, the larger the wave amplitude and the more power the duck must supply to produce these waves. The maximum power available from their leg muscles limits the maximum swimming speed of ducks to only about 0.7 m/s (2.5 km/h) 32
32 Waves Intensity Wave intensity for a three dimensional wave from a point source: I P in units of W/m 2 4r 4r r I 2 1 I I I 1 2 r r Example: earthquake, sound waves 33
33 Wave boundary/ interference 34
34 35
35 The principle of superposition When two waves overlap, the actual displacement of any point at any time is obtained by adding the displacement the point would have if only the first wave were present and the displacement it would have if only the second wave were present: y( x, t) y ( x, t) y ( x, t)
36 Superposition of equal amplitude waves Constructive Destructive 37
37 Reflection (from a fixed end) Animations courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Kettering University 38
38 Reflection (from a loose end) Animations courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Kettering University 39
39 Superposition of equal amplitude waves Constructive Destructive 40
40 Standing Wave 42
41 Adding waves harmonic waves in opposite directions incident wave reflected wave resultant wave (standing wave) Animations courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Kettering University 43
42 44
43 Standing Waves Resonance y1( x, t) y 2 ( x, t) Acos Acos kx t kx t y( x, t) Acos kx t Acoskx t cos x - cos y = -2 sin ((x - y)/2) sin( (x + y)/2 ) y( x, t) 2Asin( kx)sin( t) 45
44 Nodes and Antinodes Node position of no displacement Antinode position of maximum displacement y 2Asin kx cos t Nodes 2 kx x 0,,2, x 0,,,,
45 Confined waves Only waves with wavelengths that just fit in survive (all others cancel themselves out) 2 kx x 0,,2,3... 2L n 3 x 0,,,, v 2L L n n f n n nf1 2 47
46 Allowed frequencies = 2L =L f 0 =V/ = V/2L Fundamental tone f 1 =V/ = V/L=2f 0 =(2/3)L =L/2 1 st overtone f 2 =V/=V/(2/3)L=3f 0 2 nd overtone f 3 =V/=V/(1/2)L=4f 0 3 rd overtone =(2/5)L f 4 =V/=V/(2/5)L=5f 0 4 th overtone 48
47 VIDEO + UITWERKING L = 1.8 m String mass= 188 gr Tension = 3N v f n n n L µ = kg/m T v m / Hz s
48
49 Fundamental, 2nd, 3rd... Harmonics n 2 L 2nd harmonic 3rd harmonic Fundamental (n=1) Fig 14.18, p. 443 Slide 25 51
50 Loose Ends L 2n 1 4 L 4 n 4L (2n 1) L 3 4 f n (2n (2n 1) 1) v 4L f 1 L 5 4 (Organ pipes open at one end) 52
51 Harmonics with a bridge 53
52 Stringed instruments Three types Plucked: guitar, bass, harp, harpsichord Bowed: violin, viola, cello, bass (Bowing excites many vibration modes simultaneously mixture of tones (richness) Struck: piano All use strings that are fixed at both ends Use different diameter strings (mass per unit length is different) The string tension is adjustable tuning f 1 1 2L T 54
53 A 1.00 m string fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at 440 Hz. What is the speed of the waves on this string? m/s m/s m/s m/s km/s 55
54 A 1.00 m string fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at 440 Hz. What is the speed of the waves on this string? m/s m/s m/s m/s f n n nf km/s v 2L v f 2L 1 56
55 A stretched string is fixed at points 1 and 5. When it is vibrating at the second harmonic frequency, the nodes of the standing wave are at points 1. 1 and , 3, and and and , 2, 3, 4, and 5. 57
56 A stretched string is fixed at points 1 and 5. When it is vibrating at the second harmonic frequency, the nodes of the standing wave are at points 1. 1 and , 3, and and and , 2, 3, 4, and 5. 58
57 A stretched string of length L, fixed at both ends, is vibrating in its third harmonic. How far from the end of the string can the blade of a screwdriver be placed against the string without disturbing the amplitude of the vibration? 1. L/6 2. L/4 3. L/5 4. L/2 5. L/3 59
58 A stretched string of length L, fixed at both ends, is vibrating in its third harmonic. How far from the end of the string can the blade of a screwdriver be placed against the string without disturbing the amplitude of the vibration? 1. L/6 2. L/4 3. L/5 4. L/2 5. L/3 60
59 Drum: 2D standing waves Mode (0,1) Mode (1,1) Mode (2,1) Mode (0,2) Animations courtesy of Dr. Dan Russell, Kettering University 61
60 62
61 Summary 63
62 Summary 64
63 Applied Natural Sciences Thank you for your attention Merry Christmas Have a happy holiday and see you next year 65
64
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
1 f. result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by
 result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 14. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by Wayne Anderson
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Exam 3 results Class Average - 57 (Approximate grade
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Exam 3 results Class Average - 57 (Approximate grade
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
General Physics I. Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1. Mechanical Waves
 Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
Physics 142 Mechanical Waves Page 1 Mechanical Waves This set of notes contains a review of wave motion in mechanics, emphasizing the mathematical formulation that will be used in our discussion of electromagnetic
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Chapter 13. Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition. Next Week!
 Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Chapter 13 Hooke s Law: F = - kx Periodic & Simple Harmonic Motion Springs & Pendula Waves Superposition Next Week! Review Physics 2A: Springs, Pendula & Circular Motion Elastic Systems F = kx Small Vibrations
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
is a What you Hear The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration.
 is a What you Hear The ear converts sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse which is transmitted to the brain. The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration. electroencephalogram v S
is a What you Hear The ear converts sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse which is transmitted to the brain. The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration. electroencephalogram v S
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
No Lecture on Wed. But, there is a lecture on Thursday, at your normal recitation time, so please be sure to come!
 Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Announcements Quiz 6 tomorrow Driscoll Auditorium Covers: Chapter 15 (lecture and homework, look at Questions, Checkpoint, and Summary) Chapter 16 (Lecture material covered, associated Checkpoints and
Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th
 Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th Wave superposition Spatial interference Temporal interference (beating) Standing waves and resonance Sources of musical sound Doppler effect Sonic boom Examples,
Chapter 14: Wave Motion Tuesday April 7 th Wave superposition Spatial interference Temporal interference (beating) Standing waves and resonance Sources of musical sound Doppler effect Sonic boom Examples,
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Waves 2006 Physics 23. Armen Kocharian Lecture 3: Sep
 Waves 2006 Physics 23 Armen Kocharian Lecture 3: Sep 12. 2006 Last Time What is a wave? A "disturbance" that moves through space. Mechanical waves through a medium. Transverse vs. Longitudinal e.g., string
Waves 2006 Physics 23 Armen Kocharian Lecture 3: Sep 12. 2006 Last Time What is a wave? A "disturbance" that moves through space. Mechanical waves through a medium. Transverse vs. Longitudinal e.g., string
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
PHYS Homework # 10 (Mendes, Fall 2015) due in class on Nov 20. 1) Exercise 15.4, p. 501, University Physics by Young & Freedman
 PHYS 98 - Homework # 10 (Mendes, Fall 015) due in class on Nov 0 1) Exercise 154, p 501, Universit Phsics b Young & Freedman IDENTIFY: f v SET UP: 10 mm 00010 m v 1500m/s 6 EXECUTE: f 15 10 Hz 00010 m
PHYS 98 - Homework # 10 (Mendes, Fall 015) due in class on Nov 0 1) Exercise 154, p 501, Universit Phsics b Young & Freedman IDENTIFY: f v SET UP: 10 mm 00010 m v 1500m/s 6 EXECUTE: f 15 10 Hz 00010 m
PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics. Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester
 PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Sounds of the Universe NASA/JPL, September 2016 2 Properties of Waves Wavelength: λ, length
PHY 103: Standing Waves and Harmonics Segev BenZvi Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Rochester Sounds of the Universe NASA/JPL, September 2016 2 Properties of Waves Wavelength: λ, length
Chapter 14. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by Wayne Anderson
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 14 To describe oscillations in
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 14 To describe oscillations in
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 32 Electromagnetic Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 32 To learn why a light
Chapter 32 Electromagnetic Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 32 To learn why a light
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Applied Natural Sciences
 Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html Applied Natural Sciences Leo Pel e mail: 3nab0@tue.nl http://tiny.cc/3nab0 Bijles Email: p.j.neuraij@tue.nl
Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html Applied Natural Sciences Leo Pel e mail: 3nab0@tue.nl http://tiny.cc/3nab0 Bijles Email: p.j.neuraij@tue.nl
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
University Physics Volume I Unit 2: Waves and Acoustics Chapter 16: Waves Conceptual Questions
 Unit : Waves and Acoustics University Physics Volume I Unit : Waves and Acoustics Conceptual Questions. Give one example of a transverse wave and one example of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note
Unit : Waves and Acoustics University Physics Volume I Unit : Waves and Acoustics Conceptual Questions. Give one example of a transverse wave and one example of a longitudinal wave, being careful to note
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
Welcome to: Physics I. I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide!
 Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Interference superposition principal: most waves can be added y(x, t) =y 1 (x vt)+y 2 (x + vt) wave 1 + wave 2 = resulting wave y 1 +
Welcome to: Physics I I m Dr Alex Pettitt, and I ll be your guide! Interference superposition principal: most waves can be added y(x, t) =y 1 (x vt)+y 2 (x + vt) wave 1 + wave 2 = resulting wave y 1 +
Simple Harmonic Motion continued and Waves. Monday, November 28, 11
 Simple Harmonic Motion continued and Waves Sinusoidal Relationships Mathematical Description of Simple Harmonic Motion Frequency and Period The frequency of oscillation depends on physical properties of
Simple Harmonic Motion continued and Waves Sinusoidal Relationships Mathematical Description of Simple Harmonic Motion Frequency and Period The frequency of oscillation depends on physical properties of
Physics 41: Waves, Optics, Thermo
 Physics 41: Waves, Optics, Thermo Particles & Waves Localized in Space: LOCAL Have Mass & Momentum No Superposition: Two particles cannot occupy the same space at the same time! Particles have energy.
Physics 41: Waves, Optics, Thermo Particles & Waves Localized in Space: LOCAL Have Mass & Momentum No Superposition: Two particles cannot occupy the same space at the same time! Particles have energy.
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Chapter 16 - Waves. I m surfing the giant life wave. -William Shatner. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 213. Chapter 16 - Waves
 I m surfing the giant life wave. -William Shatner David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 213 There are three main types of waves in physics: (a) Mechanical waves: described by Newton s laws and propagate
I m surfing the giant life wave. -William Shatner David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 213 There are three main types of waves in physics: (a) Mechanical waves: described by Newton s laws and propagate
Let s Review What is Sound?
 Mathematics of Sound Objectives: Understand the concept of sound quality and what it represents. Describe the conditions which produce standing waves in a stretched string. Be able to describe the formation
Mathematics of Sound Objectives: Understand the concept of sound quality and what it represents. Describe the conditions which produce standing waves in a stretched string. Be able to describe the formation
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16
 Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
Old Exams - Questions Ch-16 T081 : Q1. The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by: y( x, t) = y sin( kx ω t + ϕ). At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 m has a displacement
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) κ I ω = g L L g T = 2π mgh rot com I rot
 α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
WAVES( SUB) 2. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity and inertia
 WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
Standing Waves If the same type of waves move through a common region and their frequencies, f, are the same then so are their wavelengths, λ.
 Standing Waves I the same type o waves move through a common region and their requencies,, are the same then so are their wavelengths,. This ollows rom: v=. Since the waves move through a common region,
Standing Waves I the same type o waves move through a common region and their requencies,, are the same then so are their wavelengths,. This ollows rom: v=. Since the waves move through a common region,
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 5 2 Reading chapter 14.2 14.3 Waves on a string Speed of waves on a string Reflections Harmonic waves Speed of waves 3 The
LECTURE 5 WAVES ON STRINGS & HARMONIC WAVES Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 5 2 Reading chapter 14.2 14.3 Waves on a string Speed of waves on a string Reflections Harmonic waves Speed of waves 3 The
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Transverse Wave - Only in solids (having rigidity), in liquids possible only on the surface. Longitudinal Wave
 Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Wave is when one particle passes its motion to its neighbour. The Elasticity and Inertia of the medium play important role in the propagation of wave. The elasticity brings the particle momentarily at
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Physics 111. Lecture 31 (Walker: ) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Standing Waves Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature
 Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation: Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, t =
 Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
Question 15.1: A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
PROJECT WAVES & SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION EVERY WAVE, REGARDLESS OF HOW HIGH AND FORCEFUL IT CRESTS, MUST EVENTUALLY COLLAPSE WITHIN ITSELF. - STEFAN ZWEIG What s a Wave? A wave is a wiggle in time and space
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Downloaded from
 Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Important because SHM is a good model to describe vibrations of a guitar string, vibrations of atoms in molecules, etc.
 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory motion under a restoring force proportional to the amount of displacement from equilibrium A restoring force is a force that tries to move the system back to equilibrium
Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory motion under a restoring force proportional to the amount of displacement from equilibrium A restoring force is a force that tries to move the system back to equilibrium
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
PW W A V E S Syllabus : Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves, speed of wave. Dplacement relation for a progressive wave. Principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, Standing waves
Course Name: AP Physics. Team Names: Jon Collins. Velocity Acceleration Displacement
 Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Course Name: AP Physics Team Names: Jon Collins 1 st 9 weeks Objectives Vocabulary 1. NEWTONIAN MECHANICS and lab skills: Kinematics (including vectors, vector algebra, components of vectors, coordinate
Waves Part 1: Travelling Waves
 Waves Part 1: Travelling Waves Last modified: 15/05/2018 Links Contents Travelling Waves Harmonic Waves Wavelength Period & Frequency Summary Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Transverse & Longitudinal
Waves Part 1: Travelling Waves Last modified: 15/05/2018 Links Contents Travelling Waves Harmonic Waves Wavelength Period & Frequency Summary Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Transverse & Longitudinal
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
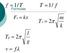 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. FINAL EXAM December 10, :00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 25, 2007 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
What is a Wave. Why are Waves Important? Power PHYSICS 220. Lecture 19. Waves
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
Music 206: Digital Waveguides
 Music 206: Digital Waveguides Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) January 22, 2016 1 Motion for a Wave The 1-dimensional digital waveguide model
Music 206: Digital Waveguides Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) January 22, 2016 1 Motion for a Wave The 1-dimensional digital waveguide model
Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves
 Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves Last modified: 24/01/2018 Contents Links Contents Superposition Standing Waves Definition Nodes Anti-Nodes Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves
Waves Part 3A: Standing Waves Last modified: 24/01/2018 Contents Links Contents Superposition Standing Waves Definition Nodes Anti-Nodes Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
KEY SOLUTION. 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME M 1 M 1. Fig. 1a Fig. 1b Fig. 1c
 KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
What is a wave? Waves
 What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
What is a wave? Waves Waves What is a wave? A wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one place to another. Classifying waves 1. Mechanical Waves - e.g., water waves, sound waves, and waves on strings.
-Electromagnetic. Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical.
 Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Waves Waves - disturbance that propagates through space & time - usually with transfer of energy -Mechanical requires a medium -Electromagnetic no medium required Mechanical waves: sound, water, seismic.
Lecture 30. Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t)
 To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
To do : Lecture 30 Chapter 21 Examine two wave superposition (-ωt and +ωt) Examine two wave superposition (-ω 1 t and -ω 2 t) Review for final (Location: CHEM 1351, 7:45 am ) Tomorrow: Review session,
Physics 121H Fall Homework #15 23-November-2015 Due Date : 2-December-2015
 Reading : Chapters 16 and 17 Note: Reminder: Physics 121H Fall 2015 Homework #15 23-November-2015 Due Date : 2-December-2015 This is a two-week homework assignment that will be worth 2 homework grades
Reading : Chapters 16 and 17 Note: Reminder: Physics 121H Fall 2015 Homework #15 23-November-2015 Due Date : 2-December-2015 This is a two-week homework assignment that will be worth 2 homework grades
CHAPTER 15 Wave Motion. 1. The speed of the wave is
 CHAPTER 15 Wave Motion 1. The speed of the wave is v = fλ = λ/t = (9.0 m)/(4.0 s) = 2.3 m/s. 7. We find the tension from the speed of the wave: v = [F T /(m/l)] 1/2 ; (4.8 m)/(0.85 s) = {F T /[(0.40 kg)/(4.8
CHAPTER 15 Wave Motion 1. The speed of the wave is v = fλ = λ/t = (9.0 m)/(4.0 s) = 2.3 m/s. 7. We find the tension from the speed of the wave: v = [F T /(m/l)] 1/2 ; (4.8 m)/(0.85 s) = {F T /[(0.40 kg)/(4.8
Vibrations of string. Henna Tahvanainen. November 8, ELEC-E5610 Acoustics and the Physics of Sound, Lecture 4
 Vibrations of string EEC-E5610 Acoustics and the Physics of Sound, ecture 4 Henna Tahvanainen Department of Signal Processing and Acoustics Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering November 8,
Vibrations of string EEC-E5610 Acoustics and the Physics of Sound, ecture 4 Henna Tahvanainen Department of Signal Processing and Acoustics Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering November 8,
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
Chapter 16 Lectures. Oscillatory Motion and Waves
 Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
Chapter 16 Lectures January-06-18 5:48 PM Oscillatory Motion and Waves Oscillations are back-and-forth motions. Sometimes the word vibration is used in place of oscillation; for our purposes, we can consider
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
