On the Maximally-Permissive Range Control Problem in Partially-Observed Discrete Event Systems
|
|
|
- Marcus Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On the Mximlly-Permissie Rnge Control Prolem in Prtilly-Osered Disrete Eent Systems Xing Yin nd Stéphne Lfortune EECS Deprtment, Uniersity of Mihign 55th IEEE CDC, De 2-4, 206, Ls Vegs, USA X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
2 Introdution S(s) Plnt G S: E o Γ Superisor s P P(s) E = E E u = E o E uo Superisor: S: E o 2 E ; Disle eents in E sed on its osertions Closed-loop Behior: L(S/G) X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
3 Disrete Eent Systems: Logil Properties Sfety: Regulr sulnguge L L(G) Mximl Permissieness: Optimlity riterion is set inlusion. Only disle n eent if solutely neessry to gurntee sfety When Σ Σ o, there exists unique mximlly-permissie superisor, i.e., the supreml ontrollle & norml superisor [Lin nd Wonhm, 988] Mximl superisor is NOT unique in generl X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
4 Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions 0 o 2 o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 4/4
5 Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions 0 o 2 o 4 B E = Two inomprle solutions, E o = *o+ o o o 4 X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 4/4
6 Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions 0 o 2 o 4 B E = Two inomprle solutions, E o = *o+ o o o 4 Computtion of Solutions: [Cho & Mrus, 989], [Ben Hdj-Aloune, Lfortune & Lin, 996], [Tki & Ushio, 200], [Komend & n Shuppen, 2005], [Ci, Zhng & Wonhm, 205], [Yin & Lfortune, 206] X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 4/4
7 Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions Non-Uniqueness of Lolly Mximl Solutions 0 o 2 o 4 B E = Two inomprle solutions, E o = *o+ o o o 4 Computtion of Solutions: [Cho & Mrus, 989], [Ben Hdj-Aloune, Lfortune & Lin, 996], [Tki & Ushio, 200], [Komend & n Shuppen, 2005], [Ci, Zhng & Wonhm, 205], [Yin & Lfortune, 206] How to hoose mong lolly mximl solutions? X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 4/4
8 Rnge Control Prolem Using Lower Bound Lnguge s Criterion Forml Gurntees: Sfety + Mximlity + Minimlly Required Behior X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 5/4
9 Rnge Control Prolem Using Lower Bound Lnguge s Criterion Forml Gurntees: Sfety + Mximlity + Minimlly Required Behior L(G) L X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 5/4
10 Rnge Control Prolem Using Lower Bound Lnguge s Criterion Forml Gurntees: Sfety + Mximlity + Minimlly Required Behior L(G) L L r X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 5/4
11 Rnge Control Prolem Using Lower Bound Lnguge s Criterion Forml Gurntees: Sfety + Mximlity + Minimlly Required Behior L(G) L L r Prolem (Rnge Control Prolem for Sfety nd Mximl-Permissieness) Let G e the plnt nd L r nd L e two prefix-losed lnguges. Find superisor S: E o Γ suh tht C. L r L S/G L C2. For ny S stisfying C, we he L S/G L S /G X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 5/4
12 Rnge Control Prolem Using Lower Bound Lnguge s Criterion Forml Gurntees: Sfety + Mximlity + Minimlly Required Behior L(G) L Mx L r Mx 2 Mx Prolem (Rnge Control Prolem for Sfety nd Mximl-Permissieness) Let G e the plnt nd L r nd L e two prefix-losed lnguges. Find superisor S: E o Γ suh tht C. L r L S/G L C2. For ny S stisfying C, we he L S/G L S /G X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 5/4
13 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
14 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
15 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
16 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ The effet of enling n eent depends on future informtion y o o o o 0 n x z o o o o 4 m B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
17 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ The effet of enling n eent depends on future informtion y o o o o 0 n x z o o o o 4 m B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
18 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ The effet of enling n eent depends on future informtion y o o o o 0 n x z o o o o 4 m B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
19 Diffiulties in the Rnge Control Prolem Enling less now my result in lrger future ehior 5 o o 4 B E =, E o = *o+ The effet of enling n eent depends on future informtion y o o o o 0 n x z o o o o 4 m B E =, E o = *o+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 6/4
20 Solution Oeriew System Model G Sfety Speifition H s.t. L H = L Lower Bound Speifition R s.t. L R = L r All Inlusie Controller (AIC) Strit Su-Automton Control Simultion Reltion (CSR) Mximlly-Permissie Sfe Superisor Ahieing the Miniml Required Behior X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 7/4
21 Solution Oeriew System Model G Sfety Speifition H s.t. L H = L Lower Bound Speifition R s.t. L R = L r All Inlusie Controller (AIC) Strit Su-Automton Control Simultion Reltion (CSR) Mximlly-Permissie Sfe Superisor Ahieing the Miniml Required Behior Assumptions A There exists superisor hieing L R (W.l.o.g.; infiml losed ontrollle & osererle super-lnguge [Rudie & Wonhm, 992]) A2 R H G (W.l.o.g.; [Cho & Mrus, 989]) X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 7/4
22 Biprtite Trnsition System Definition. (BTS). [Yin & Lfortune, IEEE TAC, 206] A iprtite trnsition system T w.r.t. G is 7-tuple T = (Q Y, Q Z, h YZ, h ZY, E, Γ, y 0 ) where Q Y I is the set of Y-sttes; Q Z I Γ is the set of Z-sttes so tht z = (I z, Γ z ); h YZ : Q Y Γ Q Z represents the unoserle reh; h ZY : Q Z E Q Y represents the osertion trnsition; 5 w w w , * + * + *, w+,5, *, w+ 5,6, 6 G: E =, w, E o = *,, + A BTS X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 8/4
23 All Inlusie Controller Definition. (AIC). The All Inlusie Controller AIC(G) = (Q AIC Y, Q AIC Z, h AIC YZ, h AIC ZY, E, Γ, y 0 ), is defined s the lrgest BTS suh. For ny y Q Y AIC, there exists t lest one ontrol deision 2. For ny z Q Z AIC, we he 2.. ll fesile oserle eents re defined 2.2. I z only ontins legl sttes 5 w w w G , * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 9/4
24 Control Simultion Reltion Definition. (Control Simultion Reltion) Let T nd T 2 e two BTSs. A reltion Φ = Φ Y Φ Z Q Y T Q Y T 2 (QZ T Q Z T 2 ) is sid to e ontrol simultion reltion from T to T 2 if the following onditions hold:. y 0, y 0 Φ Y ; 2. For eery y, y 2 γ γ 2 Φ Y, we he tht: for ny y z in T, there exists y 2 z 2 suh tht z, z 2 Φ Z nd γ γ 2.. For eery z, z 2 Φ z, we he tht: for ny z σ y in T, there exists z 2 σ y2 suh tht y, y 2 Φ Y. X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 0/4
25 Control Simultion Reltion Definition. (Control Simultion Reltion) Let T nd T 2 e two BTSs. A reltion Φ = Φ Y Φ Z Q Y T Q Y T 2 (QZ T Q Z T 2 ) is sid to e ontrol simultion reltion from T to T 2 if the following onditions hold:. y 0, y 0 Φ Y ; 2. For eery y, y 2 γ γ 2 Φ Y, we he tht: for ny y z in T, there exists y 2 z 2 suh tht z, z 2 Φ Z nd γ γ 2.. For eery z, z 2 Φ z, we he tht: for ny z σ y in T, there exists z 2 σ y2 suh tht y, y 2 Φ Y. There exists unique mximl CSR from T to T 2 Φ T, T 2 = lim k F k ( Q Y T Q Y T 2 QZ T Q Z T 2 ) At most Q Y T Q Y T 2 + Q Z T Q Z T 2 itertions X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 0/4
26 Synthesis Steps Synthesis Steps:. Construt AIC(G) tht ontins ll sfe superisors 2. Construt BTS T R tht relizes the superisor hieing L r. Compute the mximl CSR Φ from T R to AIC(G) 4. Construt BTS T tht relizes mximl superisor hieing L r y using T R, AIC(G) nd Φ - For eh Y-stte, enle s mny eents s possile without iolting Φ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
27 Exmple G 2 5 w w w R X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
28 Exmple G 2 5 w w w R Step : Construt AIC(G), * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
29 Exmple G 2 5 w w w R Step 2: Construt the BTS T R, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, * +, * +,{} T R X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
30 Exmple G 2 5 w w w R, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + Φ, * + * + 5,6, T R Step : Compute the mximl CSR Φ,{} X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
31 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
32 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
33 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T * +, * + X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
34 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T * +, * + X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
35 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T * +, * + X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
36 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T, * + * + *, w+,5, *, w+ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
37 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T * +, * + *, w+,5, *, w+ 6 X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
38 Exmple, * +,5, *, w+ *, w+ * +,2,,,,5, 6 AIC(G),4,5,,4,4, * + 5,6, Φ * +, * +,{} T R Step 4: Construt mximl BTS T * +, * + *, w+,5, *, w+ 5,6, 6 X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 2/4
39 Synthesis Steps Reisited Synthesis Steps:. Construt AIC(G) tht ontins ll sfe superisors 2. Construt BTS T R tht relizes the superisor hieing L r. Compute the mximl CSR Φ from T R to AIC(G) 4. Construt BTS T tht relizes mximl superisor hieing L r y using T R, AIC(G) nd Φ - For eh Y-stte, enle s mny eents s possile without iolting Φ X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
40 Synthesis Steps Reisited Synthesis Steps:. Construt AIC(G) tht ontins ll sfe superisors 2. Construt BTS T R tht relizes the superisor hieing L r. Compute the mximl CSR Φ from T R to AIC(G) 4. Construt BTS T tht relizes mximl superisor hieing L r y using T R, AIC(G) nd Φ - For eh Y-stte, enle s mny eents s possile without iolting Φ The strtegy is not ompletely greedy. Future informtion hs lredy een pre-proessed nd onsidered! X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
41 Synthesis Steps Reisited Synthesis Steps:. Construt AIC(G) tht ontins ll sfe superisors 2. Construt BTS T R tht relizes the superisor hieing L r. Compute the mximl CSR Φ from T R to AIC(G) 4. Construt BTS T tht relizes mximl superisor hieing L r y using T R, AIC(G) nd Φ - For eh Y-stte, enle s mny eents s possile without iolting Φ The strtegy is not ompletely greedy. Future informtion hs lredy een pre-proessed nd onsidered! X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
42 Synthesis Steps Reisited Synthesis Steps:. Construt AIC(G) tht ontins ll sfe superisors 2. Construt BTS T R tht relizes the superisor hieing L r. Compute the mximl CSR Φ from T R to AIC(G) 4. Construt BTS T tht relizes mximl superisor hieing L r y using T R, AIC(G) nd Φ - For eh Y-stte, enle s mny eents s possile without iolting Φ Complexity O 2 2 X +2 E = O AIC 2 Mximl CSR Φ + O AIC Depth First Serh X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 /4
43 Summry Contriution Sole the Mximlly-Permissie Rnge Control Prolem New pproh using AIC nd CSR Gurntees oth mximl-permissieness nd miniml requirement Softwre DPO-SYNT: Future Work Consider non-lokingness in ddition to sfety X.Yin & S.Lfortune (UMih) CDC 206 4/4
Supervisory Control under Partial Observation
 Supervisory Control under Prtil Observtion Dr Rong Su S1-B1b-59, Shool of EEE Nnyng Tehnologil University Tel: +65 6790-6042, Emil: rsu@ntu.edu.sg EE6226 Disrete Event Dynmi Systems 1 Outline Motivtion
Supervisory Control under Prtil Observtion Dr Rong Su S1-B1b-59, Shool of EEE Nnyng Tehnologil University Tel: +65 6790-6042, Emil: rsu@ntu.edu.sg EE6226 Disrete Event Dynmi Systems 1 Outline Motivtion
Petri Nets. Rebecca Albrecht. Seminar: Automata Theory Chair of Software Engeneering
 Petri Nets Ree Alreht Seminr: Automt Theory Chir of Softwre Engeneering Overview 1. Motivtion: Why not just using finite utomt for everything? Wht re Petri Nets nd when do we use them? 2. Introdution:
Petri Nets Ree Alreht Seminr: Automt Theory Chir of Softwre Engeneering Overview 1. Motivtion: Why not just using finite utomt for everything? Wht re Petri Nets nd when do we use them? 2. Introdution:
CONTROLLABILITY and observability are the central
 1 Complexity of Infiml Oservle Superlnguges Tomáš Msopust Astrt The infiml prefix-losed, ontrollle nd oservle superlnguge plys n essentil role in the reltionship etween ontrollility, oservility nd o-oservility
1 Complexity of Infiml Oservle Superlnguges Tomáš Msopust Astrt The infiml prefix-losed, ontrollle nd oservle superlnguge plys n essentil role in the reltionship etween ontrollility, oservility nd o-oservility
Behavior Composition in the Presence of Failure
 Behior Composition in the Presene of Filure Sestin Srdin RMIT Uniersity, Melourne, Austrli Fio Ptrizi & Giuseppe De Giomo Spienz Uni. Rom, Itly KR 08, Sept. 2008, Sydney Austrli Introdution There re t
Behior Composition in the Presene of Filure Sestin Srdin RMIT Uniersity, Melourne, Austrli Fio Ptrizi & Giuseppe De Giomo Spienz Uni. Rom, Itly KR 08, Sept. 2008, Sydney Austrli Introdution There re t
Abstraction of Nondeterministic Automata Rong Su
 Astrtion of Nondeterministi Automt Rong Su My 6, 2010 TU/e Mehnil Engineering, Systems Engineering Group 1 Outline Motivtion Automton Astrtion Relevnt Properties Conlusions My 6, 2010 TU/e Mehnil Engineering,
Astrtion of Nondeterministi Automt Rong Su My 6, 2010 TU/e Mehnil Engineering, Systems Engineering Group 1 Outline Motivtion Automton Astrtion Relevnt Properties Conlusions My 6, 2010 TU/e Mehnil Engineering,
State Complexity of Union and Intersection of Binary Suffix-Free Languages
 Stte Complexity of Union nd Intersetion of Binry Suffix-Free Lnguges Glin Jirásková nd Pvol Olejár Slovk Ademy of Sienes nd Šfárik University, Košie 0000 1111 0000 1111 Glin Jirásková nd Pvol Olejár Binry
Stte Complexity of Union nd Intersetion of Binry Suffix-Free Lnguges Glin Jirásková nd Pvol Olejár Slovk Ademy of Sienes nd Šfárik University, Košie 0000 1111 0000 1111 Glin Jirásková nd Pvol Olejár Binry
Bisimulation, Games & Hennessy Milner logic
 Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Chapter 4 State-Space Planning
 Leture slides for Automted Plnning: Theory nd Prtie Chpter 4 Stte-Spe Plnning Dn S. Nu CMSC 722, AI Plnning University of Mrylnd, Spring 2008 1 Motivtion Nerly ll plnning proedures re serh proedures Different
Leture slides for Automted Plnning: Theory nd Prtie Chpter 4 Stte-Spe Plnning Dn S. Nu CMSC 722, AI Plnning University of Mrylnd, Spring 2008 1 Motivtion Nerly ll plnning proedures re serh proedures Different
Behavior Composition in the Presence of Failure
 Behvior Composition in the Presene of Filure Sestin Srdin RMIT University, Melourne, Austrli Fio Ptrizi & Giuseppe De Giomo Spienz Univ. Rom, Itly KR 08, Sept. 2008, Sydney Austrli Introdution There re
Behvior Composition in the Presene of Filure Sestin Srdin RMIT University, Melourne, Austrli Fio Ptrizi & Giuseppe De Giomo Spienz Univ. Rom, Itly KR 08, Sept. 2008, Sydney Austrli Introdution There re
Stealthy Deception Attacks for Cyber-Physical Systems
 2017 IEEE 56th Annul Conferene on Deision nd Control (CDC) Deemer 12-15, 2017, Melourne, Austrli Stelthy Deeption Attks for Cyer-Physil Systems Rômulo Meir Góes, Eunsuk Kng, Rymond Kwong nd Stéphne Lfortune
2017 IEEE 56th Annul Conferene on Deision nd Control (CDC) Deemer 12-15, 2017, Melourne, Austrli Stelthy Deeption Attks for Cyer-Physil Systems Rômulo Meir Góes, Eunsuk Kng, Rymond Kwong nd Stéphne Lfortune
Prefix-Free Regular-Expression Matching
 Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing Yo-Su Hn, Yjun Wng nd Derik Wood Deprtment of Computer Siene HKUST Prefix-Free Regulr-Expression Mthing p.1/15 Pttern Mthing Given pttern P nd text T, find ll sustrings
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
CS311 Computational Structures Regular Languages and Regular Grammars. Lecture 6
 CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica REPORTRAPPORT. Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems
 Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informtic REPORTRAPPORT Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems A. Overkmp Deprtment of Opertions Reserch, Sttistics, nd System Theory BS-R9411 1994 Supervisory Control
Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informtic REPORTRAPPORT Supervisory control for nondeterministic systems A. Overkmp Deprtment of Opertions Reserch, Sttistics, nd System Theory BS-R9411 1994 Supervisory Control
Technische Universität München Winter term 2009/10 I7 Prof. J. Esparza / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenberger 11. Februar Solution
 Tehnishe Universität Münhen Winter term 29/ I7 Prof. J. Esprz / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenerger. Ferur 2 Solution Automt nd Forml Lnguges Homework 2 Due 5..29. Exerise 2. Let A e the following finite utomton:
Tehnishe Universität Münhen Winter term 29/ I7 Prof. J. Esprz / J. Křetínský / M. Luttenerger. Ferur 2 Solution Automt nd Forml Lnguges Homework 2 Due 5..29. Exerise 2. Let A e the following finite utomton:
Formal Language and Automata Theory (CS21004)
 Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Formal Languages and Automata
 Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Logic, Set Theory and Computability [M. Coppenbarger]
![Logic, Set Theory and Computability [M. Coppenbarger] Logic, Set Theory and Computability [M. Coppenbarger]](/thumbs/90/103901048.jpg) 14 Orer (Hnout) Definition 7-11: A reltion is qusi-orering (or preorer) if it is reflexive n trnsitive. A quisi-orering tht is symmetri is n equivlene reltion. A qusi-orering tht is nti-symmetri is n orer
14 Orer (Hnout) Definition 7-11: A reltion is qusi-orering (or preorer) if it is reflexive n trnsitive. A quisi-orering tht is symmetri is n equivlene reltion. A qusi-orering tht is nti-symmetri is n orer
On Determinisation of History-Deterministic Automata.
 On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages
 Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER MACHINES AND THEIR LANGUAGES ANSWERS
 The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
NON-DETERMINISTIC FSA
 Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Learning Moore Machines from Input-Output Traces
 Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
More general families of infinite graphs
 More generl fmilies of infinite grphs Antoine Meyer Forml Methods Updte 2006 IIT Guwhti Prefix-recognizle grphs Theorem Let G e grph, the following sttements re equivlent: G is defined y reltions of the
More generl fmilies of infinite grphs Antoine Meyer Forml Methods Updte 2006 IIT Guwhti Prefix-recognizle grphs Theorem Let G e grph, the following sttements re equivlent: G is defined y reltions of the
Automata and Languages
 Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Safety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscale Symbolic Models
 Sfety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscle Symolic Models Antoine Girrd Lortoire des Signux et Systèmes Gif sur Yvette, Frnce Séminire du LAAS Toulouse, 29 Juin, 2016 A. Girrd (L2S-CNRS)
Sfety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscle Symolic Models Antoine Girrd Lortoire des Signux et Systèmes Gif sur Yvette, Frnce Séminire du LAAS Toulouse, 29 Juin, 2016 A. Girrd (L2S-CNRS)
A Symbolic Approach to Control via Approximate Bisimulations
 A Symolic Approch to Control vi Approximte Bisimultions Antoine Girrd Lortoire Jen Kuntzmnn, Université Joseph Fourier Grenole, Frnce Interntionl Symposium on Innovtive Mthemticl Modelling Tokyo, Jpn,
A Symolic Approch to Control vi Approximte Bisimultions Antoine Girrd Lortoire Jen Kuntzmnn, Université Joseph Fourier Grenole, Frnce Interntionl Symposium on Innovtive Mthemticl Modelling Tokyo, Jpn,
Transition systems (motivation)
 Trnsition systems (motivtion) Course Modelling of Conurrent Systems ( Modellierung neenläufiger Systeme ) Winter Semester 2009/0 University of Duisurg-Essen Brr König Tehing ssistnt: Christoph Blume In
Trnsition systems (motivtion) Course Modelling of Conurrent Systems ( Modellierung neenläufiger Systeme ) Winter Semester 2009/0 University of Duisurg-Essen Brr König Tehing ssistnt: Christoph Blume In
Theory of Computation Regular Languages. (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall / 38
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Foundation of Diagnosis and Predictability in Probabilistic Systems
 Foundtion of Dignosis nd Preditility in Proilisti Systems Nthlie Bertrnd 1, Serge Hddd 2, Engel Lefuheux 1,2 1 Inri Rennes, Frne 2 LSV, ENS Chn & CNRS & Inri Sly, Frne De. 16th FSTTCS 14 Dignosis of disrete
Foundtion of Dignosis nd Preditility in Proilisti Systems Nthlie Bertrnd 1, Serge Hddd 2, Engel Lefuheux 1,2 1 Inri Rennes, Frne 2 LSV, ENS Chn & CNRS & Inri Sly, Frne De. 16th FSTTCS 14 Dignosis of disrete
Theory of Computation Regular Languages
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Model Reduction of Finite State Machines by Contraction
 Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Lecture 6 Regular Grammars
 Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Running an NFA & the subset algorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fall 2018 gilray.org/classes/fall2018/cs350/
 Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
Running n NFA & the suset lgorithm (NFA->DFA) CS 350 Fll 2018 gilry.org/lsses/fll2018/s350/ 1 NFAs operte y simultneously exploring ll pths nd epting if ny pth termintes t n ept stte.!2 Try n exmple: L
Regular languages refresher
 Regulr lnguges refresher 1 Regulr lnguges refresher Forml lnguges Alphet = finite set of letters Word = sequene of letter Lnguge = set of words Regulr lnguges defined equivlently y Regulr expressions Finite-stte
Regulr lnguges refresher 1 Regulr lnguges refresher Forml lnguges Alphet = finite set of letters Word = sequene of letter Lnguge = set of words Regulr lnguges defined equivlently y Regulr expressions Finite-stte
Solutions for HW9. Bipartite: put the red vertices in V 1 and the black in V 2. Not bipartite!
 Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Safety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscale Symbolic Models
 Sfety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscle Symolic Models Antoine Girrd Lortoire des Signux et Systèmes Gif sur Yvette, Frnce Workshop on switching dynmics & verifiction Pris, Jnury
Sfety Controller Synthesis for Switched Systems using Multiscle Symolic Models Antoine Girrd Lortoire des Signux et Systèmes Gif sur Yvette, Frnce Workshop on switching dynmics & verifiction Pris, Jnury
11.1 Finite Automata. CS125 Lecture 11 Fall Motivation: TMs without a tape: maybe we can at least fully understand such a simple model?
 CS125 Lecture 11 Fll 2016 11.1 Finite Automt Motivtion: TMs without tpe: mybe we cn t lest fully understnd such simple model? Algorithms (e.g. string mtching) Computing with very limited memory Forml verifiction
CS125 Lecture 11 Fll 2016 11.1 Finite Automt Motivtion: TMs without tpe: mybe we cn t lest fully understnd such simple model? Algorithms (e.g. string mtching) Computing with very limited memory Forml verifiction
Prefix-Free Subsets of Regular Languages and Descriptional Complexity
 Prefix-Free Susets of Regulr Lnguges nd Descriptionl Complexity Jozef Jirásek Jurj Šeej DCFS 2015 Prefix-Free Susets of Regulr Lnguges nd Descriptionl Complexity Jozef Jirásek, Jurj Šeej 1/22 Outline Mximl
Prefix-Free Susets of Regulr Lnguges nd Descriptionl Complexity Jozef Jirásek Jurj Šeej DCFS 2015 Prefix-Free Susets of Regulr Lnguges nd Descriptionl Complexity Jozef Jirásek, Jurj Šeej 1/22 Outline Mximl
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
Let's start with an example:
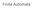 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite State Automata and Determinisation
 Finite Stte Automt nd Deterministion Tim Dworn Jnury, 2016 Lnguges fs nf re df Deterministion 2 Outline 1 Lnguges 2 Finite Stte Automt (fs) 3 Non-deterministi Finite Stte Automt (nf) 4 Regulr Expressions
Finite Stte Automt nd Deterministion Tim Dworn Jnury, 2016 Lnguges fs nf re df Deterministion 2 Outline 1 Lnguges 2 Finite Stte Automt (fs) 3 Non-deterministi Finite Stte Automt (nf) 4 Regulr Expressions
Parse trees, ambiguity, and Chomsky normal form
 Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
Formal Methods in Software Engineering
 Forml Methods in Softwre Engineering Lecture 09 orgniztionl issues Prof. Dr. Joel Greenyer Decemer 9, 2014 Written Exm The written exm will tke plce on Mrch 4 th, 2015 The exm will tke 60 minutes nd strt
Forml Methods in Softwre Engineering Lecture 09 orgniztionl issues Prof. Dr. Joel Greenyer Decemer 9, 2014 Written Exm The written exm will tke plce on Mrch 4 th, 2015 The exm will tke 60 minutes nd strt
Laboratory for Foundations of Computer Science. An Unfolding Approach. University of Edinburgh. Model Checking. Javier Esparza
 An Unfoling Approh to Moel Cheking Jvier Esprz Lbortory for Fountions of Computer Siene University of Einburgh Conurrent progrms Progrm: tuple P T 1 T n of finite lbelle trnsition systems T i A i S i i
An Unfoling Approh to Moel Cheking Jvier Esprz Lbortory for Fountions of Computer Siene University of Einburgh Conurrent progrms Progrm: tuple P T 1 T n of finite lbelle trnsition systems T i A i S i i
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Good-for-Games Automata versus Deterministic Automata.
 Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
CS415 Compilers. Lexical Analysis and. These slides are based on slides copyrighted by Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Linda Torczon at Rice University
 CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
Strong Bisimulation. Overview. References. Actions Labeled transition system Transition semantics Simulation Bisimulation
 Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
Unfoldings of Networks of Timed Automata
 Unfolings of Networks of Time Automt Frnk Cssez Thoms Chtin Clue Jr Ptrii Bouyer Serge H Pierre-Alin Reynier Rennes, Deemer 3, 2008 Unfolings [MMilln 93] First efine for Petri nets Then extene to other
Unfolings of Networks of Time Automt Frnk Cssez Thoms Chtin Clue Jr Ptrii Bouyer Serge H Pierre-Alin Reynier Rennes, Deemer 3, 2008 Unfolings [MMilln 93] First efine for Petri nets Then extene to other
Automatic Synthesis of New Behaviors from a Library of Available Behaviors
 Automti Synthesis of New Behviors from Lirry of Aville Behviors Giuseppe De Giomo Università di Rom L Spienz, Rom, Itly degiomo@dis.unirom1.it Sestin Srdin RMIT University, Melourne, Austrli ssrdin@s.rmit.edu.u
Automti Synthesis of New Behviors from Lirry of Aville Behviors Giuseppe De Giomo Università di Rom L Spienz, Rom, Itly degiomo@dis.unirom1.it Sestin Srdin RMIT University, Melourne, Austrli ssrdin@s.rmit.edu.u
= state, a = reading and q j
 4 Finite Automt CHAPTER 2 Finite Automt (FA) (i) Derterministi Finite Automt (DFA) A DFA, M Q, q,, F, Where, Q = set of sttes (finite) q Q = the strt/initil stte = input lphet (finite) (use only those
4 Finite Automt CHAPTER 2 Finite Automt (FA) (i) Derterministi Finite Automt (DFA) A DFA, M Q, q,, F, Where, Q = set of sttes (finite) q Q = the strt/initil stte = input lphet (finite) (use only those
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
9/6/28 Stereotypicl computer CISC 49 Theory of Computtion Finite stte mchines & Regulr lnguges Professor Dniel Leeds dleeds@fordhm.edu JMH 332 Centrl processing unit (CPU) performs ll the instructions
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Harvard University Computer Science 121 Midterm October 23, 2012
 Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
Hrvrd University Computer Science 121 Midterm Octoer 23, 2012 This is closed-ook exmintion. You my use ny result from lecture, Sipser, prolem sets, or section, s long s you quote it clerly. The lphet is
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Nondeterministic Automata vs Deterministic Automata
 Nondeterministi Automt vs Deterministi Automt We lerned tht NFA is onvenient model for showing the reltionships mong regulr grmmrs, FA, nd regulr expressions, nd designing them. However, we know tht n
Nondeterministi Automt vs Deterministi Automt We lerned tht NFA is onvenient model for showing the reltionships mong regulr grmmrs, FA, nd regulr expressions, nd designing them. However, we know tht n
Finite-State Automata: Recap
 Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Finite-Stte Automt: Recp Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 09 August 2016 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Forml Definitions nd Nottion 3 Closure under
Infinite-Step Opacity of Stochastic Discrete-Event Systems
 7 th Asin Control Conferene (ASCC) Gold Cost Convention Centre, Austrli Deemer 7-, 7 Infinite-Step Opity of Stohsti Disrete-Event Systems Xing Yin, Zhojin Li, Weilin Wng nd Shoyun Li Astrt Opity is n importnt
7 th Asin Control Conferene (ASCC) Gold Cost Convention Centre, Austrli Deemer 7-, 7 Infinite-Step Opity of Stohsti Disrete-Event Systems Xing Yin, Zhojin Li, Weilin Wng nd Shoyun Li Astrt Opity is n importnt
Deterministic Finite-State Automata
 Deterministic Finite-Stte Automt Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 12 August 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Exmple DFA 1 DFA for Odd number of
Deterministic Finite-Stte Automt Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute of Science, Bnglore. 12 August 2013 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Exmple DFA 1 DFA for Odd number of
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Transition Graphs. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Trnsition Grphs Chpter 6 Deprtment of Computer Science Relxing Restrints on Inputs We cn uild n FA tht ccepts only the word! 5 sttes ecuse n FA cn only process one letter t
CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Trnsition Grphs Chpter 6 Deprtment of Computer Science Relxing Restrints on Inputs We cn uild n FA tht ccepts only the word! 5 sttes ecuse n FA cn only process one letter t
DFA minimisation using the Myhill-Nerode theorem
 DFA minimistion using the Myhill-Nerode theorem Johnn Högerg Lrs Lrsson Astrct The Myhill-Nerode theorem is n importnt chrcteristion of regulr lnguges, nd it lso hs mny prcticl implictions. In this chpter,
DFA minimistion using the Myhill-Nerode theorem Johnn Högerg Lrs Lrsson Astrct The Myhill-Nerode theorem is n importnt chrcteristion of regulr lnguges, nd it lso hs mny prcticl implictions. In this chpter,
Unit 4. Combinational Circuits
 Unit 4. Comintionl Ciruits Digitl Eletroni Ciruits (Ciruitos Eletrónios Digitles) E.T.S.I. Informáti Universidd de Sevill 5/10/2012 Jorge Jun 2010, 2011, 2012 You re free to opy, distriute
Unit 4. Comintionl Ciruits Digitl Eletroni Ciruits (Ciruitos Eletrónios Digitles) E.T.S.I. Informáti Universidd de Sevill 5/10/2012 Jorge Jun 2010, 2011, 2012 You re free to opy, distriute
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 13 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 13 Jul 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 13 Jul 2018](/thumbs/95/124646994.jpg) Detetion nd Mitigtion of Clsses of Attks in Supervisory Control Systems Lilin Kwkmi Crvlho, Yi-Chin Wu b, Rymond Kwong, Stéphne Lfortune d Deprtment of Eletril Engineering, Universidde Federl do Rio de
Detetion nd Mitigtion of Clsses of Attks in Supervisory Control Systems Lilin Kwkmi Crvlho, Yi-Chin Wu b, Rymond Kwong, Stéphne Lfortune d Deprtment of Eletril Engineering, Universidde Federl do Rio de
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata. Fall 2018 Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Rep Fun Gme Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Fun Gme Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep 2 Fun Gme 3 Properties
Rep Fun Gme Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Fun Gme Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep 2 Fun Gme 3 Properties
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term Dr. Dave Parker. Department of Computer Science University of Oxford
 Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Bayesian Networks: Approximate Inference
 pproches to inference yesin Networks: pproximte Inference xct inference Vrillimintion Join tree lgorithm pproximte inference Simplify the structure of the network to mkxct inferencfficient (vritionl methods,
pproches to inference yesin Networks: pproximte Inference xct inference Vrillimintion Join tree lgorithm pproximte inference Simplify the structure of the network to mkxct inferencfficient (vritionl methods,
Assignment 1 Automata, Languages, and Computability. 1 Finite State Automata and Regular Languages
 Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
Revision Sheet. (a) Give a regular expression for each of the following languages:
 Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
a,b a 1 a 2 a 3 a,b 1 a,b a,b 2 3 a,b a,b a 2 a,b CS Determinisitic Finite Automata 1
 CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
The size of subsequence automaton
 Theoreticl Computer Science 4 (005) 79 84 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Note The size of susequence utomton Zdeněk Troníček,, Ayumi Shinohr,c Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering, FEE CTU in Prgue,
Theoreticl Computer Science 4 (005) 79 84 www.elsevier.com/locte/tcs Note The size of susequence utomton Zdeněk Troníček,, Ayumi Shinohr,c Deprtment of Computer Science nd Engineering, FEE CTU in Prgue,
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Kleene s Theorem. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
Gold s algorithm. Acknowledgements. Why would this be true? Gold's Algorithm. 1 Key ideas. Strings as states
 Acknowledgements Gold s lgorithm Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin nd Tim Otes for previous versions of these slides. Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscuert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning Fernu, Thierry Murgue, Frnck
Acknowledgements Gold s lgorithm Lurent Miclet, Jose Oncin nd Tim Otes for previous versions of these slides. Rfel Crrsco, Pco Cscuert, Rémi Eyrud, Philippe Ezequel, Henning Fernu, Thierry Murgue, Frnck
System Validation (IN4387) November 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00
 System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
Tutorial Automata and formal Languages
 Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
CS 275 utomt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Prolem (II) Chpter II.5.: Properties of Context Free Grmmrs (14) nton Setzer (Bsed on ook drft y J. V. Tucker nd K. Stephenson)
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. Comparing DFAs and NFAs (cont.) Finite Automata 2
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata
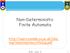 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt http://users.comlb.ox.c.uk/luke. ong/teching/moc/nf2up.pdf 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q1 q2 2 Alphbet ={} Two choices q1 q2 3 Alphbet ={} Two choices
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt http://users.comlb.ox.c.uk/luke. ong/teching/moc/nf2up.pdf 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q1 q2 2 Alphbet ={} Two choices q1 q2 3 Alphbet ={} Two choices
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep
Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep
LIP. Laboratoire de l Informatique du Parallélisme. Ecole Normale Supérieure de Lyon
 LIP Lortoire de l Informtique du Prllélisme Eole Normle Supérieure de Lyon Institut IMAG Unité de reherhe ssoiée u CNRS n 1398 One-wy Cellulr Automt on Cyley Grphs Zsuzsnn Rok Mrs 1993 Reserh Report N
LIP Lortoire de l Informtique du Prllélisme Eole Normle Supérieure de Lyon Institut IMAG Unité de reherhe ssoiée u CNRS n 1398 One-wy Cellulr Automt on Cyley Grphs Zsuzsnn Rok Mrs 1993 Reserh Report N
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
Exercise 3 Logic Control
 Exerise 3 Logi Control OBJECTIVE The ojetive of this exerise is giving n introdution to pplition of Logi Control System (LCS). Tody, LCS is implemented through Progrmmle Logi Controller (PLC) whih is lled
Exerise 3 Logi Control OBJECTIVE The ojetive of this exerise is giving n introdution to pplition of Logi Control System (LCS). Tody, LCS is implemented through Progrmmle Logi Controller (PLC) whih is lled
State Minimization for DFAs
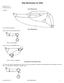 Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
DFA Minimization and Applications
 DFA Minimiztion nd Applictions Mondy, Octoer 15, 2007 Reding: toughton 3.12 C235 Lnguges nd Automt Deprtment of Computer cience Wellesley College Gols for ody o Answer ny P3 questions you might hve. o
DFA Minimiztion nd Applictions Mondy, Octoer 15, 2007 Reding: toughton 3.12 C235 Lnguges nd Automt Deprtment of Computer cience Wellesley College Gols for ody o Answer ny P3 questions you might hve. o
NFA and regex. the Boolean algebra of languages. non-deterministic machines. regular expressions
 NFA nd regex l the Boolen lger of lnguges non-deterministi mhines regulr expressions Informtis The intersetion of two regulr lnguges is regulr Run oth mhines in prllel? Build one mhine tht simultes two
NFA nd regex l the Boolen lger of lnguges non-deterministi mhines regulr expressions Informtis The intersetion of two regulr lnguges is regulr Run oth mhines in prllel? Build one mhine tht simultes two
Alpha Algorithm: Limitations
 Proess Mining: Dt Siene in Ation Alph Algorithm: Limittions prof.dr.ir. Wil vn der Alst www.proessmining.org Let L e n event log over T. α(l) is defined s follows. 1. T L = { t T σ L t σ}, 2. T I = { t
Proess Mining: Dt Siene in Ation Alph Algorithm: Limittions prof.dr.ir. Wil vn der Alst www.proessmining.org Let L e n event log over T. α(l) is defined s follows. 1. T L = { t T σ L t σ}, 2. T I = { t
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
Overview HC9. Parsing: Top-Down & LL(1) Context-Free Grammars (1) Introduction. CFGs (3) Context-Free Grammars (2) Vertalerbouw HC 9: Ch.
 Overview H9 Vertlerouw H 9: Prsing: op-down & LL(1) do 3 mei 2001 56 heo Ruys h. 8 - Prsing 8.1 ontext-free Grmmrs 8.2 op-down Prsing 8.3 LL(1) Grmmrs See lso [ho, Sethi & Ullmn 1986] for more thorough
Overview H9 Vertlerouw H 9: Prsing: op-down & LL(1) do 3 mei 2001 56 heo Ruys h. 8 - Prsing 8.1 ontext-free Grmmrs 8.2 op-down Prsing 8.3 LL(1) Grmmrs See lso [ho, Sethi & Ullmn 1986] for more thorough
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
