GUIDED NOTES 6.4 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
|
|
|
- Pamela Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GUIDED NOTES 6.4 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. FINDING THE DOMAIN OF A LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION Write out the 3 step process for identifying the domain, given a logarithmic function. 1. Try It: Read Example 1 in the text, then answer the following. What is the domain of f(x) = log 5 (x 2) + 1? Try It: Read Example 2 in the text, then answer the following. What is the domain of f(x) = log(x 5) + 2?
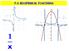
2 GRAPHING LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Study the box in your textbook section titled characteristics of the graph of the parent function, f(x) = log b x. For any real number x and constant b > 0, b 1, we can see the following characteristics in the graph of f(x) = log b (x): function Vertical asymptote: Domain: Range: x-intercept:, key point: y-intercept: Increasing if b 1 Decreasing if 0 b 1 Sketch the logarithmic function in the form f(x) = log b x, when b > 1 0 < b < 1
3 Write out the 5 step process for graphing a function, given a logarithmic function with the form f(x) = log b (x) Try It: Read Example 3 in the text, then answer the following. Graph f(x) = log1(x). State the domain, range, and asymptote. 5
4 GRAPHING TRANSFORMATIONS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS Study the box in your textbook section titled horizontal shifts of the parent function y = log b (x). For any constant c, the function f(x) = log b (x + c) Shifts the parent function c units if c > 0 Shifts the parent function c units if c < 0 the vertical asymptote is Domain: Range: Write out the 5 step process for graphing a translation, given a logarithmic function with the form f(x) = log b (x + c). 1. a. b. 4.
5 5. Try It: Read Example 4 in the text, then answer the following. Sketch a graph of f(x) = log 3 (x + 4) alongside its parent function. Include the key points and asymptotes on the graph. State the domain, range, and asymptote. Study the box in your textbook section titled vertical shifts of the parent function y = log b (x). For any constant d, the function f(x) = log b (x) + d Shifts the parent function y = log b (x) d units if d > 0 Shifts the parent function y = log b (x) d units if d < 0 the vertical asymptote is Domain: Range:
6 Write out the 5 step process for graphing a translation, given a logarithmic function with the form f(x) = log b (x) + d. 1. a. b Try It: Read Example 5 in the text, then answer the following. Sketch a graph of f(x) = log 2 (x) + 2 alongside its parent function. Include the key points and asymptotes on the graph. State the domain, range, and asymptote.
7 Study the box in your textbook section titled vertical stretches and compressions of the parent function y = log b (x). For any constant a > 1, the function f(x) = alog b (x) Stretches the parent function y = log b (x) by a factor of units if a 0 Compresses the parent function y = log b (x) by a factor of units if a 0 the vertical asymptote is (1,0) is the Domain: Range: Write out the 5 step process for graphing a translation, given a logarithmic function with the form f(x) = a log b (x), a > a. b
8 Try It: Read Example 6 in the text, then answer the following. Sketch a graph of f(x) = 1 log 2 4 (x) alongside the parent function. Include the key points and asymptotes on the graph. State the domain, range, and asymptote. Try It: Read Example 7 in the text, then answer the following. Sketch a graph of f(x) = 3 log(x 2) + 1. State the domain, range, and asymptote. Study the box in your textbook section titled reflections of the parent function y = log b (x). The function f(x) = log b (x) the parent function y = log b (x) about the the vertical asymptote is Domain:
9 Range: The function f(x) = log b ( x) the parent function y = log b (x) about the the vertical asymptote is Domain: Range: Write out the 5 step process for graphing a translation, given a logarithmic function with the parent function f(x) = log b (x). If f(x) = log b (x) If f(x) = log b ( x)
10 Try It: Read Example 8 in the text, then answer the following. Graph f(x) = log( x). State the domain, range, and asymptote. Study your textbook section to fill in the following table.
11 Shift Translation Translations of the Parent Function y = log b (x) Form y = Stretch and Compress y = Reflect about the x-axis Reflect about the y-axis General equation for all translations y = y = y = Study the box in your textbook section titled translations of logarithmic functions. All translations of the parent logarithmic function, f(x) = log b (x), have the form f(x) =, where the parent function f(x) = log b (x), b > 1, is Shifted vertically d units Shifted horizontally to the c units vertically by a factor of a if a > 1 vertically by a factor of a if 0 < a < 1 Reflected about the x-axis when a 0 * For f(x) = log( x), the graph of the parent function is reflected about the y-axis.
12 Try It: Read Example 10 in the text, then answer the following. What is the vertical asymptote of f(x) = 3 + ln(x 1)? Try It: Read Example 11 in the text, then answer the following. Give the equation of the natural logarithm graphed in Figure 16.
GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identify
GUIDED NOTES 5.6 RATIONAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identify
4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL TRANSLATIONS
 MCR3U Sections 1.6 1.8 Transformations HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL TRANSLATIONS A change made to a figure or a relation such that the figure or graph of the relation is shifted or changed in shape. Translations,
MCR3U Sections 1.6 1.8 Transformations HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL TRANSLATIONS A change made to a figure or a relation such that the figure or graph of the relation is shifted or changed in shape. Translations,
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient. Sign of Leading Coefficient
 Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Graduate T.A. Department of Mathematics Dynamical Systems and Chaos San Diego State University April 9, 11 Definition (Exponential Function) An exponential function with base a is a function of the form
Graduate T.A. Department of Mathematics Dynamical Systems and Chaos San Diego State University April 9, 11 Definition (Exponential Function) An exponential function with base a is a function of the form
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
Skill 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Skill 6a: Graphs of Exponential Functions Skill 6b: Solving Exponential Equations (not requiring logarithms) Skill 6c: Definition of Logarithms Skill 6d: Graphs
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
GUIDED NOTES 6.1 EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Evaluate exponential functions. Find the equation of an exponential function. Use compound interest formulas. Evaluate
GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE
 GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve equations in one variable algebraically. Solve a rational equation. Find a linear equation. Given
GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve equations in one variable algebraically. Solve a rational equation. Find a linear equation. Given
8 + 6) x 2 ) y = h(x)
 . a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
. a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
Section 4.5 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 6 Chapter 4 Section 4. Graphs of Logarithmic Functions Recall that the eponential function f ( ) would produce this table of values -3 - -1 0 1 3 f() 1/8 ¼ ½ 1 4 8 Since the arithmic function is an inverse
6 Chapter 4 Section 4. Graphs of Logarithmic Functions Recall that the eponential function f ( ) would produce this table of values -3 - -1 0 1 3 f() 1/8 ¼ ½ 1 4 8 Since the arithmic function is an inverse
Rewrite logarithmic equations 2 3 = = = 12
 EXAMPLE 1 Rewrite logarithmic equations Logarithmic Form a. log 2 8 = 3 Exponential Form 2 3 = 8 b. log 4 1 = 0 4 0 = 1 log 12 = 1 c. 12 12 1 = 12 log 4 = 1 d. 1/4 1 4 1 = 4 GUIDED PRACTICE for Example
EXAMPLE 1 Rewrite logarithmic equations Logarithmic Form a. log 2 8 = 3 Exponential Form 2 3 = 8 b. log 4 1 = 0 4 0 = 1 log 12 = 1 c. 12 12 1 = 12 log 4 = 1 d. 1/4 1 4 1 = 4 GUIDED PRACTICE for Example
Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications
 34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name
 Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name Textbook problems for practice: p. 285-293; p. 293 #9-14, p. 294-5 #1-34, 49-52, 55,56, 57; p. 297-321 logs; p. 280-1 #11-84 *Blood Alcohol, Bungee-from binder
Exp, Log, Poly Functions Quarter 3 Review Name Textbook problems for practice: p. 285-293; p. 293 #9-14, p. 294-5 #1-34, 49-52, 55,56, 57; p. 297-321 logs; p. 280-1 #11-84 *Blood Alcohol, Bungee-from binder
If a function has an inverse then we can determine the input if we know the output. For example if the function
 1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
1 Inverse Functions We know what it means for a relation to be a function. Every input maps to only one output, it passes the vertical line test. But not every function has an inverse. A function has no
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
The coordinates of the vertex of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the parabola opens upward. If a < 0, the parabola opens downward.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
A. Evaluate log Evaluate Logarithms
 A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
A. Evaluate log 2 16. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate Logarithms B. Evaluate. C. Evaluate. Evaluate Logarithms D. Evaluate log 17 17. Evaluate Logarithms Evaluate. A. 4 B. 4 C. 2 D. 2 A. Evaluate log 8 512.
Learning Target: I can sketch the graphs of rational functions without a calculator. a. Determine the equation(s) of the asymptotes.
 Learning Target: I can sketch the graphs of rational functions without a calculator Consider the graph of y= f(x), where f(x) = 3x 3 (x+2) 2 a. Determine the equation(s) of the asymptotes. b. Find the
Learning Target: I can sketch the graphs of rational functions without a calculator Consider the graph of y= f(x), where f(x) = 3x 3 (x+2) 2 a. Determine the equation(s) of the asymptotes. b. Find the
What You Need to Know for the Chapter 7 Test
 Score: /46 Name: Date: / / Hr: Alg 2C Chapter 7 Review - WYNTK CH 7 What You Need to Know for the Chapter 7 Test 7.1 Write & evaluate exponential expressions to model growth and decay situations. Determine
Score: /46 Name: Date: / / Hr: Alg 2C Chapter 7 Review - WYNTK CH 7 What You Need to Know for the Chapter 7 Test 7.1 Write & evaluate exponential expressions to model growth and decay situations. Determine
8-1 Exploring Exponential Models
 8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
8- Eploring Eponential Models Eponential Function A function with the general form, where is a real number, a 0, b > 0 and b. Eample: y = 4() Growth Factor When b >, b is the growth factor Eample: y =
Math 137 Exam #3 Review Guide
 Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
Concept Category 2. Exponential and Log Functions
 Concept Category 2 Exponential and Log Functions Concept Category 2 Check List *Find the inverse and composition of functions *Identify an exponential from a table, graph and equation *Identify the difference
Concept Category 2 Exponential and Log Functions Concept Category 2 Check List *Find the inverse and composition of functions *Identify an exponential from a table, graph and equation *Identify the difference
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 12 Review
 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
Lesson 5.6 Exercises, pages
 Lesson 5.6 Eercises, pages 05 0 A. Approimate the value of each logarithm, to the nearest thousanth. a) log 9 b) log 00 Use the change of base formula to change the base of the logarithms to base 0. log
Lesson 5.6 Eercises, pages 05 0 A. Approimate the value of each logarithm, to the nearest thousanth. a) log 9 b) log 00 Use the change of base formula to change the base of the logarithms to base 0. log
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW
 RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
6.1 - Vertical and Horizontal Shifts
 6.1 - Vertical and Horizontal Shifts Vertical Shifts If y g x is a function and k is a constant, then the graph of y g x k is the graph of y g x y g x k is the graph of y g x Graph f x x, f x x 3, and
6.1 - Vertical and Horizontal Shifts Vertical Shifts If y g x is a function and k is a constant, then the graph of y g x k is the graph of y g x y g x k is the graph of y g x Graph f x x, f x x 3, and
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = 3
 Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
Chapter 1- Polynomial Functions
 Chapter 1- Polynomial Functions WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 1.1 Power Functions MHF4U Jensen 1) Identify which of the following are polynomial functions: a) p x = cos x b) h x = 7x c) f x = 2x, d) y = 3x / 2x 0
Chapter 1- Polynomial Functions WORKBOOK MHF4U W1 1.1 Power Functions MHF4U Jensen 1) Identify which of the following are polynomial functions: a) p x = cos x b) h x = 7x c) f x = 2x, d) y = 3x / 2x 0
We want to determine what the graph of an exponential function. y = a x looks like for all values of a such that 0 > a > 1
 Section 5 B: Graphs of Decreasing Eponential Functions We want to determine what the graph of an eponential function y = a looks like for all values of a such that 0 > a > We will select a value of a such
Section 5 B: Graphs of Decreasing Eponential Functions We want to determine what the graph of an eponential function y = a looks like for all values of a such that 0 > a > We will select a value of a such
An equation of the form y = ab x where a 0 and the base b is a positive. x-axis (equation: y = 0) set of all real numbers
 Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts.
 Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Transformation of functions
 Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function.
 Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
MCR3U - Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MCR3U - Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following relations is not a function? 2. Which graph is not a function?
MCR3U - Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following relations is not a function? 2. Which graph is not a function?
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8)
 Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
To get horizontal and slant asymptotes algebraically we need to know about end behaviour for rational functions.
 Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
2.6. Graphs of Rational Functions. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
2.6 Graphs of Rational Functions Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. Rational Functions What you ll learn about Transformations of the Reciprocal Function Limits and Asymptotes Analyzing Graphs of Rational Functions
Reteach 2-3. Graphing Linear Functions. 22 Holt Algebra 2. Name Date Class
 -3 Graphing Linear Functions Use intercepts to sketch the graph of the function 3x 6y 1. The x-intercept is where the graph crosses the x-axis. To find the x-intercept, set y 0 and solve for x. 3x 6y 1
-3 Graphing Linear Functions Use intercepts to sketch the graph of the function 3x 6y 1. The x-intercept is where the graph crosses the x-axis. To find the x-intercept, set y 0 and solve for x. 3x 6y 1
MCR3U 1.1 Relations and Functions Date:
 MCR3U 1.1 Relations and Functions Date: Relation: a relationship between sets of information. ie height and time of a ball in the air. In relations, the pairs of time and heights are "ordered"; ie ordered
MCR3U 1.1 Relations and Functions Date: Relation: a relationship between sets of information. ie height and time of a ball in the air. In relations, the pairs of time and heights are "ordered"; ie ordered
Use a graphing utility to approximate the real solutions, if any, of the equation rounded to two decimal places. 4) x3-6x + 3 = 0 (-5,5) 4)
 Advanced College Prep Pre-Calculus Midyear Exam Review Name Date Per List the intercepts for the graph of the equation. 1) x2 + y - 81 = 0 1) Graph the equation by plotting points. 2) y = -x2 + 9 2) List
Advanced College Prep Pre-Calculus Midyear Exam Review Name Date Per List the intercepts for the graph of the equation. 1) x2 + y - 81 = 0 1) Graph the equation by plotting points. 2) y = -x2 + 9 2) List
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 8) 4x 2 = 100
 Algebra 2 1.1 Worksheet Name Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 1) 3x 5(2 4x) = 18 2) 17 + 11x = -19x 25 3) 2 6x+9 b 4 = 7 4) = 2x 3 4 5) 3 = 5 7 x x+1
Algebra 2 1.1 Worksheet Name Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 1) 3x 5(2 4x) = 18 2) 17 + 11x = -19x 25 3) 2 6x+9 b 4 = 7 4) = 2x 3 4 5) 3 = 5 7 x x+1
Vertex Form of a Parabola
 Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
Logarithms Dr. Laura J. Pyzdrowski
 1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
1 Names: (8 communication points) About this Laboratory An exponential function of the form f(x) = a x, where a is a positive real number not equal to 1, is an example of a one-to-one function. This means
MAC Learning Objectives. Logarithmic Functions. Module 8 Logarithmic Functions
 MAC 1140 Module 8 Logarithmic Functions Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. evaluate the common logarithmic function. 2. solve basic exponential and logarithmic equations.
MAC 1140 Module 8 Logarithmic Functions Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. evaluate the common logarithmic function. 2. solve basic exponential and logarithmic equations.
GOOD LUCK! 2. a b c d e 12. a b c d e. 3. a b c d e 13. a b c d e. 4. a b c d e 14. a b c d e. 5. a b c d e 15. a b c d e. 6. a b c d e 16.
 MA109 College Algebra Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam 2018-12-12 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be
MA109 College Algebra Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam 2018-12-12 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be
MAC Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Rev.S08
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC Module 8. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Learning Objectives. - Exponential Functions - Logarithmic Functions
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
GUIDED NOTES 2.5 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 5 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve quadratic equations by factoring. Solve quadratic equations by the square root property. Solve quadratic equations
GUIDED NOTES 5 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve quadratic equations by factoring. Solve quadratic equations by the square root property. Solve quadratic equations
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Summer Math Packet for AP Calculus BC
 Class: Date: Summer Math Packet for AP Calculus BC 018-19 1. Find the smallest value in the range of the function f (x) = x + 4x + 40. a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7 e. 8 f. 16 g. 4 h. 40. Find the smallest value
Class: Date: Summer Math Packet for AP Calculus BC 018-19 1. Find the smallest value in the range of the function f (x) = x + 4x + 40. a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7 e. 8 f. 16 g. 4 h. 40. Find the smallest value
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions
 Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
Intermediate Algebra Section 9.3 Logarithmic Functions We have studied inverse functions, learning when they eist and how to find them. If we look at the graph of the eponential function, f ( ) = a, where
We want to determine what the graph of the logarithmic function. y = log a. (x) looks like for values of a such that a > 1
 Section 9 A: Graphs of Increasing Logarithmic Functions We want to determine what the graph of the logarithmic function y = log a looks like for values of a such that a > We will select a value a such
Section 9 A: Graphs of Increasing Logarithmic Functions We want to determine what the graph of the logarithmic function y = log a looks like for values of a such that a > We will select a value a such
f(x) = 2x + 5 3x 1. f 1 (x) = x + 5 3x 2. f(x) = 102x x
 1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
Name: Class: Date: Rationals Multiple Choice Pre-Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: _ Class: _ Date: Rationals Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Solve the equation for g: 3 2g + 1 6g = 3. - 5
Name: _ Class: _ Date: Rationals Multiple Choice Pre-Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Solve the equation for g: 3 2g + 1 6g = 3. - 5
Section 6.1: Composite Functions
 Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Section 6.1: Composite Functions Def: Given two function f and g, the composite function, which we denote by f g and read as f composed with g, is defined by (f g)(x) = f(g(x)). In other words, the function
Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions
 Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
Algebra Honors Unit 6 Rational Functions Name Quest Review Questions Mission 1 Simplify and Multiply Rational Expressions 1) Compare the two functions represented below. Determine which of the following
Section 2.5 Absolute Value Functions
 16 Chapter Section.5 Absolute Value Functions So far in this chapter we have been studying the behavior of linear functions. The Absolute Value Function is a piecewise-defined function made up of two linear
16 Chapter Section.5 Absolute Value Functions So far in this chapter we have been studying the behavior of linear functions. The Absolute Value Function is a piecewise-defined function made up of two linear
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. (b) Find the center and the radius of the circle given above.
 INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
Concept Category 2. Exponential and Log Functions
 Concept Category 2 Exponential and Log Functions Concept Category 2 Check List *Find the inverse and composition of functions *Identify an exponential from a table, graph and equation *Identify the difference
Concept Category 2 Exponential and Log Functions Concept Category 2 Check List *Find the inverse and composition of functions *Identify an exponential from a table, graph and equation *Identify the difference
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Graphing Exponentials 6.0 Topic: Graphing Growth and Decay Functions
 Graphing Exponentials 6.0 Topic: Graphing Growth and Decay Functions Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Graph Exponential Functions) Main Ideas: Mother Function Exponential Assignment: Parent Function: f(x) = b
Graphing Exponentials 6.0 Topic: Graphing Growth and Decay Functions Date: Objectives: SWBAT (Graph Exponential Functions) Main Ideas: Mother Function Exponential Assignment: Parent Function: f(x) = b
11 /2 12 /2 13 /6 14 /14 15 /8 16 /8 17 /25 18 /2 19 /4 20 /8
 MAC 1147 Exam #1a Answer Key Name: Answer Key ID# Summer 2012 HONOR CODE: On my honor, I have neither given nor received any aid on this examination. Signature: Instructions: Do all scratch work on the
MAC 1147 Exam #1a Answer Key Name: Answer Key ID# Summer 2012 HONOR CODE: On my honor, I have neither given nor received any aid on this examination. Signature: Instructions: Do all scratch work on the
Exponential and Log Functions Quiz (non-calculator)
 Exponential and Log Functions Quiz (non-calculator) [46 marks] Let f(x) = log p (x + ) for x >. Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through A(6, 2), has an x-intercept at ( 2, 0) and
Exponential and Log Functions Quiz (non-calculator) [46 marks] Let f(x) = log p (x + ) for x >. Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through A(6, 2), has an x-intercept at ( 2, 0) and
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
Graphs of Increasing Logarithmic Functions
 Section 5 4A: Graphs of Increasing Logarithmic Functions We want to determine what the graph of the logarithmic function y = log a looks like for values of a such that a > We will select a value a such
Section 5 4A: Graphs of Increasing Logarithmic Functions We want to determine what the graph of the logarithmic function y = log a looks like for values of a such that a > We will select a value a such
Name Advanced Math Functions & Statistics. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C.
 1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs
 Section 3. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Look at the graph of f(x) = x Does this graph pass the Horizontal Line Test? es What does this mean? that its inverse is a function Find the inverse of
Section 3. Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Look at the graph of f(x) = x Does this graph pass the Horizontal Line Test? es What does this mean? that its inverse is a function Find the inverse of
Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions
 Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions In Algebra 1 and Algebra 2, you have studied transformations of functions. Today, you will revisit and generalize that knowledge. Goals: The goals
Exploring and Generalizing Transformations of Functions In Algebra 1 and Algebra 2, you have studied transformations of functions. Today, you will revisit and generalize that knowledge. Goals: The goals
Chapter 3. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 Logarithmic Functions 1/23 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 3.2 4, 8, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 39, 42, 54, 56, 62, 68,
Absolute Value Functions
 Absolute Value Functions Absolute Value Functions The Absolute Value Function is a piecewise-defined function made up of two linear functions. In its basic form f ( x) x it is one of our toolkit functions.
Absolute Value Functions Absolute Value Functions The Absolute Value Function is a piecewise-defined function made up of two linear functions. In its basic form f ( x) x it is one of our toolkit functions.
MAC 1147 Exam 2 Review Spring 2018
 Spring 2018 This review, produced by the Broward Teaching Center, contains a collection of questions which are representative of the type you may encounter on the exam. Other resources made available by
Spring 2018 This review, produced by the Broward Teaching Center, contains a collection of questions which are representative of the type you may encounter on the exam. Other resources made available by
4.1 Exponential Functions
 Graduate T.A. Department of Mathematics Dynamical Systems and Chaos San Diego State University April 9, 211 Definitions The functions that involve some combinations of basic arithmetic operations, powers,
Graduate T.A. Department of Mathematics Dynamical Systems and Chaos San Diego State University April 9, 211 Definitions The functions that involve some combinations of basic arithmetic operations, powers,
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS
 7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
Exponential Functions and Graphs - Grade 11 *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m30856 1 Exponential Functions and Graphs - Grade 11 * Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
OpenStax-CNX module: m30856 1 Exponential Functions and Graphs - Grade 11 * Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Heather Williams This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. 3. Pg #17-57 column; column and (need graph paper)
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 6 Notes Packet Name: Period: # Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 1. Worksheet 2. Worksheet 3. Pg 483-484 #17-57 column; 61-73 column and 76-77 (need graph paper) 4. Pg 483-484 #20-60
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 6 Notes Packet Name: Period: # Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 1. Worksheet 2. Worksheet 3. Pg 483-484 #17-57 column; 61-73 column and 76-77 (need graph paper) 4. Pg 483-484 #20-60
4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs)
 1. Understand the meaning of and use logs of base 10 and base a 4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs) We have been looking at exponential functions of the form
1. Understand the meaning of and use logs of base 10 and base a 4A: #1e-l,2-5,6g-l (Base 10 logs) 4B: #1-3last col,4,5,6 last col (Base a logs) We have been looking at exponential functions of the form
MATH-AII Boulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MTH-II oulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:G9SY6 1 If f (x ) = x 3 + x - 8, what is f (-8)? -568 456-456 568 Which of the following functions does NOT have a range
MTH-II oulton Functions Review Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam I:G9SY6 1 If f (x ) = x 3 + x - 8, what is f (-8)? -568 456-456 568 Which of the following functions does NOT have a range
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
8 f(8) = 0 (8,0) 4 f(4) = 4 (4, 4) 2 f(2) = 3 (2, 3) 6 f(6) = 3 (6, 3) Outputs. Inputs
 In the previous set of notes we covered how to transform a graph by stretching or compressing it vertically. In this lesson we will focus on stretching or compressing a graph horizontally, which like the
In the previous set of notes we covered how to transform a graph by stretching or compressing it vertically. In this lesson we will focus on stretching or compressing a graph horizontally, which like the
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts. d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. ( x 1 + x 2 2., y 1 + y 2. (x h) 2 + (y k) 2 = r 2. m = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1
 Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
Week 8 Exponential Functions
 Week 8 Exponential Functions Many images below are excerpts from the multimedia textbook. You can find them there and in your textbook in sections 4.1 and 4.2. With the beginning of the new chapter we
Week 8 Exponential Functions Many images below are excerpts from the multimedia textbook. You can find them there and in your textbook in sections 4.1 and 4.2. With the beginning of the new chapter we
Final Exam Review Problems
 Final Exam Review Problems Name: Date: June 23, 2013 P 1.4. 33. Determine whether the line x = 4 represens y as a function of x. P 1.5. 37. Graph f(x) = 3x 1 x 6. Find the x and y-intercepts and asymptotes
Final Exam Review Problems Name: Date: June 23, 2013 P 1.4. 33. Determine whether the line x = 4 represens y as a function of x. P 1.5. 37. Graph f(x) = 3x 1 x 6. Find the x and y-intercepts and asymptotes
10/22/16. 1 Math HL - Santowski SKILLS REVIEW. Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions. Lesson Objectives. (A) Rational Functions
 Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 15 Graphs of Rational Functions SKILLS REVIEW! Use function composition to prove that the following two funtions are inverses of each other. 2x 3 f(x) = g(x) = 5 2 x 1 1 2 Lesson Objectives! The
Lesson 18: Problem Set Sample Solutions
 Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts. d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2., y 1 + y 2. ( x 1 + x 2 2
 Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
Final Examination 201-NYA-05 May 18, 2018
 . ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
. ( points) Evaluate each of the following limits. 3x x + (a) lim x x 3 8 x + sin(5x) (b) lim x sin(x) (c) lim x π/3 + sec x ( (d) x x + 5x ) (e) lim x 5 x lim x 5 + x 6. (3 points) What value of c makes
Title: Jul 7 8:49 PM (1 of 18)
 Title: Jul 7 8:49 PM (1 of 18) Let's review some of the terms used to describe functions. domain: continuous: bounded: even: the set of values from which the input values, x values, are taken every point
Title: Jul 7 8:49 PM (1 of 18) Let's review some of the terms used to describe functions. domain: continuous: bounded: even: the set of values from which the input values, x values, are taken every point
Rational Functions. Elementary Functions. Algebra with mixed fractions. Algebra with mixed fractions
 Rational Functions A rational function f (x) is a function which is the ratio of two polynomials, that is, Part 2, Polynomials Lecture 26a, Rational Functions f (x) = where and are polynomials Dr Ken W
Rational Functions A rational function f (x) is a function which is the ratio of two polynomials, that is, Part 2, Polynomials Lecture 26a, Rational Functions f (x) = where and are polynomials Dr Ken W
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms
 a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions by division. For 3 example, b (or equivalent) seen. 8 00 ab 6th 5 50 ab Solves for
a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions by division. For 3 example, b (or equivalent) seen. 8 00 ab 6th 5 50 ab Solves for
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms
 Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions
Name: AK-Nummer: Ergänzungsprüfung January 29, 2016
 INSTRUCTIONS: The test has a total of 20 pages including this title page and 9 questions which are marked out of 10 points; ensure that you do not omit a page by mistake. Please write your name and AK-Nummer
INSTRUCTIONS: The test has a total of 20 pages including this title page and 9 questions which are marked out of 10 points; ensure that you do not omit a page by mistake. Please write your name and AK-Nummer
THE LANGUAGE OF FUNCTIONS *
 PRECALCULUS THE LANGUAGE OF FUNCTIONS * In algebra you began a process of learning a basic vocabulary, grammar, and syntax forming the foundation of the language of mathematics. For example, consider the
PRECALCULUS THE LANGUAGE OF FUNCTIONS * In algebra you began a process of learning a basic vocabulary, grammar, and syntax forming the foundation of the language of mathematics. For example, consider the
