Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums
|
|
|
- Jayson Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums Anmol Sakarda Nhat Pham May 20, 2018 Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
2 Outline 1 Abstract 2 Sums and Recurrences 3 Manipulating Sums 4 Multiple Sums 5 Finite and Infinite Calculus 6 Infinite Series Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
3 Abstract In this paper, we explore various methodologies to calculate sums. We begin by looking at simple methods: converting sums into recurrences. We proceed to discuss common manipulations, such as using the repertoire method or perturbation. Finally, we conclude by extrapolating sums to both finite and infinite calculus mainly by building integrals. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
4 Sums and Recurrences The sum is the recurrence S n = n k=0 S 0 = a 0 a k S n 1 + a n for n > 0 Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
5 Sums and Recurrences Continued Therefore, sums can be evaluated in closed form by solving recurrences. Assuming a n equals a constant plus a multiple of n, the recurrence above can be rewritten as R 0 = α R n = R n 1 + β + γn for n > 0 Thus, we can generalize a solution such that: R(n) = A(n)α + B(n)β + C(n)γ Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
6 Manipulating Sums Distributive Property ca k = c k K k K a k Associative Property k K(a k + b k ) = k K a k + k K b k Commutative Property (a k ) = k K p(k) K a p(k) Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
7 Manipulating Sums Continued Iverson Convention From any logical statements made in middle of a formula, the values 0 or 1 can be obtained. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
8 Multiple Sums Continued Example The following example demonstrates an important rule for combining different sets of indices. If K and K are any sets of integers, then a k + a k = a k + a k k K k K k K K k K K This is derived from the general formulas a k = a k [k K] k K k and [k K] + [k K ] = [k K K ] + [k K K ] We use this method to either combine 2 almost disjoint index sets or to split off a single term from a set. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
9 Manipulating Sums Continued Perturbation Start with an unknown sum and call it S n + a n+1 = a k = a k n+1 1 k n+1 = a k+1 n+1 = a k n a k+1 a k+1 This expression can then be simply expressed in terms of S n a k Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
10 Manipulation Sums Perturbation Example We then have S n = k2 k 0 k n S n + (n + 1)2 n+1 = (k + 1)2 (k+1) 0 k n Using the associative property gives k2 (k+1) + 0 k n 0 k n 2 (k+1) Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
11 Manipulation Sums Perturbation Example The first sum is simply 2S n The second sum is just a geometric progression that yields 2 n+2 2 Therefore, the total sum becomes (n 1)2 n Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
12 Multiple Sums Multiple Sums The terms of a sum might be specified by two or more indices. General Distributive Law j J,k K a j b k = ( j J a j ) + ( k K b k ) Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
13 Multiple Sums Continued Example Evaluate Replace k with k + j S n = = Summing on j, which is trivial, gives = 1 k n 1 j<k n 1 j<k+j n 1 k j 1 k 1 j n k 1 k = 1 k n n k k Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
14 Multiple Sums Continued Example Then, by the associative law, we have 1 k n n k 1 k n 1 = n( 1 k n 1 k ) n This has the harmonic mean, and is a final answer for the original sum. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
15 Finite Calculus Difference Operator, Definite Sum, and Shift f (x) = f (x + 1) f (x) b g(x)δx = g(k) a a k<b Ef (x) = f (x + 1) Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
16 Finite Calculus Properties Multiplicative Rule: fg = f g + Eg f Integration analogue b g(x)δx = a a g(x)δx b b g(x)δx + a c g(x)δx = b c g(x)δx a Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
17 Finite Calculus Properties (cont.) Fundamental Theorem of (Finite) Calculus: g(x) = f (x) b g(x) = f (b) f (a) a Chain Rule: u v = uv Ev u Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
18 Finite Calculus Analogues: Rising and Falling Powers Definition Rising and Falling Powers m > 0 : x m = x(x 1)(x 2)...(x m + 1) m > 0 : x m = x(x + 1)(x + 2)...(x + m 1) x 0 = x 0 = 1 m > 0 : x m 1 = (x + 1)(x + 2)...(x + m) m > 0 : x m = 1 (x 1)(x 2)...(x m) Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
19 Finite Calculus Analogues: Rising and Falling Powers Properties of Rising and Falling Powers x m = mx m 1 k m = nm+1 m k<n a k<b c k = cb c a c 1 Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
20 Infinite Series Definition Infinite Series: Suppose a k 0 k K. If there is a number A such that for any finite F K: a k A k F Then k K a k exists and is equal to the least such A. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
21 Infinite Series Generalization for any (multi-dimensional) index set K and any sequence a k : A = a k = a + k a k k K k K k K where: a + k = a k.[a k > 0] a k = a k.[a k < 0] Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
22 Infinite Series We have the following scenarios: A + and A are finite: A converges absolutely to A + + A. A + is infinite, A is finite: A diverges to. A is infinite, A + is finite: then A diverges to. A + and A are infinite: A is undefined. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
23 Infinite Series Fundamental Principle of Multiple Sums Absolutely convergent sums over 2 or more indices can always be summed first with respect to any one of those indices. Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
24 Infinite Series Formally, if J and the elements of {K j j J} are sets of indices such that: a j,k converges absolutely to A j J,k K j Then there exists A j for each j J such that a j,k converges absolutely to A j k K j A j converges absolutely to A j J Anmol Sakarda, Nhat Pham Concrete Mathematics: Exploring Sums May 20, / 24
Sums. ITT9131 Konkreetne Matemaatika
 Sums ITT9131 Konkreetne Matemaatika Chapter Two Notation Sums and Recurrences Manipulation of Sums Multiple Sums General Methods Finite and Innite Calculus Innite Sums Contents 1 Sequences 2 Notations
Sums ITT9131 Konkreetne Matemaatika Chapter Two Notation Sums and Recurrences Manipulation of Sums Multiple Sums General Methods Finite and Innite Calculus Innite Sums Contents 1 Sequences 2 Notations
cse547, math547 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse547, math547 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 9a CHAPTER 2 SUMS Part 1: Introduction - Lecture 5 Part 2: Sums and Recurrences (1) - Lecture 5 Part 2: Sums and Recurrences (2)
cse547, math547 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 9a CHAPTER 2 SUMS Part 1: Introduction - Lecture 5 Part 2: Sums and Recurrences (1) - Lecture 5 Part 2: Sums and Recurrences (2)
Finding the sum of a finite Geometric Series. The sum of the first 5 powers of 2 The sum of the first 5 powers of 3
 Section 1 3B: Series A series is the sum of a given number of terms in a sequence. For every sequence a 1, a, a 3, a 4, a 5, a 6, a 7,..., a n of real numbers there is a series that is defined as the sum
Section 1 3B: Series A series is the sum of a given number of terms in a sequence. For every sequence a 1, a, a 3, a 4, a 5, a 6, a 7,..., a n of real numbers there is a series that is defined as the sum
Sequences and Summations
 COMP 182 Algorithmic Thinking Sequences and Summations Luay Nakhleh Computer Science Rice University Chapter 2, Section 4 Reading Material Sequences A sequence is a function from a subset of the set of
COMP 182 Algorithmic Thinking Sequences and Summations Luay Nakhleh Computer Science Rice University Chapter 2, Section 4 Reading Material Sequences A sequence is a function from a subset of the set of
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2924: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2924: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan 8. Sequences We start this section by introducing the concept of a sequence and study its convergence. Convergence of Sequences. An infinite
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2924: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan 8. Sequences We start this section by introducing the concept of a sequence and study its convergence. Convergence of Sequences. An infinite
Testing Series with Mixed Terms
 Testing Series with Mixed Terms Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Series with Mixed Terms Today 1 / 17 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Absolute v.s. Conditional Convergence 3 Alternating Series
Testing Series with Mixed Terms Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Series with Mixed Terms Today 1 / 17 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Absolute v.s. Conditional Convergence 3 Alternating Series
Derivatives in 2D. Outline. James K. Peterson. November 9, Derivatives in 2D! Chain Rule
 Derivatives in 2D James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Derivatives in 2D! Chain Rule Let s go back to
Derivatives in 2D James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 9, 2016 Outline Derivatives in 2D! Chain Rule Let s go back to
Evaluating ζ(2m) via Telescoping Sums.
 /25 Evaluating ζ(2m) via Telescoping Sums. Brian Sittinger CSU Channel Islands February 205 2/25 Outline 2 3 4 5 3/25 Basel Problem Find the exact value of n= n 2 = 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 +. 3/25 Basel Problem
/25 Evaluating ζ(2m) via Telescoping Sums. Brian Sittinger CSU Channel Islands February 205 2/25 Outline 2 3 4 5 3/25 Basel Problem Find the exact value of n= n 2 = 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 +. 3/25 Basel Problem
1 Examples of Weak Induction
 More About Mathematical Induction Mathematical induction is designed for proving that a statement holds for all nonnegative integers (or integers beyond an initial one). Here are some extra examples of
More About Mathematical Induction Mathematical induction is designed for proving that a statement holds for all nonnegative integers (or integers beyond an initial one). Here are some extra examples of
Cse547. Chapter 1 Problem 16 GENERALIZATION
 Cse547 Chapter 1 Problem 16 GENERALIZATION Use the Repertoire method to solve the general fiveparameter recurrence: g(1) = α g(2n+ j) = 3g(n) + Ɛn 2 + γn + β j, for j = 0, 1 and n 1 and n є N Convert recursive
Cse547 Chapter 1 Problem 16 GENERALIZATION Use the Repertoire method to solve the general fiveparameter recurrence: g(1) = α g(2n+ j) = 3g(n) + Ɛn 2 + γn + β j, for j = 0, 1 and n 1 and n є N Convert recursive
Math 141: Lecture 19
 Math 141: Lecture 19 Convergence of infinite series Bob Hough November 16, 2016 Bob Hough Math 141: Lecture 19 November 16, 2016 1 / 44 Series of positive terms Recall that, given a sequence {a n } n=1,
Math 141: Lecture 19 Convergence of infinite series Bob Hough November 16, 2016 Bob Hough Math 141: Lecture 19 November 16, 2016 1 / 44 Series of positive terms Recall that, given a sequence {a n } n=1,
2. Associative Law: A binary operator * on a set S is said to be associated whenever (A*B)*C = A*(B*C) for all A,B,C S.
 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 2.1 Introduction Binary logic deals with variables that have two discrete values: 1 for TRUE and 0 for FALSE. A simple switching circuit containing active elements such as a diode and transistor
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 2.1 Introduction Binary logic deals with variables that have two discrete values: 1 for TRUE and 0 for FALSE. A simple switching circuit containing active elements such as a diode and transistor
Testing Series With Mixed Terms
 Testing Series With Mixed Terms Philippe B. Laval Series with Mixed Terms 1. Introduction 2. Absolute v.s. Conditional Convergence 3. Alternating Series 4. The Ratio and Root Tests 5. Conclusion 1 Introduction
Testing Series With Mixed Terms Philippe B. Laval Series with Mixed Terms 1. Introduction 2. Absolute v.s. Conditional Convergence 3. Alternating Series 4. The Ratio and Root Tests 5. Conclusion 1 Introduction
Mathematical Induction
 Chapter 6 Mathematical Induction 6.1 The Process of Mathematical Induction 6.1.1 Motivating Mathematical Induction Consider the sum of the first several odd integers. produce the following: 1 = 1 1 + 3
Chapter 6 Mathematical Induction 6.1 The Process of Mathematical Induction 6.1.1 Motivating Mathematical Induction Consider the sum of the first several odd integers. produce the following: 1 = 1 1 + 3
3.3 Accumulation Sequences
 3.3. ACCUMULATION SEQUENCES 25 3.3 Accumulation Sequences Overview. One of the most important mathematical ideas in calculus is that of an accumulation of change for physical quantities. As we have been
3.3. ACCUMULATION SEQUENCES 25 3.3 Accumulation Sequences Overview. One of the most important mathematical ideas in calculus is that of an accumulation of change for physical quantities. As we have been
Generating Functions
 Semester 1, 2004 Generating functions Another means of organising enumeration. Two examples we have seen already. Example 1. Binomial coefficients. Let X = {1, 2,..., n} c k = # k-element subsets of X
Semester 1, 2004 Generating functions Another means of organising enumeration. Two examples we have seen already. Example 1. Binomial coefficients. Let X = {1, 2,..., n} c k = # k-element subsets of X
Math 456: Mathematical Modeling. Tuesday, March 6th, 2018
 Math 456: Mathematical Modeling Tuesday, March 6th, 2018 Markov Chains: Exit distributions and the Strong Markov Property Tuesday, March 6th, 2018 Last time 1. Weighted graphs. 2. Existence of stationary
Math 456: Mathematical Modeling Tuesday, March 6th, 2018 Markov Chains: Exit distributions and the Strong Markov Property Tuesday, March 6th, 2018 Last time 1. Weighted graphs. 2. Existence of stationary
Series. 1 Convergence and Divergence of Series. S. F. Ellermeyer. October 23, 2003
 Series S. F. Ellermeyer October 23, 2003 Convergence and Divergence of Series An infinite series (also simply called a series) is a sum of infinitely many terms a k = a + a 2 + a 3 + () The sequence a
Series S. F. Ellermeyer October 23, 2003 Convergence and Divergence of Series An infinite series (also simply called a series) is a sum of infinitely many terms a k = a + a 2 + a 3 + () The sequence a
Introduction to Series and Sequences Math 121 Calculus II Spring 2015
 Introduction to Series and Sequences Math Calculus II Spring 05 The goal. The main purpose of our study of series and sequences is to understand power series. A power series is like a polynomial of infinite
Introduction to Series and Sequences Math Calculus II Spring 05 The goal. The main purpose of our study of series and sequences is to understand power series. A power series is like a polynomial of infinite
(x 3)(x + 5) = (x 3)(x 1) = x + 5. sin 2 x e ax bx 1 = 1 2. lim
 SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
SMT Calculus Test Solutions February, x + x 5 Compute x x x + Answer: Solution: Note that x + x 5 x x + x )x + 5) = x )x ) = x + 5 x x + 5 Then x x = + 5 = Compute all real values of b such that, for fx)
INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES In section 11.9, we were able to find power series representations for a certain restricted class of functions. INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
11 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES In section 11.9, we were able to find power series representations for a certain restricted class of functions. INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
CHAPTER 2 INFINITE SUMS (SERIES) Lecture Notes PART 1
 CHAPTER 2 INFINITE SUMS (SERIES) Lecture Notes PART We extend now the notion of a finite sum Σ n k= a k to an INFINITE SUM which we write as Σ n= a n as follows. For a given a sequence {a n } n N {0},
CHAPTER 2 INFINITE SUMS (SERIES) Lecture Notes PART We extend now the notion of a finite sum Σ n k= a k to an INFINITE SUM which we write as Σ n= a n as follows. For a given a sequence {a n } n N {0},
SECTION 9.2: ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES and PARTIAL SUMS
 (Chapter 9: Discrete Math) 9.11 SECTION 9.2: ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES and PARTIAL SUMS PART A: WHAT IS AN ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE? The following appears to be an example of an arithmetic (stress on the me ) sequence:
(Chapter 9: Discrete Math) 9.11 SECTION 9.2: ARITHMETIC SEQUENCES and PARTIAL SUMS PART A: WHAT IS AN ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE? The following appears to be an example of an arithmetic (stress on the me ) sequence:
Infinite Series. MATH 211, Calculus II. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 Infinite Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Background Consider the repeating decimal form of 2/3. 2 3 = 0.666666 = 0.6 + 0.06 + 0.006 + 0.0006 + = 6(0.1)
Infinite Series MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Background Consider the repeating decimal form of 2/3. 2 3 = 0.666666 = 0.6 + 0.06 + 0.006 + 0.0006 + = 6(0.1)
 = (, ) V λ (1) λ λ ( + + ) P = [ ( ), (1)] ( ) ( ) = ( ) ( ) ( 0 ) ( 0 ) = ( 0 ) ( 0 ) 0 ( 0 ) ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) = ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) = ( + ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) P V V V V V P V P V V V
= (, ) V λ (1) λ λ ( + + ) P = [ ( ), (1)] ( ) ( ) = ( ) ( ) ( 0 ) ( 0 ) = ( 0 ) ( 0 ) 0 ( 0 ) ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) = ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) = ( + ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) P V V V V V P V P V V V
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 4332 BLECHER NOTES
 INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 4332 BLECHER NOTES You will be expected to reread and digest these typed notes after class, line by line, trying to follow why the line is true, for example how it
INTRODUCTION TO REAL ANALYSIS II MATH 4332 BLECHER NOTES You will be expected to reread and digest these typed notes after class, line by line, trying to follow why the line is true, for example how it
Positive Series: Integral Test & p-series
 Positive Series: Integral Test & p-series Calculus II Josh Engwer TTU 3 March 204 Josh Engwer (TTU) Positive Series: Integral Test & p-series 3 March 204 / 8 Bad News about Summing a (Convergent) Series...
Positive Series: Integral Test & p-series Calculus II Josh Engwer TTU 3 March 204 Josh Engwer (TTU) Positive Series: Integral Test & p-series 3 March 204 / 8 Bad News about Summing a (Convergent) Series...
Ron Paul Curriculum 9th Grade Mathematics Problem Set #2
 Problem Set # Find the value of each expression below, and then name the sets of numbers to which each value belongs:.. + 6.8. 7. 8 (.6). 8+ 5 5. 9/ Name the property illustrated by each equation: 6. z
Problem Set # Find the value of each expression below, and then name the sets of numbers to which each value belongs:.. + 6.8. 7. 8 (.6). 8+ 5 5. 9/ Name the property illustrated by each equation: 6. z
From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form
 MATH 3333 INTERMEDIATE ANALYSIS BLECHER NOTES 75 8. Infinite series of numbers From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form = a m + a m+ + a m+2 + ( ) Let us call this expression (*).
MATH 3333 INTERMEDIATE ANALYSIS BLECHER NOTES 75 8. Infinite series of numbers From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form = a m + a m+ + a m+2 + ( ) Let us call this expression (*).
Math Homework 5 Solutions
 Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Some Fun with Divergent Series
 Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
Some Fun with Divergent Series 1. Preliminary Results We begin by examining the (divergent) infinite series S 1 = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + = k=1 k S 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 + 5 2 + 6 2 + = k=1 k 2 (i)
From Fibonacci Numbers to Central Limit Type Theorems
 From Fibonacci Numbers to Central Limit Type Theorems Murat Koloğlu, Gene Kopp, Steven J. Miller and Yinghui Wang Williams College, October 1st, 010 Introduction Previous Results Fibonacci Numbers: F n+1
From Fibonacci Numbers to Central Limit Type Theorems Murat Koloğlu, Gene Kopp, Steven J. Miller and Yinghui Wang Williams College, October 1st, 010 Introduction Previous Results Fibonacci Numbers: F n+1
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
(Infinite) Series Series a n = a 1 + a 2 + a a n +...
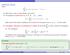 (Infinite) Series Series a n = a 1 + a 2 + a 3 +... + a n +... What does it mean to add infinitely many terms? The sequence of partial sums S 1, S 2, S 3, S 4,...,S n,...,where nx S n = a i = a 1 + a 2
(Infinite) Series Series a n = a 1 + a 2 + a 3 +... + a n +... What does it mean to add infinitely many terms? The sequence of partial sums S 1, S 2, S 3, S 4,...,S n,...,where nx S n = a i = a 1 + a 2
EECS 1028 M: Discrete Mathematics for Engineers
 EECS 1028 M: Discrete Mathematics for Engineers Suprakash Datta Office: LAS 3043 Course page: http://www.eecs.yorku.ca/course/1028 Also on Moodle S. Datta (York Univ.) EECS 1028 W 18 1 / 16 Sequences and
EECS 1028 M: Discrete Mathematics for Engineers Suprakash Datta Office: LAS 3043 Course page: http://www.eecs.yorku.ca/course/1028 Also on Moodle S. Datta (York Univ.) EECS 1028 W 18 1 / 16 Sequences and
9.2 Geometric Series
 9.2 Geometric Series series: add the terms in a sequence geometric series ratio between any two consecutive terms is constant: n 1 ax i = a + ax + ax 2 +... + ax n 1 sum of the first n terms? 9.2 Geometric
9.2 Geometric Series series: add the terms in a sequence geometric series ratio between any two consecutive terms is constant: n 1 ax i = a + ax + ax 2 +... + ax n 1 sum of the first n terms? 9.2 Geometric
7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius
 284 CHAPTER 7. POWER SERIES METHODS 7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius Note: or.5 lectures, 8.4 and 8.5 in [EP], 5.4 5.7 in [BD] While behaviour of ODEs at singular points is more complicated,
284 CHAPTER 7. POWER SERIES METHODS 7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius Note: or.5 lectures, 8.4 and 8.5 in [EP], 5.4 5.7 in [BD] While behaviour of ODEs at singular points is more complicated,
Math 0230 Calculus 2 Lectures
 Math 00 Calculus Lectures Chapter 8 Series Numeration of sections corresponds to the text James Stewart, Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, Second edition. Section 8. Sequences A sequence is a
Math 00 Calculus Lectures Chapter 8 Series Numeration of sections corresponds to the text James Stewart, Essential Calculus, Early Transcendentals, Second edition. Section 8. Sequences A sequence is a
ELECTRICAL NETWORK THEORY AND RECURRENCE IN DISCRETE RANDOM WALKS
 ELECTRICAL NETWORK THEORY AND RECURRENCE IN DISCRETE RANDOM WALKS DANIEL STRAUS Abstract This paper investigates recurrence in one dimensional random walks After proving recurrence, an alternate approach
ELECTRICAL NETWORK THEORY AND RECURRENCE IN DISCRETE RANDOM WALKS DANIEL STRAUS Abstract This paper investigates recurrence in one dimensional random walks After proving recurrence, an alternate approach
SERIES REVIEW SHEET, SECTIONS 11.1 TO 11.5 OF OZ
 SERIES REVIEW SHEET, SECTIONS 11.1 TO 11.5 OF OZ Fill in the blanks and give the indicated examples, including reasons. Don t simply fill in the blanks and give the examples. Take this opportunity to really
SERIES REVIEW SHEET, SECTIONS 11.1 TO 11.5 OF OZ Fill in the blanks and give the indicated examples, including reasons. Don t simply fill in the blanks and give the examples. Take this opportunity to really
Definitions, Theorems and Exercises. Abstract Algebra Math 332. Ethan D. Bloch
 Definitions, Theorems and Exercises Abstract Algebra Math 332 Ethan D. Bloch December 26, 2013 ii Contents 1 Binary Operations 3 1.1 Binary Operations............................... 4 1.2 Isomorphic Binary
Definitions, Theorems and Exercises Abstract Algebra Math 332 Ethan D. Bloch December 26, 2013 ii Contents 1 Binary Operations 3 1.1 Binary Operations............................... 4 1.2 Isomorphic Binary
Notes on uniform convergence
 Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
Notes on uniform convergence Erik Wahlén erik.wahlen@math.lu.se January 17, 2012 1 Numerical sequences We begin by recalling some properties of numerical sequences. By a numerical sequence we simply mean
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL
 PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ALG EBRA 2 HONORS Course Overview and Essential Skills This course is an in-depth study of the language, concepts, and techniques of Algebra that will prepare
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ALG EBRA 2 HONORS Course Overview and Essential Skills This course is an in-depth study of the language, concepts, and techniques of Algebra that will prepare
1 Mathematical Preliminaries
 Mathematical Preliminaries We shall go through in this first chapter all of the mathematics needed for reading the rest of this book. The reader is expected to have taken a one year course in differential
Mathematical Preliminaries We shall go through in this first chapter all of the mathematics needed for reading the rest of this book. The reader is expected to have taken a one year course in differential
The infinite series is written using sigma notation as: lim u k. lim. better yet, we can say if the
 Divergence and Integral Test With the previous content, we used the idea of forming a closed form for the n th partial sum and taking its limit to determine the SUM of the series (if it exists). *** It
Divergence and Integral Test With the previous content, we used the idea of forming a closed form for the n th partial sum and taking its limit to determine the SUM of the series (if it exists). *** It
Worksheet 1. Difference
 Worksheet Differences Remember: The difference of a sequence u n is: u n u n+ u n The falling factorial (power), n to the k falling, when k > 0, is: n k n(n )... (n k + ), Please complete the following
Worksheet Differences Remember: The difference of a sequence u n is: u n u n+ u n The falling factorial (power), n to the k falling, when k > 0, is: n k n(n )... (n k + ), Please complete the following
Stat 426 : Homework 1.
 Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
D(f/g)(P ) = D(f)(P )g(p ) f(p )D(g)(P ). g 2 (P )
 We first record a very useful: 11. Higher derivatives Theorem 11.1. Let A R n be an open subset. Let f : A R m and g : A R m be two functions and suppose that P A. Let λ A be a scalar. If f and g are differentiable
We first record a very useful: 11. Higher derivatives Theorem 11.1. Let A R n be an open subset. Let f : A R m and g : A R m be two functions and suppose that P A. Let λ A be a scalar. If f and g are differentiable
15. Polynomial rings Definition-Lemma Let R be a ring and let x be an indeterminate.
 15. Polynomial rings Definition-Lemma 15.1. Let R be a ring and let x be an indeterminate. The polynomial ring R[x] is defined to be the set of all formal sums a n x n + a n 1 x n +... a 1 x + a 0 = a
15. Polynomial rings Definition-Lemma 15.1. Let R be a ring and let x be an indeterminate. The polynomial ring R[x] is defined to be the set of all formal sums a n x n + a n 1 x n +... a 1 x + a 0 = a
Induction, sequences, limits and continuity
 Induction, sequences, limits and continuity Material covered: eclass notes on induction, Chapter 11, Section 1 and Chapter 2, Sections 2.2-2.5 Induction Principle of mathematical induction: Let P(n) be
Induction, sequences, limits and continuity Material covered: eclass notes on induction, Chapter 11, Section 1 and Chapter 2, Sections 2.2-2.5 Induction Principle of mathematical induction: Let P(n) be
Chapter 11 - Sequences and Series
 Calculus and Analytic Geometry II Chapter - Sequences and Series. Sequences Definition. A sequence is a list of numbers written in a definite order, We call a n the general term of the sequence. {a, a
Calculus and Analytic Geometry II Chapter - Sequences and Series. Sequences Definition. A sequence is a list of numbers written in a definite order, We call a n the general term of the sequence. {a, a
On integral representations of q-gamma and q beta functions
 On integral representations of -gamma and beta functions arxiv:math/3232v [math.qa] 4 Feb 23 Alberto De Sole, Victor G. Kac Department of Mathematics, MIT 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA 239, USA
On integral representations of -gamma and beta functions arxiv:math/3232v [math.qa] 4 Feb 23 Alberto De Sole, Victor G. Kac Department of Mathematics, MIT 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA 239, USA
Statistical Inference
 Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Statistical Inference Lecture 1: Probability Theory MING GAO DASE @ ECNU (for course related communications) mgao@dase.ecnu.edu.cn Sep. 11, 2018 Outline Introduction Set Theory Basics of Probability Theory
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
( f ^ M _ M 0 )dµ (5.1)
 47 5. LEBESGUE INTEGRAL: GENERAL CASE Although the Lebesgue integral defined in the previous chapter is in many ways much better behaved than the Riemann integral, it shares its restriction to bounded
47 5. LEBESGUE INTEGRAL: GENERAL CASE Although the Lebesgue integral defined in the previous chapter is in many ways much better behaved than the Riemann integral, it shares its restriction to bounded
Notes on generating functions in automata theory
 Notes on generating functions in automata theory Benjamin Steinberg December 5, 2009 Contents Introduction: Calculus can count 2 Formal power series 5 3 Rational power series 9 3. Rational power series
Notes on generating functions in automata theory Benjamin Steinberg December 5, 2009 Contents Introduction: Calculus can count 2 Formal power series 5 3 Rational power series 9 3. Rational power series
Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7
 Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions /19/7 Question 1 Write the following as an integer: log 4 (9)+log (5) We have: log 4 (9)+log (5) = ( log 4 (9)) ( log (5)) = 5 ( log
Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions /19/7 Question 1 Write the following as an integer: log 4 (9)+log (5) We have: log 4 (9)+log (5) = ( log 4 (9)) ( log (5)) = 5 ( log
Analysis I. Classroom Notes. H.-D. Alber
 Analysis I Classroom Notes H-D Alber Contents 1 Fundamental notions 1 11 Sets 1 12 Product sets, relations 5 13 Composition of statements 7 14 Quantifiers, negation of statements 9 2 Real numbers 11 21
Analysis I Classroom Notes H-D Alber Contents 1 Fundamental notions 1 11 Sets 1 12 Product sets, relations 5 13 Composition of statements 7 14 Quantifiers, negation of statements 9 2 Real numbers 11 21
Infinite Series - Section Can you add up an infinite number of values and get a finite sum? Yes! Here is a familiar example:
 Infinite Series - Section 10.2 Can you add up an infinite number of values and get a finite sum? Yes! Here is a familiar example: 1 3 0. 3 0. 3 0. 03 0. 003 0. 0003 Ifa n is an infinite sequence, then
Infinite Series - Section 10.2 Can you add up an infinite number of values and get a finite sum? Yes! Here is a familiar example: 1 3 0. 3 0. 3 0. 03 0. 003 0. 0003 Ifa n is an infinite sequence, then
As f and g are differentiable functions such that. f (x) = 20e 2x, g (x) = 4e 2x + 4xe 2x,
 srinivasan (rs7) Sample Midterm srinivasan (690) This print-out should have 0 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Determine if
srinivasan (rs7) Sample Midterm srinivasan (690) This print-out should have 0 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Determine if
Chapter 3. Rings. The basic commutative rings in mathematics are the integers Z, the. Examples
 Chapter 3 Rings Rings are additive abelian groups with a second operation called multiplication. The connection between the two operations is provided by the distributive law. Assuming the results of Chapter
Chapter 3 Rings Rings are additive abelian groups with a second operation called multiplication. The connection between the two operations is provided by the distributive law. Assuming the results of Chapter
What is a Linear Space/Vector Space?
 What is a Linear Space/Vector Space? The terms linear space and vector space mean the same thing and can be used interchangeably. I have used the term linear space in the discussion below because I prefer
What is a Linear Space/Vector Space? The terms linear space and vector space mean the same thing and can be used interchangeably. I have used the term linear space in the discussion below because I prefer
Sets, Proofs and Functions. Anton Velinov
 Sets, Proofs and Functions Anton Velinov DIW WS 2018 Takeaways Sets and set operations. De Morgan s laws. Logical quantifiers and operators. Implication. Methods of proof, deduction, induction, contradiction.
Sets, Proofs and Functions Anton Velinov DIW WS 2018 Takeaways Sets and set operations. De Morgan s laws. Logical quantifiers and operators. Implication. Methods of proof, deduction, induction, contradiction.
Mathematical Induction Assignments
 1 Mathematical Induction Assignments Prove the Following using Principle of Mathematical induction 1) Prove that for any positive integer number n, n 3 + 2 n is divisible by 3 2) Prove that 1 3 + 2 3 +
1 Mathematical Induction Assignments Prove the Following using Principle of Mathematical induction 1) Prove that for any positive integer number n, n 3 + 2 n is divisible by 3 2) Prove that 1 3 + 2 3 +
MATH 118, LECTURES 27 & 28: TAYLOR SERIES
 MATH 8, LECTURES 7 & 8: TAYLOR SERIES Taylor Series Suppose we know that the power series a n (x c) n converges on some interval c R < x < c + R to the function f(x). That is to say, we have f(x) = a 0
MATH 8, LECTURES 7 & 8: TAYLOR SERIES Taylor Series Suppose we know that the power series a n (x c) n converges on some interval c R < x < c + R to the function f(x). That is to say, we have f(x) = a 0
A Local-Global Principle for Diophantine Equations
 A Local-Global Principle for Diophantine Equations (Extended Abstract) Richard J. Lipton and Nisheeth Vishnoi {rjl,nkv}@cc.gatech.edu Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332, USA. Abstract.
A Local-Global Principle for Diophantine Equations (Extended Abstract) Richard J. Lipton and Nisheeth Vishnoi {rjl,nkv}@cc.gatech.edu Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA 30332, USA. Abstract.
Cookie Monster Meets the Fibonacci Numbers. Mmmmmm Theorems!
 Cookie Monster Meets the Fibonacci Numbers. Mmmmmm Theorems! Olivial Beckwith, Murat Koloğlu, Gene Kopp, Steven J. Miller and Yinghui Wang http://www.williams.edu/mathematics/sjmiller/public html Colby
Cookie Monster Meets the Fibonacci Numbers. Mmmmmm Theorems! Olivial Beckwith, Murat Koloğlu, Gene Kopp, Steven J. Miller and Yinghui Wang http://www.williams.edu/mathematics/sjmiller/public html Colby
17 Advancement Operator Equations
 November 14, 2017 17 Advancement Operator Equations William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Review of Recurrence Equations (1) Problem Let r(n) denote the number of regions determined by n lines that
November 14, 2017 17 Advancement Operator Equations William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Review of Recurrence Equations (1) Problem Let r(n) denote the number of regions determined by n lines that
Mathematical Induction
 Mathematical Induction MAT30 Discrete Mathematics Fall 018 MAT30 (Discrete Math) Mathematical Induction Fall 018 1 / 19 Outline 1 Mathematical Induction Strong Mathematical Induction MAT30 (Discrete Math)
Mathematical Induction MAT30 Discrete Mathematics Fall 018 MAT30 (Discrete Math) Mathematical Induction Fall 018 1 / 19 Outline 1 Mathematical Induction Strong Mathematical Induction MAT30 (Discrete Math)
On model theory, non-commutative geometry and physics. B. Zilber. University of Oxford. zilber/
 On model theory, non-commutative geometry and physics B. Zilber University of Oxford http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/ zilber/ 1 Plan I. Generalities on physics, logical hierarchy of structures and Zariski geometries.
On model theory, non-commutative geometry and physics B. Zilber University of Oxford http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/ zilber/ 1 Plan I. Generalities on physics, logical hierarchy of structures and Zariski geometries.
Mathematics 132 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Exam 3 Review Sheet April 15, 2008
 Mathematics 32 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Eam 3 Review Sheet April 5, 2008 Sample Eam Questions - Solutions This list is much longer than the actual eam will be (to give you some idea of
Mathematics 32 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Eam 3 Review Sheet April 5, 2008 Sample Eam Questions - Solutions This list is much longer than the actual eam will be (to give you some idea of
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS
 MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
MULTI-RESTRAINED STIRLING NUMBERS JI YOUNG CHOI DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS SHIPPENSBURG UNIVERSITY SHIPPENSBURG, PA 17257, U.S.A. Abstract. Given positive integers n, k, and m, the (n, k)-th m- restrained
Vector Spaces and Subspaces
 Vector Spaces and Subspaces Our investigation of solutions to systems of linear equations has illustrated the importance of the concept of a vector in a Euclidean space. We take time now to explore the
Vector Spaces and Subspaces Our investigation of solutions to systems of linear equations has illustrated the importance of the concept of a vector in a Euclidean space. We take time now to explore the
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test
 Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 5, 2018 Outline 1 Geometric Series
Geometric Series and the Ratio and Root Test James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 5, 2018 Outline 1 Geometric Series
( ε > 0) ( N N) ( n N) : n > N a n A < ε.
 CHAPTER 1. LIMITS OF SEQUENCES 1.1. An Ad-hoc Definition. In mathematical analysis, the concept of limits is of paramount importance, in view of the fact that many basic objects of study such as derivatives,
CHAPTER 1. LIMITS OF SEQUENCES 1.1. An Ad-hoc Definition. In mathematical analysis, the concept of limits is of paramount importance, in view of the fact that many basic objects of study such as derivatives,
Diagnostic quiz for M337 Complex analysis
 Diagnostic quiz for M337 Complex analysis The aim of this diagnostic quiz is to help you assess how well prepared you are for M337, and to identify topics that you should revise or study before beginning
Diagnostic quiz for M337 Complex analysis The aim of this diagnostic quiz is to help you assess how well prepared you are for M337, and to identify topics that you should revise or study before beginning
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
Core Mathematics 3 Differentiation
 http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
http://kumarmaths.weebly.com/ Core Mathematics Differentiation C differentiation Page Differentiation C Specifications. By the end of this unit you should be able to : Use chain rule to find the derivative
Generating Functions and the Fibonacci Sequence
 Department of Mathematics Nebraska Wesleyan University June 14, 01 Fibonacci Sequence Fun Fact: November 3rd is Fibonacci Day! (1, 1,, 3) Definition The Fibonacci sequence is defined by the recurrence
Department of Mathematics Nebraska Wesleyan University June 14, 01 Fibonacci Sequence Fun Fact: November 3rd is Fibonacci Day! (1, 1,, 3) Definition The Fibonacci sequence is defined by the recurrence
Series. richard/math230 These notes are taken from Calculus Vol I, by Tom M. Apostol,
 Series Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math230 These notes are taken from Calculus Vol I, by Tom
Series Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math230 These notes are taken from Calculus Vol I, by Tom
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes
 Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
 REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
REVIEW OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS DONU ARAPURA 1. Limits and continuity To simplify the statements, we will often stick to two variables, but everything holds with any number of variables. Let f(x, y) be
Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5).
 Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5). Equations with regular-singular points. s: Equations with regular-singular points. Method to find solutions. : Method to find solutions. Recall: The
Equations with regular-singular points (Sect. 5.5). Equations with regular-singular points. s: Equations with regular-singular points. Method to find solutions. : Method to find solutions. Recall: The
Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications
 Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications James B Silva Abstract The Bernoulli numbers are a set of numbers that were discovered by Jacob Bernoulli (654-75). This set of numbers holds a deep relationship
Bernoulli Numbers and their Applications James B Silva Abstract The Bernoulli numbers are a set of numbers that were discovered by Jacob Bernoulli (654-75). This set of numbers holds a deep relationship
Introduction to Proofs
 Introduction to Proofs Notes by Dr. Lynne H. Walling and Dr. Steffi Zegowitz September 018 The Introduction to Proofs course is organised into the following nine sections. 1. Introduction: sets and functions
Introduction to Proofs Notes by Dr. Lynne H. Walling and Dr. Steffi Zegowitz September 018 The Introduction to Proofs course is organised into the following nine sections. 1. Introduction: sets and functions
Contradiction MATH Contradiction. Benjamin V.C. Collins, James A. Swenson MATH 2730
 MATH 2730 Contradiction Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson Contrapositive The contrapositive of the statement If A, then B is the statement If not B, then not A. A statement and its contrapositive
MATH 2730 Contradiction Benjamin V.C. Collins James A. Swenson Contrapositive The contrapositive of the statement If A, then B is the statement If not B, then not A. A statement and its contrapositive
WILLIAM LOWELL PUTNAM MATHEMATICAL COMPETITION. (3k(k + 1) + 1), for n 1.
 Problem A1. Find the sum n (3k(k + 1) + 1), for n 1. k=0 The simplest way to solve this problem is to use the fact that the terms of the sum are differences of consecutive cubes: 3k(k + 1) + 1 = 3k 2 +
Problem A1. Find the sum n (3k(k + 1) + 1), for n 1. k=0 The simplest way to solve this problem is to use the fact that the terms of the sum are differences of consecutive cubes: 3k(k + 1) + 1 = 3k 2 +
11.4 The Comparison Tests. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 11.4 The Comparison Tests Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Comparison Tests In the comparison tests the idea is to compare a given series with a series that is known to be convergent
11.4 The Comparison Tests Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Comparison Tests In the comparison tests the idea is to compare a given series with a series that is known to be convergent
Correlation with College Board Advanced Placement Course Descriptions
 Correlation with College Board Advanced Placement Course Descriptions The following tables show which sections of Calculus: Concepts and Applications cover each of the topics listed in the 2004 2005 Course
Correlation with College Board Advanced Placement Course Descriptions The following tables show which sections of Calculus: Concepts and Applications cover each of the topics listed in the 2004 2005 Course
ON THE KERNELS OF THE PRO-l OUTER GALOIS REPRESENTATIONS ASSOCIATED TO HYPERBOLIC CURVES OVER NUMBER FIELDS
 Hoshi, Y. Osaka J. Math. 52 (205), 647 675 ON THE KERNELS OF THE PRO-l OUTER GALOIS REPRESENTATIONS ASSOCIATED TO HYPERBOLIC CURVES OVER NUMBER FIELDS YUICHIRO HOSHI (Received May 28, 203, revised March
Hoshi, Y. Osaka J. Math. 52 (205), 647 675 ON THE KERNELS OF THE PRO-l OUTER GALOIS REPRESENTATIONS ASSOCIATED TO HYPERBOLIC CURVES OVER NUMBER FIELDS YUICHIRO HOSHI (Received May 28, 203, revised March
Math /Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined
 Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Chapter 4. Measure Theory. 1. Measure Spaces
 Chapter 4. Measure Theory 1. Measure Spaces Let X be a nonempty set. A collection S of subsets of X is said to be an algebra on X if S has the following properties: 1. X S; 2. if A S, then A c S; 3. if
Chapter 4. Measure Theory 1. Measure Spaces Let X be a nonempty set. A collection S of subsets of X is said to be an algebra on X if S has the following properties: 1. X S; 2. if A S, then A c S; 3. if
Homework #5 Solutions
 Homework #5 Solutions p 83, #16. In order to find a chain a 1 a 2 a n of subgroups of Z 240 with n as large as possible, we start at the top with a n = 1 so that a n = Z 240. In general, given a i we will
Homework #5 Solutions p 83, #16. In order to find a chain a 1 a 2 a n of subgroups of Z 240 with n as large as possible, we start at the top with a n = 1 so that a n = Z 240. In general, given a i we will
AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence
 AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
AP Calculus BC Scope & Sequence Grading Period Unit Title Learning Targets Throughout the School Year First Grading Period *Apply mathematics to problems in everyday life *Use a problem-solving model that
DERIVATIONS. Introduction to non-associative algebra. Playing havoc with the product rule? BERNARD RUSSO University of California, Irvine
 DERIVATIONS Introduction to non-associative algebra OR Playing havoc with the product rule? PART VI COHOMOLOGY OF LIE ALGEBRAS BERNARD RUSSO University of California, Irvine FULLERTON COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
DERIVATIONS Introduction to non-associative algebra OR Playing havoc with the product rule? PART VI COHOMOLOGY OF LIE ALGEBRAS BERNARD RUSSO University of California, Irvine FULLERTON COLLEGE DEPARTMENT
A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol
 Mathematica Moravica Vol. 12-1 (2008), 37 42 A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol Aleksandar Petoević Abstract. In this paper we give elementary proofs of the generating functions for the Pochhammer symbol
Mathematica Moravica Vol. 12-1 (2008), 37 42 A Note about the Pochhammer Symbol Aleksandar Petoević Abstract. In this paper we give elementary proofs of the generating functions for the Pochhammer symbol
arxiv: v1 [math-ph] 12 Dec 2007
![arxiv: v1 [math-ph] 12 Dec 2007 arxiv: v1 [math-ph] 12 Dec 2007](/thumbs/94/122297431.jpg) arxiv:0712.2030v1 [math-ph] 12 Dec 2007 Green function for a two-dimensional discrete Laplace-Beltrami operator Volodymyr Sushch Koszalin University of Technology Sniadeckich 2, 75-453 Koszalin, Poland
arxiv:0712.2030v1 [math-ph] 12 Dec 2007 Green function for a two-dimensional discrete Laplace-Beltrami operator Volodymyr Sushch Koszalin University of Technology Sniadeckich 2, 75-453 Koszalin, Poland
Applied Linear Algebra
 Applied Linear Algebra OTTO BRETSCHER http://www.prenhall.com/bretscher Chapter 4 Linear Spaces Chia-Hui Chang Email: chia@csie.ncu.edu.tw National Central University, Taiwan October 28, 2002 4.1 Introduction
Applied Linear Algebra OTTO BRETSCHER http://www.prenhall.com/bretscher Chapter 4 Linear Spaces Chia-Hui Chang Email: chia@csie.ncu.edu.tw National Central University, Taiwan October 28, 2002 4.1 Introduction
